Effects of Different Fertilizers on Soil Microbial Diversity during Long-Term Fertilization of a Corn Field in Shanghai, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Location
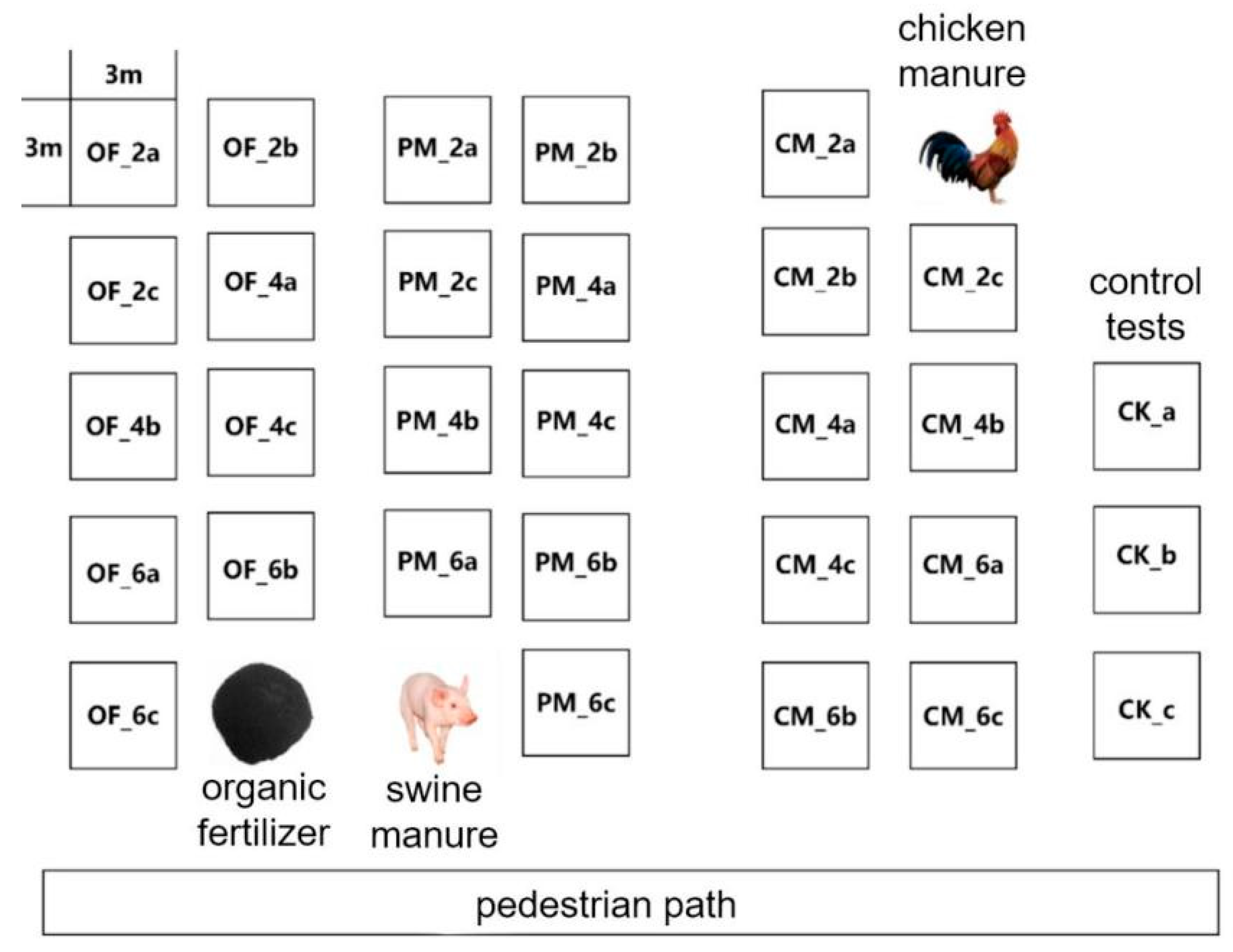
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Soil Sample Collection
2.4. Analysis Methods
2.4.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics
2.4.2. Microbial Community Characterization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Physical and Chemical Characteristics
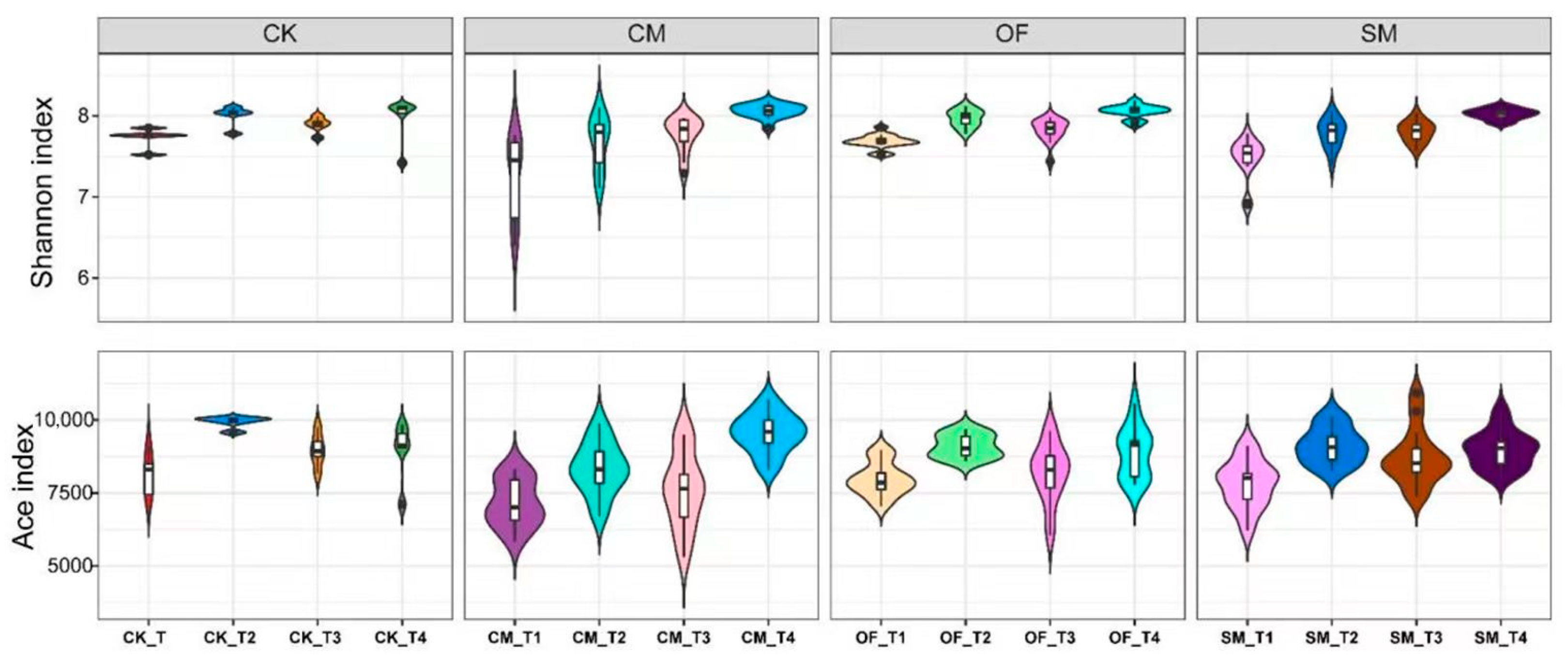
3.2. Diversity and Richness of Microbial Communities in Long-Term Fertilization
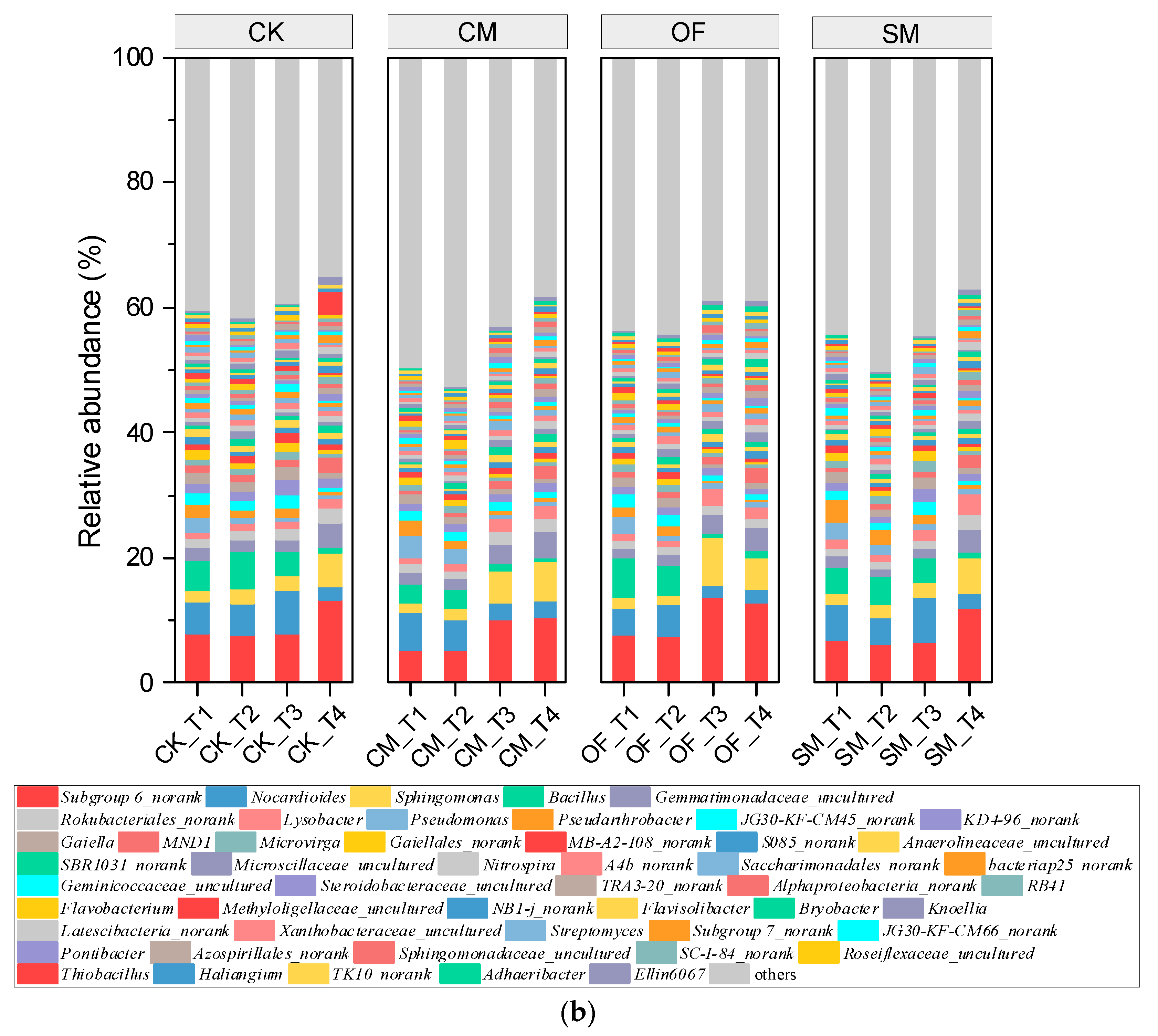
3.3. Microbial Composition and Structure in Long-Term Fertilization
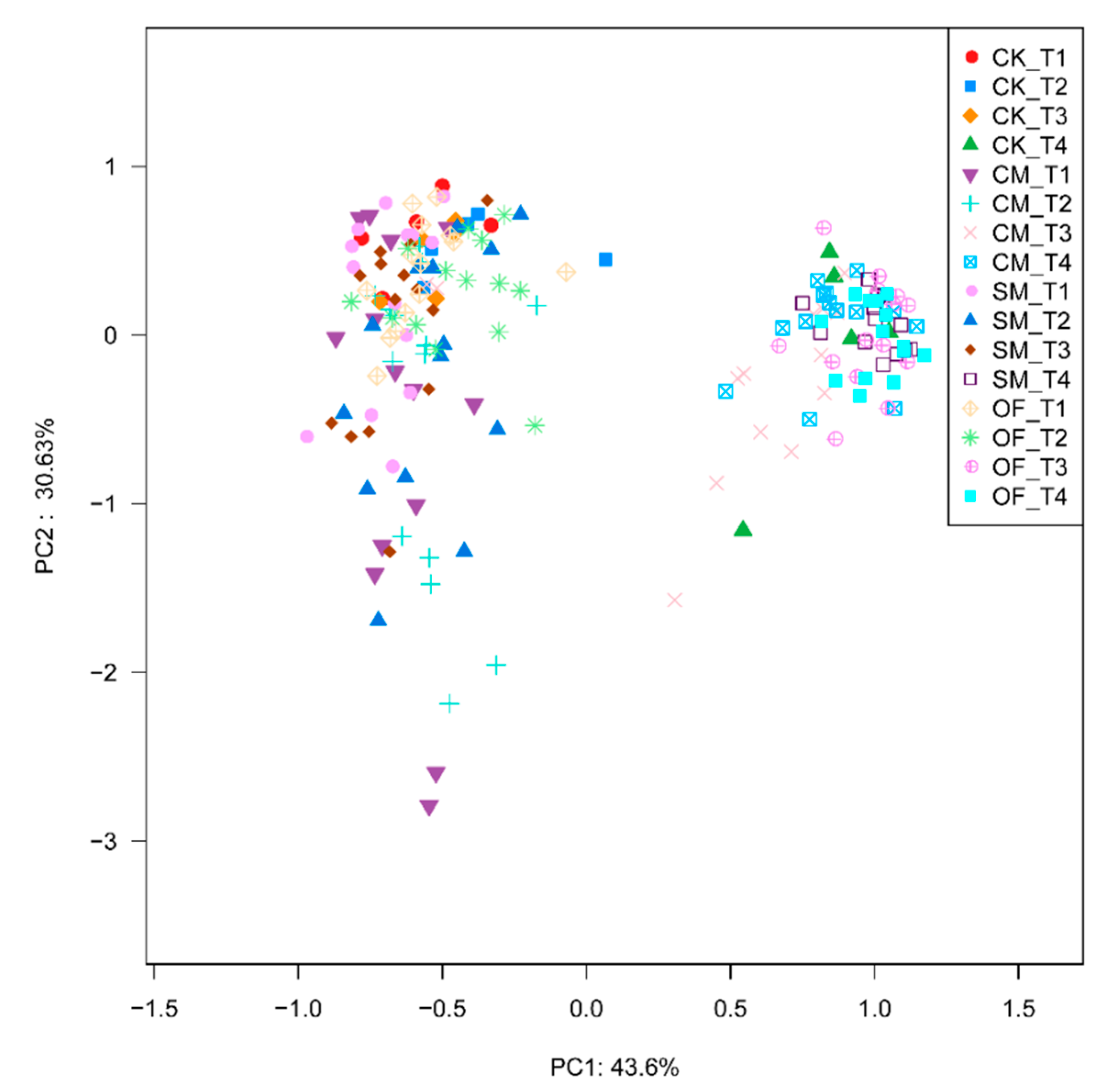
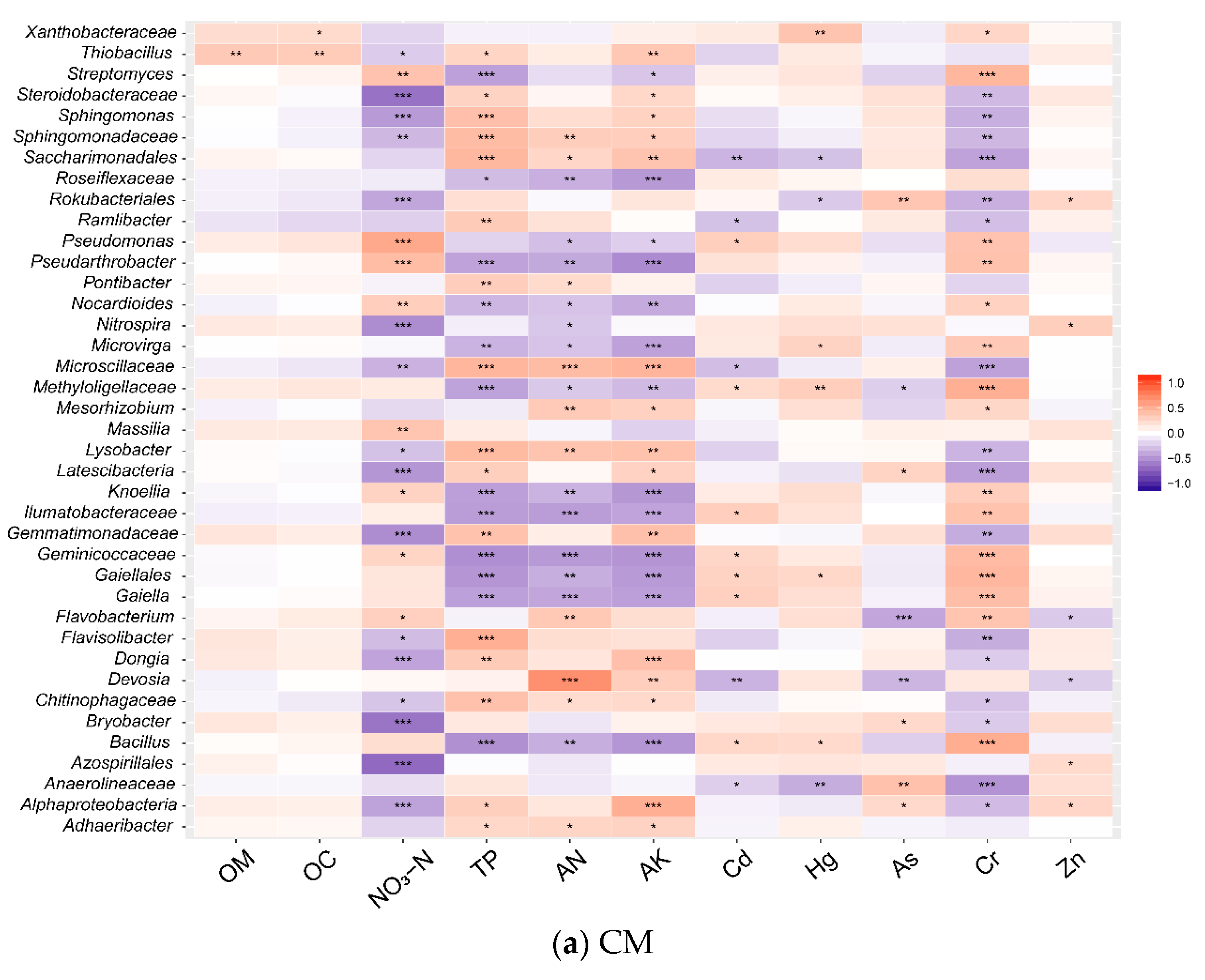
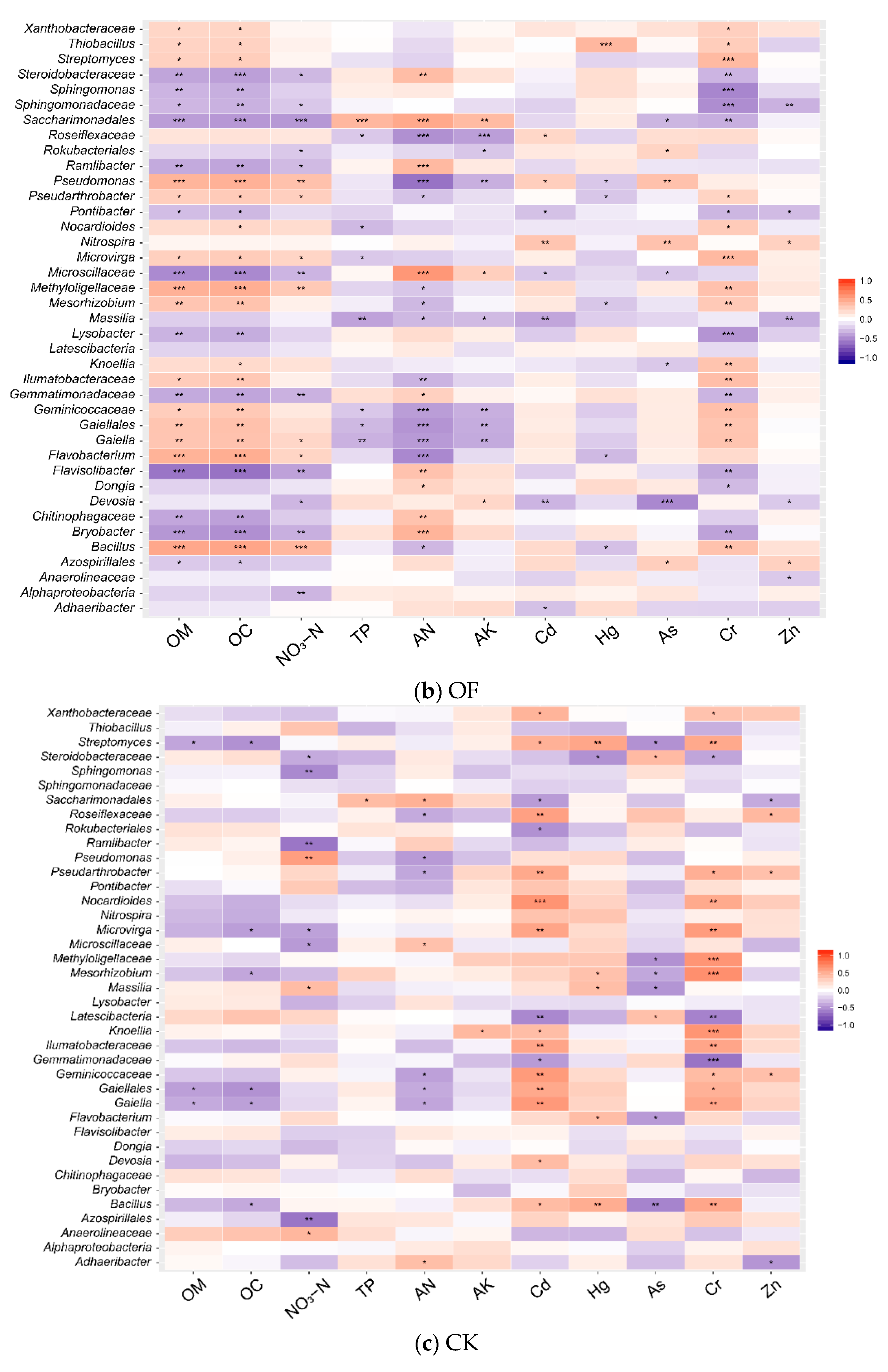
3.4. Correlations between Environmental Factors and Microbial Communities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, U.; Kumar Nayak, A.; Shahid, M.; Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Panneerselvam, P.; Mohanty, S.; Kaviraj, M.; Kumar, A.; Chatterjee, D.; Lal, B.; et al. Continuous application of inorganic and organic fertilizers over 47 years in paddy soil alters the bacterial community structure and its influence on rice production. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 262, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monard, C.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P.; Le Bot, B.; Binet, F. Relationship between bacterial diversity and function under biotic control: The soil pesticide degraders as a case study. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Ma, M.; Guan, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Du, B.; Li, J. Characteristics and driving factors of soil bacterial and archaeal communities under long-term fertilization regimes in black soil. J. Plant Nutr. Ferti. 2015, 21, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Giacometti, C.; Cavani, L.; Baldoni, G.; Ciavatta, C.; Marzadori, C.; Kandeler, E. Microplate-scale fluorometric soil enzyme assays as tools to assess soil quality in a long-term agricultural field experiment. App. Soil. Ecol. 2014, 75, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Xiong, W.; Huang, T.; Ran, W.; Li, D.; Shen, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R. Swine manure and quicklime have different impacts on chemical properties and composition of bacterial communities of an acidic soil. App. Soil. Ecol. 2016, 100, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Huang, S. Bacterial Community Structure after Long-term Organic and Inorganic Fertilization Reveals Important Associations between Soil Nutrients and Specific Taxa Involved in Nutrient Transformations. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilio, A.; González, I.; Vicente, M.F.; Gorrochategui, J.; Cabello, A.; González, A.; Genilloud, O. Patterns of antimicrobial activities from soil actinomycetes isolated under different conditions of pH and salinity. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioli, D.; Schulz, E.; Lentendu, G.; Wubet, T.; Buscot, F.; Reitz, T. Mineral vs. Organic Amendments: Microbial Community Structure, Activity and Abundance of Agriculturally Relevant Microbes Are Driven by Long-Term Fertilization Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. Response of soil microbial community to long-term fertilization regimes in different black soil locations of northease China. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2018, 28, 751–763. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. Effects of different fertilization systems on soil microbial properties in wheat-corn rotation system. Agric. Univ. HEBEI 2014. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD201501&filename=1015515560.nh (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 7, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Su, W.; Chen, H.; Barberán, A.; Xu, J. Long-term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro-ecosystems across the globe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, J.M.; Hutchison, M.L. Distribution and decline of human pathogenic bacteria in soil after application in irrigation water and the potential for soil-splash-mediated dispersal onto fresh produce. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Luo, T.; Du, M.; Ni, J.; Gong, J. Effects of livestock and poultry manure amendment and wetting-drying cycle on functional diversity of soil microial community. Guangdong Agri. Sci. 2018, 45, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Peng, S. Influence of long-term manure application in paddy soil on the functional diversity of microbial community. Chin. J. App. Environ. Biol. 2019, 25, 0593–0602. [Google Scholar]
- Girvan, M.S.; Campbell, C.D.; Killham, K.; Prosser, J.I.; Glover, L.A. Bacterial diversity promotes community stability and functional resilience after perturbation. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, Q.; Lu, X.; Zheng, M.; Li, Y. Effect of CaO2 addition on anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge at different temperatures and the promotion of valuable carbon source production under ambient condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Xiang, X.; Han, Y.; Si, T.; Yang, L. Effects of pig manure type of organic fertilizr on soil fertility of spring maize planting land and yield of spring maize. Hunan Agri. Sci. 2011, 9, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ksheem, A.M.; Bennett, J.M.; Antille, D.L.; Raine, S.R. Towards a method for optimized extraction of soluble nutrients from fresh and composted chicken manures. Waste Manage. 2015, 45, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Nordberg, Å.; Vinnerås, B. A comparison in product-value potential in four treatment strategies for food waste and faeces—Assessing composting, fly larvae composting and anaerobic digestion. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.M.; Ullman, J.L.; Bary, A.; Cogger, C.G.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Antibiotic Degradation During Thermophilic Composting. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY 525-2012; Organic Fertilizer. Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Cardinale, B.J. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity (vol 486, pg 59, 2012). Nature 2012, 489, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, V.; Murphy, G.; Romanuk, T.N. Experimental design and the outcome and interpretation of diversity–stability relations. Oikos 2011, 120, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ruijven, J.; Berendse, F. Diversity enhances community recovery, but not resistance, after drought. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Williams, M.A.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Sanderlin, J.S.; Reeves, J.H.; Jenkins, M.B.; Endale, D.M.; Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil microbial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipson, D.A. Relationships between temperature responses and bacterial community structure along seasonal and altitudinal gradients. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 59, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, A.; Otto, A.; König, S.; Becher, D.; Albrecht, D.; Schüler, M.; Teeling, H.; Amann, R.I.; Schweder, T. Functional characterization of polysaccharide utilization loci in the marine Bacteroidetes ‘Gramella forsetii’ KT0803. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuartero, J.; Özbolat, O.; Sánchez-Navarro, V.; Egea-Cortines, M.; Zornoza, R.; Canfora, L.; Orrù, L.; Pascual, J.A.; Vivo, J.-M.; Ros, M. Changes in Bacterial and Fungal Soil Communities in Long-Term Organic Cropping Systems. Agriculture 2021, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkiew, S.; Koottatep, T.; Polprasert, C.; Prombutara, P.; Jinsart, W.; Khanal, S.K. Bioponic system for nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from chicken manure: Evaluation of manure loading and microbial communities. Waste Manage 2021, 125, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, S.; Huiliñir, C.; Castillo, A.; Pagés-Díaz, J.; Guerrero, L. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from liquid swine wastes: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2020, 95, 2335–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, G.; Panneerselvam, P.; Bindu, G.H.; Ganeshamurthy, A.N. Pseudomonads: Plant growth promotion and beyond. In Plant Microbes Symbiosis: Applied Facets; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 193–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, R.S.; Lade, H.; Paul, D. Methylotrophic bacteria in sustainable agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, A.; Sahin, N.; Fujitani, Y.; Kato, A.; Sato, K.; Kimbara, K. Methylobacterium species promoting rice and barley growth and interaction specificity revealed with whole-cell matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS) analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijanowska, A.; Kaczorek, E.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Olszanowski, A. Cell hydrophobicity of Pseudomonas spp. and Bacillus spp. bacteria and hydrocarbon biodegradation in the presence of Quillaya saponin. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Chicken Manure | Swine Manure | Organic Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.31 ± 1.23 b | 6.60 ± 0.78 b | 7.42 ± 0.93 a |
| Moisture (%) | 64.2 ± 9.28 a | 56.9 ± 6.01 b | 40.8 ± 4.79 c |
| OM (g·kg−1) | 844 ± 39.92 a | 790 ± 18.80 a | 551 ± 25.61 b |
| TN (g·kg−1) | 34.3 ± 8.23 a | 32.2 ± 3.08 a | 21.6 ± 2.46 b |
| AN (mg·kg−1) | 3.17 ± 0.47 a | 2.73 ± 0.22 a | 1.16 ± 0.23 b |
| TP (g·kg−1) | 18.2 ± 0.23 b | 29.10 ± 4.22 a | 12.60 ± 1.27 c |
| AP(mg·kg−1) | 3.02 ± 0.18 a | 3.24 ± 0.35 a | 0.574 ± 0.09 b |
| TK (g·kg−1) | 3.73 ± 0.55 a | 2.05 ± 0.39 b | 2.05 ± 0.11 b |
| AK (mg·kg−1) | 21.7 ± 5.43 a | 9.93 ± 1.91 b | 12.7 ± 2.09 b |
| Heavy Metal | Chicken Manure | Swine Manure | Organic Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd (mg·kg−1) | 0.24 ± 0.02 a | 0.27 ± 0.04 a | 0.25 ± 0.00 a |
| Hg (mg·kg−1) | 0.156 ± 0.04 a | 0.173 ± 0.01 a | 0.157 ± 0.01 a |
| As (mg·kg−1) | 0.64 ± 0.09 a | 0.43 ± 0.00 b | 0.14 ± 0.00 c |
| Pb (mg·kg−1) | 19.2 ± 0.04 a | 13.3 ± 1.03 b | 15.0 ± 1.21 ab |
| Cr (mg·kg−1) | 23 ± 0.97 a | 25 ± 2.73 a | 15.5 ± 3.88 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sha, C.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, C.; Shen, C.; Su, J.; Wang, M. Effects of Different Fertilizers on Soil Microbial Diversity during Long-Term Fertilization of a Corn Field in Shanghai, China. Diversity 2023, 15, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010078
Sha C, Wu J, Wu J, Ye C, Shen C, Su J, Wang M. Effects of Different Fertilizers on Soil Microbial Diversity during Long-Term Fertilization of a Corn Field in Shanghai, China. Diversity. 2023; 15(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010078
Chicago/Turabian StyleSha, Chenyan, Jian Wu, Jianqiang Wu, Chunmei Ye, Cheng Shen, Jinghua Su, and Min Wang. 2023. "Effects of Different Fertilizers on Soil Microbial Diversity during Long-Term Fertilization of a Corn Field in Shanghai, China" Diversity 15, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010078
APA StyleSha, C., Wu, J., Wu, J., Ye, C., Shen, C., Su, J., & Wang, M. (2023). Effects of Different Fertilizers on Soil Microbial Diversity during Long-Term Fertilization of a Corn Field in Shanghai, China. Diversity, 15(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010078







