Abstract
(1) Background: An estuary is a zone in which sea and river waters mix. It is a specific area with a very non-stable environment and salinity gradient. However, little is known about the diversity of ciliate communities in estuarine benthic ecosystems in the Arctic. The aim of this paper is to describe the diversity of intertidal ciliates in the Chernaya river estuary (Kandalaksha Gulf, White Sea), which is characterized by a pronounced salinity gradient (0–22‰), on the basis of a recently published dataset. (2) Methods: We conducted our own investigations during the summer periods of 1998–2000. Material was collected at five permanent stations along the salinity gradient (0–22%) of the estuary. For each observation, the coordinates of the sampling sites, the number of individuals observed and the sampling date were recorded. The total effort comprised 35 sampling days, with five sampling sites at each date. (3) Results: The dataset contains 4270 unique occurrences of 119 ciliates taxa (109 species, 8 unidentified species of the genus level and 2 unidentified species on the family level). The total number of specimens represented is 64,475. (4) Conclusions: The largest classes in terms of species diversity are Hypotrichea (27 species), Gymnostomatea (26 species), Oligohymenophorea (17 species) and Karyorelictea (16 species).
Dataset: https://doi.org/10.15468/ccku5d.
Dataset License: Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 License.
1. Summary
Ciliates are unicellular protists with a high level of diversity and wide distribution [1]. Intertidal sediments are characterized by a high species abundance and richness of ciliates, with up to 2500 cells/mL [2,3,4]. Hamels et al. [5] detected 53 species from a volume of 0.2 mL of intertidal sediment. Burkovsky and Mazei [6,7] reported 125 ciliate species from an area of one square meter of intertidal sediment during a long-term study. With their high abundance and species richness, interstitial ciliates are suitable for evaluating the distribution patterns of protists and the major factors regulating their dispersal on different spatial scales [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Previous studies have reported high levels of diversity of interstitial ciliates and other protists in the White Sea [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41].
High environmental variability and a critical salinity level (3–8‰) cause peculiarities in ciliate community composition and complexity in brackish waters when compared with other biotopes [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Herein, we describe intertidal ciliate fauna in a non-stable environment with a pronounced salinity gradient (0–22‰) based on a recently published dataset.
2. Data Description
2.1. Dataset Description
In the dataset (Table 1), each observation includes basic information: the date of observation, coordinates (latitude/longitude), observer name, identifier name and publications (if available). The coordinates were determined using satellite images.

Table 1.
Description of the data in the dataset.
The dataset contains 4270 unique occurrences of 119 ciliates taxa (species, genera and families) from the Chernaya River estuary (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea). The dataset is based on field studies by Yuri A. Mazei and Igor V. Burkovsky which were performed in the period 1998–2000 [29,36].
2.2. Figures, Tables and Schemes
The dataset contains 4270 unique occurrences of 119 ciliates taxa (109 species, 8 genera and 2 families) from the Chernaya River estuary (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea). The total number of specimens represented is 64,475. Hypotrichea (27 species), Gymnostomatea (26), Oligohymenophorea (17) and Karyorelictea (16) are the largest classes in terms of species richness. Karyorelictea (24,868) and Oligohymenophorea (19,260) are the largest classes in terms of abundance. Class Litostomatea were represented by only one species and one individual (Table 2).

Table 2.
Species diversity of ciliate classes from the dataset.
Twenty species presented in the database have corrected names compared to the original studies [29,36,48]: Biholosticha discocephalus (Kahl, 1932) Berger, 2003, Anigsteinia clarissimum Kahl, 1928, Anigsteinia salinarum (Florentin, 1899) Kahl, 1932, Enchelyodon sulcatus Kahl, 1930, Holosticha gibba (Müller, 1786) Wrzesniowski, 1877, Kentrophoros fasciolatus Sauerbrey, 1928, Kentrophoros latus Raikov, 1962, Kentrophoros uninucleatus (Raikov, 1962) Raikov, 1962, Pleuronema coronatum Kent, 1881, Pleuronema crissum Dujardin, 1841, Protogastrostyla pulchra (Pereyaslawzewa, 1886) Gong, Kim, Kim, Min, Roberts, Warren & Choi, 2007, Limnostrombidium viride (Stein, 1867) Krainer, 1995, Tracheloraphis oligostriata Raikov, 1962, Prototrachelocerca caudata (Dragesco & Raikov, 1966) Foissner, 1986, Trachelocerca incaudata Kahl, 1933, Apotrachelocerca arenicola (Kahl, 1933), Trachelostyla pediculiformis (Cohn, 1866) Borror, 1972, Trichotaxis multinucleatus Burkovsky, 1970, Uroleptus caudatus (Stokes, 1886) Bardele, 1981, Uronema marinum Dujardin, 1841 and Urosoma caudatum (Ehrenberg, 1833) Berger, 1999.
In the marine zone (station 1, see Figure 1), the highest species richness was observed. As it moves towards the river mouth, we detected decreases in the abundance and richness of most stenohaline marine species and corresponding increases in marine euryhaline and brackish water (oligohaline) species. We did not find species of freshwater origin in the estuary.
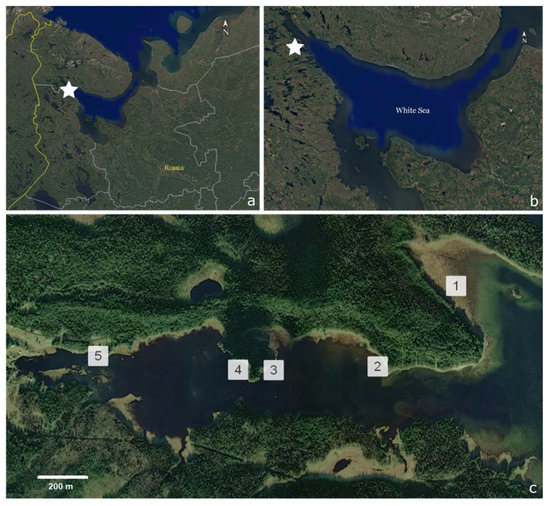
Figure 1.
Sampling sites in the White Sea. (a,b) The white stars on the satellite images showing the location of Chernaya River estuary. The basis for the maps (a,b) was https://www.google.com/maps/ (accessed on 5 June 2023). (c) A scheme of the locations of stations 1–5 in the estuary; numbers in the figure showing exact sampling sites at each station. The basis for the map (c) was https://360earthview.com/ (accessed on 5 June 2023).
For the entire period of observation, there were 45 families and 34,191 individuals recorded at station 1, 44 families and 15,223 individuals at station 2, 42 families and 7707 individuals at station 3, 39 families and 4003 individuals at station 4 and 34 families and 3351 individuals at station 5.
Each year, between 21 and 65 taxa were detected in one sample at station 1, between 15 and 46 taxa were detected at station 2, between 7 and 36 taxa were detected at station 3, between 6 and 27 taxa were detected at station 4 and between 8 and 30 taxa were detected at station 5.
The following taxa were found the most often in the most marine part of the estuary at Station 1: Apotrachelocerca arenicola, Cardiostomatella vermiformis, Coleps tesselatus, Didinium balbiani, Diophrys scutum, Discocephalus rotatorius, Geleia fossata, Histobalantium majus, Histobalantium marinum, Lacrymaria affinis, Limnostrombidium viride, Pleuronema marina, Prorodon, Remanella margaritifera, Trachelocerca incaudata, Urostrongylum caudatum and Uronema marinum. Moreover, Apotrachelocerca renicola, Histobalantium marinum, Remanella margaritifera, Trachelocerca incaudata and Uronema marinum were found in each sample the entire period of observation (Table 3).

Table 3.
Abundance (individuals per square centimeter) and number of unique occurrences of most common ciliate species from the dataset.
The most common taxa found at Station 2 were Cardiostomatella vermiformis, Cyclidium fuscum, Didinium balbiani, Enchelyodon, Limnostrombidium viride, Histobalantium marinum, Prorodon, Remanella margaritifera, Sonderia vorax, Trachelocerca incaudata, Trachelocercidae, Tracheloraphis kahli, Trachelostyla caudata, Urostrongylum caudatum and Uronema marinum.
The most common taxa found at Station 3 were Cardiostomatella vermiformis, Coleps tesselatus, Cyclidium fuscum, Didinium balbiani, Enchelyodon, Histobalantium marinum, Pleuronema crassum, Prorodon, Sonderia vorax, Trachelocercidae, Trachelostyla caudata and Uronema marinum.
The most common taxa found at Station 4 were Anigsteinia clarissimum, Cyclidium fuscum, Enchelyodon, Glaucoma pyriformis, Lacrymaria affinis, Lacrymaria cohnii, Lacrymaria coronata, Oxytrichidae, Paraprorodon morgani, Pleuronema crassum, Prorodon and Uronema marinum.
The most common taxa found at Station 5 were Anigsteinia clarissimum, Cyclidium fuscum, Cyrtohymena marina, Enchelyodon, Lacrymaria affinis, Lacrymaria cohnii, Lacrymaria conifera, Lacrymaria coronata, Oxytrichidae, Paraprorodon morgani, Pleuronema crassum, Prorodon, Uronema marinum and Urosoma caudatum.
The following taxa were found at all stations for the entire period of observation: Apotrachelocerca arenicola, Aspidisca fusca Kahl, 1928, Anigsteinia clarissimum, Cardiostomatella vermiformis, Condylostoma curva Burkovsky, 1970, Cyclidium fuscum, Didinium balbiani, Diophrys scutum, Enchelyodon, Enchelyodon sulcatus Kahl, 1930, Euplotes trisulcatus Kahl, 1932, Frontonia fusca Quennerstedt, 1869, Frontonia marisalbi Burkovsky, 1970, Frontonia tchibisovae, Helicostoma notatum Kahl, 1931, Histobalantium marinum, Lacrymaria affinis, Lacrymaria caudata Kahl, 1933, Lacrymaria cohnii, Lacrymaria conifera, Lacrymaria coronata Claparède & Lachmann, 1859, Lacrymaria marina Meunier, 1907, Limnostrombidium viride, Mesodinium pulex (Claparède & Lachmann, 1859) Stein, 1867, Oxytrichidae, Paraprorodon morgani, Pleuronema coronatum Kent, 1881, Pleuronema crassum, Pleuronema marina, Prorodon, Sonderia vorax, Strombidium sulcatum Claparède & Lachmann, 1859, Trachelocercidae, Trachelostyla caudata, Trachelostyla pediculiformis (Cohn, 1866) Borror, 1972, Uroleptus caudatus (Stokes, 1886) Bardele, 1981, Uronema marinum, Uronychia transfuga (Müller, 1776) Stein, 1859 and Urostrongylum caudatum.
Ciliate species richness was slightly different in different years: 78 taxa in 1998, 79 taxa in 1999 and 94 taxa in 2000. As salinity decreases, the number of species decreases as well. General data on species richness at different stations in 1998, 1999 and 2000 are presented in Figure 2.
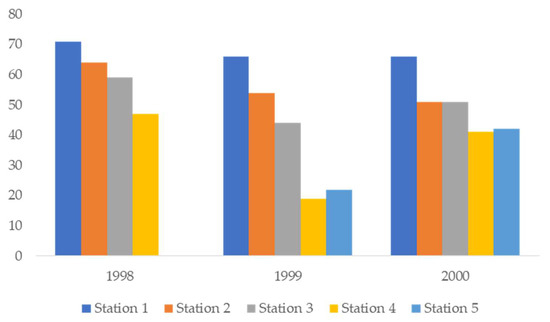
Figure 2.
Number of taxa at different stations in all years.
3. Methods
The investigations were conducted during the summer periods of 1998–2000 periods in the Chernaya river estuary (the Kandalaksha Bay, the White Sea). Material was collected at five permanent stations. The stations were located at the middle horizon of the intertidal zone along the estuary on the borders, dividing relatively homogenous zones (Figure 1). The distance from the shore to a station differed at different stations due to the topography characteristics. Thus, at station 1 it was 60 m, at station 2 it was 10 m, at station 3 it was 5 m, at station 4 it was 12 m and at station 5 it was 2 m. The sampling was carried out in intervals of 5–7 days. The total effort comprised 14 sampling days in 1998, 5 sampling days in 1999 and 16 sampling days in 2000.
Each sample was a series of 15 subsamples (1 cm2 in square, 3 cm in height, which resulted in a 45 cm3 total sample) collected from a strictly fixed square 50 × 50 cm. A random sampling, corresponding to 1/15 of the total sample (3 cm3), was examined (i.e., under one mean statistical square centimeter). Fifteen simultaneously taken subsamples allowed one to grade the possible spatial heterogeneity and to receive as much information as possible about the species biodiversity. The ciliates were extracted from the sediment by washing, according to the Uhlig method [55], one hour after sampling. The quantitative counting of ciliates was performed on live individuals under the stereomicroscope BIOMED-9 (Russia) at a magnification of ×32–56. The ciliates were identified on silver-impregnated slides [56], according to Carey [57]. All individuals found were identified at species, genus or family levels. Most of the species were morphologically described in our previous publications [58,59,60,61].
Environmental factors (water temperature, salinity and pH) were measured at each station. The interstitial water temperature was measured using an ordinary thermometer (graduated to 0.1 °C), and salinity and pH were measured with a conductivity meter and pH meter, correspondingly (HANNA Instruments, Belgium).
The results of measuring different environmental parameters (Table 4) show that the Chernaya river estuary is a very spatially heterogeneous and temporally unstable environment. The spatial heterogeneity of the biotope is, first of all, connected with the mosaic distribution of mineral and organic sediments in the intertidal zone, which also determines other important environmental characteristics (pH, Eh and the granulometric composition of sediment). Temporal instability is conditioned by tidal rhythms and the unsteadiness of the river flow. More detailed information about environmental parameters for particular sampling points are provided in Table S1.

Table 4.
Environmental parameters of samples from five stations.
All calculations were made with the use of MS Excel and PAST 4.11 packages.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15070873/s1, Table S1: Environmental parameters for particular sampling points in the Chernaya river estuary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.V.B. and Y.A.M.; methodology, I.V.B. and Y.A.M.; software, D.A.S.; validation, X.L., A.S.E. and D.A.S.; formal analysis, A.S.E.; investigation, I.V.B. and Y.A.M.; resources, I.V.B. and Y.A.M.; data curation, Y.A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L. and A.S.E.; writing—review and editing, X.L., A.S.E., I.V.B., D.A.S. and Y.A.M.; visualization, A.S.E.; supervision, Y.A.M.; project administration, Y.A.M.; funding acquisition, Y.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (19-14-00102).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lynn, D.H. The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification, and Guide to the Literature, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1–605. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. Complexity of ecological systems (the case of marine ciliate community). Russ. J. Ecosyst. Ecol. 2016, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musat, N.; Werner, U.; Knittel, K.; Kolb, S.; Dodenhof, T.; van Beusekom, J.E.E.; de Beer, D.; Dubilier, N.; Amann, R. Microbial Community Structure of Sandy Intertidal Sediments in the North Sea, Sylt-Rømø Basin, Wadden Sea. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 29, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, S.A.; Gieseke, A.; Berninger, U. Benthic Ciliate Identification and Enumeration: An Improved Methodology and Its Application. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 22, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamels, I.; Muylaert, K.; Sabbe, K.; Vyverman, W. Contrasting Dynamics of Ciliate Communities in Sandy and Silty Sediments of an Estuarine Intertidal Flat. Eur. J. Protistol. 2005, 41, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkovsky, I.; Mazei, Y. Long-Term Dynamics of Marine Interstitial Ciliate Community. Protistology 2010, 6, 147–172. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. 21-Year Dynamics of Marine Benthic Ciliate Community in the White Sea Intertidal Flat: Gradual or Discrete? Russ. J. Ecosyst. Ecol. 2017, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A.; Saburova, M.; Tikhonenkov, D.; Khazanova, K.; Esaulov, A.; Mazei, Y. Composition, Diversity and Distribution of Microbenthos across the Intertidal Zones of Ryazhkov Island (the White Sea). Eur. J. Protistol. 2013, 49, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azovsky, A.; Chertoprud, E.; Garlitska, L.; Mazei, Y.; Tikhonenkov, D. Does Size Really Matter in Biogeography? Patterns and Drivers of Global Distribution of Marine Micro- and Meiofauna. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A.; Mazei, Y.A.; Saburova, M.; Sapozhnikov, P. Patterns in diversity and composition of microbenthos of subarctic intertidal beaches with different morphodynamics. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 648, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A.I.; Mazei, Y.A. Ciliates of coarse ground on the northeastern Black Sea coast. Zool. Zhurnal 2003, 82, 899–912. [Google Scholar]
- Azovsky, A.I.; Mazei, Y.A. Distribution and community structure of benthic ciliates in the north-eastern part of the Black Sea. Protistology 2005, 4, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Azovsky, A.I.; Mazei, Y.A. New data on benthic ciliates of the Pechora River shoal and analysis of the Barents Sea ciliate fauna. Zool. Zhurnal 2007, 86, 387–402. [Google Scholar]
- Azovsky, A.I.; Mazei, Y.A. Structure of Subtidal and Intertidal Communities of Psammophilous Ciliates of the Pechora Sea. Oceanology 2007, 47, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A.I.; Mazei, Y.A. Do Microbes Have Macroecology? Large-Scale Patterns in the Diversity and Distribution of Marine Benthic Ciliates. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A.; Mazei, Y. Diversity and Distribution of Free-Living Ciliates from the High-Arctic Kara Sea Sediments. Protist 2018, 169, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, K.; Warren, A.; Lei, Y.; Dai, R. Benthic Ciliate and Meiofaunal Communities in Two Contrasting Habitats of an Intertidal Estuarine Wetland. J. Sea Res. 2012, 70, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.-L.; Stumm, K.; Wickham, S.A.; Berninger, U.-G. Distributions and Biomass of Benthic Ciliates, Foraminifera and Amoeboid Protists in Marine, Brackish, and Freshwater Sediments. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2014, 61, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhao, F.; Xu, K. Complementary DNA Sequencing (CDNA): An Effective Approach for Assessing the Diversity and Distribution of Marine Benthic Ciliates along Hydrographic Gradients. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarragô, L.D.; Ferreira, P.M.A.; Utz, L.R.P. Benthic Marine Ciliate Assemblages from Southern Brazil and Their Relationship with Seasonality and Urbanization Level. Diversity 2020, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, X.; Warren, A.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H. Functional Diversity of Benthic Ciliate Communities in Response to Environmental Gradients in a Wetland of Yangtze Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Soininen, J. Spatial Patterns of Functional Diversity and Composition in Marine Benthic Ciliates along the Coast of China. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 627, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Soininen, J.; Zhang, S.; Fan, X. Disentangling the Relative Roles of Natural and Anthropogenic-Induced Stressors in Shaping Benthic Ciliate Diversity in a Heavily Disturbed Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Stoeck, T.; Forster, D.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X. Environmental Status Assessment Using Biological Traits Analyses and Functional Diversity Indices of Benthic Ciliate Communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Soetaert, K.; Xu, Y. The Relative Roles of Multiple Drivers on Benthic Ciliate Communities in an Intertidal Zone. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azovsky, A. Colonization of Sand “Islands” by Psammophilous Ciliates: The Effect of Microhabitat Size and Stage of Succession. Oikos 1988, 51, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkovsky, I.V. Quantitative data on vertical distribution of psammophilic infusoria in the Velikaya Salma (Kandalaksha Bay, the White Sea). Zool. Zhurnal 1968, 47, 1407–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovskii, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. A Study of Ciliate Colonization of Unpopulated Substrates of an Estuary in the White Sea. Oceanology 2001, 41, 845–852. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovskii, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. Ciliate community structure in the zone of mixing sea and river waters. Zool. Zhurnal 2001, 80, 267–268. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. Changes in the structure of marine psammophilous ciliate communities for the time period characteristic of thousands generations. Uspekhi Sovrem. Biol. 2008, 128, 383–398. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. Interannual variability of seasonal succession in psammophilous ciliate community in the White Sea. Uspekhi Sovrem. Biol. 2008, 128, 591–608. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.; Mazei, Y. Long-term changes of psammophilous ciliate populations in the White Sea. Uspekhi Sovrem. Biol. 2010, 130, 200–215. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A.; Esaulov, A.S. Influence of the Period of Existence of a Biotope on the Formation of the Species Structure of a Marine Psammophilous Ciliate Community. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2011, 37, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A.; Esaulov, A.S. The Stability of the Species Structure of the Marine Ciliate Community to Variations in Environmental Factors: The Roles of Physiological, Population, and Cenotic Mechanisms. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2012, 38, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazei, Y.; Burkovsky, I. Vertical Structure of the Interstitial Ciliate Community in the Chernaya River Estuary (the White Sea). Protistology 2003, 3, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mazei, Y.; Burkovsky, I. Species Composition of Benthic Ciliate Community in the Chernaya River Estuary (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea) with a Total Checklist of the White Sea Benthic Ciliate Fauna. Protistology 2005, 4, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mazei, Y.; Burkovsky, I.V. Patterns of Psammophilous Ciliate Community Structure along the Salinity Gradient in the Chernaya River Estuary (the Kandalaksha Gulf, the White Sea). Protistology 2006, 4, 251–268. [Google Scholar]
- Mazei, Y.; Burkovsky, I.V.; Saburova, M.A.; Polikarpov, I.; Stolyarov, A.P. Trophic Structure of Psammophilous Ciliate Community in the Chernaya River Estuary. Zool. Zhurnal 2001, 80, 1290–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonenkov, D.; Mazei, Y. Distribution of Heterotrophic Flagellates at the Littoral of Estuary of Chernaya River (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2006, 32, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonenkov, D.V.; Mazei, Y.A.; Mylnikov, A.P. Species Diversity of Heterotrophic Flagellates in White Sea Littoral Sites. Eur. J. Protistol. 2006, 42, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhonenkov, D.; Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y. Is There a Relation between the Distribution of Heterotrophic Flagellates and the Zonation of a Marine Intertidal Flat? Oceanology 2015, 55, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebovich, V. Some Peculiar Features of the Hydrochemical Regime and the Fauna of Mesohaline Waters. Mar. Biol. 1968, 2, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebovich, V. Aspects of Animal Evolution Related to Critical Salinity and Internal State. Mar. Biol. 1969, 2, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebovich, V. Applied Aspects of the Concept of Critical Salinity. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2015, 5, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkovskii, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. The effect of a lower salinity level on marine psammophilous ciliate community (field experiment). Zool. Zhurnal 2001, 80, 389–397. [Google Scholar]
- Saburova, M.A.; Polikarpov, I.G.; Burkovsky, I.V.; Mazei, Y.A. Marcoscale [Macroscale] distribution of interstitial microphytobenthos in the Chernaya River Estuary (Kandalaksha Bay, the White Sea). Ekol. Morya 2001, 58, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mazei, Y.; Burkovsky, I. Spatial and temporal changes of psammophilous ciliate community in the White Sea estuary. Uspekhi Sovrem. Biol. 2002, 122, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Mazei, Y.; Burkovsky, I.V.; Stolyarov, A.P. Salinity as a factor of forming ciliate community (Colonization Experiments). Zool. Zhurnal 2002, 81, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Udalov, A.A.; Burkovskii, I.V.; Mokievskii, V.O.; Stolyarov, A.P.; Mazei, Y.A.; Saburova, M.A.; Chertoprud, M.V.; Chertoprud, E.S.; Il’inskii, V.V.; Kolobov, M.Y.; et al. Changes in the general characteristics of micro-, meio-, and macrobenthos along the salinity gradient in the White Sea estuary. Oceanology 2004, 44, 514–525. [Google Scholar]
- Telesh, I.; Khlebovich, V. Principal Processes within the Estuarine Salinity Gradient: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 61, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesh, I.; Schubert, H.; Skarlato, S. Revisiting Remane’s Concept: Evidence for High Plankton Diversity and a Protistan Species Maximum in the Horohalinicum of the Baltic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 421, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesh, I.; Schubert, H.; Skarlato, S. Life in the Salinity Gradient: Discovering Mechanisms behind a New Biodiversity Pattern. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 135, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesh, I.; Schubert, H.; Skarlato, S. Size, Seasonality, or Salinity: What Drives the Protistan Species Maximum in the Horohalinicum? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 161, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonenkov, D.V.; Mazei, Y.A. Distribution of benthic heterotrophic flagellates along salinity gradient: Correlation between active and cryptic species diversity in the White Sea estuary. Uspekhi Sovrem. Biol. 2013, 133, 178–190. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlig, G. Eine einfache Methode zur Extraktion der vagilen mesopsammalen Mikrofauna. Helgoll. Wiss. Meeresuntersuch. 1964, 11, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissner, W. Basic light and scanning electron microscopic methods for taxonomic studies of ciliated Protozoa. Eur. J. Protistol. 1991, 27, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, P.G. Marine Interstitial Ciliates. An Illustrated Key; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1992; pp. 1–351. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.V. The Ciliates of the Mesopsammon of the Kandalaksha Gulg (White Sea). I. Acta Protozool. 1970, 7, 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovsky, I.V. The Ciliates of the Mesopsammon of the Kandalaksha Gulg (White Sea). II. Acta Protozool. 1970, 8, 47–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mazei, Y.; Gao, S.; Warren, A.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Song, W.; Esaulov, A. Reinvestigation of the Marine Ciliate Trachelocerca ditis (Wright, 1982) Foissner and Dragesco, 1996 (Ciliophora, Karyorelictea) from the Yellow Sea and an Assessment of Its Phylogenetic Position Inferred from the Small Subunit RRNA Gene Sequence. Acta Protozool. 2009, 48, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Esaulov, A.; Lin, X.; Mazei, Y.; Hu, X.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Warren, A. Morphological Studies on Five Trachelocercids from the Yellow Sea Coast of China, with a Description of Tracheloraphis huangi spec. nov. (Ciliophora, Karyorelictea). Acta Protozool. 2011, 50, 205–218. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).