Inocybaceae (Basidiomycota) in Ectomycorrhizal Symbiosis with Halimium (Cistaceae), and the Description of Two New Species of Inocybe from Sardinia (Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
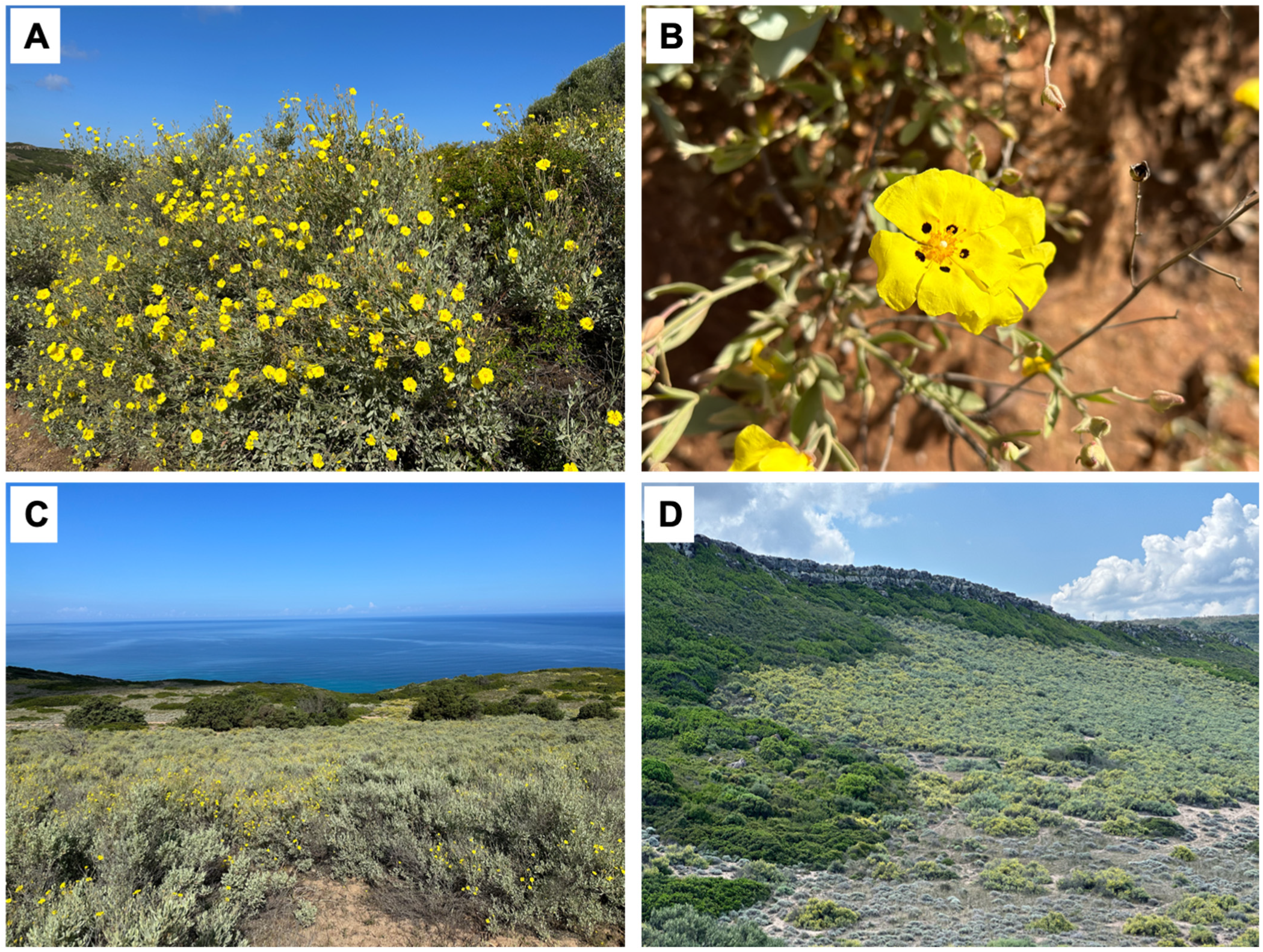
2.1. Collecting Site and Fungal Sampling
2.2. Morphological Observations
2.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
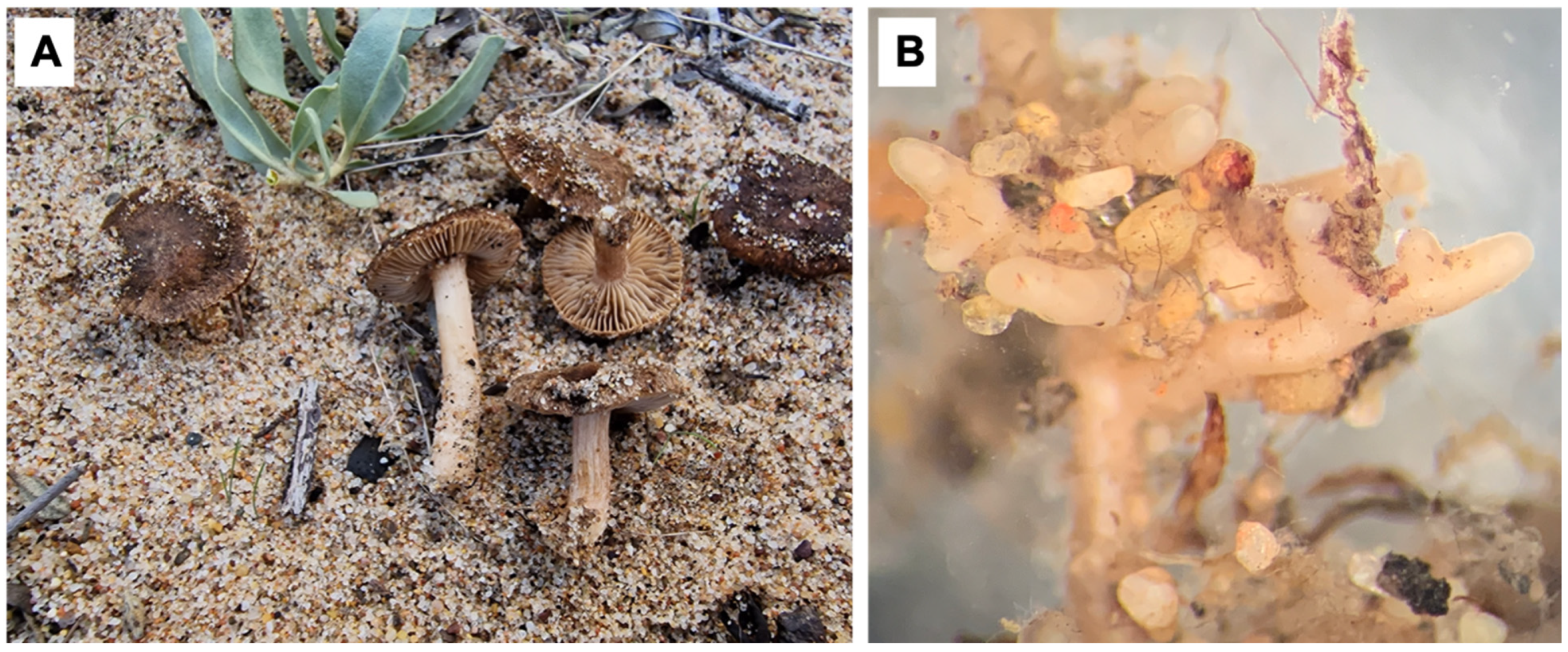
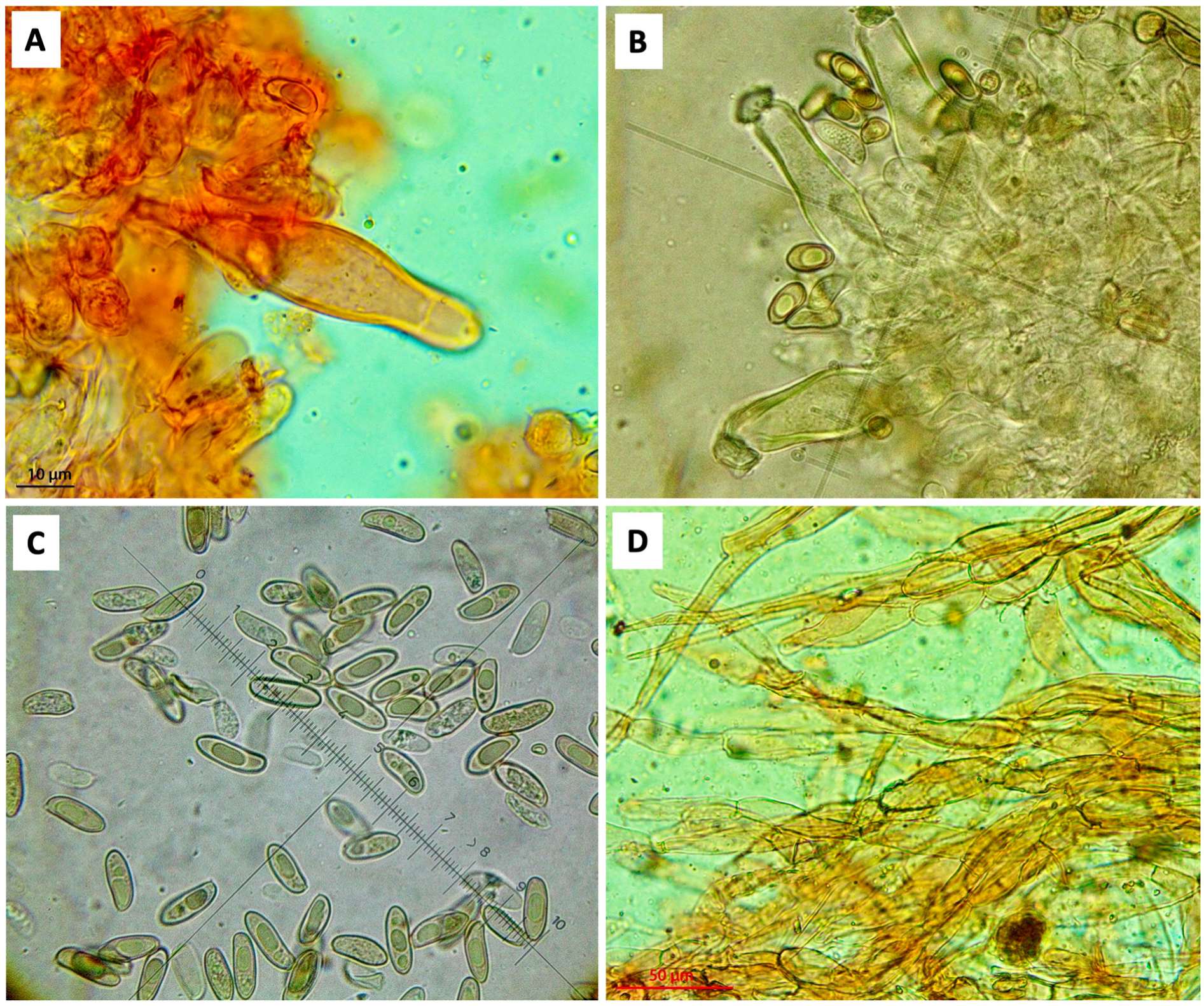
4. Taxonomy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henne, P.D.; Elkin, C.; Franke, C.; Colombaroli, D.; Calò, C.; La Mantia, T.; Pasta, S.; Conedera, M.; Dermody, O.; Tinner, W. Reviving extinct Mediterranean forests communities may improve ecosystem potential in a warmer future. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, R.; Vrahnakis, M.; Rodriguez Rojo, M.P.; Giuga, L.; Salvatore, P. Grasslands and Shrublands of the Mediterranean Region. In Encyclopedia of the World’s Biomes; Goldstein, M.I., DellaSala, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 638–655. [Google Scholar]
- Comandini, O.; Contu, M.; Rinaldi, A.C. An overview of Cistus ectomycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza 2006, 16, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WorldPlants. Available online: https://www.worldplants.de (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Govaerts, R.; Nic Lughadha, E.; Black, N.; Turner, R.; Paton, A. The World Checklist of Vascular Plants, a continuously updated resource for exploring global plant diversity. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Flora Online Plant List. Available online: https://wfoplantlist.org/ (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Guzmán, B.; Vargas, P. Systematics, character evolution, and biogeography of Cistus L. (Cistaceae) based on ITS, trnL-trnF, and matK sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 37, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, B.; Vargas, P. Historical biogeography and character evolution of Cistaceae (Malvales) based on analysis of plastid rbcL and trnL-trnF sequences. Org. Divers. Evol. 2009, 9, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civeyrel, L.; Leclercq, J.; Demoly, J.-P.; Agnan, Y.; Quèbre, N.; Pélissier, C.; Otto, T. Molecular systematics, character evolution, and pollen morphology of Cistus and Halimium (Cistaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2011, 295, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunzunegui, M.; Díaz Barradas, M.C.; Aguilar, F.; Ain Lhout, F.; Clavijo, A.; García Novo, F. Growth response of Halimium halimifolium at four sites with different soil water availability regimes in two contrasted hydrological cycles. Plant Soil 2002, 247, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunzunegui, M.; Ain-Lhout, F.; Díaz Barradas, M.C.; Álvarez-Cansino, L.A.; Esquivias, M.P.; García Novo, F. Physiological, morphological and allocation plasticity of a semi-deciduous shrub. Acta Oecol. 2009, 35, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camprubi, A.; Estaun, V.; Calvet, C. Greenhouse inoculation of psammophilic plant species with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to improve survival and early growth. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscardo, E.; Rodríguez-Echeverría, S.; Barrico, L.; García, M.Á.; Freitas, H.; Martín, M.P.; De Angelis, P.; Muller, L.A.H. Is the potential for the formation of common mycorrhizal networks influenced by fire frequency? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 46, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddiar, A.; Adouane, M.; Boudiaf, I.; Fraga, A. Mycorrhizal status of main spontaneous or introduced forest trees in El Tarf province (Algerian north-east). Online J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, M.; Neves, M.A.; Comandini, O.; Rinaldi, A.C. Scleroderma meridionale ectomycorrhizae on Halimium halimifolium: Expanding the Mediterranean symbiotic repertoire. Symbiosis 2018, 76, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.; Furtado, A.N.M.; Comandini, O.; Geml, J.; Rinaldi, A.C. Halimium as an ectomycorrhizal symbiont. New records and an appreciation of known fungal diversity. Mycol. Prog. 2020, 19, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jülich, W. Higher Taxa of Basidiomycetes; J. Cramer: Vaduz, Liechtenstein, 1981; Volume 85, pp. 1–485. [Google Scholar]
- Matheny, P.B. Improving phylogenetic inference of mushrooms using RPB1 and RPB2 sequences (Inocybe; Agaricales). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryberg, M.; Larsson, E.; Jacobsson, S. An evolutionary perspective on morphological and ecological characters in the mushroom family Inocybaceae (Agaricomycotina, Fungi). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 55, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheny, P.B.; Hobbs, A.M.; Esteve-Raventós, F. Genera of Inocybaceae: New skin for the old ceremony. Mycologia 2020, 112, 83–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervini, M. Inocybe messapica (Inocybaceae, Agaricales, Basidiomycota), a new species in section Splendentes, from Mediterranean oak woods. Phytotaxa 2021, 480, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovana, F.; Bizio, E.; Garbelotto, M.; Ferisin, G. Inocybe cervenianensis (Agaricales, Inocybaceae), a new species in the I. flavoalbida clade from Italy. Phytotaxa 2021, 484, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.; Mua, A.; Porcu, G.; Casula, M.; Rinaldi, A.C.; Mifsud, S.; Garrido-Benavent, I. Pseudosperma calciphilum (Inocybaceae), a new Mediterranean species Sardinia (Italy), Malta, and Valencia (Spain). Phytotaxa 2024, 633, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.; Mua, A.; Porcu, G.; Casula, M.; Rinaldi, A.C. Pseudosperma subvolvatum (Inocybaceae), sp. nov. Fungal Divers. Notes 2024, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Parmasto, E.; Parmasto, I. Variation in Basidiospores in the Hymenomycetes and Its Significance to Their Taxonomy; Cramer in d. Borntraeger-Verl.-Buchh: Berlin, Germany, 1987; Volume 115, pp. 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, R. Color Standards and Color Nomenclature; The Author: Washington, DC, USA, 1912; pp. 1–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kuyper, T.W. A revision of the genus Inocybe in Europe I. Subgenus Inosperma and the smooth-spored species of subgenus Inocybe. Persoonia 1986, 3, 1–247. [Google Scholar]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for Basidiomycetes—Application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, W.P.; Maddison, D.R. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis, Version 3.61. 2019. Available online: http://mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 18 February 2024).
- Edler, D.; Klein, J.; Antonelli, A.; Silvestro, D. raxmlGUI 2.0: A graphical interface and toolkit for phylogenetic analyses using RAxML. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree, v1. 4.0; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2012. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for Inference of Large Phylogenetic Trees Conference: Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE). In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Esteve-Raventós, F.; Vila, J.; Llimona, X. Estudios sobre el género Inocybe (Cortinariales) en los jarales de Cataluña. I. Rev. Catalana Micol. 2002, 24, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Fachada, V.; Bandini, D.; Beja-Pereira, A. Two new species of Inocybe from Mediterranean Cistaceae heathlands. Mycologia 2024, 116, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Arroyo, B. (Ed.) Inventario Micológico Básico de Andalucía; Consejería de Medio Ambiente, Junta de Andalucía: Córdoba, Spain, 2004; pp. 1–680. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, P.A.; Corriol, G.; Borgarino, D.; Auber, P.; Lavoise, C.; Richard, F.; Selosse, M.-A. Contribution à la connaissance des champignons de l’étage thermoméditerranéen Corse II. Bull. Semest. Féd. Assoc. Mycol. Méditerr. 2007, 31, 9–31. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, P.A.; Corriol, G.; Borgarino, D.; Auber, P.; Lavoise, C. Contribution à la connaissance des champignons de l’étage thermoméditerranéen Corse III. Bull. Semest. Féd. Assoc. Mycol. Méditerr. 2007, 31, 33–84. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado, P.; Manjón, J.L.; Matheny, P.B.; Esteve-Raventós, F. Tubariomyces, a new genus of Inocybaceae from the Mediterranean region. Mycologia 2010, 102, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, D.; Oertel, B.; Eberhardt, U. A fresh outlook on the smooth-spored species of Inocybe: Type studies and 18 new species. Mycol. Prog. 2021, 20, 1019–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.; Ryberg, M.; Moreau, P.-A.; Delcuse Mathiesen, Å.; Jacobsson, S. Taxonomy and evolutionary relationships within species of section Rimosae (Inocybe) based on ITS, LSU and mtSSU sequence data. Persoonia 2009, 23, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, M.; Ahmad, I.; Khalid, A.N. New reports of Inocybe from pine forests in Pakistan. Mycotaxon 2015, 130, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerer, R. Fungal relationships and structural identity of their ectomycorrhizae. Mycol. Prog. 2006, 5, 67–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalopoulos, V.; Polemis, E.; Fryssouli, V.; Kottis, L.; Bandini, D.; Dima, B.; Zervakis, G.I. Mallocybe heimii ectomycorrhizae with Cistus creticus and Pinus halepensis in Mediterranean littoral sand dunes-assessment of phylogenetic relationships to M. arenaria and M. agardhii. Mycorrhiza 2021, 31, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, M.; Comandini, O.; Sanjust, E.; Rinaldi, A.C. Conservation status of milkcaps (Basidiomycota, Russulales, Russulaceae), with notes on poorly known species. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, T.; Lücking, R.; Dahlberg, A.; Gaya, E.; Suz, L.M.; Mikryukov, V.; Liimatainen, K.; Druzhinina, I.; Westrip, J.R.S.; Mueller, G.M.; et al. Pushing the frontiers of biodiversity research: Unveiling the global diversity, distribution, and conservation of fungi. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2023, 48, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biketova, A.Y.; Simonini, G.; Rinaldi, A.C. Nomenclatural novelties: Cyanoboletus mediterraneensis Biketova, A. Rinaldi & Simonini, sp. nov. Index Fungorum 2022, 516, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.R.; Suwannarach, N.; Sysouphanthong, P.; Abdel-Wahab, M.A.; Abdel-Aziz, F.A.; Abeywickrama, P.D.; Abreu, V.P.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 1512–1610: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions on genera and species of fungal taxa. Fungal Divers. 2022, 117, 1–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkonen, K.; Vauras, J. Eleven new boreal species of Inocybe with nodulose spores. Mycol. Prog. 2012, 11, 299–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cripps, C.L.; Larsson, E.; Vauras, J. Nodulose-spored Inocybe from the Rocky Mountain alpine zone molecularly linked to European and type specimens. Mycologia 2019, 112, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandini, D.; Oertel, B.; Schüssler, C.; Eberhardt, U. Noch mehr Risspilze: Fünfzehn neue und zwei wenig bekannte Arten der Gattung Inocybe. Mycol. Bavar. 2020, 20, 13–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bon, M. Clé monographique dù genre Inocybe (Fr.) Fr. Doc. Mycol. 1997, 27, 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Malençon, G.; Bertault, R. Flore des Champignons Superieurs du Maroc; Faculté des Sciences: Rabat, Morocco, 1970; Volume 1, pp. 1–604. [Google Scholar]
- Stangl, J.; Veselský, J. Zweiter Beitrag zur Kenntnis der selteneren Inocybe-Arten. Česká Mykol. 1973, 27, 11–25. [Google Scholar]





| Species | Host | Reference | GenBank nrITS Accession Number | GenBank nrLSU Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inocybe asterospora Quél. | Halimium sp., Halimium halimifolium | [38] | ||
| Inocybe calida Velen. | Halimium halimifolium | [38] (a) | ||
| Inocybe corydalina Quél. | Halimium sp. | [38] | ||
| Inocybe halimiphila sp. nov. | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP941799 | PP941805 |
| Inocybe halimiphila sp. nov. | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP941800 | |
| Inocybe halimiphila sp. nov. | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP941802 | PP941806 |
| Inocybe halimiphila sp. nov. (b) | Halimium halimifolium | [16] (ECM) | MT594518 | |
| Inocybe halophila R. Heim. (c) | Halimium halimifolium | [39,40] | ||
| Inocybe iberilepora Fachada & Bandini | Halimium sp. (?) | [37] | OQ690007 | |
| Inocybe lacera (Fr.) P. Kumm. | Halimium halimifolium | [38] | ||
| Inocybe phaeosquamosa Fachada & Bandini | Halimium cfr. umbellatum (?) | [37] | OQ690006 | |
| Inocybe pruinosa R. Heim (d) | Halimium sp. | [38] | ||
| Inocybe rocabrunae Esteve-Rav. & Vila (d) | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP935492 | PP935502 |
| Inocybe rubripes sp. nov. | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP941804 | |
| Inocybe rubripes sp. nov. | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP941801 | PP941847 |
| Inocybe rubripes sp. nov. | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP941803 | PP941846 |
| Inocybe rubripes sp. nov. (e) | Halimium halimifolium | [16] (ECM) | MT594517 | |
| Inocybe tigrina R. Heim | Halimium halimifolium | [16] | MT594512 | |
| Inocybe tigrina R. Heim | Halimium halimifolium | [16] | MT594513 | |
| Inocybe tigrina R. Heim | Halimium halimifolium | [16] | MT594514 | |
| Inocybe tigrina R. Heim | Halimium halimifolium | [16] | MT594516 | |
| Inocybe tigrina R. Heim | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP935492 | PP935539 |
| Inocybe tigrina R. Heim | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP946889 | PP946893 |
| Inocybe tigrina R. Heim | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP946890 | PP946896 |
| Inocybe sp. 1 (Hal-BP-68) | Halimium halimifolium | [16] | MT594515 | |
| Inocybe sp. 4 (Hal-BP-32) | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP859462 | |
| Pseudosperma sp. | Halimium halimifolium | this study | PP958644 | PP958508 |
| Tubariomyces hygrophoroides Esteve-Rav., P.-A. Moreau & C.E. Hermos | Halimium halimifolium | [41] | ||
| Tubariomyces inexpectatus (M. Villarreal, Esteve-Raventós, Heykoop & E. Horak) Esteve-Raventós & Matheny | Halimium halimifolium | [39] (f) |
| Species | Voucher/Strain | Country | GenBank nrITS Accession Number | GenBank nrLSU Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inocybe abdita | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901691, holotype | GERMANY | OP164062 | OP164062 |
| Inocybe abjecta | UBC:F19032 18S | CANADA | HQ604518 | HQ604518 |
| Inocybe appendiculata | FV2020082103 | FRANCE | ON622929 | n/a |
| Inocybe appendiculata | TUR203986 | ITALY | OR387048 | n/a |
| Inocybe assimilata | DB5-9-14-11 | GERMANY | MG136880 | MG137006 |
| Inocybe assimilata | M 0020105, epitype | GERMANY | KM873366 | n/a |
| Inocybe culicis | TUR-A 203492 | FINLAND | OP164108 | OP164108 |
| Inocybe curvipes | EL6703 | SWEDEN | AM882813 | AM882813 |
| Inocybe curvipes | AB 18-10-80 | FRANCE | ON322974 | n/a |
| Inocybe flocculosa | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901628 | NETHERLANDS | OK057165 | OK057165 |
| Inocybe furfurea | G:G00053152, lectotype | FRANCE | MG012472 | n/a |
| Inocybe giacomi | JV21543 | FINLAND | MK153656 | MK153656 |
| Inocybe giacomi | EL80-12 | NORWAY | MK153657 | MK153657 |
| Inocybe glabripes | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0900979, neotype | GERMANY | MW845881 | MW845881 |
| Inocybe glabripes | XC98-04-20-18 | FRANCE | ON129669 | n/a |
| Inocybe griseovelata | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901568, epitype | GERMANY | MW845942 | MW845942 |
| Inocybe griseovelata | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901457 | NETHERLANDS | MW845883 | MW845883 |
| Inocybe halimiphila | CAG B/5.6.4 (GA15M), holotype | ITALY | PP941799 | P941805 |
| Inocybe halimiphila | 1446MS | ITALY | PP941800 | n/a |
| Inocybe halimiphila | GJ13M | ITALY | PP941802 | PP941806 |
| Inocybe halimiphila | 4I, ectomycorrhiza | ITALY | MT594518 | n/a |
| Inocybe helobia | L:L-0053536, holotype | NETHERLANDS | MN319699 | n/a |
| Inocybe impexa | 9773 | ITALY | JF908134 | n/a |
| Inocybe impexa | SMNS-STU-F-0901710 | FINLAND | OP164066 | OP164066 |
| Inocybe juniperina | AMB 19289, paratype | ITALY | OR656747 | OR656748 |
| Inocybe lacera | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901707 | NETHERLANDS | OP164102 | OP164102 |
| Inocybe lacera | STU: SMNS-STU-F-0901696 | GERMANY | OP164052 | OP164052 |
| Inocybe lacera | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901583, neotype | NETHERLANDS | OK057130 | OK057130 |
| Inocybe lacera var. heterosperma | WTU:F 043782, isotype | CANADA | KY923044 | n/a |
| Inocybe maculipes | 21532 | ITALY | JF908217 | n/a |
| Inocybe melanopus | JV4986 | FINLAND | AM882727 | AM882727 |
| Inocybe melanopus | BJ920904 | SWEDEN | AM882725 | AM882725 |
| Inocybe mixtilis | M 0219661, epitype | GERMANY | KM873369 | n/a |
| Inocybe mixtilis | EL8904 | SWEDEN | AM882836 | AM882836 |
| Inocybe moravica | BRNM:07012/39, holotype | CZECH REPUBLIC | OP712321 | n/a |
| Inocybe moravica | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901700 | NETHERLANDS | OP164097 | n/a |
| Inocybe moravica | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901695 | NETHERLANDS | OP164099 | OP164099 |
| Inocybe mortenii | O:O-F-259432 | NORWAY | OP164040 | n/a |
| Inocybe mortenii | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901737 | AUSTRIA | OP164072 | OP164072 |
| Inocybe mytiliodora | PBM1572 | USA | OR387055 | JN974947 |
| Inocybe mytiliodora | TUR190149_L4343920 | FINLAND | OR387054 | n/a |
| Inocybe phaeodisca | XC2001-16 | FRANCE | ON129688 | n/a |
| Inocybe phaeodisca | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901574 | GERMANY | MW845950 | MW845950 |
| Inocybe pluppiana | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901254, holotype | NETHERLANDS | MN512327 | MN512327 |
| Inocybe pluppiana | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901729 | NETHERLANDS | OP164088 | OP164088 |
| Inocybe pruinosa | EL24106 | FRANCE | FN550904 | FN550904 |
| Inocybe pruinosa | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0900987 | GERMANY | MT101877 | MT101877 |
| Inocybe pseudodestricta | PRM:PRM716231, holotype | GERMANY | MG012468 | n/a |
| Inocybe pseudodestricta | KR:KR-M-0043223 | NETHERLANDS | MT101892 | n/a |
| Inocybe pseudoumbrina | M:M-0151614, holotype | GERMANY | MF782552 | n/a |
| Inocybe pusio | M133 | HUNGARY | OM228863 | n/a |
| Inocybe pusio | DB16-8-14-24 | GERMANY | MH366588 | n/a |
| Inocybe rocabrunae | AH 34437 | SPAIN | OR364880 | OR364880 |
| Inocybe rocabrunae | 1833MS | ITALY | PP935492 | PP935502 |
| Inocybe rubripes | GC13M | ITALY | PP941804 | n/a |
| Inocybe rubripes | CAG B/5.6.5 (1926MS), holotype | ITALY | PP941801 | PP941847 |
| Inocybe rubripes | 1838MS | ITALY | PP941803 | PP941846 |
| Inocybe rubripes | ML2020 2I, ectomycorrhiza | ITALY | MT594517 | n/a |
| Inocybe rufuloides | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901442 | GERMANY | MT101878 | n/a |
| Inocybe rufuloides | CM044 | ALGERIA | KP826750 | n/a |
| Inocybe subcarpta | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901736 | GERMANY | OP164086 | OP164086 |
| Inocybe subcarpta | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901690 | AUSTRIA | OP164077 | OP164077 |
| Inocybe subgiacomi | JV29938, holotype | SWEDEN | MK153665 | MK153665 |
| Inocybe subgiacomi | CLC1330 | USA | MK153664 | MK153664 |
| Inocybe subnudipes | DB23-9-90-Vauras | FINLAND | OP164034 | n/a |
| Inocybe subnudipes | BJ920916 | SWEDEN | AM882809 | n/a |
| Inocybe tarda | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901730, epitype | GERMANY | OP164094 | OP164094 |
| Inocybe tarda | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901443 | GERMANY | MW845922 | MW845922 |
| Inocybe tenuicystidiata | M:M-0281792, holotype | GERMANY | MW856453 | MW856453 |
| Inocybe tigrina | STU:SMNS-STU-F-0901532, epitype | GERMANY | MW845933 | MW845933 |
| Inocybe tigrina | 1844MS | ITALY | PP935492 | PP935539 |
| Inocybe tigrina | EV06M | ITALY | PP946889 | PP946893 |
| Inocybe tigrina | FG09M | ITALY | PP946890 | PP946896 |
| Inocybe treneri | M-0276188(M) | GERMANY | MF083695 | n/a |
| Inocybe virgatula | G:G00058741, lectotype | FRANCE | MW845923 | n/a |
| Nothocybe distincta | CAL 1310, holotype | INDIA | KX171343 | KX171344 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanna, M.; Mua, A.; Casula, M.; Rinaldi, A.C. Inocybaceae (Basidiomycota) in Ectomycorrhizal Symbiosis with Halimium (Cistaceae), and the Description of Two New Species of Inocybe from Sardinia (Italy). Diversity 2024, 16, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080505
Sanna M, Mua A, Casula M, Rinaldi AC. Inocybaceae (Basidiomycota) in Ectomycorrhizal Symbiosis with Halimium (Cistaceae), and the Description of Two New Species of Inocybe from Sardinia (Italy). Diversity. 2024; 16(8):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080505
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanna, Massimo, Alberto Mua, Marco Casula, and Andrea C. Rinaldi. 2024. "Inocybaceae (Basidiomycota) in Ectomycorrhizal Symbiosis with Halimium (Cistaceae), and the Description of Two New Species of Inocybe from Sardinia (Italy)" Diversity 16, no. 8: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080505
APA StyleSanna, M., Mua, A., Casula, M., & Rinaldi, A. C. (2024). Inocybaceae (Basidiomycota) in Ectomycorrhizal Symbiosis with Halimium (Cistaceae), and the Description of Two New Species of Inocybe from Sardinia (Italy). Diversity, 16(8), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16080505







