Selected Case Studies on Fastidious Eukaryotic Microorganisms: Issues and Investigation Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. General Concept of Fastidious Microorganisms
1.2. General Concepts on Fastidious Bacteria
1.3. General Concepts on Fastidious Eukaryotic Microorganisms
2. Case Studies
2.1. Case-Study 1: Isolation and Long-Term Preservation of Slow-Growing Fungi from Extreme Environments
- (i)
- Repeated washings (when possible) of the environmental samples with sterile water added with 0.1 Tween 20 to remove potential contaminants [32];
- (ii)
- Inoculation of a small portion (or dilution) of environmental samples on properly “poisoned” media (e.g., Rose–Bengal agar medium) to significantly deplete the growth of fast-growing fungi [33];
- (iii)
- Incubation for a long time (even for months) through reproduction of the stress to which slow-growing fungi are adapted (e.g., low temperatures, i.e., 4–15 °C, for the isolation of psychrophilic fungi);
- (iv)
- Continuous inspection of cultures to remove possible contaminants and even to transfer slow-growing colonies onto new media.
2.2. Case-Study 2: Culturing of Haematococcus lacustris (Girod-Chantrans) Rostafinski
- (i)
- Motile phase;
- (ii)
- Non motile phase.
2.3. Case-Study 3: Isolation of Unialgal Strains from Mixed Populations of Cyanidiophytina (Rhodophyta)
2.4. Case-Study 4: Identification of Yeasts of the Metschnikowia pulcherrima Clade
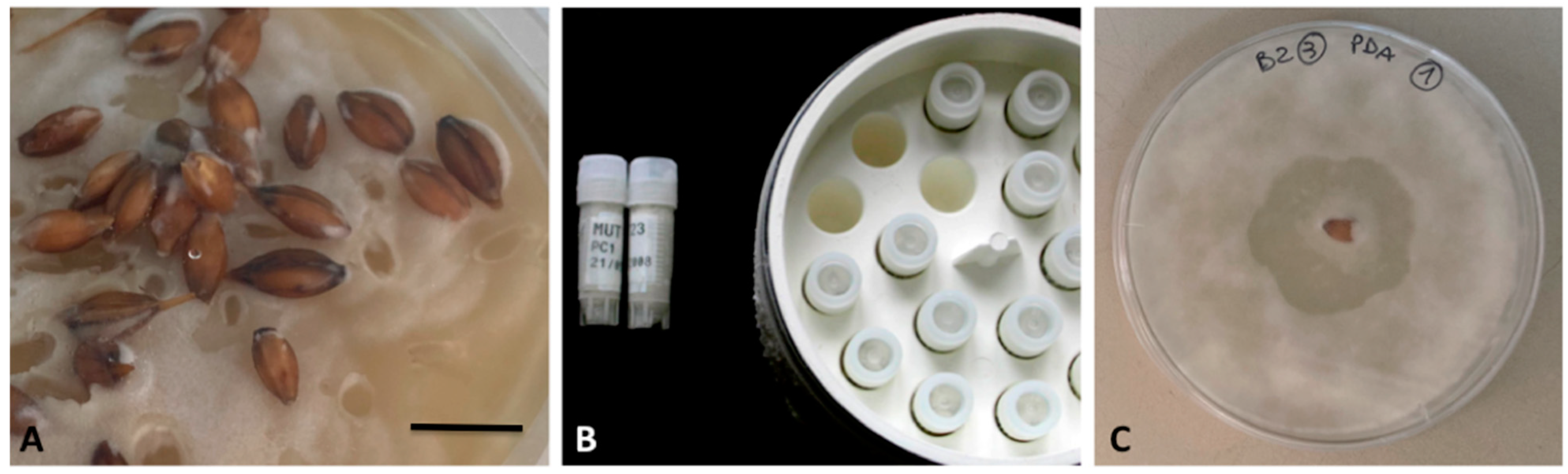
2.5. Case-Study 5: Isolation and Preservation of Pyricularia Species
- (i)
- Storage of portions of infected plants at −20 °C;
- (ii)
- (iii)
- Incubation of unsealed plates at room temperature and under light;
- (iv)
- Periodical checking of plates to detect the presence of conidiophores bearing macroconidia [94];
- (v)
- Isolation of mycelia in potato dextrose agar (PDA) solid medium for the production of macroconidia;
- (vi)
- Transfer of single macroconidia in TWA solid medium; spatial set to obtain monosporic cultures is shown in Figure 2;
- (vii)
- Checking of conidia germination after 24 h;
- (viii)
- Transfer of new colonies in modified rice–meal–yeast extract agar (RYA) solid medium [84], where colonization typically takes 15–25 days to give ripe conidiophores.

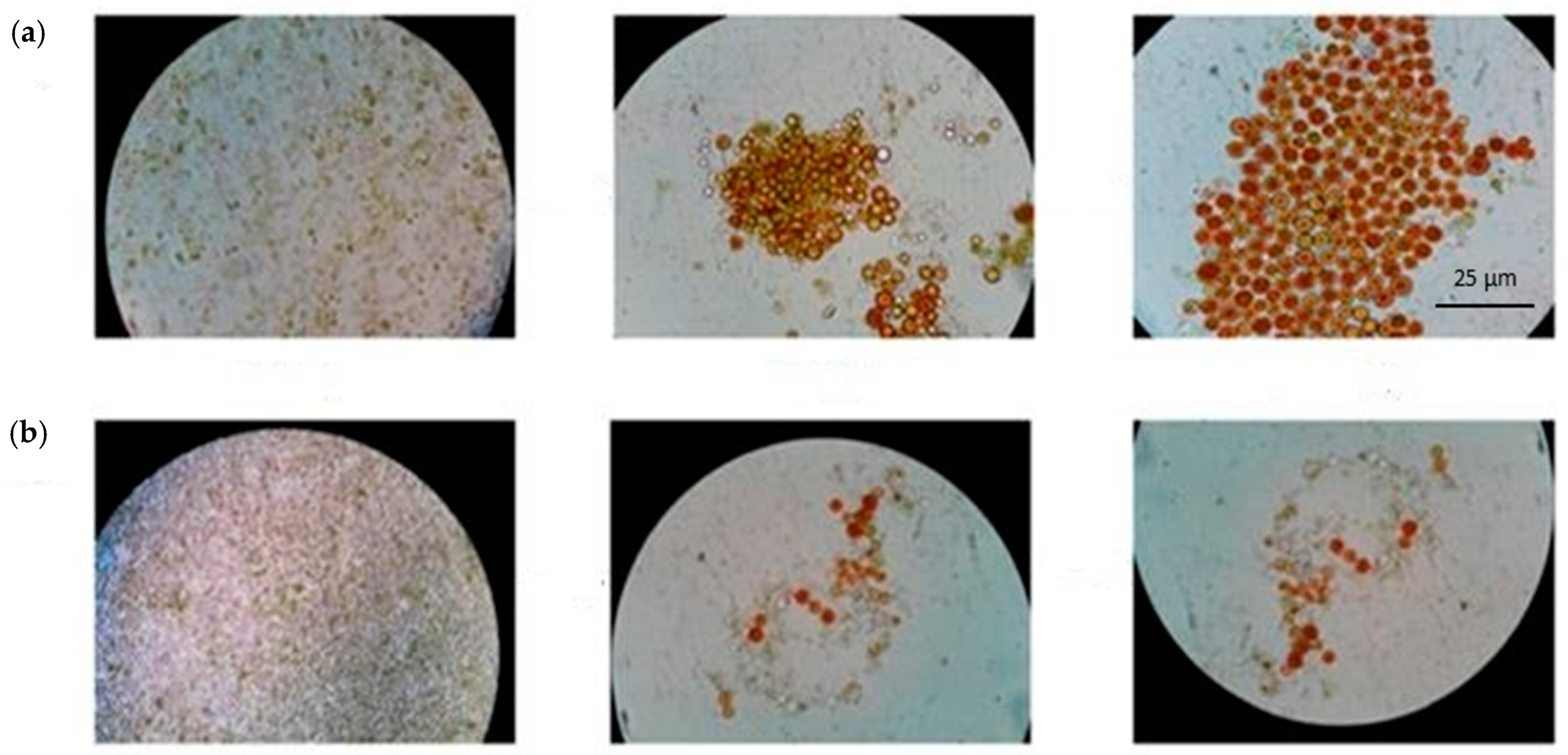
2.6. Case-Study 6: Preservation of Halophytophtora spp. (Peronosporomycetes) from Marine Environment
- (i)
- Collection of 2 mm mycelium plugs from colonies pre-grown on PDA in a 10% glycerol solution;
- (ii)
- Fast controlled with the glycerol solution;
- (iii)
- As an alternative, freezing (−1 °C/minute up to −80 °C and then transfer at −152 °C) of the material collected in the cryovials direct submersion of colonies in 10% glycerol solution followed by an overnight incubation at 5 °C before freezing (to overcome the difficulties encountered in collecting mycelium plugs).
- (i)
- Inoculum of H. lusitanica strains on PDA plates and incubation at their optimal temperature for growth (15 °C) for two weeks;
- (ii)
- Addition of sterile wheat grains (about 30 for each strain) to the surface of actively growing colonies and incubation at 15 °C for about 3 weeks;
- (iii)
- Transfer of wheat grains colonized by H. lusitanica strains into cryotubes containing 10% glycerol aqueous solution;
- (iv)
- Six months cryopreservation at both −80 °C and −152 °C.
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mobed, A.; Baradaran, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Agazadeh, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Rezaee, M.A.; Mosafer, J.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Hamblin, M.R. Advances in detection of fastidious bacteria: From microscopic observation to molecular biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamagata, Y.; Tamaki, H. Culturing of uncultured fastidious microbes. Microbes Environ. 2005, 20, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, P.E.; Dubourg, G.; Raoult, D. Clinical detection and characterization of bacterial pathogens in the genomics era. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarecki, R.; Oberhardt, M.A.; Reshef, L.; Gophna, U.; Ruppin, E. A novel nutritional predictor links microbial fastidiousness with lowered ubiquity, growth rate, and cooperativeness. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Prakash, O.; Nimonkar, Y.; Desai, D. A recent overview of microbes and microbiome preservation. Indian J. Microbiol. 2020, 60, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doern, G.V. Detection of selected fastidious bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishmawi, N.; Ghneim, R.; Kattan, R.; Ghneim, R.; Zoughbi, M.; Abu-Diab, A.; Turkuman, S.; Dauodi, R.; Shomali, I.; Issa, A.R.; et al. Survival of fastidious and nonfastidious aerobic bacteria in three bacterial transport swab systems. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvesvara, G.S.; Garcia, L.S. Culture of protozoan parasites. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayser, P.; Haze, P.; Papavassilis, C.; Pickel, M.; Gfuender, K.; Guého, E. Differentiation of Malassezia species: Selectivity of Cremophor EL, castor oil and ricinoleic acid for M. furfur. British J. Dermatol. 1997, 137, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Shimada, S.; Yamanaka, K. A new method for the preservation of fungus stock cultures by deep freezing. Mycoscience 2002, 43, e143–e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, M.; Suliman, M.E.; Sage-Palloix, A.M.; Mohamed, Y.F.; Nicot, P.C. Inoculum production and long-term conservation methods for cucurbits and tomato powdery mildews. Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, F.H.; Mozley-Standridge, S.E.; Porter, D.; Boyle, D.G.; Hyatt, A.D. Preservation of Chytridiomycota in culture collections. Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharin, K.; Wongsa, P. Semi-defined medium for in vitro culturing of the fastidious insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps unilateralis. Mycopathologia 2006, 161, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffnagle, G.B.; Noverr, M.C. The emerging world of the fungal microbiome. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittar, F.; Gouriet, F.; Khelaifia, S.; Raoult, D.; Ranque, S. FastFung: A novel medium for the culture and isolation of fastidious fungal species from clinical samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 180, 106108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houseknecht, J.L.; Suh, S.O.; Zhou, J.J. Viability of fastidious Phytophthora following different cryopreservation treatments. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salah, I.; Makni, F.; Cheikhrouhou, F.; Neji, S.; Sellami, H.; Ayadi, A. Malassezia species: Pathology, isolation and identification media. J. Mycol. Med. 2010, 20, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Koticha, A.; Ubale, M.; Wanjare, S.; Mehta, P.; Khopkar, U. Identification and speciation of Malassezia in patients clinically suspected of having Pityriasis versicolor. Indian J. Dermatol. 2013, 58, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.S.; Asman, A.; Shao, J.; Firmansyah, A.P.; Susilo, A.W.; Rosmana, A.; McMahon, P.; Junaid, M.; Guest, D.; Kheng, T.Y.; et al. Draft genome sequence of fastidious pathogen Ceratobasidium theobromae, which causes vascular-streak dieback in Theobroma cacao. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 30, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredericks, D.; Relman, D.A. Sequence-based identification of microbial pathogens: A reconsideration of Koch’s postulates. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, S.J.; Kühbacher, T.; Musfeldt, M.; Rosenstiel, P.; Hellmig, S.; Rehman, A.; Drews, O.; Weichert, W.; Timmis, K.N.; Schreiber, S. Fungi and inflammatory bowel diseases: Alterations of composition and diversity. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlan, P.D.; Marchesi, J.R. Micro-eukaryotic diversity of the human distal gut microbiota: Qualitative assessment using culture-dependent and -independent analysis of faeces. ISME J. 2008, 2, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, I.; Sokhna, C.; Raoult, D.; Bittar, F. Molecular detection of eukaryotes in a single human stool sample from Senegal. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humber, R.A. Special considerations for operating a culture collection of fastidious fungal pathogens. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Onions, A.H.S. The Preservation and Maintenance of Living Fungi, 2nd ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gostinčar, C.; Grube, M.; De Hoog, S.; Zalar, P.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Extremotolerance in fungi: Evolution on the edge. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 71, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostinčar, C.; Zalar, P.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. No need for speed: Slow development of fungi in extreme environments. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2022, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M.; Gostinčar, C. Glycerol metabolism genes in Aureobasidium pullulans and Aureobasidium subglaciale. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalar, P.; Zupančič, J.; Gostinčar, C.; Zajc, J.; de Hoog, G.S.; De Leo, F.; Azua-Bustos, A.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. The extremely halotolerant black yeast Hortaea werneckii—A model for intraspecific hybridization in clonal fungi. IMA Fungus 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleine, C.; Stajich, J.E.; Selbmann, L. Fungi are key players in extreme ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbmann, L.; Isola, D.; Egidi, E.; Zucconi, L.; Gueidan, C.; De Hoog, G.S.; Onofri, S. Mountain tips as reservoirs for new rock-fungal entities: Saxomyces gen. nov. and four new species from the Alps. Fungal Divers. 2014, 65, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, A.M.; Singh, N.K.; Simpson, A.C.; Seuylemezian, A.; Mason, C.E.; Venkateswaran, K. Draft genome sequences of fungi isolated from Mars 2020 spacecraft assembly facilities. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 1, e00464-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muggia, L.; Coleine, C.; De Carolis, R.; Cometto, A.; Selbmann, L. Antarctolichenia onofrii gen. nov. sp. nov. from Antarctic endolithic communities untangles the evolution of rock-inhabiting and lichenized fungi in Arthoniomycetes. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hoog, G.S.; Beguin, H.; Batenburg-van de Vegte, W.H. Phaeotheca triangularis, a new meristematic black yeast from a humidifier. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1997, 71, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Heitman, J. Is sex necessary? BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, T.; Ota, S. What is the correct name for the type of Haematococcus Flot. (Volvocales, Chlorophyceae)? Taxon 2016, 65, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekanov, K. Diversity and Distribution of Carotenogenic Algae in Europe: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cai, M.; Lin, M.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Ke, H.; Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, D.; Yang, S. Enhanced biomass and astaxanthin production of Haematococcus pluvialis by a cell transformation strategy with optimized initial biomass density. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Li, K.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Transcriptome sequencing and metabolic pathways of astaxanthin accumulated in Haematococcus pluvialis mutant under 15% CO2. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Kunisawa, R.; Mandel, M.C.B.G.; Cohen-Bazire, G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 171–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Cell cycles and proliferation patterns in Haematococcus pluvialis. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2017, 35, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Mehariya, S.; Iovine, A.; Larocca, V.; Di Sanzo, G.; Martino, M.; Casella, P.; Chianese, S.; Musmarra, D. Extraction of astaxanthin and lutein from microalga Haematococcus pluvialis in the red phase using CO₂ supercritical fluid extraction technology with ethanol as co-solvent. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Rimauro, J.; Casella, P.; Cerbone, A.; Larocca, V.; Chianese, S.; Karatza, D.; Mehariya, S.; Ferraro, A.; Hristoforou, E.; et al. Extraction of astaxanthin from microalga Haematococcus pluvialis in red phase by using generally recognized as safe solvents and accelerated extraction. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 283, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslan, S.N.H.; Shoparwe, N.F.; Yusoff, A.H.; Rahim, A.A.; Chang, C.S.; Tan, J.S.; Oslan, S.N.; Arumugam, K.; Ariff, A.B.; Sulaiman, A.Z.; et al. A review on Haematococcus pluvialis bioprocess optimization of green and red stage culture conditions for the production of natural astaxanthin. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, P.; Rimauro, J.; Iovine, A.; Mehariya, S.; Musmarra, D.; Molino, A. Characterization of extracts from Haematococcus pluvialis red phase by using accelerated solvent extraction. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 74, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Mehariya, S.; Sharma, N.; Iovine, A.; Casella, P.; Marino, T.; Larocca, V.; Molino, A.; Musmarra, D. An integrated strategy for nutraceuticals from Haematoccus pluvialis: From culturing to extraction. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, T.D. Thermophilic Microorganisms and Life at High Temperatures; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.L.; Chiang, Y.R.; Yoon, H.S.; Fu, H.Y. Comparative genome analysis reveals Cyanidiococcus gen. nov., a new extremophilic red algal genus sister to Cyanidioschyzon (Cyanidioschyzonaceae, Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertano, P.; Ciniglia, C.; Pinto, G.; Pollio, A. The taxonomic position of Cyanidium, Cyanidioschyzon and Galdieria: An update. Hydrobiologia 2000, 433, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.B. Studies with Cyanidium caldarium, an anomalously pigmented chlorophyte. Arch. Mikrobiol. 1959, 32, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, R.; Southwick, W.; Fresco, J.R. Laboratory culturing of a thermophilic alga at high temperature. Science 1966, 153, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, V.; Di Martino Rigano, V.; Esposito, S.; Di Martino, C.; Rigano, C. Growth, photosynthesis, respiration, and intracellular free amino acid profiles in the unicellular alga Cyanidium caldarium. Effect of nutrient limitation and resupply. Physiol. Plant. 1992, 85, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoda, A.; Sakagami, R.; Yagisawa, F.; Kuroiwa, T.; Tanaka, K. Improvement of culture conditions and evidence for nuclear transformation by homologous recombination in a red alga, Cyanidioschyzon merolae 10D. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnuma, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Inouye, T.; Sekine, Y.; Tanaka, K. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-mediated transient gene expression in a red alga, Cyanidioschyzon merolae 10D. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; Taddei, R. Due alghe delle fumarole acide dei Campi Flegrei (Napoli): Cyanidium caldarium? Delpinoa 1970, 10, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Merola, A.; Castaldo, R.; De Luca, P.; Gambardella, R.; Musacchio, A.; Taddei, R. Revision of Cyanidium caldarium. Three species of acidophilic algae. Plant Biosyst. 1981, 115, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; Taddei, R.; Varano, L. Cyanidioschyzon merolae: A new alga of thermal acidic environments. Webbia 1978, 33, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaize, J.F.; Suter, E.; Corbo, C.P. Serial Dilutions and Plating: Microbial Enumeration. JoVE-Protocol-1050. 2019. Available online: https://www.jove.com/v/10507/serial-dilutions-and-plating-microbial-enumeration (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Del Mondo, A. Development of Non-Invasive Diagnostic Methods for Monitoring Biodeterioration of Monuments. Ph.D. Thesis, Doctorate School in Biology, University of Naples, Federico II, Naples, Italy, 2017; pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lachance, M.A. Metschnikowia: Half tetrads, a regicide and the fountain of youth. Yeast 2016, 33, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turland, N.J.; Wiersema, J.H.; Barrie, F.R.; Greuter, W.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Herendeen, P.S.; Knapp, S.; Kusber, W.H.; Li, D.Z.; Marhold, K.; et al. International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Shenzhen Code). In Proceedings of the Nineteenth International Botanical Congress, Shenzhen, China, 23–29 July 2017; [Regnum Vegetabile no. 159]. Koeltz Botanical Books: Glashütten, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Bao, J.; Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Q. Comparative genomic analyses provide insight into the pathogenicity of Metschnikowia bicuspidata LNES0119. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 939141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, A.; Loira, I.; Escott, C.; Del Fresno, J.M.; Bañuelos, M.A.; Suárez-Lepe, J.A. Applications of Metschnikowia pulcherrima in wine biotechnology. Fermentation 2019, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Ruiz, J.; Belda, I.; Benito-Vázquez, I.; Marquina, D.; Calderón, F.; Santos, A.; Benito, S. The genus Metschnikowia in enology. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewald, M.; Hittinger, C.; Bensch, K.; Opulente, D.; Shen, X.-X.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; LaBella, A.; Zhou, X.; Limtong, S.; et al. A genome-informed higher rank classification of the biotechnologically important fungal subphylum Saccharomycotina. Stud. Mycol. 2023, 105, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Steenwyk, J.L.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Y.; James, T.Y.; Stajich, J.E.; Spatafora, J.W.; Groenewald, M.; Dunn, C.W.; Hittinger, C.T.; et al. A Genome-Scale Phylogeny of the Kingdom Fungi. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipiczki, M. Metschnikowia pulcherrima and related pulcherrimin-producing yeasts: Fuzzy species boundaries and complex antimicrobial antagonism. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipiczki, M. When barcoding fails: Genome chimerisation (admixing) and reticulation obscure phylogenetic and taxonomic relationships. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 1762–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipiczki, M. Taxonomic revision of the pulcherrima clade of Metschnikowia (Fungi): Merger of species. Taxonomy 2022, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, E.; Larini, I.; Binati, R.L.; Gatto, V.; Torriani, S.; Buzzini, P.; Turchetti, B.; Salvetti, E.; Felis, G.E. Finding a correct species assignment for a Metschnikowia strain: Insights from the genome sequencing of strain DBT012. FEMS Yeast Res. 2023, 23, foad024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Kauff, F.; Gabaldon, T. A phylogenomics approach for selecting robust sets of phylogenetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libkind, D.; Čadež, N.; Opulente, D.A.; Langdon, Q.K.; Rosa, C.A.; Sampaio, J.P.; Gonçalves, P.; Hittinger, C.T.; Lachance, M.A. Towards yeast taxogenomics: Lessons from novel species descriptions based on complete genome sequences. FEMS Yeast Res. 2020, 20, foaa042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.Y.; Kauff, F.; Schoch, C.L.; Matheny, P.B.; Hofstetter, V.; Cox, C.J.; Celio, G.; Gueidan, C.; Fraker, E.; Miadlikowska, J.; et al. Reconstructing the early evolution of Fungi using a six-gene phylogeny. Nature 2006, 443, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekhout, T.; Aime, M.C.; Begerow, D.; Gabaldón, T.; Heitman, J.; Kemler, M.; Khayhan, K.; Lachance, M.A.; Louis, E.J.; Sun, S.; et al. The evolving species concepts used for yeasts: From phenotypes and genomes to speciation networks. Fungal Div. 2021, 109, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piombo, E.; Sela, N.; Wisniewski, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Gullino, M.L.; Allard, M.W.; Levin, E.; Spadaro, D.; Droby, S. Genome sequence, assembly and characterization of two Metschnikowia fructicola strains used as biocontrol agents of postharvest diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, A.; Murray, A.L.; Boyle, A.B.; Quinn Farrington, L.; Maher, T.J.; Ó’Gaora, P.; Wolfe, K.H.; O’Brien, C.E.; Butler, G. Draft genome sequence of a highly heterozygous yeast strain from the Metschnikowia pulcherrima subclade, UCD127. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00550-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmat, E.; Park, I.; Kang, Y. The whole-genome sequence of the novel yeast species Metschnikowia persimmonesis isolated from medicinal plant Diospyros kaki Thunb. G3 Genes Genomes Gen. 2021, 11, jkab246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, C.; Yi, L.; Deng, L.; Zeng, K. Metschnikowia citriensis FL01 antagonize Geotrichum citriaurantii in citrus fruit through key action of iron depletion. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 357, 109384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadaro, D.; Ciavorella, A.A.; Lopez-Reyes, J.G.; Garibaldi, A.; Gullino, M.L. Effect of culture age, protectants, and initial cell concentration on viability of freeze-dried cells of Metschnikowia pulcherrima. Can. J. Microbiol. 2010, 56, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalley, L.; Tsiboe, F.; Durand-Morat, A.; Shew, A.; Thoma, G. Economic and environmental impact of rice blast pathogen (Magnaporthe oryzae) alleviation in the United States. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z. The Magnaporthe grisea species complex and plant pathogenesis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Luo, J.; Rossman, A.Y.; Aoki, T.; Chuma, I.; Crous, P.W.; Dean, R.; de Vries, R.P.; Donofrio, N.; Hyde, K.D.; et al. Generic names in Magnaporthales. IMA Fungus 2016, 7, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotti, E.; Rigano, M.M.; Rodino, D.; Rodolfi, M.; Castiglione, S.; Picco, A.M.; Sala, F. Genetic structure of Pyricularia grisea (Cooke) Sacc. isolates from Italian paddy fields. J. Phytopathol. 2005, 153, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debona, D.; Rodrigues, F.Á.; Rios, J.A.; Nascimento, K.J.T. Biochemical changes in the leaves of wheat plants infected by Pyricularia oryzae. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, B. Understanding effector biology and biotrophic strategies used by the ascomycete fungus Magnaporthe (Pyricularia) oryzae to cause the devastating rice blast disease. In Proceedings of the American Phytopathological Society (APS) Annual Meeting, S. Antonio, TX, USA, 5–9 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.; Yang, F.; Niu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Luo, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, M. Loss function of SL (sekiguchi lesion) in the rice cultivar Minghui 86 leads to enhanced resistance to (hemi)biotrophic pathogens. BMC Plant. Biol. 2020, 20, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, B.; Crawford, M.S.; Weaver, C.G.; Chumley, F.G. Genetic studies of fertility and phatogenicity in Magnaphorte grisea (Pyricularia oryzae). Iowa State J. Res. 1986, 60, 569–594. [Google Scholar]
- Thierry, M.; Charriat, F.; Milazzo, J.; Adreit, H.; Ravel, S.; Cros-Arteil, S.; Borron, S.; Sella, V.; Kroj, T.; Ioos, R. Maintenance of divergent lineages of the Rice Blast fungus Pyricularia oryzae through niche separation, loss of sex and post-mating genetic incompatibilities. PLoS Pathogens. 2022, 18, e1010687. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseyni-Moghaddam, M.; Soltani, J. An investigation on the effects of photoperiod, aging and culture media onvegetative growth and sporulation of rice blast pathogen Pyricularia oryzae. Prog. Biol. Sci. 2013, 3, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, C.H. Cultural studies of leaf saprophytes. In Ecology of Leaf Surface Microorganisms; Preece, T.F., Dickinson, C.H., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1971; pp. 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.L. Modified method for fungal slide culture. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 24, 460–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, J.M. Detection and isolation of fungal and bacterial pathogens. In Plant Pathologist’s Pocketbook; Waller, J.M., Lenne, J.M., Waller, S.J., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Oxon, UK, 2002; pp. 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.R. Germination and infectivity of microconidia in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, C.; Horta Jung, M.; Carella, G.; Milenković, I.; Janoušek, J.; Tomšovský, M.; Mosca, S.; Schena, L.; Cravador, A.; Moricca, S.; et al. Eight new Halophytophthora species from marine and brackish-water ecosystems in Portugal and an updated phylogeny for the genus. Persoonia 2022, 48, 54–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adl, S.M.; Bass, D.; Laned, C.E.; Luke, J.; Schochg, C.L.; Smirnovh, A.; Agathai, S.; Berneyj, C.; Brownk, M.W.; Burkim, F.; et al. Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2019, 66, 4–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govers, L.L.; Man in ‘t Veld, W.A.; Meffert, J.P.; Bouma, T.J.; van Rijswick, P.C.J.; Heusinkveld, J.H.T.; Orth, R.J.; van Katwijk, M.M.; van der Heide, T. Marine Phytophthora species can hamper conservation and restoration of vegetated coastal ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man in ‘t Veld, W.A.; Rosendahl, K.C.H.M.; Van Rijswick, P.C.J.; Meffert, J.P.; Boer, E.; Westenberg, M.; van der Heide, T.; Govers, L.L. Multiple Halophytophthora spp. and Phytophthora spp. including P. gemini, P. inundata and P. chesapeakensis sp. nov. isolated from the seagrass Zostera marina in the Northern hemisphere. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 153, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Ren, X.; Yun, L.; Hou, Q.; Feng, F.; Liu, H. Simple and inexpensive long-term preservation methods for Phytophthora infestans. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 152, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vero, L.; Boniotti, M.B.; Budroni, M.; Buzzini, P.; Cassanelli, S.; Comunian, R.; Gullo, M.; Logrieco, A.F.; Mannazzu, I.; Musumeci, R.; et al. Preservation, characterization and exploitation of microbial biodiversity: The perspective of the Italian network of Culture Collections. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, M. The fungi: 1, 2, 3… 5.1 million species? Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawksworth, D.L.; Crous, P.W.; Redhead, S.A.; Reynolds, D.R.; Samson, R.A.; Seifert, K.A.; Taylor, J.W.; Wingfield, M.J.; Abaci, O.; Aime, C.; et al. The Amsterdam declaration on fungal nomenclature. IMA Fungus 2011, 2, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Words Present Anywhere in the Articles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +Pathogen | +Medium | +Environment | +Culture Collection | ||
| Fastidious microorganisms | 3500 | 1600 | 2900 | 2120 | 390 |
| Fastidious bacteria | 10,100 | 7550 | 7610 | 6280 | 857 |
| Fastidious fungi | 139 | 113 | 132 | 128 | 31 |
| Fastidious algae | 12 | / | 1 | 1 | / |
| Fastidious eukaryotes | / | / | / | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turchetti, B.; Bevivino, A.; Casella, P.; Coleine, C.; Felis, G.E.; Girometta, C.E.; Molino, A.; Perugini, I.; Pollio, A.; Prigione, V.; et al. Selected Case Studies on Fastidious Eukaryotic Microorganisms: Issues and Investigation Strategies. Diversity 2023, 15, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070862
Turchetti B, Bevivino A, Casella P, Coleine C, Felis GE, Girometta CE, Molino A, Perugini I, Pollio A, Prigione V, et al. Selected Case Studies on Fastidious Eukaryotic Microorganisms: Issues and Investigation Strategies. Diversity. 2023; 15(7):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070862
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurchetti, Benedetta, Annamaria Bevivino, Patrizia Casella, Claudia Coleine, Giovanna E. Felis, Carolina Elena Girometta, Antonio Molino, Iolanda Perugini, Antonino Pollio, Valeria Prigione, and et al. 2023. "Selected Case Studies on Fastidious Eukaryotic Microorganisms: Issues and Investigation Strategies" Diversity 15, no. 7: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070862
APA StyleTurchetti, B., Bevivino, A., Casella, P., Coleine, C., Felis, G. E., Girometta, C. E., Molino, A., Perugini, I., Pollio, A., Prigione, V., Selbmann, L., Varese, G. C., & Buzzini, P. (2023). Selected Case Studies on Fastidious Eukaryotic Microorganisms: Issues and Investigation Strategies. Diversity, 15(7), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070862
















