Host Range Expansion of Nest-Parasitic Moths Pyralis regalis and Hypsopygia mauritialis in Social Wasp Nests: New Findings and Implications for Biological Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Identification
3. Results
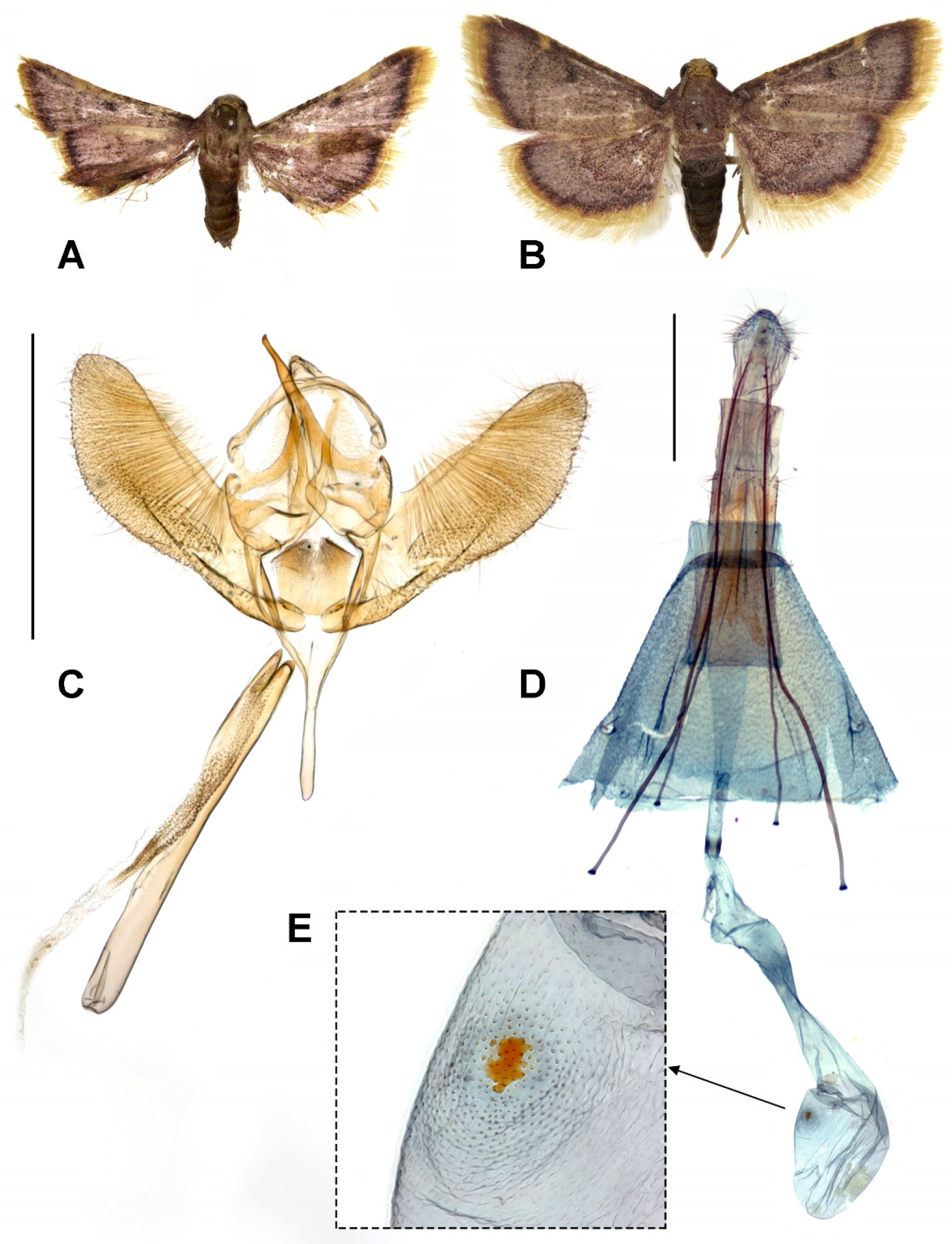
3.1. Systematic Accounts
- Family Pyralidae Latreille, 1809 [32]
- Subfamily Pyralinae Latreille, 1809 [32]
- Genus Hypsopygia Hübner, 1825 [33]
- Hypsopygia mauritialis (Boisduval, 1833) [34]
- Asopia mauritialis Boisduval, 1833:119. TL: Mauritius; TD: BMNH. [34]
- Pyralis lucillalis Walker, 1859: 268 [35]
- Pyralis regalis Walker, 1866: 1241 [36]
- Pyralis ducalis Walker, 1866: 1242 [36]
- Endotricha crobulus Lucas, 1891: 305 [37]
- Hypsopygia laticilialis Ragonot, 1891: 28 [38]
- Hypsopygia sanguinalis Warren, 1897: 125 [39]
- Hypsopygia atralis Caradja, 1932: 121 [40]
- Hypsopygia pfeifferi Amsel, 1954: 310 [41]
3.2. DNA Barcode
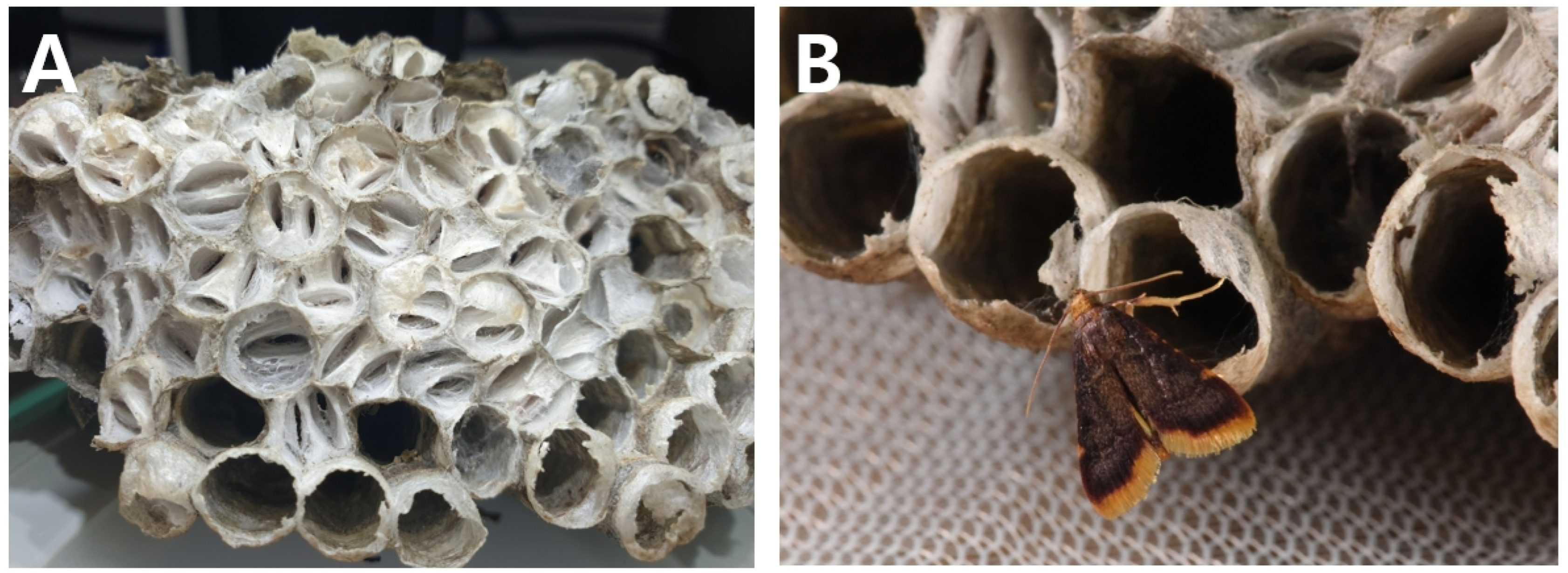
3.3. New Host Records for Nest-Parasitic Moths
3.4. Parasitic Moths from Invasive Social Wasp Nests
4. Discussion
4.1. Occurrence of Moths in Social Wasp Nests
4.2. First Occurrence in Invasive Alien Social Wasp Nests
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuura, M.; Yamane, S. Biology of the Vespine Wasps; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.M. Parasites and symbionts of nests of Polistes wasps12. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1968, 61, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, S. List of parasitoids of polistine wasps. Sphecos 1985, 10, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, A.C.; Hodges, G.S.; Espelie, K.E. Parasitoids and parasites of Polistes metricus Say (Hymenotera: Vespidae) in Northeast Georgia. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2003, 96, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Yamada, Y.Y.; Matsuura, M.; Tsukada, M. Mating, oviposition, and prey use by larvae of Hypsopygia postflava (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), a moth parasitic on nests of the paper wasp, Polistes jokahamae. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2007, 51, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Yamada, Y.Y.; Matsuura, M.; Tsukada, M. Life cycle of Hypsopygia postflava (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), a moth parasitic on nests of the paper wasp, Polistes jokahamae. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2007, 51, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, C.K.; Nelson, J.M. Differential nest parasitism in three sympatric social wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae: Polistes spp.) in the West Indies. Sociobiology 2015, 62, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyano, S. Life tables of colonies and workers in a paper wasp, Polistes chinensis antennalis, in central Japan (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Res. Popul. Ecol. 1980, 22, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, S. Paper wasps as hosts of parasitoids. Kotaigun Seitaigakkai Kaihô (Bull. Soc. Popul. Ecol.). 1983, 37, 53–66. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, H. Pyralidae. In Moths of Japan 1; Inoue, H., Sugi, S., Kuroko, H., Moriuti, S., Kawabe, A., Owada, M., Eds.; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1982; pp. 307–404. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Strassmann, J.E. Evolutionary implications of early male and satellite nest production in Polistes exclamans colony cycles. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1981, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassmann, J.E. Parasitoids, predators, and group size in the paper wasp, Polistes exclamans. Ecology 1981, 62, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.J. Occurrence of the pyralid moth Hypsopygia mauritialis (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae) in the nests of Vespa affinis (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Jpn. J. Entomol. 1992, 60, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.R. The European wasp (Vespula germanica Fabricius) in New Zealand. Inform. Ser. Dep. Sci. Ind. Res. N. Z. 1960, 27, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gambino, P. Dolichovespula (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), Hosts of Aphomia sociella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. N. Y. Entomol. Soc. 1995, 103, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, S.; Fukuda, T.; Makino, S. Observations on a nest of a paper wasp (Polistes sp.) infested by a pyralid moth, Hypsopygia mauritialis (Boisduval, 1833). Lepid. Sci. 2022, 73, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.B.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.W. Checklist and distribution of Korean Vespidae Revisited. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 52, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.B.; Martin, S.J.; Lee, J.W. Distribution, spread, and impact of the invasive hornet Vespa velutina in South Korea. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.B.; Kim, T.G.; Kwon, O. Recent trends in wasp nest removal and Hymenoptera stings in South Korea. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.B. Defensive behavior of the invasive alien hornet Vespa velutina nigrithorax against potential human aggressors. Entomol. Res. 2021, 51, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.B. Foraging behavior of an invasive alien hornet (Vespa velutina) at Apis mellifera hives in Korea: Foraging duration and success rate. Entomol. Res. 2021, 51, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchi, L.; Derijard, B. Options for the biological and physical control of Vespa velutina nigrithorax (Hym.: Vespidae) in Europe: A review. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 142, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.J.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.K. A study on the colony development, parasite infestation rate and colony survival rate of the paper wasp, Polistes jadwigae Dalla Torre according to their nesting habitat (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Nat. Sci. 1987, 3, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.W.; Bae, Y.S. A review of the tribe Pyralini Latreille (Lepidoptera, Pryaralidae, Pyralinae) from Korea. Trans. Lepidopterol. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 58, 47–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.K.; Byun, B.K. Taxonomic revision of the family Cosmopterigidae (Lepidoptera) in Korea. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, U.H. Guidebook of Moth Larvae; Jayeongwasaengtae: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Holloway, J.D.; Bradley, J.D.; Carger, D.J. CIE Guides to Insects of Importance to Man, 1: Lepidoptera; CA B International: London, UK, 1987; p. 262. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, P.D.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the Neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Janzen, D.H.; Burns, J.M.; Hallwachs, W.; Hebert, P.D. DNA barcodes distinguish species of tropical Lepidoptera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA 11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, J.C.; Mitter, C.; Solis, M.A.; Hayden, J.E.; Landry, B.; Nuss, M.; Simonsen, T.J.; Yen, S.H.; Zwick, A.; Cummings, M.P. A molecular phylogeny for the pyraloid moths (Lepidoptera: Pyraloidea) and its implications for higher-level classification. Syst. Entomol. 2012, 37, 635–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latreille, P.A. Genera Crustaceorum et Insectorum Secundum Ordinem Naturalem in Familias Disposita, Iconibus Exemplisque Pluribus Explicate; Cornell University Library: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1809; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Hübner, J. Verzeichnis Bekannter Schmettlinge; Biodiversity Heritage Library: Augsburg, Germany, 1816; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Boisduval, J.B.A. Faune Entomologique de Madagascar, Bourbon et Maurice: Lépidoptéres; Librairie Encyclopédique de Roret: Paris, France, 1833; p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, F. List of the Specimens of Lepidopterous Insects in the Collection of the British Museum: Part XVIII. Pyralides 1859, 17, 256–508. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, F. List of the Specimens of Lepidopterous Insects in the Collection of the British Museum: Part XXXIV. Pyralides 1965, 34, 1121–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, T.P. On Queensland and other Australian Macro-Lepidoptera, with localities and descriptions of new species. Proc. Linn. Soc. N. S. W. Ser. 1891, 2, 277–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragnot, E.L. Essai sur une classification des Pyralites (suite). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 1891, 60, 15–114. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, W. New genera and species of moths from the Old-World regions in the Tring Museum. Novit. Zool. 1897, 4, 12–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradja, A.V. Dritter Beitrag zur Kleinfalterfauna Chinas nebst kurzer Zusammenfassung der bisherigen biogeographischen Ergebnisse. Acad. Roum. Bull. Sect. Sci. 1932, 15, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Amsel, H.G. Die Microlepidopteren der Brandt’schen Iran-Ausbeute. Teil Arkiv För Zoologi. 1954, 6, 255–326. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, Y.S. Family Pyraloidea: Pyraustinae & Pyralinae. Economic Insects of Korea 9. Insecta Koreana Suppl. 2001, 16, 251. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, P.H. Biology of Hypsopygia postflava (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), a snout moth parasitic on the nest of the paper wasp Polistes olivaceus (Vespidae: Polistes). Biol. Forum Int. J. 2014, 6, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-K.; Choi, M.; Moon, T.-Y. Occurrence of Vespa velutina Lepeletier from Korea, and a revised key for Korean Vespa species (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Entomol. Res. 2006, 36, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carisio, L.; Cerri, J.; Lioy, S.; Bianchi, E.; Bertolino, S.; Porporato, M. Impacts of the invasive hornet Vespa velutina on native wasp species: A first effort to understand population-level effects in an invaded area of Europe. J. Insect Conserv. 2022, 26, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrouzet, E.; Gévar, J.; Dupont, S. A scientific note about a parasitoid that can parasitize the yellow-legged hornet, Vespa velutina nigrithorax, in Europe. Apidologie 2015, 46, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemant, C.; Zuccon, D.; Rome, Q.; Muller, F.; Poinar, G.O., Jr.; Justine, J.L. Can parasites halt the invader? Mermithid nematodes parasitizing the yellow-legged Asian hornet in France. PeerJ 2015, 3, e947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Choi, M.B. First Discovery of Vespa velutina nigrithorax du Buysson (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), an Invasive Hornet in the Feces of the Yellow-Throated Marten in South Korea. Insects 2021, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Cui, L.; Ostiguy, N.; Cox-Foster, D. Intricate transmission routes and interactions between picorna-like viruses (Kashmir bee virus and sacbrood virus) with the honeybee host and the parasitic varroa mite. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurze, C.; Routtu, J.; Moritz, R.F.A. Parasite resistance and tolerance in honeybees at the individual and social level. Zoology 2016, 119, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreck, N.L.; Ball, B.V.; Martin, S.J. Honey bee colony collapse and changes in viral prevalence associated with Varroa destructor. J. Apic. Res. 2010, 49, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baty, J.W.; Bulgarella, M.; Dobelmann, J.; Felden, A.; Lester, P.J. Viruses and their effects in ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol. News 2020, 30, 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Beggs, J.R.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Corley, J.C.; Kenis, M.; Masciocchi, M.; Muller, F.; Rome, Q.; Villemant, C. Ecological effects and management of invasive alien Vespidae. BioControl 2011, 56, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L.; Donnelly, C.R.; Gamboa, G.J. A ten-year comparative study of the population dynamics and parasitoidism in the native paper wasp Polistes fuscatus and the invasive P. dominulus. Insect. Soc. 2013, 60, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacko, S.; Henderson, G. A preliminary investigation of the interactions between the brood parasite Chalcoela iphitalis and its Polistine wasp hosts. Insects 2017, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diéguez-Antón, A.; Escuredo, O.; Seijo, M.C.; Rodríguez-Flores, M.S. Embryo, relocation and secondary nests of the invasive species Vespa velutina in Galicia (NW Spain). Animals 2022, 12, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Nest No. | Hosts (Social Wasp) | † Collected Location of Host Nest | Nest Collecting Date | Date of Moth Emergence | Stage of Development | Number of Emergence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pyralis regalis | ||||||
| 1 | Dolichovespula kuami | Pocheon | 5 Jun. 2018 | 5 Jun. 2018 | A | 2 |
| 2 | D. kuami | Jeongeup | 17 Aug. 2018 | 23–29 Aug. 2018 | A | 16 |
| 3 | D. kuami | Andong | 11 Oct. 2020 | 12 Oct. 2020 | L | 3 |
| 4 | Vespa crabro flavofasciata | Masan | 15 Dec. 2017 | 3–22 May. 2018 | A | 47 |
| 5 | V. crabro flavofasciata | Uljin | 28 Sep. 2020 | 3 Oct. 2020 | L | 4 |
| 6 | V. simillima simillima | Andong | 30 Aug. 2020 | 16 Sep. 2020 | L | 6 |
| 7 | V. simillima | Andong | 15 Oct. 2021 | 19 Oct. 2021 | L | 14 |
| 8 | V. velutina nigrithorax | Gurye | 5 Nov. 2018 | 11 Nov. 2018 | L | 7 |
| 9 | V. velutina nigrithorax | Andong | 28 Nov. 2018 | 11 Feb.–6 Mar. 2019 | A | 24 |
| L | 19 | |||||
| 10 | V. velutina nigrithorax | Andong | 13 Nov. 2019 | 16 Nov.2019 | L | 8 |
| 11 | V. velutina nigrithorax | Andong | 3 Aug. 2021 | 3 Aug. 2021 | A | 7 |
| L | 36 | |||||
| 12 | V. velutina nigrithorax | Andong | 9 Dec. 2021 | 15 Feb.–28 Mar. 2022 | A | 8 |
| 13 | V. ducalis | 11 Oct. 2019 | 13 Oct. 2019 | L | 2 | |
| 14 | V. analis parallela | Andong | 1 Oct. 2021 | 1 Oct. 2021 | L | 6 |
| 15 | V. dybowskii | Andong | 25 Sep. 2019 | 25 Sep. 2019 | L | 4 |
| 16 | V. mandarinia | Yecheon | 20 Sep. 2019 | 20 Sep. 2019 | L | 6 |
| 17 | V. mandarinia | Andong | 27 Oct. 2022 | 27 Oct. 2022 | L | 2 |
| 18 | V. mandarinia | Uiseong | 20 Oct. 2022 | 22 Jan.–18 Mar. 2023 | A | 22 |
| L | 45 | |||||
| 19 | V. mandarinia | Uiseong | 20 Oct. 2022 | 2 Feb.–3 Mar. 2023 | A | 39 |
| L | 52 | |||||
| 20 | Polistes rothneyi koreanus | Yecheon | 23 Aug. 2021 | 25 Aug. 2021 | A | 4 |
| 21 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Yecheon | 30 Jul. 2021 | 7 Aug. 2021 | L | 2 |
| 22 # | P. rothneyi koreanus | Gunwi | 2 Sep. 2017 | 2 Sep. 2017 | A | 8 |
| 23 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Gunwi | 16 Dec. 2014 | 9–22 Feb. 2015 | A | 4 |
| 24 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Gunwi | 28 Sep. 2016 | 20 Jan.–23 Feb. 2017 | A | 11 |
| L | 20 | |||||
| 25 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Gunwi | 1 Oct. 2018 | 22 Jan.–2 Mar. 2019 | A | 7 |
| L | 5 | |||||
| 26 | P. yokahamae | Yeongcheon | 3 Oct. 2021 | 3 Oct. 2021 | L | 2 |
| 27 | P. nipponensis | Seongju | 28 Oct. 2022 | 12 Feb. 2023 | L | 1 |
| 2. Anatrachyntis japonica | ||||||
| 28 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Gunwi | 6 Dec. 2014 | 20 Feb. 2015 | A | 15 |
| 29 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Gunwi | 2 Sep. 2017 | 2 Sep. 2017 | A | 18 |
| 30 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Andong | 22 Jun. 2021 | 15 Jul. 2021 | A | 2 |
| 31 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Yecheon | 20 Jul. 2021 | 3 Aug. 2021 | A | 41 |
| 32 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Andong | 24 Jul. 2021 | 24 Jul. 2021 | A | 8 |
| 33 | V. crabro flavofasciata | Gunwi | 16 Sep. 2015 | 16 Sep. 2015 | A | 3 |
| 3. Hypsopygia mauritialis | ||||||
| 34 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Gurye | 10 Sep. 2021 | 23 Jan. 2022 | A | 13 |
| 35 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Jeonju | 31 Dec. 2021 | 2 Jan. 2022 | A | 32 |
| 36 | P. rothneyi koreanus | Seongju | 28 Oct. 2022 | 16 Jan. 2023 | A | 5 |
| 37 | V. velutina nigrithorax | Jinju | 22 Jan. 2021 | 30 Jan.–18 Mar. 2021 | A | 11 |
| L | 4 | |||||
| 38 | V. velutina nigrithorax | Jinju | 11 Aug. 2022 | 11 Aug. 2022 | L | 8 |
| 22 Aug. 2022 | A | 6 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, Y.-M.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, I.-K.; Kim, C.-J.; Choi, M.B. Host Range Expansion of Nest-Parasitic Moths Pyralis regalis and Hypsopygia mauritialis in Social Wasp Nests: New Findings and Implications for Biological Control. Diversity 2023, 15, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060789
Shin Y-M, Lee HS, Kim I-K, Kim C-J, Choi MB. Host Range Expansion of Nest-Parasitic Moths Pyralis regalis and Hypsopygia mauritialis in Social Wasp Nests: New Findings and Implications for Biological Control. Diversity. 2023; 15(6):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060789
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Young-Min, Heung Sik Lee, Il-Kwon Kim, Chang-Jun Kim, and Moon Bo Choi. 2023. "Host Range Expansion of Nest-Parasitic Moths Pyralis regalis and Hypsopygia mauritialis in Social Wasp Nests: New Findings and Implications for Biological Control" Diversity 15, no. 6: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060789
APA StyleShin, Y.-M., Lee, H. S., Kim, I.-K., Kim, C.-J., & Choi, M. B. (2023). Host Range Expansion of Nest-Parasitic Moths Pyralis regalis and Hypsopygia mauritialis in Social Wasp Nests: New Findings and Implications for Biological Control. Diversity, 15(6), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060789








