The Greater Midlands—A Mid-Elevation Centre of Floristic Endemism in Summer-Rainfall Eastern South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Delineating and Defining the Greater Midlands Centre of Floristic Endemism
3.2. Profile of Spermatophyte Endemism
3.3. Extra-Limital Species: What Taxa Were Excluded?
4. Discussion
4.1. General Comments
4.2. Phytogeographical Context and Affiliations
4.3. Role of Geological and Lithological Drivers
4.4. Conservation Imperatives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plants of the World Online—World Checklist of Vascular Plants (2020) Version 2.0. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Available online: https://wcvp.science.kew.org/ (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Antonelli, A.; Fry, C.; Smith, R.J.; Simmonds, M.S.J.; Kersey, P.J.; Pritchard, H.W.; Abbo, M.S.; Acedo, C.; Adams, J.; Ainsworth, A.M.; et al. State of the World’s Plants and Fungi 2020; Royal Botanic Gardens Kew: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Joppa, L.N.; Roberts, D.L.; Myers, N.; Pimm, S.L. Biodiversity hotspots house most undiscovered plant species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13171–13176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joppa, L.N.; Roberts, D.L.; Pimm, S.L. How many species of flowering plants are there? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Edwards, D.P. The search for unknown biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12971–12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Achard, F.; Peedell, S.; Schmitt, S. Big data, big opportunities. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Henwood, W.D.; Gilfedder, L.A. Global plight of native temperate grasslands: Going, going, gone? Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 2911–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Mutke, J.; Rafiqpoor, D.; Kier, G.; Kreft, H. Global centres of vascular plant diversity. Nova Acta Leop. 2005, 92, 61–83. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, N. Threatened biotas: “Hot spots” in tropical forests. Environmentalist 1988, 8, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareiva, P.; Marvier, M. Conserving Biodiversity Coldspots. Am. Sci. 2003, 91, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, B. Biotic Diversity in Southern Africa: Concepts and Conservation; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 1989; pp. 1–380. [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedel, U.; Dengler, J.; Luther-Mosebach, J.; Gröngröft, A.; Muche, G.; Petersen, A.; Strohbach, B.J.; Jürgens, N. Patterns and dynamics of vascular plant diversity along the BIOTA transects in southern Africa. In Biodiversity in Southern Africa. Volume 2: Patterns and Processes at Regional Scale; Schmiedel, U., Jürgens, N., Eds.; Klaus Hess Publishers: Göttingen, Germany; Windhoek, Namibia, 2010; pp. 118–135. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk, A.E.; Smith, G.F. Regions of Floristic Endemism in Southern Africa; Umdaus Press: Hatfield, South Africa, 2001; pp. 1–199. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, V.R.; Barker, N.P.; Mucina, L. The Sneeuberg: A new centre of floristic endemism on the Great Escarpment, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2009, 75, 196–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C. The Drakensberg Mountain Centre: A necessary revision of southern Africa’s high-elevation centre of plant endemism. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 508–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, V.R.; Burrows, J.E.; Turpin, B.C.; Balkwill, K.; Lötter, M.; Siebert, S.J. The Limpopo–Mpumalanga–Eswatini Escarpment—Extra-Ordinary Endemic Plant Richness and Extinction Risk in a Summer Rainfall Montane Region of Southern Africa. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 765854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeldså, J.; Lovett, J.C. Geographical patterns of old and young species in African forest biota: The significance of specific montane areas as evolutionary centres. Biodivers. Conserv. 1997, 6, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowling, R.M.; Procheş, S. Patterns and evolution of plant diversity in the Cape Floristic Region. Biol. Skr. 2005, 55, 273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Mutke, J.; Sommer, J.H.; Kreft, H.; Kier, G.; Barthlott, W. Vascular plant diversity in a changing world: Global centres and biome-specific patterns. In Biodiversity Hotspots; Zachos, F.E., Habel, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Mishler, B.D.; Knerr, N.; González-Orozco, C.E.; Thornhill, A.H.; Laffan, S.W.; Miller, J.T. Phylogenetic measures of biodiversity and neo-and paleo-endemism in Australian Acacia. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoveka, L.N.; Van der Bank, M.; Bezeng, B.S.; Davies, T.J. Identifying biodiversity knowledge gaps for conserving South Africa’s endemic flora. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2803–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucina, L.; Rutherford, M.C. The Vegetation of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2006; pp. 1–807. [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Shaw, C.R. Rare and Threatened Plants of KwaZulu-Natal and Neighbouring Regions; KwaZulu-Natal Nature Conservation Service: Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 1999; pp. 1–182. [Google Scholar]
- Engler, A. Führer Durch Den Königlich Botanischen Garten Der Universität Zu Breslau; J.U. Kerns Verlag (Max Müller): Breslau, Germany, 1886; pp. 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- New York Botanical Garden. Index Herbariorum. Available online: https://sweetgum.nybg.org/science/ih/ (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- South African National Biodiversity Institute. New Plants of Southern Africa. Available online: https://posa.sanbi.org/ (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- South African National Biodiversity Institute. Red List of South African Plants. Available online: http://redlist.sanbi.org/ (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Ithaka. JSTOR Global Plants Database. Available online: https://plants.jstor.org/ (accessed on 21 October 2019).
- Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens Kew. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/ (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/ (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Pooley, E. A Field Guide to Wildflowers KwaZulu-Natal and the Eastern Region; Natal Flora Publications Trust: Durban, South Africa, 1998; pp. 1–630. [Google Scholar]
- Boon, R. Pooley’s Trees of Eastern South Africa; Flora and Fauna Publications Trust: Durban, South Africa, 2010; pp. 1–624. [Google Scholar]
- Council for Geoscience. 1: 1,000,000 Simplified Geology Map of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland; Council for Geoscience: Pretoria, South Africa, 2003; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. Plant Growth Forms Classification Scheme Version 1.1. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/fr/resources/classification-schemes (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Mucina, L.; Lötter, M.C.; Rutherford, M.C.; Van Niekerk, A.; Macintyre, P.D.; Tsakalos, J.L.; Timberlake, J.; Adams, J.B.; Riddin, T.; Mccarthy, L.K. Forest biomes of Southern Africa. N. Z. J. Bot. 2022, 60, 377–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Edwards, T.J. Reconciling ecological and phytogeographical spatial boundaries to clarify the limits of the montane and alpine regions of sub-Sahelian Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 98, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, G.P. Terrain Morphological Map of Southern Africa; Department of Agriculture: Pretoria, South Africa, 1983; p. 1.
- Partridge, T.C.; Dollar, E.S.J.; Moolman, J.; Dollar, L.H. The geomorphic provinces of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland: A physiographic subdivision for earth and environmental scientists. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 2010, 65, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, A.B.; Rebelo, A.G. Vegetation of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland: A Companion to the Vegetation Map of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland; Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism: Pretoria, South Africa, 1996; pp. 1–85.
- Janks, M.R. Montane Wetlands of the South African Great Escarpment: Plant Communities and Environmental Drivers. Master’s Thesis, Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carbutt, C. The curious case of a grass-like poker. PlantLife 2020, 50, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda-Zárate, M.; Johnson, S.D.; van der Niet, T. Description of a new species within the Satyrium longicauda (Orchidaceae) complex from South Africa, based on integrative taxonomy. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 148, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Edwards, T.J. The endemic and near-endemic angiosperms of the Drakensberg Alpine Centre. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2006, 72, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, H.P. On areas of endemism, with an example from the African Restionaceae. Syst. Biol. 2001, 50, 892–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procheş, Ş.; Ramdhani, S. Ancient plant lineages endemic to Africa and its islands: An analysis on the distribution and diversity. Diversity 2023, 15, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, D.I. Poleward migration of early Angiosperm flora: Angiosperms only displaced the relict Jurassic-type flora at high latitudes in Late Cretaceous time. Science 1959, 130, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiffard, C.; Gomez, B.; Daviero-Gomez, V.; Dilcher, D.L. Rise to dominance of angiosperm pioneers in European Cretaceous environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20955–20959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Lauer, W.; Placke, A. Global distribution of species diversity in vascular plants: Towards a world map of phytodiversity. Erdkunde 1996, 50, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerlekar, A.N.; Veldman, J.W. High plant diversity and slow assembly of old-growth grasslands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18550–18556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Kirkman, K. Ecological Grassland Restoration—A South African Perspective. Land 2022, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, M.K.; Scott, L.; Finkelstein, S.A. Reconstructing past biomes states using machine learning and modern pollen assemblages: A case study from Southern Africa. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 212, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, J.E.; Rundel, P.W. Fire and the Miocene expansion of grasslands. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, C.P. Atmosphere, ecology and evolution: What drove the Miocene expansion of C4 grasslands? J. Ecol. 2008, 96, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.R.; Bezuidenhout, H. Grassland vegetation of southern Africa. In Encyclopedia of the World’s Biomes; Goldstein, M.I., DellaSala, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 814–826. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzesi, L.; Hidalgo, O.; Barreda, V.D.; Forest, F.; Höhna, S. The rise of grasslands is linked to atmospheric CO2 decline in the late Palaeogene. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, W.J.; Midgley, G.F.; Woodward, F.I. What controls South Africa vegetation—Climate or fire? S. Afr. J. Bot. 2003, 69, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myburgh, A. Patterns and Drivers of Forb Diversity in South African grasslands. Master’s Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Carbutt, C.; Martindale, G. Temperate indigenous grassland gains in South Africa: Lessons being learned in a developing country. Parks 2014, 20, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollerton, J.; Liede-Schumann, S.; Endress, M.E.; Meve, U.; Rech, A.R.; Shuttleworth, A.; Keller, H.A.; Fishbein, M.; Alvarado-Cárdenas, L.O.; Amorim, F.W.; et al. The diversity and evolution of pollination systems in large plant clades: Apocynaceae as a case study. Ann. Bot. 2019, 123, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livshultz, T.; Mead, J.V.; Goyder, D.J.; Brannin, M. Climate niches of milkweeds with plesiomorphic traits (Secamonoideae; Apocynaceae) and the milkweed sister group link ancient African climates and floral evolution. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 1966–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, C.; Galetto, L. Are nectar sugar composition and corolla tube length related to the diversity of insects that visit Asteraceae flowers? Plant Biol. 2002, 4, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, J.E.; Smith, G.F. The conservation imperative and setting plant taxonomic research priorities in South Africa. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, J.; Smith, G.; Van Wyk, A.; Ribeiro, S. Plant taxonomic capacity in South Africa. Phytotaxa 2015, 238, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.L.; Crouch, N.R. Locating sufficient plant distribution data for accurate estimation of geographic range: The relative value of herbaria and other sources. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 109, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, M.; Lykke, A.M.; Fagg, C.W.; Gereau, R.E.; Lewis, G.P.; Marchant, R.; Marshall, A.R.; Ndayishimiye, J.; Bogaert, J.; Svenning, J.C. Realising the potential of herbarium records for conservation biology. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 105, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhtajan, A. Floristic Regions of the World; University of California Press: Berkley, CA, USA, 1986; pp. 1–522. [Google Scholar]
- White, F. The Vegetation of Africa: A Descriptive Memoir to Accompany the UNESCO/AETFAT/UNSO Vegetation Map of Africa; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1983; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ramdhani, S.; Barker, N.P.; Baijnath, H. Exploring the Afromontane centre of endemism: Kniphofia Moench (Asphodelaceae) as a floristic indicator. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 2258–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daru, B.H.; van der Bank, M.; Maurin, O.; Yessoufou, K.; Schaefer, H.; Slingsby, J.A.; Davies, T.J. A novel phylogenetic regionalization of the phytogeographic zones of southern Africa reveals their hidden evolutionary affinities. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daru, B.H.; van der Bank, M.; Davies, T.J. Unravelling the evolutionary origins of biogeographic assemblages. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C. Cape Elements on High-Altitude Corridors and Edaphic Islands. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Gavaldà, C.; Galbany-Casals, M.; Susanna, A.; Andrés-Sánchez, S.; Bayer, R.J.; Brochmann, C.; Cron, G.V.; Bergh, N.G.; Garcia-Jacas, N.; Gizaw, A.; et al. Repeatedly northwards and upwards: Southern African grasslands fuel the colonization of the African sky islands in Helichrysum (Compositae). Plants 2023, 12, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirie, M.D.; Kandziora, M.; Nürk, N.M.; Le Maitre, N.C.; Mugrabi de Kuppler, A.; Gehrke, B.; Oliver, E.G.H.; Bellstedt, D.U. Leaps and bounds: Geographical and ecological distance constrained the colonization of the Afrotemperate by Erica. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Edwards, T.J. Cape elements on high-altitude corridors and edaphic islands: Historical aspects and preliminary phytogeography. Syst. Geogr. Plants 2001, 71, 1033–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Edwards, T.J. The flora of the Drakensberg Alpine Centre. Edinb. J. Bot. 2004, 60, 581–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, W.S.; Van Wyk, A.E.; Bredenkamp, G.J. Endemic flora of the north-eastern Transvaal Escarpment, South Africa. Biol. Conserv. 1993, 63, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.C. The Natal Monocline: Explaining the Origin and Scenery of Natal; University of KwaZulu-Natal Press: Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 1972; pp. 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Van Breemen, N.; Buurman, P. Soil Formation; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–408. [Google Scholar]
- Paoli, G.D.; Curran, L.M.; Zak, D.R. Soil nutrients and beta diversity in the Bornean Dipterocarpaceae: Evidence for niche partitioning by tropical rain forest trees. J. Ecol. 2006, 94, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, J.; Verboom, G.A.; Bergh, N.G. Erosive processes after tectonic uplift stimulate vicariant and adaptive speciation: Evolution in an Afrotemperate-endemic paper daisy genus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luskin, C.; Wilson, A.H.; Gold, D.; Hofmann, A. The Pongola Supergroup: Mesoarchaean deposition following Kaapvaal Craton stabilization: Methods and protocols. In The Archaean Geology of the Kaapvaal Craton, Southern Africa; Kröner, A., Hofmann, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 225–254. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore, G.; Uken, R.; Meth, D. KwaZulu-Natal: 3500 Million Years of Geological History; Richards Bay Minerals and the Geology Education Museum: Richards Bay, South Africa, 1999; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Maske, S. The petrography of the Ingeli Mountain Range. Ann. Uni. Stellenbosch 1966, 41, 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, P.C.; Naldrett, A.J.; Hawkesworth, C.J. The geology and geochemistry of the Waterfall Gorge section of the Insizwa complex with particular reference to the origin of the nickel sulfide deposits. Econ. Geol. 1984, 79, 1857–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.S.; Allen, P.; Fenner, N. The geochemical structure of the Insizwa lobe of the Mount Ayliff complex with implications for the emplacement and evolution of the complex and its Ni-sulphide potential. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2003, 106, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund. Ecosystem Profile: Maputaland–Pondoland–Albany Biodiversity Hotspot. Available online: https://www.cepf.net/our-work/biodiversity-hotspots (accessed on 17 April 2022).
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, D.C.; von Staden, L.; Donaldson, J.S. Lessons from the conservation assessment of the South African megaflora. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2013, 99, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, J.J.; Hui, C.; Castillo, M.L.; Iriondo, J.M.; Keet, J.H.; Khapugin, A.A.; Médail, F.; Rejmánek, M.; Theron, G.; Yannelli, F.A.; et al. Recent anthropogenic plant extinctions differ in biodiversity hotspots and coldspots. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2912–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, I.A.W. Man’s role in changing the face of southern Africa. In Biotic Diversity in Southern Africa. Concepts and Conservation; Huntley, B.J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 1989; pp. 51–77. [Google Scholar]
- Plantlife International. Identifying and Protecting the World’s Most Important Plant Areas: A Guide to Implementing Target 5 of the Global Strategy for Plant Conservation; Plantlife International: Salisbury, UK, 2004; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Darbyshire, I.; Anderson, S.; Asatryan, A.; Byfield, A.; Cheek, M.; Clubbe, C.; Ghrabi, Z.; Harris, T.; Heatubun, C.D.; Kalema, J. Important Plant Areas: Revised selection criteria for a global approach to plant conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 1767–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kier, G.; Mutke, J.; Dinerstein, E.; Ricketts, T.H.; Küper, W.; Kreft, H.; Barthlott, W. Global patterns of plant diversity and floristic knowledge. J. Biogeogr. 2005, 32, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowno, A.L.; Poole, C.J.; Raimondo, D.C.; Sink, K.J.; Van Deventer, H.; Van Niekerk, L.; Harris, L.R.; Smith-Adao, L.B.; Tolley, K.A.; Zengeya, T.A.; et al. National Biodiversity Assessment 2018: The Status of South Africa’s Ecosystems and Biodiversity; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2019; pp. 1–214. [Google Scholar]
- Royal Botanic Gardens Kew. State of the World’s Plants 2016; Royal Botanic Gardens Kew: Surrey, UK, 2016; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mankga, L.T.; Yessoufou, K. Factors driving the global decline of cycad diversity. AoB Plants 2017, 9, plx022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, J.S.; Hurter, P.J.H. A Red List account of Africa’s cycads and implications of considering life-history and threats. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.; Maurin, O.; Shiba, S.N.S.; van der Bank, H.; Pfab, M.; Pilusa, M.; Kabongo, R.M.; van der Bank, M. Exposing the illegal trade in cycad species (Cycadophyta: Encephalartos) at two traditional medicine markets in South Africa using DNA barcoding. Genome 2016, 59, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C.; Tau, M.; Stephens, A.; Escott, B. The conservation status of temperate grasslands in southern Africa. Grassroots 2011, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Convention on Biological Diversity—Strategic Plan 2011–2020 (Aichi Targets). Available online: www.cbd.int/sp/targets (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- IUCN. Conserving at Least 30% of the Planet by 2030—What Should Count? IUCN WCPA: Gland, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Carbutt, C.; Goodman, P.S. Assessing the Management Effectiveness of State-Owned, Land-Based Protected Areas in KwaZulu-Natal; Ezemvelo KZN Wildlife: Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 2010; pp. 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Shaw, C.R.; Morris, C.D. Grazing depletes forb species diversity in the mesic grasslands of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2015, 32, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craib, C. Grass Aloes in the South African Veld; Umdaus Press: Hatfield, South Africa, 2005; pp. 1–156. [Google Scholar]
- Klopper, R.R.; Crouch, N.R.; Smith, G.F.; Van Wyk, A.E. A synoptic review of the aloes (Asphodelaceae, Alooideae) of KwaZulu-Natal, an ecologically diverse province in eastern South Africa. PhytoKeys 2020, 142, 1–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, B.-E.; Smith, G.F. Guide to Aloes of South Africa, 2nd ed.; Briza Publications: Pretoria, South Africa, 2003; pp. 1–376. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G.F.; Crouch, N.R. Aloe nicholsii Gideon F.Sm. & N.R.Crouch (Asphodelaceae): A new leptoaloe from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Bradleya 2010, 28, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, D.S.; Reid, C. A new variety of Aloe from the Vryheid district: Aloe reitzii var. vernalis. Bothalia 1981, 13, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Obermeyer, A.A.; Immelman, K.L. Protasparagus. In Flora of Southern Africa 5, Part 3: Dracenaceae, Asparagaceae, Luzuriagaceae and Smilacaceae; Leistner, O.A., Ed.; National Botanical Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 1992; pp. 11–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kupicha, F.K. Studies on African Asclepiadaceae. Kew Bull. 1984, 38, 599–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Notes on some plants of Southern Africa chiefly from Natal: XIV. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1988, 45, 77–94. [Google Scholar]
- Vollesen, K. Blepharis (Acanthaceae): A Taxonomic Revision; Royal Botanic Gardens Kew: Richmond, UK, 2000; pp. 1–342. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, R.H. Plantae novae Africanae: Series XXXII. J. S. Afr. Bot. 1967, 33, 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Victor, J.E. Ceropegia craibii (Apocynaceae). Curtis’s Bot. Mag. 2001, 18, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craib, C. Ceropegia craibii: A new discovery from the Vryheid District in KwaZulu-Natal. Aloe 2002, 39, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Styles, D.G.A.; Meve, U. Ceropegia heidukiae (Apocynaceae-Asclepiadoideae)—A morphologically intriguing and rare novelty from South Africa. Phytotaxa 2021, 497, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.A. Two new species of Brachystelma. Bothalia 1977, 12, 254–255. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, R.A. Asclepiadaceae: New species of Brachystelma. Bothalia 1976, 12, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heiduk, A. Ceropegia stylesii (Apocynaceae-Asclepiadoideae)—A novel species with rotate flowers from Ngome, South Africa. Phytotaxa 2023, 579, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Notes on some plants of Southern Africa chiefly from Natal: XII. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1986, 43, 189–228. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, G.; Jeppe, B.; Voigt, L. Field Guide to the Amaryllis Family of Southern Africa and Surrounding Territories; Galley Press: Nelspruit, South Africa, 2020; pp. 1–548. [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle, L.M.; Van Zyl, E.A.; Jordaan, J.J. Ecological factors determining the distribution patterns of Cyrtanthus nutans R.A.Dyer (Amaryllidaceae) in northwestern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Bothalia 2022, 52, a6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Dierama: The Hairbells of Africa; Acorn Books: Johannesburg, South Africa; London, UK, 1991; pp. 1–152. [Google Scholar]
- Vorster, P. Encephalartos aemulans (Zamiaceae), a new species from northern Natal. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1990, 56, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.E. Eugenia pusilla. Kew Bull. 1912, 6, 276–277. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk, A.E. Contributions Towards a New Classification of Eugenia L. (Myrtaceae) in Southern Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, R.; Saunders, R. Saunders’ Field Guide to Gladioli of South Africa; Struik Nature: Cape Town, South Africa, 2021; pp. 1–360. [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard, O.M. Gnaphaliinae (first part). In Flora of Southern Africa 33: Asteraceae, Part 7, Inuleae, Fascicle 2; Leistner, O.A., Ed.; National Botanical Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 1983; pp. 1–325. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, C.; Archer, R.H. A new species of Holothrix Lindl. (Orchidaceae) from northern KwaZulu-Natal. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1996, 62, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.D.; Bytebier, B. Orchids of South Africa—A Field Guide; Struik Nature: Cape Town, South Africa, 2015; pp. 1–536. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, L.E. Asphodelaceae (first part): Kniphofia. In Flora of Southern Africa 5, Part 1, Fascicle 2; Germishuizen, G., Momberg, B.A., Eds.; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2005; pp. 1–91. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk, B.E. A synopsis of the genus Lotononis (Fabaceae: Crotalarieae). Contrib. Bolus Herb. 1991, 14, 1–292. [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt, P. Contributions to the knowledge of Moraea (Iridaceae) in the summer rainfall region of South Africa. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1973, 60, 204–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, G. An undescribed Nerine from the SE Transvaal. J. S. Afr. Bot. 1971, 37, 267–268. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.M.N. A revision of the genus Pachycarpus in southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1988, 54, 399–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, S.P.; Nicholas, A. Periglossum podoptyches (Apocynaceae-Asclepiadoideae), a new species from KwaZulu-Natal province, South Africa. Phytotaxa 2016, 282, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markötter, E.I. Flora van Oranje Vry Staat en Natal. Ann. Univ. Stellenbosch 1930, 8, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Linder, H.P. An annotated revision of the genus Schizochilus Sond. (Orchidaceae). J. S. Afr. Bot. 1980, 46, 379–434. [Google Scholar]
- Moffett, R.O. Rhus. In Flora of Southern Africa, 19, Part 3: Anacardiaceae, Fascicle 1; Leistner, O.A., Ed.; National Botanical Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 1993; pp. 1–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard, O.M. The Tribe Selagineae (Scrophulariaceae); Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 1999; pp. 1–312. [Google Scholar]
- Bester, S.P.; Nicholas, A. New combinations in Stenostelma (Apocynaceae—Asclepiadoideae) and two novel species from South Africa. Phytotaxa 2018, 361, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Streptocarpus: An African Plant Study, 1st ed.; University of Natal Press: Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 1971; pp. 1–410. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, T.J. Two new species of Streptocarpus (Gesneriaceae) from South Africa. Novon 2003, 13, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwenya, M.A. Syncolostemon aurulentus (Lamiaceae), a new species from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Bothalia 2018, 48, a2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, L.E. The genus Syncolostemon (Lamiaceae). Bothalia 1976, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Otieno, D.F.; Balkwill, K.; Paton, A.J.; Savolainen, V. A reassessment of Hemizygia and Syncolostemon (Ocimeae–Lamiaceae). Taxon 2006, 55, 941–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, K.; Changwe, K.; Reddy, R.A.; Pike, B. Thorncroftia greenii. Flower. Plants Afr. 2009, 61, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, H.D.; Hummel, E.; Hillmer, S.; Sauer-Gürth, H.; Gonzalez, J.; Wink, M. A revision of African Velloziaceae based on leaf anatomy characters and rbcL nucleotide sequences. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 172, 22–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Van Wyk, A.E.; Baijnath, H. Taxonomic notes on the genus Zantedeschia Spreng. (Araceae) in southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1996, 62, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, P.J.D.; Magee, A.R.; Phephu, N.; Tilney, P.M.; Downie, S.R.; van Wyk, B.-E. A new generic classification for African peucedanoid species (Apiaceae). Taxon 2008, 57, 347–364. [Google Scholar]
- Plowes, D.C.H. Aloe inconspicua, a new species from Natal. Aloe 1986, 23, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, G.W. The Aloes of South Africa; A.A. Balkema: Cape Town, South Africa, 1969; pp. 1–520. [Google Scholar]
- Klopper, R.R.; Smith, G.F. Asphodelaceae: Alooideae: Aloe neilcrouchii, a new robust Leptaloe from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Bothalia 2010, 40, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Klopper, R.R.; Smith, G.F. Asphodelaceae: Alooideae: Reinstatement of Aloe spectabilis. Bothalia 2010, 40, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.F.; Crouch, N.R. Aloe vanrooyenii: A distinctive new maculate Aloe from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Bothalia 2006, 36, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Edwards, T.J. A synopsis of Argyrolobium (tribe Genisteae, Papilionoideae) in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2005, 71, 380–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, A.; Goyder, D.J. Aspidonepsis (Asclepiadaceae), a new southern African genus. Bothalia 1992, 22, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermeyer, A.A. Notes and new records of African plants: Barleria argillicola. Bothalia 1961, 7, 444–445. [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill, M.-J.; Balkwill, K.; Vincent, L.P.D. Systematic studies in the Acanthaceae: A new species of Barleria from Natal. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1990, 56, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, A.J.; Beckett, R.P.; Edwards, T.J.; Stirton, C.H. Revision of the genus Calpurnia (Sophoreae: Leguminosae). Bothalia 1999, 29, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peckover, R.G. A new species of Brachystelma (Asclepiadaceae) from Natal. Aloe 1992, 29, 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, R.A. New species of Ceropegia. Bothalia 1978, 12, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dyer, R.A. Ceropegia, Brachystelma and Riocreuxia in Southern Africa; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 1–242. [Google Scholar]
- Heiduk, A.; Crouch, N.R.; Styles, D.G.A. Ceropegia gilboaensis (Apocynaceae), a new species from the Midlands of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Phytotaxa 2023, 591, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, R.A. New records of Brachystelma. J. S. Afr. Bot. 1977, 43, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cron, G.V.; Balkwill, K.; Knox, E.B. A revision of the genus Cineraria (Asteraceae, Senecioneae). Kew Bull. 2006, 61, 449–535. [Google Scholar]
- Maurin, O.; Van Wyk, A.E.; Jordaan, M.; van der Bank, M. A new species of Combretum section Ciliatipetala (Combretaceae) from southern Africa, with a key to the regional members of the section. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Conium (Umbelliferae) in southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1985, 51, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polhill, R.M. Crotalarieae. In Flora Zambesiaca 3 (Part 7); Pope, G.V., Polhill, R.M., Martins, E.S., Eds.; Royal Botanic Gardens Kew: Richmond, UK, 2003; pp. 55–246. [Google Scholar]
- Lavis, M. Notes on the genus Delosperma (Mesembrieae). J. S. Afr. Bot. 1969, 35, 145–147. [Google Scholar]
- Meve, U. Emplectanthus N.E.Br.: A close relative of Riocreuxia Decne. in the Asclepiadaceae-Stapelieae. Bot. Jahrb. Syst. 1998, 120, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lavranos, J.J.; Goode, D. Notes on southern African Cycadales II. Durb. Mus. Novit. 1989, 14, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Vorster, P.J. Encephalartos msinganus (Zamiaceae): A new species from KwaZulu-Natal. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1996, 62, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorster, P.J. Focus on Encephalartos msinganus. Encephalartos 1997, 51, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, E.G.H.; Oliver, I.M. Two new species of Erica (Ericaceae); one from Western Cape and one from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Bothalia 2004, 34, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nicholas, A. A Taxonomic Reassessment of the Subtribe Asclepiadinae (Asclepiadaceae) in Southern Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Durban Westville, Westville, South Africa, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Van Jaarsveld, E.J.; Van Wyk, A.E. Gasteria tukhelensis, a new species from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Bothalia 2005, 35, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. A revision of Geranium in Africa south of the Limpopo. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1985, 42, 171–225. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, I.M.; Crouch, N.R.; Edwards, T.J. Gerbera sylvicola (Asteraceae: Mutisieae), a new forest species from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Phytotaxa 2014, 186, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jordaan, M.; Van Wyk, A.E. Systematic studies in subfamily Celastroideae (Celastraceae) in southern Africa: Two new species of Gymnosporia from KwaZulu-Natal and the Eastern Cape. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2000, 66, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbutt, C. A second population of the Ixopo Everlasting (Helichrysum citricephalum: Asteraceae). PlantLife 2021, 51, 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Schlechter, F.R.R. Plantae Pentherianae III. Ann. K. K. Naturhist. Hofmus. 1905, 20, 14–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tölken, H.R. Crassulaceae. In Flora of Southern Africa 14; Leistner, O.A., Ed.; Botanical Research Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 1985; pp. 1–244. [Google Scholar]
- Baijnath, H. Kniphofia albomontana (Asphodelaceae): A new caulescent species from South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1987, 53, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, N.R.; Edwards, T.J.; Beaumont, A. Ledebouria ovatifolia subsp. scabrida. Flowering Plants Afr. 2007, 60, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Boatwright, J.S.; Wink, M.; van Wyk, B.E. The generic concept of Lotononis (Crotalarieae, Fabaceae): Reinstatement of the genera Euchlora, Leobordea and Listia and the new genus Ezoloba. Taxon 2011, 60, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdcourt, B. A revision of Macrotyloma (Leguminosae). Hooker’s Icones Plant. 1982, 38, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt, P. The Moraeas of Southern Africa: A systematic monograph of the genus in South Africa, Lesotho, Swaziland, Transkei, Botswana, Namibia, and Zimbabwe. Ann. Kirstenbosch Bot. Gard. 1986, 14, 1–224. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, C.A. The genus Nerine. Nerine Soc. Bull. 1974, 6, 7–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bruyns, P.V. Monograph of Orbea and Ballyanthus (Apocynaceae-Asclepiadoideae-Ceropegieae). Syst. Bot. Monogr. 2002, 63, 1–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Notes on some plants of Southern Africa chiefly from Natal: XI. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1985, 42, 227–260. [Google Scholar]
- Glen, M.; Nicholas, A.; Lamb, J.; Shuttleworth, A. A new species of Pachycarpus (Apocynaceae: Asclepiadoideae) from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Novon 2011, 21, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Jaarsveld, E. The Southern African Plectranthus and the Art of Turning Shade to Glade; Fernwood Press: Simon’s Town, South Africa, 2006; pp. 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiters, A.K.; Tilney, P.M.; Van Wyk, B.E.; Magee, A.R. Taxonomy of the Genus Phymaspermum (Asteraceae, Anthemideae). Syst. Bot. 2016, 41, 430–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Notes on some plants of Southern Africa chiefly from Natal: VIII. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1979, 37, 285–325. [Google Scholar]
- Weigend, M.; Edwards, T.J. Notes on Streptocarpus primulifolius (Gesneriaceae). S. Afr. J. Bot. 1994, 60, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrire, B.D. A synopsis of Tephrosia subgenus Barbistyla (Fabaceae) in southern Africa. Bothalia 1987, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retief, E.; Reyneke, W.F. The genus Thunbergia in southern Africa. Bothalia 1984, 15, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goldblatt, P. The genus Watsonia—A systematic monograph. Ann. Kirstenbosch Bot. Gard. 1989, 19, 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt, P.; Manning, J.C. Watsonia palustris (Iridaceae), a new species from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa and a revised key to allied summer rainfall species. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 106, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, C.J.; Johnson, I.M. Watsonia vicschuettei (Iridaceae, Watsonieae), a replacement name for the illegitimate Watsonia palustris. Phytotaxa 2018, 364, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, J.; Verboom, G.A.; Bergh, N.G. Species-level phylogenetic analysis in the Relhania clade of “everlastings” and a new generic treatment of species previously assigned to Macowania and Arrowsmithia (Asteraceae: Gnaphalieae). Taxon 2017, 66, 1421–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Notes on some plants of Southern Africa chiefly from Natal: XV. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1988, 45, 179–223. [Google Scholar]
- Peckover, R.G.; Van Wyk, A.E. Brachystelma molaventi (Asclepiadaceae), a new species from the southern midlands of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Aloe 1999, 36, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Heiduk, A.; Styles, D.G.A.; Meve, U. Long-lost Ceropegia rudatisii (Apocynaceae-Asclepiadoideae)—Rediscovered and redescribed after 100 years. Phytotaxa 2021, 498, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Craterocapsa Hilliard & Burtt genus novum. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1973, 32, 314–327. [Google Scholar]
- Nordenstam, B. Re-classification of Chrysanthemum L. in South Africa. Bot. Not. 1976, 129, 137–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard, O.M.; Burtt, B.L. Notes on some plants of Southern Africa chiefly from Natal: V. Notes Roy. Bot. Gard. Edinb. 1976, 34, 253–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, M. Focus on Encephalartos friderici-guilielmi. Encephalartos 1989, 18, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stirton, C.H.; Gordon-Gray, K.D. The Eriosema cordatum complex. I. The Eriosema populifolium group. Bothalia 1978, 12, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, O.M. Gnaphalium (Compositae) in Africa and Madagascar. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1981, 82, 267–292. [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill, M.-J.; Balkwill, K. The genus Lessertia DC. (Fabaceae-Galegeae) in KwaZulu-Natal (South Africa). S. Afr. J. Bot. 1999, 65, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillans, N.S. The genus Phylica Linn. J. S. Afr. Bot. 1942, 8, 1–164. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, L.E. Lamiaceae: A new species of Stachys; a new species of Thorncroftia. Bothalia 1986, 16, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.E.; Cooke, T.; Skan, S.A. Stachys sessilifolia E. Meyer. Flora Capensis 1912, 5, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard, O.M. New species in Petalacte (Compositae) and Struthiola (Thymelaeaceae). Edinb. J. Bot. 1993, 50, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.J. Notes on the Lamiaceae: A new Tetradenia and a new Thorncroftia from South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2006, 72, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
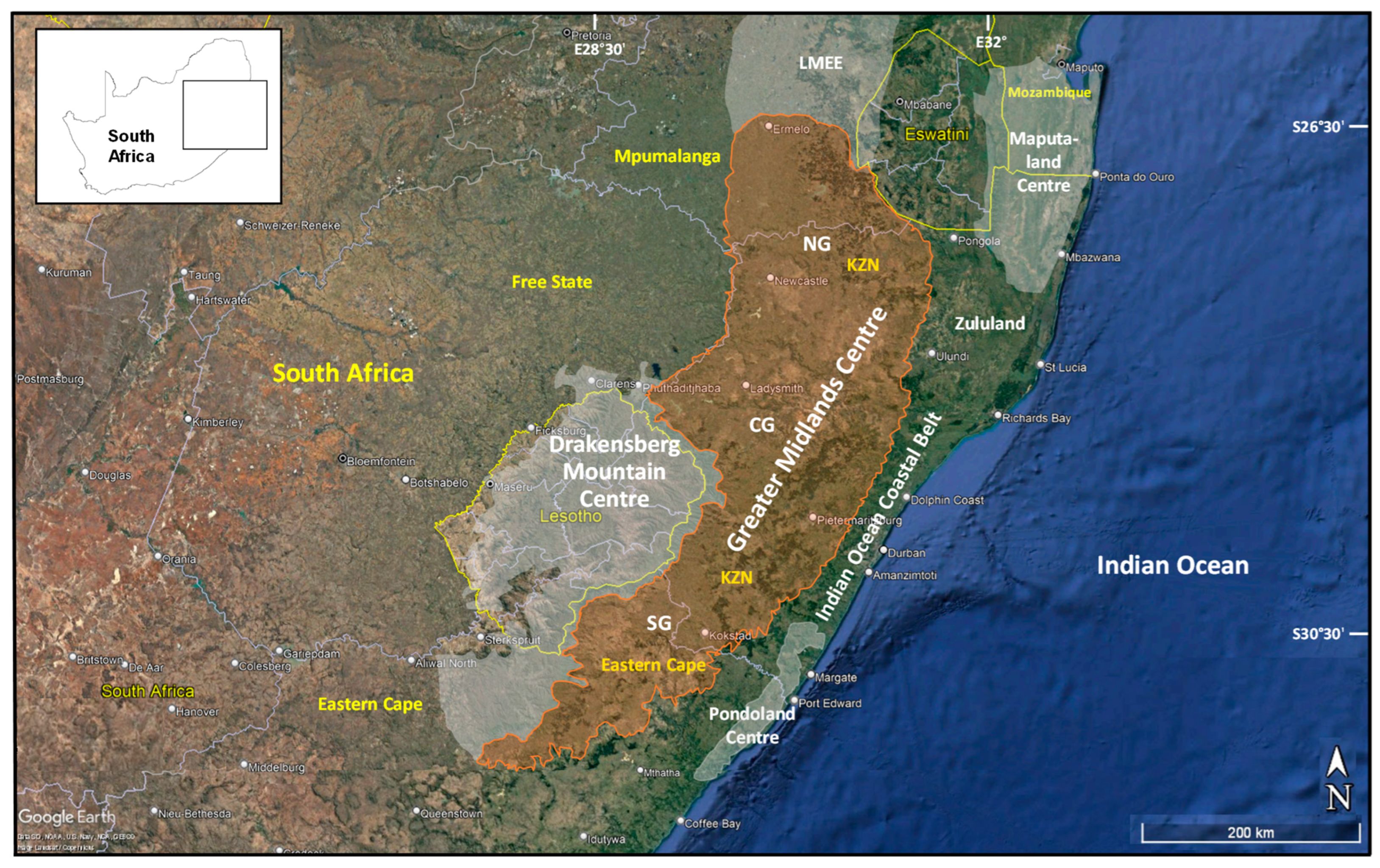

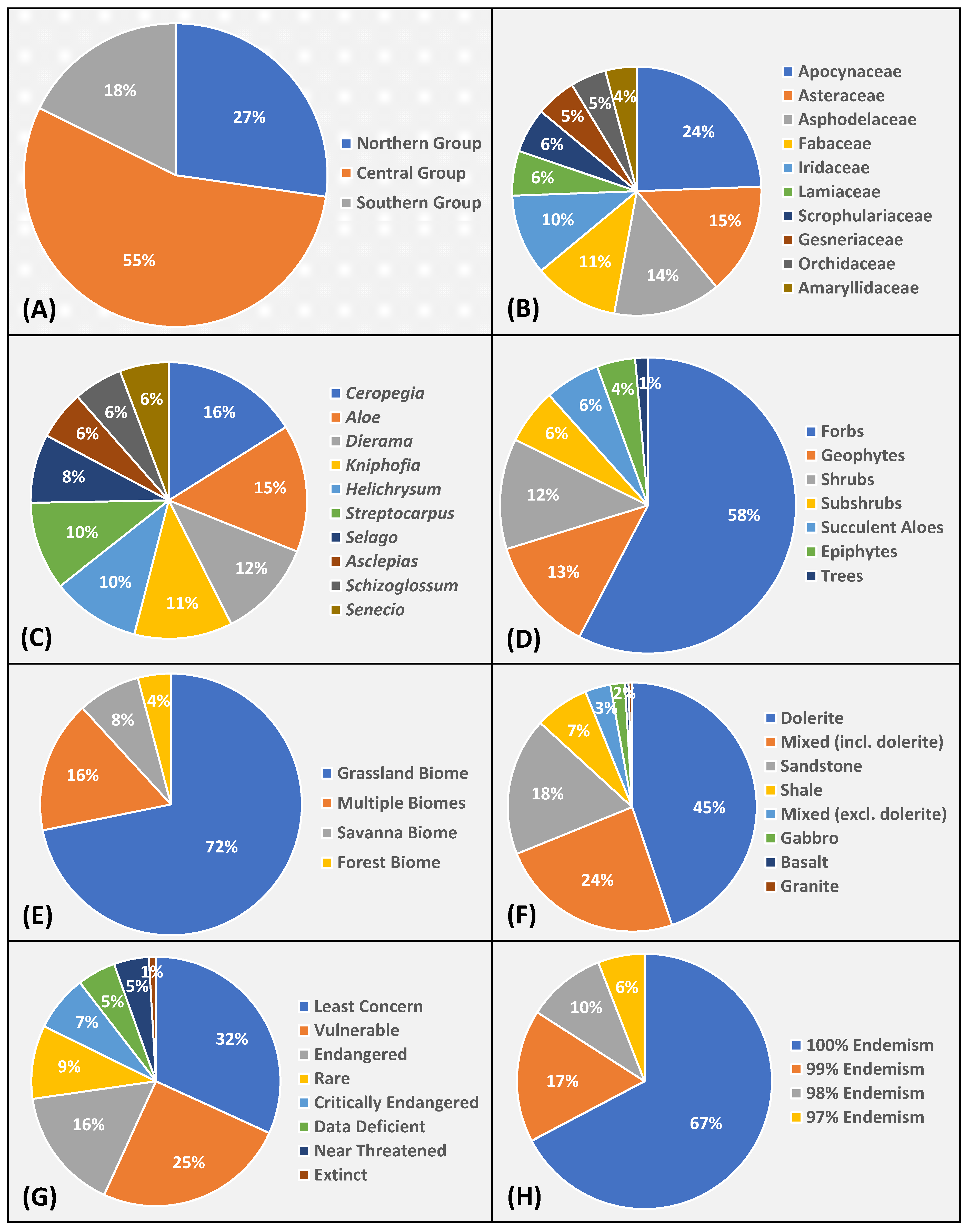
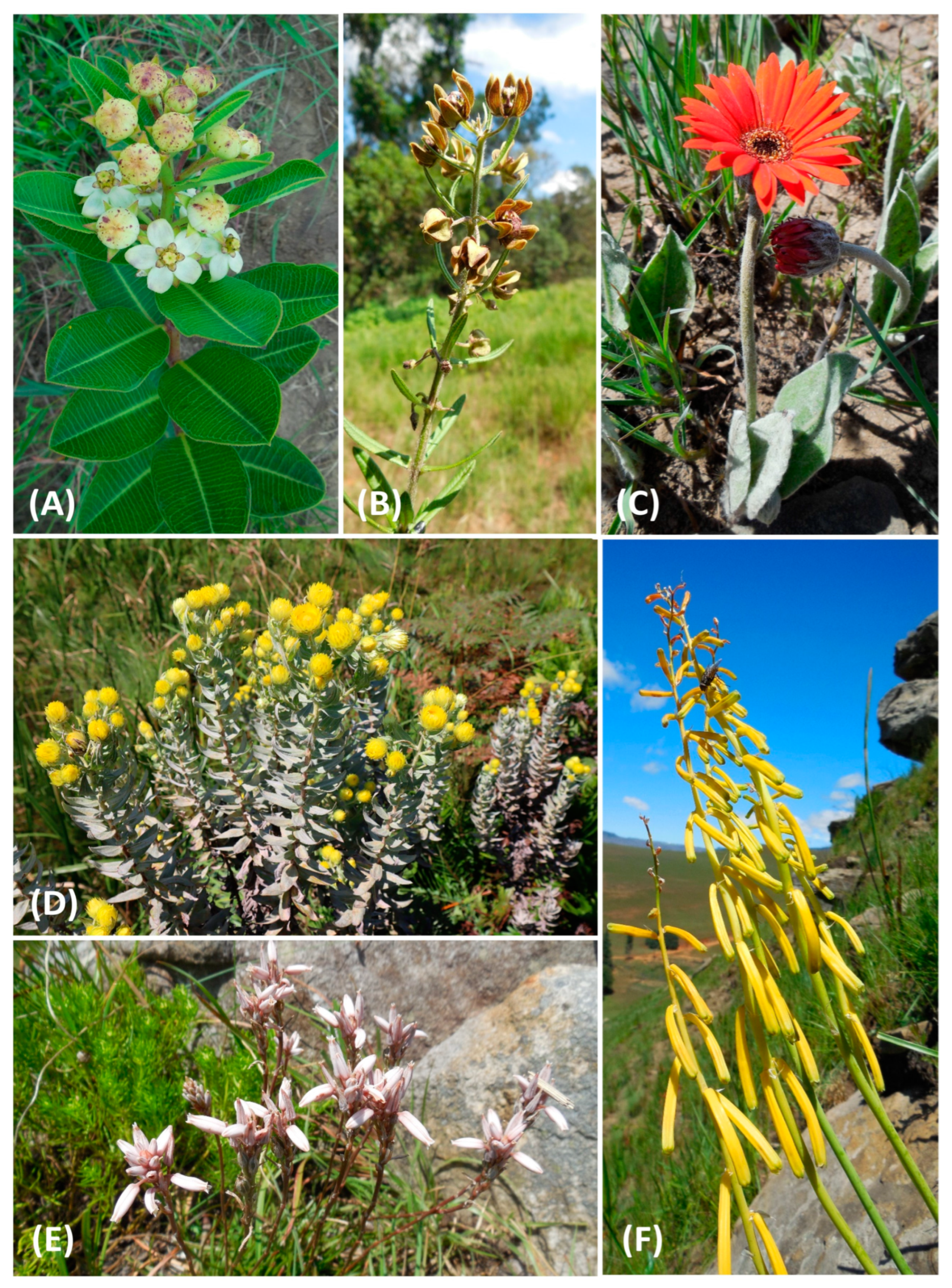

| Provinces by Contribution (%) | Area (km2) | Elevation Range (m a.s.l.) | Highest Point (m a.s.l.) | Dominant Eco-Thermal Belts | Geomorphic Province | Terrain Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KZN (60) EC (23) Mp (17) | 77,000 | ca. 700–2200 (1000–1600) Mid-elevation Sub-escarpment Foothills | Swartberg Mtn (2322) | Sub-montane Lower-montane | South-eastern Coastal Hinterland | Moderately undulating plains and hills–low mountains |
| Rainfall Regime | Rise to Dominance | Dominant Biome | Dominant Bioregion | Dominant Habitat | Dominant Broad Vegetation Types | Dominant Spermatophytes |
| Mesic Summer (October–April) | Late Oligocene–Early Miocene (34–20 Ma) | Grassland | Sub-escarpment Grassland Bioregion | Moist C4 grassland | North-eastern Mountain Grassland; Short Mistbelt Grassland; Moist Upland Grassland; Natal Central Bushveld | Angiosperms |
| No. of Spermatophyte Taxa | Larger Families | Larger Genera | Floristic Affiliations | Dominant Growth Form | Geodiversity | Geology and Lithology |
| 220 endemics ~3000–4000 flora | Apocynaceae Asteraceae Asphodelaceae Fabaceae Iridaceae | Ceropegia Aloe Dierama Kniphofia Helichrysum Streptocarpus | DMC Afromontane LMEE Greater CFR Sub-tropical/coastal | Forb | High | Complex; variable; heterogenous |
| Dominant Lithological Affinity | Threatened or Rare Taxa | Threat Status | Biodiversity Value | Conservation Value | Formal Protection | Connectivity and Ecological Resilience |
| Dolerite | 60% | Highly imperilled (“nature imperilled”) | Globally and regionally outstanding (global centre of plant diversity) | High priority (global biodiversity hotspot) | Extremely low < 1% | Poor; highly transformed or overgrazed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbutt, C. The Greater Midlands—A Mid-Elevation Centre of Floristic Endemism in Summer-Rainfall Eastern South Africa. Diversity 2023, 15, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15111137
Carbutt C. The Greater Midlands—A Mid-Elevation Centre of Floristic Endemism in Summer-Rainfall Eastern South Africa. Diversity. 2023; 15(11):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15111137
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbutt, Clinton. 2023. "The Greater Midlands—A Mid-Elevation Centre of Floristic Endemism in Summer-Rainfall Eastern South Africa" Diversity 15, no. 11: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15111137
APA StyleCarbutt, C. (2023). The Greater Midlands—A Mid-Elevation Centre of Floristic Endemism in Summer-Rainfall Eastern South Africa. Diversity, 15(11), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15111137






