Abstract
The invasive red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, has become an abundant and important component in the food web of the coastal Barents Sea and can affect the structure and functioning of the local benthic communities through competition and predation. Although dietary composition and feeding behavior of the crab have been intensively studied, prey selectivity in this species under natural conditions remains poorly defined. For this reason, juvenile red king crabs and benthic samples were collected simultaneously at five coastal sites in Kola Bay to reveal the species composition and structure of feeding habits and the diet of red king crabs. The results of stomach and gut content analyses coupled with calculated Ivlev’s indices indicated that 2–5-year-old crabs frequently consumed bivalve mollusks in relative proportions to prey field biomasses. At all sites, juveniles selectively rejected polychaetes. In soft-bottom communities, when the average density of Bivalvia decreased, the crabs showed increased preference for Gastropoda, Crustacea, and Echinodermata. As a result of selective feeding focused on infaunal suspension-feeding mollusks, juvenile red king crabs have altered the structure of benthic communities in the mouth of Kola Bay. Our results may have important implications for evaluating the consequences of the crab introduction and its population management.
1. Introduction
Biological invasions are considered an important issue both at global and local scales and are currently the focus of considerable conservation management and ecological research [1]. Determining the rate and level of alien invasions and understanding processes controlling the success of invaders and their consequences to ecosystems are important research topics for the effective management of biological invasions [2,3]. Although increasing knowledge on the significance of biological invasions should help mitigate their consequences, many aspects of non-native or alien species’ expansion and their impact on ecosystems are still poorly known. Although incidental arrivals of non-native species in new habitats are considered an important invasion vector [4], it is human activity, including transport, aquaculture activities, wild fisheries, and live food trade, that is currently responsible for an increasing proportion of alien species naturalized in new communities [5,6]. Moreover, some human-assisted biological invasions are intentional. A prime example of such a situation is the transoceanic introduction of the red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius, 1815) from the North Pacific to the Barents Sea. This experiment was conducted in the 1960s by Soviet scientists who transported eggs, juveniles, and adult red king crabs collected in the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk and released them at coastal sites of the Kola Peninsula [7]. Some 30 years later, the crab population was considerable, and this species had spread enough to judge that it had formed a new self-sustaining population in the Barents Sea [7,8,9]. Since then, as a result of further growth and range expansion, this population has provided a basis for commercial fisheries in Norway and Russia. The Russian fishery was opened in 2004 [7,10], and currently, annual processing has increased from 9187 metric tons in 2018 to 11,629 t in 2021 [11,12,13]. Recently, a small-scale amateur fishery was reopened with a quota of 100 t per year [14]. Crabmeat is a high-quality product containing large amounts of valuable substances [15]. It is considered a delicacy that is valued by food markets and has a stable demand supporting high prices. Moreover, by-products of P. camtschaticus such as hepatopancreas, hemolymph, and shells are also considered important sources for chitin, chitosan, proteolytic enzymes, fatty acids, and other substances [16,17,18].
Red king crab fisheries maintain a lot of industries; thus, the economic benefits of the crab introduction are not in question [14]. Despite negative predictions, fluctuations in native fish and shellfish stocks have been shown to be associated with natural factors and did not correlate with this introduction [9]. At the same time, a number of reports have shown that at some coastal sites, there were significant alterations in the community structure and abundance of benthic animals after the crab invaded these areas [19,20,21,22,23,24]. One of the key questions is whether red king crabs are the only cause of the shifts in the native benthic communities or whether other factors (e.g., habitat loss, climate change) are also involved [25].
Because the red king crab is an opportunistic predator with a high feeding rate [26,27], its feeding activity is considered the most important driver of species composition and biomass of the resident biota in coastal waters of the Barents Sea [8,25]. Like other invasive species, P. camtschaticus has the potential to cause niche displacements of benthic community members and can act as a trigger of strong top-down processes indirectly affecting non-prey species through competition and cascading effects [28]. For this reason, significant ecological research has been undertaken to evaluate different aspects of feeding in red king crabs including food composition, food habits, feeding behavior, and trophic position [19,20,25,27,28,29,30]. One of the interesting but less-explored problems is food selectivity of the Barents Sea red king crab. Many marine predators including crabs have been shown to consume food items disproportionately, thus demonstrating food preference and selectivity [31,32,33,34]. Previous laboratory studies have demonstrated individual preferences in the diet of different-sized red king crabs and size-dependent prey selection [35,36], but there is a lack of data regarding prey selectivity in P. camtschaticus in the wild.
The coastal zone of the Barents Sea is the nursery area for red king crabs, and young animals occupy this area during their first five years of life [37,38], whereas adult crabs exhibit seasonal migrations [7,8]. For this reason, the coastal zone of the Barents Sea is optimal for studies on the red king crab feeding biology.
This study was undertaken to answer the question of whether juvenile red king crabs exhibit diet selectivity under natural conditions in the coastal Barents Sea for a better understanding of the role of P. camtschaticus in altering local benthic communities. In particular, we studied the structure of benthic communities, distribution of red king crabs, and contents of their digestive tracts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study was undertaken in Kola Bay (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Location of the sampling sites in Kola Bay.
It is a typical 51-km long fjord with its width gradually decreasing from 3.0–3.5 km near its mouth to 1.5–2.5 km in the center to 1.0–1.5 km at its southern end [39]. It extends up to 60 km into the mainland and has two bends dividing the area into three parts: northern, middle, and southern. The depth increases from the apex to the mouth of the basin with a maximum of 321 m. Kola Bay is separated from the open sea by a sill at 104 m water depth. Bottom substrata vary from silt or sandy silt and muddy sand at deeper sites to sand, pebbles, and rocks at sites with high water flow velocity [40]. Two rivers flow into the apex of the bay, and the main interactions between the river and seawater occur in the southern part of the area. Fresh water is slightly mixed with seawater and forms a thin layer on the surface in the middle and northern parts of Kola Bay. As a result, bottom salinity is about 33–34 psu except for a small area in the southern part of the bay. The bay’s dominant water source is the Atlantic Ocean, and the Atlantic inflow entering from the Barents Sea shelf is characterized by relatively high temperatures. At shallow-water sites (15–20 m), water temperature varies from 8 °C (southern part) to 10 °C (northern part) in summer and from 0.3 °C (southern part) to 1 °C (northern part) in winter [41,42]. The influx of Atlantic waters keeps most of the bay from freezing, although in cold winters, the southern part is covered with ice (30–40 cm). Water dynamics in the fjord are determined by tidal currents and winds which provide 100% water renewal over a 6-d period [43]. The water is stratified during the spring–summer period, so distinct halocline and thermocline are formed in surface layers [39]. Red king crabs have been registered in the bay since the 1990s. Although shallow-water sites are often occupied by juveniles, their abundance is higher in the offshore zone of Kola Bay [44,45].
2.2. Sampling
Red king crabs and benthic samples were collected during several diving surveys at 5 coastal sites in February 2006 (Site 4), May 2006 (Site 3), September 2006 (Site 5), and May 2013 (Sites 1 and 2) at depths ranging from 5 to 20 m (Figure 1). Temperature conditions in coastal areas of the Kola Peninsula were quite similar in 2006 and 2013 [38]. Our field data are in accordance with the general pattern (see below). To estimate the average density of P. camtschaticus, divers visually inspected distribution patterns of red king crabs along each transect (width 20–30 m, length 60–200 m, area 1200–6000 m2). The samples were taken once at each transect laid perpendicular to the coast along a meter-marking rope. In the case of sparse distribution, all crabs were collected. When crab-dense aggregations were detected, the divers undertook random crab sampling (n = 10–20) after measuring the length of the dense patch and then photographed crabs in patches with high and low crab densities [46]. The average density was determined visually by analyzing the photographs. These data were used to calculate the average crab density (P) as follows:
where Sa is the square of the patch with high density, Sb is the square of the patch with low density, S is the total area, Pa is the crab density in the patch with high density, and Pb is the crab density in the path with low density [46].
P = (SaPa + SbPb)/S,
The crabs were transferred to the laboratory of Murmansk Marine Biological Institute for further analyses. For each crab, the sex and shell condition (determined visually) were recorded following criteria in Donaldson and Byersdorfer [47]. The crabs were weighed and measured for carapace length (CL, the distance from the posterior margin of the right eye orbit to the medial-posterior margin of the carapace). Each crab was dissected, and its stomach and gut were removed and then placed in neutral buffered 4% formalin.
The macroinvertebrate sampling effort was distributed among the same sites simultaneously with crab sampling. Two to three benthic stations were sampled by divers at each site in all accessible habitats using 25 × 25 cm metal frames (0.0625 m2, three replicates at each station), knives, hand scoops, mesh bags, and plastic containers. On hard bottoms, epifauna and epiphytes were dissected off rocks and boulders within each sampling quadrate, and the upper sediment layers under boulders (5–10 cm) were also removed and placed into mesh bags. On soft bottoms, the divers collected the upper sediment layer (10–15 cm) within each 25 × 25 cm quadrate. Each sample was washed through a 0.5-mm sieve and then fixed with 4% neutral-buffered formalin.
2.3. Sample Analysis
In the laboratory, benthic samples were washed again, fixed in 75% ethanol, and identified to the lowest taxonomic level possible. Individuals within each taxon were calculated and weighed (precision = 0.0001 g) for each sample replicate. Mollusks were weighed with their shells, tube-dwelling polychaetes with mucous tubes were weighed with their tubes, and polychaete species with incrusting tubes were weighed without their tubes.
Stomach and gut contents were sorted under a stereoscope or light microscope and identified to the lowest possible taxon, and the presence or absence of diet items was determined for each stomach and gut. Fullness was expressed in % of the total stomach or gut volume. For further analyses, we reconstructed the initial biomass for each consumed organism found in the digestive tracts [19,20,26]. The number of sea urchins was determined by counting same-colored and same-sized sea urchin teeth [29]. The number of polychaetes was reconstructed according to the number of partly digested specimens or their front body parts. The number of gastropods was determined using their undigested opercula or radulae. The number of bivalves was assessed by counting the number of same-sized tops of the shell or different-sized shell fragments. The number of barnacles consumed was determined by counting their scuta and terga of different sizes [20]. Then, we measured linear sizes of body fragments: tooth width for sea urchins, diameter of prostomium or peristomium for polychaete worms, disc diameter for brittle stars, and operculum length for gastropods. These data were used to calculate wet weight for each organism found in the digestive tracts. When high abundances of bivalves (mainly blue mussels) were found in the stomach, we multiplied the total weight of their fragments by 20 according to our observations under controlled conditions [26]. In our study, we used weight data for sea stars as-is, assuming their regeneration ability. Alcohol weights were converted into wet weights using previously determined coefficients [48]. For each prey item, we calculated its contribution to the diet as the ratio of its weight to the total weight of food items found in the digestive tract. Because macrophytes, fish, and fish roe are not benthic invertebrates, are not regular prey, and had incidental occurrence in the digestive tracts, these food items were excluded from the analysis. Benthic organisms were divided into feeding and functional groups according to their life-history traits [49,50]. We pooled stomach content data for male and female red king crabs because their diets are quite similar [51,52].
We used Ivlev’s index of electivity (E) [53] to reveal prey selection by red king crabs in Kola Bay. The index was calculated as follows:
where ri is the percent of item i by weight in the stomach, and pi is the percent of item i by weight in the habitat. Values of electivity range from −1.0 (total selection against or inaccessibility of a prey item) to +1.0 (total selection for a prey item). A value near zero implies random selection.
E = (ri − pi)/(ri + pi),
2.4. Statistical Analysis
CL variations in red king crabs in relation to sites were tested using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test at α < 0.05 with Bonferroni p-value adjustment.
Pearson correlation coefficients were used to describe the relationships between weight proportions of benthic organisms in the crab diet and their proportions in the habitat where the crabs were collected. Before this analysis, the data were checked for normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk test and variance homogeneity using a modified Levene’s test, and then the data were square-root transformed to ensure assumptions required for parametric analyses.
Cluster analysis based on the Bray–Curtis similarity index (group average linkage) was performed to test similarities in the benthic community and in the diet content of crabs among stations. Analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) based on Bray–Curtis similarity matrices of the contribution of benthic species to the total community biomass or gut content was used to test for differences between survey sites. We used the SIMPER procedure to reveal the contribution (in %) of each benthic taxon to the total dissimilarity within the different stations.
Statistical analyses were performed in the software packages PAST 3.26 and PIMER 5.0.
3. Results
3.1. Red King Crabs
Dense aggregations of red king crabs were registered in the northern part and near the border between the northern and middle parts of Kola Bay (Table 1).

Table 1.
Red king characteristics at five sites in Kola Bay, southern Barents Sea.
A 10-fold decrease in the average crab density was registered in the southern part (Sites 4 and 5). The average CL and weight differed significantly among sites (Kruskal–Wallis test, df = 4, H = 57.85, p < 0.001 for CL and df = 4, H = 58.16, p < 0.001 for weight). We found no differences in CL and weight between Sites 1 and 2 (Dunn’s test, p > 0.05) where larger crabs were present (Age 4–5 yrs) and Sites 3, 4, and 5 (Dunn’s test, p > 0.05 for each pair) comprised of smaller crabs (Age 2 yrs). All crabs had new shells. Red king crabs prevailed on muddy sand or mixed sediments, i.e., within the most common biotopes within the study area.
3.2. Benthic Communities
Benthic community characteristics demonstrated significant differences across an oceanographic gradient from the apex to the mouth of Kola Bay (Table 2).

Table 2.
Benthic community characteristics at five sites studied for food selectivity of red king crabs in Kola Bay, southern Barents Sea.
Cluster analysis separated the benthic stations into three distinct groups at 23% level of similarity (Figure 2).
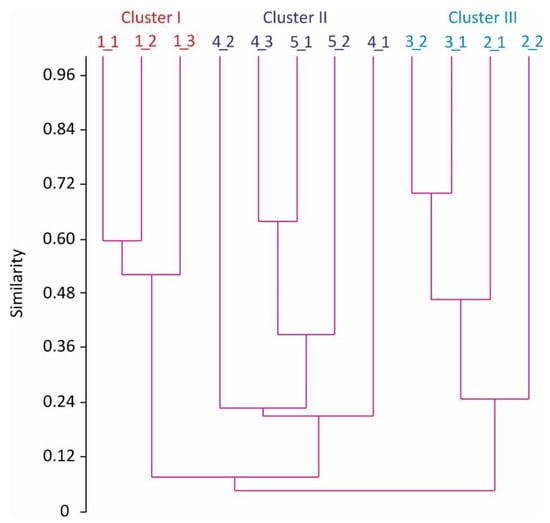
Figure 2.
Percent similarity cluster dendrogram of contributions of benthic animals to the total community biomass (%) in Kola Bay.
The ANOSIM indicated that there were significant differences in the contribution of benthic species for the three groupings delineated with the cluster analysis (Global R = 0.991, p < 0.001). Cluster I was composed of muddy-sand stations dominated by the bivalves Macoma calcarea and Crenella decussata and the polychaete Cistenides granulata. Cluster II included stations at Sites 4 and 5 dominated by Laonice cirrata. Cluster III consisted of stations located on hard bottoms and mixed sediments where the sessile polychaete Spirobranchus triqueter was the most common. The SIMPER analysis showed that three taxa (Spirobranchus triqueter, Laonice cirrata, and Macoma calcarea) primarily accounted for the observed differences in the benthic groups (Table 3).

Table 3.
List of taxa which contributed the most to dissimilarity within groups of benthic communities delineated with cluster analysis in Kola Bay.
In the inner part of the bay (Site 5), the contribution of dominant polychaetes and bivalve mollusks to the community in soft-bottom habitats was two times higher (35–38%) in comparison to the open part (15–17%, Site 1). Polydominant communities were also registered on mixed sediments at Site 2, whereas a monodominant community composed of the sessile polychaete S. triqueter (70%) was found on hard-bottom substrate at Site 3. We registered diverse benthic fauna within the survey area. In habitats of mixed sediments and on hard bottoms, from 9 to 11 phyla of invertebrates were registered, while 7 phyla were found on soft bottoms (Table 2).
The total benthic biomass was relatively low, especially on muddy sand at Site 1. The lowest proportion of epifaunal biota was registered at the apex of the bay. Polychaeta and Bivalvia were the most common groups in terms of their biomass within the entire study area except for hard-bottom habitats (Site 3) where only polychaete species predominated. The lowest species richness and biomass were found for Porifera, Cnidaria, Nemertea, Priapulida, Pycnogonida, Bryozoa, and Ascidiacea. From the mouth to the apex of Kola Bay, there was a clear trend of a decrease in the contribution of rare taxa accompanied by an increase in the average biomass of the most abundant taxa (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Percent composition by biomass of near-shore invertebrate communities and diet composition of red king crabs in Kola Bay: (a)—Polychaeta; (b)—Crustacea; (c)—Gastropoda; (d)—Bivalvia; (e)—Echinodermata; (f)—others.
The abundance values were quite consistent within the study area apart from Site 2 where the lowest abundance of benthic animals was found (Table 2). The highest contributions to the total abundance were registered for polychaetes at Sites 1 (52%), 4 (86%), and 5 (96%), for bivalves at Site 3 (44%), and for gastropods at Site 2 (52%).
We found a variety of trophic groups from dominating suspension feeders, deposit feeders, carnivores, and herbivores to less frequent omnivorous, detritus-feeding, parasitic, and chemosynthetic organisms (Table 1). The most diverse trophic structure occurred on mixed sediments reflecting the presence of various ecological niches. There was a pattern of decrease in the number of trophic groups from the north to the south of Kola Bay. The highest biomass was registered for suspension feeders such as infaunal burrowing semi-mobile bivalve mollusks Astarte borealis and A. elliptica (in the northern part of the survey area) and Arctica islandica (in the southern part) as well as for epifaunal tubiculous sessile serpulid polychaetes S. triqueter and Hydroides norvegica.
3.3. Diet Composition
A total of 67 digestive tracts were analyzed for food items consumed. There were no crabs with empty digestive tracts. Both stomachs and guts had relatively high fullness (60–100%). A total of 62 benthic taxa were identified (Table S1).Their contribution to the diet seemed to depend on crab size. Indeed, the most frequently occurring diet items for larger crabs at Sites 1 and 2 were the bivalve mollusks Astarte islandica, Ennucula tenuis, Mya truncata, M. calcarea, and Mytilus edulis as well as the green sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. In soft-bottom habitats, smaller crabs more frequently fed on bivalves Parvicardium pinnullatum and gastropods in the genus Littorina, Cistenides hyperborea, and, sometimes, the brittle star Ophiopholis aculeata. On hard substrata, their main food items were the bivalve Heteranomia squamula and the barnacles Balanus (Table S1). The cluster analysis revealed two groups of stations at a 23% level of similarity: one with larger crabs (Sites 1 and 2) and the other with smaller crabs (Sites 3, 4, and 5). A significant difference in the diet composition between the two groups was confirmed by the ANOSIM test (Global R = 0.895, p = 0.001). The SIMPER analysis showed that the most important contributors to dissimilarity were M. truncata (10.7%), Littorina sp. (10.4%), A. islandica (7.6%), S. droebachiensis (7.0%), and C. hyperborea (6.9%).
The total number of species involved in the crab diet tended to decrease from the mouth to the apex of Kola Bay. The most expressed patterns were found for polychaetes, gastropods, and bivalves with the latter demonstrating a 2-fold lower diversity in the southern part of the study area when compared to the northern part. Bivalve mollusks demonstrated the highest contribution to the diet of red king crabs, especially at Site 1 (Table S1). We found no significant relationship between the proportional weight of bivalves in the crab diet and their abundance in the environment (r = 0.44, p = 0.45). We also found no significant relationships between the proportional weight of bivalves and their biomass in the field (r = −0.28, p = 0.64) and their mean weight in the field (r = −0.42, p = 0.47). The proportional biomass of polychaetes in the diet showed a strong significant negative correlation with the average density of bivalves on soft bottoms (r = −0.99, p = 0.007) and no correlations with their own average density and biomass in the field (r = 0.94, p = 0.21 and r = 0.87, p = 0.33, respectively).
3.4. Comparison of the Crab Diet with Benthic Fauna
The contribution of other benthic organisms to the diet of red king crabs was mainly dependent on the community type and crab size. In particular, when polychaetes and the mollusks C. granulata, M. calcarea and C. decussata dominated a benthic community, other benthic groups had a much lower contribution for large-sized crabs. On mixed sediments where the polychaete S. triqueter and the mollusk A. borealis were most prevalent, sea urchins and polyplacophorans also contributed significantly to the stomach and gut contents. On hard bottoms occupied by dominating polychaetes (S. triqueter), red king crabs actively consumed barnacles as well as gastropod and polyplacophoran mollusks. In habitats where muddy fine sand was the main sediment fraction dominated by the polychaetes Alitta virens and L. cirrata and by the blue mussel Mytilus edulis, small-sized crabs preyed on Gastropoda (mainly Littorina spp.) and Polychaeta. In a similar community located in the southern part of the survey area (Site 5), the diet of crabs was more diverse through the inclusion of sea urchins and brittle stars (Figure 3, Table S1).
The percentage contribution of epifauna and infauna in the diet of P. camtschaticus did not reflect their ratios in the corresponding natural habitats. Infaunal species dominated the digestive tracts of crabs at Site 1 only (Figure 4a).
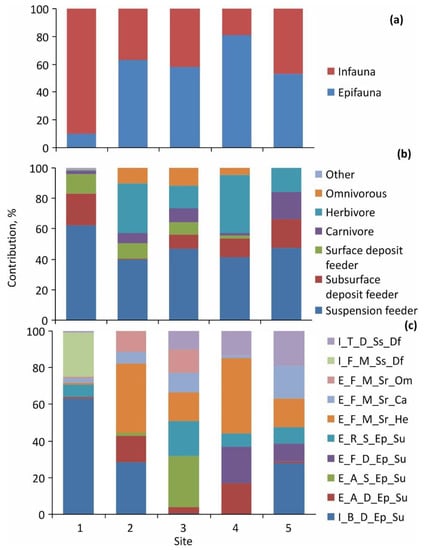
Figure 4.
Contribution of benthic organisms to the diet of red king crabs in Kola Bay: (a)—living forms; (b)—trophic groups; (c)—functional groups; I_B_D_Ep_Su—Infaunal burrowing semi-mobile epibenthic suspension feeder; E_A_D_Ep_Su—Epifaunal attached semi-mobile epibenthic suspension feeder; E_A_S_Ep_Su—Epifaunal attached sessile epibenthic suspension feeder; E_F_D_Ep_Su—Epifaunal free-living semi-mobile epibenthic suspension feeder; E_R_S_Ep_Su—Epifaunal encrusting sessile epibenthic suspension feeder; E_F_M_Sr_He—Epifaunal free-living mobile surface herbivore; E_F_M_Sr_Ca—Epifaunal free-living mobile surface carnivore; E_F_M_Sr_Om—Epifaunal free-living mobile surface omnivorous; I_F_M_Ss_Df—Infaunal free-living mobile subsurface deposit feeder; I_T_D_Ss_Df—Infaunal tubiculous semi-mobile subsurface deposit feeder.
Moreover, at Site 5 with the lowest importance of epifauna in the local community (Table 2), red king crabs predominantly fed on epifaunal invertebrates. At Site 1, suspension feeders were most abundant in the crabs’ stomachs and guts, although in the environment, this ecological group was less frequent than subsurface deposit feeders. The lowest contribution of suspension feeders to the diet was found at Sites 2 and 4 (Figure 4b) where the crabs fed on herbivorous species despite the fact that the latter were less prevalent than other groups. Subsurface deposit feeders had rare occurrences in the digestive tracts of P. camtschaticus collected on mixed sediments at Site 2, while surface deposit feeders were present at Sites 4 and 5.
Benthic organisms found in the digestive tracts belonged to 18 functional groups with a more diverse composition (14 groups) at Site 1 and less diverse (8–10 groups) at the remaining sites. The contribution of the 10 most prevalent groups varied from one site to another (Figure 4c) with infaunal burrowing semi-mobile epibenthic suspension feeders being the most preferable food items at Sites 1 and 5. Epifaunal free-living herbivorous species dominated in the stomachs and guts of red king crabs captured at Sites 2 and 4, while epifaunal attached suspension feeders were the most preferable diet items at Site 3.
We found a disproportional occurrence of different ecological groups in the crabs’ digestive tracts and in the field (Table 2). For example, at Site 1, benthic communities were composed mainly of infaunal free-living semi-mobile deposit feeders, while red king crabs preyed mainly on infaunal burrowing semi-mobile suspension feeders. Interestingly, infaunal free-living semi-mobile deposit feeders and epifaunal tubiculous sessile epibenthic suspension feeders made up a large percentage of the fauna in the environment but zero in the digestive tracts, suggesting that these groups are not a favored food.
3.5. Prey Selectivity
Food selectivity was clearly evident in red king crabs from Kola Bay (Table 4).

Table 4.
Ivlev’s electivity (E) for major taxa, trophic groups, and functional groups of benthic food items of red king crabs in Kola Bay.
At all sites, juveniles, both large- and small-sized, showed avoidance for polychaete worms that dominated in terms of abundance and biomass (Figure 2). Other abundant organisms, bivalve mollusks, had low positive or negative electivity indices indicating that Bivalvia were not selected for or against by P. camtschaticus. The same result was found for the majority of benthic taxa with low occurrence except for echinoderms which were selected by juvenile red king crabs.
Trophic groups demonstrated various electivity indices depending on location (Table 4). Red king crabs showed preference towards herbivores at all sites apart from Site 1. Although suspension feeders predominated along the entire area, there was a lack of preference for this group at all sites. In the northern part, where the average abundance of subsurface deposit feeders was high, red king crabs demonstrated avoidance for these organisms. Suspension feeders were actively selected by red king crabs at Site 1 where subsurface deposit feeders made up the largest proportion of the total biomass in the environment.
Electivity indices of benthic functional groups also displayed substantial variations (Table 4). At all sites, P. camtschaticus showed avoidance for surface deposit feeders and preference for epifaunal suspension feeders attached to substrata through broad bases (barnacles and bivalve mollusks Heteranomia spp.), especially in infaunal communities. Red king crabs also preferred epifaunal mobile herbivores (Gastropoda and Crustaceans) at all sites except Site 1. In contrast, the crabs demonstrated avoidance for epifaunal tubiculous sessile epibenthic suspension feeders (serpulid polychaetes) although the latter made up the majority of the total biomass in the environment at Site 3. With respect to infaunal semi-mobile burrowing suspension feeders, red king crabs showed both preference (at Site 1) and avoidance (at Sites 2–5) (Table 4).
4. Discussion
4.1. Red King Crabs
According to size-at-age data [54], our red king crabs belonged to the 2–5-year-old size classes, which correspond to the gregarious phase of juvenile red king crabs [55]. This result reflects behavioral patterns in this species: small crabs do not migrate far offshore and tend to aggregate in the coastal areas of the Barents Sea in contrast to adult animals which usually migrate to deeper water after spring mating in the case of males or stay at coastal sites during summer and move to the offshore waters in fall in the case of females [8,56,57]. A similar distribution pattern was noted in the eastern Murman coastal waters [37]. The predominance of new-shell individuals is explained by frequent molting events in juvenile red king crabs (2–4 times per year) which would not be expected to have old shells [58,59,60].
Densities of juvenile P. camtschaticus at different sites of Kola Bay were similar to those found in other coastal areas of the Barents Sea. So, density of young crabs at the gregarious stage varied from 1.7 to 42 ind. 1000 m–2 at a coastal site located to the east of Kola Bay [61] and from 2 to 159 ind. 1000 m–2 at sites located to the west of Kola Bay [62]. The higher density of red king crabs in the northern part of our study area is more likely associated with a higher proportion of recruiting adults and better conditions for juvenile survival due to the presence of more favorable hard substrata with rich epifauna [19,20]. Red king crabs were unevenly distributed within the entire study area with larger specimens being more frequent in the northern part of Kola. Smaller crabs tended to be more abundant in the inner part of our survey area where they often exhibited “podding” behavior, i.e., formed dense aggregations [63]. In this type of aggregation, small red king crabs are so densely packed that it would be difficult for predators to distinguish individuals or remove them [64]. In lithodid crabs, segregation by size is a well-known pattern served to avoid inter-cohort cannibalism [65].
4.2. Benthic Communities
The range of benthic biomass found for soft-bottom communities in Kola Bay is similar to that reported at sites located to the east of this fjord (20–70 g m–2) [21,66,67], although in some coastal regions the biomass may exceed 200 g m–2 [68]. Furthermore, polychaetes and bivalves were also found to be dominating taxa along the eastern half of the Kola Peninsula, and α-diversity indices were similar to our values. Much higher benthic biomasses (500–3500 g m–2) are usually registered in hard-bottom habitats in the southern Barents Sea [21,66,69], but values comparable to Kola Bay may also occur. Within the survey area, bivalves and polychaetes were most prevalent on hard substrata together with sea urchins. In contrast to Kola Bay, other studies have shown the highest contributions to the total benthic biomass for echinoderms (mainly sea urchins) and bivalves or barnacles [21,66,69]. The observed differences in the structure of benthic communities along a gradient of environmental factors in Kola Bay (Table 2, Figure 2) agree with those found in several estuarine systems with expressed salinity gradients [70,71,72,73].
4.3. Diet Composition
The diet of adult and juvenile red king crabs has been shown to include a range of macrobenthic organisms among which Bivalvia, Polychaeta, Gastropoda, and Echinodermata were most important [21,28,51,52,74,75,76]. In general, our results agree with those data, and the diet variations observed in Kola Bay were most likely associated with differences in the structure of local benthic communities.
Bivalve mollusks which often dominated benthic communities were the most common prey items for juvenile red king crabs. Polychaetes, other dominating organisms, were much less commonly found in the digestive tracts, especially at Site 1. Gastropods and echinoderms were favorable prey organisms of P. camtschaticus collected on mixed sediments and hard bottoms; barnacles were also favored by red king crabs in hard-bottom habitats. This trend, when the diversity of dietary components decreased from the mouth (open sea) to the apex of the bay, apparently reflected a decrease in the benthic diversity and biomass of preferable prey organisms in the environment [65]. Indeed, on soft substrata, we registered dramatic changes in the structure of local benthic communities (Figure 2, Table 2). So, there was a 2.3-fold decrease in the total number of bivalve species so that only five species (A. islandica, M. calcarea, M. truncata, P. pinnulatum, and M. edulis) occurred at Sites 4 and 5. The average density of Bivalvia also decreased from 1950 ind. m–2 at Site 1 to 570 and 160 ind. m–2 at Sites 4 and 5, respectively. It is known that a low density significantly reduces the chance for a prey organism to be eaten by predator crabs [77]. The decreased density and, in turn, availability of bivalves is a reason for their lower occurrence in the digestive tracts of P. camtschaticus caught in the inner part of Kola Bay. To compensate for this deficit, red king crabs have to consume alternative food sources that can explain the increased contributions of polychaetes and epifaunal gastropods and echinoderms. This assumption is confirmed by a strong negative relationship between the bivalve density in the environment and the contribution of polychaetes to the crab diet. Similar patterns have been reported for other invader crabs [78,79].
As the bivalve density decreases and the polychaete density increases, the nutritional conditions of such infaunal biotopes become less favorable or even unfavorable for juvenile red king crabs, causing them to shift their feeding behavior from passive grazing at Site 1 to active predation at Sites 4 and 5. When occupying a predatory role in soft-bottom habitats, the crabs start to consume epifaunal organisms despite their low biomass and high abundance and availability of small sedentary infaunal polychaetes. Thus, a polydominant diet composition may be considered an indicator of poor bivalve biomass in the environment.
Spatial differences found in the dietary composition of red king crabs may also be attributed to different size classes at study sites. Indeed, according to Manushin and Anisimova [76], adult specimens preferred the polychaete Spiochaetopterus typicus at deep-water sites of the Barents Sea. Fuhrmann et al. [24] suggested that in larger red king crabs (71–147 mm CL), this prey item was found at twice the rate (31.1–33.3%) of their smaller conspecifics (0–70 mm CL, 14.6%) in Porsangerfjord, Norway. Ontogenetic shifts in feeding behavior and food preference have been reported for many crab species [63,80,81]. Such shifts reflect changes in the physiology of crabs and increasing energy needs associated with their growth, increased locomotor activity, and maturation [82].
4.4. Prey Selectivity
Both positive and negative electivity indices were evident in juvenile red king crabs. Although this pattern was dependent on habitat conditions, at all sites examined, the crabs demonstrated avoidance for polychaete worms. This pattern contradicts that registered for the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) which preferred polychaetes and replaced them with bivalves only if the former occurred at low densities [34]. This result may be explained by species-specific preferences in crab-like lithodid crabs and true crabs. The bivalve contribution to the diet of red king crabs was usually the same as in the field, but in regions with high abundances of infaunal (Site 1) and epifaunal Bivalvia (Site 3), we registered positive electivity indices for this group. In hard-bottom epifaunal communities, P. camtschaticus showed preference for crustaceans and avoidance for quite abundant gastropods. In contrast, in the inner part of Kola Bay, we found a much higher contribution of gastropods to the diet in comparison to the natural biomass. This finding is in accordance with laboratory observations by Logvinovich [83] and Zubkova [84] who registered Gastropoda as very desirable prey items for red king crabs. We found high and positive electivity indices for Echinodermata. This result is explained by the fact that this group is a source of calcium, an essential element for shell-hardening in crabs [85], especially in frequently-molting juvenile red king crabs. Prey selectivity is known to be a function of prey availability [86]. One may assume that young crabs avoided some common benthic species such as small infaunal polychaetes due to their ability to dwell themselves or their small sizes. The avoidance of sedentary epifaunal polychaetes might be associated with their solid tubes that require significant efforts for removal, and crabs may take claw damage when trying to crack these tubes. As a rule, crabs prefer easy-to-obtain prey items [87]. At the same time, in Kola Bay, young red king crabs often consumed typical attached sessile species such as barnacles Balanus and Verruca as well as bivalves Heteranomia. This fact confirms species-specific and site-specific prey selectivity in red king crabs and their high potential for adaptation to various food habits. A wide dietary composition has also been recorded in other lithodid crabs [65,88,89,90].
4.5. Impact of Red King Crabs on Benthic Communities
As juvenile red king crabs demonstrate preference or avoidance for potential prey organisms and have a higher consumption-to-biomass ratio than adults [19,20,27], they can have a substantial top-down influence on benthic community abundance and composition through their feeding activities, especially at high densities. In soft-bottom habitats, one can expect a shift in the community structure towards an increased contribution of polychaetes and a decreased contribution of bivalves. At sites with low bivalve densities, feeding activity of red king crabs may cause a rapid decline in biomasses of gastropods and echinoderms. A similar result was reported by Rzhavsky et al. [91] who evaluated long-term changes in the structure of soft-bottom benthic communities in Dalnezelenetskaya Bay and reported decreased biomasses of sea urchins, bivalves, and sea cucumbers. Hard-bottom communities seem to be less vulnerable. The same conclusion has been made by Britaev et al. [92] for Dalnezelenetskaya Bay, but some changes in the size composition of prey animals and their abundance in the field may be evident [93]. The benthic trophic structure, therefore, can also be shifted towards a predominance of deposit feeders instead of suspension feeders. We can also predict a lower percentage of epifaunal species in benthic communities dominated by surface detritus feeders at high crab densities.
Our results indicated that both the structure and composition of the benthic community at Site 1 were altered demonstrating low benthic biomass and relatively minor contribution of dominating trophic groups such as subsurface deposit feeders and suspension feeders to the total benthic biomass. Typically, in such benthic habitats with active turbulence, transport of suspended particles prevails over their deposition, and communities of suspension feeders are well developed [94]. Most likely, such a community existed at Site 1 before the crab introduction and range expansion, but by the time of our study, it had been significantly altered as a result of P. camtschaticus feeding activity. Oug et al. [22] found reduced abundances of echinoderms, non-moving burrowing and tube-dwelling polychaetes, and most bivalves. A relative reduction in the average abundance of suspension and surface deposit-feeding species, as a consequence of the red king crab grazing [23], has been argued to be responsible for degradation of the sediment habitat quality in the Varanger region. Recently, we have shown that bivalve mollusks from the crabs’ digestive tracts were larger than those in the field [30]. For this reason, subsurface deposit feeders for which the crabs show avoidance can become a leading group by biomass.
5. Conclusions
Our data showed a high diversity of benthic functional groups and a complex structure of benthic communities in Kola Bay. Taking into account that the functioning of a community depends on its structure and diversity and that our study area is as diverse and complex as other coastal sites in the Barents Sea, our results may be extrapolated to the entire inshore zone of the Kola Peninsula. Our study indicated that bivalve mollusks are dominant prey items in the diet of juvenile P. camtschaticus, both by abundance and biomass. Despite their wide occurrence, polychaete worms showed a much lower contribution to the stomach and gut contents. Red king crabs have to change their feeding as the bivalve abundance decreases. At soft-bottom sites, increased proportions of polychaetes coupled with decreased proportions of bivalves will lead to an increase in crab pressure on relatively rare epifaunal gastropods, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Benthic taxa with negative electivity indices such as infaunal polychaetes, sedentary serpulid polychaetes, encrusting bryozoans, and most cnidarians are expected to save their contribution to the total biomass or even increase it. This pattern should be taken into account when studying the possible role of other factors in altering benthic communities in the Barents Sea. The feeding activity of red king crabs can mask climate-driven and anthropogenic-driven shifts in the environment. The aforementioned taxa which are avoided by P. camtschaticus may be recommended as more reliable indicators for monitoring environmental changes than impacted species. Further research is needed to more clearly understand the ecosystem effects of red king crabs for maintaining the proper management of their stocks and monitoring benthic communities in the Barents Sea.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d14070568/s1, Table S1. Percent composition of biomass (M, %) and Ivlev’s electivity (E) for benthic food items of red king crabs in Kola Bay.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.V.P. and A.G.D.; data curation, L.V.P. and A.G.D.; validation, L.V.P. and A.G.D.; formal analysis, L.V.P.; methodology, L.V.P.; software, A.G.D.; visualization, L.V.P. and A.G.D.; project administration, A.G.D.; writing—original draft, L.V.P. and A.G.D.; writing—review and editing, L.V.P. and A.G.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Zuyev Ya.A. and Goldin S.V. for diving works. We are grateful to four anonymous reviewers for their constructive and helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chan, F.T.; Briski, E. An overview of recent research in marine biological invasions. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giangrande, A.; Pierri, C.; Del Pasqua, M.; Gravili, C.; Gambi, M.C.; Gravina, M.F. The Mediterranean in check: Biological invasions in a changing sea. Mar. Ecol. 2020, 41, e12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D. Biological invasions: What’s worth fighting and what can be won? Ecol. Eng. 2014, 65, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieritz, A.; Gallardo, B.; Baker, S.J.; Britton, J.R.; Van Valkenburg, J.L.; Verreycken, H.; Aldridge, D.C. Changes in pathways and vectors of biological invasions in Northwest Europe. Biol. Invas. 2017, 19, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.T. The global dispersal of marine and estuarine crustaceans. In In the Wrong Place: Alien Marine Crustaceans—Distribution, Biology and Impacts; Galil, B.S., Clark, P.F., Carlton, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, F.T.; Stanislawczyk, K.; Sneekes, A.C.; Dvoretsky, A.; Gollasch, S.; Minchin, D.; David, M.; Jelmert, A.; Albretsen, J.; Bailey, S.A. Climate change opens new frontiers for marine species in the Arctic: Current trends and future invasion risks. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) fisheries in Russian waters: Historical review and present status. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2018, 28, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, S.A.; Gudimova, E.N. Introduction of the Kamchatka (Red King) Crab in the Barents Sea. Peculiarities of Biology, Perspectives of Fishery; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 2002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Commercial fish and shellfish in the Barents Sea: Have introduced crab species affected the population trajectories of commercial fish? Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Inter-annual dynamics of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) stock indices in relation to environmental factors. Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. New echinoderm-crab epibiotic associations from the coastal Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epibiotic communities of common crab species in the coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and infestation patterns. Diversity 2022, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakanev, S.V. Red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) of the Barents Sea. In Materials of Total Allowable Catches of Water Biological Resources in Fishing Areas in Inland Seas of the Russian Federation, on the Continental Shelf of the Russian Federation, in the Exclusive Economical Zone of the Russian Federation, in the Azov and Caspian Seas in 2023; Sologub, D.O., Ed.; FGBUN VNIRO (Polar branch): Murmansk, Russia, 2022; pp. 10–30. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Renewal of the recreational red king crab fishery in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Potential benefits and costs. Mar. Policy 2022, 136, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acid composition of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) leg meat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomareva, T.; Timchenko, M.; Filippov, M.; Lapaev, S.; Sogorin, E. Prospects of red king crab hepatopancreas processing: Fundamental and applied biochemistry. Recycling 2021, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acid composition in the hepatopancreas of the Barents Sea red king crab. Biol. Bull. 2020, 47, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acids in the circulatory system of an invasive king crab from the Barents Sea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 110, 104528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V. Effect of juvenile red king crabs on zoobenthos in Kola Bay (Barents Sea). Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2008, 422, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V. Red king crab trophic relations and its influence on bottom biocenoses. In Biology and Physiology of the Red King Crab from the Coastal Zone of the Barents Sea; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 2008; pp. 77–104. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Britayev, T.A.; Rzhavsky, A.V.; Pavlova, L.V.; Dvoretskij, A.G. Studies on impact of the alien Red King Crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) on the shallow water benthic communities of the Barents Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2010, 26, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oug, E.; Cochrane, S.K.J.; Sundet, J.H.; Norling, K.; Nilsson, H.C. Effects of the invasive red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) on soft-bottom fauna in Varangerfjorden, northern Norway. Mar. Biodiv. 2011, 41, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oug, E.; Sundet, J.H.; Cochrane, S.K.J. Structural and functional changes of soft-bottom ecosystems in northern fjords invaded by the red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus). J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 180, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, M.M.; Pedersen, T.; Ramasco, V.; Nilssen, E.M. Macrobenthic biomass and production in a heterogenic subarctic fjord after invasion by the red king crab. J. Sea Res. 2015, 106, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk-Petersen, J.; Renaud, P.; Anisimova, N. Establishment and ecosystem effects of the alien invasive red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the Barents Sea—A review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 68, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V.; Britayev, T.A.; Rzhavsky, A.V. Benthos elimination by juvenile red king crabs Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius, 1815) in the Barents Sea coastal zone: Experimental data. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2007, 414, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, L.V. Ration of the red king crab on coastal shoals of the Barents Sea. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2015, 463, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrmann, M.M.; Pedersen, T.; Nilssen, E.M. Trophic niche of the invasive red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus in a benthic food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 565, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V. Estimation of foraging on the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis (Echinoidea: Echinoida) by the red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus (Malacostraca: Decapoda) in coastal waters of the Barents Sea. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2009, 35, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V. The red king crab Paralithodes camchaticus (Tilesius, 1815) (Decapoda: Anomura): The use of species equality indicators to assess the influence on the benthos of the Barents Sea. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2021, 47, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, F. Behavioral plasticity in prey-size selectivity of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus feeding on bivalve prey. J. Anim. Ecol. 1995, 64, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.C.; Lovrich, G.A.; Tapella, F.; Thatje, S. Feeding ecology of the crab Munida subrugosa (Decapoda: Anomura: Galatheidae) in the Beagle Channel, Argentina. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 2004, 84, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeta, A.; Cabral, H.N.; Marques, J.C.; Pardal, M.A. Feeding ecology of the green crab, Carcinus maenas (L., 1758) in temperate estuary, Portugal. Crustaceana 2007, 79, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, R.D.; Knick, K.E.; Westphal, M. Diet selectivity of juvenile blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) in Chesapeake Bay. Integr. Compar. Biol. 2011, 51, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.L.; Primicerio, R. Impact scenario for the invasive red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius, 1815) (Reptantia, Lithodidae) on Norwegian, native, epibenthic prey. Hydrobiologia 2007, 590, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, H.K. Prey Selection of the Red King Crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) Preying on Lumpfish Eggs (Cyclopterus lumpus), Sea Urchins (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis) and Scallops (Chlamys islandica). Master’s Thesis, University of Tromsø, Tromsø, Norway, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Population dynamics of the invasive lithodid crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, in a typical bay of the Barents Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Effects of environmental factors on the abundance, biomass, and individual weight of juve-nile red king crabs in the Barents Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, V.G.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Life cycle of Oithona similis (Copepoda, Cyclopoida) in Kola Bay (Barents Sea). Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryugin, K.M. Fauna of the Kola Fjord and the conditions of its existence. Trans. Imp. Acad. Sci. St. Petersburg 1915, 34, 1–929. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dzhenyuk, S.L.; Savelieva, S.P. Hydrological characteristics. In The Kola Bay: Oceanography, Biology, Ecosystems, Pollutants; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 1997; pp. 51–58. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zuyev, Y.A. The Upper Sublitoral Megabenthos of Kola Bay (Barents Sea). Ph.D. Thesis, MMBI RAS, Murmansk, Russia, 2012. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Potanin, V.A.; Larin, B.V. Dynamics of waters of the southern part of the Kola Bay. In Nature and Economy of the North; Anonymous, Ed.; Book Press: Murmansk, Russia, 1989; pp. 66–71. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, L.V.; Nekhaev, I.O.; Panteleeva, N.N.; Akhmetchina, O.Y.; Garbul, E.A.; Dikaeva, D.R.; Zimina, O.L.; Lyubina, O.C.; Frolov, A.A.; Frolova, E.A. Shallow benthos of Kola Bay (Barents Sea): Biodiversity and assessment of the current state of communities. Transact. Kola Sci. Cent. RAS. Ser. 5 2018, 4, 61–92. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, L.V.; Zuyev, Y.A. The red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in Kola bay: Distribution, population and size/age structure changes from 2006 to 2008. Rybn. Khoz. 2010, 6, 66–69. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Blinova, E.I.; Vilkova, O.Y.; Milyutin, D.M.; Pronina, O.A.; Shtrik, B.A. Methods of Landscape Research and Assessment of Stocks of Benthic Invertebrates and Algae in the Marine Coastal Zone. Study of Ecosystems of Unsustainable Water Bodies, Collection and Processing of Data on Aquatic Biological Resources, Equipment and Technology for their Extraction and Processing; VNIRO: Moscow, Russia, 2005. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, W.E.; Byersdorfer, S.E. Biological Field Techniques for Lithodid Crabs; University of Alaska: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brotskaya, V.A.; Zenkevich, L.A. Counting of the Barents Sea bottom-living fauna. Tr. VNIRO 1939, 4, 3–150. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, P.S.; Holsman, K.K.; Beauchamp, D.A.; Dumbauld, B.R.; Armstrong, D.A. Bioenergetics modeling to investigate habitat use by the non-indigenous crab, Carcinus maenas, in Willapa Bay, Washington, USA. Estuar. Coasts 2006, 29, 1132–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumars, P.A.; Dorgan, K.M.; Lindsay, S.M. Diet of worms emended: An update of polychaete feeding guilds. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzhavkiy, A.V.; Pereladov, M.V. Feeding of king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) on the Varanger-fjord shoalness (Barents Sea): Studies of the alimentary canal content and visual observations. Tr. VNIRO 2003, 51, 120–130. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tarverdieva, M.I. On the feeding of immature king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the Teriberka Bay of the Barents Sea. Tr. VNIRO 2003, 142, 92–102. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivlev, V.S. Experimental Ecology of the Feeding of Fishes; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size-at-age of juvenile red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the coastal Barents Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2014, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, G.C.; Nickerson, R.B. Aggregations among juvenile king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus), Kodiak, Alaska. Anim. Behav. 1965, 13, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Tipisova, E.V.; Elfimova, A.E.; Alikina, V.A.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Sex hormones in hemolymph of red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size at maturity of female red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, from the costal zone of Kola Peninsula (southern Barents Sea). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2015, 56, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Hemolymph molting hormone concentrations in red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Does spine removal affect molting process in the king red crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the Barents Sea? Aquaculture 2012, 326–329, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Tipisova, E.V.; Alikina, V.A.; Elfimova, A.E. Thyroid hormones in hemolymph of red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Animals 2022, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deart, Y.V.; Antokhina, T.I.; Spiridonov, V.A.; Britayev, T.A. Seasonal distribution of red king crab in Zelenaya Inlet (Murmansk coast, Barents Sea). Tr. VNIRO 2018, 172, 149–159. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridonov, V.A.; Zalota, A.K.; Pereladov, M.V.; Deart, Y.V.; Tiunov, A.V.; Britayev, T.A. Fjordic lagoons of the Barents Sea as models for study of the dynamics of coastal communities with the introduced red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus (Decapoda, Lithodidae). Zool. Zhurn. 2020, 99, 801–818. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dew, C.B. Behavioral ecology of podding red king crab Paralithodes camtschatica. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 1944–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.G. Biology and ecology of juvenile king crabs. In King Crabs of the World: Biology and Fisheries Management; Stevens, B.G., Ed.; CRC Press (Taylor and Francis): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 261–284. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, L.M.; Andrade, C.; Zenteno-Devaud, L.; Garrido, B.; Rivera, C. Trophic ecology of juvenile southern king crab associated with kelp forest: Evidence of cannibalism. Diversity 2021, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britayev, T.A.; Rzhavsky, A.V.; Pavlova, L.V.; Kuzmin, S.A.; Dvoretsky, A.G. Modem state of bottom communities and settlements of rnacrozoobenthos in shal1ow-waters of the Barents Sea and the role of anthropogenic factor in their dynamics. In Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems and Modern Problems of Conservation of Biological Resources of the Russian Seas; Tarasov, V.G., Ed.; Dalnauka: Vladivostok, Russia, 2007; pp. 314–356. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lyubina, O.S.; Zimina, O.L.; Frolova, E.A.; Frolov, A.A.; Dikaeva, D.R.; Panteleeva, N.N.; Nekhaev, I.O.; Garbul, E.A. Distribution of zoobenthos on soft bottom in the Ivanovskaya and Drozdovka bays of the eastern Murman coast. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2012, 447, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deart, Y.V.; Britayev, T.A. “New” benthic community dominated by Oweniidae (Polychaeta, Oweniidae) at the Murman coast: Structure and causes of appearance. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2014, 454, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimova, N.A.; Frolova, E.A. Benthos of the Dolgaya Bay in the Eastern Murman. Composition, quantitative distribution. In Hydrobiological Essays in Gulfs and Bays of the Russian Arctic Seas; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; KSC Press: Apatity, Russia, 1994; pp. 43–91. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kennish, M.J.; Haag, S.M.; Sakowicz, G.P.; Durand, J.B. Benthic macrofaunal community structure along a well-defined salinity gradient in the Mullica River-Great Bay estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 45, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, E.S.; Kasai, A.; Ueno, M.; Ishihi, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Yamashita, Y. Spatial-temporal feeding dynamics of benthic communities in an estuary-marine gradient. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 112, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-L.; Yu, O.-H. Understanding the spatial and temporal distribution and environmental characteristics of polychaete assemblages in the coastal waters of Ulleungdo, East Sea of Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Martínez, B.; Hernández-Alcántara, P.; Salas-de-León, D.A.; Solís-Weiss, V. Polychaete (Annelida) diversity patterns in Southern Gulf of Mexico: The influence of spatial structure and environmental variables. Diversity 2021, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimova, O.V. Analysis of king crab (Paralithodes camtschatica) trophic links in the Barents Sea. ICES CM 1997, GG:03, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sundet, J.H.; Rafter, E.E.; Nilssen, E. Sex and seasonal variation in the stomach content of the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus in the southern Barents Sea. In The Biodiversity Crisis and Crustacea; Klein, C.V.V., Schram, F.R., Eds.; Balkema Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Manushin, I.; Anisimova, N. Selectivity in the red king crab feeding in the Barents Sea. In Research on the Red King Crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) from the Barents Sea in 2005–2007; Sundet, J.H., Berenboim, B., Eds.; IMR/PINRO: Bergen/Murmansk, Norway/Russia, 2008; pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston, D.B.; Lipcius, R.N.; Hines, A.H. Density-dependent predation by blue crabs upon infaunal clam species with contrasting distribution and abundance patterns. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 85, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegele-Drywa, J.; Normant, M. Feeding ecology of the American crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Crustacea, Decapoda) in the coastal waters of the Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 2009, 51, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rosewarne, P.J.; Mortimer, R.J.; Newton, R.J.; Grocock, C.; Wing, C.D.; Dunn, A.M. Feeding behaviour, predatory functional responses and trophic interactions of the invasive Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) and signal crayfish (Pacifastacus leniusculus). Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelló, P. Note on the diet of Lithodes ferox (Anomura: Lithodidae) off Namibia. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1995, 15, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divine, L.M.; Bluhm, B.A.; Mueter, F.J.; Iken, K. Diet analysis of Alaska Arctic snow crabs (Chionoecetes opilio) using stomach contents and δ13C and δ15N stable isotopes. Deep-Sea Res. II 2017, 135, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, T.A.; Burd, B.J.; Macdonald, V.I.; van Roodselaar, A. Taxonomic and Feeding Guild Classification for the Marine Benthic Macroinvertebrates of the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia; Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences: Sidney, BC, Canada, 2010; Volume 2874, pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Logvinovich, D.N. Aquarium observations on the feeding of the Kamchatka crab. Izv. TINRO 1945, 19, 79–97. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zubkova, N.A. An attempt of king crab keeping in aquaria. Tr. Murmansk Mar. Biol. Inst. 1964, 5, 161–169. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway, P. Calcium balance and moulting in the Crustacea. Biol. Rev. 1985, 60, 425–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.J.; Dettmers, J.M.; Wahl, D.H.; Czesny, S.J. Effects of predator–prey interactions and benthic habitat complexity on selectivity of a foraging generalist. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 139, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elner, R.W.; Hughes, R.N. Energy maximization in the diet of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. J. Anim. Ecol. 1978, 47, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrich, G.A.; Tapella, F. Southern king crabs. In King Crabs of the World: Biology and Fisheries Management; Stevens, B.G., Ed.; CRC Press (Taylor and Francis): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 449–484. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, B.G.; Jewett, S.C. Growth, molting, and feeding of king crabs. In King Crabs of the World: Biology and Fisheries Management; Stevens, B.G., Ed.; CRC Press (Taylor and Francis): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 315–362. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C.; Rivera, C.; Daza, E.; Almonacid, E.; Ovando, F.; Morello, F.; Pardo, L.M. Trophic niche dynamics and diet partitioning of king crab Lithodes santolla in Chile’s Sub-Antarctic water. Diversity 2022, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzhavsky, A.V.; Pavlova, L.V.; Kuzmin, S.A.; Kulikova, V.I. On the distribution of some species of macrobenthos in the Dal’nezelenetskaya Bay (Barents Sea) after red king crab introduction. In Shelf Zoobenthos Investigations. Information Support of the Ecosystem Investigations; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; KSC Press: Apatity, Russia, 2004; pp. 105–116. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Britaev, T.A.; Rzhavsky, A.V.; Pavlova, L.V. 2006. The state of the hard bottom communities of the Barents Sea shallow after the red king crab introduction. In Current State of Crabs’ Populations in the Barents Sea and their Interaction with Bottom Biocenoses; Matishov, G.G., Kuzmin, S.A., Zenzerov, V.S., Eds.; Sever Press: Murmansk, Russia, 2006; pp. 15–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, L.V. Dynamics of the benthos biomass in the hard bottom of the Dalnezelenetskaya Bay (Barents Sea) in connection with red king crab introduction. In Proceedings of the Materials of the 22nd Conference of Young Scientists of the Murmansk Marine Biological Institute, Murmansk, Russia, May 2014; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; MMBI Press: Murmansk, Russia, 2004; pp. 83–89. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- McNair, J.N.; Newbold, J.D.; Hart, D.D. Turbulent transport of suspended particles and dispersing benthic organisms: How long to hit bottom? J. Theor. Biol. 1997, 188, 29–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).