Abstract
The biodiversity, infestation patterns, and spatial distribution of organisms living in association with the introduced red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus were studied in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay, southern Barents Sea, in 2009–20013 to update a list of species, reveal long-term changes in this epibiotic community, and identify key factors affecting the prevalence and intensity of infestation. A total of 90 associated species were found throughout the study period, or twice as many as in 2004–2008, reflecting relatively low similarity between these periods. Half of the species were found on one to three crabs only. Copepods had the maximum diversity (23 species). For the first time, macroalgae were found as epibionts of red king crabs. Overall, the highest prevalences were found for the amphipod Ischyrocerus commensalis (74.2%), the copepods Tisbe furcata (57.7%) and Harpacticus uniremis (29.4%), the amphipod Ischyrocerus anguipes (27.3%), and the fish leech Johanssonia arctica (16.2%). Redundancy analysis showed that host size was the most important driver of species abundance, followed by shell condition, water temperatures in the coastal Barents Sea in May and June, and sex. These factors, coupled with the range expansion of red king crabs and climate changes in the Barents Sea, provide good explanations for the differences between the 2004–2008 and 2009–2013 fouling communities. Distribution patterns for common taxa on the host reflect larval settlement patterns and/or relationships between the host and associated species. These results expand our knowledge of infestation patterns for the invasive red king crab and provide a reference point for further monitoring.
1. Introduction
A wide range of environmental conditions resulting from interactions between cold Arctic and warm Atlantic waters make the Barents Sea the most productive shelf region of the Arctic [1,2,3,4,5], with traditional marine fisheries being mainly focused on northeast Arctic cod, northeast Arctic haddock, and other fish species [6,7,8,9,10]. However, there are no commercially important native crab species in the region. For this reason, the red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus, a large, economically important crustacean, was intentionally introduced into the Barents Sea by Soviet scientists in the 1960s [6,7]. By the mid-1990s, this species had formed a new, self-sustaining population and, by the early 2000s, its population had reached levels suitable for its commercial exploration. Crabmeat and byproducts are high-quality products containing large amounts of valuable substances [11,12,13,14]. Official large-scale fisheries were initiated in 2002 in Norway and in 2004 in Russia [7,15]. In 2018, 2019, 2020, and 2021, the total abundance levels of P. camtschaticus were estimated to be 38, 44, 58, and 52 million crabs, and landings reached 9187, 9836, 10,820, and 11,629 metric tons, respectively [11,12,14,16]. In 2021, a small-scale amateur fishery was reopened with an annual quota of 100 t [17].
Biological invasions are considered a significant threat to recipient communities, being responsible for major shifts in ecosystem structure and functioning [18,19,20,21]. The ecological impacts of the red king crab population are not well-understood but, in their comprehensive review, Falk-Petersen et al. [22] stated that adult and juvenile red king crabs can alter the benthic community structure because epibenthic species are vulnerable to this crab’s predation, and reduced biodiversity and biomass have been recorded following invasions by P. camtschaticus at some coastal sites [23,24,25]. Although some authors have proposed that predation by red king crabs on fish eggs laid on the seabed may have population-level consequences for some important fishes [22], cross-correlation analyses have shown that introduction of this crustacean has had no negative economic or fishery impacts in the Barents Sea, at least in Russian waters [6].
As the exoskeleton of the red king crab is a well-known substratum in its native areas for both attached and mobile species [26,27], an indirect impact of P. camtschaticus on the ecosystem may occur through co-invasion of new species or the spread of native parasites and epibionts, as has been suggested for other crustacean–symbiont systems [28,29,30,31]. For this reason, systematic surveys of epibiotic organisms as part of regular monitoring of the red king crab population in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay, a site where the release of red king crab larvae and juveniles was a stage in the introduction of this crustacean, have been undertaken since the early 2000s [32,33,34,35]. The results of our five-year study conducted in 2004–2008 showed that most symbiotic species were not introduced with the red king crab from their native area. However, some rare species have become rather abundant in areas where they were not previously documented, suggesting that their distribution is associated with the introduction of the red king crab and its range expansion [32]. Physical and biological conditions in the Barents Sea are favorable for P. camtschaticus, helping to explain their success and distribution in the area after 2008. Taking into account the high invasive potential of P. camtschaticus and its role in benthic communities, as well as its commercial importance, regular studies of symbiotic associations with this species were continued in subsequent years to track the establishment and adaptation processes of red king crab in the Barents Sea [34,35].
This study aimed to update the list of the species living in association with red king crabs, describe infestation patterns, and compare the new data with our previous survey.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Red king crabs were collected in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay, Barents Sea, Russia (Figure 1), in late July each year from 2009 to 2013 by divers at 5–32 m depths.
Figure 1.
Location for the sampling (square) of the red king crab in the southern Barents Sea.
Dalnezelenetskaya Bay is a small, shallow-water, semi-closed bay with a total area of 2.23 km2. The lowest water temperature (0.7 °C) is registered in February and the highest (9.7 °C) in August or, in some warm years, in July [36,37]. The minimum level of dissolved oxygen (94%) is found in December, while the maximum is registered in May (124%) [38].
2.2. Sampling and Processing
The crabs were transferred to the coastal laboratory immediately after capture. For each crab, the sex, size (carapace length (CL) = the greatest straight-line distance across the carapace from the posterior margin of the right eye orbit to the medial-posterior margin of the carapace), number of injured legs, and shell condition (determined visually following Donaldson and Byesrsdorfer [39]) were recorded. For further analysis, the crabs were divided into two groups, immature (CL = 1–90 mm) and mature (CL > 91 mm), according to size-at-age, size-at-maturity, and histological data [12,14,40,41,42].
The crabs were examined for associated species by eye, in keeping with our previous study conducted in the same area [32]. The crab body was divided into the following sections: carapace (dorsal surface), limbs (including chelae), abdomen (including female egg clutch), mouthparts (including antennae and eyes), and gills. The gills were removed, fixed in 4% formalin, and then examined using a stereomicroscope. The numbers of organisms of each solitary taxon were recorded for each body region.
We used the following standard indices of infestation [43]: (i) prevalence = proportion of crabs colonized by a species (%) and (ii) intensity = number of the associated specimens per colonized host. Intensity of infestation was determined for solitary species only.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Variations in the prevalence of infestation between different groups of red king crabs were examined using Chi-squared tests. For these analyses, we used data for crabs with the same shell condition (new shells). Chi-squared analyses were also applied to test the statistical significance of the deviations from a 1:1 sex ratio. The normal distribution and homogeneity of each dataset containing numerical values (intensity of infestation, CL, and weight) were determined using Shapiro–Wilk and modified Levene tests. When needed, data were normalized by square-root or log transformation. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed on normal data and the Kruskal–Wallis test (KWT) was performed on non-normal data.
To determine the relative importance of different factors that affected the intensity of infestation and the numbers of associated taxa per crab, we used redundancy analysis (RDA) with the following explanatory factors: (a) depth of sampling; (b) water temperature at sampling transects; (c) mean yearly temperature in the coastal Barents Sea; (d–g) mean temperatures in April, May, June, and July (these months were selected according to the crab’s molting calendar [12,14,44,45]); (h) mean yearly salinity; (i) number of injured legs; (j) age of exoskeleton (this parameter was set as categorical, with levels 1, 2, 3, and 4 corresponding to soft, new, old, and premolt shells, respectively); (k) carapace length; and (l) sex (this parameter was set as a nominal variable). RDA is a method for examining the variation in a set of response variables (i.e., epibiotic communities) using a set of explanatory variables and is conceptually synonymous with multivariate regression. RDA was chosen because the values for the gradient lengths expressed in standard deviation units of the environmental variables and the taxonomic categories were <3, as determined by detrended correspondence analysis (DCA), indicating a linear response [46]. Forward selection was performed in order to test the statistical significance of the environmental variables that contributed most strongly to the canonical model. Depths and water temperatures at sampling transects were obtained from diving reports, while temperature and salinity data for the coastal zone of the Barents Sea were taken from a long-term dataset collected by the polar branch of the Russian Federal Research Institute of Fisheries and Oceanography [47]. As environmental conditions in the coastal Barents Sea are determined by the temperature characteristics of Murmansk coastal waters, we used average values from stations 1–3 of the Kola Section, a standard transect in the Barents Sea, in the 50–200 m layer, since these variables quite adequately relate to near-bottom temperatures [36,48,49]. Rare species (occurrence <10%) were excluded from the analysis and only 12 common taxa and the total numbers of associated taxa per crab were included in the final model. Environmental variables were considered significant if their sequential addition improved the fit of species along the major RDA axes (p < 0.05, Monte-Carlo permutation test).
To evaluate long-term differences in the epibiotic communities of red king crabs, we compared our data with the 2004–2008 dataset obtained from Dvoretsky and Dvoretsky [32]. Mean intensity for each period was square-root transformed to reduce the effects of highly dominant taxa and used to calculate the Bray–Curtis similarity index [50]. The diversity of associated fauna was studied by measuring species richness S, the Shannon–Weaver (H’) diversity index, and the Pielou evenness (E).
All statistical analyses were performed using STATISTICA 10, PRIMER 5, and CANOCO 4.5. p-values below 0.05 were considered significant. All data are presented as means ± standard errors (X ± SE).
3. Results
A total of 388 Paralithodes camtschaticus individuals were collected in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay throughout the study period (n2009 = 62, n2010 = 133, n2011 = 77, n2012 = 58, and n2013 = 58). Immature individuals (CL < 90 mm) were less abundant than mature specimens (Figure 2), and their sex ratio (F:M = 1:1.2) did not differ significantly from equality (χ2 = 1.12, df = 1, p = 0.290).
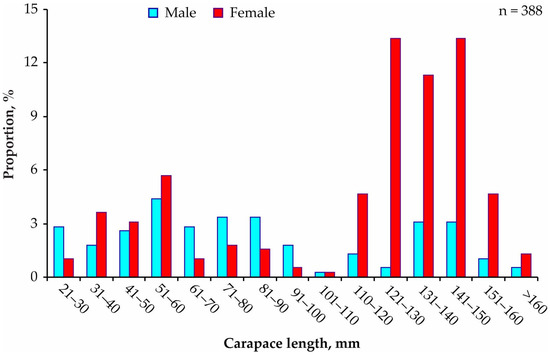
Figure 2.
Size–frequency distribution of red king crabs analyzed for associated taxa in 2009–2013.
Among adult crabs (CL > 90 mm), the sex ratio was different from the 1:1 expected ratio, with females outnumbering males (F:M = 4.3:1, χ2 = 91.18, df = 1, p < 0.001). Mature crabs were mainly represented by individuals belonging to the 121–130, 131–140, and 141–150 mm size classes (Figure 2). Mean CL and weight were higher in females (113.9 ± 2.4 mm and 1311 ± 49 g) than in males (84.0 ± 3.6 mm and 812 ± 90 g), which was confirmed by statistical analysis (ANOVA, df = 1, p < 0.001 in both cases).
The majority of red king crabs had new shells (age of exoskeleton <1 year prior to sampling): 97.4% among small crabs, 97.4% among large females, and 48.9% among large males. New-shelled crabs had no brown scratching on the coxa or ventral surface of the exoskeleton, spines and dactyls showed only slight wear, and the gills were light cream in color. Premolt and soft-shell (recently molted) crabs were most frequent among immature specimens (2.6%). Crabs with old shells represented 51.1% of mature males and only 1.0% of mature females.
The organisms found on the red king crabs collected in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay, as well as their infestation indices, are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of taxa found on immature and mature red king crabs and their indices of infestation (prevalence (PR), %; intensity (IN), individuals per crab) in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013.
A total of 90 taxa were identified: 34 on immature and 88 on mature crabs. Copepoda represented the highest number of species (n = 23, 25.6%) followed by Polychaeta (n = 12, 13.3%), Hydrozoa (n = 8, 8.9%), Bryozoa (n = 8, 8.9%), and Amphipoda (n = 7, 7.8%). The number of species per crab ranged from 0 to 23, with a median level of 3 species.
Forty taxa were found on one, two, or three crabs with prevalences as low as <1%; four species had prevalence levels of 5–10%; and ten species had high prevalences (>10%). Among these, the amphipods Ischyrocerus commensalis and I. anguipes, the copepods Tisbe furcata and Harpacticus uniremis, and the fish leech Johanssonia arctica were most frequent (Table 1). Symbiotic copepods and amphipods, as well as the spirorbid worm Circeis armoricana and the bivalve mollusk Heteranomia squamula, demonstrated the highest values for the mean and maximum intensity of infestation (Table 1).
The RDA used to investigate how the environmental variables explained the variance in the crab–epibiont communities showed that the first two axes explained large proportions of the variance in the species–environment data (axis 1 = 89.1% and axis 2 = 9.1%) (Figure 3).
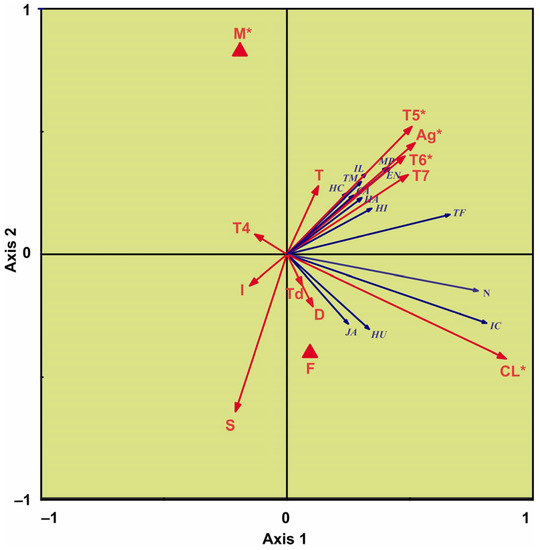
Figure 3.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) biplot showing relationships between biotic variables (square-root-transformed intensity of common crab-associated organisms and total number of species per crab) and environmental variables. Abbreviations of biotic variables (blue arrows): CA—Circeis armoricana, EN—Ectinosoma normani, HI—Harmothoe imbricata, HA—Hiatella arctica, HC—Harpacticus chelifer, HU—Harpacticus uniremis, JA—Johanssonia arctica, IC—Ischyrocerus commensalis, IL—Ischyrocerus latipes, MP—Mesochra pygmaea, TF—Tisbe furcata, TM—Tisbe minor. The environmental variables are shown with red arrows: T and S—annual bottom temperature and salinity, T and T4–T7—annual temperature and mean bottom temperatures at station 1 in the Kola Transect in April–July, I—number of injured legs, CL—carapace length, Ag—shell condition, D—depth of sampling. The sex of crabs (M—male, F—female) is represented with red triangles (nominal variable). Asterisks indicate significant factors (Monte-Carlo permutation test, p < 0.05).
The ordination diagram revealed that the first axis was strongly correlated with carapace length, shell condition, and water temperature in the Kola Section in May–July, while the second axis was mainly associated with the sex of crabs and salinity (Figure 3). The high intensities of Circeis armoricana, Ectinosoma normani, Harmothoe imbricata, Harpacticus chelifer, Ischyrocerus latipes, Mesochra pygmaea, Tisbe furcata, and Tisbe minor were positively related to shell condition and water temperature in the Kola Section in May–July. The intensities of Ischyrocerus commensalis, Harpacticus uniremis, and Johanssonia arctica, as well as the total number of species per crab, were positively associated with carapace length, depth of sampling, salinity, and bottom temperature on the day of sampling (Figure 3). The forward selection procedure revealed that, of the thirteen environmental variables, only five (carapace length, shell condition, water temperature in the Kola Section in May–June, and sex) significantly contributed to the species–environment model (Monte-Carlo permutation test, full model, n = 999, p < 0.05) (Table 2).

Table 2.
List of environmental variables influencing mean intensities of epibiotic species on red king crabs collected in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013 (Monte-Carlo permutation test in RDA).
Similar patterns were found for the prevalence of infestation. T. furcata copepods, I. commensalis amphipods, and J. arctica fish leeches were more frequent on adult females, while Mesochra pygmaea copepods and Ischyrocerus latipes amphipods had higher incidences on adult males with the same shell conditions (Figure 4 and Supplementary Material Table S1).
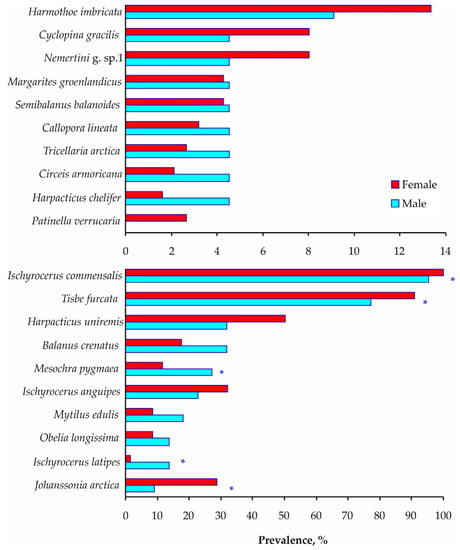
Figure 4.
Total infestation prevalence on Paralithodes camtschaticus adult males and females with new shells in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013. Asterisks indicate significant differences (Chi-squared test, p < 0.05).
In this study, female sizes (135.8 ± 0.94 mm CL) were significantly larger compared to male sizes (122.0 ± 4.7 mm CL) (KWT, H = 7.30, df = 1, p = 0.007). Considering the most common taxa colonizing immature and mature crabs, significantly different prevalences of infestation were found in 20 of the 24 cases (Figure 5 and Table S2).
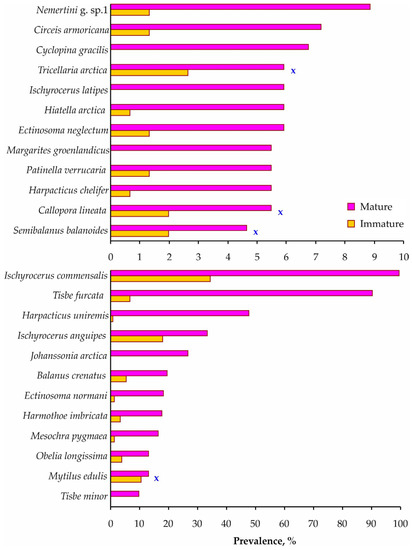
Figure 5.
Total infestation prevalence on Paralithodes camtschaticus immature and mature individuals in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013. X indicates insignificant differences (Chi-squared test, p > 0.05).
Furthermore, mature red king crabs with old shells tended to be infested more frequently than crabs with new shells. This pattern was found for 13 of the 20 common taxa (Figure 6 and Table S3).
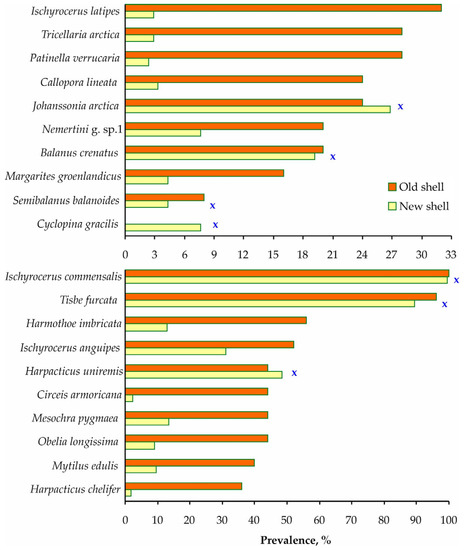
Figure 6.
Total infestation prevalence on adult red king crabs with new and old shells in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013. X indicates insignificant differences (Chi-squared test, p > 0.05).
A comparison of epibiotic assemblages associated with immature crabs revealed low similarity between the 2004–2008 and 2009–2013 datasets (Bray–Curtis index = 32.8%). In the case of adult crabs, the degree of similarity was higher (Bray–Curtis index = 52.1%). Biodiversity patterns among the associated assemblages during the two periods varied substantially. Species richness and Shannon–Weaver diversity were higher in the period 2009–2013 for both immature and mature crabs.
A similar pattern was found in the case of the Pielou’s index for mature crabs, while the evenness was higher in 2004–2008 for immature crabs. Male crabs had higher diversity indices than females (Table 3).

Table 3.
Diversity indices of fauna associated with red king crabs in the coastal Barents Sea.
These differences were attributed to the appearance of symbiotic copepods on crabs in 2009–2013 and the significantly higher prevalence levels registered for the majority of common taxa in that period (Figure 7 and Table S4).
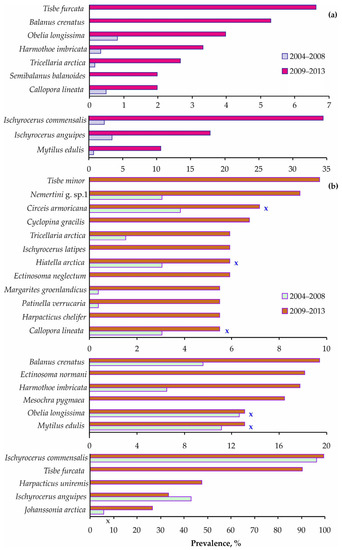
Figure 7.
Total infestation prevalence on red king crabs from Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the 2004–2008 [32] and 2009–2013 periods. (a) Immature crabs, (b) mature crabs. X indicates insignificant differences (Chi-squared test, p > 0.05).
In contrast, the mean intensities of the most frequent species did not differ significantly between the study periods, except for the symbiotic amphipods Ischyrocerus commensalis and I. anguipes, which demonstrated opposite patterns on adult crabs: the former species was more abundant in 2009–2013 and the latter in 2004–2008 (Figure 8 and Table S5).
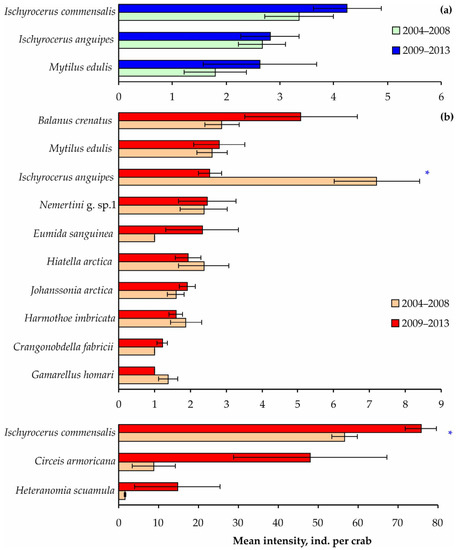
Figure 8.
Mean intensity of common taxa on red king crabs from Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the 2004–2008 [32] and 2009–2013 periods. Horizontal bars show standard errors. (a) Immature crabs, (b) mature crabs. Asterisks indicate significant differences (Kruskal–Wallis test, p < 0.05).
Mean carapace lengths of immature crabs were 31.4 ± 0.6 mm and 55.6 ± 1.5 mm in 2004–2008 and 2009–2013, respectively (ANOVA, F = 289.61, df = 1, p < 0.001). Mature crabs were also significantly smaller (132.8 ± 0.7 mm vs. 135.0 ± 1.0) in the 2004–2008 period (ANOVA, F = 289.61, df = 1, p < 0.001).
Localization patterns of common groups on the red king crabs from Dalnezelenetskaya Bay are presented in Figure 9.
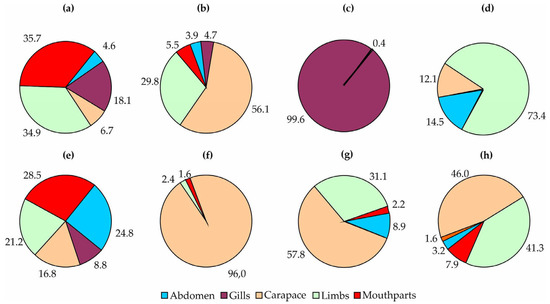
Figure 9.
Localization patterns of common taxa on red king crabs from Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013. (a) Ischyrocerus commensalis, (b) Ischyrocerus anguipes, (c) Tisbe furcata, (d) Hirudinea, (e) Mytilus edulis, (f) Balanus crenatus, (g) Bryozoa, (h) Hydrozoa.
The amphipod I. commensalis was common on the limbs and mouthparts, whereas I. anguipes was abundant on the carapace and, to a lesser degree, on the limbs. Almost all specimens of Tisbe were found in the gills. The fish leech J. arctica was predominantly found on red king crab limbs. The blue mussel M. edulis was most frequently found on the mouthparts, followed by the abdomen. The highest numbers of the barnacle B. crenatus were registered on the carapace, while bryozoans and hydrozoans exhibited a preference for the carapace and limbs. The latter two groups demonstrated consistent localization patterns in 2004–2008 and 2009–2013, and the same was observed for fish leeches (Figure 10).
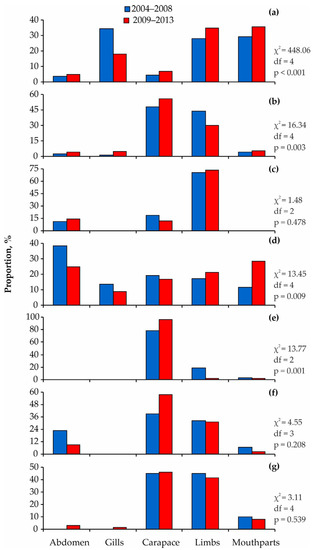
Figure 10.
Comparison of localization patterns of common taxa on red king crabs from Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the 2004–2008 [33] and 2009–2013 periods. (a) Ischyrocerus commensalis, (b) Ischyrocerus anguipes, (c) Hirudinea, (d) Mytilus edulis, (e) Balanus crenatus, (f) Bryozoa, (g) Hydrozoa.
We found significant differences in the spatial distribution of other common associated species on red king crabs during the periods studied (Figure 10). This result corresponded with a significant difference in the distribution of adult females with different-aged shells (χ2 = 14.43, df = 3, p = 0.002): in 2004–2008, we found a higher proportion of individuals with old shells (7.4%) and a lower proportion of specimens with new shells (91.8%).
4. Discussion
The size–frequency distribution of Paralithodes camtschaticus observed in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay throughout the study period showing the predominance of adult crabs contrasts with the earlier period when immature red king crabs were found more frequently than mature individuals [32,51]. This pattern may partially be explained by the different study periods: during 2009–2013, the crabs were collected in July, while during 2004–2008, most animals were captured in August, the period when large females start to migrate to deep-water sites. However, it is more likely that the lower proportion of small crabs is associated with a shift in climatic conditions in the Barents Sea ecosystem. The maximum temperature anomalies that occurred in the period 2001–2006 were followed by a smooth decrease in subsequent years, with a new, less pronounced peak in 2012 [36]. Climatic conditions have been shown to affect stock indices of juvenile red king crabs. For example, a significant decrease in the abundance of small individuals was registered after the freeze-over of Kola Bay in winter 2010–2011. This factor has greater importance for 0–2 year old crabs and, as a result, the proportion of such animals was lower in 2004–2008, which also explains the higher CLs of immature crabs in 2009–2013. The skewed sex ratio in adult crabs has been attributed to migration behavior during the mating period of mature male P. camtschaticus because most of the males migrate to deep-water areas after mating in spring, leaving a greater proportion of females at coastal sites [40]. The high proportion of females in the total catch explains their higher mean CL and weight when compared to males.
Crustaceans serve as hosts for many sessile and mobile taxa worldwide, contributing significantly to the biodiversity of marine ecosystems globally [29,52,53]. Our study provides an expanded list of taxa that can be found on the body of P. camtschaticus in the Barents Sea. The majority of these organisms have low frequencies of occurrence and may be considered occasional visitors. This pattern, however, is not absolute. For example, the hydrozoan Coryne hincksi occurs exclusively on the bodies of host organisms such as other hydrozoans and spider crabs [54,55] and, in the Barents Sea, it may be considered a facultative symbiont of invertebrates, including red king crabs [56]. The group of symbiotic species also included amphipods, copepods, polynoid polychaetes, and fish leeches. The amphipods Ischyrocerus spp. were found to colonize the northern stone crab Lithodes maja [35,57], the spider crab Hyas araneus [55], and the snow crab Chionoecetes opilio [58]. They successfully reproduce on red king crabs and receive some benefits from the symbiotic lifestyle [59,60,61,62]. Copepoda is a new group of red king crab symbionts in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay [63]. However, the first record of Tisbe sp. on Paralithodes camtschaticus was reported much earlier by Jansen et al. [64], who studied infestation patterns for red king crabs in Varangerfjord, northern Norway. The appearance of this symbiotic copepod in Dalnezelenetskay Bay (a site situated approximately 285 km east of Varangerfjord) in 2009, and a subsequent increase in the copepod diversity [33], may be attributed to the range expansion of infested red king crabs from the western sites of the Kola Peninsula. Similar situations have been described for the amphipods Ischyrocerus and fish leeches Johannsonia, which became abundant in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay and in the open Barents Sea after the introduction of red king crabs [32,65]. At the same time, the occurrence of other frequent copepods leads us to believe that other factors may contribute to the colonization process on red king crabs. The majority of copepods were found in 2012 and 2013 when water temperature increased considerably in comparison to the three previous years [36]. This assumption is confirmed by the role of water temperature in driving the fouling communities on red king crabs (Figure 3, Table 2). Interestingly, the water temperature on the day of sampling, the mean July temperature, and the annual temperature were insignificant factors, whereas temperatures in May and June significantly explained 4 and 2% of the total variation. Fouling communities on crustacean hosts are not formed immediately. This process requires some time for the establishment of biofilms and the settlement of planktonic larvae in the case of sessile epibionts or for the search for a host and its colonization in the case of mobile symbionts [66]. The majority of red king crabs in the study area were mature females, which usually molt in mid-April after mating and spawning [40]. It seems that, in the following two months, the new shells of these females are colonized by the majority of epibiotic species. Both rapid and unforeseen changes in the Arctic climate system, referred to as “borealization” [67], and the introduction of red king crab into the Barents Sea may affect the diversity, structure, and biomass of benthic communities. Such shifts may also contribute to the increased biodiversity of fouling communities on P. camtschaticus in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay. This is especially important for typical epibiotic species, such as hydrozoans, bryozoans, barnacles, and mollusks, because the dispersion and survival of their larvae, as well as successful settlement, strongly depend on water temperature and the presence of suitable substrata [68,69], such as carapaces of red king crabs. In this regard, we can also highlight the first observation of macrophytes on P. camtschaticus in 2013. Until that year, macroalgae in the Barents Sea were registered as epibionts of the great spider crab Hyas araneus [55]. Moreover, epiphytes tend to colonize brachyuran crabs, probably due to their food preference and the chemical composition of carapaces [35].
The results of statistical analyses showed that host size is the most important factor affecting the indices of infestation (Table 2). Greater prevalence levels for associated species on larger crabs seem to be a common pattern in crustaceans and other hosts [70,71,72,73]. Large adult crabs provide a larger area for settling organisms. Furthermore, mature red king crabs molt less frequently (usually 1 time per year or less often in the case of crabs with CLs greater than 110 mm, which can skip-molt for several years [40]), providing a more stable substrate for colonization. In general, both immature and mature crabs were larger in 2009–2013 than in 2004–2008, which can, in part, explain the higher biodiversity of associated species and their higher prevalences in both periods (Figure 7). There was, however, one exception to the rule: the amphipod Ischyrocerus anguipes was more prevalent and had a higher intensity of infestation in the period 2004–2008. This result might be associated with inter-species interactions. Previous analysis of co-occurrence indicated direct competition for space between I. anguipes and its congener I. commensalis on the body of red king crabs in such a way that larger specimens of I. commensalis with larger gnathopods displaced I. anguipes from the hosts, thus decreasing the infestation levels of the latter species [74].
Shell condition also significantly affected the indices of infestation on red king crabs. As expected, the crabs with old shells had higher prevalence rates than those with new shells. The intermolt period in mature male crabs with old shells may reach 1–4 years [40], providing more time for larval settlement and development of crab-associated populations.
We found that crab sex was also a significant contributor to the total variation in the infestation indices. The prevalences of Johanssonia arctica, Tisbe furcata, and Ischyrocerus commensalis were higher on females, which may be explained by their larger sizes in the sample of adult crabs with new shells. In native areas, female red king crabs have been found to have higher prevalences of infestation by brood parasites, such as nemertean worms, which were concentrated on egg masses [75]. In the Barents Sea, we found only a few amphipod specimens on the female egg clutches, but the symbionts ingested dead eggs and may be considered scavengers rather than parasites [76]. However, higher proportions of red king crabs infested by the amphipod Ischyrocerus latipes and the copepod Mesochra pygmaea, as well as a higher mean intensity of Tisbe furcata, were observed among males. Male red king crabs, in contrast to females, can migrate long distances [40] and more frequently have old shells [51], perhaps resulting in increased symbiotic organism overgrowth.
The spatial distribution of associated species on the host body may be interpreted as a result of larval settlement patterns [71,77,78], host–symbiont relationships, or inter- and intra-specific relationships between symbionts/epibionts [74,79,80,81]. Indeed, cirripedians, bryozoans, and hydrozoans dominated the carapace and limbs; i.e., the most accessible crab body parts for epibiotic species. Most of the analyzed blue mussels were relatively adult individuals, indicating their colonization via direct attachment to a resting host or when the host feeds on mussel beds, explaining the predominance of these mollusks on the crab abdomen and mouthparts. Fish leeches (Hirudinea) use the limbs of crustacean hosts for cocoon ovipositioning both in the Pacific Ocean and in the Barents Sea [27,82,83,84,85]. Thus, their localization on the appendages of P. camtschaticus from Dalnezelenetskaya Bay is not surprising. Feeding on the host’s food is one reason explaining the relatively high concentrations of I. commensalis amphipods on the mouthparts of red king crabs. Smaller specimens have to migrate to other parts of the host as a result of intra-specific competition [79]. The sympatric amphipod I. anguipes occupies the carapace and limbs and is less abundant on the mouthparts due to inter-specific competition with I. commensalis [74]. It is known that colonization of gills provides symbionts with protection from predators and aeration. This is important for very small organisms, such as copepods and juvenile amphipods [33,62]. Significant differences in the localization of the common species in the two studied periods may be explained by varying occurrences of P. camtschaticus size classes, different proportions of crabs with new and old shells, possible differences in the crab rations, and specific interactions between epibionts and symbionts.
5. Conclusions
In Dalnezelenetskaya Bay, the communities of epibionts/symbionts living on the bodies of Paralithodes camtschaticus are complex and dynamic systems. From the 2004–2008 period to the 2009–2013 period, the biodiversity of this community and the infestation indices of common species increased considerably, reflecting changes in the size–frequency distribution of red king crabs and in environmental conditions in the coastal Barents Sea. Currently, Copepoda is the most diverse group of symbionts, followed by Polychaeta and Amphipoda. The majority of epibiotic species belong to the Hydrozoa and Bryozoa groups. For the first time, macroalgae as epibionts of a lithodid crab were documented in the Barents Sea. The growing number of epibiotic species on the crabs indicates that they have become a suitable host for native benthic organisms, including rare species. This epibiotic system provides a unique opportunity for further research on red king crab invasion history, as well as studies on the biology of their common symbionts, which are difficult to access using standard sampling methods. From this perspective, our data may be useful for further monitoring of host–symbiont interactions and infestation patterns in the Barents Sea red king crab population.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15010029/s1, Table S1. Comparisons of prevalence levels (%) of common taxa on mature male and female red king crabs with new shells in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013. Table S2. Comparisons of prevalence levels (%) of common taxa on immature and mature red king crabs from Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013. Table S3. Comparisons of prevalence levels (%) of common taxa on mature red king crabs with new and old shells in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the period 2009–2013. Table S4. Comparisons of prevalence levels (%) of common taxa on adult red king crabs with new shells in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the 2004–2008 and 2009–2013 periods. Table S5. Comparisons of mean intensities (individuals per crab) of common taxa on adult red king crabs with new shells in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay in summers during the 2004–2008 and 2009–2013 periods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G.D.; data curation, A.G.D. and V.G.D.; formal analysis, A.G.D. and V.G.D.; methodology, A.G.D. and V.G.D.; investigation, A.G.D. and V.G.D.; project administration, V.G.D.; resources, V.G.D.; software, V.G.D.; supervision, A.G.D.; validation, A.G.D. and V.G.D.; visualization, V.G.D.; writing—original draft, A.G.D.; writing—review and editing, A.G.D. and V.G.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was carried out in accordance with Russian legislation guidelines (Federal Act 52-F3 of 24/04/1995) and approved by the Institutional Review of Murmansk Marine Biological Institute RAS (6732/253-ok, 01/12/2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for valuable comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wassmann, P.; Reigstad, M.; Haug, T.; Rudels, B.; Carroll, M.L.; Hop, H.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Falk-Petersen, S.; Denisenko, S.G.; Arashkevich, E.; et al. Food webs and carbon flux in the Barents Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2006, 71, 232–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Copepod communities off Franz Josef Land (northern Barents Sea) in late summer of 2006 and 2007. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Estimated copepod production rate and structure of mesozooplankton communities in the coastal Barents Sea during summer–autumn 2007. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 1321–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Cucumaria in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Biological aspects and aquaculture potential. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 613453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Ecology and distribution of red king crab larvae in the Barents Sea: A review. Water 2022, 14, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Commercial fish and shellfish in the Barents Sea: Have introduced crab species affected the population trajectories of commercial fish? Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) fisheries in Russian waters: Historical review and present status. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2018, 28, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglestad, J.L.; Benestad, R.; Ivanov, V.; Jørgensen, L.L.; Kovacs, K.M.; Nilssen, F.; Skjoldal, H.R.; Tchernova, J. Ecosystems of the Barents Sea Region. In Governing Arctic Seas: Regional Lessons from the Bering Strait and Barents Sea; Young, O., Berkman, P., Vylegzhanin, A., Eds.; Informed Decisionmaking for Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Coastal mesozooplankton assemblages during spring bloom in the eastern Barents Sea. Biology 2022, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Summer-fall macrozooplankton assemblages in a large Arctic estuarine zone (south-eastern Barents Sea): Environmental drivers of spatial distribution. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 173, 105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acid composition of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) leg meat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Tipisova, E.V.; Elfimova, A.E.; Alikina, V.A.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Sex hormones in hemolymph of red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acids in the circulatory system of an invasive king crab from the Barents Sea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Tipisova, E.V.; Alikina, V.A.; Elfimova, A.E.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Thyroid hormones in hemolymph of red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Animals 2022, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Inter-annual dynamics of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) stock indices in relation to environmental factors. Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakanev, S.V.; Stesko, A.V. Red king crab. In Materials Justifying Changes to the Previously Approved Total Allowable Catch in Fishing Areas in Inland Seas of the Russian Federation, on the Continental Shelf of the Russian Federation, in the Exclusive Economical Zone of the Russian Federation, in the Azov and Caspian Seas in 2021; FGBUN VNIRO (Polar Branch): Murmansk, Russia, 2021; pp. 2–16. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Renewal of the recreational red king crab fishery in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Potential benefits and costs. Mar. Policy 2022, 136, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, R.N.; Simberloff, D.; Lonsdale, W.M.; Evans, H.; Clout, M.; Bazzaz, F.A. Biotic invasions: Causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.T.; Stanislawczyk, K.; Sneekes, A.C.; Dvoretsky, A.; Gollasch, S.; Minchin, D.; David, M.; Jelmert, A.; Albretsen, J.; Bailey, S.A. Climate change opens new frontiers for marine species in the Arctic: Current trends and future invasion risks. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, V.R. Confusing invader: Acanthocyclops americanus (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) and its biological, anthropogenic and climate-dependent mechanisms of rapid distribution in Eurasia. Water 2021, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.; Fournari-Konstantinidou, I.; Sourbès, L.; Koutsoubas, D.; Katsanevakis, S. Long term interactions of native and invasive species in a marine protected area suggest complex cascading effects challenging conservation outcomes. Diversity 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk-Petersen, J.; Renaud, P.; Anisimova, N. Establishment and ecosystem effects of the alien invasive red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the Barents Sea—A review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 68, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britayev, T.A.; Rzhavsky, A.V.; Pavlova, L.V.; Dvoretskij, A.G. Studies on impact of the alien Red King Crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) on the shallow water benthic communities of the Barents Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2010, 26 (Suppl. 2), 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oug, E.; Cochrane, S.K.J.; Sundet, J.H.; Norling, K.; Nilsson, H.C. Effects of the invasive red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) on soft-bottom fauna in Varangerfjorden, northern Norway. Mar. Biodiv. 2011, 41, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Prey selectivity in juvenile red king crabs from the coastal Barents Sea. Diversity 2022, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaklan, S.D. Review of the Family Lithodidae (Crustacea: Anomura: Paguroidea): Distribution, biology and fisheries. In Crabs in Cold Water Regions: Biology, Management, and Economics Alaska Sea Grant College Program, AK-SG-02-01; MacIntosh, R.A., Ed.; Anchorage College: Anchorage, AK, USA, 2002; pp. 751–845. [Google Scholar]
- Klitin, A.K. The Red King Crab along the Shores of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands: Biology, Distribution, and Functional Structure of the Area; Natsrybresursy: Moscow, Russia, 2003. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bernier, R.Y.; Locke, A.; Hanson, J.M. Lobsters and crabs as potential vectors for tunicate dispersal in the southern Gulf of St. Lawrence, Canada. Aquat. Invas. 2009, 4, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, R. Harpacticoid copepods—Their symbiotic associations and biogenic substrata: A review. Zootaxa 2016, 4174, 448–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, R.N.; Valentich-Scott, P.; Hilgers, M.; Singh, R. New host record for the California mussel Mytilus californianus (Bivalvia, Mytilidae), epibiotic on the pacific sand crab Emerita analoga (Decapoda, Hippidae) from Monterey Bay, California (U.S.A.). Crustaceana 2017, 90, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizzera, A.; Bojko, J.; Cremonte, F.; Vázquez, N. Symbionts of invasive and native crabs, in Argentina: The most recently invaded area on the Southwestern Atlantic coastline. J. Invert. Pathol. 2021, 184, 107650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epifauna associated with an introduced crab in the Barents Sea: A 5-year study. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Copepods associated with the red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius, 1815) in the Barents Sea. Zool. Stud. 2013, 52, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. New echinoderm-crab epibiotic associations from the coastal Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epibiotic communities of common crab species in the coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and infestation patterns. Diversity 2022, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Effects of environmental factors on the abundance, biomass, and individual weight of juvenile red king crabs in the Barents Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evseeva, O.Y.; Ishkulova, T.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Environmental drivers of an intertidal bryozoan community in the Barents Sea: A case study. Animals 2022, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Aquaculture of green sea urchin in the Barents Sea: A brief review of Russian studies. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, W.E.; Byersdorfer, S.E. Biological Field Techniques for Lithodid Crabs; Alaska Sea Grant College Program: Fairbanks, AK, USA; University of Alaska: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmin, S.A.; Gudimova, E.N. Introduction of the Kamchatka (Red King) Crab in the Barents Sea. Peculiarities of Biology, Perspectives of Fishery; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 2002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size-at-age of juvenile red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the coastal Barents Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2014, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size at maturity of female red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, from the costal zone of Kola Peninsula (southern Barents Sea). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2015, 56, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Hemolymph molting hormone concentrations in red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Does spine removal affect molting process in the king red crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the Barents Sea? Aquaculture 2012, 326–329, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Smilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Kola Meridian Section. 2021. Available online: http://www.pinro.ru/labs/hid/kolsec22.php (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Mesozooplankton in the Kola Transect (Barents Sea): Autumn and winter structure. J. Sea Res. 2018, 142, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Summer macrozooplankton assemblages of Arctic shelf: A latitudinal study. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 188, 103967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 225–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Population dynamics of the invasive lithodid crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, in a typical bay of the Barents Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vader, W.; Tandberg, A.H.S. Amphipods as associates of other Crustacea: A survey. J. Crust. Biol. 2015, 35, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Britayev, T.A. Symbiotic polychaetes revisited: An update of the known species and relationships (1998–2017). Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 2018, 56, 371–448. [Google Scholar]
- Scheuring, L. Die Hydroiden. Untersuchungsfahrt des Reichsforschungsdampfer “Poseidon” in das Barentsmeer im Juni and Juli 1913. Wiss. Meeresuntersuch. Helgolandn. Ser. 1922, 13, 157–179. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G. Epibionts of the great spider crab, Hyas araneus (Linnaeus, 1758), in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteleeva, N.N. Hydroids (Cnidaria, Hydroidea) in the overgrowth of the red king crab from the coastal zone of the Barents Sea. In Proceedings of the International Symposium “Role of Climate and Fishery in the Structure Change of Shelf Zoobenthos”, Murmansk, Russia, 19–23 March 2003; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; MMBI KSC RAS: Murmansk, Russia, 2003; pp. 69–70. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epifauna associated with the northern stone crab Lithodes maia in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2008, 31, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, D.H.; Hooper, R.G.; Keats, D. Two corophioid amphipods commensal on spider crabs in Newfoundland. J. Crust. Biol. 1986, 6, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Some aspects of the biology of the amphipods Ischyrocerus anguipes associated with the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Distribution of amphipods Ischyrocerus on the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus: Possible interactions with the host in the Barents Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fouling community of the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius 1815), in a subarctic fjord of the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Population biology of Ischyrocerus commensalis, a crab-associated amphipod, in the southern Barents Sea: A multi-annual summer study. Mar. Ecol. 2011, 32, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Checklist of fauna found in zooplankton samples from the Barents Sea. Polar. Biol. 2010, 33, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, P.A.; Mackenzie, K.; Hemmingsen, W. Some parasites and commensals of red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus in the Barents Sea. Bull. Europ. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1998, 18, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen, W.; Jansen, P.A.; MacKenzie, K. Crabs, leeches and trypanosomes: An unholy trinity? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, T. Marine epibiosis: Concepts, ecological consequences and host defence. In Marine and Industrial Biofouling; Flemming, H.C., Sriyutha Murthy, P., Venkatesan, R., Cooksey, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Polyakov, I.V.; Alkire, M.B.; Bluhm, B.A.; Brown, K.A.; Carmack, E.C.; Chierici, M.; Danielson, S.L.; Ellingsen, I.; Ershova, E.A.; Gårdfeldt, K.; et al. Borealization of the Arctic Ocean in response to anomalous advection from sub-arctic seas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; McQuaid, C.D.; Porri, F. Barnacle settlement on rocky shores: Substratum preference and epibiosis on mussels. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 473, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, D.; Annushrie, A.; Niranjana, M.; Gnanasekaran, R.; Gopinath, M.; Iyyappan, J. A review on process and characterization of mussels and cirripeds for adhesive properties and applications thereof. Cur. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.D.; McDermott, J.J. Hermit crab biocoenoses; a worldwide review of the diversity and natural history of hermit crab associates. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 305, 1–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaw, I.J. Epibionts of sympatric species of Cancer crabs in Barkley sound, British Columbia. J. Crust. Biol. 2006, 26, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Camillo, C.; Bo, M.; Puce, S.; Tazioli, S.; Froglia, C.; Bavestrello, G. The epibiontic assemblage of Geryon longipes (Crustacea: Decapoda: Geryonidae) from the Southern Adriatic Sea. Ital. J. Zool. 2008, 75, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.K. Epibiont communities of the two spider crabs Schizophrys aspera (H. Milne Edwards, 1834) and Hyastenus hilgendorfi (De Man, 1887) in Great Bitter Lakes, Suez Canal, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2012, 16, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Interspecific relationships of symbiotic amphipods on the red king crab in the Barents Sea. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2010, 433, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuris, A.M.; Blau, S.F.; Paul, A.J.; Shields, J.D.; Wickham, D.E. Infestation by brood symbionts and their impact on egg mortality of the red king crab, (Paralithodes camtschatica) in Alaska. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 48, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. The amphipod Ischyrocerus commensalis on the eggs of the red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus: Egg predator or scavenger? Aquaculture 2010, 298, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, M.E.; Ramírez-Félix, E. Settlement of the barnacle Balanus trigonus Darwin, 1854, on Panulirus gracilis Streets, 1871, in western Mexico. Nauplius 2019, 27, e2019020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Biological aspects, fisheries, and aquaculture of Yesso scallops in Russian waters of the Sea of Japan. Diversity 2022, 14, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Intraspecific relationships of the red king crab symbionts in the Barents Sea. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2008, 422, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Interspecific competition of symbiotic and fouling species of red king crab in the Barents Sea. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2011, 440, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccinelli, E.; McQuaid, C.D. Commensalism, antagonism or mutualism? Effects of epibiosis on the trophic relationships of mussels and epibiotic barnacles. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2021, 540, 151549. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.A. Biology of marine piscicolid leech Johanssonia arctica (Johansson) from Newfoundland. Proc. Helmintol. Soc. Wash. 1982, 48, 266–278. [Google Scholar]
- Utevsky, S.Y.; Trontelj, P. Phylogenetic relationships of fish leeches (Hirudinea, Piscicolidae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences and morphological data. Zool. Scr. 2004, 33, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoie, L.; Miron, J.; Biron, M. Fouling community of the snow crab Chionoecetes opilio in Atlantic Canada. J. Crust. Biol. 2007, 27, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoie, L.; Miron, J.; Biron, M. Fouling community of the snow crab Chionoecetes opilio in Sydney Bight, Canada: Preliminary observations in relation to sampling period and depth/geographical location. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2007, 48, 347–359. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).