Intensification of Human Land Use Decreases Taxonomic, Functional, and Phylogenetic Diversity of Macroinvertebrate Community in Weihe River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
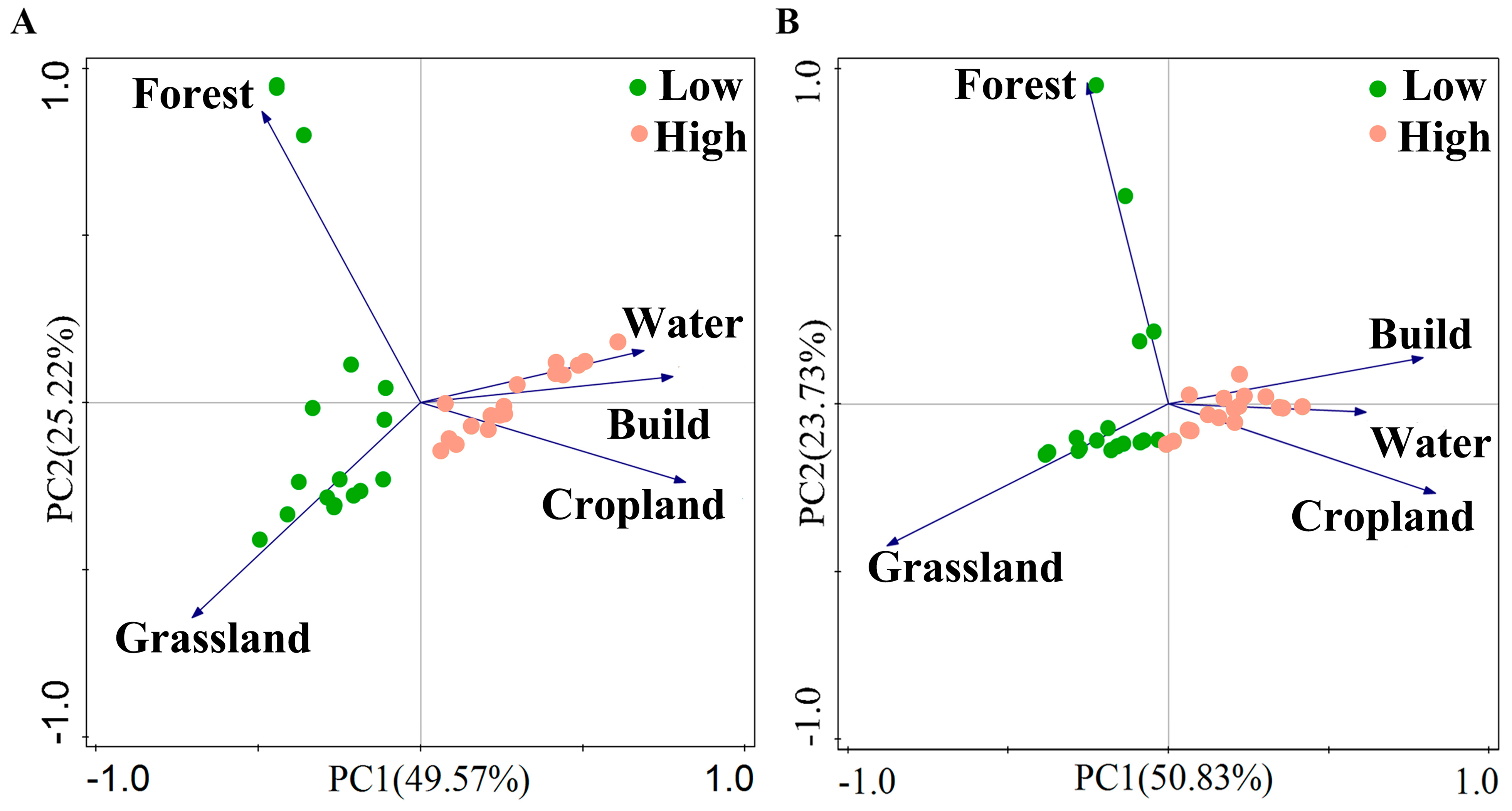
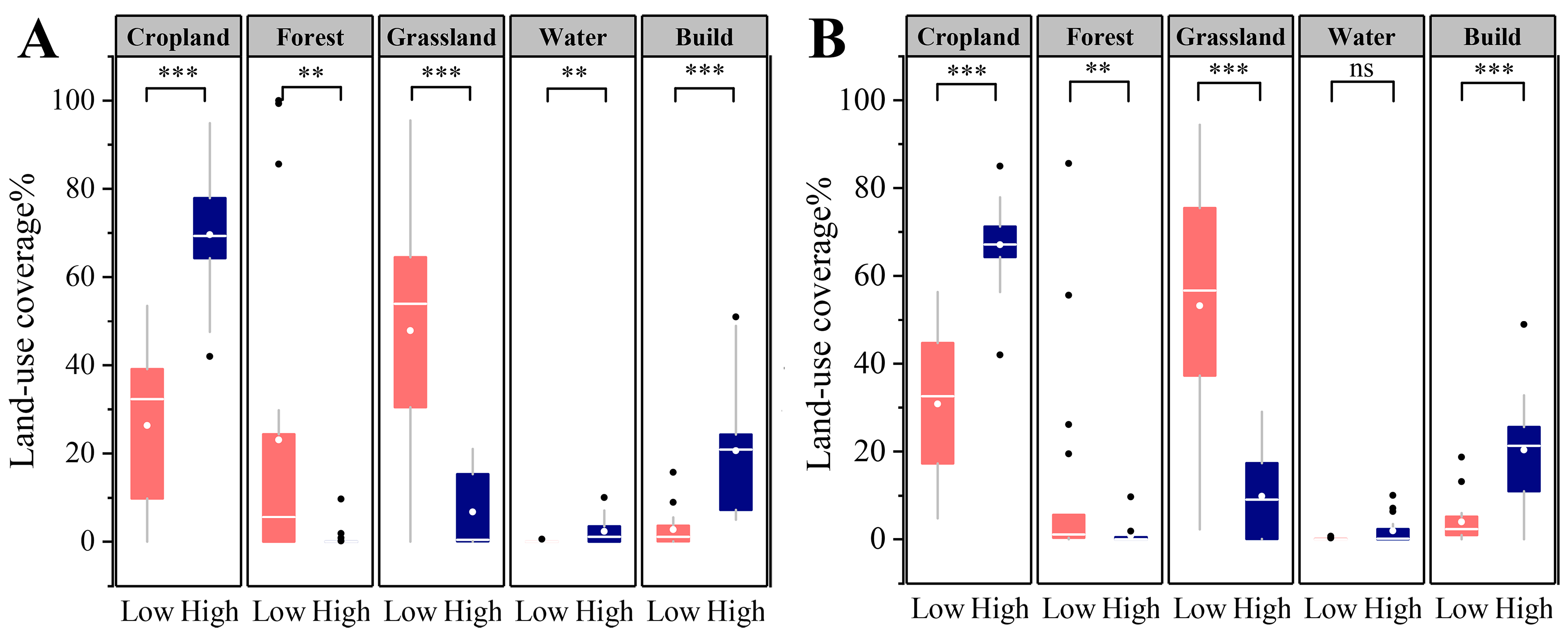
2.2. Land-Use Data and Site Classification
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
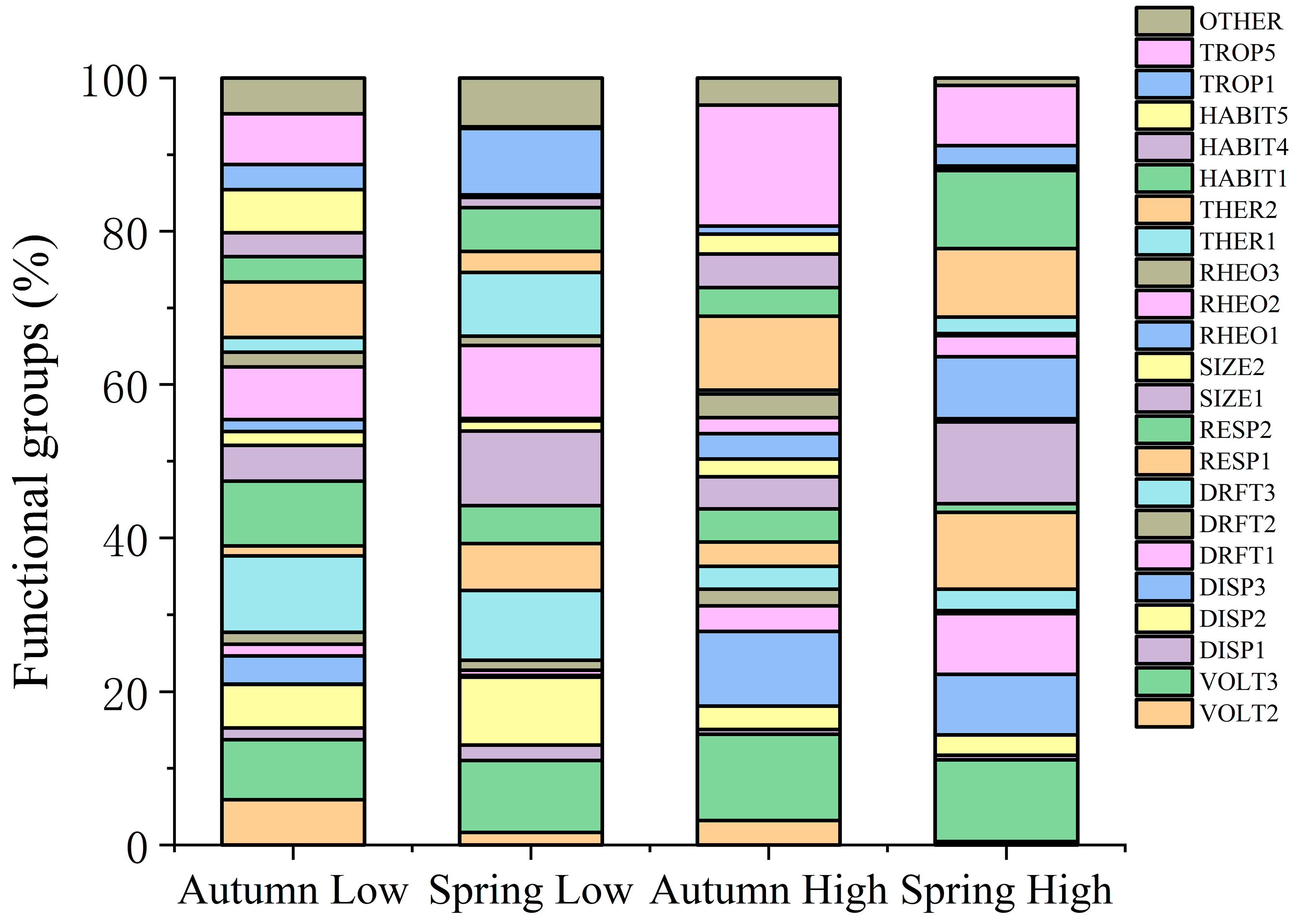
2.4. Macroinvertebrates Functional Traits
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
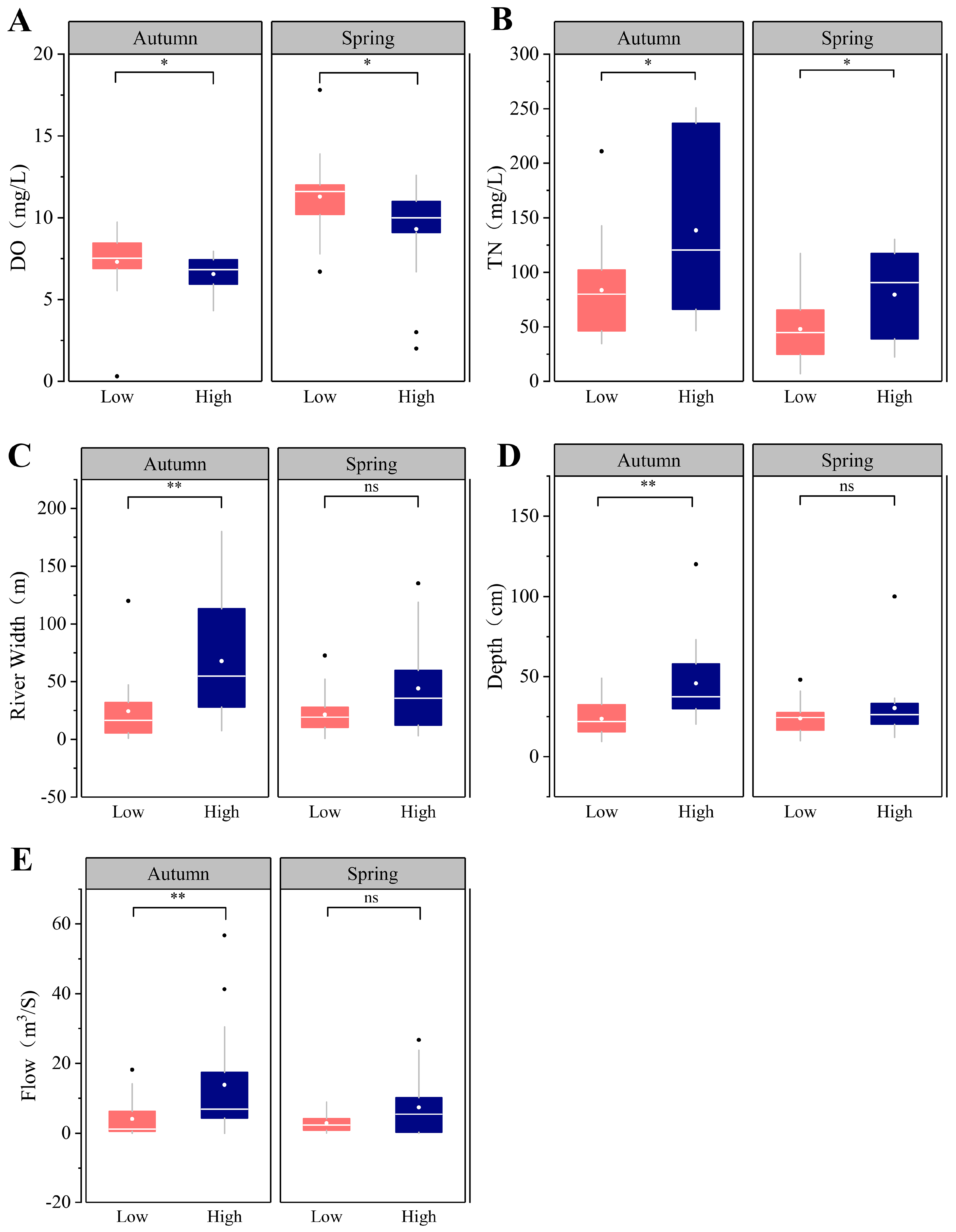
3.1. Environmental Characteristics
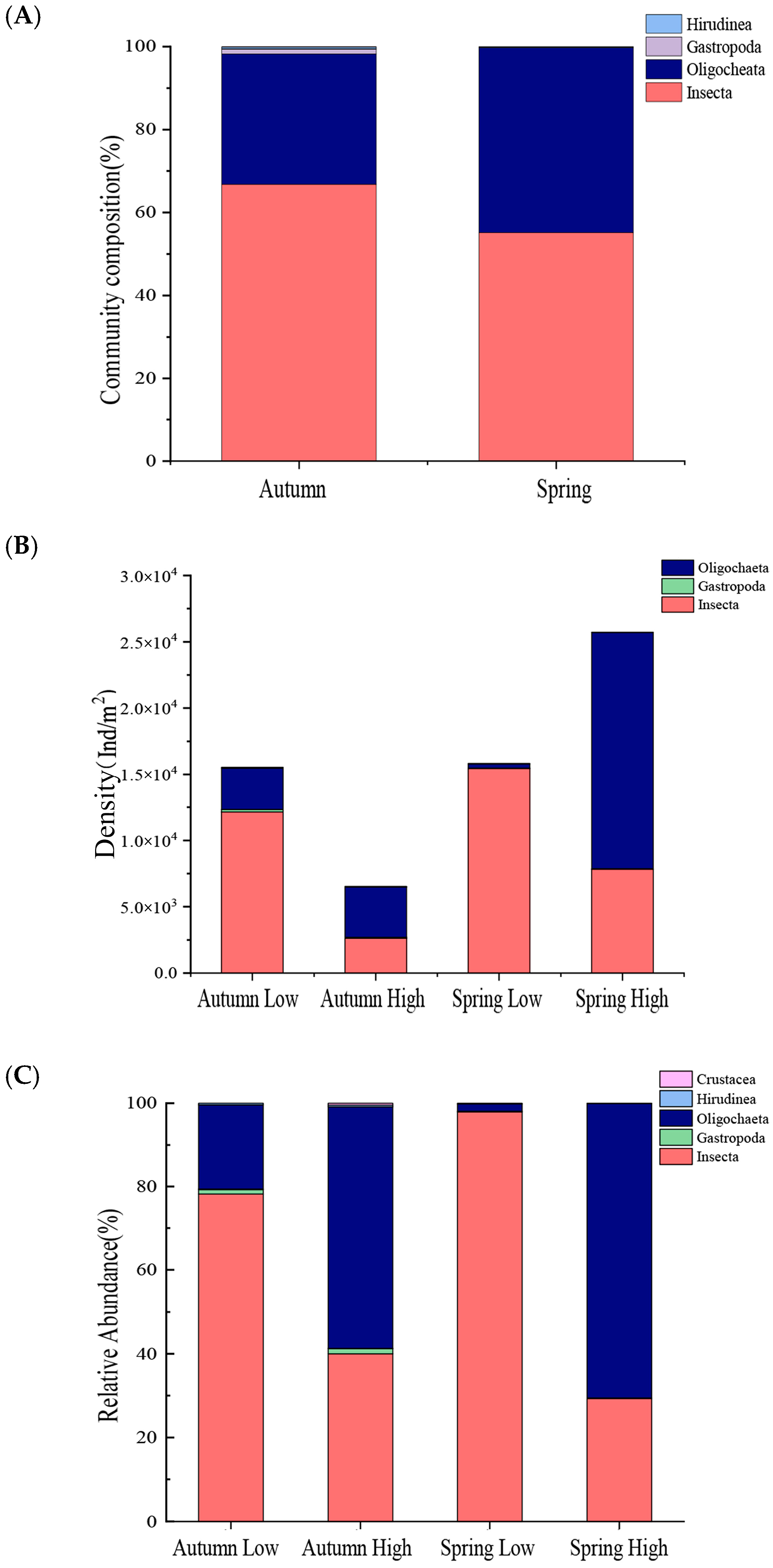
3.2. Macroinvertebrates Community Characteristics
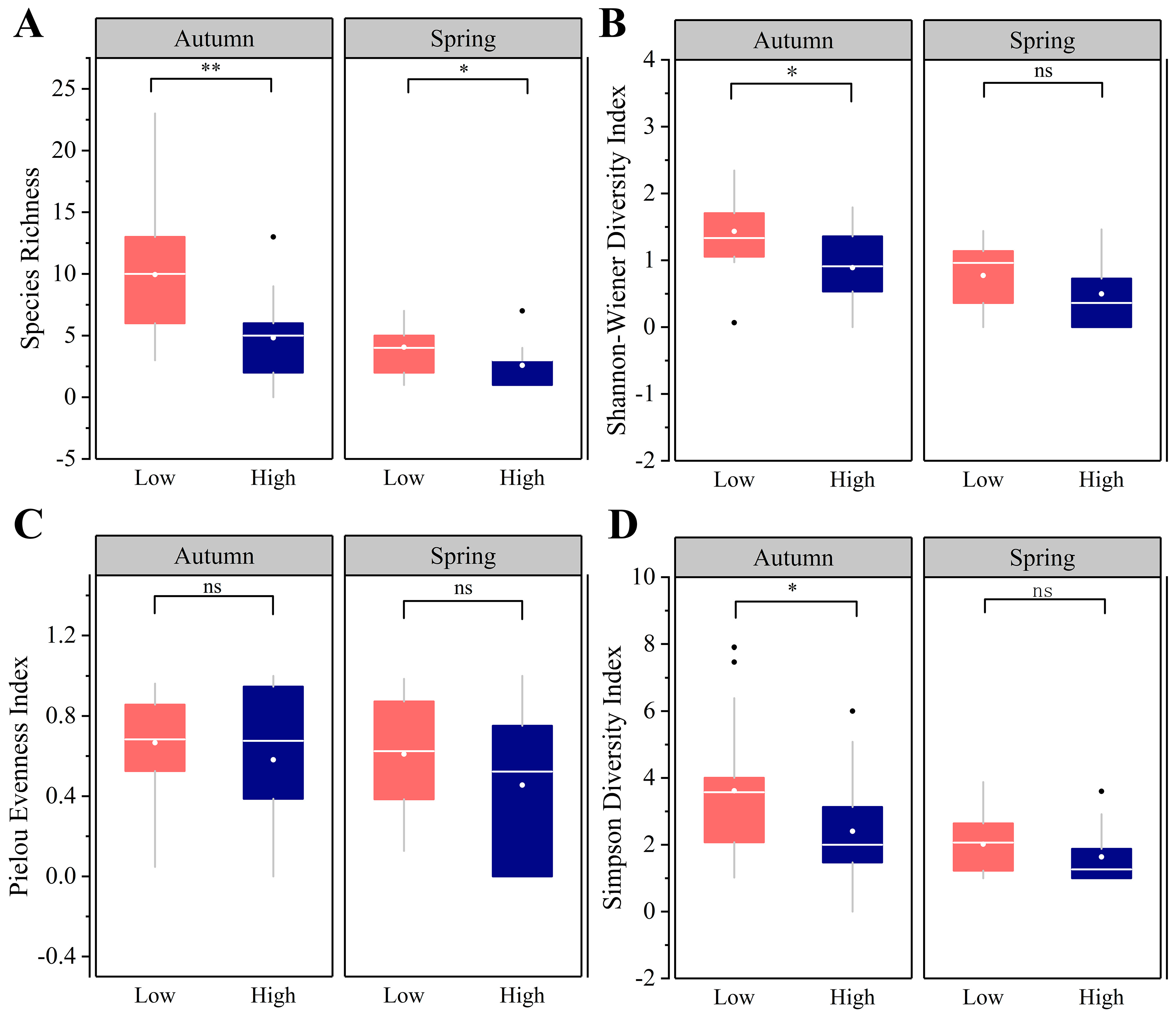
3.3. Taxonomic α Diversity Patterns
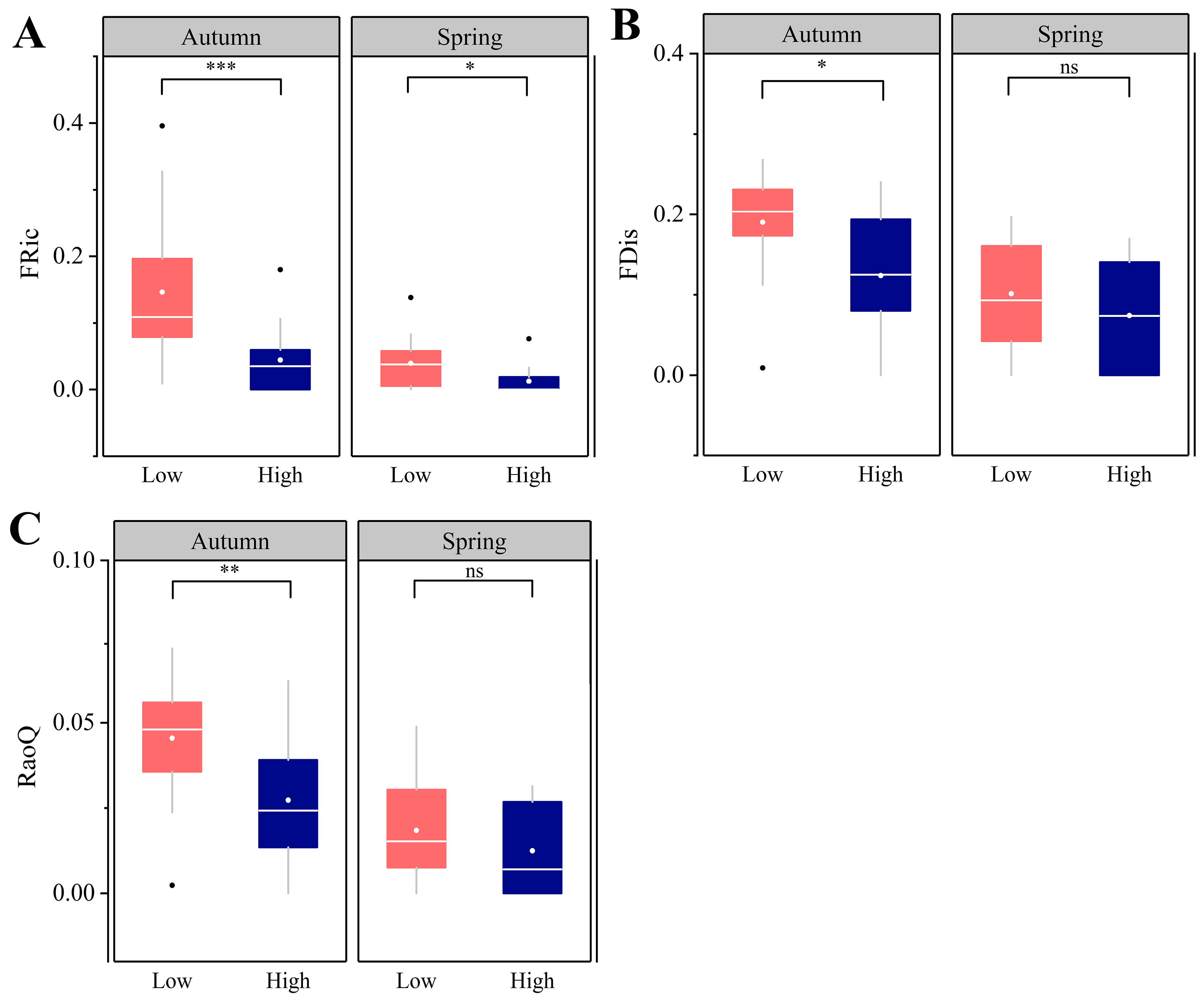
3.4. Functional α Diversity Patterns
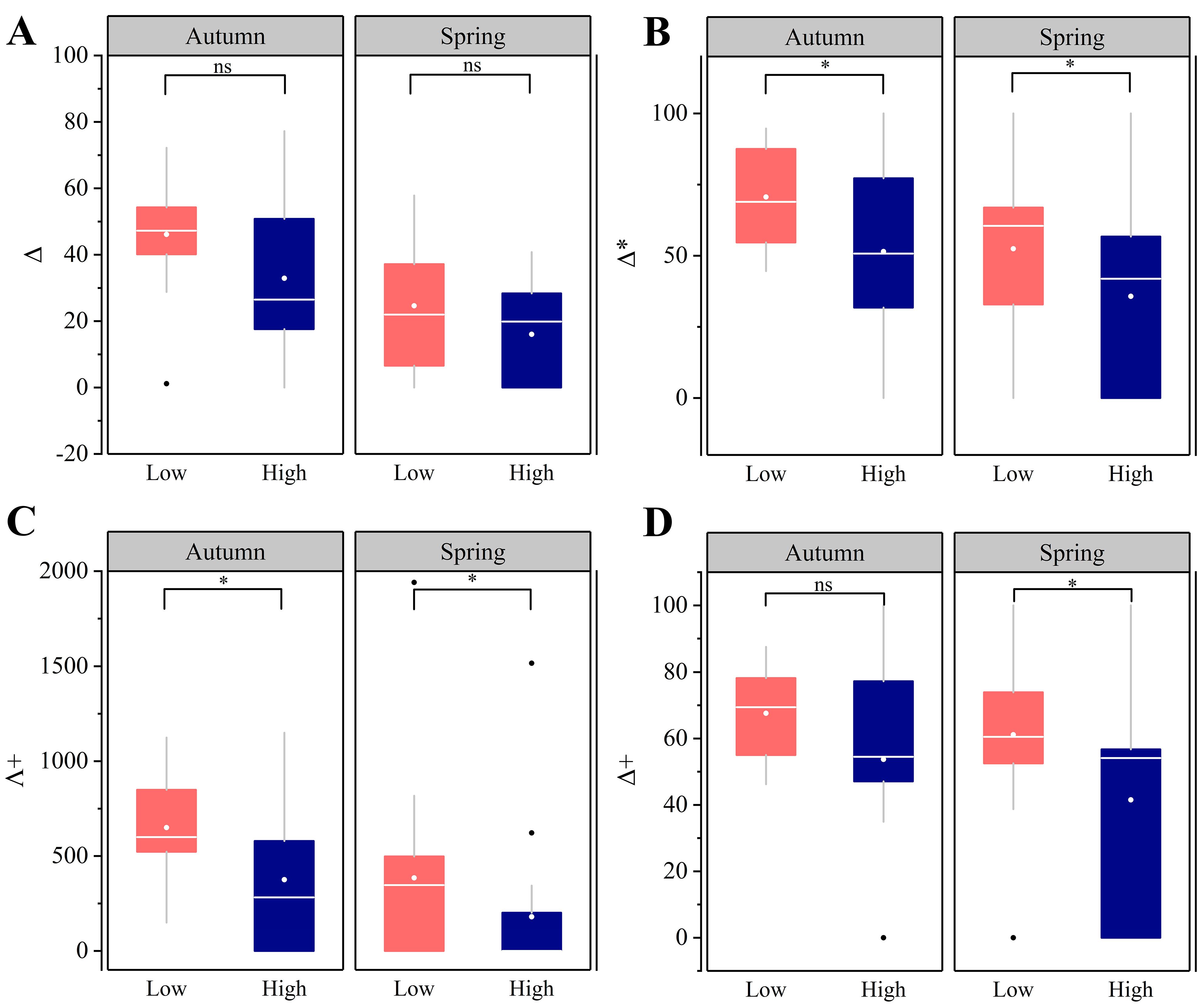
3.5. Phylogenetic Diversity α Diversity Patterns
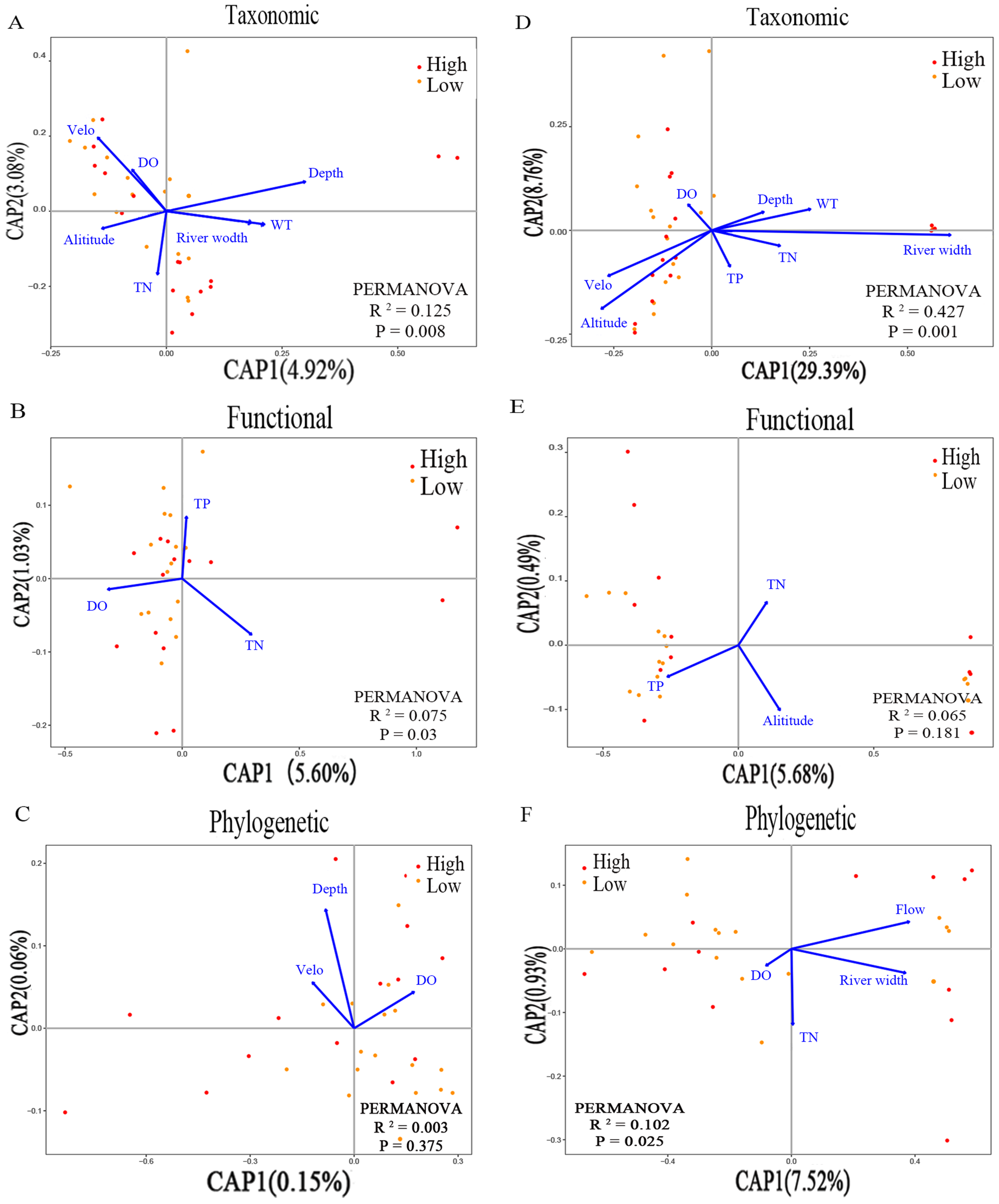
3.6. Relationship between Land-Use Intensity, Environmental Factors, and Macroinvertebrate Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Factors and Macroinvertebrates Community Characteristics under the Different Human Land-Use Intensities
4.2. Intensive Human Land-Use Decreases Taxonomic Diversity
4.3. Intensive Human Land-Use Decreases Functional Diversity
4.4. Intensive Human Land-Use Decreases Phylogenetic Diversity
4.5. Land-Use Intensity and Environmental Factors Affect the Diversity of Macroinvertebrates
4.6. Limitations and Suggestions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Hill, S.L.; Contu, S.; Lysenko, I.; Senior, R.A.; Börger, L.; Bennett, D.J.; Choimes, A.; Collen, B.J.N.; et al. Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 2015, 520, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, C.; Ovando, X.M.; Loyola, R.; Izquierdo, A.; Romero, F.; Molineri, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Rueda Martín, P.; Fernández, H.; Manzo, V.; et al. The role of macroinvertebrates for conservation of freshwater systems. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 5502–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M. Deforesting the Earth: From Prehistory to Global Crisis; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, T.M.; Blackburn, G.A.; Whyatt, J.D.; Atkinson, P.M. Global land cover trajectories and transitions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miserendino, M.L.; Casaux, R.; Archangelsky, M.; Di Prinzio, C.Y.; Brand, C.; Kutschker, A.M. Assessing land-use effects on water quality, in-stream habitat, riparian ecosystems and biodiversity in Patagonian northwest streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M.; Williams, D.R.; Kimmel, K.; Polasky, S.; Packer, C. Future threats to biodiversity and pathways to their prevention. Nature 2017, 546, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, C.C.; Winemiller, K.O.; Petrere, M.; Castello, L.; Hess, L.L.; Freitas, C.E. Relationships between forest cover and fish diversity in the Amazon River floodplain. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Kong, P. Land use changes and socio-economic development strongly deteriorate river ecosystem health in one of the largest basins in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; García-Girón, J.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Z. Anthropogenic impacts on multiple facets of macroinvertebrate α and β diversity in a large river-floodplain ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z. Understanding the relationship of land uses and water quality in Twenty First Century: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Taniwaki, R.H.; de Paula, F.R.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; Macedo, D.R.; Leal, C.G.; Rodrigues, C.B.; Hughes, R.M. Multiscale land use impacts on water quality: Assessment, planning, and future perspectives in Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; dos Santos, A.C.A.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Effects of land use and land cover on water quality of low-order streams in Southeastern Brazil: Watershed versus riparian zone. Catena 2018, 167, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, R.B.; Kühn, B.; Malaj, E.; König, A.; Gergs, R. Contribution of organic toxicants to multiple stress in river ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palt, M.; Le Gall, M.; Piffady, J.; Hering, D.; Kail, J. A metric-based analysis on the effects of riparian and catchment landuse on macroinvertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, V.C.; Frascareli, D.; Gontijo, E.S.; Melo, D.S.; Friese, K.; Silva, D.C.; Rosa, A.H. Water quality indices as a tool for evaluating water quality and effects of land use in a tropical catchment. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mao, R.; Li, M.; Xia, J.; Song, J.; Cheng, D.; Sun, H. Assessment of aquatic ecological health based on determination of biological community variability of fish and macroinvertebrates in the Weihe River Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 267, 110651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, V.; Estrany, J.; Ranzini, M.; de Cicco, V.; Martín-Benito, J.M.T.; Hedo, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Effects of land use and seasonality on stream water quality in a small tropical catchment: The headwater of Córrego Água Limpa, São Paulo (Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidsma, P.; Tekelenburg, T.; Van den Berg, M.; Alkemade, R. Impacts of land-use change on biodiversity: An assessment of agricultural biodiversity in the European Union. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Soininen, J.; Heino, J. Ecological indicators for aquatic biodiversity, ecosystem functions, human activities and climate change. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, R.F.V.; Varandas, S.G.; Pacheco, F.A.; Pereira, V.R.; Santos, C.F.; Cortes, R.M.; Fernandes, L.F.S. Impacts of land use conflicts on riverine ecosystems. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallacher, D. The application of rapid bioassessment techniques based on benthic macroinvertebrates in East Asian rivers (a review). Int. Ver. Für Theor. Und Angew. Limnol. Verhandlungen 2001, 27, 3503–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, W.; Argent, D. Community concordance between fishes and benthic macroinvertebrates among adventitious and ordinate tributaries of a major river system. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, H.A.; Salem, E.S.S.; El-Kafrawy, S.B.; Bashar, M.A.; Shaban, W.M.; El-Gayar, E.E.; Ahmed, H.O.; Ashour, M.; Abou-Mahmoud, M.E. An integrated field data and remote sensing approach for impact assessment of human activities on epifauna macrobenthos biodiversity along the western coast of Aqaba Gulf. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, P.; Bertrán, C.; Tapia, J.; Hauenstein, E.; Peña-Cortés, F.; Vergara, C.; Cerna, C.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Effects of local land-use on riparian vegetation, water quality, and the functional organization of macroinvertebrate assemblages. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Ringler, N. The response of fish and macroinvertebrate assemblages to multiple stressors: A comparative analysis of aquatic communities in a perturbed watershed (Onondaga Lake, NY). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, K.; Xu, S.; Wang, B. Influences of environmental factors on macroinvertebrate assemblages: Differences between mountain and lowland ecoregions, Wei River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Brosse, S.; Qu, X.; Xia, W.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Land use outweighs other stressors in declining fish biodiversity in lakes of Eastern China during the 1980s–2010s. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 152, 110390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Castro, D.M.; Tan, X.; Jiang, X.; Meng, X.; Ge, Y.; Xie, Z. Effects of different types of land-use on taxonomic and functional diversity of benthic macroinvertebrates in a subtropical river network. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44339–44353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dudgeon, D.; Cheng, D.; Thoe, W.; Fok, L.; Wang, Z.; Lee, J.H. Impacts of land use and water quality on macroinvertebrate communities in the Pearl River drainage basin, China. Hydrobiologia 2010, 652, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Yin, X. Effect of Different Land Use Types on the Taxonomic and Functional Diversity of Macroinvertebrates in an Urban Area of Northern China. Water 2022, 14, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, F.; Benedetti, Y.; Perna, P.; Santolini, R. Associations among taxonomic diversity, functional diversity and evolutionary distinctiveness vary among environments. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 88, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillot, D.; Graham, N.A.; Villéger, S.; Mason, N.W.; Bellwood, D.R. A functional approach reveals community responses to disturbances. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Gutiérrez, J.; Malhi, Y.; Lewis, S.L.; Fauset, S.; Adu-Bredu, S.; Affum-Baffoe, K.; Baker, T.R.; Gvozdevaite, A.; Hubau, W.; Moore, S.; et al. Long-term droughts may drive drier tropical forests towards increased functional, taxonomic and phylogenetic homogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Dong, G. Application of species, phylogenetic and functional diversity to the evaluation on the effects of ecological restoration on biodiversity. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 32, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q.; Peng, J.; Song, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, D.; Bai, H.; Li, Q. Variability in macroinvertebrate community structure and its response to ecological factors of the Weihe River Basin, China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 140, 105595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, A. Dynamic changes of sediment load and water discharge in the Weihe River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Zuo, D. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on green and blue water resources in the Weihe River Basin of northwest China. Catena 2016, 137, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Altermatt, F.; Yang, J.; An, S.; Li, A.; Zhang, X. Human activities’ fingerprint on multitrophic biodiversity and ecosystem functions across a major river catchment in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 6867–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Shen, J.; An, S.; Leng, X. Intensive human land uses cause the biotic homogenization of algae and change their assembly process in a major watershed of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-W.; Xu, Z.-X.; Gao, X.; Bai, H.-F.; Wu, W.; Song, J.-X. Macrobenthos community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in Weihe River basin, Northwest China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, G. Fauna Sinica Phylum Mollusca Class Gastropoda; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, R.W.; Cummins, K.W. An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America; Kendall Hunt: Dubuque, IA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, J.H.; Covich, A.P. Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Fauna sinica Phylum Mollusca Class Bivalvia; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T. Fauna Sinica Annelida Hiruclinea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- China SE Monitoring and Determination Methods for Water and Wastewater; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Poff, N.L.; Olden, J.D.; Vieira, N.K.; Finn, D.S.; Simmons, M.P.; Kondratieff, B.C. Functional trait niches of North American lotic insects: Traits-based ecological applications in light of phylogenetic relationships. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2006, 25, 730–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Yin, X. Assembly mechanism of macroinvertebrate metacommunities and ecological factors of multiple aspects of beta diversity in a boreal river basin, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1131403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Y.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Vidal, N.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B. Different responses of functional traits and diversity of stream macroinvertebrates to environmental and spatial factors in the Xishuangbanna watershed of the upper Mekong River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Heino, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, T.; Xie, Z. Discriminating the effects of local stressors from climatic factors and dispersal processes on multiple biodiversity dimensions of macroinvertebrate communities across subtropical drainage basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Meng, X.; Heino, J.; Jiang, X.; Xiong, X.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Z. Different responses of taxonomic and functional structures of stream macroinvertebrate communities to local stressors and regional factors in a subtropical biodiversity hotspot. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmilauer, P.; Lepš, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO 5; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khudhair, N.; Yan, C.; Liu, M.; Yu, H. Effects of habitat types on macroinvertebrates assemblages structure: Case study of sun island bund wetland. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2650678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Sólymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; Academic Press: Oulu, Finland, 2012; Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Laliberté, E.; Legendre, P.; Shipley, B.; Laliberté, M.E. Package ‘fd’, Measuring Functional Diversity from Multiple Traits, and Other Tools for Functional Ecology; Academic Press: Québec, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Legras, G.; Loiseau, N.; Gaertner, J.-C. Functional richness: Overview of indices and underlying concepts. Acta Oecologica 2018, 87, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, N.W.; Mouillot, D.; Lee, W.G.; Wilson, J.B. Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: The primary components of functional diversity. Oikos 2005, 111, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, M.A.; Villéger, S.; Mason, N.W.; Mouillot, D. Functional diversity measures: An overview of their redundancy and their ability to discriminate community assembly rules. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoine, S.; Dolédec, S. The apportionment of quadratic entropy: A useful alternative for partitioning diversity in ecological data. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2005, 12, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Peng, W.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Wu, N. Phylogenetic and functional diversity could be better indicators of macroinvertebrate community stability. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘ggplot2’. Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics; Academic Press: Houston, TX, USA, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Xu, Z.; Yang, F.; Yin, X.; Wu, W.; Li, J. Comparison of Fish, Macroinvertebrates and Diatom Communities in Response to Environmental Variation in the Wei River Basin, China. Water 2020, 12, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jin, G.; Tang, H.; Mo, Y.; Wang, Y.-G.; Li, L. Response of water quality to land use and sewage outfalls in different seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębska, K.; Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Gozdowski, D. Changes in Selected Water Quality Parameters in the Utrata River as a Function of Catchment Area Land Use. Water 2021, 13, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martien, R.F.; Benke, A.C. Distribution and production of two crustaceans in a wetland pond. Am. Midl. Nat. 1977, 98, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremicael, T.; Mohamed, Y.; Van der Zaag, P. Attributing the hydrological impact of different land use types and their long-term dynamics through combining parsimonious hydrological modelling, alteration analysis and PLSR analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chao, Y.; Fan, R.; Ren, F.; Qi, B.; Ji, K.; Xu, B. Spatial-temporal trends of rainfall erosivity and its implication for sustainable agriculture in the Wei River Basin of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Q.; Kang, M. Impacts of land use on surface water quality in a subtropical River Basin: A case study of the Dongjiang River Basin, Southeastern China. Water 2015, 7, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Tolonen, K.E.; Yin, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Cai, Y. Substrate degradation and nutrient enrichment structuring macroinvertebrate assemblages in agriculturally dominated Lake Chaohu Basins, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Song, D.; Ming, K.; Jin, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhao, C.; Huo, T. Response of macroinvertebrate communities to land use and water quality in Wudalianchi Lake. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Jo, H.; Park, K.; Kwak, I.-S. Assessing spatial distribution of benthic macroinvertebrate communities associated with surrounding land cover and water quality. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakr, A.; Gojar, A.A.; Balkhi, M.; Malik, R. Macro-invertebrates (Annelida; Oligochaeta) as bio-Indicator of water quality under temperate climatic conditions. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2018, 6, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, T.J.; Davis, J.A.; Thompson, R.M. The influence of urbanisation on macroinvertebrate biodiversity in constructed stormwater wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, E.C.; Gauthier, N.; Klein Goldewijk, K.; Bliege Bird, R.; Boivin, N.; Díaz, S.; Fuller, D.Q.; Gill, J.L.; Kaplan, J.O.; Kingston, N.; et al. People have shaped most of terrestrial nature for at least 12,000 years. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023483118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiapi, M.; Mazaris, A.D.; Charalampous, E.; Moustaka-Gouni, M. Watershed land use types as drivers of freshwater phytoplankton structure. In Phytoplankton Responses to Human Impacts at Different Scales; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, C.W.; Rahbek, C.; Morueta-Holme, N. Land-use change and biodiversity: Challenges for assembling evidence on the greatest threat to nature. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 5414–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurangwa, M.L.; Aguirre-Gutiérrez, J.; Matthews, T.J.; Niyigaba, P.; Wayman, J.P.; Tobias, J.A.; Whittaker, R.J. Effects of land-use change on avian taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic diversity in a tropical montane rainforest. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 1732–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, L.; Rodriguez, M.; Gullo, B.; Capítulo, A.R. Impacts of urban and industrial pollution on functional traits of benthic macroinvertebrates: Are some traits advantageous for survival? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, D.M.P.; Dolédec, S.; Callisto, M. Land cover disturbance homogenizes aquatic insect functional structure in neotropical savanna streams. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Provost, G.; Thiele, J.; Westphal, C.; Penone, C.; Allan, E.; Neyret, M.; Van Der Plas, F.; Ayasse, M.; Bardgett, R.D.; Birkhofer, K.; et al. Contrasting responses of above-and belowground diversity to multiple components of land-use intensity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadamsuren, O.; Morse, J.C.; Hayford, B.; Gelhaus, J.K.; Adler, P.H. Macroinvertebrate community responses to land use: A trait-based approach for freshwater biomonitoring in Mongolia. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1887–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintzen, V.; Anderson, M.J.; Roberts, C.D.; Diebel, C.E. Increasing variation in taxonomic distinctness reveals clusters of specialists in the deep sea. Ecography 2011, 34, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, Z.; García-Girón, J.; Chen, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, Z. Human-induced loss of functional and phylogenetic diversity is mediated by concomitant deterministic processes in subtropical aquatic insect communities. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Bona, F.; Fenoglio, S.; Bo, T. Functional Traits Drive the Changes in Diversity and Composition of Benthic Invertebrate Communities in Response to Hydrological Regulation. Water 2024, 16, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, R.J.; Heino, J.; Ryder, D.S.; Chessman, B.C.; Growns, I.O.; Thompson, R.M.; Gido, K.B. Scaling biodiversity responses to hydrological regimes. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 971–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, M.J.; Morgan, R.P.; Stranko, S. Relations between macroinvertebrates, nutrients, and water quality criteria in wadeable streams of Maryland, USA. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1167–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, T.L.; Leprieur, F.; Floury, M.; Stephenson, F.; Verburg, P.; Tonkin, J.D. Climate and land-use driven reorganisation of structure and function in river macroinvertebrate communities. Ecography 2022, 2022, e06148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trait Group Trait | Trait State (Modality) | Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Life history | |||
| Voltinism | Semivoltine (<1 generation/y) | Volt1 | |
| Univoltine (1 generation/y) | Volt2 | ||
| Bi- or multivoltine (>1 generation/y) | Volt3 | ||
| Mobility | |||
| Female dispersal | Low (<1 km flight before laying eggs) | Disp1 | |
| High (>1 km flight before laying eggs) | Disp2 | ||
| No | Disp3 | ||
| Occurrence in drift | Rare (catastrophic only) | Drft1 | |
| Common (typically observed) | Drft2 | ||
| Abundant (dominant in drift samples) | Drft3 | ||
| Morphology | |||
| Respiration | Tegument | Resp1 | |
| Gills | Resp2 | ||
| Plastron, spiracle (aerial) | Resp3 | ||
| Size at maturity | Small (<9 mm) | Size1 | |
| Medium (9–16 mm) | Size2 | ||
| Large (>16 mm) | Size3 | ||
| Ecology | |||
| Rheophily | Depositional only | Rheo1 | |
| Depositional and erosional | Rheo2 | ||
| Erosional | Rheo3 | ||
| Thermal preference | Cold stenothermal or cool eurythermal | Ther1 | |
| Cool/warm eurythermal | Ther2 | ||
| Warm eurythermal | Ther3 | ||
| Habit | Burrow | Habi1 | |
| Climb | Habi2 | ||
| Sprawl | Habi3 | ||
| Cling | Habi4 | ||
| Swim | Habi5 | ||
| Skate | Habi6 | ||
| Trophic habit | Collector-gatherer | Trop1 | |
| Collector-filterer | Trop2 | ||
| Herbivore (scraper, piercer, and shedder) | Trop3 | ||
| Predator (piercer and engulfer) | Trop4 | ||
| Shredder (detritivore) | Trop5 | ||
| Autumn | Spring | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Low | High | Low | High |
| Arthropoda | Insecta | Ephemeroptera | Baetidae | Baetis | 0.141 | 0.045 | - | - |
| Arthropoda | Insecta | Trichoptera | Hydropsychidae | Hydropsyche | 0.051 | 0.099 | 0.041 | - |
| Arthropoda | Insecta | Diptera | Chironomidae | Orthocladius | 0.269 | 0.047 | - | - |
| Arthropoda | Insecta | Diptera | Chironomidae | Cricotopus | - | - | 0.305 | 0.05 |
| Arthropoda | Insecta | Diptera | Chironomidae | Sympotthastia | - | - | 0.042 | - |
| Annelida | Oligocheata | Tubificida | Tubificidae | Limnodrilus | 0.129 | 0.208 | - | 0.124 |
| Annelida | Oligocheata | Tubificida | Tubificidae | Branchiura | - | 0.024 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Yin, X.; Liu, G.; Song, J. Intensification of Human Land Use Decreases Taxonomic, Functional, and Phylogenetic Diversity of Macroinvertebrate Community in Weihe River Basin, China. Diversity 2024, 16, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16090513
Ma J, Yin X, Liu G, Song J. Intensification of Human Land Use Decreases Taxonomic, Functional, and Phylogenetic Diversity of Macroinvertebrate Community in Weihe River Basin, China. Diversity. 2024; 16(9):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16090513
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jixin, Xuwang Yin, Gang Liu, and Jinxi Song. 2024. "Intensification of Human Land Use Decreases Taxonomic, Functional, and Phylogenetic Diversity of Macroinvertebrate Community in Weihe River Basin, China" Diversity 16, no. 9: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16090513
APA StyleMa, J., Yin, X., Liu, G., & Song, J. (2024). Intensification of Human Land Use Decreases Taxonomic, Functional, and Phylogenetic Diversity of Macroinvertebrate Community in Weihe River Basin, China. Diversity, 16(9), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16090513






