Predator-Induced Nocturnal Benthic Emergence: Field and Experimental Evidence for an Unknown Behavioral Escape Mechanism along the Coral Reef–Seagrass Interface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Descriptions
2.2. Distributional Patterns of Nocturnally Active Predators
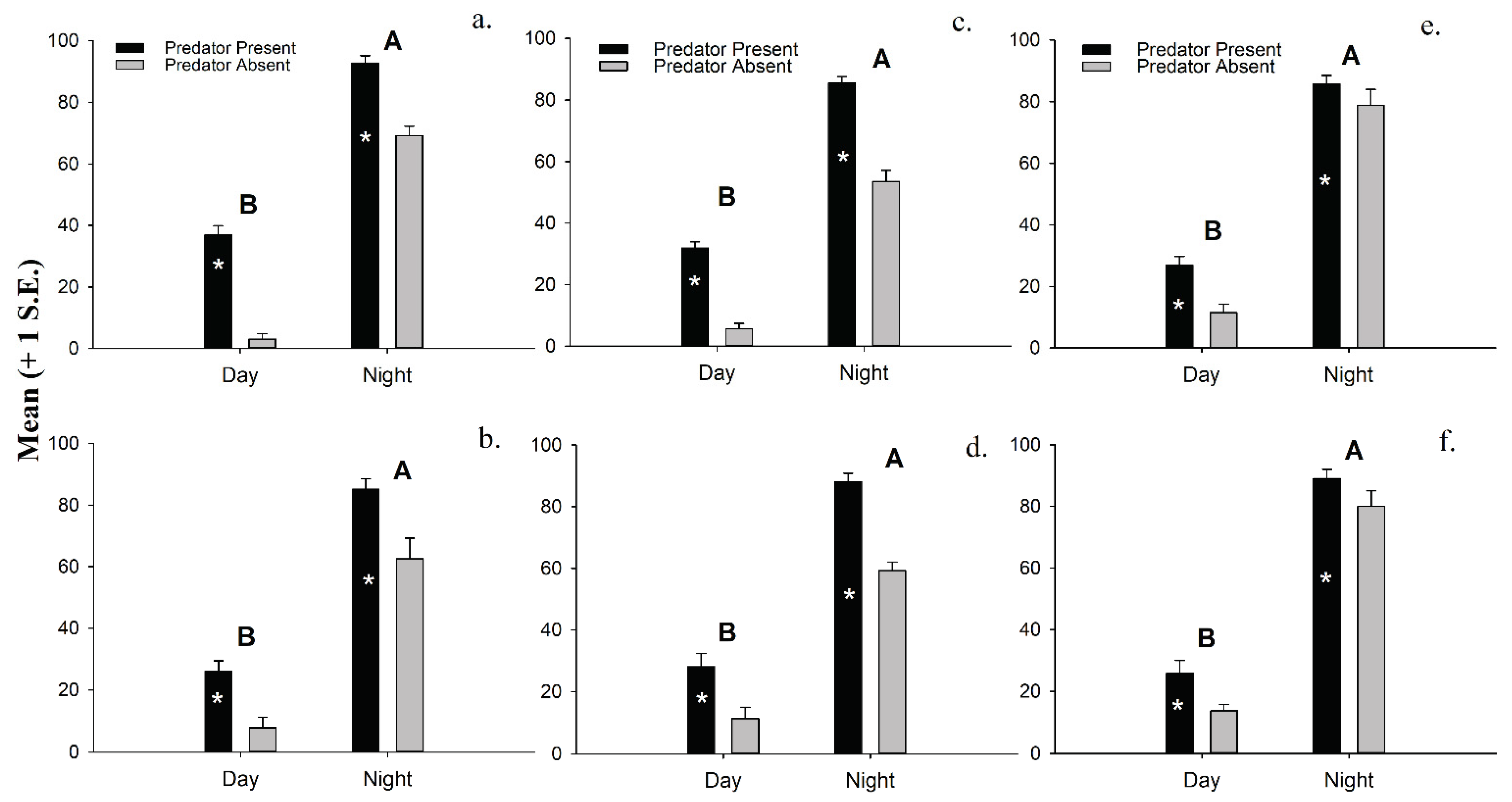
2.3. Predator Impacts on Macroinvertebrate Emergence
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Field Surveys
2.4.2. Laboratory Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Fish Density and Composition at Dry Rocks Reef
3.2. Patterns of Fish Density and Composition at Newfound Harbor
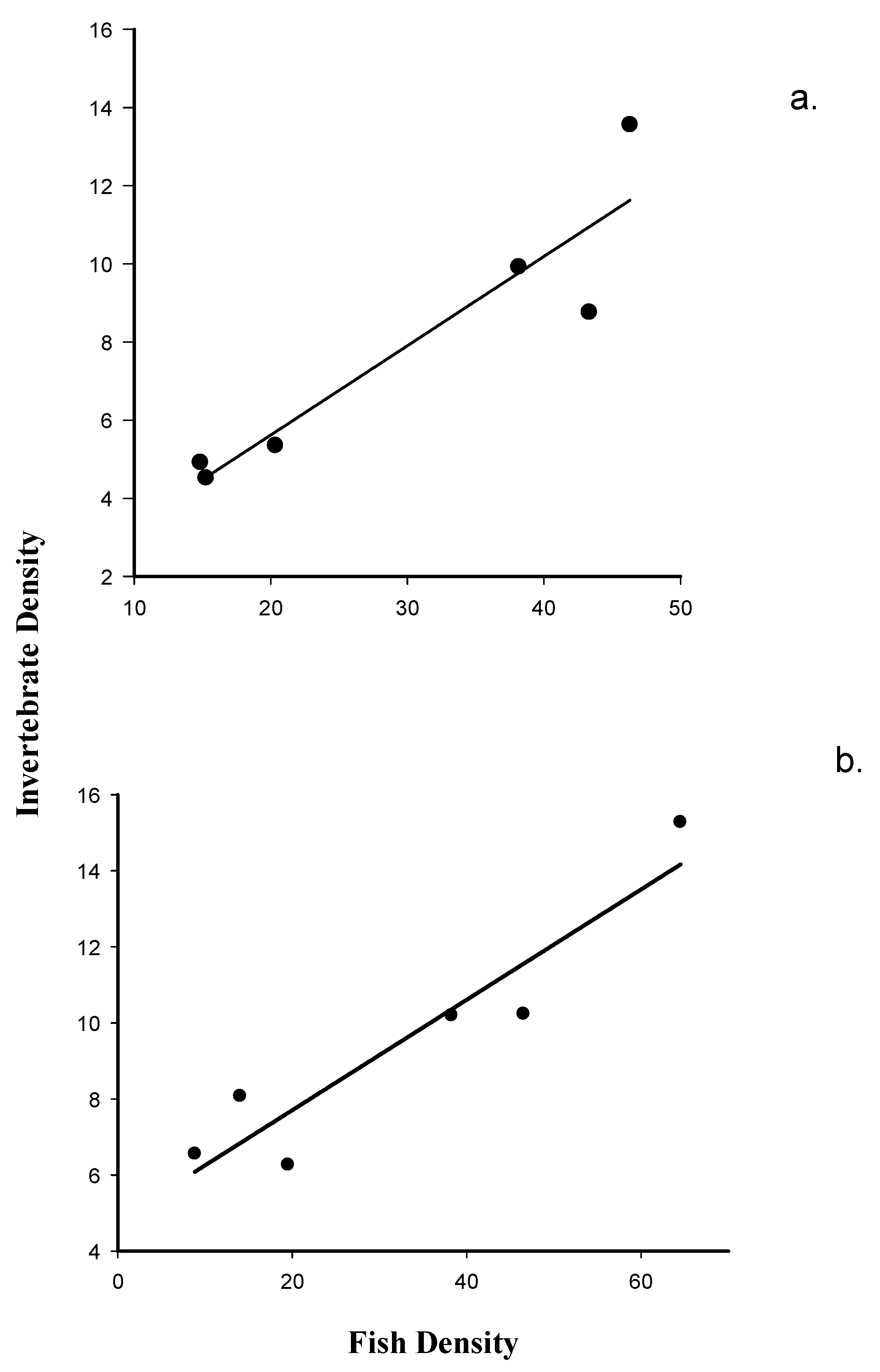
3.3. The Relationship between Fish Density and Macroinvertebrate Emergence at Dry Rocks and Newfound Harbor Reefs
3.4. Laboratory Experiments
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shurin, J.B.; Borer, E.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Anderson, K.; Blanchette, C.A.; Broitman, B.; Cooper, S.D.; Halpern, B.S. A cross-ecosystem comparison of the strength of trophic cascades. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L.; Valentine, J.F. The primacy of top-down effects in shallow benthic ecosystems. Estuaries Coasts 2007, 30, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heithaus, M.R.; Fri, A.; Wirsing, A.J.; Worm, B. Predicting ecological consequences of marine top predator declines. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sih, A.; Wooster, D.E. Prey Behavior, Prey Dispersal, and Predator Impacts on Stream Prey. Ecology 1994, 75, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, C.F.; Roy, A.H. Seasonal succession in fishless ponds: Effects of enrichment and invertebrate predators on zooplankton community structure. Hydrobiologia 2003, 490, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, L.M.; Heithaus, M.R.; Walters, C.J. Behaviorally mediated indirect interactions in marine communities, and the conservation implications. Ecology 2003, 84, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisser, E.L.; Bolnick, D.I.; Benard, M.F. Scared to death? the effects of intimidation and consumption in predator–prey interactions. Ecology 2005, 86, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catano, L.B.; Rojas, M.C.; Malossi, R.J.; Peters, J.R.; Heithaus, M.R.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Burkepile, D.E. Reefscapes of fear: Predation risk and reef heterogeneity interact to shape herbivore foraging behavior. J. Anim. Ecol. 2016, 85, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heithaus, M.R.; Dill, L.M. Food availability and tiger shark predation risk influence bottlenose dolphin habitat use. Ecology 2002, 83, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Thompson, K.R.; Cowan, J.H.; Heck, K.L. Comparison of predation pressure in temperate and subtropical regions based on chronographic tethering. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 224, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.F.; Heck, K.L.; Blackmon, D.; Goecker, M.E.; Christian, J.; Kroutil, R.M.; Peterson, B.J.; Vanderklift, M.A.; Kirsch, K.D.; Beck, M. Exploited species impacts on trophic linkages along reef–seagrass interfaces in the Florida Keys. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1501–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, P.F. (Ed.) The Ecology of Fishes on Coral Reefs, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hitt, S.; Pittman, S.; Nemeth, R. Diel movements of fishes linked to benthic seascape structure in a Caribbean coral reef ecosystem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 427, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flecker, A.S. Fish Predation and The Evolution of Invertebrate Drift Periodicity: Evidence from Neotropical Streams. Ecology 1992, 73, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, K.; Bell, S.S. Diel patterns of active vertical migration in seagrass meiofauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 34, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehner, T. Diel vertical migration of freshwater fishes-proximate triggers, ultimate causes and research perspectives. Freshwat. Biol. 2012, 57, 1342–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmon, D.C.; Valentine, J.F. Recurring nocturnal benthic emergence along the coral reef–seagrass interface in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary: Evidence of a possible novel prey escape response. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 448, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, J.; Sbragaglia, V.; Tecchio, S.; Company, J.B. Rhythmic behavior of marine benthopelagic species and the synchronous dynamics of benthic communities. Deep Sea Res. I 2015, 95, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.W.; Reynolds, L.K.; Scheffel, W.A.; Tiffany, S.; Kopetman, S. Diel Variability and Influence of Artificial Light on Fish and Macroinvertebrate Communities in Gulf of Mexico Seagrass Beds. Estuaries Coasts 2021, 44, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.E. Grazing Effect on Sea Grasses by Herbivorous Reef Fishes in the West Indies. Ecology 1965, 46, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, J.C.; Zieman, J.C. Ecological aspects of coral reef-seagrass bed contacts in the Caribbean. Proc. Third Int. Coral Reef Symp. 1977, 1, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, N.C. Nocturnal foraging habitats of French and bluestriped grunts, Haemulon flavolineatum and H. sciurus, at Tobacco Caye, Belize. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 42, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, D.B.; Grover, J.J.; Lipcius, R.N. Ontogenetic diet shifts in Nassau grouper: Trophic linkages and predator impact. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1998, 63, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.J.; Valentine, J.F.; Heck, K.L. The snapper–grunt pump: Habitat modification and facilitation of the associated benthic plant communities by reef-resident fish. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 441, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkel, P.; Welicky, R.; Artim, J.; McCammon, A.; Sellers, J.; Coile, A.M.; Jenkins, W. Nocturnal migration reduces exposure to micropredation in a coral reef fish. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2017, 93, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.; Howard, R.K. Diel trophic interactions between vertically-migrating zooplankton and their fish predators in an eelgrass community. Mar. Biol. 1978, 48, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiddink, J.G.; Kock, R.P.; Wolff, W.J. Active pelagic migrations of the bivalve Macoma balthica are dangerous. Mar. Biol. 2002, 140, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.F.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Blackmon, D.; Goecker, M.E.; Christian, J.; Kroutil, R.M.; Kirsch, K.D.; Peterson, B.J.; Beck, M.; Vanderklift, M.A. Food web interactions along seagrass-coral reef boundaries: Effects of piscivore reductions on cross-habitat energy exchange. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 333, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, T.J.T.; Aronson, R.B. Scale-dependent spatial variability of coral assemblages along the Florida Reef Tract. Coral Reefs 1999, 18, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichter, J.J.; Stewart, H.L.; Miller, S.L. Episodic nutrient transport to Florida coral reefs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 4th ed.; W. H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 937. [Google Scholar]
- Hamner, W.M. The importance of ethology for investigations of marine zooplankton. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 414–424. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Kitchell, J.F. The Trophic Cascade in Lakes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; p. 385. [Google Scholar]
- Dawidowicz, P.; Pijanowska, J. Diel vertical migration of aquatic crustaceans-adaptive role, underlying mechanisms, and ecosystem consequences. In The Natural History of Crustaceans; Thiel, M., Wellborn, G., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; Volume 5, pp. 231–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, S.L. Identification of Stream Drift Mechanisms: An Experimental and Observational Approach. Ecology 1985, 66, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polis, G.A.; Hurd, S.D. Linking Marine and Terrestrial Food Webs: Allochthonous Input from the Ocean Supports High Secondary Productivity on Small Islands and Coastal Land Communities. Am. Nat. 1996, 147, 396–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.F.; Heck, K.L. Perspective review of the impacts of overfishing on coral reef food web linkages. Coral Reefs 2005, 24, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Mean Square | Degrees of Freedom | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ostracods | ||||
| Time | 45,630.55 | 1 | 513.77 | <0.0001 |
| Predator | 10,141.29 | 1 | 114.18 | <0.0001 |
| Time × predator | 318.06 | 1 | 3.58 | 0.065 |
| Error | 88.815 | 46 | ||
| Polychaetes | ||||
| Time | 40,084.77 | 1 | 171.38 | <0.0001 |
| Predator | 4461.07 | 1 | 19.07 | <0.0001 |
| Time × predator | 140.79 | 1 | 0.602 | 0.442 |
| Error | 233.89 | 45 | ||
| Amphipods | ||||
| Time | 31,482.12 | 1 | 449.6 | <0.0001 |
| Predator | 10,331.55 | 1 | 147.55 | <0.0001 |
| Time × predator | 103.87 | 1 | 1.483 | 0.229 |
| Error | 70.02 | 46 | ||
| Isopods | ||||
| Time | 35,502.1 | 1 | 229.14 | <0.0001 |
| Predator | 6340.79 | 1 | 40.93 | <0.0001 |
| Time × predator | 445.22 | 1 | 2.874 | 0.097 |
| Error | 154.94 | 45 | ||
| Mysids | ||||
| Time | 20,661.5 | 1 | 147.17 | <0.0001 |
| Predator | 598.26 | 1 | 4.26 | <0.022 |
| Time × predator | 163.62 | 1 | 1.165 | 0.322 |
| Error | 140.39 | 42 | ||
| Tanaids | ||||
| Time | 51,055.82 | 1 | 317.43 | <0.0001 |
| Predator | 1365.16 | 1 | 8.49 | <0.006 |
| Time × predator | 29.55 | 1 | 0.184 | 0.67 |
| Error | 160.84 | 45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blackmon, D.C.; Valentine, J.F. Predator-Induced Nocturnal Benthic Emergence: Field and Experimental Evidence for an Unknown Behavioral Escape Mechanism along the Coral Reef–Seagrass Interface. Diversity 2022, 14, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090762
Blackmon DC, Valentine JF. Predator-Induced Nocturnal Benthic Emergence: Field and Experimental Evidence for an Unknown Behavioral Escape Mechanism along the Coral Reef–Seagrass Interface. Diversity. 2022; 14(9):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090762
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlackmon, Derrick C., and John F. Valentine. 2022. "Predator-Induced Nocturnal Benthic Emergence: Field and Experimental Evidence for an Unknown Behavioral Escape Mechanism along the Coral Reef–Seagrass Interface" Diversity 14, no. 9: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090762
APA StyleBlackmon, D. C., & Valentine, J. F. (2022). Predator-Induced Nocturnal Benthic Emergence: Field and Experimental Evidence for an Unknown Behavioral Escape Mechanism along the Coral Reef–Seagrass Interface. Diversity, 14(9), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090762









