Are Intermittent Rivers in the Karst Mediterranean Region of the Balkans Suitable as Mayfly Habitats?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
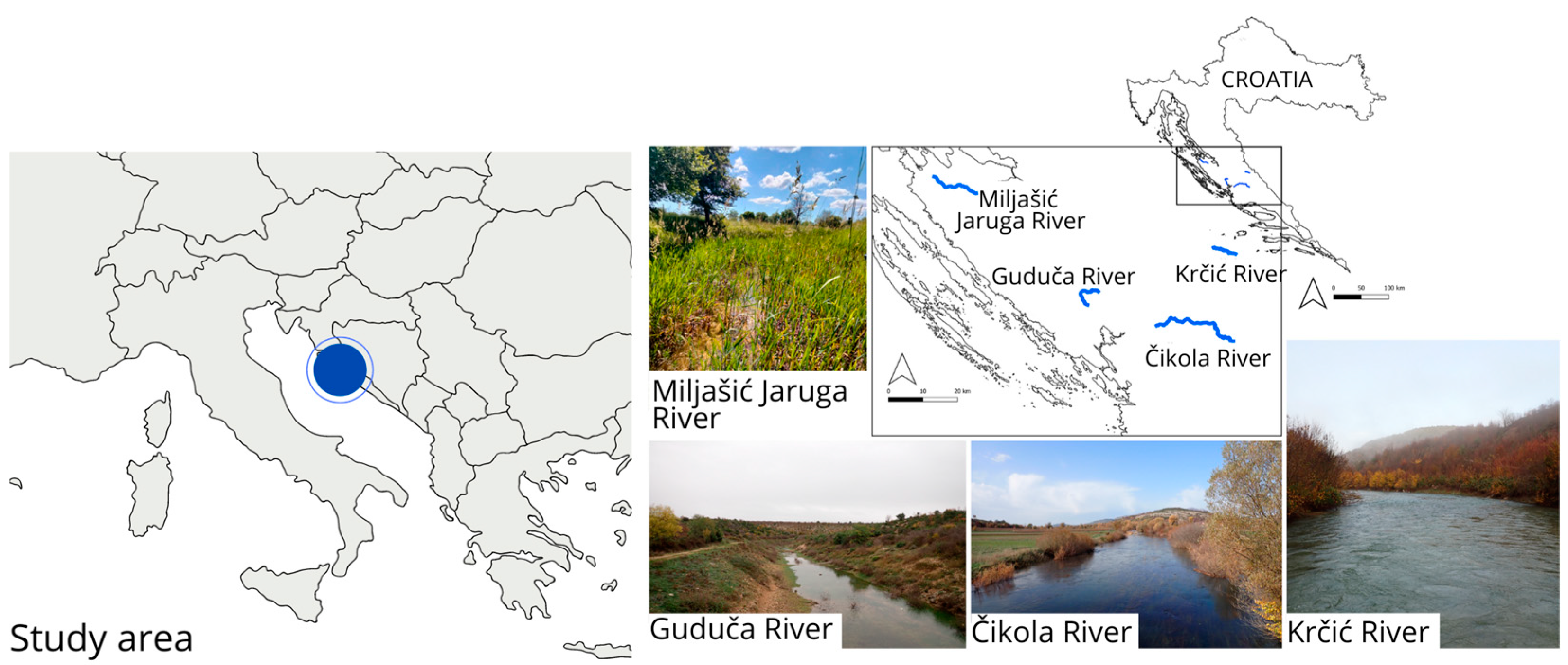
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Environmental Variables
2.3. Mayfly Sampling and Identification
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
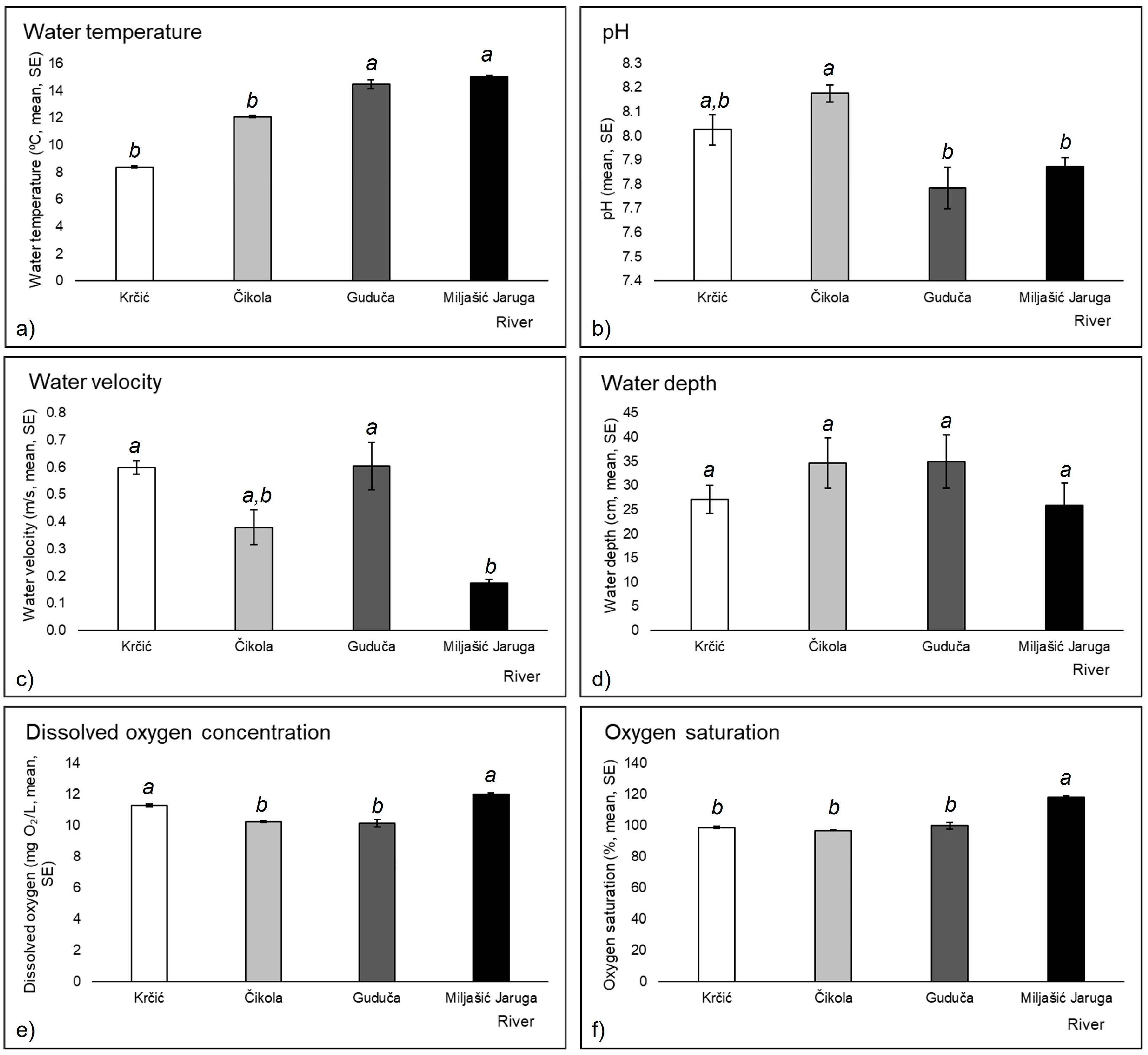
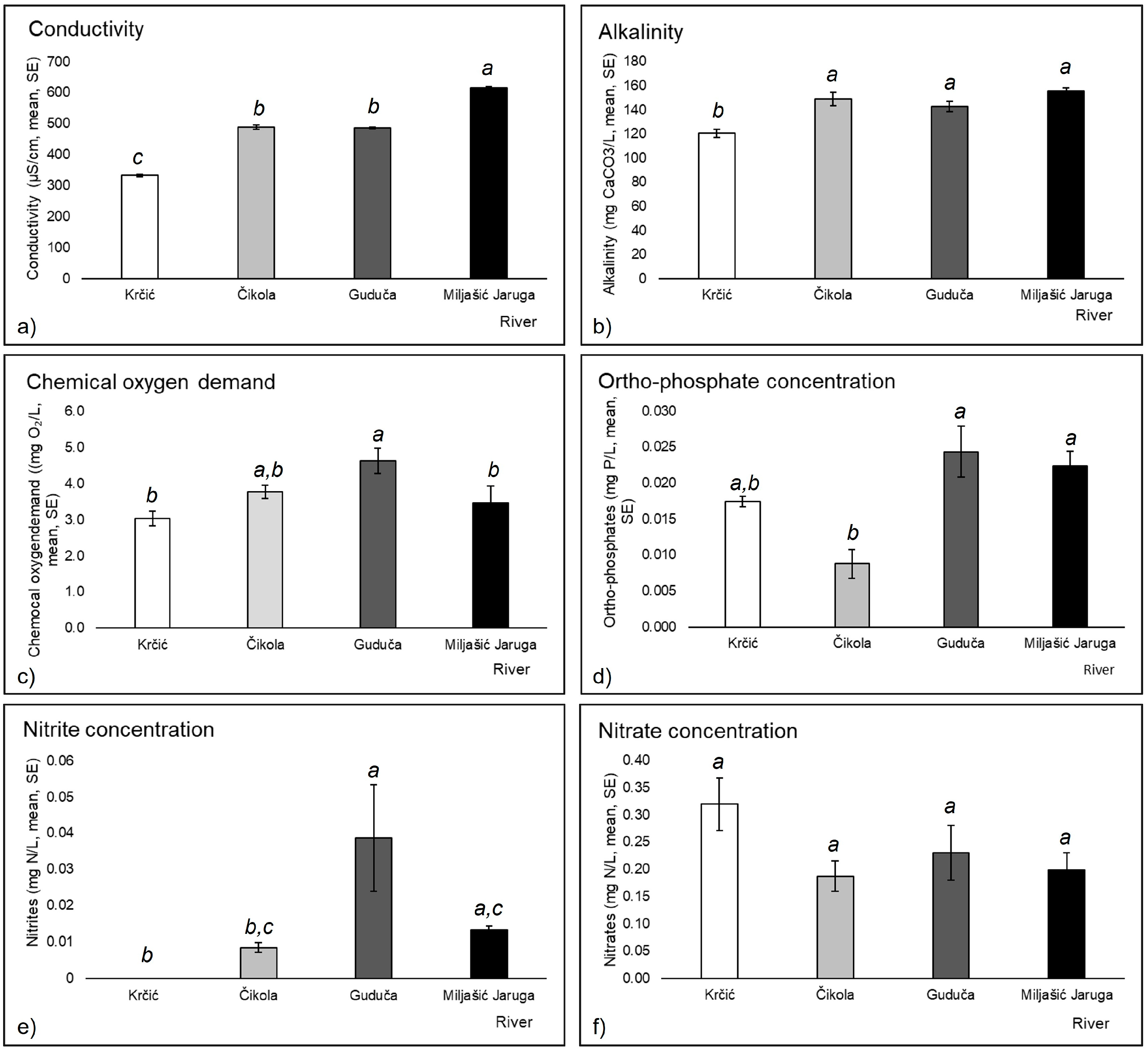
3.1. Environmental Variables
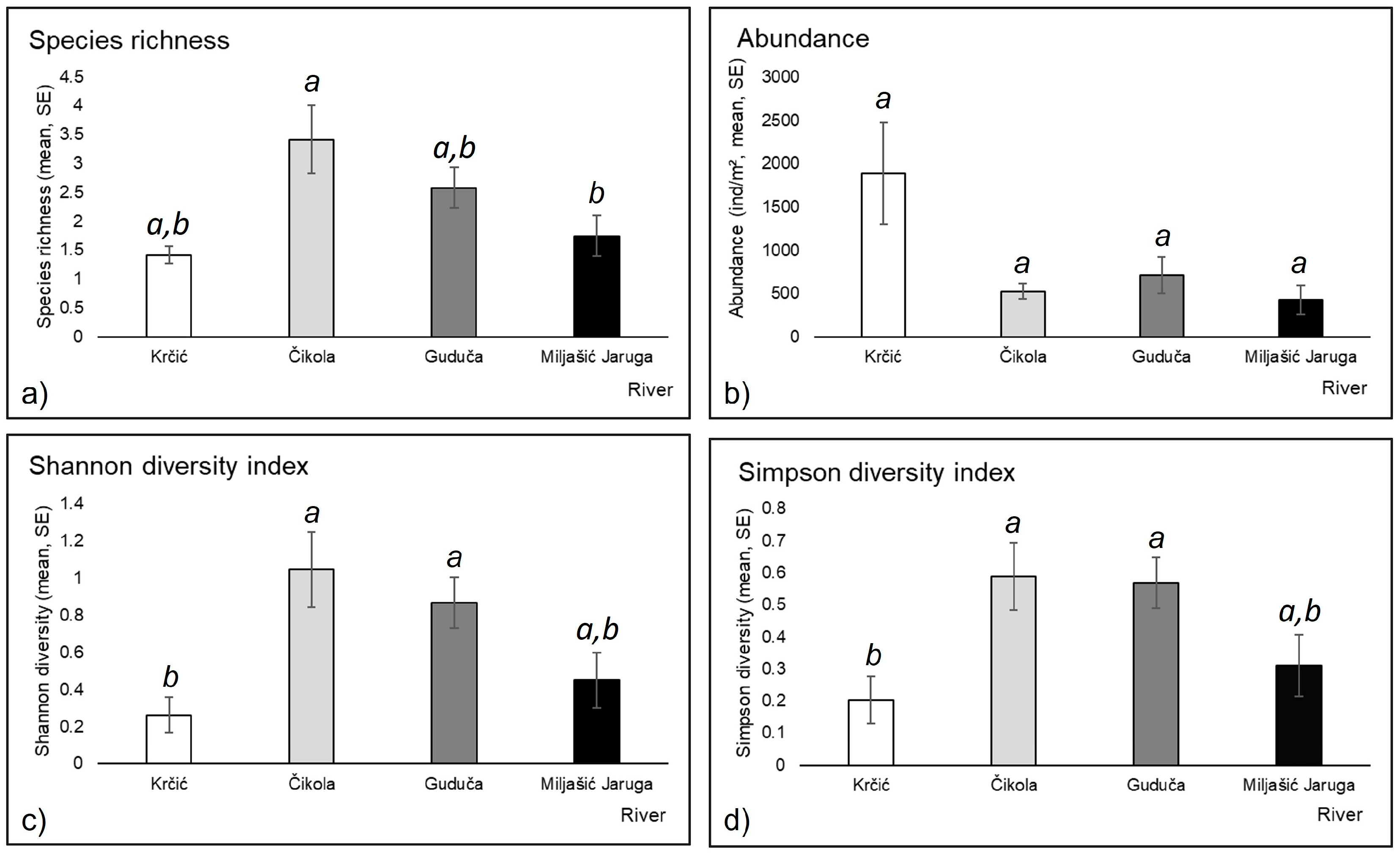
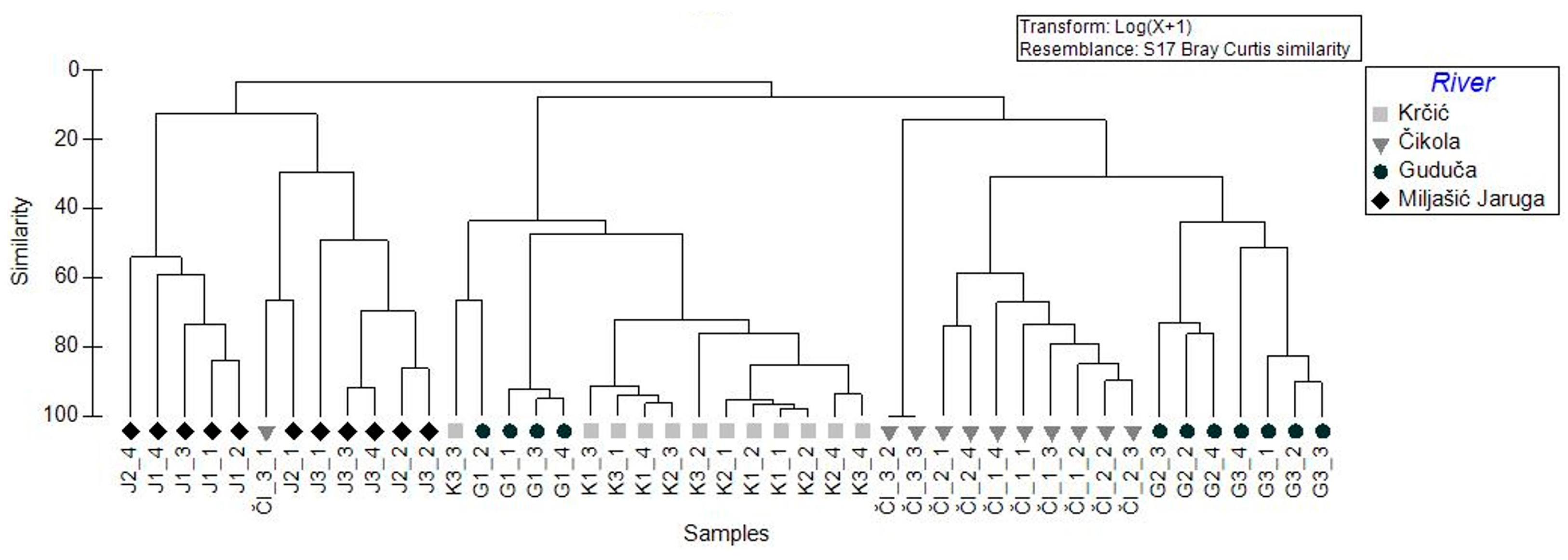
3.2. Mayfly Assemblages
3.3. Mayfly Assemblages and Environmental Variables
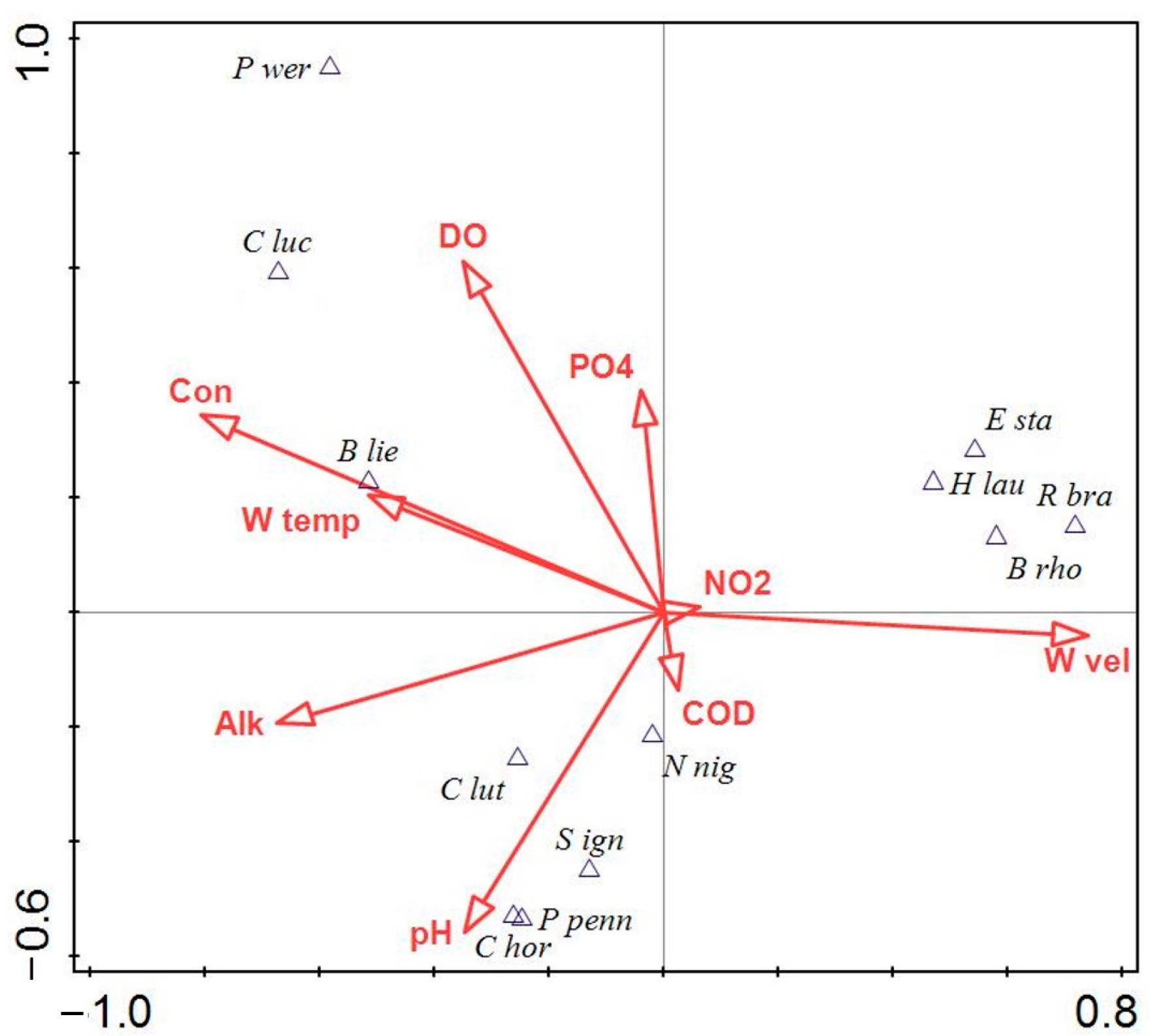
3.4. Mayfly Species and Environmental Variables
3.5. Mayflies and Microhabitats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arthington, A.H.; Bernardo, J.M.; Ilhéu, M. Temporary Rivers: Linking Ecohydrology, Ecological Quality and Reconciliation Ecology. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, K.H.; Jaeger, K.L.; Goss, C.W.; Fritz, K.M.; Goebel, P.C. Understanding Controls on Flow Permanence in Intermittent Rivers to Aid Ecological Research: Integrating Meteorology, Geology and Land Cover. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, K.; Leigh, C.; Sauquet, E.; Kennard, M.; Datry, T.; Boulton, A. Flow Regimes in Intermittent Rivers and Ephemeral Streams. In Intermittent Rivers and Ephemeral Streams—Ecology and Management; Datry, T., Bonada, N., Boulton, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 51–58. ISBN 9780128038352. [Google Scholar]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Barca, E.; Pappagallo, G.; Lo Porto, A. Simulating Ecologically Relevant Hydrological Indicators in a Temporary River System. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 180, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larned, S.T.; Datry, T.; Arscott, D.B.; Tockner, K. Emerging Concepts in Temporary-River Ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 717–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magand, C.; Alves, M.H.; Calleja, E.; Datry, T.; Dörflinger, G.; England, J.; Gallart, F.; Gomez, R.; Jorda-Capdevila, D.; Marti, E.; et al. Intermittent Rivers and Ephemeral Streams: What Water Managers Need to Know; European Cooperation in Science and Technology: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datry, T.; Larned, S.T.; Fritz, K.M.; Bogan, M.T.; Wood, P.J.; Meyer, E.I.; Santos, A.N. Broad-Scale Patterns of Invertebrate Richness and Community Composition in Temporary Rivers: Effects of Flow Intermittence. Ecography 2014, 37, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datry, T.; Larned, S.T.; Tockner, K. Intermittent Rivers: A Challenge for Freshwater Ecology. BioScience 2014, 64, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, C.; Boulton, A.J.; Courtwright, J.L.; Fritz, K.; May, C.L.; Walker, R.H.; Datry, T. Ecological Research and Management of Intermittent Rivers: An Historical Review and Future Directions. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 1181–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Franssen, W.H.P.; Yearsley, J.R.; Ludwig, F.; Haddeland, I.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Kabat, P. Global River Discharge and Water Temperature under Climate Change. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, M.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Kingston, D.G.; Stagge, J.H.; Laaha, G.; Van Lanen, H.A.J.; Scholz, P.; Chelcea, S.M.; Haslinger, K. The European 2015 Drought from a Climatological Perspective. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1397–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pařil, P.; Polášek, M.; Loskotová, B.; Straka, M.; Crabot, J.; Datry, T. An Unexpected Source of Invertebrate Community Recovery in Intermittent Streams from a Humid Continental Climate. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 1971–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, M.; Polášek, M.; Syrovátka, V.; Stubbington, R.; Zahrádková, S.; Němejcová, D.; Šikulová, L.; Řezníčková, P.; Opatřilová, L.; Datry, T.; et al. Recognition of Stream Drying Based on Benthic Macroinvertebrates: A New Tool in Central Europe. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, M.; Polášek, M.; Csabai, Z.; Zweidick, O.; Graf, W.; Meyer, E.I.; Mišíková Elexová, E.; Lešťáková, M.; Pařil, P. Stream Drying Bioindication in Central Europe: A Biodrought Index Accuracy Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döll, P.; Müller Schmied, H.; Döll, P.; Müller Schmied, H. How Is the Impact of Climate Change on River Flow Regimes Related to the Impact on Mean Annual Runoff? A Global-Scale Analysis. ERL 2012, 7, 014037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, A.V.; Tzoraki, O.; Bruno, D.; Kaletová, T.; Mendoza-Lera, C.; Alamanos, A.; Brummer, M.; Datry, T.; De Girolamo, A.M.; Jakubínský, J.; et al. Rethinking Ecosystem Service Indicators for Their Application to Intermittent Rivers. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbington, R.; Acreman, M.; Acuña, V.; Boon, P.J.; Boulton, A.J.; England, J.; Gilvear, D.; Sykes, T.; Wood, P.J. Ecosystem Services of Temporary Streams Differ between Wet and Dry Phases in Regions with Contrasting Climates and Economies. People Nat. 2020, 2, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, M.; Leigh, C.; Datry, T.; Bini, L.M.; Bonada, N. Biodiversity in Perennial and Intermittent Rivers: A Meta-Analysis. Oikos 2017, 126, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.D.; Bass, J.A.B. Long-Term Resilience and Short-Term Vulnerability of South Winterbourne Macroinvertebrates. Proc. Dorset Nat. Hist. Archaeol. Soc. 2013, 134, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Stubbington, R.; Bogan, M.T.; Bonada, N.; Boulton, A.J.; Datry, T.; Leigh, C.; Vander Vorste, R. The Biota of Intermittent Rivers and Ephemeral Streams. In Intermittent Rivers and Ephemeral Streams—Ecology and Management; Datry, T., Bonada, N., Boulton, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 217–243. ISBN 9780128038352. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, J.M.; Humpesch, U.H.; Macan, T.T. Larvae of the British Ephemeroptera: A Key with Ecological Notes. Sci. Publ. Freshw. Biol. Assoc. 1988, 49, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Sartori, M.; Brittain, J.E. Order Ephemeroptera. In Thorp and Covich’s Freshwater Invertebrates: Ecology and General Biology; Thorp, J., Rodgers, D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 873–891. ISBN 9780123850270. [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind, E.; Soldán, T. The Mayflies of Europe (Ephemeroptera); Appolo Books: Ollerup, Denmark, 2012; ISBN 978-87-88757-45-3. [Google Scholar]
- Vilenica, M.; Brigić, A.; Kerovec, M.; Gottstein, S.; Ternjej, I. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Changes of Mayflies (Insecta, Ephemeroptera) in a Western Balkan Peat Bog. Zookeys 2016, 637, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Mičetić Stanković, V.; Sartori, M.; Kučinić, M.; Mihaljević, Z. Environmental Factors Affecting Mayfly Assemblages in Tufa-Depositing Habitats of the Dinaric Karst. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Bilić, M.; Mičetić Stanković, V.; Kučinić, M. Mayfly Ecological Traits in a European Karst Spring: Species, Microhabitats and Life Histories. Community Ecol. 2018, 19, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Brigić, A.; Sartori, M.; Mihaljević, Z. Microhabitat Selection and Distribution of Functional Feeding Groups of Mayfly Larvae (Ephemeroptera) in Lotic Karst Habitats. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2018, 419, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobus, L.M.; Macadam, C.R.; Sartori, M. Mayflies (Ephemeroptera) and Their Contributions to Ecosystem Services. Insects 2019, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilenica, M.; Vučković, N.; Mihaljević, Z. Littoral Mayfly Assemblages in South-East European Man-Made Lakes. J. Limnol. 2019, 78, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Kerovec, M.; Pozojević, I.; Mihaljević, Z. Mayfly Response to Different Stress Types in Small and Mid-Sized Lowland Rivers. Zookeys 2020, 980, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, C.D.; Hitt, N.P.; Smith, D.R.; Daily, J.P. Evaluating Bioassessment Designs and Decision Thresholds Using Simulation Techniques. Appl. Threshold Concepts Nat. Resour. Decis. Mak. 2014, 9781489980410, 157–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illies, J. Limnofauna Europaea. Gustav Fisch. Verl. 1978, i-xvi, 532. [Google Scholar]
- Šegota, T.; Filipčić, A.; Članak, S.; Zagreb, P.; Odsjek, G. Köppen’s Classification of Climates and the Problem of Corresponding Croatian Terminology. Geoadria 2003, 8, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaninović, K.; Gajić-Čapka, M.; Perčec Tadić, M.; Vučetić, M.; Milković, J.; Bajić, A.; Cindrić, K.; Cvitan, L.; Katušin, Z.; Kaučić, D.; et al. Climate Atlas of Croatia 1961–1990, 1971–2000; Zaninović, K., Ed.; Meteorological and Hydrological Service of Croatia: Zagreb, Croatia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Državni Hidrometeorološki Zavod Hrvatske. Available online: https://hidro.dhz.hr/ (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Miliša, M.; Mihaljević, Z.; Pozojević, I. Report on Fitting a Macroinvertebrate Classification Method with the Results of the Completed Intercalibration of the MED GIG (R-M5); Technical report; University of Zagreb, Faculty of Science: Zagreb, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacci, O. Hydrological investigations of the Dinaric karst at the Krčić catchment and the river Krka springs (Yugoslavia). J. Hydrol. 1985, 82, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, O.; Jukić, D.; Ljubenkov, I. Definition of catchment area in karst: Case of the rivers Krčić and Krka, Croatia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 682–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, O. Ecohydrology of karst poljes and their vulnerability. In Dinaric Karst Poljes—Floods for Life; Sackl, P., Durst, R., Kotrošan, D., Stumberger, B., Eds.; Euronatur: Radolfzell, Germany, 2014; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacci, O.; Terzić, J.; Roje-Bonacci, T.; Frangen, T. An Intermittent Karst River: The Case of the Čikola River (Dinaric Karst, Croatia). Water 2019, 11, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Rumišek, M.; Rebrina, F.; Kepčija, R.M.; Medak, K.; Gulin, V.; Brigić, A. Dinaric Karst Intermittent Rivers Harbour Some Rare Mayflies (Insecta, Ephemeroptera). Nat. Croat. 2021, 30, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Rebrina, F.; Ružanović, L.; Gulin, V.; Brigić, A. Odonata Assemblages as a Tool to Assess the Conservation Value of Intermittent Rivers in the Mediterranean. Insects 2022, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, U. Rhithrogena braaschi n. Sp., Eine Neue Heptageniidae Aus Bulgarien (Insecta, Ephemeroptera). Entomol. Nachr. Berl. 1974, 18, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind, E.; Humpesch, U. Die Eintagsfliegen Zentraleuropas—Bestimmung und Ökologie; Naturhistorisches Museum: Vienna, Austria, 2001; Volume 4, p. 240. [Google Scholar]
- Waltz, R.D.; Mccafferty, W.P.; Thomas, A. Systematics of Alainites n. Gen., Diphetor, Indobaetis, Nigrobaetis n. Stat., and Takobia n. Stat. (Ephemeroptera, Baetidae). Bull. Soc. d’Hist. Nat. Toulouse 1994, 130, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- TlBCO Statistica 2017. StatSoft, Statistica 10.0 for Windows; StatSoft Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2017.
- Clarke, K.; Gorley, R. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial (Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research); PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ter Braak, C.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vilenica, M.; Ternjej, I.; Mihaljević, Z. What Is New in Croatian Mayfly Fauna? Nat. Croat. 2021, 30, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernfeind, E.; Moog, O. Mayflies (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) and the Assessment of Ecological Integrity: A Methodological Approach. Hydrobiologia 2000, 422, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffagni, A.; Cazzola, M.; Lopez-Rodriguez, M.; Alba-Tercedor, J.; Armanini, D.G. Distribution and Ecological Preferences of European Freshwater Organisms. Volume 3, Ephemeroptera; Schmidt-Kloiber, A., Hering, D., Eds.; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria; Moscow, Russia, 2009; Volume 3, ISBN 9789546425089. [Google Scholar]
- Buffagni, A.; Armanini, D.; Cazzola, M.; Alba-Tercedor, J.; Lopez-Rodriguez, M.; Murphy, J.; Sandin, L.; Schmidt-Kloiber, A. Dataset “Ephemeroptera”. The Taxa and Autecology Database for Freshwater Organisms, Version 8.0. Available online: www.freshwaterecology.info (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Schmidt-Kloiber, A.; Hering, D. www.freshwaterecology.info—An online tool that unifies, standardises and codifies more than 20,000 European freshwater organisms and their ecological preferences. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 53, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmedtje, U.; Colling, M. Ökologische Typisierung der Aquatischen Makrofauna; Bayerisches Landesamt für Wasserwirtschaft: Munchen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Goulart, M.; Callisto, M. Mayfly Diversity in the Brazilian Tropical Headwaters of Serra Do Cipó. Brazil. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2005, 48, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Previšić, A.; Ivković, M.; Popijač, A.; Vučković, I.; Kučinić, M.; Kerovec, M.; Gattolliat, J.L.; Sartori, M.; Mihaljević, Z. Mayfly (Insecta: Ephemeroptera) Assemblages of a Regulated Perennial Mediterranean River System in the Western Balkans. Biology 2016, 71, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Vidaković Maoduš, I.; Mihaljević, Z. The Impact of Hydromorphological Alterations on Mayfly Assemblages of a Mid-Sized Lowland River in South-Eastern Europe. Insects 2022, 13, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilenica, M.; Gattolliat, J.L.; Mihaljević, Z.; Sartori, M. Croatian Mayflies (Insecta, Ephemeroptera): Species Diversity and Distribution Patterns. Zookeys 2015, 523, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgić, I.; Vilenica, M.; Brigić, A.; Dorić, V.; Mihaljević, Z.; Previšić, A. Seasonal and Spatial Dynamics of the Aquatic Insect Communities of an Intermittent Mediterranean River. Limnologica 2022, 93, 125953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezníčková, P.; Soldán, T.; Pařil, P.; Zahrádková, S. Comparison of Mayfly (Ephemeroptera) Taxocenes of Permanent and Intermittent Central European Small Streams via Species Traits. Biologia 2010, 65, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenica, M.; Ivković, M. A Decade-Long Study on Mayfly Emergence Patterns. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 72, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, O. Fauna Aquatica Austriaca; Wasserwirtschaftskataster, Bundesministerium für Land-und Forstwirtschaft: Vienna, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sroka, P.; Klecka, J.; Boukal, D.S. Spatial Heterogeneity and Habitat Permanence Affect Community Assembly, Structure and Phenology of Mayflies (Ephemeroptera) in Sandpit Pools. Zoosymposia 2016, 11, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedieu, N.; Rhone, M.; Vigouroux, R.; Céréghino, R. Assessing the Impact of Gold Mining in Headwater Streams of Eastern Amazonia Using Ephemeroptera Assemblages and Biological Traits. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mayfly Species/ River | Species Codes | Krčić | Čikola | Guduča | Miljašić Jaruga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baetis liebenauae Keffermüller, 1974 | B lie | 42.3 | 346.7 | ||
| Baetis rhodani (Pictet, 1843) | B rho | 1872.7 | 198.7 | ||
| Nigrobaetis niger (Linnaeus, 1761) | N nig | 1.3 | 61.2 | 210.7 | |
| Centroptilum luteolum Müller, 1776 | C lut | 93.8 | 20.0 | 4.0 | |
| Procloeon pennulatum (Eaton, 1870) | P penn | 208.0 | |||
| Serratella ignita (Poda, 1761) | S ign | 87.2 | 36.0 | ||
| Caenis horaria (Linnaeus, 1758) | C hor | 35.7 | |||
| Caenis luctuosa (Burmeister, 1839) | C luc | 2.3 | |||
| Habrophlebia lauta Eaton, 1884 | H lau | 32.0 | |||
| Paraleptophlebia werneri Ulmer, 1919 | P wer | 78.7 | |||
| Ecdyonurus starmachi Sowa, 1971 | E sta | 217.3 | |||
| Rhithrogena braaschi Jacob, 1974 | R bra | 14.7 | |||
| Abundance (ind/m2) | 1888.7 | 528.2 | 714.7 | 431.7 | |
| Species richness | 3 | 6 | 6 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vilenica, M.; Rebrina, F.; Ružanović, L.; Rumišek, M.; Matoničkin Kepčija, R.; Brigić, A. Are Intermittent Rivers in the Karst Mediterranean Region of the Balkans Suitable as Mayfly Habitats? Diversity 2023, 15, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020155
Vilenica M, Rebrina F, Ružanović L, Rumišek M, Matoničkin Kepčija R, Brigić A. Are Intermittent Rivers in the Karst Mediterranean Region of the Balkans Suitable as Mayfly Habitats? Diversity. 2023; 15(2):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020155
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilenica, Marina, Fran Rebrina, Lea Ružanović, Mario Rumišek, Renata Matoničkin Kepčija, and Andreja Brigić. 2023. "Are Intermittent Rivers in the Karst Mediterranean Region of the Balkans Suitable as Mayfly Habitats?" Diversity 15, no. 2: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020155
APA StyleVilenica, M., Rebrina, F., Ružanović, L., Rumišek, M., Matoničkin Kepčija, R., & Brigić, A. (2023). Are Intermittent Rivers in the Karst Mediterranean Region of the Balkans Suitable as Mayfly Habitats? Diversity, 15(2), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020155








