Abstract
Two new Uromunna species, Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. and Uromunna jejuensis sp. n., are described from the Korean Peninsula, representing the first record of the genus in Korean waters. Genetic analyses using two mitochondrial (COI, Cytb) and one ribosomal (18S rRNA) gene allowed us to confirm high pair-wise interspecific differences with the establishment of reliable barcoding gaps of COI (19.9%) and 18S (0.4%) between the new species. Finally, the phylogenetic relationship between the Uromunna species as well as the position of the genus within the munnoid groups are reconstructed using 18S.
1. Introduction
It is currently conceptionally agreed that species are defined as entities that emerge during the speciation event as separately evolving segments of metapopulation lineages [1,2,3,4]. A central issue for modern taxonomists is to characterize the accordance between such theoretical concepts and extant taxa, given that the species is the fundamental unit of biodiversity research [5,6,7]. Inference of speciation between population lineages is generally assessed by comparing the population’s variabilities in biological properties such as morphological and genetic differences, reproductive isolation, and monophyly [8]. These characteristics remain the optimal lines of evidence for identifying the lineage divergence and delimiting species [6,9]. However, the evolutionary history of compared traits often differ within a particular lineage, indicating a lack of universal criterion to delimit species boundaries [10]. Morphological characters, for instance, have been undoubtedly the prime source for identifying species in most metazoan groups. However, the genetic information accumulated by the advance of molecular techniques over the past few decades has allowed researchers to uncover unexpected genetic diversity within species throughout the tree of life [11,12]. Indeed, a multisource approach, the so-called “Integrative Taxonomy”, which takes advantage of complementarity among several disciplines, has been suggested as a method to establish more robust criteria for species delimitation, and subsequently, for a description of a new entity [7,8,13,14]. The utility of integrated taxonomy simultaneously develops knowledge of species concept and evolutionary processes that provides a definite nomenclatural outcome, even if debate remains about the hierarchy of the types of characters and criteria to use for species delimitation [15,16,17].
Isopod crustaceans are major constituents of the marine ecosystems with many species described based on morphological characters with little taxonomic resolution [18]. Identification of some isopod species using general diagnostic characters, including male genitalia, is impossible when species have several genetic lineages and can be considered cryptic [19,20,21,22,23]. Therefore, an integrative approach that would combine more detailed morphological studies and genetics is a welcome method in the isopod taxonomy. Most isopods are bottom dwellers and are brooders without a larval life stage, indicating that their dispersal ability can be restricted by geographical barriers such as underwater ridges [24,25,26]. In this regard, the speciation potential of these animals is assumed to be increased due to their low vagility and small body size [27]. Previous studies, based on genetic data, reported the existence of species complexes, with the putatively widespread marine isopods, e.g., Betamorpha fusiformis (Barnard, 1920) [28], Atlantoserolis vemae (Menzies, 1962) [29], and Coxicerberus fukudai (Ito, 1974) [30]. These results imply the need for multiple lines of evidence to establish more rigorous species identification and delimitation of isopod species for comprehensive taxonomic work.
Isopods of the family Munnidae Sars, 1897 are small free-living crustaceans with a global distribution, ranging from tropical to polar regions of both hemispheres [31]. They are found in various habitats from shallow to abyssal depths, including mud, sand, intertidal rock pools, seagrass meadows, sponges, and coral reefs [31]. Most munnid isopods are known as detritivores, typically feeding on dead, decomposing organic matter on the bottom layer [32] and the algal substrate [33]. They often appear locally in great abundance, representing a valuable indicator of environmental conditions [33,34]. Munnidae currently accounts for more than 100 described species classified across six genera [35]. The genus Uromunna Menzies, 1962, is after Munna Krøyer, 1839 the second largest group, with 26 recorded species [35]. Initially, it was described as a subgenus within Munna [36] with species having spineless, flat, leaf-like ventral rami of the uropod. After several systematic re-evaluations [37,38,39], Poore [40] erected Uromunna to the genus rank, provided a species list, and a new diagnosis. Esquete et al. [34] described a new species of Uromunna from the Iberian Peninsula with a note on the seasonal variation of emergence. Finally, Esquete and Wilson [41] established a classification key for all species recorded up to that time, along with the description of three new species of Australian water.
We examined Munnidae collected from various localities along the east and west coasts of the Korean Peninsula. Initially, they were identified as either Uromunna serricauda Müller, 1992 or Munna japonica Shimomura & Mawatari, 2001. Both species have been previously reported from Hokkaido Island [42]. However, we assume that Korean populations might show differences in morphology and genetics, considering the substantial geographical distances and heterogeneous habitat conditions among the regions. Therefore, we first address the question of populational geographic diversification by comparing the morphological characters with the original description. We amplified two mitochondrial genetic markers to examine the genetic distance among populations and used this to check the genetic identity of the species based on the barcoding concept [43]. We also compared the genetic data of one ribosomal gene with the publicly available sequences of other “munnoid” groups that share a so-called munnoid body shape, with an elongated carpus of pereopod I, small or reduced eyes, and pleopods covering the anus [44,45], to evaluate the phylogenetic relationship of the species within the genus Uromunna and family Munnidae. As a result, we describe two new Uromunna species based on both morphological and genetic characters.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Morphological Examination
Sample collection was carried out from the littoral zone of Mun Island south of Jeju Island (33°13′39.6″ N 126°33′56.7″ E; April 2020), Mudong port, Gijang-gun of Busan (35°18′21.6″ N 129°15′29.3″ E), Homigot, Pohang (36°04′43.6″ N 129°34′10.2″ E), Jangho port, Samcheok (37°17′22.1″ N 129°19′07.9″ E), and Daepunggam Cliff of Ulleung Island (37°31′23.7″ N 130°47′34.1″ E), Republic of Korea, respectively (Figure 1). At Mun Island, sediment samples (depth of about 15 m) were collected by scuba diving with a plastic corer and initially kept in a plastic bag. At the rest, brown algae (Phaeophyceae) (depth of about 50 cm) were collected using a trowel and kept in a plastic bag with seawater. The algae and sediment samples were transferred to a bucket containing fresh water and the top layer of water was strained through nets with a mesh size of 38 μm. Then, the filtered material was transferred to 250 mL bottles and preserved in 96% ethanol. The sorting and dissection of the specimens was performed using an Olympus SZX 12 stereo-binocular microscope. Dissected appendages were mounted onto glass slides in lactophenol. Line drawings were made using an Olympus BX 51 (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) compound microscope equipped with a camera lucida. The line drawings’ measurements were performed following Riehl and Brandt’s protocol [46]. All measurements from the dorsal view of the line drawings were made using the distance measurement tools of Adobe Acrobat Professional (Adobe, CA, USA). The ratios of the appendages were measured in distal to proximal order, excluding the setae. The body ratios were measured from the anteromedial to posteromedial end. The ratio measurements were made based on the holotype specimen. Terminology was mostly based on Esquete and Wilson [41]. The term ‘unequally bifid’ seta was abbreviated as UB seta. All studied material was deposited at the invertebrate collection of the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) and Marine Biodiversity Institute of Korea (MABIK) in Republic of Korea.
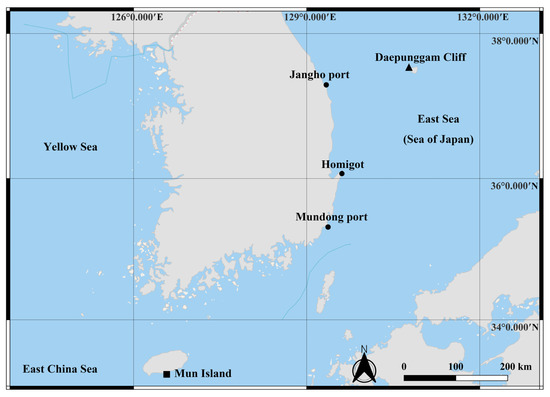
Figure 1.
Sample collection sites on the Korean Peninsula and the adjacent sea. Black square: Mun Island south of Jeju Island. Black circles: Inland collection sites along the east coast of the Korean Peninsula, Mudong port, Homigot, and Jangho port. Black triangle: Daepunggam Cliff of Ulleung Island.
2.2. DNA Amplification and Sequencing
Ten individuals were randomly selected from each locality, except from Daepunggam, where only two individuals were sorted. The specimens were transferred into distilled water for 15 min before amplification to eliminate ethanol. Genomic DNA was isolated from the specimens using a LaboPassTM Kit (Cosmo, Seoul, Republic of Korea) following the manufacturer’s protocols. Fragments of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase (COI), cytochrome b (Cytb), and the complete 18S ribosomal genes were amplified through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) a TaKaRa PCR thermal cycler (TaKaRaBio, Kusatsu, Japan). The universal primer pair, jgLCO1490 (5′–TIT CIA CIA AYC AYA ARG AYA TTG G–3′) and jgHCO2198 (5′–TAI ACY TCI GGR TGI CCR AAR AAY CA–3′) [47] was used for COI with the following amplification protocol: denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min, 30 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing at 48 °C for 1 min, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, final extension at 72 °C for 10 min, and stored at 4 °C. CytbF (5′–GGW TAY GTW YTW CCW TGR GGW CAR AT–3′) and CytbR (5′–GCR TAW GCR AAW ARR AAR TAY CAY TCW GG–3′) primers [48] were used for Cytb with the following protocol: denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, 40 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 sec, annealing at 42 °C for 2 min, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and final extension at 72 °C for 10 min, and stored at 4 °C. For 18S rDNA, the unique primer sets and amplification protocol for the deep sea asellote phylogeny were used [49]. The PCR products were purified for sequencing reactions using the LaboPass™ PCR Purification Kit (Cosmo, Seoul, Republic of Korea) following the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA was sequenced with the ABI automatic capillary sequencer (Bionics, Seoul, Republic of Korea) using the same set of primers.
2.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
All acquired sequences were confirmed with BLAST search [49]. Sequences were visualized using Geneious Prime (Biomatters Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand) [50]. Multiple sequence alignments were performed with MAFFT v7.490 [51] as implemented in Geneious using the default setting. The alignment was made with the following settings: automatic algorithm choice; scoring matrix 200 PAM/k = 2; Gap open penalty: 1.53; Offset value: 0.123. Uncorrected pairwise distances were calculated from the aligned sequences and presented as difference (%). Mitochondrial sequences were checked for potential stop codons with ORF finder on the NCBI website (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/ (accessed on 2 November 2022)) using the invertebrate mitochondrial code. Newly obtained COI (OP737458–OP737461), Cytb (OP745425–OP745443), and 18S (OP730547–OP730554) sequences are publicly available on GenBank.
Phylogenetic inference was carried out using the maximum likelihood (ML) approach with 10,000 replicates of ultrafast bootstrapping [52] using the IQ-Tree web application [53]. The best-fit evolutionary model was determined using ModelFinder in IQ-Tree [54] based on Bayesian Information Criterion [55]. The COI phylogram was generated with additional GenBank sequences of Munna japonica (KX186724) [56], Munnidae sp. (KJ736157), and rooted with the sequence of Proasellus cavaticus (Leydig, 1871) (JQ921083), belonging to the Asellidae, a freshwater lineage. The Cytb phylogram was not constructed due to the failure to amplify this fragment in U. jejuensis. The 18S phylogram comprised additional sequences of Uromunna nana (Nordenstam, 1933) and a putatively related deep-sea family Dendrotionidae (Dendromunna sp. (AY461464), Acanthomunna spinipes (Vanhöffen, 1914) (EU414421)), and Haplomunnidae (Thylakogaster sp. 1 (AY461470), sp. 2 (EU414424)). In order to check the monophyly of “munnoid” groups, Iais pubescens (Dana, 1853) (EU414437) of Janiridae, the sister taxon of Dendrotionidae and Haplomunnidae, was used [44]. The phylogram was rooted with Stenasellus racovitzai Razzauti, 1925 (AF496663), belonging to the Stenasellidae, which is a primitive asellote group inhabiting fresh water [57]. The phylograms were visualized and graphically enhanced using FigTree v1.4.4. [58] (https://github.com/rambaut/figtree/ (accessed on 17 November 2022)).
3. Results
3.1. Taxonomy
Suborder: Asellota Latreille, 1802
Superfamily: Janiroidea Sars, 1897
Family: Munnidae Sars, 1897
Genus: Uromunna Menzies, 1962
Munna (Uromunna) Menzies, 1962: 36; Kussakin 1962:
68, 1988: 326; Frankenberg & Menzies 1966: 201; Fresi
& Mazella 1974: 51.
Munnoides Carvacho, 1977, p. 6.
Munna (Pangamunna) Schultz, 1979: 577.
Uromunna—Poore 1984: 70.
Type species. Uromunna ubiquita (Menzies, 1952)
3.2. Uromunna mundongensis sp. n.
Type locality. Shallow water (depth 2–3 m) of East Sea (Sea of Japan), Mundong port, Gijang-gun, Republic of Korea, 38°17′43.8″ N 128°33′15.1″ E.
Type material examined. Holotype: adult male, (MABIK CR00252867) in micropreparations; Paratypes: one adult male (NIBRIV0000900870) in micropreparations, Mundong port, Gijang-gun, (38°17′43.8″ N 128°33′15.1″ E); one ovigerous female (MABIK CR00252868) in micropreparations, Mundong port, Gijang-gun; one adult female (MABIK CR00252869) in micropreparations, Homigot, Pohang (36°04′43.6″ N 129°34′10.2″ E); one adult female (MABIK CR00252870) in micropreparations, Jangho port, Samcheok (37°17′22.1″ N 129°19′07.9″ E).
Diagnosis. Pleotelson 1.3 times longer than wide, 0.3 times of whole body, first antennular article with four plumose and four simple setae distally, maxillipedal endite with three coupling hooks proximomedially, palp second article with three simple setae, third article with four simple setae, fifth article with three simple and two robust setae, pereopod 1 with setal formula as follows (except for claws of dactylus): 5: 3: 6: 6: 13: 4, uropodal endopod with two simple and three plumose setae.
3.2.1. Description of the Male Holotype
Color: preserved specimens, brown.
Body (Figure 2A,B): flattened in dorsal view, total length 1.04 mm, length 2.5 times longer than wide.
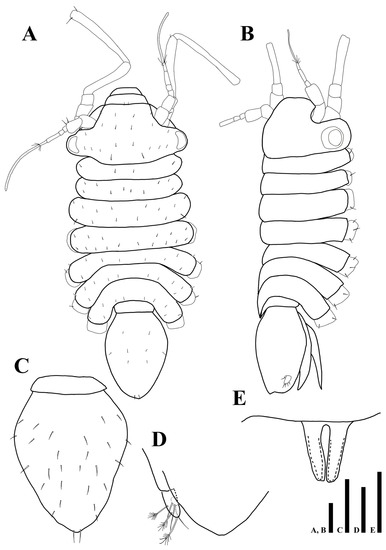
Figure 2.
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) habitus; (B) habitus, dorsolateral; (C) pleotelson; (D) uropod; penial papillae. Scale bars = 100 µm (A–C), 50 µm (D,E).
Cephalothorax (Figure 2A,B): 0.6 times longer than wide and 0.2 times of whole body, anterior margin narrower than posterior one, eyes present, ommatidia on eyelobe outer border, dorsal margin covered with 22 min setae.
Pereon (Figure 2A,B): 0.5 times of whole body, maximal body width in pereonite 4, equal to maximal width of cephalothorax, dorsal margin of each pereonite armed with minute simple setae, first pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, second pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, third pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, fourth pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, fifth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, sixth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, seventh pereonite 0.3 times longer than wide.
Pleonite (Figure 2A,B): 0.3 times longer than wide, without setae.
Pleotelson (Figure 2C): pyriform; 1.3 times longer than wide, 0.3 times of whole body, dorsal margin covered with 28 simple setae.
Uropod (Figure 2D): protopod not visible in dorsal view; endopod with two simple and three plumose setae; exopod minute, with one simple seta.
Penial papillae (Figure 2E): bifurcate distally, distal margin slightly round, located ventrally on posteromedial margin of pereonite 7.
Antennula (Figure 3A): six articles; first article 1.1 times longer than wide, with two plumose setae; second article 1.2 times longer than first article, 1.7 times longer than wide, with four plumose and four simple setae distally; third article rectangular, 1.4 times longer than wide, with one simple setae distally; fourth article 1.3 times longer than wide, with one seta on proximal margin; fifth article 4.1 times longer than wide, without setae; sixth article 2.8 times longer than wide, with four simple, one plumose setae, and one elongate aesthetasc distally.
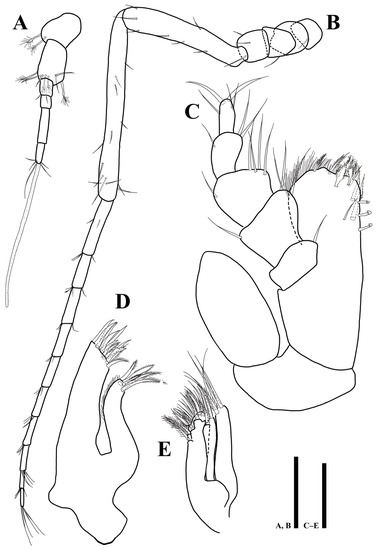
Figure 3.
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) antennula; (B) antenna; (C) maxilliped; (D) maxillula; (E) maxilla. Scale bars = 100 µm (A,B), 50 µm (C–E).
Antenna (Figure 3B): six peduncular and ten flagellar articles; first article as long as width, with one simple seta laterally; second article 1.4 longer than wide, without seta; third article as long as width, with one simple seta laterally; fourth article as long as width, with three simple setae laterally; fifth article 6.2 times longer than wide, with seven simple setae; sixth article longest, 12.2 times longer than wide, with 13 simple setae; flagellar first article longest, 5.9 times longer than wide, with five simple setae; setal formula of following articles as follows: 4: 3: 3: 3: 4: 4: 4: 4: 4.
Mandibles (Figure 4): right mandible (Figure 4A) pars incisiva with five cusps bearing four robust serrate setae; lacking lacinia mobilis; pars molaris truncate, with grinding surface; one simple seta arising from basal margin; left mandible (Figure 4B) pars incisiva with five cusps, lacinia mobilis with four cusps, three serrate setae located below lacinia mobilis; palp inserted on cuticular projection; first article 1.9 times longer than wide, with one simple seta distally; second article 2.6 times longer than wide, without setae, third article 2.3 times longer than wide with two plumosesetae apically.
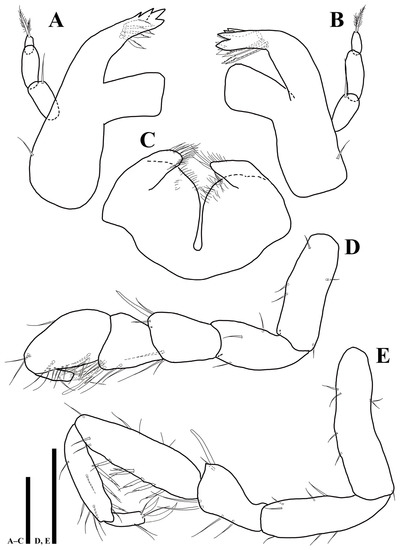
Figure 4.
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) right mandible; (B) left mandible; (C) labium; (D) pereopod 1; (E) maxilla. Scale bars = 50 µm (A–C), 100 µm (D,E).
Labium (Figure 4C): body separated into two lobes by deep medial incision, distal margin of each lobe covered with elongated thin setae.
Maxillula (Figure 3D): lateral lobe longer and thicker than medial one, with 11 robust apical setae, three of which denticulate; medial lobe with five robust setae on distal margin, along lateral margin with fine setae.
Maxilla (Figure 3E): lateral and mesial lobes each with one pectinate and three robust simple setae distally; medial lobe coalescent with basis, broader than others, with 18 robust setae along distal margin, some of them setulated.
Maxilliped (Figure 3C): epipod 2 times longer than wide, distal end reaching to palp second article; basis 2.4 times longer than wide; endite 1.4 times longer than wide, distal margin covered with numerous hairs, one simple, five plumose, and two fan-like setae distally, three robust serrated setae on ventral margin, three coupling hooks along proximomedially; palp first article 0.7 times longer than wide, with one simple seta on distomesial corner; second article 0.95 times longer than wide, 1.6 times longer than first article, with two simple and one setae on distomesial and distolateral corners, respectively; third article as long as width, with four simple setae on distomesial margin and one seta on distolateral corner; fourth article 1.5 times longer than wide, with three simple setae on distal margin; fifth article 2 times longer than wide, with three simple and two robust setae on distal end.
Pereopods: coxae of pereonites 4–7 visible in dorsal view, each coxa with two or three simple setae (Figure 2B); pereopod 1 subchelate, dactylus of pereopods partly covered by articular plate projected from distal margin of propodus.
Pereopod 1 (Figure 4D) article length and width (L/W) ratios 2.8: 1.6: 1.4: 1.1: 1.8: 3.4; basis with five simple setae; ischium with three simple setae; merus with five simple and one robust setae distally; carpus with four simple, one robust and one UB setae; propodus with 12 simple and one robust setae; dactylus tapering distally, with four simple setae and two claws on distal apex with different length.
Pereopod 2 (Figure 4E): article L/W ratios 4: 3.1: 1.6: 3.3: 4.1: 2.3; basis with seven simple setae; ischium with seven simple setae; merus with five simple and one robust setae; carpus with four simple and six UB setae; propodus ventral margin with seven simple and three UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae.
Pereopod 3 (Figure 5A): article L/W ratios 2.9: 2.5: 1.7: 4.3: 7.3: 3; basis with six simple and four plumose setae; ischium with five simple setae; merus with three simple and one robust setae; carpus with four simple and five UB setae; propodus with four simple and eight UB setae; dactylus with two robust claws and four simple setae.
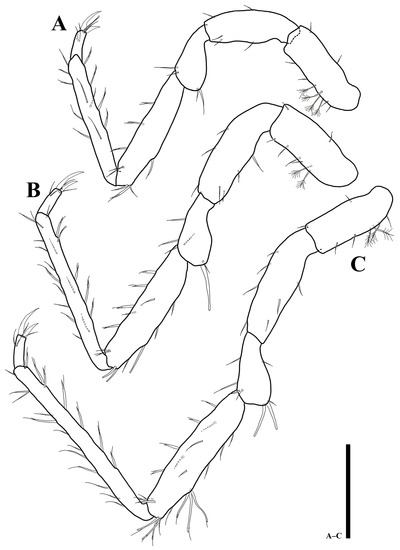
Figure 5.
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) pereopod 3; (B) pereopod 4; (C) pereopod 5. Scale bar = 100 µm.
Pereopod 4 (Figure 5B): article L/W ratios 2.7: 3: 2.1: 4.2: 11.3: 2.6; basis with six simple and two plumose setae; ischium with seven simple setae; merus with five simple and one robust setae; carpus with nine simple and five UB setae; propodus with 13 simple and six UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae.
Pereopod 5 (Figure 5C): article L/W ratios 2.6: 3.3: 2.1: 4.5: 12: 2.7; basis with five simple and three plumose setae; ischium with seven simple setae; merus with seven simple setae; carpus with ten simple and 11 UB setae; propodus with nine simple and nine UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae distally.
Pereopod 6 (Figure 6A): article L/W ratios 3: 3.5: 2: 4.7: 12.5: 3; basis with four simple and three plumose setae; ischium with six simple setae; merus with five simple and two robust setae; carpus with four simple and 14 UB setae; propodus with 14 simple and 13 UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae distally.
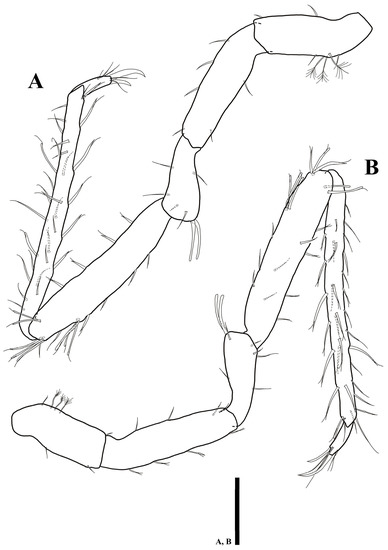
Figure 6.
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) pereopod 6; (B) pereopod 7. Scale bar = 100 µm.
Pereopod 7 (Figure 6B): article L/W ratios 2.4: 4: 2.3: 4.9: 14.3: 3.5; basis with four simple and three plumose setae; ischium with four simple and four UB setae; merus with six simple setae and two robust setae on distal corner; carpus with six simple and 12 UB setae; propodus with 17 simple and 16 UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae distally.
Pleopod 1 (Figure 7A): consisting of two coalescent halves, 1.9 times longer than maximum wide (measured at widest section of proximal part); proximal part enlarged and tapering distally, separated in half by medial stylet-guiding groove running from proximal end, distal margin of each lobe tapering distolaterally, four simple setae on ventral margin, each distal lobe with three setae.
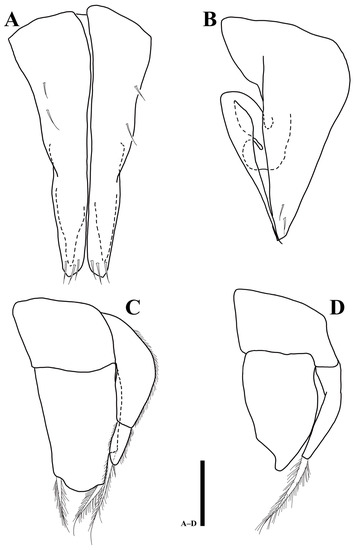
Figure 7.
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) pleopod 1; (B) pleopod 2; (C) pleopod 3; (D) pleopod 4. Scale bar = 100 µm.
Pleopod 2 (Figure 7B): protopod elongate, 2.7 times longer than wide, with two subapical setae; endopodal stylet, elongate, medially swollen but becoming narrower until distal tip, without any ornamentation; exopod distally round, located below stylet distomedially in protopod.
Pleopod 3 (Figure 7C): protopod rectangular, 0.8 times longer than wide; endopod 1.6 times longer than wide, suboval, with three stout, plumose setae distally; exopod consisting of two articles, proximal article 2.7 times longer than distal one, lateral margin covered with hairs, distal article 2.6 times longer than wide with one apical seta.
Pleopod 4 (Figure 7D): protopod 0.6 times longer than wide; endopod 1.6 times longer than wide, with distolateral protrusion; exopod 5.5 times longer than wide, with one long plumose seta.
3.2.2. Sexual Dimorphism
Body (Figure 8A): total length 1.03 mm, 1.8 times longer than wide.
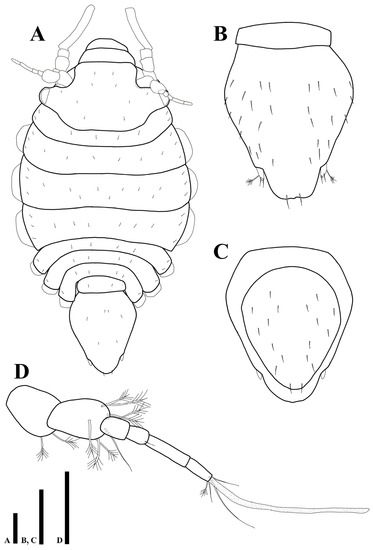
Figure 8.
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. paratype ovigerous female (MABIK CR00252868): (A) habitus; (B) pleotelson; (C) pletelson; (D) antennula. Scale bars = 100 µm (A–C), 50 µm (D).
Cephalothorax (Figure 8A): 0.5 times longer than wide and 0.2 times of whole body.
Pereon (Figure 8A): 0.5 times of whole body, pereonites 2–4 distinctly expanded than other pereonites, maximal body width in pereonite 3, 1.3 times wider than maximal width of cephalothorax. first pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, second pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, third pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, fourth pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, fifth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, sixth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, seventh pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide.
Pleonite (Figure 8A): 0.3 times longer than wide, without setae.
Pleotelson (Figure 8B): 1.2 times longer than wide, dorsal margin covered with 30 simple setae.
Female operculum (Figure 8C): oval-shaped, 1.3 times longer than wide, with 18 simple setae on dorsal margin.
Antennula (Figure 8D): first article 1.4 times longer than wide, with two plumose setae; second article 1.5 times longer than wide, with seven plumose and one simple setae distally; third article 1.4 times longer than wide, without setae; fourth article 1.4 times longer than wide, with one seta distally; fifth article 3.9 times longer than wide, without setae; sixth article 2.5 times longer than wide, with three simple, one plumose setae, and one elongate aesthetasc distally.
Etymology: The new species is named after the locality where specimens were collected, Mundong port.
3.2.3. Remarks
Uromunna mundongensis sp. n. is most similar to U. serricauda, recorded in Hokkaido, Japan, showing a round distal apex of male pleopod I with three pairs of apical setae [42]. However, the examined specimens of U. mundongensis differ in the ornamentation of antennular articles (2: 8: 1: 0: 0: 6 vs. 1: 6: 0: 1: 0: 6), the shape and L/W ratio of antennular article 3 (rectangular, 1.4 vs. trapezoidal, 0.9), the ornamentation of antennal peduncular articles (1: 0: 1: 3: 7: 13 vs. 0: 0: 1: 1: 4: 10), the number of maxillipedal coupling hooks (3 vs. 2), the setal formula of the maxillipedal palp (1: 3: 5: 3: 6 vs. 0: 3: 3: 3: 5), the numbers of apical robust setae on the medial lobe of the maxillula (5 vs. 4), the numbers of robust setae on the medial lobe of the maxilla (18 vs. 9), the setal formula of all pereopods, the numbers of setae on endopod of uropod (5 vs. 4), and the lateral shape of the pleotelson (smooth vs. serrated). The female of U. mundongensis is distinguished from U. serricauda by the relative L/W ratio of operculum (1.3 vs. 0.9) with setal formula.
3.3. Uromunna jejuensis sp. n.
Type locality. Shallow water (depth 2–3 m) of East Sea (Sea of Japan), littoral zone of Mun Island of Jeju Island, 33°13′39.6″ N 126°33′56.7″ E.
Type materials examined. Holotype: adult male, (MABIK CR00252871) in micropreparations; Paratypes: one ovigerous female (NIBRIV0000900871) in micropreparations; one ovigerous female (MABIK CR00252872) in micropreparations; one adult female (MABIK CR00252873) in micropreparations.
Diagnosis. Pleotelson 1.3 times longer than wide, 0.3 times of whole body, antennular first article with two plumose and one simple setae, second article with six plumose, two simple setae distally, maxillipedal endite with two coupling hooks proximomedially, palp first article with one simple seta, second article with four simple setae, fifth article with four simple and two robust setae, pereopod 1 with setal formula as follows (except for claws of dactylus): 5: 2: 6: 6: 14: 4, uropodal endopod with four simple and four plumose setae.
3.3.1. Description of the Male Holotype
Color: preserved specimens, brown.
Body (Figure 9A): total length measured with holotype 1.03 mm, length 2.3 times longer than wide.
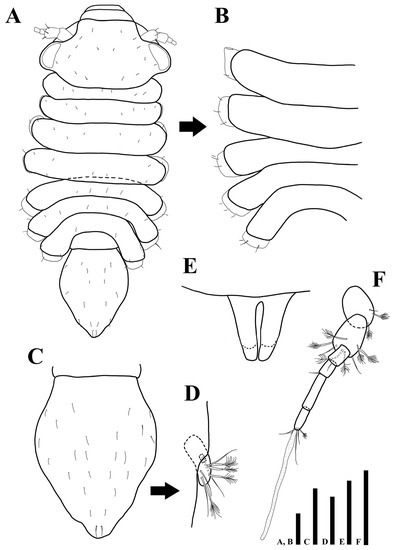
Figure 9.
Uromunna jejuensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) habitus; (B) pleonites 3–7; (C) pleotelson; (D) uropod; penial papillae. Scale bars = 100 µm (A–C,F), 50 µm (D,E).
Cephalothorax (Figure 9A): 0.5 times longer than wide and 0.2 times of whole body, anterior margin narrower than posterior one, ommatidia on eyelobe outer border, dorsal margin covered with 15 min setae.
Pereon (Figure 9A,B): 0.5 times of whole body, maximal body width in pereonite 4, 1.06 times of maximal width of cephalothorax, each pereonite armed with minute setae dorsally, first pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, second pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, third pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, fourth pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, fifth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, sixth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, seventh pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide.
Pleonite (Figure 9A): 0.4 times longer than wide and as long as whole body.
Pleotelson (Figure 9C): 1.3 times longer than wide, 0.3 times of whole body, dorsal margin covered with 26 simple setae.
Uropod (Figure 9D): protopod not visible in dorsal view; endopod with four simple and four plumose setae; exopod with one simple seta.
Penial papillae (Figure 9E): bifurcate distally, distal apex slightly round, located on posteromedial margin of seventh pereonite.
Antennula (Figure 9F): six articles; first article 1.5 times longer than wide, with one plumose and one simple setae; second article 1.1 times longer than first article, 1.8 times longer than wide, with six plumose and two simple setae distally; third article 1.5 times longer than wide, with one simple setae distally; fourth article 1.5 times longer than wide, with one distal seta; fifth article 4.1 times longer than wide, without setae; sixth article 2.9 times longer than wide, with one plumose, four simple setae, and one elongate aesthetasc distally.
Mandibles (Figure 10): right mandible (Figure 10A) pars incisiva with five cusps bearing four robust serrate setae; lacinia mobilis absent; pars molaris truncate, with grinding surface distally; left mandible (Figure 10B) pars incisiva with five, lacinia mobilis with four cusps, three serrate setae under lacinia mobilis; basal margin of both mandibles with two simple setae; palp inserted on cuticular projection; first article 2.2 times longer than wide, with one simple seta distally; second article 2.2 times longer than wide, without setae, third article 2.3 longer than wide with two plumose apical setae.
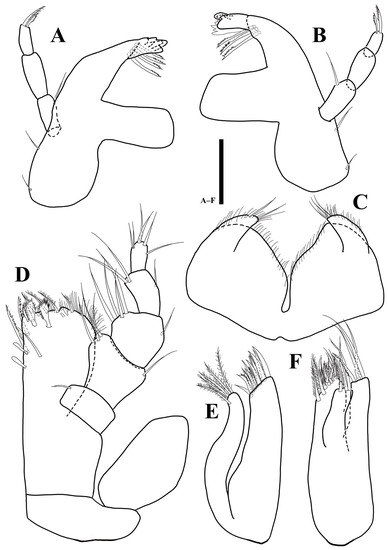
Figure 10.
Uromunna jejuensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) right mandible; (B) left mandible; (C) labium; (D) maxilliped; (E) maxillula; (F) maxilla. Scale bars = 50 µm.
Labium (Figure 10C): body divided into two lobes by deep medial incision, each lobe covered with elongated thin setae on distal margin.
Maxillula (Figure 10E): lateral with 11 robust apical setae, three of which denticulate; medial lobe with five robust setae distally, fine setae along lateral margin.
Maxilla (Figure 10F): lateral and mesial lobes each with one pectinate and three robust simple setae distally; medial lobe coalescent with basis, distal margin with 18 robust setae, some of them setulated.
Maxilliped (Figure 10D): epipod 1.9 times longer than wide; basis 2.4 times longer than wide; endite 1.5 times longer than wide, distal margin covered with numerous hairs, with six plumose, one simple, and two fan-like setae distally, two robust serrated setae ventrally, two coupling hooks along proximomedial edge; palp first article 0.6 times longer than wide, with one simple seta on distomesial corner; second article 0.7 times longer than wide, 1.4 times longer than first article, with three simple and one setae on distomesial and distolateral corners, respectively; third article as long as width, with four setae distomesially and one simple distolaterally; fourth article 1.8 times longer than wide, with three simple setae distally; fifth article 1.9 times longer than wide, with three simple and two robust setae distally.
Pereopods coxae of all pereonites visible in dorsal view, each coxa with two or three setae (Figure 8B); dactylus of pereopods partly covered by articular plate generated from propodus distal margin.
Pereopod 1 (Figure 11A) article L/W ratios 2.3: 1.8: 1.3: 0.8: 1.5: 2.8; basis with five simple setae; ischium with two simple setae; merus with five simple and one robust setae distally; carpus with four simple, one robust and one UB setae; propodus with 11 simple and three robust UB setae; dactylus tapering distally, with four simple setae and two claws on distal apex with different length.
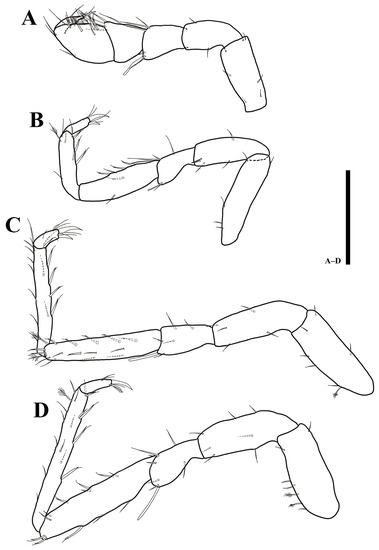
Figure 11.
Uromunna jejuensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) pereopod 1; (B) pereopod 2; (C) pereopod 3; (D) pereopod 4. Scale bars = 100 µm.
Pereopod 2 (Figure 11B): article L/W ratios 3.8: 3.1: 1.6: 3.2: 3.8: 3.2; basis with five simple setae; ischium with four simple setae; merus with five simple and one robust setae; carpus with two simple and four UB setae; propodus with one plumose, four simple, and four UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae.
Pereopod 3 (Figure 11C): article L/W ratios 2.7: 3.1: 2: 5: 7.4: 2.4; basis dorsal margin with one plumose, six simple setae; ischium with five simple setae; merus with five simple and one robust setae; carpus with three plumose, six simple, eight UB setae; propodus with one plumose, ten simple, and six UB setae; dactylus with two robust claws and four simple setae.
Pereopod 4 (Figure 11D): article L/W ratios 2.5: 2.9: 1.7: 4.1: 9.8: 3.5; basis with two plumose, five simple setae; ischium with seven simple setae; merus with seven simple and one robust setae; carpus with six simple, six UB setae; propodus with one plumose, eleven simple, and five UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae.
Pereopod 5 (Figure 12A): article L/W ratios 2.8: 2.6: 1.7: 4.6: 10.8: 2.9; basis with one plumose, six simple setae; ischium with seven simple setae; merus with six simple and two robust setae; carpus with nine simple, nine UB setae; propodus with one plumose, 15 simple, and six UB setae; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae distally.
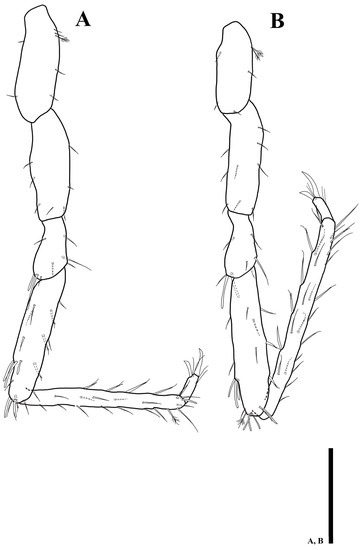
Figure 12.
Uromunna jejuensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) pereopod 5; (B) pereopod 6. Scale bars = 100 µm.
Pereopod 6 (Figure 12B): article L/W ratios 2.6: 3.2: 1.9: 4.5: 11.8: 3.8; basis with two plumose, four simple setae; ischium with nine simple setae; merus with six simple and two robust setae; carpus with one plumose, eight simple, and ten UB setae; propodus with 16 simple and ten UB setae along margin; dactylus with two claws and four simple setae distally.
Pleopod 1 (Figure 13A): 2.1 times longer than maximum wide (measured at widest section of proximal part); proximal part enlarged and becoming narrower distally, separated in half by medial stylet-guiding groove running from proximal end, four simple setae on mediolateral margin; distal margin of each lobe tapering distolaterally and with six simple setae.
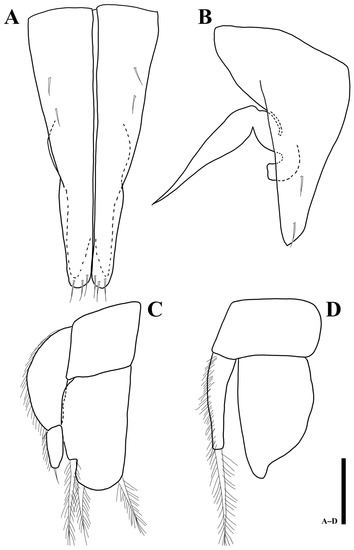
Figure 13.
Uromunna jejuensis sp. n. holotype male: (A) pleopod 1; (B) pleopod 2; (C) pleopod 3; (D) pleopod 4. Scale bars = 100 µm.
Pleopod 2 (Figure 13B): protopod elongate, 1.8 times longer than wide, with two apical setae; endopodal stylet, medially swollen but becoming narrower until distal tip; exopod distal apex round, located below protopod.
Pleopod 3 (Figure 13C): protopod as long as width; endopod 1.8 times longer than wide, suboval, with three elongate, plumose setae apically; exopod with two articles, proximal article 2.5 longer than wide and 2.4 times longer than distal one, distal article 2.6 times longer than wide with one simple seta distally.
Pleopod 4 (Figure 13D): protopod 0.6 times longer than wide; endopod 1.6 times longer than wide, with distolateral protrusion; exopod 4.6 times longer than wide, with one elongate plumose seta distally.
3.3.2. Sexual Dimorphism
Body (Figure 14A): total length 800 µm, 1.9 times longer than wide.
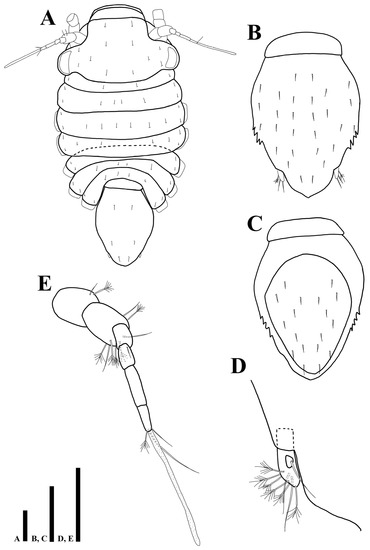
Figure 14.
Uromunna jejuensis sp. n. paratype ovigerous female (MABIK CR00252872): (A) habitus; (B) pleotelson; (C) pleotelson; (D) uropod; (E) antennula. Scale bars = 100 µm(A–C), 50 µm (D,E).
Cephalothorax (Figure 14A): 0.5 times longer than wide and 0.3 times of whole body.
Pereon (Figure 14A): 0.4 times of whole body, pereonites 2–4 distinctly expanded than other pereonites, maximal body width in pereonite 3, 1.1 times wider than maximal width of cephalothorax, first pereonite 0.07 times longer than wide, second pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, third pereonite 0.2 times longer than wide, fourth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, fifth pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide, sixth pereonite 0.08 times longer than wide, seventh pereonite 0.1 times longer than wide.
Pleonite (Figure 14A): 0.3 times longer than wide, without setae.
Pleotelson (Figure 14B): 1.3 times longer than wide, lateral margin serrated, dorsal margin covered with 28 simple setae.
Female operculum (Figure 14C): oval-shaped, 1.4 times longer than wide, with 18 simple setae on dorsal margin.
Uropod (Figure 14D): endopod with two simple and six plumose setae; exopod with one simple seta.
Antennula (Figure 14E): first article 1.2 times longer than wide, with one plumose, one simple setae; second article 1.5 times longer than wide, with five plumose and three simple setae distally; third article 1.6 times longer than wide, without setae; fourth article 1.6 times longer than wide, with one seta on proximal margin; fifth article 3.4 times longer than wide, without setae; sixth article 2.9 times longer than wide, with two simple, one plumose setae, and one elongate aesthetasc distally.
Etymology: The new species is named after Jeju Island, where the type locality of Mun Island is located.
3.3.3. Remarks
The male antenna and pereopod 7 are not described due to the lack of an additional male specimen. Uromunna jejuensis sp. n. extremely resembles U. serricauda and U. mundongensis in the general appearance of the habitus, mouthparts, pereopods, and pleopods. However, the new species is distinguishable based on the following characteristics of the examined specimens: the setal formula of the antennula, the numbers of setae on the basal margin of the mandibles (2 vs. 1), the setal formulas of the maxilipedal palp and all pereopods, the relative distance between setae on the distal margin of pleopod 2 and the setal formula of the endopod of uropod. The female of U. jejuensis is distinguished from U. mundongensis by the lateral shape of the pleotelson (serrated vs. smooth).
3.4. Key to the East Asian species of Uromunna
Key to the identification of males:
- 1.
- Antennula second article with six setae; maxillipedal palp first article without setae; lateral margin of pleotelson serrated ............................................................ U. serricauda
- −
- Antennula second article with eight setae; maxillipedal palp first article with one seta; lateral margin of pleotelson smooth …………………………..…………...……………. 2
- 2.
- Antennula first article with two setae; antennula fourth article without setae; three maxillipedal coupling hooks; one seta on basal margin of mandible ……………………………………………………………………… U. mundongensis sp. n.
- −
- Antennula first article with three setae; antennula fourth article with one seta; two maxillipedal coupling hooks; two setae on basal margin of mandible …………………………………………………………………………… U. jejuensis sp. n.
Key to the identification of females:
- 1.
- Lateral margin of pleotelson smooth............................................ U. mundongensis sp. n.
- −
- Lateral margin of pleotelson serrated ……………...……………………...……………. 2
- 2.
- Operculum as long as broad with eight simple setae on dorsal surface …………………………………………………………………………………. U. serricauda
- −
- Operculum longer than wide with 18 simple setae on dorsal surface …………………………………………………………………………… U. jejuensis sp. n.
3.5. Phylogeny
The COI, Cytb, and 18S sequences of U. mundongensis were acquired from two, eighteen, and three individuals, respectively. For U. jejuensis, one COI and four 18S sequences were obtained; however, the Cytb sequence could not be amplified. BLAST searches of COI and Cytb sequences detected no pseudogenes. Final COI alignment resulted in a dataset with the following characteristics: six sequences with 666 nucleotide sites, 268 parsimony-informative sites, 120 singleton sites, and 278 constant sites. The sequences translated into a polypeptide of 222 amino acids and revealed no stop codon. The best-fit evolutionary model for the COI dataset according to BIC was K3Pu + F + G4. The Cytb alignment included nineteen sequences and was trimmed to the length of 391 nucleotide sites with the following characteristics: 1 parsimony-informative site, 160 singleton sites, and 230 constant sites. The sequences translated into a polypeptide of approximately 130 amino acids with no stop codon. The 18S alignment comprised fifteen sequences trimmed into 2422 nucleotide sites with the following characteristics: 546 parsimony-informative sites, 394 singleton sites, and 1482 constant sites. The model, SYM + I + G4, was chosen as the best-fit evolutionary model for the 18S dataset according to BIC.
The COI uncorrected p-distance (Table S1) between U. mundongensis and U. jejuensis was 19.9%, while the distance between the two M. japonica specimens was 2.01%. The specimens collected from Daepunggam Cliff of Ulleung Island were identified as M. japonica. The distances between the Uromunna species and M. japonica ranged between 37.8 and 39.6%. The highest p-distance between the in-group and out-group was estimated in U. jejuensis at 43.9%, and the lowest was found in M. japonica (KX186724) at 33.9%. The Cytb uncorrected p-distance between U. mundongensis and M. japonica was estimated (Table S1), ranging from 41.4 to 41.7%. The highest distance between the U. mundongensis populations was estimated as 0.26% from the specimens of Homigot, Pohang. The 18S uncorrected p-distance between U. mundongensis and U. jejuensis was 0.4% (Table S1). The distances between the new species and U. nana ranged from 6.4 to 6.5%. The highest generic distance between Uromunna and Munna was estimated at 31.4%.
The resulting ML phylogram of COI (Figure 15) showed that two sequences of U. mundongensis clustered separately from a sequence of U. jejuensis but with a moderate support (80.5). Two sequences of M. japonica formed a well-supported (95) independent clade. The separation of Uromunna and Munna was well supported (85.9).
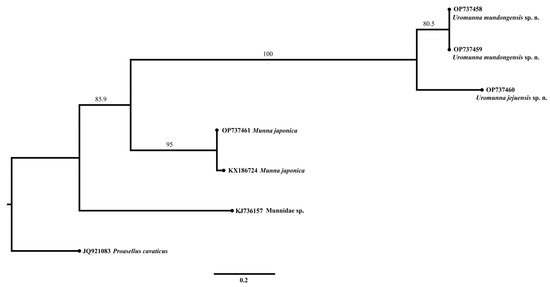
Figure 15.
Maximum-likelihood (ML) phylogram of COI sequences showing the phylogenetic relationships of U. mundongensis and U. jejuensis sp. n. Scale shows substitutions per site. Numbers above the branches represent bootstrap support.
The 18S phylogram (Figure 16) showed that the Uromunna species, including U. mundongensis, U. jejuensis, and U. nana, grouped together and formed a monophyletic clade with high confidence (100). Munna japonica was grouped beside the Uromunna clades, together forming a superficial monophyletic clade of Munnidae with a low supporting value (70.9). Each deep sea group of Dendrotionidae and Haplomunnidae clustered in its own unique clade, as previously seen by [47]. Iais pubescens was grouped with the clades of Dendrotionidae and Haplomunnidae with a high supporting value (99.9).
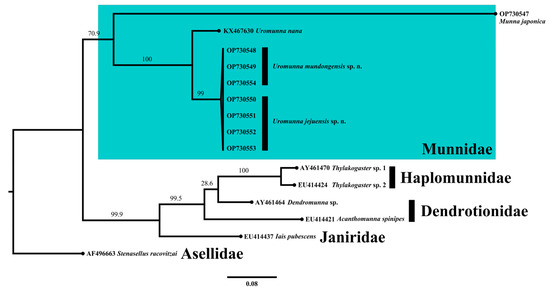
Figure 16.
Maximum-likelihood phylogram of 18S sequences showing the phylogenetic relationships of U. mundongensis and U. jejuensis sp. n. with related groups. The clade in the green rectangle indicates Munnidae. Scale shows substitutions per site. Numbers above the branches represent bootstrap support.
4. Discussion
In this study, we describe two Uromunna species from the Korean Peninsula with subtle differences in the chaetotaxy and L/W ratios of appendages based on the male morphology. The values of the COI uncorrected pairwise distances between the Korean new species fall within the broadly recognized barcoding gap for closely related asellote species with 0–2% differences within species and 10–40% between species [25,59,60,61,62,63]. For 18S, on the other hand, the p-distance lay within the intraspecific level and was slightly lower than the interspecific threshold, ranging between 1–4% [61,64]. Overall, our genetic results, which are the first phylogenetic information in the entire family, supported the morphology-based establishment of a new taxa by determining the unique genetic identity of U. mundongensis and U. jejuensis. A high genetic divergence rate is in contrast with a low degree of morphological differences. First of all, we failed to detect any difference in the male pleopods 1–2 between U. mundongensis and U. jejuensis, which is one of the crucial key characteristics in Uromunna taxonomy [41]. Interestingly, this is not the first case. For instance, Esquete et al. [34], found only a few differences between U. naherba Esquete, Wilson & Troncoso, 2014 and U. serricauda, despite the fact that these species are described from the Iberian Peninsula and the Malaysian waters, respectively. Uromunna serricauda also has male pleopods similar to U. nana, U. humei Poore, 1984, U. phillipi Poore, 1984, U. rhamnda Esquete & Wilson, 2016, and the new Korean species herein. Such phenomenon across the Uromunna species is noteworthy, given that morphological variability in the invertebrate genital organ can influence the copulation success rate, resulting in reproductive isolation among morphologically diverged individuals [65,66]. The males of Janiroidea have highly modified pleopods specialized for insemination, forming a channel with a combination of pleopods 1, 2, and the penial papillae to deliver the sperm into the female genitalia [67]. Interspecific morphological variability in these organs is common in most of the janiroidean isopods. In this sense, we assume the morphological homogeneity of Uromunna’s pleopods is the case of character displacement. The evolutionary process of this sort is known to be driven by the ecological, behavioral, and reproductive competition between closely related species for resources, leading to dramatic diversification, more greatly between sympatric populations than between allopatric ones [68,69,70,71]. The constant morphological state of genitalia regarded as the outcome of character displacement has been observed in various invertebrate taxa [72,73,74,75].
Our 18S sequence analysis provides a preliminary insight into the previously unknown phylogenetic relationship between Uromunna and other related genera groups. The monophyly of Munnidae consisting of only three species in this analysis is not well-supported, and this can be due to the long branch attraction between M. japonica and Uromunna species. In addition, the monophyly of the “munnoid” groups was not recovered due to the distant relationship between the Munnidae, Dendrotionidae, and Haplomunnidae, despite the apparent morphological synapomorphies [56]. Notably, Acanthomunna, which is morphologically the least derived genus within the Dendrotionidae, with plesiomorphic traits (e.g., retention of eyes and occurrence in shallow bathyal and deep waters) [76], did not show any phylogenetic relationship with Uromunna and Munna indicating an unlikely evolutionary linkage to the Munnidae. Our result seems to superficially support the hypothesis of deep sea colonization by the Dendrotionidae and Haplomunnidae, which took place separately from Munnidae, corresponding to the previously known evolutionary phenomenon of multiple origins of deep sea janiroidean isopods [47,56,77]. However, this issue requires further study given that inferring the deep phylogenetic relationship between families is beyond the scope of our paper. Furthermore, our dataset included only a small number of species and a single genetic marker representing each family. We believe additional sequence data, from multiple genetic markers, are necessary to establish a better understanding of the intergeneric relationship of “munnoids” that will allow a more detailed evolutionary linkage, between shallow and deep sea “munnoids”, to be ascertained.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d15010020/s1, Table S1: Uncorrected pair-wise distance matrix of COI, Cytb, and 18S. Data S1: MAFFT multiple sequence alignment of COI data. Data S2: MAFFT multiple sequence alignment of 18S data.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization, J.K. (Jeongho Kim); methodology, J.K. (Jeongho Kim) and J.K. (Jaehyun Kim); software, J.K. (Jeongho Kim) and J.K. (Jaehyun Kim); validation, J.K. (Jeongho Kim) and J.K. (Jaehyun Kim); formal analysis, J.K. (Jeongho Kim) and J.K. (Jaehyun Kim); investigation, J.K. (Jeongho Kim) and J.K. (Jaehyun Kim); resources, W.L. and I.K.; data curation, J.K. (Jeongho Kim) and J.K. (Jaehyun Kim); writing—original draft preparation, J.K. (Jeongho Kim); writing—review and editing, W.L. and I.K.; visualization, J.K. (Jeongho Kim) and J.K. (Jaehyun Kim); supervision, W.L. and I.K.; project administration, W.L. and I.K.; funding acquisition, W.L. and I.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Marine Biodiversity Institute of Korea (MABIK), grant number 2022M01100.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The voucher specimens of the species examined in the present study were deposited in the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) and National Marine Biodiversity Institute of Korea (MABIK). The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in Genbank and this published article (and its Supplementary Materials).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Myo-kyoung Kim (Korea University) for providing valuable comments on making line art.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bock, W.J. Species: The concept, category and taxon. J. Zoolog. Syst. Evol. Res. 2004, 42, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, J. On the failure of modern species concepts. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, K. Branches in the lines of descent: Charles Darwin and the evolution of the species concept. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 2011, 103, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausdorf, B. Progress toward a general species concept. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 2011, 65, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sites, J.W., Jr.; Marshall, J.C. Delimiting species: A Renaissance issue in systematic biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, K. Species concepts and species delimitation. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, D.K.; Seago, A.; Nelson, L.; Cameron, S.L.; Joseph, L.E.O.; Trueman, J.W. Integrative taxonomy, or iterative taxonomy? Syst. Entomol. 2011, 36, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial, J.M.; Miralles, A.; De la Riva, I.; Vences, M. The integrative future of taxonomy. Front. Zool. 2010, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Queiroz, K. A unified concept of species and its consequences for the future of taxonomy. In Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences; Leviton, A.E., Williams, G.C., Aldrich, M.L., Eds.; California Academy of Sciences: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 54, pp. 196–215. [Google Scholar]
- Fišer, C.; Robinson, C.T.; Malard, F. Cryptic species as a window into the paradigm shift of the species concept. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Ingram, K.K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayrat, B.; Gosliner, T.M. Species names and metaphyly: A case study in Discodorididae (Mollusca, Gastropoda, Euthyneura, Nudibranchia, Doridina). Zool. Scr. 2005, 34, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M.; Seifert, B.; Stauffer, C.; Christian, E.; Crozier, R.H. Integrative taxonomy: A multisource approach to exploring biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andújar, C.; Arribas, P.; Ruiz, C.; Serrano, J.; Gómez--Zurita, J. Integration of conflict into integrative taxonomy: Fitting hybridization in species delimitation of Mesocarabus (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 4344–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pante, E.; Schoelinck, C.; Puillandre, N. From integrative taxonomy to species description: One step beyond. Syst. Biol. 2015, 64, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanovic, T.; Djurakic, M.; Eberhard, S.M. Cryptic species or inadequate taxonomy? Implementation of 2D geometric morphometrics based on integumental organs as landmarks for delimitation and description of copepod taxa. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 304–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, G.C.B.; Bruce, N.L. Global Diversity of Marine Isopods (Except Asellota and Crustacean Symbionts). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, C.; Wägele, J.W. Cryptic speciation in the giant Antarctic isopod Glyptonotus antarcticus (Isopoda, Valvifera, Chaetiliidae). Sci. Mar. 2005, 69, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.J.; Wägele, J.W. Distinguishing cryptic species in Antarctic Asellota (Crustacea: Isopoda)—A preliminary study of mitochondrial DNA in Acanthaspidia drygalskii. Antarct. Sci. 2006, 18, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leese, F.; Kop, A.; Wägele, J.W.; Held, C. Cryptic speciation in a benthic isopod from Patagonian and Falkland Island waters and the impact of glaciations on its population structure. Front. Zool. 2008, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, S.; Riehl, T.; Leese, F. First genetic data for species of the genus Haploniscus Richardson, 1908 (Isopoda: Asellota: Haploniscidae) from neighbouring deep-sea basins in the South Atlantic. Zootaxa 2011, 2838, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, W.; Karanovic, I. The first insight into the patterns of size and shape variation of a microcerberid isopod. Water 2021, 13, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurr, S.; Brandt, A.; Brix, S.; Fiorentino, D.; Malyutina, M.; Svavarsson, J. Composition and distribution of selected munnopsid genera (Crustacea, Isopoda, Asellota) in Icelandic waters. Deep-Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2014, 84, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, S.; Brix, S.; Kihara, T.C.; Janssen, A.; Jennings, R.M. Integrative species delimitation in the deep-sea genus Thaumastosoma Hessler, 1970 (Isopoda, Asellota, Nannoniscidae) reveals a new genus and species from the Atlantic and central Pacific abyss. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 148, 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, T.; Lins, L.; Brandt, A. The effects of depth, distance, and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on genetic differentiation of abyssal and hadal isopods (Macrostylidae). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 148, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, P.R.; Papadopoulos, I.; Zardi, G.I.; McQuaid, C.D.; Edkins, M.T.; Griffiths, C.L.; Barker, N.P. Implications of life history for genetic structure and migration rates of southern African coastal invertebrates: Planktonic, abbreviated and direct development. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.J.; Malyutina, M.; Brandt, A.; Wägele, J.W. Molecular data reveal a highly diverse species flock within the munnopsoid deep-sea isopod Betamorpha fusiformis (Barnard, 1920) (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota) in the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 1820–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.; Brix, S.; Held, C.; Kihara, T.C. Molecular differentiation in sympatry despite morphological stasis: Deep-sea Atlantoserolis Wägele, 1994 and Glabroserolis Menzies, 1962 from the south-west Atlantic (Crustacea: Isopoda: Serolidae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 172, 318–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Malyutina, M.; Lee, W.; Karanovic, I. Incongruence between morphological and molecular diversity in Coxicerberus fukudai (Ito, 1974) (Isopoda: Microcerberidea) from East Asia. J. Crustac. Biol. 2018, 38, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.D.F. New insights into the colonization of the deep sea: Systematics and zoogeography of the Munnidae and the Pleurogoniidae comb. nov. (Isopoda; Janiroidea). J. Nat. Hist. 1980, 14, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessler, R.R.; Strömberg, J.O. Behavior of janiroidean isopods (Asellota), with special reference to deep-sea genera. Sarsia 1989, 74, 45–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquete, P.; Moreira, J.; Troncoso, J.S. Peracarid assemblages of Zostera meadows in an estuarine ecosystem (O Grove inlet, NW Iberian Peninsula): Spatial distribution and seasonal variation. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2011, 65, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Esquete, P.; Wilson, G.D.F.; Troncoso, J.S. Ecology and systematics of a new species of Uromunna (Crustacea: Isopoda) from Spanish eelgrass beds. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2014, 68, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boyko, C.B.; Bruce, N.L.; Hadfield, K.A.; Merrin, K.L.; Ota, Y.; Poore, G.C.B.; Taiti, S. World Marine, Freshwater and Terrestrial Isopod Crustaceans database. 2008 onwards. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/isopoda (accessed on 14 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Menzies, R.J. The zoogeography, ecology and systematics of the Chilean marine isopods. Reports of the Lund University Chile Expedition 1948–49. Lunds Univ. Arsskrift 1962, 42, 1–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kussakin, O.G. On the fauna of Munnidae (Isopoda: Asellota) from the Far-Eastern seas of the USSR. Tr. Zool. Inst. Akad. Nauk. USSR 1962, 30, 66–109. [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberg, D.; Menzies, R.J. 1966. A new species of asellote marine isopod, Munna (Uromunna) reynoldsi (Crustacea: Isopoda). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1966, 16, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kensley, B.F. A new species of Munna Kroyer from Nigeria (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1980, 93, 136–140. Available online: https://repository.si.edu/handle/10088/10269 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Poore, G.C. Redefinition of Munna and Uromunna (Crustacea: Isopoda: Munnidae), with descriptions of five species from coastal Victoria. Proc. R. Soc. Vict. 1984, 96, 61–81. [Google Scholar]
- Esquete, P.; Wilson, G.D.F. The genus Uromunna (Crustacea: Isopoda: Munnidae) in New South Wales, Australia, with a key for all known species. Mar. Biol. Res. 2016, 12, 488–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, M.; Mawatari, S.F. Munnidae from Japan (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota). Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 2011, 39, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raupach, M.J.; Mayer, C.; Malyutina, M.; Wägele, J.W. Multiple origins of deep-sea Asellota (Crustacea: Isopoda) from shallow waters revealed by molecular data. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raupach, M.J.; Held, C.; Wägele, J.W. Multiple colonization of the deep sea by the Asellota (Crustacea: Peracarida: Isopoda). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, T.; Brandt, A. Descriptions of two new species in the genus Macrostylis Sars, 1864 (Isopoda, Asellota, Macrostylidae) from the Weddell Sea (Southern Ocean), with a synonymisation of the genus Desmostylis Brandt, 1992 with Macrostylis. Zookeys 2010, 57, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, J.; Meyer, C.; Parker, M.; Hawk, H. Redesign of PCR primers for mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I for marine invertebrates and application in all--taxa biotic surveys. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boore, J.L.; Brown, W.M. Mitochondrial genomes of Galathealinum, Helobdella, and Platynereis: Sequence and gene arrangement comparisons indicate that Pogonophora is not a phylum and Annelida and Arthropoda are not sister taxa. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Min, G.S. New record of limnoriid and asellote species (Crustacea: Malacostraca: Isopoda) from South Korea. J. Species Res. 2017, 6, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wàgele, J.W. On the origin of the Microcerberidae (Crustacea: Isopoda). J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 1983, 21, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree. Tree Figure Drawing Tool. 2009. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Janssen, A.; Kaiser, S.; Meissner, K.; Brenke, N.; Menot, L.; Martínez Arbizu, P. A reverse taxonomic approach to assess macrofaunal distribution patterns in abyssal Pacific polymetallic nodule fields. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, S.; Bober, S.; Tschesche, C.; Kihara, T.C.; Driskell, A.; Jennings, R.M. Molecular species delimitation and its implications for species descriptions using desmosomatid and nannoniscid isopods from the VEMA fracture zone as example taxa. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 148, 180–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurr, S.; Osborn, K.J.; Malyutina, M.; Jennings, R.; Brix, S.; Driskell, A.; Svavarsson, J.; Martinez Arbizu, P. Hidden diversity in two species complexes of munnopsid isopods (Crustacea) at the transition between the northernmost North Atlantic and the Nordic Seas. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 813–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, J.; Brandt, A.; Frutos, I.; Schwentner, M. Diversity and distribution of Ischnomesidae (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota) along the Kuril-Kamchatka trench—A genetic perspective. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 178, 102174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, S.; Held, C.; Kaiser, S.; Jennings, R.M.; Driskell, A.; Brandt, A. Evolution and phylogeny of the deep-sea isopod families Desmosomatidae Sars, 1897 and Nannoniscidae Hansen, 1916 (Isopoda: Asellota). Org. Divers. Evol. 2021, 21, 691–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, S.; Svavarsson, J.; Leese, F. A multi-gene analysis reveals multiple highly divergent lineages of the isopod Chelator insignis (Hansen, 1916) south of Iceland. Pol. Polar Res. 2014, 2, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sota, T.; Kubota, K. Genital lock--and--key as a selective agent against hybridization. Evolution 1998, 52, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masly, J.P. 170 years of “lock-and-key”: Genital morphology and reproductive isolation. Int. J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 2012, 247352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.D.F. Functional morphology and evolution of isopod genitalia. In Crustacean Sexual Biology, 1st ed.; Raymond, T.B., Joel, W.M., Eds.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.L.; Wilson, E.O. Character displacement. Syst. Zool. 1956, 5, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, W.F. Character displacement in frogs. Am. Zool. 1974, 14, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, J. Competition and character displacement in two species of scincid lizards. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C. Character displacement via aggressive interference in Appalachian salamanders. Ecology 2004, 85, 2664–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukagoshi, A. Reproductive character displacement in the ostracod genus Cythere. J. Crustac. Biol. 1988, 8, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, K. Character displacement in giant rhinoceros beetles. Am. Nat. 2002, 159, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, K. Character displacement in stag beetles (Coleoptera: Lucanidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2003, 96, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S. Biogeographical history and morphological evolution of two closely related ostracod species, Ishizakiella ryukyuensis and I. miurensis. J. Crustac. Biol. 2003, 23, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilson, G.D.F. The systematics and evolution of Haplomunna and its relatives (Isopoda, Haplomunnidae, new family). J. Nat. Hist. 1976, 10, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, L.S.; Ho, S.Y.; Wilson, G.D.F.; Lo, N. Evidence for Permo-Triassic colonization of the deep sea by isopods. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).