Telemetry and Accelerometer Tracking of Green Toads in an Urban Habitat: Methodological Notes and Preliminary Findings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Species
2.2. Study Site
2.3. Tracking Device
2.4. Field Methods
2.5. Tracking Analysis
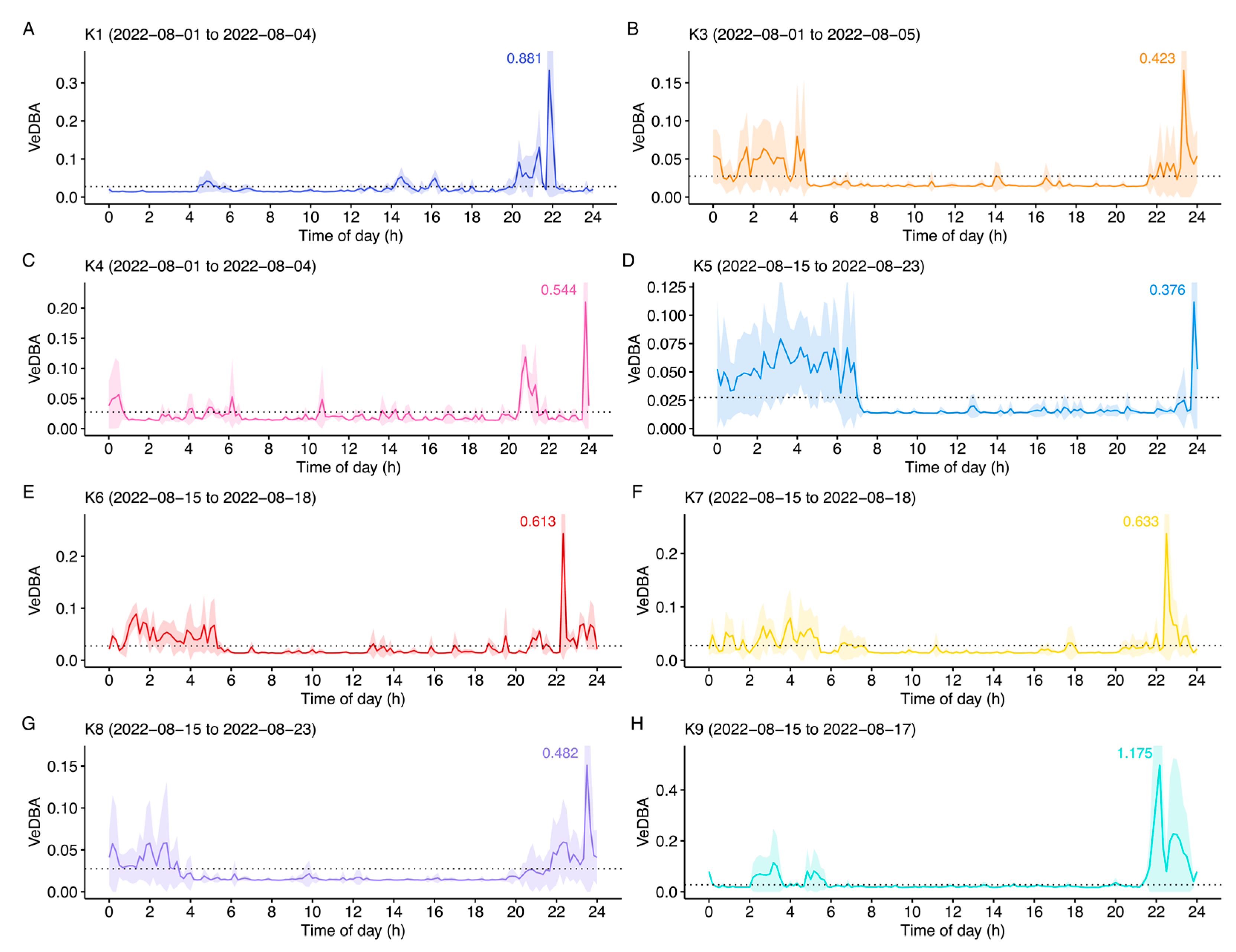
3. Results

4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cline, T.J.; Ohlberger, J.; Schindler, D.E. Effects of Warming Climate and Competition in the Ocean for Life-Histories of Pacific Salmon. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flack, A.; Fiedler, W.; Blas, J.; Pokrovsky, I.; Kaatz, M.; Mitropolsky, M.; Aghababyan, K.; Fakriadis, I.; Makrigianni, E.; Jerzak, L.; et al. Costs of Migratory Decisions: A Comparison across Eight White Stork Populations. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsch, U. Mini-Review: The Orientation Behaviour of Amphibians. Herpetol. J. 1991, 1, 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, T.; Shine, R.; Olsson, M.; Wittzell, H. Restoration of an Inbred Adder Population. Nature 1999, 402, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.W.; Fog, K.; Damgaard, C. Habitat Fragmentation Causes Bottlenecks and Inbreeding in the European Tree Frog (Hyla arborea). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, J.A.; Champlin, D.M.; Gutjahr-Gobell, R.; Grear, J.S.; Kuhn, A.; McGreevy, T.J.; Roth, A.; Bagley, M.J.; Nacci, D.E. Population Genetic Diversity and Fitness in Multiple Environments. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, E.M. ECOLOGY | Biological Impacts of Deforestation and Fragmentation. In Encyclopedia of Forest Sciences; Burley, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 85–90. ISBN 978-0-12-145160-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzat, J.L. Conservation Genetics of Population Bottlenecks: The Role of Chance, Selection, and History. Conserv. Genet. 2010, 11, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsch, U. Migration and Orientation in Anuran Amphibians. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 1990, 2, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, E. Effects of Habitat Fragmentation on Amphibians: What Do We Know and Where Do We Go From Here? In Proceedings of the a Conference on the Biology and Management of Species and Habitats at Risk, B.C. Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks, Victoria, B.C. and University College of the Cariboo, Kamloops, BC, Canada, 15–19 February 1999; pp. 885–894. [Google Scholar]
- Darcovich, K.; O’Meara, J. An Olympic Legacy: Green and Golden Bell Frog Conservation at Sydney Olympic Park 1993–2006. Aust. Zool. 2008, 34, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazgajska, J.; Mazgajski, T.D. Two Amphibian Species in the Urban Environment: Changes in the Occurrence, Spawning Phenology and Adult Condition of Common and Green Toads. Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staufer, M.; Burgstaller, S.; Horvath, A.; Landler, L. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Local Sex Ratios in a Suburban Population of the European Green Toad Bufotes viridis. under review.
- Valkanova, M.V.; Mollov, I.A.; Nikolov, B.N. Mortalities of the Green Toad, Epidalea viridis (Laurenti, 1768) in Urban Environment: A Case Study from the City of Plovdiv. Ecol. Balk. 2009, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Stöck, M.; Roth, P.; Podloucky, R.; Grossenbacher, K. Wechselkröten—Unter Berücksichtigung von Bufo viridis virdis Laurenti, 1768; Bufo variabilis (Pallas, 1769); Bufo boulengeri Lataste, 1879; Bufo balearicus Böttger, 1880 Und Bufos siculus Stöck, Sicilia, Belfiore, Lo Brutto, Lo Valvo Und Arculeo, 2008. In Handbuch der Reptilien und Amphibien Europas; AULA Verlag: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 413–498. [Google Scholar]
- Indermaur, L.; Gehring, M.; Wehrle, W.; Tockner, K.; Naef-Daenzer, B. Behavior-Based Scale Definitions for Determining Individual Space Use: Requirements of Two Amphibians. Am. Nat. 2009, 173, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blab, J. Tierwelt in der Zivilisationslandschaft, Tl.2, Raumeinbindung und Biotopnutzung bei Reptilien und Amphibien im Drachenfelser Ländchen; Kilda: Bonn, Germany, 1991; ISBN 978-3-88949-175-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sistani, A.; Burgstaller, S.; Gollmann, G.; Landler, L. The European Green Toad, Bufotes viridis, in Donaufeld (Vienna, Austria): Status and Size of the Population. Herpetozoa 2021, 34, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landler, L.; Burgstaller, S.; Schweiger, S. Land-Use Preferences of the European Green Toad (Bufotes viridis) in the City of Vienna (Austria): The Importance of Open Land in Urban Environments. Front. Zool. 2023, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.S.; Herman, L.M.; Perry, A.; Lawton, W.S.; Straley, J.M.; Wolman, A.A.; Kaufman, G.D.; Winn, H.E.; Hall, J.D.; Reinke, J.M.; et al. Migratory Movement and Population Structure of Humpback Whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) in the Central and Eastern North Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 31, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollmann, G.; Gollmann, B. Recapture Study of a Bombina variegata Population: Survival and Dispersal. Beitr. Okol. 2000, 4, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Stickel, L.F.; Stickel, W.H.; Schmid, F.C. Ecology of a Maryland Population of Black Rat Snakes (Elaphe o. obsoleta). Am. Midl. Nat. 1980, 103, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebblewhite, M.; Haydon, D.T. Distinguishing Technology from Biology: A Critical Review of the Use of GPS Telemetry Data in Ecology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.S.; Hebblewhite, M.; Goodrich, J.M.; Miquelle, D.G. Review of Research Methodologies for Tigers: Telemetry. Integr. Zool. 2010, 5, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duret, C.; Pille, F.; Denoël, M. Efficiency of Aquatic PIT-Tag Telemetry, a Powerful Tool to Improve Monitoring and Detection of Marked Individuals in Pond Environments. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztatecsny, M.; Schabetsberger, R. Into Thin Air: Vertical Migration, Body Condition, and Quality of Terrestrial Habitats of Alpine Common Toads, Bufo bufo. Can. J. Zool. 2005, 83, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentinger, J.E.; Börger, L.; Holton, M.D.; Jafari-Marandi, R.; Norman, D.A.; Smith, B.K.; Oppenheimer, S.F.; Strickland, B.K.; Wilson, R.P.; Street, G.M. A Probabilistic Framework for Behavioral Identification from Animal-Borne Accelerometers. Ecol. Model. 2022, 464, 109818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.P.; Reynolds, S.D.; Potts, J.R.; Redcliffe, J.; Holton, M.; Buxton, A.; Rose, K.; Norman, B.M. Highlighting When Animals Expend Excessive Energy for Travel Using Dynamic Body Acceleration. iScience 2022, 25, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.D.; Kays, R.; Wikelski, M.; Wilson, R.; Klimley, A. Observing the Unwatchable through Acceleration Logging of Animal Behavior. Anim. Biotelem. 2013, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Wolfe, L.; Davis, T.; Kendall, T.; Richter, B.; Wang, Y.; Bryce, C.; Elkaim, G.H.; Wilmers, C.C. Instantaneous Energetics of Puma Kills Reveal Advantage of Felid Sneak Attacks. Science 2014, 346, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Lowe, J.C.; Roskilly, K.; Hudson, P.E.; Golabek, K.A.; McNutt, J.W. Locomotion Dynamics of Hunting in Wild Cheetahs. Nature 2013, 498, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsey, L.G.; White, C.R. Measuring Energetics and Behaviour Using Accelerometry in Cane Toads Bufo marinus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidder, O.R.; di Virgilio, A.; Hunter, J.S.; McInturff, A.; Gaynor, K.M.; Smith, A.M.; Dorcy, J.; Rosell, F. Monitoring Canid Scent Marking in Space and Time Using a Biologging and Machine Learning Approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlmann, G.; O’Riain, M.J.; Hopkins, P.W.; O’Sullivan, J.; Holton, M.D.; Shepard, E.L.C.; King, A.J. Identification of Behaviours from Accelerometer Data in a Wild Social Primate. Anim. Biotelem. 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, S.; Sicks, F.; Berger, A. Behaviour Classification on Giraffes (Giraffa Camelopardalis) Using Machine Learning Algorithms on Triaxial Acceleration Data of Two Commonly Used GPS Devices and Its Possible Application for Their Management and Conservation. Sensors 2021, 21, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattenborg, N.C.; Voirin, B.; Cruz, S.M.; Tisdale, R.; Dell’Omo, G.; Lipp, H.-P.; Wikelski, M.; Vyssotski, A.L. Evidence That Birds Sleep in Mid-Flight. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollmann, G. Rote Liste der in Österreich Gefährdeten Lurche (Amphibia) und Kriechtiere (Reptilia). In Rote Listen gefährdeter Tiere Österreichs; Grüne Reihe: Vienna, Austria, 2007; pp. 39–62. [Google Scholar]
- Henle, K.; Dubois, A.; Rimpp, K.; Vershinin, V. Mass Anomalies in Green Toads (Bufotes viridis) at a Quarry in Roßwag, Germany: Inbred Hybrids, Radioactivity or an Unresolved Case? Mertensiella 2017, 25, 185–242. [Google Scholar]
- Rogell, B.; Berglund, A.; Laurila, A.; Höglund, J. Population Divergence of Life History Traits in the Endangered Green Toad: Implications for a Support Release Programme. J. Zool. 2011, 285, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staufer, M. Die Wechselkröten der Simmeringer Haide in Wien. ÖGH-Aktuell 2022, 60, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cabela, A.; Gressler, S.; Teufl, H.; Ellinger, N. Neu Geschaffene Uferstrukturen im Stauraum Freudenau und Folienteiche auf der Wiener Donauinsel: Eine Studie über ihre Wirksamkeit als Trittsteinbiotope für Amphibien. Denisia 2003, 10, 101–142. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, T.; Saçdanaku, E.; Duda, M.; Bego, F. Amphibian and Reptile Fauna of the Vjosa River, Albania. Acta ZooBot Austria 2018, 155, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, M.S. Osmotic Regulation in the Green Toad (Bufo viridis). J. Exp. Biol. 1962, 39, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altobelli, J.T.; Dickinson, K.J.M.; Godfrey, S.S.; Bishop, P.J. Methods in Amphibian Biotelemetry: Two Decades in Review. Austral Ecol. 2022, 47, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.P.; Rose, K.A.; Gunner, R.; Holton, M.D.; Marks, N.J.; Bennett, N.C.; Bell, S.H.; Twining, J.P.; Hesketh, J.; Duarte, C.M.; et al. Animal Lifestyle Affects Acceptable Mass Limits for Attached Tags. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20212005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indermaur, L.; Schmidt, B.R.; Tockner, K. Effect of Transmitter Mass and Tracking Duration on Body Mass Change of Two Anuran Species. Amphib.-Reptil. 2008, 29, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landler, L.; Burgstaller, S.; Spießberger, M.; Horvath, A.; Zhelev, Z.; Mollov, I.A.; Sinsch, U.; Nepita, J.; Schwabel, F.; Kuhn, W.; et al. A Unified Approach to Analysis of Body Condition in Green Toads. Diversity 2023, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Government Austria Basemap.at. Available online: https://basemap.at/ (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2022 Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowle, M.; Srinivasan, A. Data.Table: Extension of ‘Data.Frame’, R Package Version 1.14.2. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=data.table (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Grolemund, G.; Wickham, H. Dates and Times Made Easy with lubridate. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 40, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. Ggpubr: “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots 2020. R Package Version 0.4.0. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Pedersen, T.L. Patchwork: The Composer of Plots 2020. R Package Version 1.1.2. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=patchwork (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Wickham, H.; Seidel, D. Scales: Scale Functions for Visualization; 2022. R Package Version 1.2.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=scales (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Calenge, C. The Package “Adehabitat” for the R Software: A Tool for the Analysis of Space and Habitat Use by Animals. Ecol. Model. 2006, 197, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, H.; Kadel, K. Beobachtungen Zum Aktivitätsrythums von Kreuzkröten (Bufo calamita), Wechselkröten (Bufo viridis) und deren Bastarden. Salamandra 1971, 7, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Jungfer, W. Beiträge zur Biologie der Erdkröte (Bufo bufo L.) mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Wanderung zu den Laichgewässern. Z. Morphol. Ökol. Tiere 1943, 40, 117–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsch, U.; Schneider, H.; Tarkhnishvili, N.D. Bufo bufo Superspezies—Erdkröten-Artenkreis—Taxon bufo (Linnaeus, 1758)—Erdkröte—Taxon gredosicola L. Müll Er Und Hellm Ich 1935—Gredoserdkröte—Taxon spinosus Daudin, 1803—Riesenerdkröte—Taxon verrucosissimus (Pallas, 1811)—Kolchische Erdkröte. In Handbuch der Reptilien und Amphibien Europas; AULA Verlag: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 187–337. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsch, U. Bufo calamita Laurenti, 1768—Kreuzkröte*. In Handbuch der Reptilien und Amphibien Europas; AULA Verlag: Wiebelsheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 339–413. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, H.J.; Taylor, L.A.; Benhamou, S.; Bijleveld, A.I.; Clay, T.A.; de Grissac, S.; Demšar, U.; English, H.M.; Franconi, N.; Gómez-Laich, A. Optimizing the Use of Biologgers for Movement Ecology Research. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; da Silva, V.M. Tracking Aquatic Vertebrates in Dense Tropical Forest Using VHF Telemetry. Mar. Technol. Soc. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 1998, 32, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Glista, D.J.; Devault, T.L.; Dewoody, J.A. Vertebrate Road Mortality Predominantly Impacts Amphibians. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 11, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Puky, M. Amphibian Road Kills: A Global Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Ecology and Transportation, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 29 August 2005; pp. 325–338. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, J.P.; Shriver, W.G. Can Road Mortality Limit Populations of Pool-Breeding Amphibians? Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 13, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio, M.S.; Rossetti, M.R.; Videla, M. Negative Effects of Urbanization on Terrestrial Arthropod Communities: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1412–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, S.; Gehrt, S.D.; Wiggers, E.P. Influences of Anthropogenic Resources on Raccoon (Procyon lotor) Movements and Spatial Distribution. J. Mammal. 2004, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harveson, P.M.; Lopez, R.R.; Collier, B.A.; Silvy, N.J. Impacts of Urbanization on Florida Key Deer Behavior and Population Dynamics. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 134, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, J.; Schley, L.; Roper, T.J. Socio-spatial Organization of Urban Stone Martens. J. Zool. 2009, 277, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, H.; Besnard, A.; Cote, J.; Laporte, M.; Bonnaire, E.; Pichenot, J.; Schtickzelle, N.; Bellec, A.; Joly, P.; Léna, J.-P. Anthropogenic Disturbance Drives Dispersal Syndromes, Demography, and Gene Flow in Amphibian Populations. Ecol. Monogr. 2020, 90, e01406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, K. Individuality in the Use of Orientation Cues by Green Frogs. Anim. Behav. 1980, 28, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Antonia, P.; Sinsch, U. In Search of Water: Orientation Behaviour of Dehydrated Natterjack Toads, Bufo calamita. Anim. Behav. 2001, 61, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spieẞberger, M.; Burgstaller, S.; Mesnil, M.; Painter, M.S.; Landler, L. Telemetry and Accelerometer Tracking of Green Toads in an Urban Habitat: Methodological Notes and Preliminary Findings. Diversity 2023, 15, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030328
Spieẞberger M, Burgstaller S, Mesnil M, Painter MS, Landler L. Telemetry and Accelerometer Tracking of Green Toads in an Urban Habitat: Methodological Notes and Preliminary Findings. Diversity. 2023; 15(3):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030328
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpieẞberger, Magdalena, Stephan Burgstaller, Marion Mesnil, Michael S. Painter, and Lukas Landler. 2023. "Telemetry and Accelerometer Tracking of Green Toads in an Urban Habitat: Methodological Notes and Preliminary Findings" Diversity 15, no. 3: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030328
APA StyleSpieẞberger, M., Burgstaller, S., Mesnil, M., Painter, M. S., & Landler, L. (2023). Telemetry and Accelerometer Tracking of Green Toads in an Urban Habitat: Methodological Notes and Preliminary Findings. Diversity, 15(3), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030328






