Abstract
The risks imposed by biological invasions on marine ecosystems are increasing worldwide. The mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii has recently expanded its distribution to the northeastern Baltic Sea, where low predatory pressures and the absence of functionally similar competitors favored the establishment of the species. Few studies have addressed the effects of the mud crab on Baltic benthic communities and habitats. Even fewer have looked at the consequences of the invader on habitats dominated by Fucus vesiculosus, the main habitat-forming macrophyte in the Baltic Sea. The present study experimentally analyzed, under laboratory conditions, the effects of R. harrisii on Baltic F. vesiculosus habitats and associated communities under different temperatures simulating summer and winter regimes. Our results show that the effects of the mud crab are modulated by temperature, being more pronounced under summer conditions when the metabolic demands and food intake requirements are higher. The experiment provided new insights into the capacity of R. harrisii to disrupt recruitment in native snail populations, jeopardizing the persistence of healthy populations of key grazers in F. vesiculosus habitats. Moreover, our results conclusively demonstrated the capacity of the invader to decimate native blue mussel populations. The impacts on functionally relevant invertebrates can have far-reaching ecological consequences, altering the food web and disrupting entire coastal ecosystems in the Baltic Sea.
1. Introduction
Globalization has dramatically increased the spread of species beyond their native ranges, reshaping the boundaries of species distributions and exposing native floras and faunas to new threats to their ecological performance and persistence worldwide [1,2]. The unsustainable development and intensification of human activities, and the movement of people and goods at a pace never seen in human history, have severely compromised the capacity of ecosystems to absorb and adapt to change and increased their vulnerability to the arrival and establishment of alien species [1,3,4,5,6]. The annual rate of first records of alien species has increased since the 1950s for most taxonomic groups, with no or only marginal signs of slowing down [7,8,9]. Recent global estimations show that a fourth of the new first records are of species not previously described as alien elsewhere and that up to 16% of Earth species have the potential to become alien [10]. The risk of biological invasions is increasing worldwide and the efforts to prevent them seem insufficient and ineffective [5,10]. In this context, research aiming at describing and understanding the actual and potential effects of alien species has become essential to generate meaningful predictions of expected changes in terrestrial and marine ecosystems in the face of the worsening and apparently inevitable threats imposed by biological invasions.
Benthic decapods play a critical ecological role in the marine ecosystems where they occur. Often described as generalists, benthic decapods feed at different trophic levels and display diverse feeding strategies ranging from detritivorous and scavenging behavior to grazing on algae and plants and predation on other benthic invertebrates [11]. Through their feeding activity, decapods can exert a strong control on different community components directly via predator–prey interactions or indirectly due to the propagation of effects through trophic cascades across benthic food webs, affecting major ecosystem functions such as primary production and nutrient cycling [11,12,13]. Non-trophic interactions also mediate the effects of decapods, as these organisms compete with other species for resources and can alter the characteristics of their habitats. Crabs and lobsters, for example, can aggressively interfere with access to food by other species and displace competitors through agonistic displays or direct engagement in combat [11]. Multiple decapod species exhibit digging behavior, producing burrows in soft-bottom habitats to avoid predators, escape environmental stress, or as housing during mating and molting [14,15]. Their burrowing promotes sediment turnover and intensifies the water–sediment exchange of gases, organic matter, and nutrients, affecting not only the physical-chemical conditions of the habitat but also the composition of resident micro- and macro-communities (e.g., [15,16,17,18,19]). When present in vegetated habitats, such as seagrass meadows or macroalgal beds, decapods can shred blades and dislodge whole plants during their feeding and burrowing activities, thereby modifying the structure of these habitats (e.g., [20]). Thus, the arrival and establishment of decapods can trigger structural and functional shifts in invaded ecosystems as observational and experimental evidence has shown for different species across habitats and regions (e.g., [21,22,23,24,25]).
Decapods are one of the most successful spreading invaders worldwide [26,27]. A combination of physiological, behavioral, life history, and ecological traits explain their successful spread and establishment. Among these traits, the most prominent are: (i) their ability to live in and plastically respond to a wide diversity of habitats and a range of environmental conditions and changes; (ii) their capacity to feed on a variety of items of plant and animal origin; (iii) the fact that a large number of decapod species are r-strategists, showing multiple and highly productive reproductive events that result in the release of pelagic stages that disperse in the water column; and (iv) their aggressivity and territorialism which transform them into tough predators, preys, and competitors (Rato et al. [27] and citations therein).
Several brachyuran decapods of Asian and American origin are successfully spreading and establishing across European Seas (e.g., [28,29,30,31]). Among them, the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould, 1841) has successfully colonized multiple locations across the North Sea and the Baltic Sea [28,32]. Originally from North America, where its distribution extends from the west coast of Mexico and the United States to the southwest coast of Canada, the species was first observed in Europe in 1874 in the Netherlands. The first record of the species in the Baltic Sea is from Germany in 1936, from where it expanded to Poland (first record in 1951), and Lithuania (first record in 2000) (Kotta and Ojaveer [28], Fowler et al. [32] and citations therein). Only in the last decade, the species has expanded its Baltic distribution further north, invading the southwest coast of Finland (first record in 2009, [32]), Pärnu Bay, and close-by areas of the Gulf of Riga in Estonia (first record in 2011) [22,28]. The wide thermal tolerance and resistance to the extremely low salinity conditions of adults and early stages allowed the species to survive the cold winters and successfully reproduce in the diluted waters of the Baltic Sea [33,34]. In this region, R. harrisii has been shown to live both in macroalgae-dominated and soft-bottom habitats [35,36], where it actively feeds on bivalves, gastropods, polychaetes, other crustaceans, macroalgae, and detritus (e.g., [22,37,38,39,40,41,42]).
Only a handful of studies have analyzed, under field and laboratory conditions, the effects of R. harrisii on vegetated and soft-sediment habitats and associated native benthic communities in the Baltic Sea (e.g., [22,39,41,43,44]). Of these studies, few have analyzed the effects on habitats dominated by Fucus vesiculosus [39,41], the main canopy-forming macroalga in the Baltic Sea [45]. Available information on the impact of R. harrisii on Baltic F. vesiculosus habitats comes from field experiments, which show clear signs of deterioration in aggregated diversity indices and overall changes in the structure of invertebrate communities in treatments where the crab was present [39,41]. The results suggest that predation impacts might result in cascading effects, releasing filamentous algae from the grazing pressure imposed by native macroinvertebrates and restructuring resident macrophyte communities [41]. However, the described effects of the mud crab on Fucus habitats have not been confirmed experimentally under laboratory conditions and, therefore, potential effects of confounding biotic and abiotic factors have not been controlled. In addition, most studies on the consequences of the mud crab have focused on feeding-mediated effects on resident benthic communities, generally overlooking the abiotic changes that the activity of the invader might have in Baltic Sea habitats (but see Kotta et al. [22] for a field experiment showing changes in nutrient and chlorophyll a concentrations likely mediated by the activity of R. harrisii).
In this study, the ecological and environmental effects of R. harrisii on F. vesiculosus habitats and associated invertebrate communities in the northern Baltic Sea were investigated under laboratory conditions at different temperatures representing winter and summer regimes in this region. The experiment addressed the following questions: (i) does the activity of R. harrisii lead to changes in the abundance and biomass of functionally relevant invertebrate groups and the biomass of the habitat-forming species (i.e., F. vesiculosus)?; (ii) does the invader, either directly through its physiological activity or indirectly through feeding-mediated effects on F. vesiculosus and associated invertebrate communities, have an impact on water quality (defined by the measurement of nutrient and chlorophyll a concentrations in the water)? and (iii) how do the simulated seasonal regimes modulate both the ecological and abiotic effects of R. harrisii?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Acclimation of Mud Crabs
R. harrisii individuals were collected in July 2021 in Pärnu Bay (58°21′42.1″ N, 24°28′56.8″ E) from artificial substrates placed in the area to support the spawning of pikeperch or using fish traps. The collected crabs were placed in plastic boxes with natural seawater obtained at the collection point and immediately transported to the Kõiguste field station laboratory (58°22′22.4″ N, 22°58′55.2″ E) of the Estonian Marine Institute (University of Tartu, Estonia). The water was constantly and abundantly aerated during transportation. Upon arrival at the field station, the crabs were separated into a larger number of boxes to prevent aggressive interactions and cannibalism. The crabs were acclimated in natural seawater (6 of salinity), constantly aerated, and kept at room temperature (20 °C) before the beginning of the experiment. Over the acclimation period, the mud crabs were fed with fresh Mytilus trossulus mussels.
2.2. Collection of Fucus vesiculosus and Associated Invertebrates
The F. vesiculosus used in the experiment were collected from a site located near the laboratory of the Kõiguste field station (58°22′13.6″ N, 22°58′43.2″ E), two days before the start of the experiment. Collected F. vesiculosus individuals attached to boulders no bigger than 20 cm were transported to the field station, where they were maintained in constantly aerated natural seawater until the beginning of the experiment. All F. vesiculosus individuals and associated boulders were inspected and invertebrates were carefully separated to prevent their random inclusion in the experimental units. Invertebrates were collected using hand nets in the macroalgal stand or during the cleaning of F. vesiculosus by dipping the macroalga in freshwater for a few seconds and immediately transferring swimming invertebrates to natural seawater. The collected animals were sorted using nets and sieves to collect gastropods and amphipods—the two main groups of macroinvertebrates found in F. vesiculosus stands in the area. Mussels of the species M. trossulus were collected from the pilot mussel farm located in Tagalaht Bay (58°27′36.0″ N, 22°03′00.1″ E).
2.3. Experimental Design and Setup
The experiment lasted one month, from 18 November to 18 December 2021. Twenty plastic boxes (size: 40 × 60 × 43 cm) filled with natural seawater and continuously aerated were used as experimental units. The bottom of all the experimental units was covered with previously washed pebbles, increasing the topographic complexity of the boxes, and providing habitat for crabs and invertebrates. Two or three F. vesiculosus individuals (depending on their size) with their respective boulders were gently placed in each of the experimental units. Only healthy macroalgal individuals with no major signs of grazing were included. Regarding the associated macrofauna, 20 mussels (M. trossulus), 20 amphipods (Gammarus spp.), and 20 gastropods (predominantly Theodoxus fluviatilis) were included in each experimental unit, resembling the natural densities of invertebrates observed in the field at the time of sampling and considering the long-term information gathered by the Estonian Marine Institute during monitoring campaigns in the area.
Ten of the experimental units received two mud crabs each, recreating the densities observed in Pärnu Bay [40]. All R. harrisii individuals (carapace length (CL): 11.73–14.51 mm) used in the experiment were males, preventing potential differences in observed effects driven by the sex of individuals. Animals missing limbs or with major cracks or other signs of damage in the exoskeleton were excluded. In addition, mud crabs that did not defend themselves or exhibit escape behavior during handling were also excluded. The remaining ten experimental units without crabs were used as controls to assess the effects of the invader.
To test how seasonal thermal differences modulate the effects of the invader, 10 experimental units, 5 with crabs, and 5 controls, were kept inside the laboratory at a constant temperature of approximately 20 °C (summer conditions) while the remaining 10 were exposed to natural outdoor temperatures, which fluctuated between 0 and 6 °C (winter conditions) over the duration of the experiment. To prevent differences in light conditions between experimental units kept indoors and outdoors, the same fluorescent-lamp system installed in the laboratory was used for the experimental units kept outdoors. All experimental units were exposed to a 12:12 h light–dark cycle throughout the experiment.
2.4. Data Collection and Analysis
Temperature and salinity, the activity and mortality of the crabs, and water quality were monitored throughout the experiment.
All F. vesiculosus used in the experiment were carefully dry blotted and their wet weight was determined at the beginning of the experiment. This information was used in combination with a standard relationship between wet weight and dry weight (constructed for the species with individuals collected at the moment of the experiment) to determine the dry weight of macroalgal individuals at the start of the experiment. All macroalgal biomass included in the experimental units was collected, dried, and weighed at the end of the experiment. This information was combined with the initial dry weights to calculate changes in the F. vesiculosus biomass over the duration of the experiment.
All mud crabs were sized (CL) at the beginning and the end of the experiment. All invertebrates that remained at the end of the experiment were collected with the help of a 0.25 mm mesh-size sieve, identified to the lowest taxonomic level possible, counted, and dry weighed.
Water samples for the analysis of nutrients and chlorophyll a were obtained at the end of the experiment before collecting all biological samples to prevent potential disturbances. Water samples for the analysis of nutrients were collected and immediately frozen until further analysis. Total phosphorus, phosphates, nitrogen, and nitrites plus nitrates concentrations were determined using a Skalar San++ analyzer (see a detailed list of the methods and protocols used in Kotta et al. [22]). In the case of chlorophyll a samples, 1 L of water was collected from each experimental unit and filtered through a Whatman GF/F filter. The filters were placed in the refrigerator overnight in 50 mL tubes with 10 mL of 96% ethanol for extraction. The concentration of chlorophyll a was measured using a Biochrom Libra S32 spectrophotometer.
Changes in biological (F. vesiculosus biomass, abundance, and biomass of associated invertebrates) and water-quality variables (nutrient and chlorophyll a concentrations) due to the activity of the invader under different temperature regimes were statistically analyzed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The ANOVAs were performed using the function aov from the stats package in R version 4.1.2 [46]. The presence of crabs and temperature regime were included as explanatory variables in the models, evaluating both main and interactive effects. The Tukey’s honest significant difference (Tukey HSD) test was applied for post-hoc pairwise comparisons using the package emmeans [47]. The fulfillment of assumptions and the overall adequacy of the models were decided based on a detailed analysis of the plots of residuals. The analysis of residuals was performed using the R package DHARMa [48]. When needed, response variables were logarithmically transformed.
3. Results
The simulated seasonal regimes modulated the predation effects of R. harrisii on the invertebrate communities (Figure 1, Table 1). While the feeding activity of the invader did not significantly affect the abundance and biomass of amphipods (Figure 1a,b, Table 1), the abundance and biomass of the bivalves and gastropods were significantly reduced by the invader under summer conditions when compared to those observed under winter conditions (Figure 1c–f, Table 1 and Table S1). The invaders decimated the bivalves under summer conditions, with abundance and biomass declining by approximately 75% (Figure 1c,d). Even though reproduction partially compensated for the decrease in the abundance of gastropods caused by the invader in the summer treatment (as shown by the higher number of gastropods observed at the end of the experiment in the warm treatments both with and without crabs), R. harrisii was able to significantly disrupt gastropod recruitment, keeping the overall abundance at the level observed at the beginning of the experiment (Figure 1e). The abundance of gastropods was approximately 70% lower in the warm treatment with mud crabs than in the warm treatment without the invader (Figure 1e).
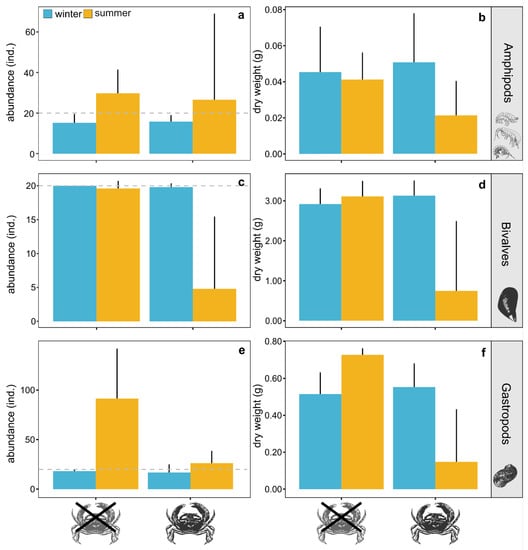
Figure 1.
Abundance and biomass (expressed as dry weight) of amphipods (a,b), bivalves (c,d), and gastropods (e,f) observed at the end of the experiment in treatments with and without the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii under simulated summer (yellow) and winter (blue) conditions. Bars represent mean values and whiskers confidence intervals at 95%. Horizontal dashed lines indicate the abundance of the different groups at the beginning of the experiment.

Table 1.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) tables for the biological response variables assessed. Model components (including both the main and interactive effects of temperature and the presence of crabs, Rh), degrees of freedom (DF), the sum of squares (SS), the mean sum of squares (MSS), the statistic (F-value), and associated significance (p-value) are presented. For significant effects, p-values are highlighted in bold. Logarithmically transformed variables are indicated with log.
The dry weight of the macroalgae decreased in all treatments over the course of the experiment, with a greater decrease in the warm treatments and especially in the treatment without crabs (Figure 2). The decrease in biomass in the warmer treatment without crabs was on average 2–3 times higher than in the colder treatments (with and without crabs) and 1.5 times higher, but marginally significant, than in the warm treatment with mud crabs (Figure 2, Table 1 and Table S1). The latter may suggest that the grazing pressure on F. vesiculosus is reduced as a result of the presence or feeding activity of the invader.
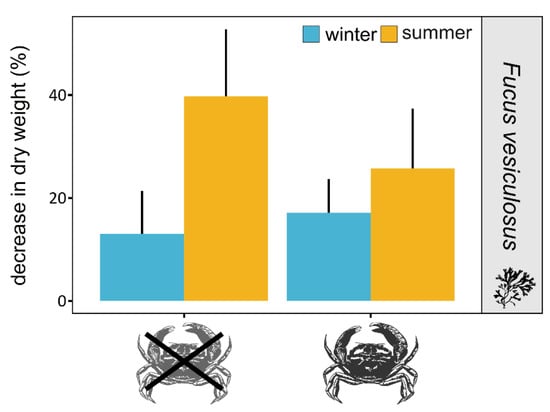
Figure 2.
Decrease in biomass (dry weight) of Fucus vesiculosus over the duration of the experiment in treatments with and without the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii under simulated summer (yellow) and winter (blue) conditions. Bars represent mean values and whiskers confidence intervals at 95%.
Although differences were, in general, not significant, on average concentrations of nitrogen-related nutrients tended to be higher in the warm treatment with crabs than in the same treatment without the invader (Figure 3a–c, Table 2). This trend was not observed for phosphorus-related nutrients (Figure 3d,e, Table 2). No significant differences were observed for chlorophyll a between treatments with and without mud crabs (Figure 3f, Table 2).
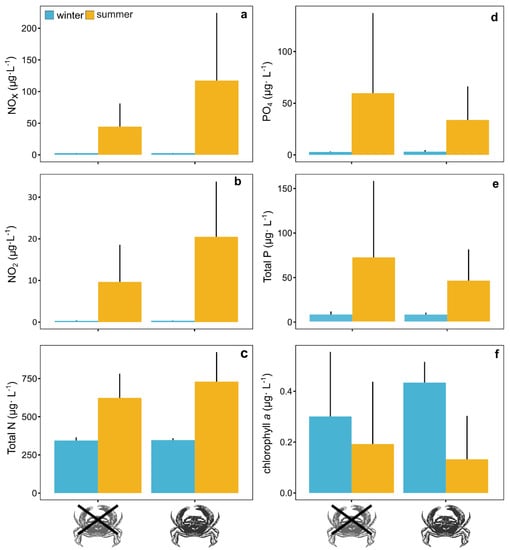
Figure 3.
Nutrient (a–e) and chlorophyll a (f) concentrations in treatments with and without the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii under simulated summer (yellow) and winter (blue) conditions. Bars represent mean values and whiskers confidence intervals at 95%.

Table 2.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) tables for the environmental response variables assessed. Model components (including both the main and interactive effects of temperature and the presence of crabs, Rh), degrees of freedom (DF), the sum of squares (SS), the mean sum of squares (MSS), the statistic (F-value), and associated significance (p-value) are presented. For significant effects, p-values were highlighted in bold. Logarithmically transformed variables are indicated with log.
4. Discussion
Our study demonstrated that temperature plays an important role in modulating the effects of the invasive mud crab R. harrisii on native F. vesiculosus stands and associated invertebrates in the northeastern Baltic Sea. The impact of the crab was more pronounced at higher temperatures, suggesting that the presence of the invader has negative consequences for native invertebrate species, particularly under summer conditions when the metabolic demands and food intake requirements of the invader are higher [49].
The experiment showed that R. harrisii can exert a strong predation pressure on native snails under summer conditions. These findings are in line with the observations made in a field experiment by Jormalainen et al. [41], who showed that the increase in the density of the mud crab in F. vesiculosus stands over three consecutive years was correlated with the decrease in the abundance of the native snails Hydrobia spp. and T. fluviatilis. Interestingly, our results provide new insights into the capacity of R. harrisii to disrupt the recruitment of native gastropods in the northeastern Baltic Sea. New snail recruits were observed in all experimental units kept at 20 °C, even though the numbers were significantly lower in the units where mud crabs were included. This suggests that the invader actively feeds on juvenile gastropods and has the potential to impair the population renewal of important grazers in F. vesiculosus stands. Invasive crabs of different species have been shown to predate on the larval stages and juveniles of native invertebrate species, suppressing their recruitment and disrupting natural population dynamics (e.g., [50,51,52]). Thus, the further expansion and increase in density of R. harrisii in F. vesiculosus habitats might impose a severe risk for the persistence of healthy native populations of gastropods in the northeastern Baltic Sea.
While previous field experiments performed in the Baltic Sea have been inconclusive about the consequences of R. harrisii on blue mussels [39,41,44], our results clearly show that the invader has the capacity to decimate native mussel populations in this region. Evidence from soft-sediment habitats suggests that the mud crab feeds voraciously on bivalves [22], the dominant filter-feeders in coastal areas of the Baltic Sea, and responsible for the flux of matter and energy from pelagic to benthic habitats [53,54]. Through their feeding activity, filter feeders reduce phytoplankton biomass in the water column, capturing and storing nutrients in the process. Thus, the reduction in filter feeders can exacerbate the symptoms of eutrophication [22]. This highlights the importance of understanding the tipping points of interactions between R. harrisii and native species to effectively predict changes in the functioning of Baltic Sea ecosystems invaded by the mud crab.
Despite the direct negative effects on benthic invertebrates, the study also found trends that might suggest the positive effects of the invader on F. vesiculosus. The apparent lower loss of F. vesiculosus biomass in the warmer treatment with R. harrisii than in the treatment without the crab, suggests that predation pressure, or just the presence of the invader (that can trigger escape behavior of prey, [55]), might repress the activity of grazers and reduce herbivory on F. vesiculosus. The spreading of cascading effects triggered by the feeding activity of R. harrisii on native grazers in F. vesiculosus stands has been previously described. However, in contrast to our results, previous evidence suggests that the feeding pressure imposed by the mud crab on mid-trophic consumers might release filamentous epiphytes from grazing, allowing them to thrive, decreasing the performance of the habitat-forming species [41]. The overall low coverage of epiphytic algae observed on F. vesiculosus at the beginning of our experiment, which were collected in November when the productivity of ephemeral algae is already low, might explain the differences between our results and the evidence presented by previous research. Alternatively, the relatively low proliferation of epiphytes in warmer treatments over the duration of the experiment could be the result of the grazing pressure imposed by amphipods and gastropods in the treatment without crabs, and by the direct consumption of epiphytic algae by R. harrisii in the treatment including the invader. Future studies should analyze the relative contribution of direct and indirect processes triggered by R. harrisii under different seasonal—both biological and environmental—scenarios to provide a thorough mechanistic understanding and accurate predictions of the invader’s impact in Baltic F. vesiculosus dominated ecosystems. Year-round experiments performed in mesocosm facilities able to recreate near-natural conditions (e.g., [56,57]), would provide the ideal context to evaluate carry-over effects of the invader on the structure and functioning of native ecosystems throughout the seasons.
Even if not statistically significant, the higher mean concentrations of nitrogen-related nutrients in the warm treatment with the invader than in the control suggests that the physiological and feeding activity of the mud crab might increase the nitrogen concentrations in the water column in summer. The overall absence of effects in chlorophyll a could be explained by the fact that the experiment was performed in a low productivity season, as clearly shown by the low concentration registered in all the experimental units by the end of the experiment. Future studies should assess the impacts of R. harrisii on water quality, and abiotic conditions in general, through experiments performed over longer periods of time and considering different seasonal contexts.
To conclude, the experiment showed that the invasive crab R. harrisii poses a serious threat to the native mussel and gastropod populations in F. vesiculosus dominated ecosystems of the Baltic Sea, especially in summer. The study also highlighted the importance of understanding the complex interactions between invasive species, native species, and abiotic factors, such as temperature, in predicting the impact of invasive species on ecosystems. Once established in macrophyte-dominated habitats of the Baltic Sea, R. harrisii could potentially have several negative ecological impacts on these low-diversity and functionally poor ecosystems. The invasive species has almost no natural predators or competitors in the northeastern Baltic Sea. As a voracious predator that feeds on a variety of prey, its introduction could have a significant impact on native populations of these organisms, which might have far-reaching ecological consequences, altering the food web and disrupting entire coastal ecosystems in the Baltic Sea.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15050644/s1, Table S1: Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference (Tukey HSD) test for those biological and environmental response variables that exhibited significant main effects of the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii or interactive effects of the invader and temperature in the analysis of variance (ANOVA). The contrast between different treatments (CW: control, winter; CS: control, summer; RhW: crab, winter; RhS: crab, summer), mean estimates (estimates), standard errors (SE), degrees of freedom (DF), the statistic (t-value) and associated significance (p-value) are presented. Logarithmically transformed variables are indicated with log.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K. and F.R.B.; Methodology, F.R.B. and J.K.; Formal Analysis, F.R.B. and I.B.B.; Investigation, I.B.B., F.R.B. and J.K.; Resources, J.K.; Data Curation, F.R.B. and I.B.B.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, F.R.B.; Writing—Review & Editing, J.K. and I.B.B.; Visualization, I.B.B. and F.R.B.; Supervision, F.R.B. and J.K.; Project Administration, J.K. and I.B.B.; Funding Acquisition, J.K. and I.B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Estonian Research Council through the Mobilitas Pluss Programme (MOBJD1044). It received financial support from the EEA grant “Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation” call I “Ecosystem resilience increased” project “Impacts of invasive alien species and climate change on marine ecosystems in Estonia” (2014-2021.1.06.21-0040).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to Teemar Püss and Vivian Tamm for technical support over the duration of the experiment, and Kristiina Nõomaa for inspiring discussions that contributed to enriching the final version of the manuscript. Special thanks to Karolin Teeveer and Trude Taevere for the processing of biological samples, Marko Rõõmusoks for the analysis of nutrient samples, and Ilmar Kotta for the processing of chlorophyll a samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, transport and trouble: Managing invasive species pathways in an era of globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capinha, C.; Essl, F.; Seebens, H.; Moser, D.; Pereira, H.M. The dispersal of alien species redefines biogeography in the Anthropocene. Science 2015, 348, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, B.; Barbier, E.B.; Beaumont, N.; Duffy, J.E.; Folke, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Jackson JB, C.; Lotze, H.K.; Micheli, F.; Palumbi, S.R.; et al. Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science 2006, 314, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.R.; Roques, A.; Hulme, P.E.; Sykes, M.T.; Pyšek, P.; Kühn, I.; Zobel, M.; Bacher, S.; Botta-Dukát, Z.; Bugmann, H.; et al. Alien species in a warmer world: Risks and opportunities. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early, R.; Bradley, B.A.; Dukes, J.S.; Lawler, J.J.; Olden, J.D.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Gonzalez, P.; Grosholz, E.D.; Ibañez, I.; Miller, L.P.; et al. Global threats from invasive alien species in the twenty-first century and national response capacities. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaila, U.R.; Tai, T.C. End overfishing and increase the resilience of the ocean to climate change. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pagad, S.; Pyšek, P.; Winter, M.; Arianoutsou, M.; et al. No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.A.; Brown, L.; Campbell, M.L.; Canning-Clode, J.; Carlton, J.T.; Castro, N.; Chainho, P.; Chan, F.T.; Creed, J.C.; Curd, A.; et al. Trends in the detection of aquatic non-indigenous species across global marine, estuarine and freshwater ecosystems: A 50-year perspective. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 1780–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyšek, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Simberloff, D.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Dawson, W.; Essl, F.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Genovesi, P.; et al. Scientists’ warning on invasive alien species. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pagad, S.; Pyšek, P.; van Kleunen, M.; Winter, M.; et al. Global rise in emerging alien species results from increased accessibility of new source pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2264–E2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, S.A.; Worm, B. Ecological role of large benthic decapods in marine ecosystems: A review. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 469, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaka-Kudla, M.L. Crustaceans. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity; Levin, S.A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 915–943. [Google Scholar]
- Silliman, B.R.; Bertness, M.D. A trophic cascade regulates salt marsh primary production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10500–10505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, M.R.; Griffen, B.D. Burrowing behavior and burrowing energetics of a bioindicator under human disturbance. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 14205–14216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Wang, A.; Li, S.; Cui, B.; Bai, J.; Shao, D. Crab contributions as an ecosystem engineer to sediment turnover in the Yellow River Delta. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1019176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, F.; Valiela, I.; Iribarne, O.; Martinetto, P.; Alberti, J. Impact of burrowing crabs on C and N sources, control, and transformations in sediments and food webs of SW Atlantic estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 293, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Jiang, L.F.; Bertness, M.D.; Fang, C.M.; Chen, J.K.; Hara, T.; Li, B. Bioturbation of burrowing crabs promotes sediment turnover and carbon and nitrogen movements in an estuarine salt marsh. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanjul, E.; Escapa, M.; Montemayor, D.; Addino, M.; Alvarez, M.F.; Grela, M.A.; Iribarne, O. Effect of crab bioturbation on organic matter processing in South West Atlantic intertidal sediments. J. Sea Res. 2015, 95, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbroich, A.; Michaud, E.; Stieglitz, T.; Fromard, F.; Gardel, A.; Tavares, M.; Thouzeau, G. Brachyuran crab community structure and associated sediment reworking activities in pioneer and young mangroves of French Guiana, South America. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 182, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, E.M.; Angelini, C.; Govers, L.L.; Christianen MJ, A.; Altieri, A.H.; van der Reijden, K.J.; Silliman, B.R.; van de Koppel, J.; van der Geest, M.; van Gils, J.A.; et al. How habitat-modifying organisms structure the food web of two coastal ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20152326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk-Petersen, J.; Renaud, P.; Anisimova, N. Establishment and ecosystem effects of the alien invasive red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the Barents Sea—A review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 68, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta, J.; Wernberg, T.; Jänes, H.; Kotta, I.; Nurkse, K.; Pärnoja, M.; Orav-Kotta, H. Novel crab predator causes marine ecosystem regime shift. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, B.R.; Francis, F.T.; Côté, I.M.; Therriault, T.W. Habitat alteration by invasive European green crab (Carcinus maenas) causes eelgrass loss in British Columbia, Canada. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 3607–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, A.; Wagner, K.; Buschbaum, C. Prey preferences, consumption rates and predation effects of Asian shore crabs (Hemigrapsus takanoi) in comparison to native shore crabs (Carcinus maenas) in northwestern Europe. Mar. Biodivers. 2021, 51, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; Franch, N.; Bernardo-Madrid, R.; López, V.; Abelló, P.; Queral, J.M.; Mancinelli, G. Severe, rapid and widespread impacts of an Atlantic blue crab invasion. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänfling, B.; Edwards, F.; Gherardi, F. Invasive alien Crustacea: Dispersal, establishment, impact and control. BioControl 2011, 56, 573–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rato, L.D.; Crespo, D.; Lemos, M.F. Mechanisms of bioinvasions by coastal crabs using integrative approaches—A conceptual review. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta, J.; Ojaveer, H. Rapid establishment of the alien crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould) in the Gulf of Riga. Est. J. Ecol. 2012, 61, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, W.; Miura, O.; Kaiser, F.; Geffray, M.; Katsube, T.; Urabe, J. Evidence of multiple introductions and genetic admixture of the Asian brush-clawed shore crab Hemigrapsus takanoi (Decapoda: Brachyura: Varunidae) along the Northern European coast. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridonov, V.A.; Zalota, A.K. Understanding and forecasting dispersal of non-indigenous marine decapods (Crustacea: Decapoda) in East European and North Asian waters. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2017, 97, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortegón, E.; Jenkins, S.; Galil, B.S.; Drake, P.; Cuesta, J.A. Accelerated invasion of decapod crustaceans in the southernmost point of the Atlantic coast of Europe: A non-natives’ hot spot? Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3487–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.E.; Forsström, T.; von Numers, M.; Vesakoski, O. The North American mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould, 1841) in newly colonized Northern Baltic Sea: Distribution and ecology. Aquat. Invasions 2013, 8, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turoboyski, K. Biology and ecology of the crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii ssp. tridentatus. Mar. Biol. 1973, 23, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normant, M.; Gibowicz, M. Salinity induced changes in haemolymph osmolality and total metabolic rate of the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii Gould, 1841 from Baltic coastal waters. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 355, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnio, K.; Törnroos, A.; Björklund, C.; Bonsdorff, E. Food web positioning of a recent coloniser: The North American Harris mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould, 1841) in the northern Baltic Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2015, 10, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, K.; Boström, C. Habitat expansion of the Harris mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould, 1841) in the northern Baltic Sea: Potential consequences for the eelgrass food web. BioInvasions Rec. 2016, 5, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybczyk, A.; Czerniejewski, P. Body weight, morphometry, and diet of the mud crab, Rhithropanopeus harrisii tridentatus (Maitland, 1874) in the Odra estuary, Poland. Crustaceana 2008, 81, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Hegele-Drywa, J.; Normant, M. Feeding ecology of the American crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Crustacea, Decapoda) in the coastal waters of the Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 2009, 51, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsström, T.; Fowler, A.E.; Manninen, I.; Vesakoski, O. An introduced species meets the local fauna: Predatory behavior of the crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii in the Northern Baltic Sea. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 2729–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkse, K.; Kotta, J.; Orav-Kotta, H.; Pärnoja, M.; Kuprijanov, I. Laboratory analysis of the habitat occupancy of the crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould) in an invaded ecosystem: The north-eastern Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jormalainen, V.; Gagnon, K.; Sjöroos, J.; Rothäusler, E. The invasive mud crab enforces a major shift in a rocky littoral invertebrate community of the Baltic Sea. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liversage, K.; Kotta, J.; Kuprijanov, I.; Rätsep, M.; Nõomaa, K. A trophic cascade facilitates native habitat providers within assemblages of multiple invasive marine species. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokko, K.; Kotta, J.; Orav-Kotta, H.; Nurkse, K.; Pärnoja, M. Introduction of a functionally novel consumer to a low diversity system: Effects of the mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii on meiobenthos. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 201, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkse, K.; Kotta, J.; Rätsep, M.; Kotta, I.; Kreitsberg, R. Experimental evaluation of the effects of the novel predators, round goby and mud crab on benthic invertebrates in the Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2018, 98, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikström, S.A.; Kautsky, L. Structure and diversity of invertebrate communities in the presence and absence of canopy-forming Fucus vesiculosus in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 72, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Lenth, R.L. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.8.5. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Hartig, F. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models. R Package Version 0.4.6. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=DHARMa (accessed on 29 April 2023).
- Hegele-Drywa, J.; Normant, M. Effect of temperature on physiology and bioenergetics of adult Harris mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould, 1841) from the southern Baltic Sea. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2014, 43, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollebone, A.L.; Hay, M.E. An invasive crab alters interaction webs in a marine community. Biol. Invasions 2008, 10, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Wallentinus, I.; Zenetos, A.; Leppäkoski, E.; Çinar, M.E.; Oztürk, B.; Grabowski, M.; Golani, D.; Cardoso, A.C. Impacts of invasive alien marine species on ecosystem services and biodiversity: A pan-European review. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 391–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geburzi, J.C.; Brandis, D.; Buschbaum, C. Recruitment patterns, low cannibalism and reduced interspecific predation contribute to high invasion success of two Pacific crabs in northwestern Europe. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 200, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M.T.; Müller-Karulis, B.; Järv, L.; Kotta, J.; Martin, G.; Minde, A.; Põllumäe, A.; Razinkovas, A.; Strake, S.; Bucas, M.; et al. Analysis of trophic networks and carbon flows in south-eastern Baltic coastal ecosystems. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 81, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.R.; Kadin, M.; Nascimento, F.J.; Tamelander, T.; Törnroos, A.; Bonaglia, S.; Bonsdorff, E.; Brüchert, V.; Gårdmark, A.; Järnström, M.; et al. The importance of benthic–pelagic coupling for marine ecosystem functioning in a changing world. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 2179–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, P.L.; Sotka, E.E. Non-consumptive predator effects indirectly influence marine plant biomass and palatability. J. Ecol. 2011, 99, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M.; Buchholz, B.; Winde, V.; Golomb, D.; Guy-Haim, T.; Müller, J.; Rilov, G.; Scotti, M.; Böttcher, M.E. A mesocosm concept for the simulation of near-natural shallow underwater climates: The Kiel Outdoor Benthocosms (KOB). Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2015, 13, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansch, C.; Hiebenthal, C. A new mesocosm system to study the effects of environmental variability on marine species and communities. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2019, 17, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).