Improving Aquatic Biodiversity Estimates in Africa: Rotifers of Angola and Ghana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
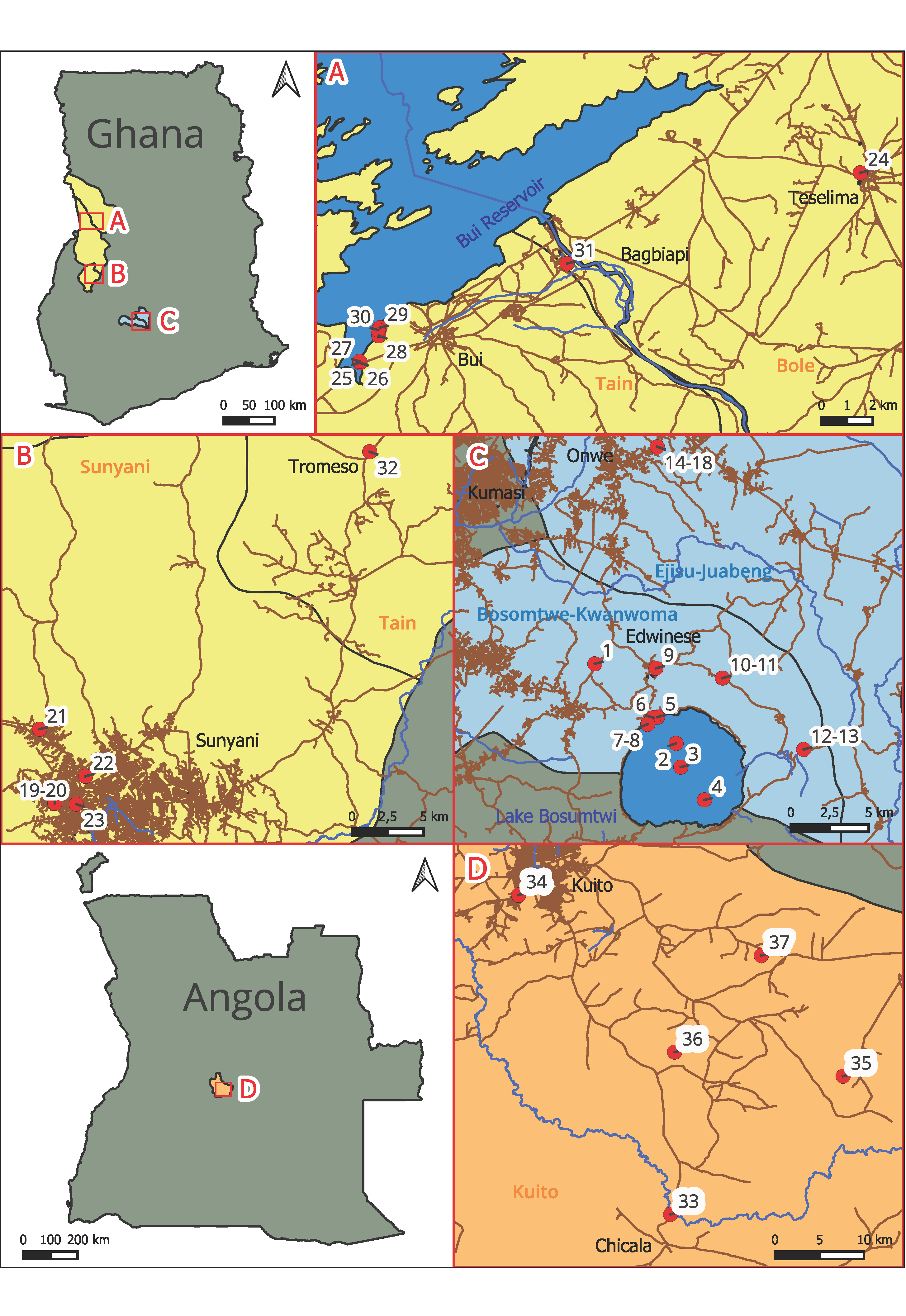
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling, Water Chemistry, and Species Richness
2.3. QB/T and QB/L Quotients
2.4. Effect of Climate Conditions on Species Distribution
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Water Physicochemical Parameters
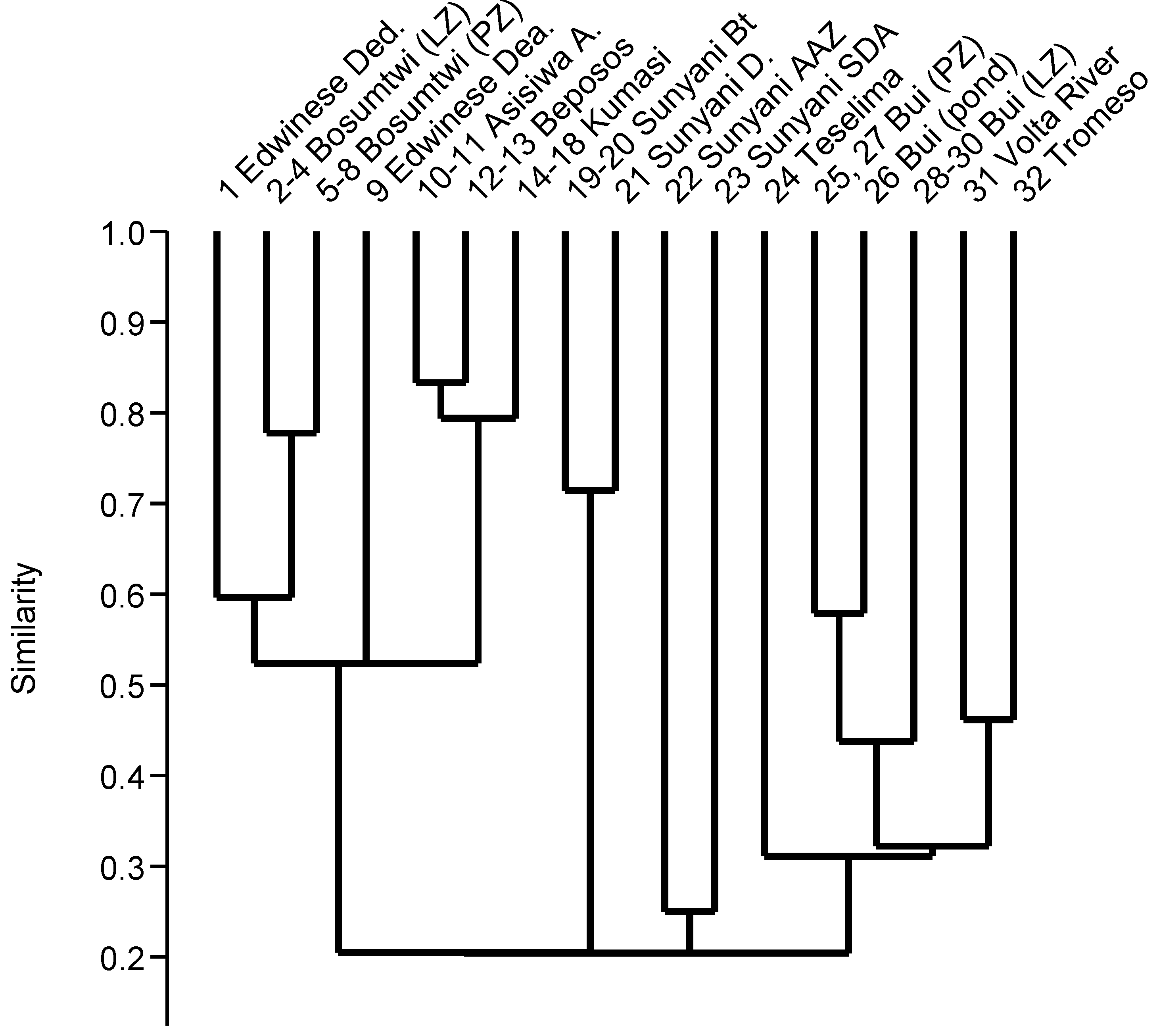
3.2. Species Richness
3.3. QB/T and QB/L Quotients
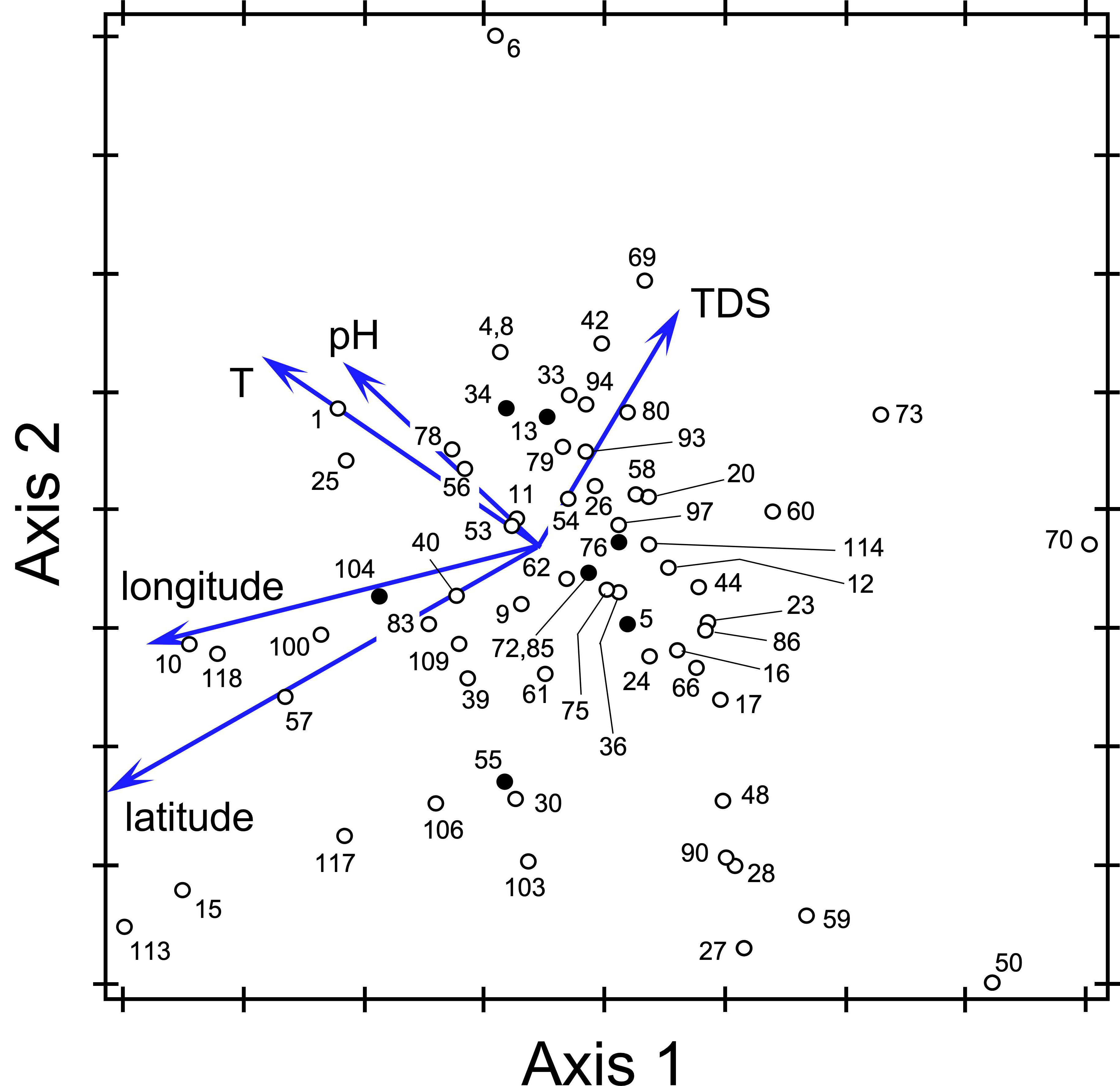
3.4. Effect of Climate Conditions on Species Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Segers, H. Global Diversity of Rotifers (Rotifera) in Freshwater. In Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment; Balian, E.V., Lévêque, C., Segers, H., Martens, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 49–59. ISBN 9781402082597. [Google Scholar]
- Collen, B.; Whitton, F.; Dyer, E.E.; Baillie, J.E.M.; Cumberlidge, N.; Darwall, W.R.T.; Pollock, C.; Richman, N.I.; Soulsby, A.-M.; Böhm, M. Global Patterns of Freshwater Species Diversity, Threat and Endemism. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.A.; Chapman, L.J. Deforestation in Tropical Africa. In Conservation, Ecology, and Management of African Fresh Waters; University of Florida Press: Gainsville, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 229–246. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaneto, D.; Barbosa, A.M.; Segers, H.; Pautasso, M. The ‘Rotiferologist’ Effect and Other Global Correlates of Species Richness in Monogonont Rotifers. Ecography 2012, 35, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, H.J. Biogeography of Rotifers. Hydrobiologia 1983, 104, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, H.; De Smet, W.H. Diversity and Endemism in Rotifera: A Review, and Keratella Bory de St Vincent. In Protist Diversity and Geographical Distribution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 69–82. ISBN 9789048128006. [Google Scholar]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J. Does the World Need Faunists? Based on Rotifer (Rotifera) Occurrence Reflections on the Role of Faunistic Research in Ecology. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2019, 104, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jersabek, C.D.; Leitner, M.F. The Rotifer World Catalog; World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Available online: https://www.rotifera.hausdernatur.at/Species/Index/222 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Fresno Lopez, Z.; Cancellario, T.; Fontaneto, D.; Kamburska, L.; Karimullah, K.; Wallace, R.L.; Walsh, E.J.; Smolak, R. A Georeferenced Dataset for Occurrence Records of the Phylum Rotifera in Africa. J. Limnol. 2023, 82, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolak, R.; Walsh, E.J.; Brown, P.D.; Wallace, R.L. A Synthesis of the Biogeographical Distribution of Rotifera in Africa. J. Plankton Res. 2023, 45, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng, L.E. Volta Lake: Physical and Biological Aspects. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 1973, 17, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Obeng-Asamoa, E.K. A Limnological Study of the Afram Arm of Volta Lake. Hydrobiologia 1977, 55, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frempong, E.; Nyjhar, B. Some Preliminary Observations on the Fauna and Flora of Barakese Lake (Ghana). Bull. l’I.F.A.N. 1973, 35, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sanful, P.O. Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Pelagic Zooplankton Community Structure and Secondary Production in Lake Bosumtwi Impact Crater, Ghana. Ph.D. Thesis, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, 2008. upublished. [Google Scholar]
- Sanful, P.O.; Frempong, E.; Aikins, S.; Hall, R.I.; Hecky, R.E. Secondary Production of Chaoborus ceratopogones (Diptera: Chaoboridae) in Lake Bosumtwi, Ghana. Aquat. Insects 2012, 34, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanful, P.O.; Frempong, E.; Aikins, S.; Hecky, R.E. Secondary Production of Crustacean Zooplankton and Biomass of Major Rotifer Species in Lake Bosumtwi/Bosomtwe, Ghana, West Africa. Afr. J. Ecol. 2013, 51, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanful, P.O.; Aikins, S.; Hecky, R.E. Depth Distribution of Zooplankton in Relation to Limnological Gradients under Different Stratification and Interannual Regimes in a Deep, Tropical Crater Lake. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2017, 53, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sanful, P.O.; Otu, M.K.; Kling, H.; Hecky, R.E. Occurrence and Seasonal Dynamics of Metalimnetic Deep Chlorophyll Maximum (DCM) in a Stratified Meromictic Tropical Lake and Its Implications for Zooplankton Community Distribution. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2017, 102, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.R. Some Rotifers from the Gold Coast. J. W. Afr. Sci. Assoc. 1956, 2, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kalous, L.; Kurfürst, J.; Petrtýl, M.; Holíková, P.; Trefil, P. Zooplankton of Small Ponds in Integrated Fish and Duck Production in Bie Province, Angola. Agric. Trop. Subtrop. 2009, 42, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, H.C. Rotifera as Indicators of Trophic Nature of Environments. Hydrobiologia 1966, 27, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejler, B. Relation to Habitat in Rotifers. In Proceedings of the Rotifera VII; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 267–278. [Google Scholar]
- Bērziņš, B.; Pejler, B. Rotifer Occurrence and Trophic Degree. Hydrobiologia 1989, 182, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontin, R.M.; Langley, J.M. The Use of Rotifer Communities to Provide a Preliminary National Classification of Small Water Bodies in England. In Proceedings of the Rotifer Symposium VI; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Sládeček, V. Rotifers as Indicators of Water Quality. Hydrobiologia 1983, 100, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Dudani, V.K. Rotifers from Some Tropical Ponds in Bihar: Species Composition, Similarities and Trophic Indicators. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 1992, 72, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.K. Synecology of Rotifers in a Tropical Flood Plain Lake of Upper Assam. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 70, 880–885. [Google Scholar]
- Tasevska, O.; Kostoski, G.; Dafina, G. Rotifers Based Assessment of the Lake Dojran Water Quality. Ohrid Repub. Maced. 2010, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tasevska, O.; Jersabek, C.D.; Kostoski, G.; Gušeska, D. Differences in Rotifer Communities in Two Freshwater Bodies of Different Trophic Degree (Lake Ohrid and Lake Dojran, Macedonia). Biologia 2012, 67, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.L.; Snell, T.W.; Smith, H.A. Chapter 13—Phylum Rotifera. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates, 4th ed.; Thorp, J.H., Covich, A.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 225–271. [Google Scholar]
- Lucena-Moya, P.; Duggan, I.C. Macrophyte Architecture Affects the Abundance and Diversity of Littoral Microfauna. Aquat. Ecol. 2011, 45, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paggi, S.B.J.; Muñoz, S.; Frau, D.; Paggi, J.C. Horizontal Distribution of Rotifers in a Subtropical Shallow Lake (Paraná Floodplain, Argentina). Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2012, 180, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J.; Karpowicz, M. Rotifera in Lake Subhabitats. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, I.C.; Green, J.D.; Thompson, K.; Shiel, R.J. Rotifers in Relation to Littoral Ecotone Structure in Lake Rotomanuka, North Island, New Zealand. In Proceedings of the Rotifera VIII: A Comparative Approach; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Duggan, I.C. The Ecology of Periphytic Rotifers. In Proceedings of the Rotifera IX; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Špoljar, M.; Fressl, J.; Dražina, T.; Meseljević, M.; Grčić, Z. Epiphytic Metazoans on Emergent Macrophytes in Oxbow Lakes of the Krapina River, Croatia: Differences Related to Plant Species and Limnological Conditions. Acta Bot. Croat. 2012, 71, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špoljar, M.; Dražina, T.; Šargač, J.; Borojević, K.K.; Žutinić, P. Submerged Macrophytes as a Habitat for Zooplankton Development in Two Reservoirs of a Flow-through System (Papuk Nature Park, Croatia). Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2012, 48, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielder, D.S.; Purser, G.J.; Battaglene, S.C. Effect of Rapid Changes in Temperature and Salinity on Availability of the Rotifers Brachionus rotundiformis and Brachionus plicatilis. Aquaculture 2000, 189, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosque, T.; Hernández, R.; Pérez, R.; Todolí, R.; Oltra, R. Effects of Salinity, Temperature and Food Level on the Demographic Characteristics of the Seawater Rotifer Synchaeta littoralis Rousselet. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2001, 258, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.S.S.; Nandini, S.; Morales-Ventura, J.; Delgado-Martínez, I.; González-Valverde, L. Effects of NaCl Salinity on the Population Dynamics of Freshwater Zooplankton (Rotifers and Cladocerans). Aquat. Ecol. 2006, 40, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielańska-Grajner, I.; Cudak, A. Effects of Salinity on Species Diversity of Rotifers in Anthropogenic Water Bodies. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.; Wepener, V.; Van Vuren, J.H.J. Aquatic Invertebrate Communities of Perennial Pans in Mpumalanga, South Africa: A Diversity and Functional Approach. Afr. Invertebr. 2012, 53, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüzer, P.; Buyurgan, Ö.; Tekatli, Ç.; Altindağ, A. Species Diversity and Community Structure of Zooplankton in Three Different Types of Water Body within the Sakarya River Basin, Turkey. Turk. J. Zool. 2017, 41, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Sánchez, A.; Reyes-Vanegas, G.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Diversity and Abundance of Rotifers during an Annual Cycle in the Reservoir Valerio Trujano (Tepecoacuilco, Guerrero, Mexico). Inland Waters 2014, 4, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bērziņš, B.; Pejler, B. Rotifer Occurrence in Relation to Oxygen Content. Hydrobiologia 1989, 183, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengol, X.; Esparcia, A.; Miracle, M.R. Rotifer Vertical Distribution in a Strongly Stratified Lake: A Multivariate Analysis. In Proceedings of the Rotifera VIII: A Comparative Approach; Wurdak, E., Wallace, R., Segers, H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, E.J.; Schröder, T.; Wallace, R.L.; Ríos-Arana, J.V.; Rico-Martínez, R. Rotifers from Selected Inland Saline Waters in the Chihuahuan Desert of México. Aquat. Biosyst. 2008, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.; Fontaneto, D.; Segers, H.; Altindağ, A. Temperature and Salinity as Interacting Drivers of Species Richness of Planktonic Rotifers in Turkish Continental Waters. J. Limnol. 2010, 69, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Schröder, T.; Ríos-Arana, J.V.; Rico-Martinez, R.; Silva-Briano, M.; Wallace, R.L.; Walsh, E.J. Processes Contributing to Rotifer Community Assembly in Shallow Temporary Aridland Waters. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 3719–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Špoljar, M.; Pronin, M.; Zhang, C.; Mleczek, M. Spring and Autumn Rotifer Community Structure Differentiates Shallow Water Bodies in Two European Ecoregions: Poland and Croatia. Hydrobiologia 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel-Alloul, B.; Niyonsenga, T.; Legendre, P.; Gril, G. Spatial and Environmental Components of Freshwater Zooplankton Structure. Écoscience 1995, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessen, D.O.; Andersen, T.; Faafeng, B.A. Replacement of Herbivore Zooplankton Species along Gradients of Ecosystem Productivity and Fish Predation Pressure. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolak, R.; Walsh, E.J. Rotifer Species Richness in Kenyan Waterbodies: Contributions of Environmental Characteristics. Diversity 2022, 14, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, J.E.; Stemberger, R.S. Zooplankton (Especially Crustaceans and Rotifers) as Indicators of Water Quality. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1978, 97, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, L.K. Can Pelagic Rotifers Be Used as Indicators of Lake Trophic State? Verh. lnternat. Verein. Limnol 1991, 24, 2761–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.S.; Marshall, H.G. The Trophic Contributions of Rotifers in Tidal Freshwater and Estuarine Habitats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, I.C.; Green, J.D.; Shiel, R.J. Distribution of Rotifers in North Island, New Zealand, and Their Potential Use as Bioindicators of Lake Trophic State. In Proceedings of the Rotifera IX; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Duggan, I.C.; Green, J.D.; Shiel, R.J. Distribution of Rotifer Assemblages in North Island, New Zealand, Lakes: Relationships to Environmental and Historical Factors. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špoljar, M.; Tomljanović, T.; Lalić, I. Eutrophication Impact on Zooplankton Community: A Shallow Lake Approach. Holist. Approach Environ. 2011, 1, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J. The Usefulness of Zooplankton as Lake Ecosystem Indicators: Rotifer Trophic State Index. Pol. J. Ecol. 2012, 60, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- García-Chicote, J.; Armengol, X.; Rojo, C. Zooplankton Species as Indicators of Trophic State in Reservoirs from Mediterranean River Basins. Inland Waters 2019, 9, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpowicz, M.; Ejsmont-Karabin, J. Diversity and Structure of Pelagic Zooplankton (Crustacea, Rotifera) in NE Poland. Water 2021, 13, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarova, N.; Napiórkowski, P. Are Rotifer Indices Suitable for Assessing the Trophic Status in Slow-Flowing Waters of Canals? Hydrobiologia 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturej, E. Assessment of the Trophic State of the Coastal Lake Gardno Based on Community Structure and Zooplankton-Related Indices. Electron. J. Pol. Agric. Univ 2006, 9, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Paturej, E. Assessment of the Trophic State of A Restored Urban Lake Based on Zooplankton Community Structure and Zooplankton-Related Indices. Pol. J. Nat. Sci. 2008, 23, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturej, E.; Gozdziejewska, A. Zooplankton-Based Assessment of the Trophic State of Three Coastal Lakes—Lebsko, Gardno, and Jamno. Bull. Sea Fish. Inst 2005, 3, 7–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gaston, K.J. Global Patterns in Biodiversity. Nature 2000, 4, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomolino, M.V.; Riddle, B.R.; Whittaker, R.J.; Brown, J.H. Biogeography, 4th ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pinel-Alloul, B.; André, A.; Legendre, P.; Cardille, J.A.; Patalas, K.; Salki, A. Large-Scale Geographic Patterns of Diversity and Community Structure of Pelagic Crustacean Zooplankton in Canadian Lakes. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovenko, N.S.; Smykla, J.; Convey, P.; Kašparová, E.; Kozeretska, I.A.; Trokhymets, V.; Dykyy, I.; Plewka, M.; Devetter, M.; Duriš, Z.; et al. Antarctic Bdelloid Rotifers: Diversity, Endemism and Evolution. Hydrobiologia 2015, 761, 5–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, J.S.; Stevens, R.D. Multiple Environmental Determinants of Regional Species Richness and Effects of Geographic Range Size. Ecography 2010, 33, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R.H.; MacArthur, J.W. On Bird Species Diversity. Ecology 1961, 42, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, R.E. Environmental Heterogeneity and Plant Species Diversity: A Hypothesis. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, D.J. Energy and Large-Scale Patterns of Animal- and Plant-Species Richness. Am. Nat. 1991, 137, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, J.; Brose, U.; Grimm, V.; Tielbörger, K.; Wichmann, M.C.; Schwager, M.; Jeltsch, F. Animal Species Diversity Driven by Habitat Heterogeneity/Diversity: The Importance of Keystone Structures. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massicotte, P.; Proulx, R.; Cabana, G.; Rodríguez, M.A. Testing the Influence of Environmental Heterogeneity on Fish Species Richness in Two Biogeographic Provinces. PeerJ 2015, 3, e760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massicotte, P.; Peeken, I.; Katlein, C.; Flores, H.; Huot, Y.; Castellani, G.; Arndt, S.; Lange, B.A.; Tremblay, J.-É.; Babin, M. Sensitivity of Phytoplankton Primary Production Estimates to Available Irradiance under Heterogeneous Sea Ice Conditions. J. Geophys. Res. C Oceans 2019, 124, 5436–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Dray, S.; Garroway, C.J. Genetic and Species-Level Biodiversity Patterns Are Linked by Demography and Ecological Opportunity. Evolution 2022, 76, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, P.; Pärt, T. Age and Reproduction in Birds—Hypotheses and Tests. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.D.; Weir, J.T.; Hooper, D.M.; Tietze, D.T.; Martens, J.; Price, T.D. Ecological Limits on Diversification of the Himalayan Core Corvoidea. Evolution 2012, 66, 2599–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, K.H.; Wiens, J.J. What Explains Patterns of Species Richness? The Relative Importance of Climatic-Niche Evolution, Morphological Evolution, and Ecological Limits in Salamanders. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 5940–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, D.D.; Egan, J.P. Systematics of Clupeiformes and Testing for Ecological Limits on Species Richness in a Trans-Marine/Freshwater Clade. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2018, 16, e180095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboriau, T.; Albouy, C.; Descombes, P.; Mouillot, D.; Pellissier, L.; Leprieur, F. Ecological Constraints Coupled with Deep-Time Habitat Dynamics Predict the Latitudinal Diversity Gradient in Reef Fishes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20191506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundholm, J.T. Plant Species Diversity and Environmental Heterogeneity: Spatial Scale and Competing Hypotheses. J. Veg. Sci. 2009, 20, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, S.G.; Blair, J.M.; Collins, S.L. Environmental Heterogeneity Has a Weak Effect on Diversity during Community Assembly in Tallgrass Prairie. Ecol. Monogr. 2016, 86, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A.; Baer, S.G. Diversity Patterns from Sequentially Restored Grasslands Support the ‘Environmental Heterogeneity Hypothesis’. Oikos 2019, 128, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestrup, Å.M.; Ricciardi, A. Environmental Heterogeneity Limits the Local Dominance of an Invasive Freshwater Crustacean. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tang, S.; Li, C.; Fang, H.; Hu, H.; Yang, J.; Ding, J.; Jiang, Z. Environmental Effects on Vertebrate Species Richness: Testing the Energy, Environmental Stability and Habitat Heterogeneity Hypotheses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Beck, J.; Meyer, C.; Waldmann, E.; Weigelt, P.; Kreft, H. Differential Effects of Environmental Heterogeneity on Global Mammal Species Richness. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Gerstner, K.; Kreft, H. Environmental Heterogeneity as a Universal Driver of Species Richness across Taxa, Biomes and Spatial Scales. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QGIS Version: 3.30.2-’s-Hertogenbosch’. 2023. Available online: https://qgis.org/en/site/forusers/visualchangelog330/ (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Turner, B.F.; Gardner, L.R.; Sharp, W.E.; Blood, E.R. The Geochemistry of Lake Bosumtwi, a Hydrologically Closed Basin in the Humid Zone of Tropical Ghana. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchniak, M.K.; Awortwi, F.E.; Sanful, P.O.; Frempong, E.; Hall, R.I.; Hecky, R.E. Effects of Physical Dynamics on the Water Column Structure of Lake Bosomtwe/Bosumtwi, Ghana (West Africa). Verh. lnternat. Verein. Limnol. 2009, 30, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeberl, C.; Reimold, W.U. Bosumtwi Impact Crater, Ghana (West Africa): An Updated and Revised Geological Map, with Explanations. Jb. Geol. B.-A. 2005, 145, 31–70. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.; Talbot, M.R.; Haskell, B.J. Mid-Holocene Climate Change in Lake Bosumtwi, Ghana. Quat. Res. 2003, 60, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poste, A.E.; Hecky, R.E.; Muir, D. Biomagnification of Mercury in a West African Crater Lake (Lake Bosomtwe, Ghana). Verh. lnternat. Verein. Limnol 2008, 30, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amisah, S.; Agbo, N.W. An Investigation into the Food and Feeding Ecology of a Potential Aquaculture Candidate, Sarotherodon Galilaeus Multifasciatus in a Meteoritic Crater Lake in Ghana. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2008, 12, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mirabdullayev, I.M.; Sanful, P.O.; Frempong, E. Mesocyclops bosumtwii sp. nov. (Copepoda: Cyclopidae) from Ghana. Annal. Zool. 2007, 57, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Whyte, S.A. Distribution, Trophic Relationships and Breeding Habits of the Fish Populations in a Tropical Lake Basin (Lake Bosumtwi-Ghana). J. Zool. 1975, 177, 25–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adom, D. The Human Impact and the Aquatic Biodiversity of Lake Bosomtwe: Rennaisance of the Cultural Traditions of Abono (Ghana)? Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2018, 20, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensengerth, O. South-South Technology Transfer: Who Benefits? A Case Study of the Chinese-Built Bui Dam in Ghana. Energy Policy 2018, 114, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortey, E.M.; Ofosu, E.A.; Kolodko, D.V.; Kabobah, A.T. Sustainability Assessment of the Bui Hydropower System. Environments 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okyereh, S.A.; Ofosu, E.A.; Kabobah, A.T. Modelling the Impact of Bui Dam Operations on Downstream Competing Water Uses. Water-Energy Nexus 2019, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESIA. Environmental and Social Impact Assessment of the Bui Hydropower Project; ERM: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alhassan, E.H. Seasonal Variations in Phytoplankton Diversity in the Bui Dam Area of the Black Volta in Ghana during the Pre- and Post-Impoundment Periods. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2015, 63, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, E.H.; Ofori-Danson, P.K.; Samman, J. Ecological Impact of River Impoundment on Zooplankton. Zool. Ecol. 2015, 25, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, E.H.; Ofori-Danson, P.K. Plankton Abundance in Relation to Physicochemical Factors in the Bui Reservoir of Ghana’s Black Volta River. Afr. J. Ecol. 2017, 55, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrbáček, J.; Blažka, P.; Brand, Z.; Fott, J.; Kořínek, V.; Kubíček, F.; Lellák, J.; Procházková, L.; Straškraba, M.; Straškrabová, V.; et al. Limnologické Metody; SPN: Praha, Czech Republic, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Segers, H. Rotifera 2: The Lecanidae (Monogononta). Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World 6; Nogrady, T., Ed.; SPB Academic Publishing: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 2, ISBN 9789051030914. [Google Scholar]
- Nogrady, T.; Pourriot, R.; Segers, H. Rotifera 3: The Notommatidae (Monogononta) and the Scaridiidae (Monogononta). Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World 8; Nogrady, T., Ed.; SPB Academic Publishing: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 3, ISBN 9789051031034. [Google Scholar]
- De Smet, W.H. Rotifera 4: The Proalidae (Monogomonta). Guides to the Identifications of Microinvertebrates of the Continental Continental Waters of the World 9; Nogrady, T., Ed.; SPB Academic Publishing: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 4, ISBN 9789051031195. [Google Scholar]
- De Smet, W.H.; Pourriot, R. Rotifera 5: The Dicranophoridae (Monogononta) and The Ituridae (Monogononta). Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World 12; Nogrardy, T., Ed.; SPB Academic Publishing: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1997; Volume 5, ISBN 9789051031355. [Google Scholar]
- Segers, H. Rotifera 6: Asplanchnidae, Gastropodidae, Lindiidae, Microcodidae, Synchaetidae, Trochosphaeridae and Filinia. Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World 18; Nogrady, T., Ed.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 6, ISBN 9780009282447. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttner-Kolisko, A. Plankton Rotifers: Biology and Taxonomy; Stuttgarut, E., Ed.; Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung: Stuttgart, Germany, 1974; Volume 26, p. 146. [Google Scholar]
- Koste, W. Die Radertiere Mitteleuropas I; Gebrüder Borntraeger: Berlin/Stuttgart, Germany, 1978; Volume 1, p. 673. [Google Scholar]
- Jersabek, C.D.; De Smet, W.H.; Hinz, C.; Fontaneto, D.; Hussey, C.G.; Michaloudi, E.; Wallace, R.L.; Segers, H. List of Available Names in Zoology, Candidate Part Phylum Rotifera, Species-Group Names Established before 1 January 2000. Available online: https://archive.org/details/LANCandidatePartSpeciesRotifera (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Karabin, A. Pelagic Zooplankton (Rotaria+Crustacea) Variation in the Process of Lake Eutrophication. II: Modifying Effect of Biotic Agents. Ekol. Pol. 1986, 33, 617–644. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, H.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Lutsko, N.J.; Dufour, A.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, X.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Miralles, D.G. High-Resolution (1 Km) Köppen-Geiger Maps for 1901–2099 Based on Constrained CMIP6 Projections. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccune, B.; Mefford, M.J. PC-ORD. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data; MjM Software: Gleneden Beach, Oregon, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, G.G. Notes on the Measurement of Faunal Resemblance. Am. J. Sci. 1960, 258, 300–311. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhí, A.; Herrmann, J.; Gascón, S.; Sala, J.; Boix, D. How Do Early Successional Patterns in Man-Made Wetlands Differ between Cold Temperate and Mediterranean Regions? Limnologica 2012, 42, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.N.; Henry, R. Is the Littoral Zone Taxonomically and Functionally More Diverse? Investigating the Rotifer Community of a Tropical Shallow Lake. Limnology 2022, 23, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennak, R.W. Structure of Zooplankton Populations in the Littoral Macrophyte Zone of Some Colorado Lakes. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1966, 85, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E. Summer Zooplankton Dynamics in the Limnetic and Littoral Zones of a Humic Acid Lake. Hydrobiologia 1991, 215, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, D.; Sala, J.; Quintana, X.D.; Moreno-Amich, R. Succession of the Animal Community in a Mediterranean Temporary Pond. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2004, 23, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louette, G.; De Meester, L. Predation and Priority Effects in Experimental Zooplankton Communities. Oikos 2007, 116, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T. Rotifer Community Structure in the South Basin of Lake Biwa. Hydrobiologia 1993, 271, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.B.; Antunes, S.C.; Pereira, R.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Gonçalves, F. Rotifer Community Structure in Three Shallow Lakes: Seasonal Fluctuations and Explanatory Factors. Hydrobiologia 2005, 543, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.J.; Sarma, S.S.S.; Merino-Ibarra, M.; Nandini, S. Seasonal Changes in the Rotifer (Rotifera) Diversity from a Tropical High Altitude Reservoir (Valle de Bravo, Mexico). J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obertegger, U.; Thaler, B.; Flaim, G. Rotifer Species Richness along an Altitudinal Gradient in the Alps. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B. Diversity of Rotifers (Rotifera, Eurotatoria) of Loktak Lake, Manipur, North-Eastern India. Trop. Ecol. 2009, 50, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J.; Hutorowicz, A.; Kapusta, A.; Stawecki, K.; Tunowski, J.; Zdanowski, B. Rotifers in Heated Konin Lakes—A Review of Long-Term Observations. Water 2020, 12, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, L.; De Smet, W.H. Diversity, Composition and Environmental Relations of Periphytic Rotifer Assemblages in Lentic Freshwater Bodies (Flanders, Lower Belgium). Diversity 2023, 15, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasevska, O.; Kostoski, G.; Gušeska, D. Recent Species Composition of Rotifera Fauna of The Lake Dojran (R. Macedonia); Hydrobiological Institute Ohrid: Ohrid, Macedonia, 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zoppi de Roa, E.; Gordon, E.; González, F.; Montiel, E. Plancton y Vegetación de Una Sabana Inundable En Mantecal. Acta Biol. Venez. 2009, 29, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade-Sossa, C.; García-Folleco, M.; Rodríguez-Munar, C.A.; Duque, S.; Realpe, E. Efectos de La Fluctuación Del Nivel Del Agua Sobre La Estructura Del Ensamblaje de Rotíferos En El Lago Largo (Sistema Yahuarcaca-Llanura de Inundación Del Río Amazonas-Colombia). Caldasia 2011, 33, 519–537. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, A.K.; Yousuf, A.R. Rotifer Community in Some Kashmir Himalayan Lakes of Varied Trophic Status. J. Res. Dev. 2003, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mäemets, A. Rotifers as Indicators of Lake Types in Estonia. Hydrobiologia 1983, 104, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.G. Zooplankton Composition, Dominance and Abundance as Indicators of Environmental Compartmentalization in Jurumirim Reservoir (Paranapanema River), São Paulo, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2001, 455, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, I.D.M.; May, L. Analysis of 1995 Zooplankton Samples-Loch Leven NNR. Available online: https://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/8967/1/N008967CR.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Dembowska, E.A.; Napiórkowski, P.; Mieszczankin, T.; Józefowicz, S. Planktonic Indices in the Evaluation of the Ecological Status and the Trophic State of the Longest Lake in Poland. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 56, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, L.; O’Hare, M. Changes in Rotifer Species Composition and Abundance along a Trophic Gradient in Loch Lomond, Scotland, UK. Hydrobiologia 2005, 546, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, T.; Hansson, L.-A. The Zooplankton Community of Five Faroese Lakes. Ann. Soc. Sci. Fær. Supp. 2002, 36, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, J.; Mehra, N.K. Seasonal Dynamics of Rotifers in Relation to Physical and Chemical Conditions of the River Yamuna (Delhi), India. Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claps, M.C.; Gabellone, N.A.; Benítez, H.H. Seasonal Changes in the Vertical Distribution of Rotifers in a Eutrophic Shallow Lake with Contrasting States of Clear and Turbid Water. Zool. Stud. 2011, 50, 454–465. [Google Scholar]
- Perbiche-Neves, G.; Fileto, C.; Laço-Portinho, J.; Troguer, A.; Serafim-Júnior, M. Relations among Planktonic Rotifers, Cyclopoid Copepods, and Water Quality in Two Brazilian Reservoirs. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 41, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R.D. Zooplankton Structure in the Loosdrecht Lakes in Relation to Trophic Status and Recent Restoration Measures. In Proceedings of the Trophic Relationships in Inland Waters; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Mittermeier, R.A.; Myers, N.; Thomsen, J.B.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Olivieri, S. Biodiversity Hotspots and Major Tropical Wilderness Areas: Approaches to Setting Conservation Priorities. Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittermeier, R.A.; Konstant, W.R. Biodiversity Conservation. Global Priorities, Trends, and the Outlook for the Future. In Footprints in the Jungle. Natural Resources Industries, Infrastructure, and Biodiversity Conservation; Bowles, I.A., Prickett, G.T., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 9–28. ISBN 0195125789. [Google Scholar]
- Paknia, O.; Rajaei Sh., H.; Koch, A. Lack of Well-Maintained Natural History Collections and Taxonomists in Megadiverse Developing Countries Hampers Global Biodiversity Exploration. Org. Divers. Evol. 2015, 15, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, M.L. Species Diversity in Space and Time. Econ. Bot. 1996, 50, 470. [Google Scholar]
- Field, R.; Hawkins, B.A.; Cornell, H.V.; Currie, D.J.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Guégan, J.-F.; Kaufman, D.M.; Kerr, J.T.; Mittelbach, G.G.; Oberdorff, T.; et al. Spatial Species-richness Gradients across Scales: A Meta-analysis. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, H.; Nwadiaro, C.S.; Dumont, H.J. Rotifera of Some Lakes in the Floodplain of the River Niger (Imo State, Nigeria). Hydrobiologia 1993, 250, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSM. OpenStreetMap, ODbL 1.0. 2016. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=4/50.18/-1.41 (accessed on 28 July 2023).
| # | Ghana/Site Name | Date | Time | T (°C) | pH | Sal. (ppm) | Cond. (µS/cm) | TDS (mg/L) | Latitude | Longitude | Alt. (m a.s.l.) | Habitat Type | Aquatic Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Edwinese Deduako | 13–Dec–18 | 9:30 | 26.5 | 7.76 | 159.0 | 298.0 | 212.0 | 6°33′58.8″ N | 1°27′41.0″ W | 238 | SWCh | LZ |
| 2 | Lake Bosumtwi (surface #1) | 13–Dec–18 | 12:40 | 31.6 | 10.13 | 640.0 | 1289.8 | 838.0 | 6°31′12.2″ N | 1°24′50.7″ W | 98 | lake | PZ |
| 3 | Lake Bosumtwi (surface #2) | 13–Dec–18 | 14:00 | 32.3 | 10.10 | 640.0 | 1293.0 | 840.0 | 6°30′22.4″ N | 1°24′40.9″ W | 98 | lake | PZ |
| 4 | Lake Bosumtwi (surface #3) | 13–Dec–18 | 15:00 | 32.2 | 10.07 | 630.0 | 1290.3 | 839.0 | 6°29′13.6″ N | 1°23′51.2″ W | 98 | lake | PZ |
| 5 | Lake Bosumtwi Abono village #1 | 14–Dec–18 | 9:00 | 33.4 | 9.65 | 747.0 | 1358.0 | 959.0 | 6°32′07.3″ N | 1°25′29.5″ W | 98 | lake | LZ |
| 6 | Lake Bosumtwi Abono village #2 | 14–Dec–18 | 10:00 | 33.4 | 9.65 | 747.0 | 1358.0 | 959.0 | 6°32′06.1″ N | 1°25′37.8″ W | 98 | lake | LZ |
| 7 | Lake Bosumtwi Paradise Resort #1 | 14–Dec–18 | 13:00 | 34.6 | 9.19 | 662.0 | 1202.0 | 855.0 | 6°31′52.1″ N | 1°25′50.1″ W | 98 | lake | LZ |
| 8 | Lake Bosumtwi Paradise Resort #2 | 14–Dec–18 | 13:20 | 34.6 | 9.19 | 662.0 | 1202.0 | 855.0 | 6°31′52.1″ N | 1°25′50.1″ W | 98 | lake | LZ |
| 9 | Edwinese Deatie | 15–Dec–18 | 10:30 | 27.6 | 8.04 | 95.0 | 171.9 | 122.0 | 6°33′49.8″ N | 1°25′32.7″ W | 270 | wetland | LZ |
| 10 | Asisiwa Asonie #1 | 15–Dec–18 | 11:20 | 26.5 | 7.88 | 65.3 | 115.3 | 81.7 | 6°33′28.9″ N | 1°23′13.4″ W | 239 | wetland | LZ |
| 11 | Asisiwa Asonie #2 | 15–Dec–18 | 11:30 | 26.5 | 7.88 | 65.3 | 115.3 | 81.7 | 6°33′28.9″ N | 1°23′13.4″ W | 239 | wetland | LZ |
| 12 | Beposos wetland #1 | 15–Dec–18 | 13:00 | 29.5 | 8.05 | 180.0 | 334.0 | 236.0 | 6°30′59.4″ N | 1°20′23.5″ W | 209 | wetland | LZ |
| 13 | Beposos wetland #2 | 15–Dec–18 | 13:10 | 29.5 | 8.05 | 180.0 | 334.0 | 236.0 | 6°30′59.4″ N | 1°20′23.5″ W | 209 | wetland | LZ |
| 14 | Kumasi-Onwe Afenasu #1 | 15–Dec–18 | 15:00 | 25.6 | 7.89 | 97.7 | 179.3 | 128.0 | 6°41′33.6″ N | 1°25′30.0″ W | 230 | wetland | LZ |
| 15 | Kumasi-Onwe Afenasu #2 | 18–Mar–23 | 7:00 | 25.6 | 6.58 | 90.0 | 192.0 | 96.0 | 6°41′33.6″ N | 1°25′30.0″ W | 230 | wetland | LZ |
| 16 | Kumasi-Onwe Afenasu #3 | 18–Mar–23 | 7:10 | 25.6 | 6.58 | 90.0 | 192.0 | 96.0 | 6°41′33.6″ N | 1°25′30.0″ W | 230 | wetland | LZ |
| 17 | Kumasi-Onwe Afenasu #4 | 18–Mar–23 | 7:20 | 25.6 | 6.58 | 90.0 | 192.0 | 96.0 | 6°41′33.6″ N | 1°25′30.0″ W | 230 | wetland | LZ |
| 18 | Kumasi-Onwe Afenasu #5 | 18–Mar–23 | 7:20 | 25.6 | 6.58 | 90.0 | 192.0 | 96.0 | 6°41′33.6″ N | 1°25′30.0″ W | 230 | wetland | LZ |
| 19 | Sunyani Berlin top #1 | 16–Dec–18 | 13:30 | 29.0 | 7.44 | 148.0 | 277.0 | 195.0 | 7°20′33.6″ N | 2°21′33.5″ W | 287 | fishpond | PZ |
| 20 | Sunyani Berlin top #2 | 16–Dec–18 | 13:30 | 29.0 | 7.44 | 148.0 | 277.0 | 195.0 | 7°20′33.6″ N | 2°21′33.5″ W | 287 | fishpond | PZ |
| 21 | Sunyani Dumasua | 16–Dec–18 | 14:15 | 28.1 | 7.84 | 75.8 | 135.3 | 96.3 | 7°23′22.9″ N | 2°22′08.2″ W | 277 | fishpond | PZ |
| 22 | Sunyani Atta Addae Zinco | 16–Dec–18 | 14:35 | 28.0 | 9.10 | 101.0 | 185.1 | 132.0 | 7°21′35.4″ N | 2°20′23.3″ W | 276 | SWCh | PZ |
| 23 | Sunyani SDA | 16–Dec–18 | 15:15 | 33.1 | 10.30 | 81.4 | 83.3 | 59.0 | 7°20′32.0″ N | 2°20′44.5″ W | 281 | fishpond | PZ |
| 24 | Teselima fishpond | 17–Dec–18 | 10:40 | 21.9 | 9.61 | 64.4 | 112.2 | 79.8 | 8°17′46.1″ N | 2°07′32.1″ W | 180 | fishpond | PZ |
| 25 | Bui reservoir (main lake #1) | 17–Dec–18 | 12:20 | 31.3 | 9.14 | 46.6 | 74.6 | 53.0 | 8°13′43.7″ N | 2°18′11.9″ W | 172 | reservoir | PZ |
| 26 | Bui reservoir (pool) | 17–Dec–18 | 12:45 | 34.1 | 8.75 | 44.4 | 69.0 | 48.9 | 8°13′43.2″ N | 2°18′11.7″ W | 172 | reservoir | PZ |
| 27 | Bui reservoir (main lake #2) | 17–Dec–18 | 13:00 | 30.9 | 8.40 | 57.2 | 102.8 | 66.0 | 8°13′44.9″ N | 2°18′12.1″ W | 172 | reservoir | PZ |
| 28 | Bui reservoir (main lake #3) | 17–Dec–18 | 14:03 | 32.7 | 8.10 | 57.2 | 82.0 | 58.9 | 8°14′17.7″ N | 2°17′47.7″ W | 172 | reservoir | LZ |
| 29 | Bui reservoir (main lake #4) | 17–Dec–18 | 14:20 | 30.7 | 8.30 | 55.3 | 86.6 | 64.5 | 8°14′28.0″ N | 2°17′46.2″ W | 172 | reservoir | LZ |
| 30 | Bui reservoir (main lake #5) | 17–Dec–18 | 14:40 | 32.5 | 8.10 | 58.9 | 77.1 | 54.3 | 8°14′25.0″ N | 2°17′48.3″ W | 172 | reservoir | LZ |
| 31 | Black Volta River (stagnant channel) | 17–Dec–18 | 15:20 | 28.2 | 8.10 | 47.8 | 80.3 | 56.5 | 8°15′50.0″ N | 2°13′47.0″ W | 106 | SWCh | LZ |
| 32 | Tromeso | 18–Dec–18 | 10:05 | 22.3 | 8.60 | 84.5 | 157.4 | 111.0 | 7°33′55.4″ N | 2°09′35.5″ W | 223 | wetland | LZ |
| 33 | Rio Kuquema | 14–May–09 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 12°46′23.6″ S | 17°03′48.7″ E | 1462 | river | PZ |
| 34 | Kalupanda | 1–Nov–09 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 12°26′33.0″ S | 16°54′21.9″ E | 1687 | fishpond | PZ |
| 35 | Chitundo | 12–May–09 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 12°37′48.0″ S | 17°14′32.3″ E | 1381 | fishpond | PZ |
| 36 | Nequilo | 4–May–08 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 12°36′18.1″ S | 17°04′03.7″ E | 1591 | fishpond | PZ |
| 37 | Chicava | 30–Oct–06 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 12°30′17.8″ S | 17°09′27.3″ E | 1524 | fishpond | PZ |
| # | Taxon | New Record | Sites Found | Occurrence [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asplanchnidae | ||||
| 1 | Asplanchna brightwellii Gosse, 1850 | Ḡ | 19–21, 29, 30 | 15.6 |
| Bdelloidea | ||||
| 2 | bdelloid (unidentified) | Ḡ | 1–3, 5, 6, 8, 10–19, 21, 25, 26, 28–32 | 75.0 |
| Brachionidae | ||||
| 3 | Anuraeopsis fissa (Gosse, 1851) | Ḡ | 27 | 3.1 |
| 4 | Brachionus angularis Gosse, 1851 | Ḡ | 19, 21 | 6.3 |
| 5 | Brachionus bidentatus Anderson, 1889 | Ḡ | 16 | 3.1 |
| 6 | Brachionus calyciflorus s.l. Pallas, 1766 | 2–6, 9, 13, 19, 20, 22–24 | 37.5 | |
| 7 | Brachionus caudatus Barrois & Daday, 1894 | Ḡ | 25, 27 | 6.3 |
| 8 | Brachionus dimidiatus Bryce, 1931 | 20, 21 | 6.3 | |
| 9 | Brachionus dorcas Gosse, 1851 | Ḡ | 2, 15, 25 | 9.4 |
| 10 | Brachionus falcatus Zacharias, 1898 | 9, 24–27, 29 | 18.8 | |
| 11 | Brachionus mirabilis Daday, 1897 | 1, 12, 13 | 9.4 | |
| 12 | Brachionus quadridentatus Hermann, 1783 | Ḡ | 7, 12, 16, 18, 21, 26 | 18.8 |
| 13 | Brachionus urceolaris Müller, 1773 | 5 | 3.1 | |
| 14 | Keratella lenzi Hauer, 1953 | Ḡ | 30 | 3.1 |
| 15 | Keratella tropica (Apstein, 1907) | Ḡ | 26–29, 31 | 15.6 |
| 16 | Plationus patulus (Müller, 1786) | 1, 7, 14–18, 26, 27, 32 | 31.3 | |
| 17 | Platyias quadricornis (Ehrenberg, 1832) | 1, 15, 16, 18, 24, 32 | 18.8 | |
| Collothecidae | ||||
| 18 | Collotheca sp. | Ḡ | 7 | 3.1 |
| 19 | Stephanoceros cf. fimbriatus (Goldfuß, 1820) | Ḡ, Ṝ | 1 | 3.1 |
| 20 | Stephanoceros sp. | Ḡ | 1, 9 | 6.3 |
| Dicranophoridae | ||||
| 21 | Dicranophoroides caudatus (Ehrenberg, 1834) | Ḡ | 1 | 3.1 |
| 22 | Dicranophorus epicharis Harring & Myers, 1928 | Ḡ | 8 | 3.1 |
| 23 | Dicranophorus forcipatus (Müller, 1786) | Ḡ | 1, 16 | 6.3 |
| Epiphanidae | ||||
| 24 | Epiphanes clavulata (Ehrenberg, 1831) | Ḡ | 1, 16, 24 | 9.4 |
| 25 | Epiphanes macroura (Barrois & Daday, 1894) | Ḡ | 19, 20, 25, 26 | 12.5 |
| 26 | Epiphanes senta (Müller, 1773) | Ḡ | 15, 20 | 6.3 |
| Euchlanidae | ||||
| 27 | Beauchampiella eudactylota (Gosse, 1886) | Ḡ | 14–17, 31, 32 | 18.8 |
| 28 | Dipleuchlanis propatula (Gosse, 1886) | Ḡ | 1, 14, 31, 21 | 12.5 |
| 29 | Euchlanis calpidia (Myers, 1930) | Ḡ, Ṝ | 26 | 3.1 |
| 30 | Euchlanis dilatata Ehrenberg, 1830 | Ḡ | 1, 13, 14, 18, 25, 30 | 18.8 |
| 31 | Euchlanis dilatata “large morph” | Ḡ | 16, 17 | 6.3 |
| 32 | Euchlanis cf. lyra Hudson, 1886 | Ḡ | 1 | 3.1 |
| Filinidae | ||||
| 33 | Filinia longiseta (Ehrenberg, 1834) | Ḡ | 19–21, 32 | 12.5 |
| 34 | Filinia passa (Müller, 1786) | Ḡ | 19, 20 | 6.3 |
| 35 | Filinia sp. | 1 | 3.1 | |
| Floscularidae | ||||
| 36 | Floscularia ringens (Linnaeus, 1758) | Ḡ | 14 | 3.1 |
| 37 | Limnias sp. (tube) | Ḡ | 23 | 3.1 |
| 38 | Ptygura melicerta Ehrenberg, 1832 | Ḡ | 7 | 3.1 |
| 39 | Sinantherina ariprepes Edmondson, 1939 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 16–18, 25 | 12.5 |
| 40 | Sinantherina semibullata (Thorpe, 1889) | 1, 25, 26 | 9.4 | |
| 41 | Sinantherina sp. | Ḡ | 25 | 3.1 |
| Hexarthridae | ||||
| 42 | Hexarthra “bosumtwii” sp. nov. | Ā Ḡ | 2, 3, 8 | 9.4 |
| 43 | Hexarthra intermedia (Wiszniewski, 1929) | 19 | 3.1 | |
| Ituridae | ||||
| 44 | Itura symmetrica Segers, Mbogo & Dumont, 1994 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 1, 14 | 6.3 |
| Lecanidae | ||||
| 45 | Lecane cf. agilis (Bryce, 1892) | Ḡ | 1 | 3.1 |
| 46 | Lecane arcula Harring, 1914 | 15 | 3.1 | |
| 47 | Lecane braumi Koste, 1988 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 16 | 3.1 |
| 48 | Lecane bulla (Gosse, 1851) | Ḡ | 1–5, 7–14, 16–18, 22, 25–32 | 78.1 |
| 49 | Lecane clara (Bryce, 1892) | Ḡ | 15 | 3.1 |
| 50 | Lecane curvicornis (Murray, 1913) | 1, 9–12, 14–16, 18, 31, 32 | 34.4 | |
| 51 | Lecane depressa (Bryce, 1891) | Ḡ, Ṝ | 16 | 3.1 |
| 52 | Lecane elongata Harring & Myers, 1926 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 15 | 3.1 |
| 53 | Lecane elsa Hauer, 1931 | Ḡ | 1, 2, 28 | 9.4 |
| 54 | Lecane ercodes Harring, 1914 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 9 | 3.1 |
| 55 | Lecane hornemanni (Ehrenberg, 1834) | Ḡ | 31 | 3.1 |
| 56 | Lecane lateralis Sharma, 1978 | Ḡ | 1, 6–8, 30 | 15.6 |
| 57 | Lecane leontina (Turner, 1892) | 25, 26, 28, 30, 32 | 15.6 | |
| 58 | Lecane luna (Müller, 1776) | 8, 15 | 6.3 | |
| 59 | Lecane papuana (Murray, 1913) | Ḡ | 1, 2, 7, 8, 10, 12–14, 17, 24–27, 31, 32 | 46.9 |
| 60 | Lecane quadridentata (Ehrenberg, 1830) | Ḡ | 1, 9, 12, 14, 21 | 15.6 |
| 61 | Lecane unguitata (Fadeev, 1925) | Ḡ | 1, 18, 25–27 | 15.6 |
| 62 | Lecane ungulata (Gosse, 1887) | Ḡ | 1, 13, 22, 25, 26, 32 | 18.8 |
| Lepadellidae | ||||
| 63 | Colurella adriatica Ehrenberg, 1831 | Ḡ | 26 | 3.1 |
| 64 | Colurella hindenburgi Steinecke, 1916 | Ḡ | 1, 8 | 6.3 |
| 65 | Colurella obtusa (Gosse, 1886) | Ḡ | 1 | 3.1 |
| 66 | Colurella sp. 1 | Ḡ | 16, 32 | 6.3 |
| 67 | Colurella sp. 2 | Ḡ | 16 | 3.1 |
| 68 | Colurella sp. 3 | Ḡ | 16 | 3.1 |
| 69 | Lepadella ovalis (Müller, 1786) | Ḡ | 1, 7–9, 22 | 15.6 |
| 70 | Lepadella patella (Müller, 1773) | 1, 2, 8–11, 13–15, 32 | 31.3 | |
| 71 | Lepadella rhomboides (Gosse, 1886) | Ḡ | 31 | 3.1 |
| Mytilinidae | ||||
| 72 | Mytilina brevispina (Ehrenberg, 1830) | Ḡ | 12 | 3.1 |
| 73 | Mytilina ventralis (Ehrenberg, 1830) | 1, 2, 6, 7, 9, 13–18, | 34.4 | |
| Notommatidae | ||||
| 74 | Cephalodella forficula (Ehrenberg, 1838) | Ḡ | 7, 8 | 6.3 |
| 75 | Cephalodella gibba (Ehrenberg, 1830) | Ḡ | 32 | 3.1 |
| 76 | Cephalodella cf. hollowdayi Koste, 1986 | Ā, Ḡ | 1 | 3.1 |
| 77 | Cephalodella misgurnus Wulfert, 1937 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 1 | 3.1 |
| 78 | Cephalodella segersi De Smet, 1998 | Ā, Ḡ | 23 | 3.1 |
| 79 | Eosphora anthadis Harring & Myers, 1922 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 9, 14, 23 | 9.4 |
| 80 | Eosphora ehrenbergi Weber, 1918 | Ā, Ḡ | 1, 5–8 | 15.6 |
| 81 | Eosphora therina Harring & Myers, 1922 | Ḡ | 1 | 3.1 |
| 82 | Notommata allantois Wulfert, 1935 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 26 | 3.1 |
| 83 | Notommata copeus Ehrenberg, 1834 | Ḡ | 12, 26 | 6.3 |
| 84 | Notommata tripus Ehrenberg, 1838 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 26 | 3.1 |
| 85 | Notommata voigti Donner, 1949 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 13 | 3.1 |
| 86 | Pleurotrocha cf. robusta (Glascott, 1893) | Ā, Ḡ | 12, 14 | 6.3 |
| 87 | Pleurotrocha sigmoidea Skorikov, 1896 | Ā, Ḡ | 18 | 3.1 |
| 88 | Taphrocampa selenura Gosse, 1887 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 26 | 3.1 |
| Philodinidae | ||||
| 89 | Rotaria macrura (Ehrenberg, 1832) | Ḡ | 19, 20 | 6.3 |
| 90 | Rotaria neptunia (Ehrenberg, 1830) | Ḡ | 1, 11, 14, 15, 24, 27, 32 | 21.9 |
| 91 | Rotaria neptunoida Harring, 1913 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 26 | 3.1 |
| Proalidae | ||||
| 92 | Proales minima (Montet, 1915) | Ā, Ḡ | 15 | 3.1 |
| 93 | Proales cf. theodora (Gosse, 1887) | Ā, Ḡ | 14, 20 | 6.3 |
| 94 | Proales sp. 1 | Ḡ | 1, 20 | 6.3 |
| 95 | Proales sp. 2 | Ḡ | 19 | 3.1 |
| 96 | Proales sp. 3 | Ḡ | 19 | 3.1 |
| Scaridiidae | ||||
| 97 | Scaridium bostjani Daems & Dumont, 1974 | Ḡ | 9, 13 | 6.3 |
| 98 | Scaridium grande Segers, 1995 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 26 | 3.1 |
| Synchaetidae | ||||
| 99 | Polyarthra dolichoptera Idelson, 1925 | Ḡ | 32 | 3.1 |
| 100 | Polyarthra luminosa Kutikova, 1962 | Ā, Ḡ | 24, 25 | 6.3 |
| 101 | Polyarthra major Burckhardt, 1900 | Ḡ | 19 | 3.1 |
| 102 | Polyarthra remata Skorikov, 1896 | Ḡ | 20 | 3.1 |
| 103 | Synchaeta pectinata Ehrenberg, 1832 | Ḡ | 14, 24, 31 | 9.4 |
| Testudinellidae | ||||
| 104 | Anchitestudinella cf. mekongensis Bērziņš, 1973 | Ā, Ḡ | 25 | 3.1 |
| 105 | Testudinella ahlstromi Hauer, 1956 | Ā, Ḡ | 26 | 3.1 |
| 106 | Testudinella patina (Hermann, 1783) | 12–15, 17, 25, 26, 29, 30 | 28.1 | |
| 107 | Testudinella tridentata Smirnov, 1931 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 30 | 3.1 |
| Trichocercidae | ||||
| 108 | Trichocerca bidens (Lucks, 1912) | Ḡ | 30 | 3.1 |
| 109 | Trichocerca elongata (Gosse, 1886) | Ḡ | 14, 25 | 6.3 |
| 110 | Trichocerca cf. insignis (Herrick, 1885) | Ḡ | 29 | 3.1 |
| 111 | Trichocerca rattus (Müller, 1776) | Ḡ | 25, 26 | 6.3 |
| 112 | Trichocerca scipio (Gosse, 1886) | Ḡ | 26 | 3.1 |
| 113 | Trichocerca similis (Wierzejski, 1893) | Ḡ | 24, 26, 29, 31 | 12.5 |
| 114 | Trichocerca similis grandis Hauer, 1965 | Ḡ, Ṝ | 9, 14 | 6.3 |
| 115 | Trichocerca vernalis (Hauer, 1936) | Ḡ | 17 | 3.1 |
| Trichotriidae | ||||
| 116 | Macrochaetus sp. nov | Ā, Ḡ | 26 | 3.1 |
| 117 | Trichotria tetractis similis (Stenroos, 1898) | Ḡ, Ṝ | 26, 31 | 6.3 |
| 118 | Trichotria truncata (Whitelegge, 1889) | Ā, Ḡ | 26, 28 | 6.3 |
| # | Taxon | New Record | Sites Found | Occurrence [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asplanchnidae | ||||
| 1 | Asplanchna brightwellii Gosse, 1850 | Ḹ | 35–37 | 60 |
| Bdelloidea | ||||
| 2 | bdelloid (unidentified) | Ḹ | 37 | 20 |
| Brachionidae | ||||
| 3 | Brachionus angularis Gosse, 1851 | Ḹ | 34 | 20 |
| 4 | Brachionus falcatus Zacharias, 1898 | 36, 37 | 40 | |
| 5 | Brachionus quadridentatus Hermann, 1783 | Ḹ | 34 | 20 |
| 6 | Keratella tropica (Apstein, 1907) | Ḹ | 33–36 | 80 |
| Filinidae | ||||
| 7 | Filinia opoliensis (Zacharias, 1898) | Ḹ | 37 | 20 |
| 8 | Filinia longiseta (Ehrenberg, 1834) | Ḹ | 37 | 20 |
| 9 | Filinia sp. | Ḹ | 37 | 20 |
| Hexarthridae | ||||
| 10 | Hexarthra intermedia (Wiszniewski, 1929) | Ḹ | 37 | 20 |
| Lecanidae | ||||
| 11 | Lecane bulla (Gosse, 1851) | Ḹ | 34 | 20 |
| 12 | Lecane cornuta (Müller, 1786) | Ḹ | 36 | 20 |
| Synchaetidae | ||||
| 13 | Polyarthra dolichoptera Idelson, 1925 | Ḹ | 37 | 20 |
| Trichocercidae | ||||
| 14 | Trichocerca pusilla (Jennings, 1903) | Ḹ | 36–37 | 40 |
| 15 | Trichocerca similis (Wierzejski, 1893) | Ḹ | 34–35 | 40 |
| Estimate | Std. Error | z Value | Pr (>|z|) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (intercept) | 6.585 | 1.84 | 3.578 | 0.000346 *** |
| temperature | −0.072 | 0.05 | −1.551 | 0.120821 |
| pH | −0.344 | 0.14 | −2.423 | 0.015375 * |
| conductivity | 0.003 | 0.001 | 2.33 | 0.019817 * |
| lake | −2.711 | 1.72 | −1.574 | 0.115418 |
| reservoir | 1.665 | 0.42 | 3.976 | 7.02 × 10−5 *** |
| SWCh | 0.291 | 0.30 | 0.968 | 0.333106 |
| wetland | 0.143 | 0.28 | 0.518 | 0.604596 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smolak, R.; Brown, P.D.; Walsmith, R.N.; Ríos-Arana, J.V.; Sanful, P.; Kalous, L.; Walsh, E.J. Improving Aquatic Biodiversity Estimates in Africa: Rotifers of Angola and Ghana. Diversity 2024, 16, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050269
Smolak R, Brown PD, Walsmith RN, Ríos-Arana JV, Sanful P, Kalous L, Walsh EJ. Improving Aquatic Biodiversity Estimates in Africa: Rotifers of Angola and Ghana. Diversity. 2024; 16(5):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050269
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmolak, Radoslav, Patrick D. Brown, Robert N. Walsmith, Judith V. Ríos-Arana, Peter Sanful, Lukáš Kalous, and Elizabeth J. Walsh. 2024. "Improving Aquatic Biodiversity Estimates in Africa: Rotifers of Angola and Ghana" Diversity 16, no. 5: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050269
APA StyleSmolak, R., Brown, P. D., Walsmith, R. N., Ríos-Arana, J. V., Sanful, P., Kalous, L., & Walsh, E. J. (2024). Improving Aquatic Biodiversity Estimates in Africa: Rotifers of Angola and Ghana. Diversity, 16(5), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050269









