Genetic Structure of Juvenile Stages of Phocanema bulbosum (Nematoda, Chromadorea: Anisakidae) Parasitizing Commercial Fish, Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua, and American Plaice Hippoglossoides platessoides in the Barents Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Morphological Examination
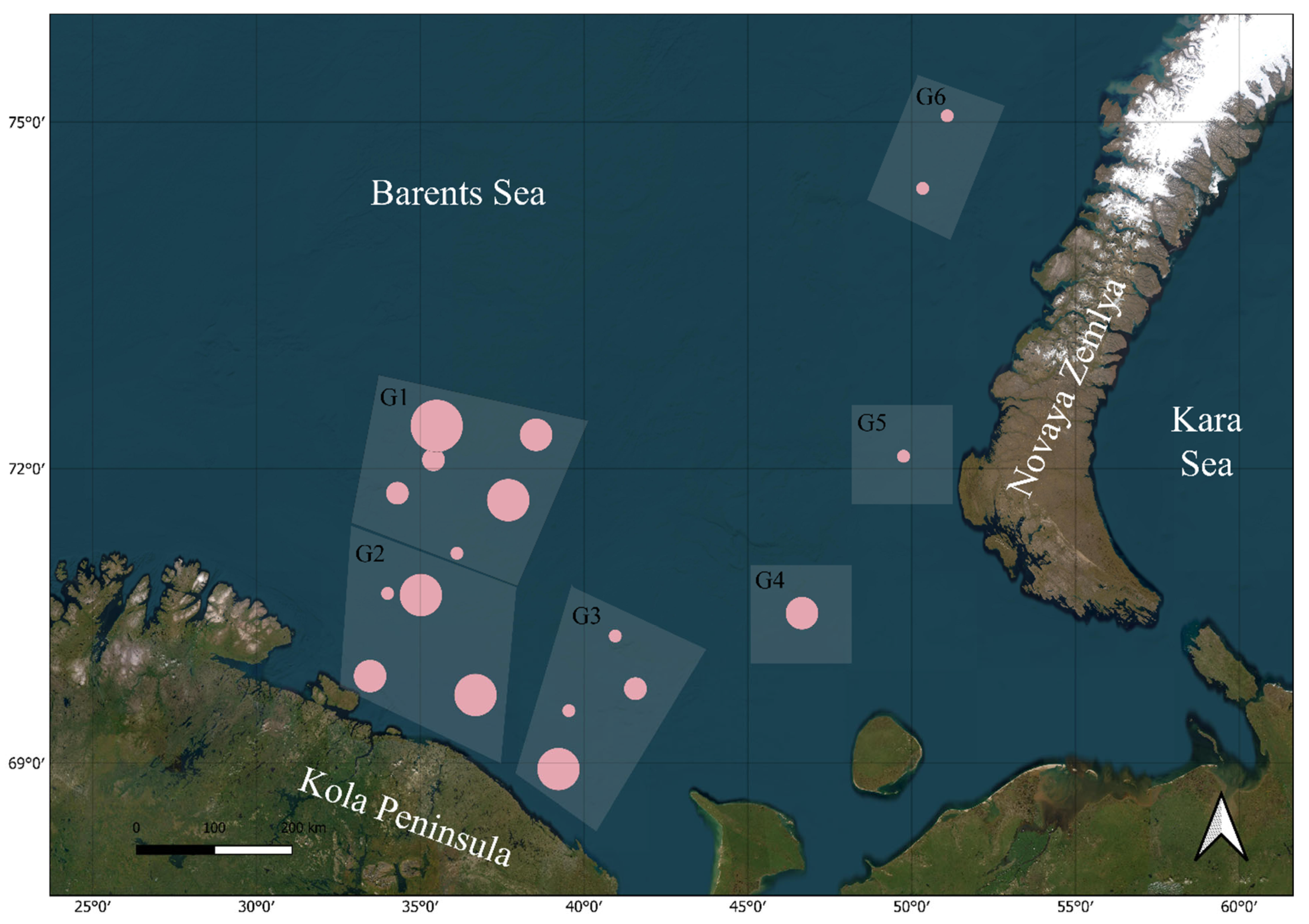
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
| GenBank Accession Number | Host | Locality * |
|---|---|---|
| OQ731840–OQ731844, OQ731846, OQ731848, OQ731849, OQ731867 | Atlantic cod Gadus morhua | G1 |
| OQ731832–OQ731839 | G2 | |
| OQ731845, OQ731850–OQ731866 | G3 | |
| OQ731847 | G5 | |
| OQ731868–OQ731874 OQ731882–OQ731887 | American plaice Hippoglossoides platessoides | G1 |
| OQ731888–OQ731896 | G2 | |
| OQ731875, OQ731897–OQ731899 | G3 | |
| OQ731876–OQ731879 | G4 | |
| OQ731880, OQ731881 | G6 |
2.3. Genetic Diversity and Haplotype Analysis
3. Results
| Samples | N | S | h | Hd ± m | σ | K | Pi | D | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 22 | 19 | 12 | 0.801 ± 0.007 | 0.088 | 2.299 | 0.005 | −2.067 | 0.010 |
| G2 | 17 | 12 | 9 | 0.890 ± 0.003 | 0.054 | 2.382 | 0.005 | −1.234 | 0.109 |
| G3 | 22 | 19 | 14 | 0.922 ± 0.002 | 0.045 | 2.861 | 0.006 | −1.668 | 0.018 |
| G4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0.833 ± 0.049 | 0.222 | 2.000 | 0.004 | −0.780 | 0.187 |
| G5 | 1 | N/A | 1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| G6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1.000 ± 0.250 | 0.5 | 1.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Cod | 36 | 20 | 15 | 0.846 ± 0.002 | 0.042 | 1.965 | 0.004 | −1.996 | 0.011 |
| Flounder | 32 | 29 | 21 | 0.921 ± 0.001 | 0.040 | 2.972 | 0.006 | −2.092 | 0.005 |
| All | 68 | 36 | 31 | 0.890 ± 0.001 | 0.027 | 2.430 | 0.005 | −2.159 | <0.00001 |

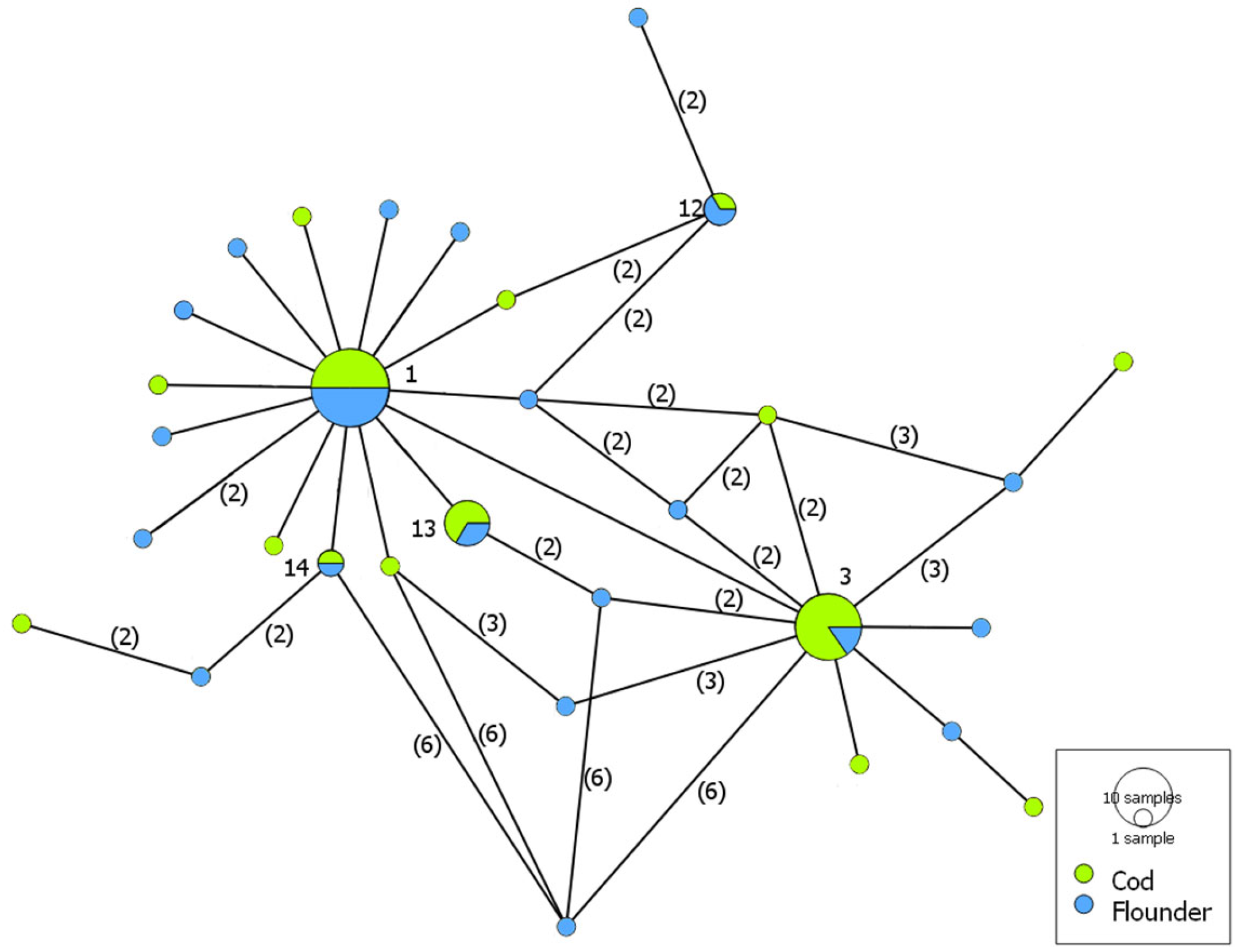
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myers, B.J. Phocanema, a new genus for the anisakid nematode of seals. Can. J. Zool. 1959, 37, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Giulietti, L.; Levsen, A.; Karlsbakk, E. Resurrection of genus Phocanema Myers, 1959, as a genus independent from Pseudoterranova Mozgovoĭ, 1953, for nematode species (Anisakidae) parasitic in pinnipeds and cetaceans, respectively. Parasitol. Int. 2023, 97, 102794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimpel, S.; Palm, H.W. Anisakid Nematode (Ascaridoidea) Life Cycles and Distribution: Increasing Zoonotic Potential in the Time of Climate Change? In Progress in Parasitology. Parasitology Research Monographs; Mehlhorn, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.D. Population biology of sealworm (Pseudoterranova decipiens) in relation to its intermediate and seal hosts. Can. Bull. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 222, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Køie, M.; Berland, B.; Burt, M.D. Development to third-stage larvae occurs in the eggs of Anisakis simplex and Pseudotetranova decipiens (Nematoda, Ascaridoidea, Anisakidae). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, R.C. Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses. In Fish Diseases and Disorders, Vol. 1: Protozoan and Metazoan Infections; Woo, P.T.K., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Oxford, UK, 1995; pp. 631–671. [Google Scholar]
- Arizono, N.; Miura, T.; Yamada, M.; Tegoshi, T.; Onishi, K. Human infection with Pseudoterranova azarasi roundworm. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, J.; Pesson, B.; Royant, M.; Lemoine, J.-P.; Pfaff, A.W.; Abou-Bacar, A.; Yera, H.; Fréalle, E.; Dupouy-Camet, J.; Merino-Espinosa, G.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of Pseudoterranova decipiens s.s. in human, France. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallero, S.; Scribano, D.; D’Amelio, S. First case report of invasive pseudoterranoviasis in Italy. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menghi, C.I.; Gatta, C.L.; Arias, L.E.; Santoni, G.; Nicola, F.; Smayevsky, J.; Degese, M.F.; Krivokapich, S.J. Human infection with Pseudoterranova cattani by ingestion of “ceviche” in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2020, 52, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel, C.; Beaudevin, M.; Chermette, R.; Grillot, R.; Ambroise-Thomas, P. Gastric anisakidosis due to Pseudoterranova decipiens larva. Lancet 1996, 347, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; Jercic, M.I.; Weitz, J.C.; Dobrew, E.K.; Mercado, R.A. Human Pseudoterranovosis, an emerging infection in Chile. J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Bandoh, N.; Goto, T.; Uemura, A.; Sasaki, M.; Harabuchi, Y. Severe laryngeal edema caused by Pseudoterranova species. Medicine 2021, 100, e24456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, N.A. Neue parasitische Nematoden. In Beitrage zur Fauna Spitzbergens; Kukenthal, W., Ed.; Archiv für Naturgeschichte: Berlin, Germany, 1888; Volume 55, pp. 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Stiles, C.W.; Hassall, A. Internal Parasites of the Fur Seal. In The Fur Seals and Fur Seal Islands of the North Pacific Ocean; Report on Fur Seal Investigations; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1899; pp. 99–177. [Google Scholar]
- Baylis, H.A. On the ascarids parasitic in seals, with special reference to the genus Contracaecum. Parasitology 1937, 29, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggi, L.; Nascetti, G.; Cianchi, R.; Orecchia, P.; Mattiucci, S.; D’amelio, S.; Berland, B.; Brattey, J.; Smith, J.W.; Bullini, L. Genetic evidence for three species within Pseudoterranova decipiens (Nematoda, Ascaridida, Ascaridoidea) in the north Atlantic and Norwegian and Barents seas. Int. J. Parasitol. 1991, 21, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Deco, M.A.; Orecchia, P.; Paggi, L.; Petrarca, V. Morphometric stepwise discriminant analysis of three genetically identified species within Pseudoterranova decipiens (Krabbe, 1878) (Nematoda: Ascaridida). Syst. Parasitol. 1994, 29, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiucci, S.; Paggi, L.; Nascetti, G.; Ishikura, H.; Kikuchi, K.; Sato, N.; Cianchi, R.; Bullini, L. Allozyme and morphological identification of shape Anisakis, Contracaecum and Pseudoterranova from Japanese waters (Nematoda, Ascaridoidea). Syst. Parasitol. 1998, 40, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Sata, N. Multigene phylogenetic analysis reveals non-monophyly of Anisakis s.l. and Pseudoterranova (Nematoda: Anisakidae). Parasitol. Int. 2022, 91, 102631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brattey, J.; Davidson, W.S. Genetic variation within Pseudoterranova decipiens (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea) from Canadian Atlantic marine fishes and seals: Characterization by RFLP analysis of genomic DNA. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiej, K.; Simard, M.; Pufall, E.; Rokicki, J. Anisakids (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from ringed seal, Pusa hispida, and bearded seal, Erignathus barbatus (Mammalia: Pinnipedia) from Nunavut region. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2014, 94, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, M.; Mattiucci, S.; Colantoni, A.; Levsen, A.; Gay, M.; Nascetti, G. Species-specific Real Time-PCR primers/probe systems to identify fish parasites of the genera Anisakis, Pseudoterranova and Hysterothylacium (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea). Fish. Res. 2018, 202, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najda, K.; Kijewska, A.; Kijewski, T.; Plauška, K.; Rokicki, J. Distribution of ascaridoid nematodes (Nematoda: Chromadorea: Ascaridoidea) in fish from the Barents Sea. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2018, 47, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggi, L.; Mattiucci, S.; Ishikura, H.; Kikuchi, K.; Sato, N.; Nascetti, G.; Cianchi, R.; Bullini, L. Molecular genetics in anisakid nematodes from the Pacific Boreal Region. In Host Response to International Parasitic Zoonoses; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 1998; pp. 83–107. [Google Scholar]
- Najda, K.; Simard, M.; Osewska, J.; Dziekońska-Rynko, J.; Dzido, J.; Rokicki, J. Anisakidae in beluga whales Delphinapterus leucas from Hudson Bay and Hudson Strait. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 115, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koitsanou, E.; Sarantopoulou, J.; Komnenou, A.; Exadactylos, A.; Dendrinos, P.; Papadopoulos, E.; Gkafas, G.A. First Report of the Parasitic Nematode Pseudoterranova spp. Found in Mediterranean Monk Seal (Monachus monachus) in Greece: Conservation Implications. Conservation 2022, 2, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, G.A.; Berland, B. On the ecology and distribution of Pseudoterranova decipiens C (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in an intermediate host, Hippoglossoides platessoides, in northern Norwegian waters. Int. J. Parasitol. 1992, 22, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpiej, K.; Dzido, J.; Rokicki, J.; Kijewska, A. Anisakid Nematodes of Greenland halibut Reinhardtius hippoglossoides from the Barents Sea. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levsen, A.; Cipriani, P.; Palomba, M.; Giulietti, L.; Storesund, J.E.; Bao, M. Anisakid parasites (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in 3 commercially important gadid fish species from the southern Barents Sea, with emphasis on key infection drivers and spatial distribution within the hosts. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1942–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert, A.; Wasmuth, J.D. Unravelling parasitic nematode natural history using population genetics. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscione, C.D.; Poulin, R.; Blouin, M.S. Molecular ecology of parasites: Elucidating ecological and microevolutionary processes. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frainer, A.; McKie, B.G.; Amundsen, P.-A.; Lafferty, K.D. Parasitism and the biodiversity-functioning relationship. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.S. Molecular prospecting for cryptic species of nematodes: Mitochondrial DNA versus internal transcribed spacer. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieberding, C.; Morand, S.; Libois, R.; Michaux, J.R. A parasite reveals cryptic phylogeographic history of its host. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. B 2004, 271, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R.E.; Rew, M.B.; Johansson, M.L.; Banks, M.A.; Jacobson, K.C. Population structure of three species of Anisakis nematodes recovered from Pacific sardines (Sardinops sagax) distributed throughout the California current system. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattiucci, S.; Giulietti, L.; Paoletti, M.; Cipriani, P.; Gay, M.; Levsen, A.; Klapper, R.; Karl, H.; Bao, M.; Pierce, G.J.; et al. Population genetic structure of the parasite Anisakis simplex (s.s.) collected in Clupea harengus L. from North East Atlantic fishing grounds. Fish. Res. 2018, 202, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Mattiucci, S.; Bondanelli, P.; Webb, S.C.; Mignucci-Giannone, A.A.; Colom-Llavina, M.M.; Nascetti, G. Genetic relationships among Anisakis species (Nematoda: Anisakidae) inferred from mitochondrial cox2 sequences, and comparison with allozyme data. J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramilo, A.; Rodríguez, H.; Pascual, S.; González, Á.F.; Abollo, E. Population genetic structure of Anisakis simplex infecting the European hake from north east Atlantic fishing grounds. Animals 2023, 13, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.H.; Nadler, S.A.; Liu, S.S.; Podolska, M.; D’Amelio, S.; Shao, R.; Gasser, R.B.; Zhu, X.Q. Mitochondrial phylogenomics yields strongly supported hypotheses for ascaridomorph nematodes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykhovskaya-Pavlovskaya, I.E. Parasites of Fishes. The Manual; Nauka: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1985; 124p. [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel, S.; Kuhn, T.; Münster, J.; Dörge, D.D.; Klapper, R.; Kochmann, J. Parasites of Marine Fish and Cephalopods; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; 169p. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Hebert, P.D. Universal primer cocktails for fish DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite ver 35: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and windows. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villesen, P. FaBox: An online toolbox for FASTA sequences. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasev, A. On infestation of cod (Gadus morhua morhua L.) with nematodes of Anisakidae Skrjabin et Karokhin, 1945 in the Barents Sea. Int. Counc. Explor. Sea CM 1980, 24, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Karasev, A. Using of parasites as biological tags when studying intraspecies structure of cod in the coastal areas of Russia and Norway. Bull. Scand. Soc. Parasitol. 1994, 4, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Karasev, A.B. Catalog of Fish Parasites in the Barents Sea; PINRO Publishing House: Murmansk, Russia, 2003; 150p. [Google Scholar]
- Karasev, A.; Bakai, Y. Infection of the Barents Sea cod Gadus morhua and redfish Sebastes mentella with larval anisakidae nematodes: Long-term data. Bull. Scand. Soc. Parasitol. 1994, 4, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Karasev, A.B.; Bakai, Y.I.; Kalashnikova, M.Y.; Bessonov, A.A. Parasitological Monitoring of Commercial Fish in the Barents Sea: History, Results, Economic Significance; PINRO Publishing House: Murmansk, Russia, 2022; 44p. [Google Scholar]
- Dolgov, А.V. Composition, Formation and Trophic Structure of the Barents Sea Fish Communities; PINRO Publishing House: Murmansk, Russia, 2016; 336p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yaragina, N.; Aglen, A.; Sokolov, K. Cod. In The Barents Sea: Ecosystem, Resources, Management. Half a Century of Russian-Norwegian Cooperation; Jakobsen, T., Ozhigin, V.K., Eds.; Tapir Academic Press: Trondheim, Norway, 2011; Chapter 5.4; pp. 225–270. [Google Scholar]
- Biørge, A. An isopod as intermediate host of cod-worm. Fiskeridir. Scr. Ser. Havunders. 1979, 16, 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Marcogliese, D. Neomysis americana (Crustacea: Mysidacea) as an intermediate host for sealworm, Pseudoterranova decipiens (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea), and spirurid nematodes (Ascaridoidea). Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martell, D.; MacClelland, G. Transmission of Pseudoterranova decipiens (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea) via bentic macrofauna to sympatric flatfishes (Hippoglossoides platessoides, Pleuronectes ferrugineus, P. americanus) on Sable Island Bank, Canada. Mar. Biol. 1995, 122, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauksson, E. Diet and sealworm infections of short spinde sea scorpions (Myoxocephalus scorpius) and Atlantic catfish (Anarhichas lupus) in Icelandic waters. Bull. Scand. Soc. Parasitol. 1999, 9, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen, W.; McKenzie, K. The parasite fauna of the Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2001, 40, 1–80. [Google Scholar]

| Localities | Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua | American Plaice Hippoglossoides platessoides | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Prevalence, % | Intensity, min–max | Mean Intensity | n | Prevalence, % | Intensity, Min–Max | Mean Intensity | |
| G1-G3 | 150 | 4.7 | 1–3 | 1.57 | 250 | 15.6 | 1–6 | 1.62 |
| G4-G6 | 75 | 4.0 | 1–2 | 1.66 | 125 | 6.4 | 1–2 | 1.25 |
| Total | 225 | 4.4 | 1–3 | 1.60 | 375 | 12.5 | 1–6 | 1.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordeev, I.I.; Bakay, Y.I.; Kalashnikova, M.Y.; Logvinenko, A.D.; Emelianova, O.R.; Sokolov, S.G. Genetic Structure of Juvenile Stages of Phocanema bulbosum (Nematoda, Chromadorea: Anisakidae) Parasitizing Commercial Fish, Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua, and American Plaice Hippoglossoides platessoides in the Barents Sea. Diversity 2023, 15, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101036
Gordeev II, Bakay YI, Kalashnikova MY, Logvinenko AD, Emelianova OR, Sokolov SG. Genetic Structure of Juvenile Stages of Phocanema bulbosum (Nematoda, Chromadorea: Anisakidae) Parasitizing Commercial Fish, Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua, and American Plaice Hippoglossoides platessoides in the Barents Sea. Diversity. 2023; 15(10):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101036
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordeev, Ilya I., Yuri I. Bakay, Marina Yu. Kalashnikova, Andrey D. Logvinenko, Olga R. Emelianova, and Sergey G. Sokolov. 2023. "Genetic Structure of Juvenile Stages of Phocanema bulbosum (Nematoda, Chromadorea: Anisakidae) Parasitizing Commercial Fish, Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua, and American Plaice Hippoglossoides platessoides in the Barents Sea" Diversity 15, no. 10: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101036
APA StyleGordeev, I. I., Bakay, Y. I., Kalashnikova, M. Y., Logvinenko, A. D., Emelianova, O. R., & Sokolov, S. G. (2023). Genetic Structure of Juvenile Stages of Phocanema bulbosum (Nematoda, Chromadorea: Anisakidae) Parasitizing Commercial Fish, Atlantic Cod Gadus morhua, and American Plaice Hippoglossoides platessoides in the Barents Sea. Diversity, 15(10), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101036








