Spatiotemporal Distribution of nirS-Type Denitrifiers in Cascade Reservoir Sediments of the Qinghai Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
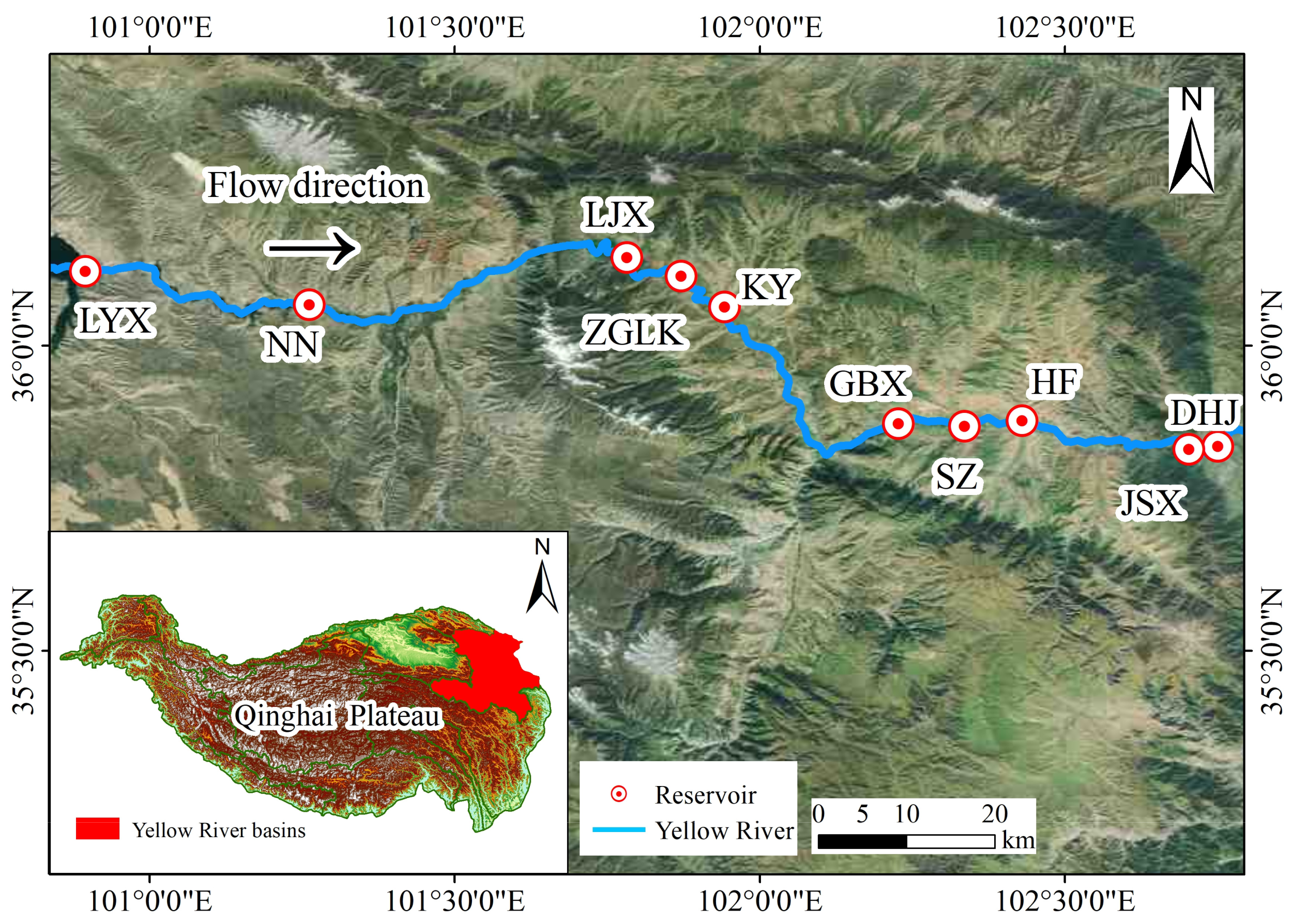
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sediment and Surface Water Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Extraction of Sediment DNA, Illumina Sequencing and Quantification PCR
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
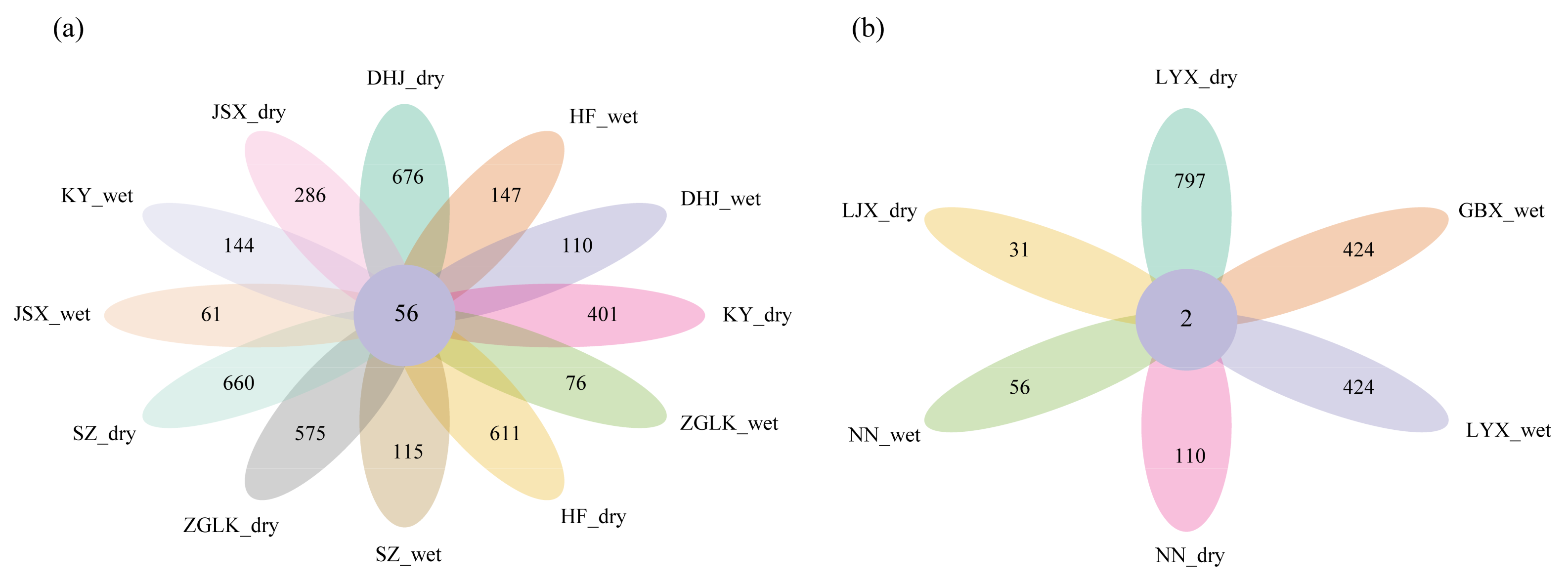
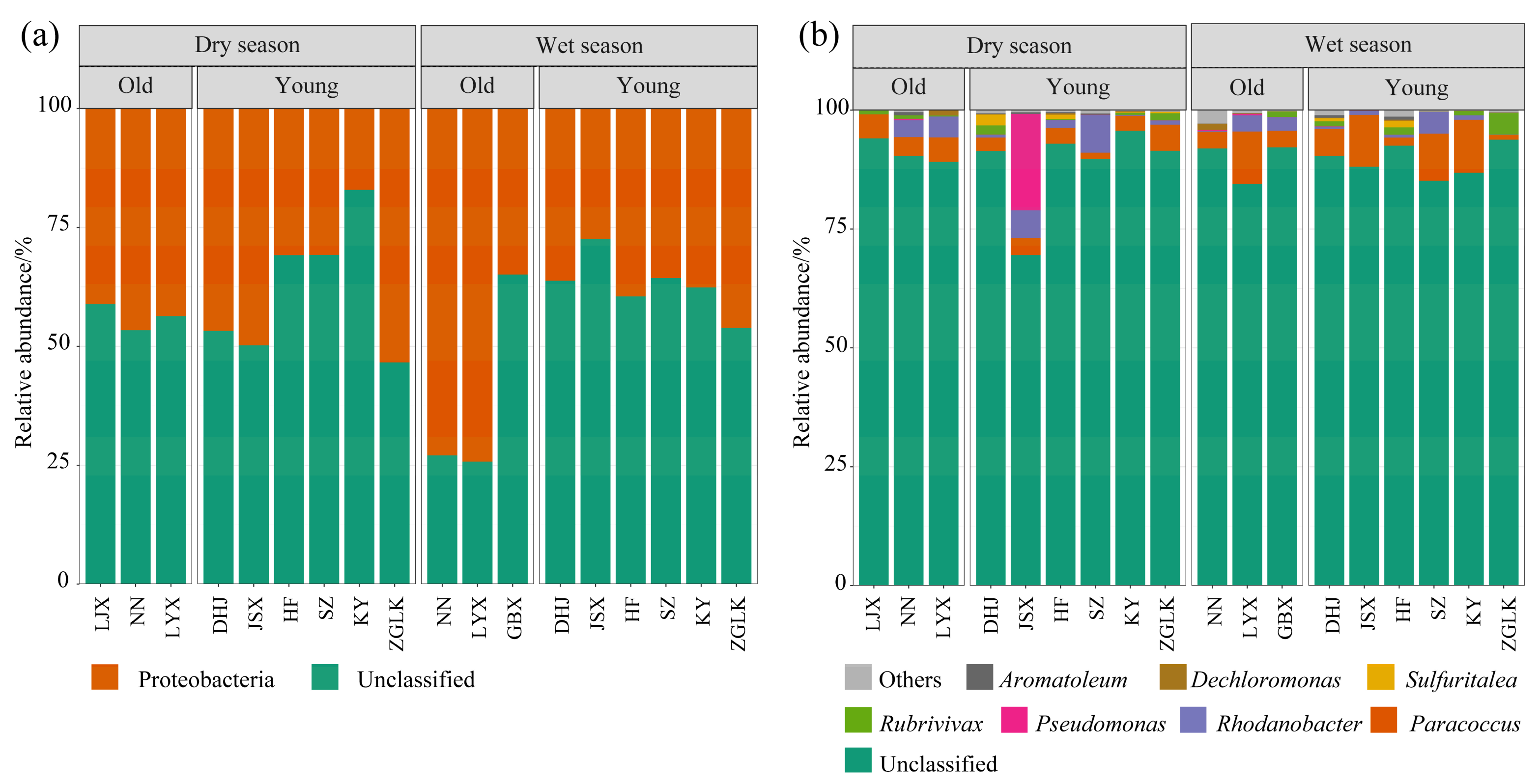
3.1. Composition of nirS-Type Denitrifying Bacterial Community
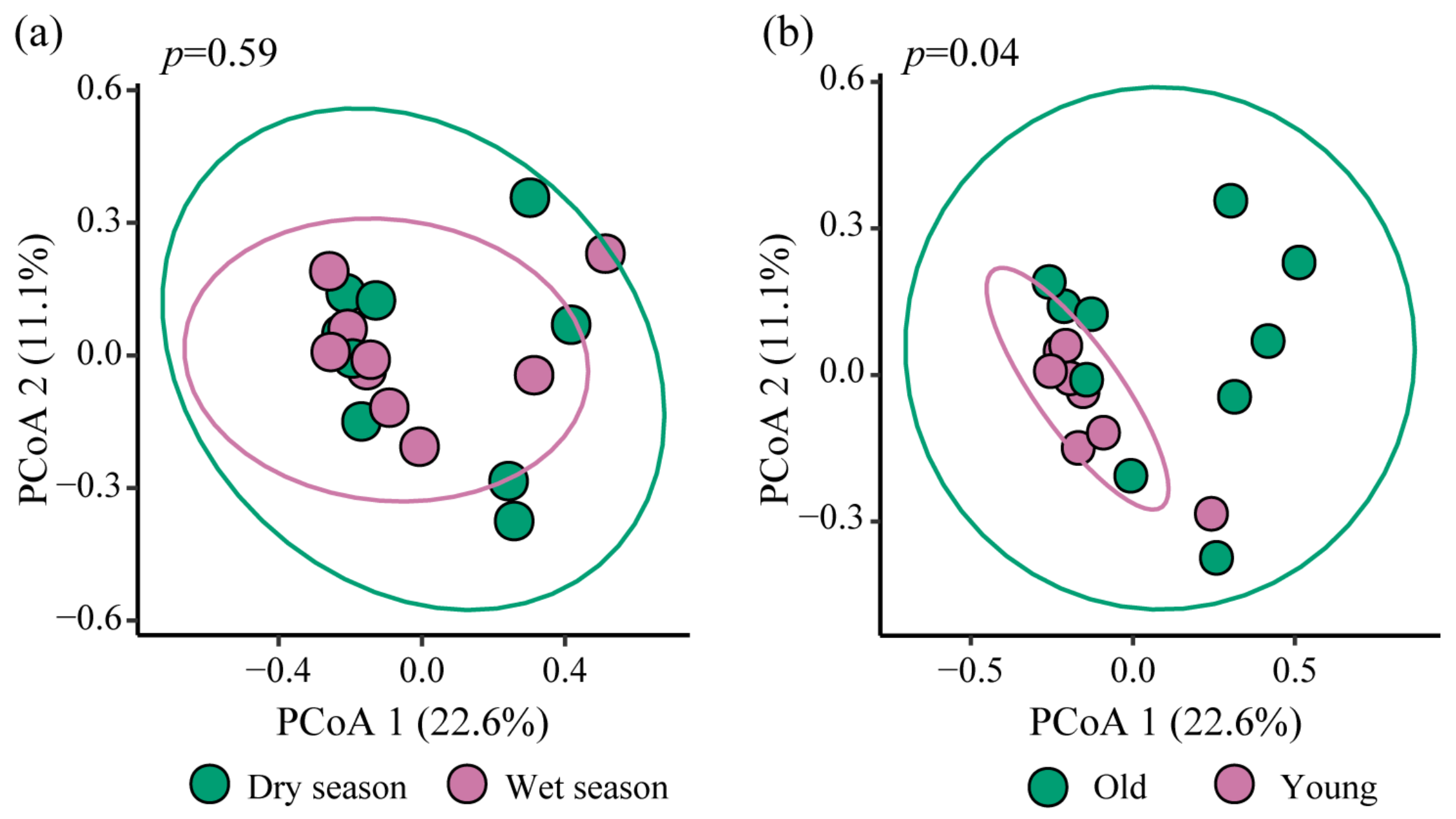
3.2. Differences in the Composition of nirS-Type Denitrifying Bacterial Community
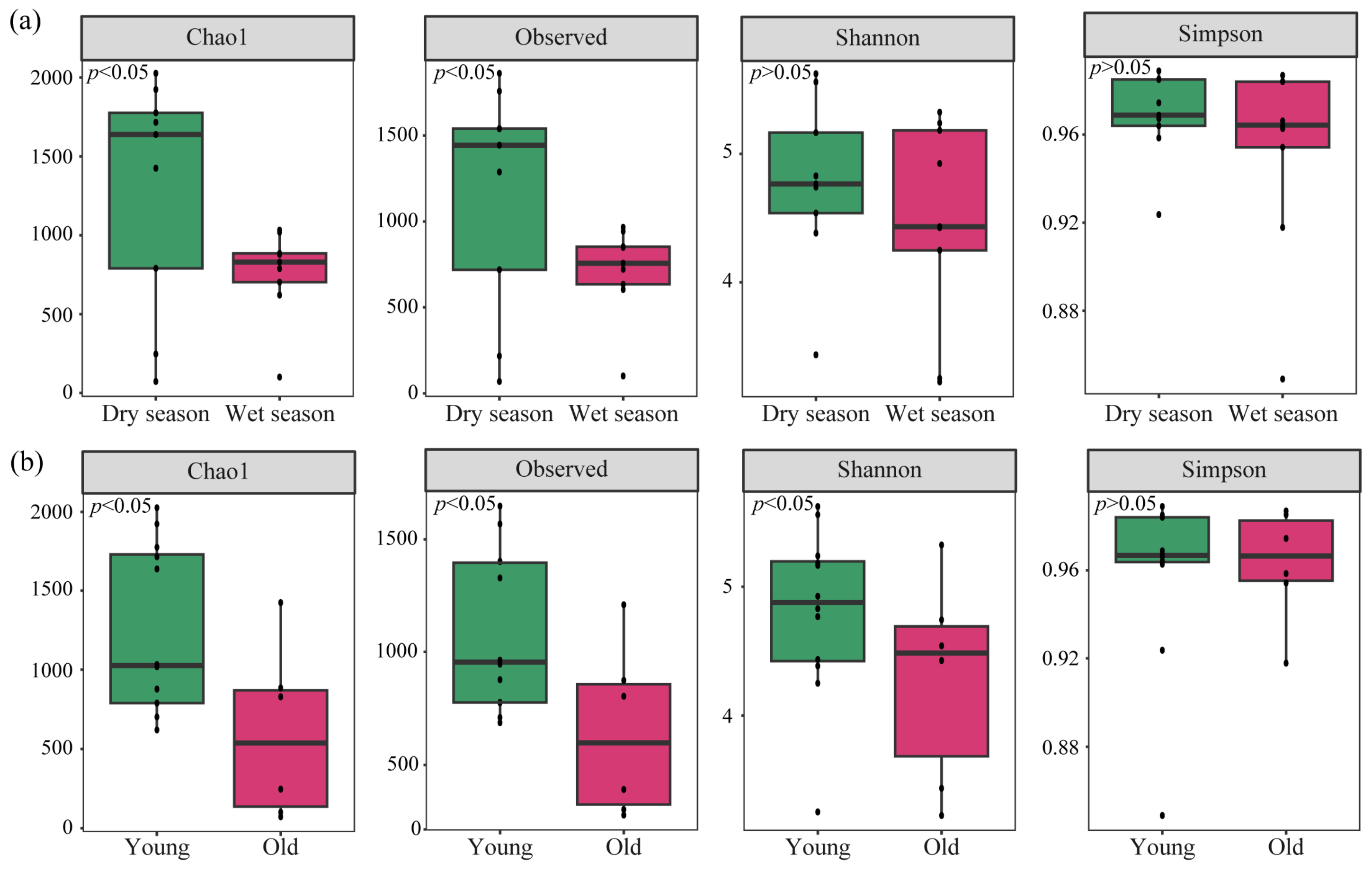
3.3. Diversity of nirS-Type Denitrifying Bacterial Community
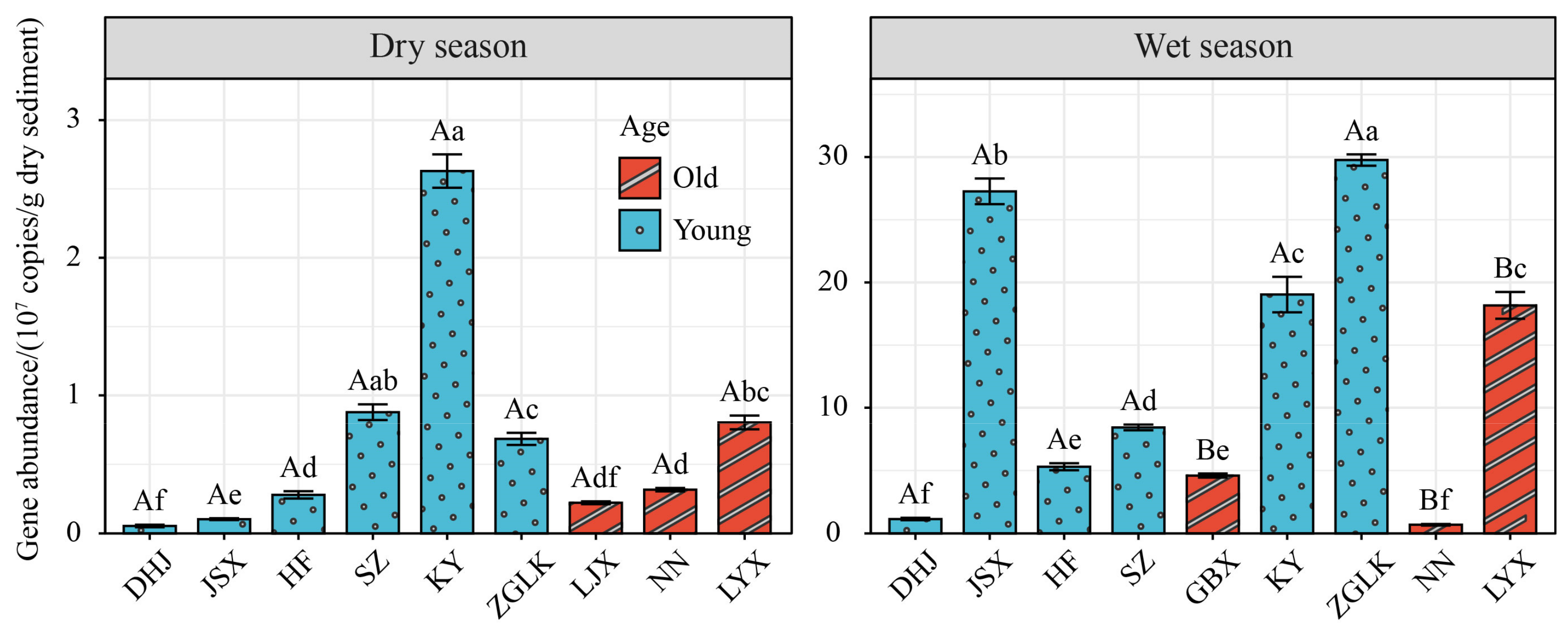
3.4. Abundance of nirS Gene
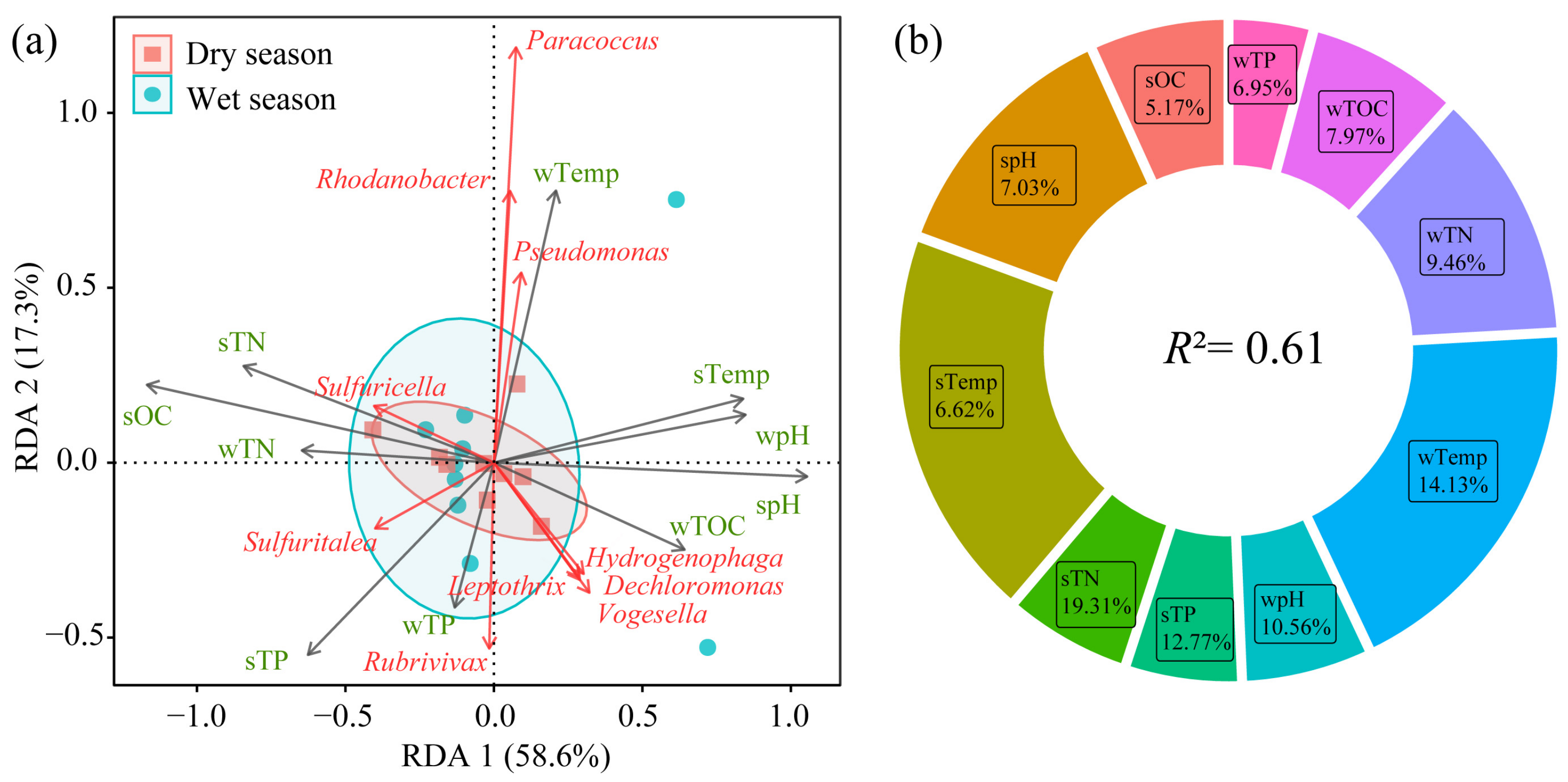
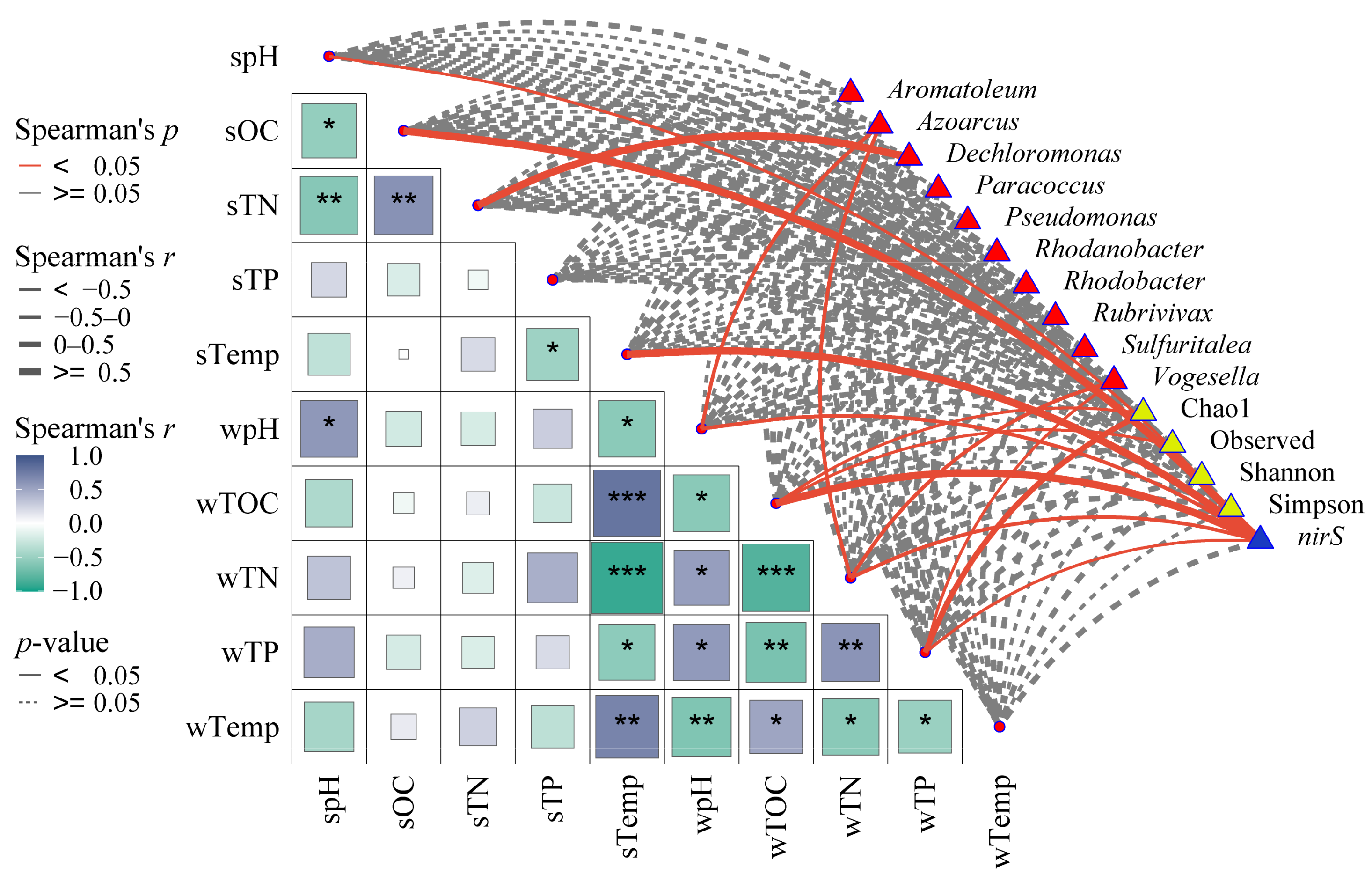
3.5. Relationship Between nirS-Type Denitrifying Bacteria and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Composition and Diversity of nirS-Type Denitrifying Bacterial Community
4.2. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of nirS Gene Abundance
4.3. Response of nirS-Type Denitrifying Bacteria to Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The dominant type of denitrifying bacteria in the upper Yellow River cascade reservoirs is probably unclassified Proteobacteria. LEfSe analysis showed that the genera with the highest LDA scores were Paracoccus and Vogesella.
- (2)
- The abundance of the nirS gene in sediment showed significant differences between different seasons (p < 0.05), with the abundance in the wet season (0.62 × 107–30.2 × 107 copies/g dry sediment) being significantly higher than that in the dry season (4.44 × 105–274 × 105 copies/g dry sediment) (p < 0.05).
- (3)
- The community structure of nirS-type denitrifying bacteria was jointly influenced by multiple environmental factors. Among them, sediment total nitrogen (19.31%) and water temperature (14.13%) had the most significant impact. Reservoir age significantly influences the nirS-type denitrifying bacterial community, suggesting a potential decreasing trend in N2O emissions as reservoir age increases.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Yao, Y.; Shi, H.; Bian, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Maavara, T.; Lauerwald, R.; Pan, S. Increased nitrous oxide emissions from global lakes and reservoirs since the pre-industrial era. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.S.; Xiong, R.N.; Zhang, H.H.; Yang, S.Q.; Gao, N. Research progress on microbial-mediated mitigation of nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural soils. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. The State of Greenhouse Gases in the Atmosphere Based on Global Observations through 2022; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Soler-Jofra, A.; Stevens, B.; Hoekstra, M.; Picioreanu, C.; Sorokin, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Pérez, J. Importance of abiotic hydroxylamine conversion on nitrous oxide emissions during nitritation of reject water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Guo, M. Nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from the high dam reservoir in longitudinal range-gorge regions on the Lancang-Mekong River, southwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Hong, Y.W.; Chen, Z.W.; Zhao, C.G.; Yang, S.P. Phylogenetic diversity of nirS-type denitrifying bacteria in Jiulong River estuary. Microbiol. China 2015, 42, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.; Beusen, A.; Griffioen, J.; Van Groenigen, J.; Hefting, M.; Oenema, O.; Van Puijenbroek, P.; Seitzinger, S.; Slomp, C.; Stehfest, E. Global trends and uncertainties in terrestrial denitrification and N2O emissions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.R. Distribution Characteristics and Driving Mechanism of nirK and nirS Denitrifiers in Soils: A Case Study from the Mid-Channel Bar. Master’s Thesis, University of South China, Hengyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, T.; Zhang, C.; Fang, K.; Xia, C.; Bai, S.; Zeng, M.; Qiu, X. Illumina MiSeq sequencing reveals the community composition of nirS-Type and nirK-Type denitrifiers in Zhoucun reservoir—A large shallow eutrophic reservoir in northern China. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 91517–91528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.Y.; Tang, Y.F.; Xu, H.F.; Qin, H.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Chen, A.L.; Zhu, B.L. Warming shapes nirS- and nosZ-type denitrifier communities and stimulates N2O emission in acidic paddy soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02965-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Vilmin, L.; Mogollón, J.M.; Beusen, A.H.; van Hoek, W.J.; Liu, X.; Pika, P.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; Bouwman, A.F. Inland waters increasingly produce and emit nitrous oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13506–13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.B.; Li, C.; Guo, J.S.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, L.H. Advances of eco-environmental effects and adaptive management in river cascading development. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Leavitt, P.R.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Anthropogenic eutrophication of shallow lakes: Is it occasional? Water Res. 2022, 221, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Fan, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Zhan, P.; Luo, S.; Yuan, C.; et al. A comprehensive geospatial database of nearly 10 0000 reservoirs in China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4017–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Fu, K.D.; Tao, Y.C.; Zhang, N.; Yang, L.S. Spatial-temporal distribution and influencing factors of nitrous oxide flux across the water-air interface in Lancang River, China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Rasul, F.; Awan, M.I.; Cui, H.; Liu, K.; Yu, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, S.; et al. nirS and nosZII bacterial denitrifiers as well as fungal denitrifiers are coupled with N2O emissions in long-term fertilized soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, A.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, G. Characteristics of climate change over the Tibetan Plateau under the global warming during 1979–2024. Clim. Change Res. 2016, 12, 374–381. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Ju, P.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, X.; Wu, N.; Gao, Y.; Feng, X.; Tian, J.; Niu, S.; Zhang, Y. Carbon and nitrogen cycling on the Qinghai–Tibetan plateau. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xia, X.; Battin, T.J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Yang, Z.; Ni, J.; Stanley, E.H. Unexpectedly minor nitrous oxide emissions from fluvial networks draining permafrost catchments of the East Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.Z.; Bao, Y.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Hao, W.L.; Liu, S.; Sun, M.; Wen, j.; Li, S.Z.; Zhao, J.W. Vertical niche differentiation of comammox bacteria and the influencingfactors in sediments of the Lancang River reservoir. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2024, 13, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.M.; Li, Y.N.; Song, H.Y.; Li, W.B.; Zhou, X.H.; Xu, X.H. The structural and functional characteristies of the sedimentarybacterial community in the root area of Acorus calamus. Environ. Chem. 2024, 44, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Methods for Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Throbäck, I.N.; Enwall, K.; Jarvis, Å.; Hallin, S. Reassessing PCR primers targeting nirS, nirK and nosZ genes for community surveys of denitrifying bacteria with DGGE. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 49, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Gao, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. iMeta 2022, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, X.Y.; Lin, M.X.; Sun, Y.X. Abundance and structure diversity of denitrifying bacterial community in sediments of Guangzhou Liuxi River. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2018, 38, 65–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, B.; Yang, A.J.; Hu, X.; Xu, K.; Ji, L. Bacterial community structure in reservoir sediments under the influence of antimony ore waste water. Microbiol. China 2021, 48, 2956–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Lücker, S.; Vejmelkova, D.; Kostrikina, N.A.; Kleerebezem, R.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Le Paslier, D.; Muyzer, G.; Wagner, M.; et al. Nitrification expanded: Discovery, physiology and genomics of a nitrite-oxidizing bacterium from the phylum Chloroflexi. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2245–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, B.; Lu, G. Structural Characteristics of Microbial Communities in the Sediments of the Niyang River in Tibet. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.X.; Chen, Q.R.; Shi, Y.Y.; Su, J.; Yu, Y.; Fan, J.F. Study on denitrification process of sediment in the Liaohe estuary analysis of the abundance of denitrification functional genes and the community structrure of nirK-type bacteria. Haiy. Xue. 2020, 42, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.F.; Liu, T.; Bai, Y.; Xiang, Q.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Chen, Q. Pyrosequencing of nirS gene revealed spatial variation of denitrifying bacterial assemblages in response to wetland desertification at Tibet plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Komatsu, N.; Ishii, Y.; Negishi, M. Effective isolation of bacterioplankton genus Polynucleobacter from freshwater environments grown on photochemically degraded dissolved organic matter. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Simultaneous Treatment of Biogas Desulfurization and Wastewater Denitrification Based on Autotrophic Denitrification. Doctoral Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Fan, B.; Mei, L. Comparative of bacterial community composition and diversity in the Wangfeng Lake between wet season and dry season. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2023, 38, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Ding, J.W.; Yan, L.Y.; Yin, W.; Gao, Z.H.; Song, Q.; Wang, L.; Liang, J. Bacterial community diversity in river sediments of Qinghai section of the Makehe River in dry and wet seasons. J. Northwest A F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaulou, D.R.; Bales, R.C.; Arnold, R.G. Effect of Temperature-Controlled Motility on Transport of Bacteria and Microspheres Through Saturated Sediment. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hou, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, M.; Yin, G.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, R.; Jiang, X. nirS-Encoding denitrifier community composition, distribution, and abundance along the coastal wetlands of China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 8573–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.X.; Chen, H.D.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liao, M.J. Abundance of aerobic ammonia-oxidizing and nirS type denitrifying microorganisms in sediments of Lancang River. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 3107–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Y.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M. Effect of reclamation activity on coastal ecological environment: Progress and perspectives. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1148–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiu, Y.; Yao, T.; Han, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X. Nutrients available in the soil regulate the changes of soil microbial community alongside degradation of alpine meadows in the northeast of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, B.; Nan, B.; Hu, P. Diversity of bacterial community and detection of nirS-and nirK-encoding denitrifying bacteria in sandy intertidal sediments along Laizhou Bay of Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 88, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.N.; Chen, S.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Tang, B.J.; Ping, X.Y.; Fan, R.L.; Li, N.N.; Quan, W.M. Abundance and structure diversity of denitrifying bacterial community in sediment of the typical habitats of Xiangshan Bay. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.C.; Francis, C.A. Denitrifier abundance and activity across the San Francisco Bay estuary. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, W.; Liu, S.F.; Fan, Y.J.; Zhuang, Z.M. Diversity of denitrifying bacteria by encoding nirS gene from surface sediments of the pear river esturary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2012, 43, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Shi, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.P.; Jing, S.Y.; Yu, L.H. Community characteristics of denitrifying microorganisms in plateau lake sediments—Taking Nanhaihu lake as example. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Lee, C.M. Isolation of the ɛ-caprolactam denitrifying bacteria from a wastewater treatment system manufactured with acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolsing, M.; Priemé, A. Observation of high seasonal variation in community structure of denitrifying bacteria in arable soil receiving artificial fertilizer and cattle manure by determining T-RFLP of nir gene fragments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, F.; Fu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qin, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.-P. Differential response of microbial diversity and abundance to hydrological residual time and age in cascade reservoirs. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohman, S.P.; Smyth, A.R.; Bean, E.Z.; Reisinger, A.J. Internal nitrogen dynamics in stormwater pond sediments are influenced by pond age and inorganic nitrogen availability. Biogeochemistry 2021, 156, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Mao, X.; Yu, H.; Li, H.; Xiao, F.; Mo, Y.; Ji, H.; Ma, Y. Spatiotemporal Distribution of nirS-Type Denitrifiers in Cascade Reservoir Sediments of the Qinghai Plateau. Diversity 2024, 16, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16110656
Wu Y, Mao X, Yu H, Li H, Xiao F, Mo Y, Ji H, Ma Y. Spatiotemporal Distribution of nirS-Type Denitrifiers in Cascade Reservoir Sediments of the Qinghai Plateau. Diversity. 2024; 16(11):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16110656
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yi, Xufeng Mao, Hongyan Yu, Hongyan Li, Feng Xiao, Yuhua Mo, Haichuan Ji, and Yuanjie Ma. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Distribution of nirS-Type Denitrifiers in Cascade Reservoir Sediments of the Qinghai Plateau" Diversity 16, no. 11: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16110656
APA StyleWu, Y., Mao, X., Yu, H., Li, H., Xiao, F., Mo, Y., Ji, H., & Ma, Y. (2024). Spatiotemporal Distribution of nirS-Type Denitrifiers in Cascade Reservoir Sediments of the Qinghai Plateau. Diversity, 16(11), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16110656







