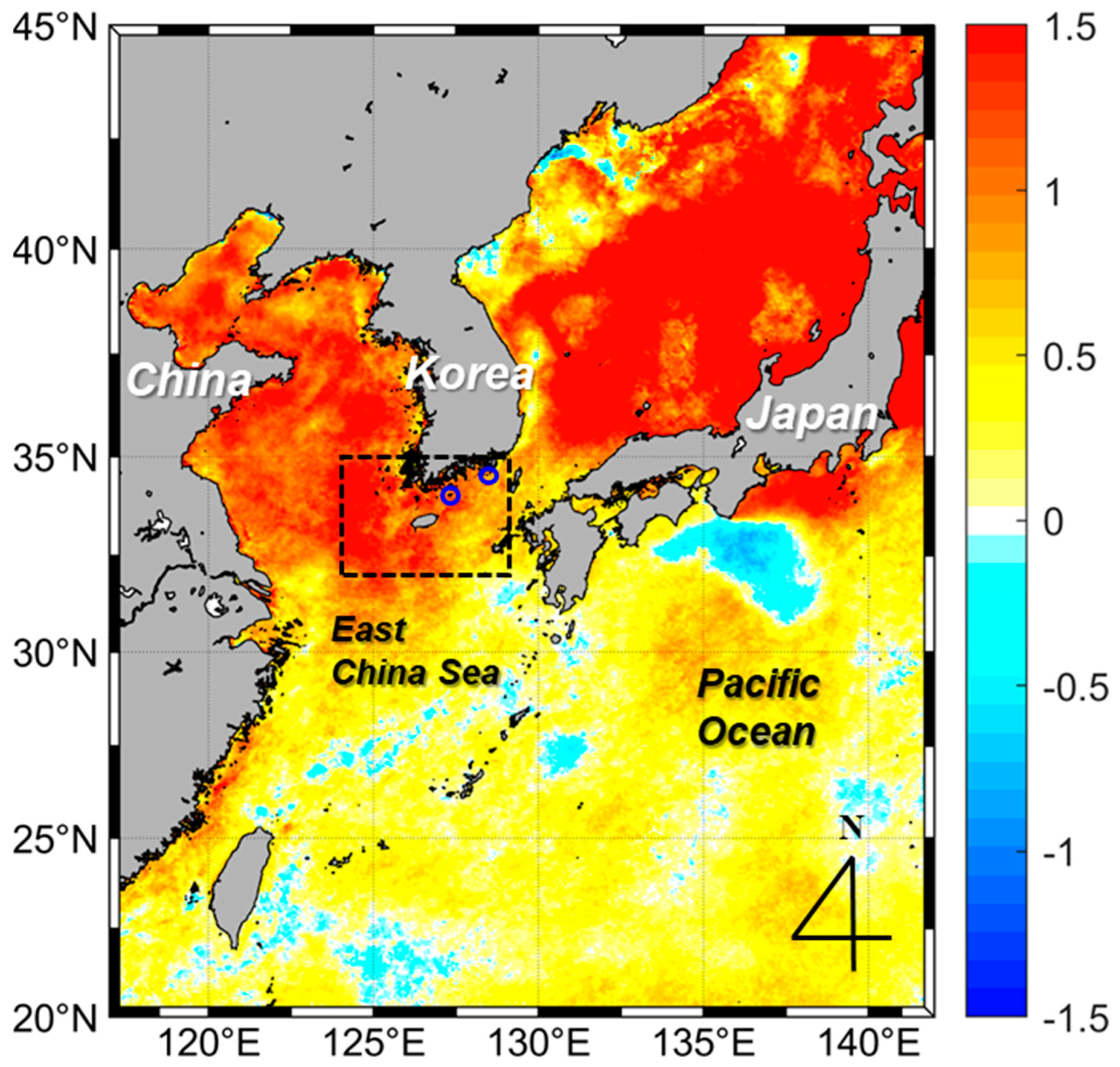
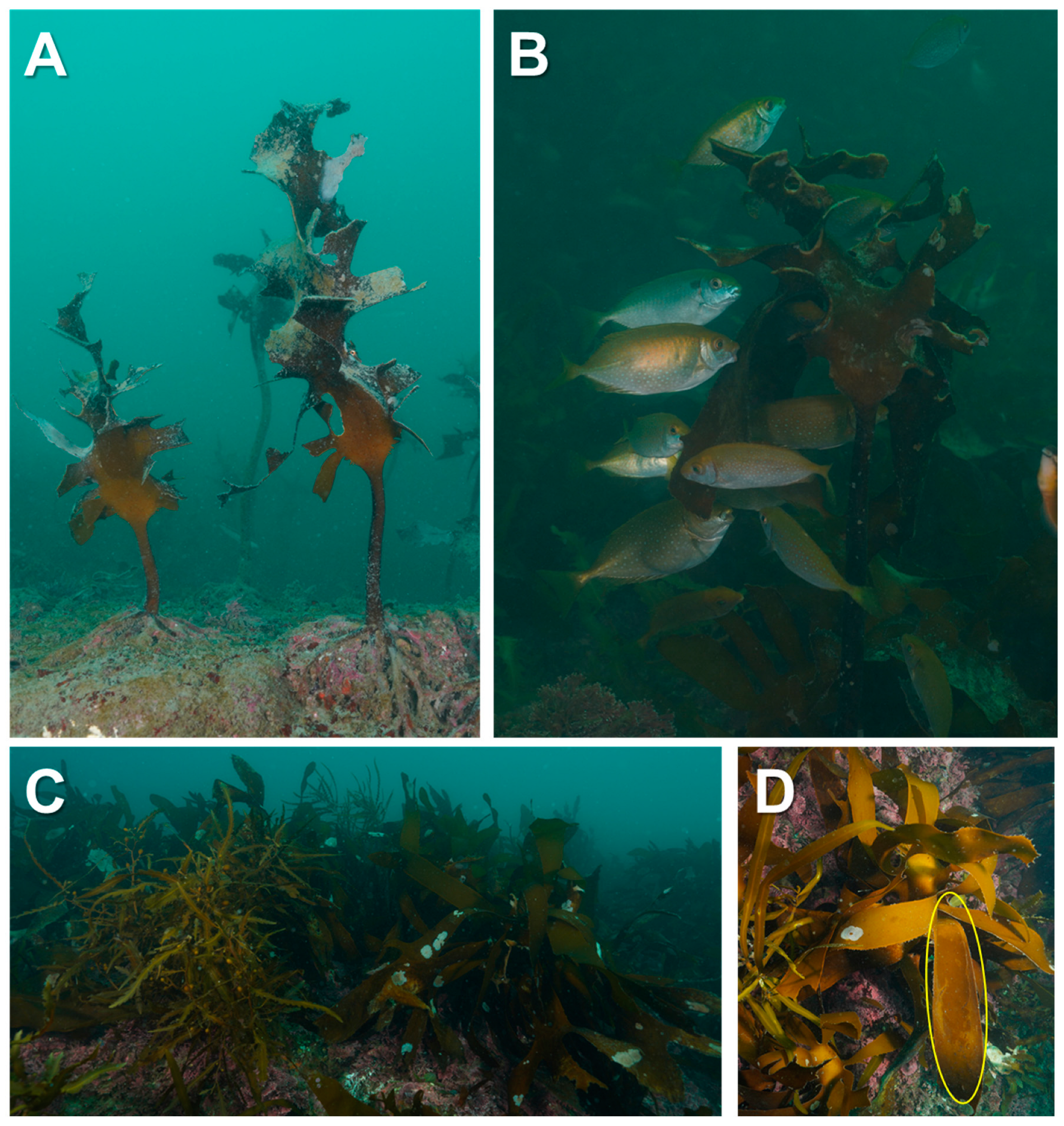
Threats to a Temperate Kelp Forest Species, Ecklonia cava, through Tropical Fish Herbivory Associated with Sea Surface Warming in the East China Sea
Abstract
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haraguchi, H.; Tanaka, K.; Imoto, Z.; Hiraoka, M. The decline of Ecklonia cava in Kochi, Japan and the challenge in marine afforestation. Kuro. Sci. 2009, 3, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, R.-S.; Won, K.-S.; Hong, K.-P.; Kim, J.-M. Population studies on the Kelp Ecklonia cava and Eisenia bicyclis in Dokdo, Korea. Algae 2001, 16, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.K.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, T.; Son, Y.B.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.R. Changes in the dynamics and nutrient budget of a macroalgal community exposed to land-based fish farm discharge off Jeju Island, Korea. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serisawa, Y.; Imoto, Z.; Ishikawa, T.; Ohno, M. Decline of the Ecklonia cava population associated with increased seawater temperatures in Tosa Bay, southern Japan. Fish. Sci. 2004, 70, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M. Isoyake studies in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. Bull. Fish. Res. Agen. 2010, 32, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, F.P.; Wethey, D.S. Three decades of high-resolution coastal sea surface temperatures reveal more than warming. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.N.; Umeda, C. Rapid warming of sea surface temperature along the Kuroshio and the China coast in the East China Sea during the twentieth century. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 4803–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Taino, S.; Haraguchi, H.; Prendergast, G.; Hiraoka, M. Warming off southwestern Japan linked to distributional shifts of subtidal canopy-forming seaweeds. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, G.-R.; Post, E.; Convey, P.; Menzel, A.; Parmesan, C.; Beebee, T.J.; Fromentin, J.-M.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bairlein, F. Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 2002, 416, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.-W.; Kim, C.-H. Recent warming in the Yellow/East China Sea during winter and the associated atmospheric circulation. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.K.; Kang, Y.H.; Park, S.R. Growth responses of kelp species Ecklonia cava to different temperatures and nitrogen sources. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2020, 38, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Endo, H.; Nagaki, M.; Agatsuma, Y. Growth and survival of juvenile sporophytes of the kelp Ecklonia cava in response to different nitrogen and temperature regimes. Fish. Sci. 2016, 82, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.H.; Adiputra, Y.T.; Burridge, C.P.; Gwo, J.C. Two spinefoot colour morphs: Mottled spinefoot Siganus fuscescens and white-spotted spinefoot Siganus canaliculatus are synonyms. J. Fish Biol. 2011, 79, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.K.; Park, C.B.; Kang, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Rho, S.; Lee, Y.D. Gonadal development and reproductive cycle of the rabbitfish (Siganus canaliculatus). Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 37, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Han, S.-H. Reproductive ecology of rabbit fish, Siganus fuscescens in the coastal waters off Jeju Island of Korea. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Ocean Technol. 2019, 55, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Perello, S.; Fairclough, D.; Dowling, C.; DiBattista, J.; Austin, R.; Wernberg, T.; Taylor, B. Maximization of fitness by phenological and phenotypic plasticity in range expanding rabbitfishes (Siganidae). J. Anim. Ecol. 2022, 91, 1666–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, M.; Kimura, H.; Fujita, D. Seasonal and diurnal feeding patterns of the herbivorous fish Siganus fuscescens and scaring by optic and auditory stimuli. Fish. Eng. 2006, 43, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H. Predation on fish in cultured Undaria undarioides. Waka. Water Res. Rep. 1994, 26, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, H.; Tsunoda, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Nishio, S.; Mizui, H.; Horiuchi, S.; Nakayama, Y. Decline of afforested Ecklonia cava community by grazing of herbivorous fish Siganus fuscescens. Fish. Eng. 2000, 37, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Inoue, K.; Furumitsu, K.; Kiriyama, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Koido, T.; Nakata, H. Behavior and migration of rabbitfish Siganus fuscescens and grey seachub Kyphosus bigibbus off Nomozaki, Kyushu, tracked by biotelemetry method. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 2006, 72, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Kang, Y.H.; Kim, T.-H.; Park, S.R. Recovery pattern and seasonal dynamics of kelp species, Ecklonia cava population formed following the large-scale disturbance. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2016, 21, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.W.; Jeon, B.-H.; Choi, C.G. Characteristics of summer marine algal community and barren ground in the southern coast of Jeju, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Mr. Environ. Saf. 2019, 25, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergés, A.; Steinberg, P.D.; Hay, M.E.; Poore, A.G.; Campbell, A.H.; Ballesteros, E.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Booth, D.J.; Coleman, M.A.; Feary, D.A. The tropicalization of temperate marine ecosystems: Climate-mediated changes in herbivory and community phase shifts. Proc. R. Soc. B 2014, 281, 20140846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergés, A.; Tomas, F.; Cebrian, E.; Ballesteros, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Spiegel, D.; Sala, E. Tropical rabbitfish and the deforestation of a warming temperate sea. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.K.; Kim, T.; Son, Y.B.; Park, S.R. Threats to a Temperate Kelp Forest Species, Ecklonia cava, through Tropical Fish Herbivory Associated with Sea Surface Warming in the East China Sea. Diversity 2024, 16, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050253
Choi SK, Kim T, Son YB, Park SR. Threats to a Temperate Kelp Forest Species, Ecklonia cava, through Tropical Fish Herbivory Associated with Sea Surface Warming in the East China Sea. Diversity. 2024; 16(5):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050253
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Sun Kyeong, Taihun Kim, Young Baek Son, and Sang Rul Park. 2024. "Threats to a Temperate Kelp Forest Species, Ecklonia cava, through Tropical Fish Herbivory Associated with Sea Surface Warming in the East China Sea" Diversity 16, no. 5: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050253
APA StyleChoi, S. K., Kim, T., Son, Y. B., & Park, S. R. (2024). Threats to a Temperate Kelp Forest Species, Ecklonia cava, through Tropical Fish Herbivory Associated with Sea Surface Warming in the East China Sea. Diversity, 16(5), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050253





