Abstract
The aim of this work was to investigate the microbial diversity characteristics and driving factors in a high elevation drop river and to analyze the potential risks of river microorganisms to human health. In March 2019, we analyzed the microbial diversity characteristics in surface water and sludge from the Huotong River using high-throughput sequencing. The Huotong River is of great importance to the production and life of the people living along this river. The sampling points were set at the estuary of the river, on a downstream section of the river, on an upstream section of the main river, at one tributary flowing through a town, at one tributary with a barrage, and at the source of one tributary. The results showed significant differences in bacterial diversity in different areas of the river. For example, actinomycetes were less abundant in water samples from the headwaters of tributaries and more abundant upriver. The results revealed that different intensities of human activities had significant different effects on functional flora. Anthropogenic disturbance and human activities reduced the abundance of probiotic bacteria and increased the abundance of pathogenic bacteria in the river. The changes in functional floral diversity may pose potential threats to human health.
1. Introduction
Microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and algae, are the foundation of the community structure in an ecosystem [1], playing an important role in the material circulation, energy flow, and stability maintenance of the ecosystem. The functions of an ecosystem are based on its microbial diversity and structure [2]. Bacteria are the most important components of aquatic ecosystems, playing an important role in energy conversion, material circulation, and element accumulation and migration [3]. For example, bacteria are essential in the carbon cycle of rivers, where they treat organic carbon in flowing water bodies [4]. River microbial diversity is highly sensitive to environmental changes, and its composition and diversity vary significantly in different water environments [5]. In addition, studies have revealed that human activities have a significant impact on microbial community structure and diversity [6].
In recent years, high-throughput sequencing technology has been widely used in bacterial taxonomy, evolutionary genomics, comparative genomics, epigenomics, metagenomics, transcriptome, single-cell sequencing, etc. [7,8,9,10]. Many international studies on river microorganisms using high-throughput sequencing have focused on environmental sciences ecology, public environmental health, water resources, and infectious diseases [11,12,13,14]. As well as being one of the most important ecosystem types, rivers are the main channel of the biosphere material cycle, through which a large number of pollutants and nutrients are degraded and transported [15] (Tang et al., 2002). As the key organisms in the river ecosystem, microorganisms play a key role in the biogeochemical cycle [16]. The development of human society and the river ecosystem are interdependent, and they interact with each other [17,18]. To date, domestic studies on river microorganisms using high-throughput sequencing have mostly focused on rivers and their tributaries with long flow, high drop in elevation, and abundant water and hydraulic resources, such as the Yangtze River and the Yellow River [19,20,21,22]. Additionally, other scholars have studied the microbial community diversity of inland rivers in China [23]. However, for rivers which directly flow into the sea with a high drop in elevation and reduced human activities, there are no extant report addressing microbial community diversity.
Huotong River is one of the main rivers in Fujian province, and has a high drop in elevation. With clear water and less freshwater fish diversity [24], it plays a key role in providing water for agriculture and domestic use, transportation, leisure, and entertainment [25]. In the present study, the high-throughput sequencing method was used to systematically study the microflora diversity in the water and sludge in the lower reaches of the Huotong River in order to understand the species composition, diversity, and community structure of microorganisms in the river, as well as to further analyze the effects of human activities on these factors. Samples of water and sludge from heterogeneous habitats of different river sections near the shore were collected to compare the diversity of the microbial community and the composition of beneficial and pathogenic microflora. In the section of the river flowing through villages and towns, sampling points were set upriver and downriver of villages and towns to compare and analyze the effects of human activities on microbial community structure. The results of this study can provide guidance for understanding the interaction between human beings and the environment, ecological environment maintenance, and biodiversity protection in the Huotong River. The main objectives of the study were: (1) to analyze the species composition and diversity of bacterial flora in water and sludge of the Huotong River; (2) to evaluate the effects of human disturbance on the species composition, diversity, and community structure of bacterial flora; (3) to analyze the spatial distribution characteristics of pathogenic bacteria and their potential effects on human health; and (4) to provide a scientific basis for the maintenance of the Huotong River ecosystem health and biodiversity protection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
Due to the influence of the Wuyi Mountains, the Jiufeng Mountains, the Taimo Mountains, etc., the terrain of Fujian province is mainly mountains and hilly. The Huotong River is located in the northeast of Fujian Province (Figure 1), with geographical coordinates of 119°04′~119°34′ E, 27°06′~26°49′ N. It originates between the northern section of the Jiufeng Mountains and the southern section of the Donggong Mountains, at about 1000–1500 m above sea level. The river is short, and the elevation gradient in the watershed varies greatly. There are many villages and towns along the river, without large cities or industrial production. There are few human activities in the upper reaches, which are mainly affected by agricultural farming and other forms of production as well as the actions of people living along the river. Tangkou River and Houlong River are the upper reaches, which meet in Baibu village in Ningde city, flow through Huotong, Jiudu, Badu, and other towns, pour into Sansha Bay, and flow into the East China Sea. The terrain of the fan-shaped drainage is high in the northwest and low in the southeast. The Huotong River has a total length of 56.8 km, a total fall of 165 m, and a river drop of 1.8%. The climate of the watershed belongs to the subtropical marine monsoon climate, with annual precipitation of 1615.8 mm and average annual runoff of 2.555 billion cubic meters.
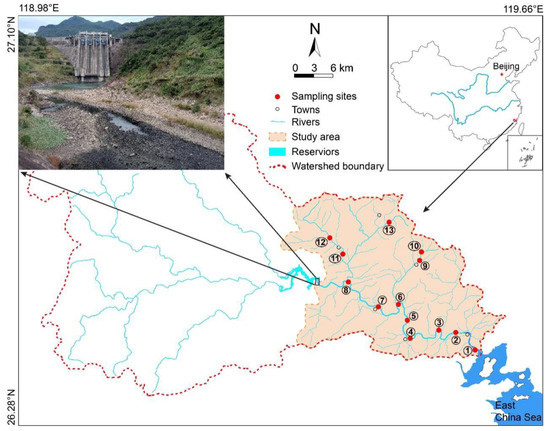
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of study area location and sampling points. The numbers ① to ⑬ represent sampling points 1# to 13#.
2.2. Sampling Points Setting
In Hongkou town, located along the upper reaches of the Huotong River, the river is cut off by the Hongkou reservoir (Figure 1). The samples were only collected from the lower reaches of the watershed in this study. Thirteen sampling points were set in the estuary, trunk, and tributary of Huotong River (Figure 1). According to the location of the sampling points and the difference in human activities, the thirteen sampling points were divided into six regions for analysis, namely, the estuary of the river (GLXS), downriver (GLXY) and upriver (GLSY) sections, one tributary flowing through a town (CZZL), one tributary with a barrage (LHBZL) and the source of one tributary (YSZL).
At the estuary of the Hutong River (GLXS), one sampling point (No. 1) was set in Badu town, which is affected by the interaction between brackish and fresh water. Downriver (GLXY), four sampling points (No. 2~5) were set in Xiaban village, Xichi village, Jiudu town, and Yuanqi village. Upriver (GLSY), three sampling points (No. 6~8) were set in the riparian zone near Baibu village, Huotong town, and Dadaotou village in Hongkou town. Additionally, a barrage has been built for agricultural irrigation in one tributary of Huotong River flowing through Chixi town (LHBZL). Two sampling points (No. 9~10) were set upriver and downriver of the barrage to explore the effects of agricultural activities and barrage construction on the microbial community. Another tributary flows through the densely populated Xiancun town (CZZL). This section of the river has been disturbed by high-intensity activities of human life, and two sampling points (No. 11~12) were set up here 1000 m upriver and 500 m downriver of the town, respectively. Located at the source of a tributary of the Huotong River, Changgang village is one of five ancient villages in Zhouning county, Ningde. The population is small and the river is less disturbed here by human activities. One sampling point (No. 13) was set up here to represent the source of one tributary (YSZL). In this article, GLXS, GLXY, GLSY, CZZL, LHBZL, and YSZL represent the estuary of the river, downriver, upriver, one tributary flowing through a town, one tributary with a barrage, and the source of one tributary, respectively.
2.3. Sample Collection
On 20 March 2019, surface water and sludge samples were collected from the thirteen sampling points on the lower reaches of the Huotong River. At each sampling point, three samples of surface water and three samples of sludge were collected at an interval of about 5 m. Water samples were collected from the surface of the river using an aseptic sampler and about 500 g of sludge was collected from the surface of the nearshore riverbed. The samples were temporarily stored in liquid nitrogen tanks in the field and sent to the laboratory for follow-up treatment within two days of collection.
2.4. Determination of Water Physicochemical Parameters
A YSI 6600 V2 multi-parameter water quality monitor (YSI 6600 V2, YSI Inc., Yellow Springs, OH, USA) was used to measure water temperature (WT), conductivity (Cond), dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, turbidity (Turb), and other water quality parameters at each sample point. The total phosphorus (TP) was determined via ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry. According to the national standard, we used alkaline potassium persulfate digestion–ultraviolet spectrophotometry to determine the content of total nitrogen (TN). A 1-L water sample was filtered through a GF/F glass fiber filter membrane and chlorophyll a (Chl-a) was extracted using 90% ethanol solution at a low temperature. The supernatant was separated at 3500–4000 RPM in the frozen centrifuge (Sigma 4–16). The content of chlorophyll a was determined via spectrophotometer (JASCO V-7000) with 90% ethanol solution as the control. Abbreviations are used for all water physicochemical parameters present in the diagrams below.
2.5. Extraction of Genome DNA and High-Throughput Sequencing
The samples were diluted five-fold with ddH2O and homogenized with a bead-beating method. Samples were suspended in 1 mL lysis buffer (LBS) containing 0.3 g sterile zirconium beads in a screw-capped tube, and the tubes were bead-beaten at 8000 rpm for 3 min in a mini-bead beater. The total genome DNA of each sample was extracted using a TIANamp Genomic DNA kit (TIANGEN) combined with the bead-beating method, as previously described. The genomic DNA was sent to a high-throughput sequencing company (Shanghai Personal Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) for high-throughput sequencing and subsequent analysis. After high-throughput sequencing, the whole genomic DNA of the samples was extracted using the TIANamp genomic DNA kit (TIANGEN) combined with the bead-beating method (Yu et al., 2015). PCR products used Illumina Miseq high-throughput sequencing and post-analysis (Project No. YF2019602).
2.6. Data Analysis
A single factor analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) was performed on the hydro-physical and chemical parameters of different sampling areas in STATISTIC7.0 software, and Fisher’s LSD was used to test whether the parameters showed significant differences between two different areas. R software (Version 3.6.2) was used for statistical analysis. Principal coordinate analysis (PCA) and Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) were performed using the package based on the UniFrac distances between samples. Metastats software (http://metastats.cbcb.umd.edu/, accessed on 5 September 2019) was used for the analysis of similarities and multi-response permutation planning methods to further assess the differences between groups. The Quantitative Insights into Microbial Ecology (QIIME) software package was processed to analyze the representative sequences of operational taxonomy units (OTUs) with their relative abundance, which were applied to calculate the rarefaction analysis and Shannon diversity index [26]. Sequences with ≥97% similarity were assigned to the same OTUs. In-house Perl scripts were used to analyze alpha (within samples) and beta (among samples) diversity. Data were presented as mean ± SD, and the statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 for correction of multiple comparisons [27]. The characteristics of microbial diversity and environmental factors in the Huotong River were analyzed using RDA with CANOCO 4.5 software.
3. Results
3.1. Water Physicochemical Parameters Analysis
The physicochemical parameters of each reach of the Huotong River are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical parameters in the six studied sections of Huotong River. Total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), chlorophyll a (Chl-a), water temperature (WT), turbidity (Turb), pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), and conductivity (Cond) of the six studied sections of Huotong River were detected and calculated. Mean ± SE. The letters a, b, c, and d indicate significant differences between different sampling points.
The TN and TP of GLXS and GLXY were higher, while those of YSZL were the lowest. The Chl-a of GLXY and CZZL was higher, and that of GLXS was the lowest. The WT of each reach was similar, ranging from 15.80 °C to 18.37 °C. The turbidity was higher in GLXS, GLXY, and CZZL. Additionally, turbidity at GLXS and CZZL was significantly higher than at GLSY, LHBZL, and YSZL. The water was slightly basic; the pH value was the highest at GLXS and the lowest at LHBZL. In general, the water was in the oxic condition (i.e., the dissolved oxygen concentration was higher). Dissolved oxygen at LHBZL, CZZL, YSZL, and GLSY was higher than at GLXS and GLXY. Conductivity was the highest at GLXS and the lowest at YSZL. Additionally, the conductivity of CZZL was higher than that of LHBZL. The average value of TN was 1.62 mg/L, and the maximum value appeared at GLXY. The average value of TP was 0.16 mg/L, and the maximum value appeared at GLXS.
In addition, we concluded that the difference of TN was less than that of TP in different reaches. The average values of Chl-a, WT, turbidity, pH, dissolved oxygen, and conductivity were 1.41 mg/m3, 16.93 °C, 13.48 NTU, 7.94, 11.08 mg/L, and 52.31 μs/cm, respectively. The maximum value of Chl-a appeared at GLXY and that of WT appeared at YSZL. The maximum values of turbidity, pH, and conductivity appeared at GLXS, and that of dissolved oxygen appeared at CZZL.
3.2. Compositions and Relative Abundance of Bacterial Communities in Water Samples
A high-throughput sequencing technique was used to investigate the composition and relative abundance of bacterial communities in water samples. A total of 1,146,857 clean reads (44,109.88 reads/sample) and 67,177 OTUs were obtained, with an average of 2583 OTUs per sample. The studied water samples illustrated high bacterial richness and diversity, with 59–71 microbial groups at the species level. As demonstrated in Figure 2A, Proteobacteria were the first dominant bacterial phylum in all samples and had the highest abundance in YSZL (88.8%). The Actinobacteria were the second dominant bacterial phylum in all samples (17.1%), accounting for the highest proportion of 32.3% at GLSY and the lowest proportion of 3.0% at YSZL. The third dominant bacterial phylum were the Bacteroidetes (5.9%), which had the highest percentage at LHBZL (9.6%). The fourth dominant bacterial phylum were the Firmicutes (2.4%), which had a similar percentage at CZZL (4.1%) and YSZL (3.6%) (Figure 2A). The abundance of other bacterial phyla was less than 1.0%.
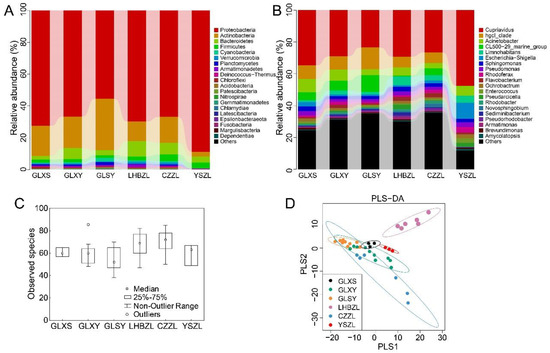
Figure 2.
The diversity and richness of water bacteria among the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups. The relative abundance of the bacteria among the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups at the phylum level (A) and genus level (B). The x-axis represents groups and the y-axis represents relative abundance presented as a percentage. The amount of observed species in the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups (C). The x-axis shows the different groups and the y-axis shows the observed species. Validation of PLS-DA for species similarity and distribution among the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups (D).
At the genus level, the genera Cupriavidu (31.7%), hgcl_clade (8.5%), CL500-29_marine_group (5.4%), Acinetobacter (5.4%), and β-proteobacteria (3.0%) had higher abundance. The compositions of the five dominant bacterial genera mentioned in the above order in each group were as follows: GLXS (34.7%, 8.5%, 4.9%, 8.5%, 1.1%), GLXY (29.0%, 8.4%, 6.8%, 7.0%, 2.6%), GLSY (23.4%, 13.7%, 10.5%, 3.7%, 1.6%), LHBZL (29.2%, 6.9%, 0.6%, 5.1%). 5.5%), CZZL (26.5%, 6.8%, 4.2%, 3.4%, 3.4%), and YSZL (47.5%, 0.03%, 0.03%, 6.1%, 4.5%) (Figure 2B). Meanwhile, the genus Rhodoferax (3.5%) and the genus Pseudomonas (3.1%) had higher abundance in YSZL.
In addition, the results showed that the number of species observed was similar at GLXY and GLXS. The highest and lowest number of species were observed at CZZL and GLSY, respectively (Figure 2C). The PLS-DA results indicated significant differences in bacterial diversity at LHBZL and relatively uniform bacterial diversity in other groups (Figure 2D).
3.3. Abundance of Bacterial Species in Water Samples
Special species in GLXS, GLXY, GLSY, LHBZL, CZZL, and YSZL water samples were studied further. The results showed that the genus Acidibacter had the highest abundance in GLXS (Figure 3). The abundance of the genera Caulobacter and Metagenome was highest at LHBZL. However, the abundance of all genera except the three genera mentioned above was highest at GLSY. Meanwhile, at YSZL there were almost no other bacteria except Caulobacter. The abundance of the genera Candidatus-Flaviluna, Candidatus-Megaira, Aurantimicrobium, Cephaloticoccus, and Polynucleobacter at GLXY was similar to that at CZZL.
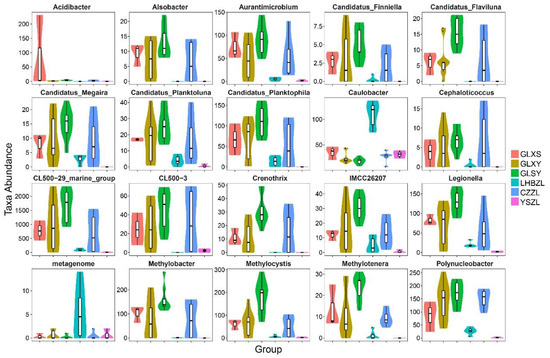
Figure 3.
Taxa abundance of different bacteria species in groups GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL sampled from river water.
3.4. Redundancy Analysis of Water Sample Results
Redundancy Analysis (RDA) was used to analyze the interference control factors of microbial diversity in the Huotong River, elaborating on how the main environmental factors contribute to the variation of microbial diversity. Before the analysis, all the data were transformed by the formula Log (x + 1), which could ensure that the expansion coefficient of all variables was less than 20. In addition, based on the detrended correspondence analysis (DCA) of the microbial abundance data of water samples, we concluded that the maximum gradient length of the four sequencing axes was 1.747, which was less than 3. The result indicated that redundancy analysis (RDA) is suitable. The Monte Carlo method was used to test the significance level of environmental factors (p < 0.05, n = 499). The result showed that turbidity and electrical conductivity were the main factors affecting the structure of the microbial community in the Huotong River (Turb: p = 0.006, F = 4.69; Cond: p = 0.026, F = 3.9).
The results of RDA showed that the first principal axis and the second principal axis explained the variance in the relative abundance of the microbial community by 54.7% and 20.7%, respectively, and the total explaining rate was 75.4% (Figure 4). The first principal axis had the greatest positive correlation with turbidity, while the second principal axis had the greatest negative correlation with conductivity. From the angle between conductivity and turbidity, we found an obvious positive correlation. Different environmental factors had different effects on the microbial community, and the effect was shown as obvious clustering. The four clusters I, II, III, and IV corresponded to the microbial community characteristics of GLXY, LHBZL, GLSY, and GLXS, respectively (Figure 4). Most of the microorganisms in cluster I had the function of degrading nitrogen and phosphorus organic matter [28]. Additionally, the positions of Armatimonadetes (MB3) and Gemmatimonadetes (MB12) in the diagram were similar, indicating that the phylum in the same cluster had a certain similarity in terms of ecological function. The effect of turbidity on the microorganisms was positive for GLXY and CZZL, while it was negative for GLSY and LHBZL. The effect of conductivity on the microorganisms was positive for GLSY and GLXS, while it was negative for GLXY and LHBZL.
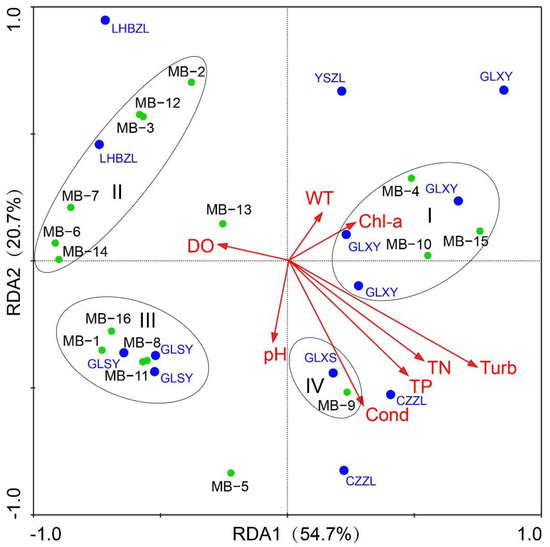
Figure 4.
RDA ordination diagram of water microbial community and environmental factors. The blue dots mean the sampling points of the six studied sections of Huotong River, while the green dots represent different microbial (MB) groups at the phylum level.
3.5. Composition and Relative Abundance of the Bacterial Community in Sludge Samples
To evaluate the microbial diversity of the Huotong River more comprehensively, the composition of bacteria in the sludge was studied. A total of 1,358,574 clean reads (52,252.84 reads/sample) and 228,762 OTUs were obtained, with an average of 8798 OTUs per sample. There were differences in bacterial richness and diversity among the sludge samples. At the phylum level, Proteobacteria had the highest average abundance (43.5%). The average abundance in descending order was = Actinobacteria (13.6%), Chloroflexi (11.1%), Acidobacteria (8.6%), and Gemmatimonadetes (4.9%). The compositions of the five dominant bacterial phyla mentioned the above order in each group were as follows: GLXS (36.8%, 6.5%, 14.7%, 10.1%, 16.0%), GLXY (40.2%, 17.9%, 12.0%, 12.4%, 5.8%), GLSY (41.6%, 12.8%, 12.8%, 6.7%, 3.1%), LHBZL (48.6%, 10.5%, 8.6%, 8.9%). 5.4%), CZZL (52.7%, 12.3%, 9.0%, 8.9%, 5.4%), and YSZL (41.1%, 14.6%, 8.0%, 7.1%, 2.0%). The phyla Planctomycetes (3.9%) and Latescibacteria (2.3%) comprised the highest percentage at GLXS. Cyanobacteria (8.0%), Bacteroidetes (6.2%), and Verrucomicrobia (4.2%) had the highest relative abundance at YSZL. Nitrospirae (6.4%) demonstrated the highest relative abundance at GLSY (Figure 5A). At the genus level, Cupriavidus (4.1%) was the dominant genus at CZZL and YSZL, accounting for 7.8% at CZZL and 4.3% at YSZL. The relative abundance at CZZL was significantly higher than that of other reaches. MND1 was the dominant bacteria at GLXS (4.2%), and Anaeromyxobacter was the dominant bacteria at LHBZL (5.4%). There were no significant differences in the relative abundance of different genera in GLXY (Figure 5B). In addition, the taxonomic results contained a large number of unknown bacteria (Figure 5C).
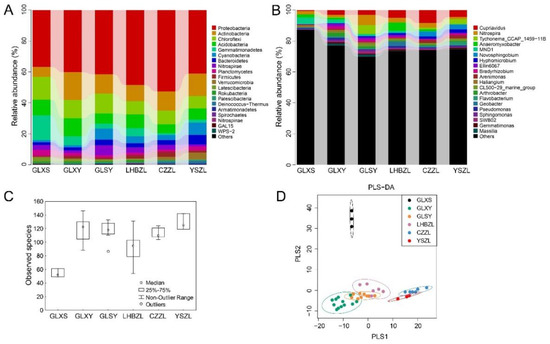
Figure 5.
The diversity and richness of sludge bacteria among the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups. The relative abundance of the bacteria among the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups at the phylum level (A) and genus level (B). The x-axis represents groups and the y-axis represents relative abundance presented as a percentage. The amount of observed species in the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups (C). The x-axis shows the different groups and the y-axis shows the observed species. Validation of PLS-DA for species similarity and distribution among the GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL groups (D).
The changes in bacterial community structure were further studied according to PLS-DA analysis, with the results indicating significant differences in bacterial diversity at GLXS and a relatively uniform bacterial diversity at CZZL and YSZL. There was relatively uniform bacterial diversity at GLSY, LHBZL, and GLXY as well (Figure 5D).
3.6. Species Abundance of Bacteria in Sludge Samples
The results for taxa abundance analysis showed that Candidatus-Entotheonella only existed at GLXS and that the abundance of Chthonobacter at GLXS was higher than that in other sampling groups (Figure 6). The genera Candidatus-Sollbacter, Labrys, mle1-7, RB41, Streptomyces, and Variovorax had the highest abundance at GLXY. Additionally, the genera Defluvllmonas, Hydrogenophaga, Phreatobacter, Piscinibacte, Tabrizicola, Rhodobacter, and Terrisporobacter existed in the highest abundance at CZZL. The genera Hyphomicrobium and Wastewater-metagenome had the highest abundance at YSZL. The abundance of the genus metagenome appeared at GLXS, YSZL, GLXY, GLSY, CZZL, and LHBZL from low to high. The genus Streptococcus only appeared at CZZL.
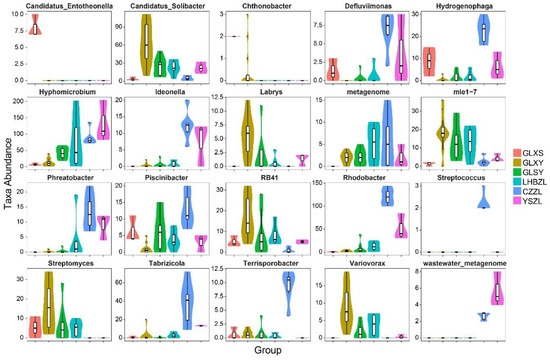
Figure 6.
Taxa abundance of different bacteria species in groups GLXS, GLSY, CZZL, GLXY, LHBZL, and YSZL sampled from sludge.
4. Discussion
Species diversity is a prerequisite for maintaining the normal function of the ecosystem, and due to the microorganism diversity of the river it plays a vital ecological function in the decomposition of organic substances, the nutrient cycle, etc. [29]. In the present study, 16SrRNA gene amplification and Illumina MiSeq sequencing were used to analyze the composition and diversity of the microbial community in the water and sludge of the Huotong River. The results showed that there were differences in the composition of the microbial community in the main river and tributaries. This is consistent with Jackson’s study, which revealed significant differences in the composition of bacterial communities in the main river and tributaries of the Mississippi River [30]. In addition, it was found that environmental stress could drive greater diversity of microorganisms in systems with high environmental heterogeneity, which is consistent with the study results of Zhu et al. [31].
Water microorganisms in the river at the phylum level were similar to studies in other rivers [32,33]. Proteobacteria was the most dominant phylum, and the abundance of Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Cyanobacteria was high. Proteobacteria are a large group of bacterial communities, mainly including α-proteobacteria, β- proteobacteria, and δ- proteobacteria, etc., which have the ability to use organic substances and fix nitrogen in soils with less nitrogen content [34] (Madigan et al., 1997). Proteobacteria accounted for more than half of the content in each reach, playing an important role in the cycle of nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic substances in the Huotong River. Actinobacteria grew slowly and are able to survive in a long-span main river [35], where they play an important role in the degradation of soluble organic substance [36,37,38]. Our results show that Actinobacteria are abundant in the main river (GLSY, GLXY, and GLXS) and less so in tributaries (LHBZL, CZZL, and YSZL). Bacteroidetes exist widely in the soil and aquatic environment, and grow in large numbers in environments with high resource availability [39,40]. Bacteroidetes can degrade organic compounds with high molecular weight, such as petroleum hydrocarbons [41,42]. In this study, we found that the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes was the highest at LHBZL, and slightly higher at YSZL than at CZZL, which might be due to the high concentration of complex organic compounds such as petroleum hydrocarbons in towns or around dams. Cyanobacteria are the key bacteria in the nutritional cycle [43]. The abundance of Cyanobacteria was the highest at GLSY and lower at YSZL and GLXS. Environment with less nutrition (river source area) and confluences of salt and fresh water (estuary region) are not conducive to Cyanobacteria. Firmicutes are metabolically diverse and participated in the degradation and transformation of many substances and elements [44].
The abundance of water microorganisms at the genus level showed that Cuprividus was the most dominant genus, and the abundance of Acinetobacter, Limnohabitans, and Pseudomonas was high as well. The genus Cupriavidus possesses characteristics such as nitrogen removal, and certain species of the genus Cupriavidus exhibit heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification [45]. Acinetobacter is pathogenic, and can cause respiratory tract infections, wound infections, urinary tract infections, etc. Generally, Acinetobacter is abundant in sewage and wastewater and widely involved in the nitrogen cycle and organic transformation [46,47]. In the Huotong River, the largest abundance of Acinetobacter was at GLXS. At this point, the content of TP, turbidity, and conductivity was the highest, while the dissolved oxygen was the lowest. The water quality was poor, and the self-purification capacity of the reach was low [48]. The discharge of domestic sewage might be why Acinetobacter was the dominant bacteria at GLXS. Certain pathogenic bacteria of Pseudomonas can be harmful to animals or humans; for instance, Pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause severe chronic infection in the host [49]. It exhibited the highest abundance at CZZL, and may pose a potential threat to the health of the local people.
The water quality results showed that the content of TN and TP at the source of the Huotong River was lower. TN was highest at GLXY, and TP was highest at GLXS (p < 0.05). This indicates that frequent human activities have caused obvious organic pollution such as nitrogen and phosphorus, providing a favorable growing environment for Actinobacteria and Bacteroidetes. The content of TN and Chl-a was high at GLXY, where a levee made of artificial stones has been built in this riparian zone. Additionally, sand digging and real estate construction phenomena have occurred nearby. The content of TN and TP at GLXS was high in areas where the water was greatly disturbed by human activities such as urban construction and transportation. It was easy to produce non-point-source pollution [50]. Generally, the saline water environment was weakly alkaline (for example, the Huotong River estuary had a pH value of 8.75 and a salinity of 6 ppt), although there were more Acidibacter found here. This might be because the drainage of domestic sewage lowered the pH of the reach, providing a favorable living environment for Acidibacter. In addition, the microorganisms found in the estuary were more tolerant to changes in salinity, and had different microbial community compositions compared with other sample sites [51]. Similar findings have been found in the United States in the Parker Estuary [52] and Tillamook Bay [53].
Jiao et al. found that the pH of sludge plays an essential role in regulating the assembly pattern of sediment bacterial communities [54]. In the present study, we did not find that WT and pH had great effects on the microbial community. This might be due to the different seasons evaluated during the study or to the differences in the water physical and chemical environment of the study area. Huotong River has high mobility, and there was no difference in pH between upstream and downstream; thus, pH was not the main influencing factor of microbial diversity in the Huotong River. Liu et al. found that conductivity was the main factor affecting the composition of the microbial community in the Jiulong River, and that these changes were closely related to agricultural pollution in the upper reaches and saltwater intrusion in the estuary [55]. We found that conductivity had significant effects on the microbial diversity of Huotong River. For example, Candidatus and Acidibacter only had the highest abundance at GLXS, with the results indicating that these two types of bacteria are more suited to habitats with higher salinity in estuaries. The “environmental impact report form of highway engineering from Baduao town in Jiaocheng district of national highway G237 to Badu interchange section of Ningdong expressway” [56] showed that due to the great seasonal variation of water volume and water level of Huotong River, which is affected by the rising and falling tide of sea water, seawater backflow occurred in the estuary, such as at GLXS. Additionally, the conductivity at GLXS was obviously higher than at other sampling points, which supports this conclusion. In a review of the microbiology of Felfoldi, the temperature, salinity, turbidity, and grazing pressure were reported to be the most important factors driving the changes in assembly patterns of the planktonic bacterial community [57]. In addition, Tinker et al. found that there was a significant positive correlation between turbidity and endemic gastrointestinal diseases in their study [58]. However, in the present case the significant effect of turbidity on the microbial diversity of Huotong River occurred because the degree of water turbidity in different reaches was significantly different due to the differences in geographical environment (such as precipitation) and to human activities,. Suspended particulate substances, organic substances, and sediment resuspension can directly impact the bacterial community, leading to turbidity having a significant impact of on microbial composition.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we found that turbidity and conductivity were the main factors which affected microbial diversity in the waters of the Huotong River. In addition, TN and TP had a great influence on microbial diversity. These results indicate that the microbial diversity of Huotong River is closely related to specific environmental factors and water nutritional status. In addition, the results show that human activities have increased the turbidity and conductivity of surface water, which has greatly affected the microbial diversity and potentially reduced the degradation ability of the river.
In conclusion, understanding the microbial diversity of rivers has profound ecological significance for maintaining river ecosystem health and water environment management. Further research needs to focus on the impact of new pollutants (such as antibiotics, microplastics, etc.) on river ecosystems in order to better protect river ecosystems and improve scientific water environmental management.
Author Contributions
Methodology, H.Q. and X.J.; software, H.Q.; formal analysis, Z.W.; investigation, X.C., Y.W. and Q.Q.; Data analysis, H.Q. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, X.J. and L.W.; writing—review and editing, H.Q. and Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work were supported by the open fund project of the State Key Laboratory of Lake Science and Environment (2022SKL014) and the project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31560133).
Institutional Review Board Statement
No humans or animals were involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
We declare that the data provided in this study are original and reliable data. As part of the data has not been published, we have not formed data link for the time being.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Shanghai Personalbio Biotechnology Co., LTD for the conducting of high throughput sequencing of water and sediment samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lew, S.; Lew, M.; Mieszczyński, T.; Szarek, J. Selected fluorescent techniques for identification of the physiological state of individual water and soil bacterial cells—Review. Folia. Microbiol. 2010, 55, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.; Meyer, K.; Bohannan, B. Linking microbial communities to ecosystem functions: What we can learn from genotype–phenotype mapping in organisms. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2020, 375, 20190244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarasiri, A. Diversity and Activity of Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria Isolated from Sedimentary Water in the Littoral Zone of Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia. Water 2021, 13, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gao, H.K. Ecological networks reveal contrasting patterns of bacterial and fungal communities in glacier-fed streams in Central Asia. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.H.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ke, M.J.; Lu, T.; Penuelas, J.; Qian, H.F. Geographic patterns of microbial traits of river basins in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.M.; Cui, L.Y.; Cao, X.Y.; Lv, Q.; Chen, T.T. Evaluation of the human interference on the microbial diversity of Poyang Lake using high-throughput sequencing analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Li, D.F.; Yang, R.F. High throughput sequencing technology and its application in microbiology research. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2011, 51, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, G.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.S.; Ha, F. Development of high throughput sequencing technology and its application in life science. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2014, 41, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk, E.L.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; Naquin, D.; Thermes, C. The Third Revolution in Sequencing Technology. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.W.; Ban, G.; Bae, D.; Kim, S.A. Microbial investigation of aquacultured olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) from farm to table based on high-throughput sequencing. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2023, 389, 110111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z.C.; Wei, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; Feng, W.Q.; Chen, H. High-throughput profiling of seasonal variations of antibiotic resistance gene transport in a peri-urban river. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Pereira, P.P.; Agostini, E.; Gonzalez, P.S. Impact assessment of bioaugmented tannery effluent discharge on the microbiota of water bodies. Ecotoxicology. 2020, 29, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, F.H.; Zhu, K.W.; Yang, C.H.; Xiang, Q.J.; Lei, B. Characteristics of planktonic and sediment bacterial communities in a heavily polluted urban river. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.C.; Kuang, S.P.; Shao, H.B.; Cheng, F.; Wang, H.H. Improving soil fertility by driving microbial community changes in saline soils of Yellow River Delta under petroleum pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Cai, Q.H.; Liu, J.K. River ecosystem health and its evaluation. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 9, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser James, I. Ecosystem processes and interactions in a morass of diversity. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 81, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Wang, D.W.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhai, J.; Yang, T.T.; Wang, A.Z. On the relationship between urban river health and urban development. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2015, 17, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.S.; He, P. Research progress, existing problems and future direction on river ecosystem service. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 852864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X.D.; Yue, Z.Y.; Zhao, P.G. Bacterioplankton community structure in Weihe River and its relationship with environmental factors. Acta. Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Sun, F.F.; Zhao, H.B.; Mi, H.S.; He, S.Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lan, H.L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.P. Compositional changes of sedimentary microbes in the Yangtze River Estuary and their roles in the biochemical cycle. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 760, 143383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.L.; Niu, Y.D.; Yuan, R.Q.; Wang, S.Q. Different Responses of Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in River Sediments to Water Diversion and Seasonal Changes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.W.; Pan, B.Z.; Sun, H.; He, H.R.; Zhao, G.N. Diversity and influencing factors of bacterial community in sediments of upper reaches of the Hanjiang River and its tributaries. Water Resour. Prot. 2022, 38, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.Y. Characteristics of Water Chemistry and Phytoplankton Bacterial Community in Le ’an River. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang, China, May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.D.; Su, Y.P.; Lu, J.; Tang, S.Q. Construction and application of river health assessment index system in Fujian Province. Hydraul. Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 16–18+22. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Wu, Y.M. Jiaocheng Huotong: A millennium old town with a fresh landscape. Mindong Daily 2018, 21, 9573. Available online: http://www.ndwww.cn/xspd/jcxw/2018/1221/109573.shtml (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Tian, P.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Shen, L.; Xin, H. Evaluation of the accuracy and sensitivity of high-throughput sequencing technology using known microbiota. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 17, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y. Degradation of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Organic Matter in Black Stink Water by Microalgae in Algal/Bacteria-Symbiotic System. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, March 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H. High throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial communities in soils of a typical Poyang Lake wetland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Millar, J.J.; Payne, J.T.; Ochs, C.A. Free-Living and Particle-Associated Bacterioplankton in Large Rivers of the Mississippi River Watershed Demonstrate Biogeographic Patterns. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2014, 80, 7186–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Langlois, G.A.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Environmental Heterogeneity and Trophic Status in Sampling Strategy on Estimation of Small-Scale Regional Biodiversity of Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenova, V.V.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Belykh, O.I. Comparative analysis of biodiversity in the planktonic and biofilm bacterial communities in Lake Baikal. Microbiology 2013, 82, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Liu, X.; Mou, X.Z.; Wu, L. Research status of microorganisms in Poyang Lake wetland, a large shallow lake. Microbiol. China 2019, 46, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.T.; Martinko, J.M.; Parker, J. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 9th ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sinkko, H.; Lukkari, K.; Sihvonen, L.M.; Sivonen, K.; Leivuori, M.; Rantanen, M.; Paulin, L.; Lyra, C. Bacteria contribute to sediment nutrient release and reflect progressed eutrophication-driven hypoxia in an organic-rich continental sea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Kouchiwa, T.; Hodoki, Y.; Hotta, K.; Uchida, H.; Harada, K.I. Distribution and identification of actinomycetes lysing cyanobacteria in a eutrophic lake. J. Appl. Phycol. 1998, 10, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmonen, E.; Sivonen, K.; Rapala, J.; Haukka, K. Diversity of cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria in cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Joutikas, Finland. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.W.; Lin, X.R.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.H. Diversity, functional characteristics, and environmental remediation potential of stress-tolerant actinomycetes. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2023, 63, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, Y.J.; Yin, M.; Zhao, J.J.; Li, X.Y. Seasonal variations in microbial community structure in Yongding River. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. 2020, 56, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Hehemann, J.H.; Rebuffet, E.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Environmental and gut Bacteroidetes: The food connection. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.C.; Mortelmaier, C.; Margesin, R. Characterization of the bacterial archaeal diversity in hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullerjahn, G.S.; Post, A.F. Physiology and molecular biology of aquatic cyanobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffredi, S.K.; Orphan, V.J. Bacterial community shifts in taxa and diversity in response to localized organic loading in the deep sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.J.; He, D.L.; Xue, Z.J. Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus by heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification of a denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating bacterium Enterobacter cloacae HW-15. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jeong, S.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ryu, E.Y.; Lee, S.J. Aerobic Denitrification of Pseudomonas putida AD-21 at Different C/N Ratios. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 106, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Marrs, C.F.; Simon, C.; Xi, C.W. Wastewater treatment contributes to selective increase of antibiotic resistance among Acinetobacter spp. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3702–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.Q.; Eglinton, T.I.; Montlucon, D.B.; McIntyre, C.; Zhao, M.X. Pre-aged soil organic carbon as a major component of the Yellow River suspended load: Regional significance and global relevance. Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 2015, 414, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.E.; Korber, D.R.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Microbial Biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, A.J.; Goldman, C.R. Limnology, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 433–456. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, L.X.; Yang, L.Z.; Zhang, F.S.; Norse, D.; Zhu, Z.L. Agricultural non-point source pollution in China: Causes and mitigation measures. Ambio 2012, 41, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, B.C.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Sogin, M.L.; Hobbie, J.E. Microbial biogeography along an estuarine salinity gradient: Combined influences of bacterial growth and residence time. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2004, 70, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, A.E.; Colbert, D.; McManus, J.; Field, K.G. Microbial community dynamics based on 16S rRNA gene profiles in a Pacific Northwest estuary and its tributaries. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 52, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, C.C.; Zhao, D.Y.; Huang, R.; He, F.; Yu, Z.B. Habitats and seasons differentiate the assembly of bacterial communities along a trophic gradient of freshwater lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.Y. Genetic diversity patterns of microbial communities in a subtropical riverine ecosystem (Jiulong River, southeast China). Hydrobiologia 2011, 678, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Impact Report of Badu’ao Village in Jiaocheng District of National Highway G237 to Badu Interchange Section of Ningdong Expressway. 2018. Available online: http://www.doc88.com/p-9704812737328.html (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Felfoldi, T. Microbial communities of soda lakes and pans in the Carpathian Basin: A review. Biol. Futura. 2020, 71, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinker, S.C.; Moe, C.L.; Klein, M.; Flanders, W.D.; Uber, J.; Amirtharajah, A.; Singer, P.; Tolbert, P.E. Drinking water turbidity and emergency department visits for gastrointestinal illness in Atlanta, 1993–2004. J. Expo. Sci. Env. Epid. 2010, 20, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).