Mesophotic Reefs of the Largest Brazilian Coastal Protected Area: Mapping, Characterization and Biodiversity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
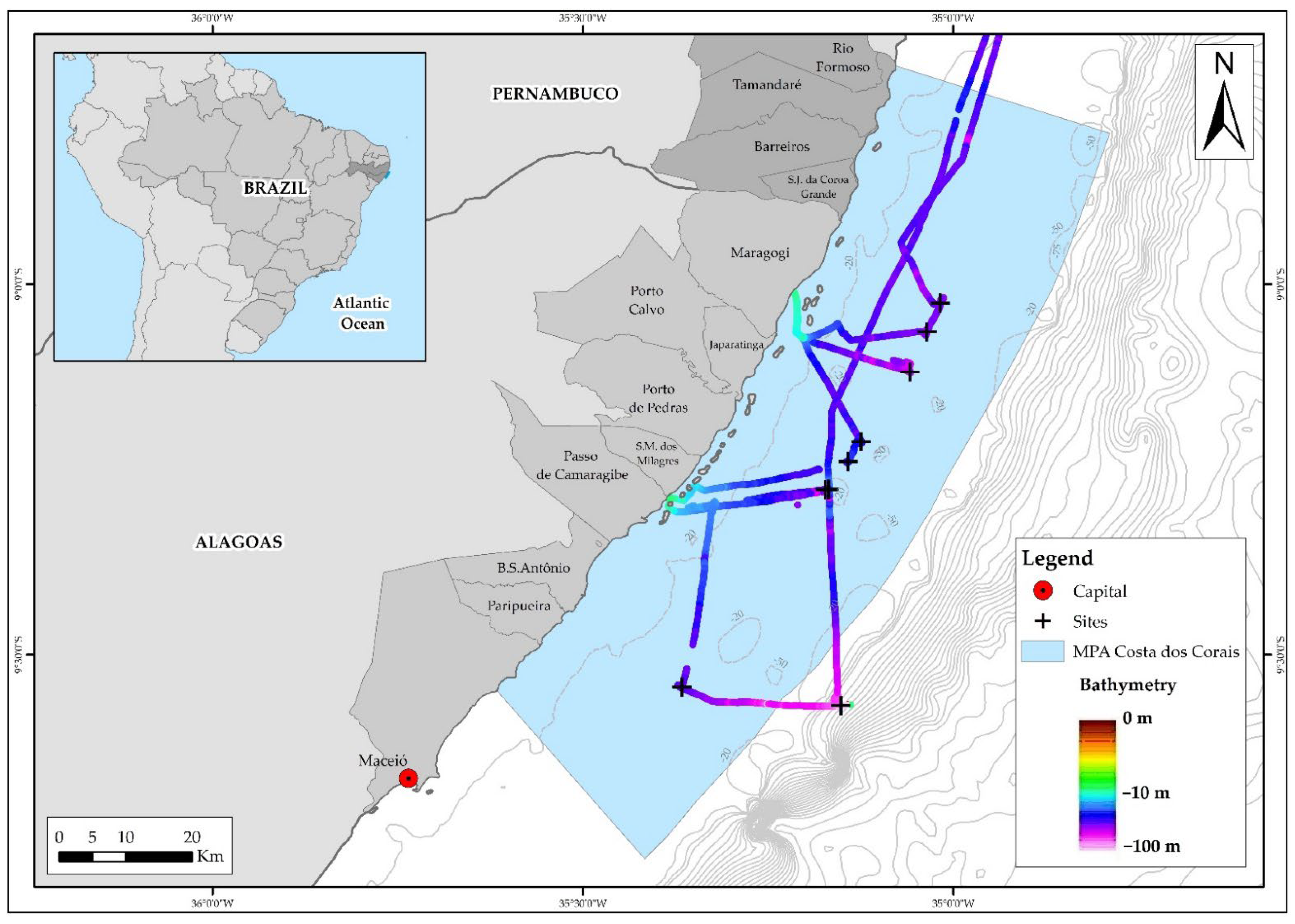
2.1. Study Area
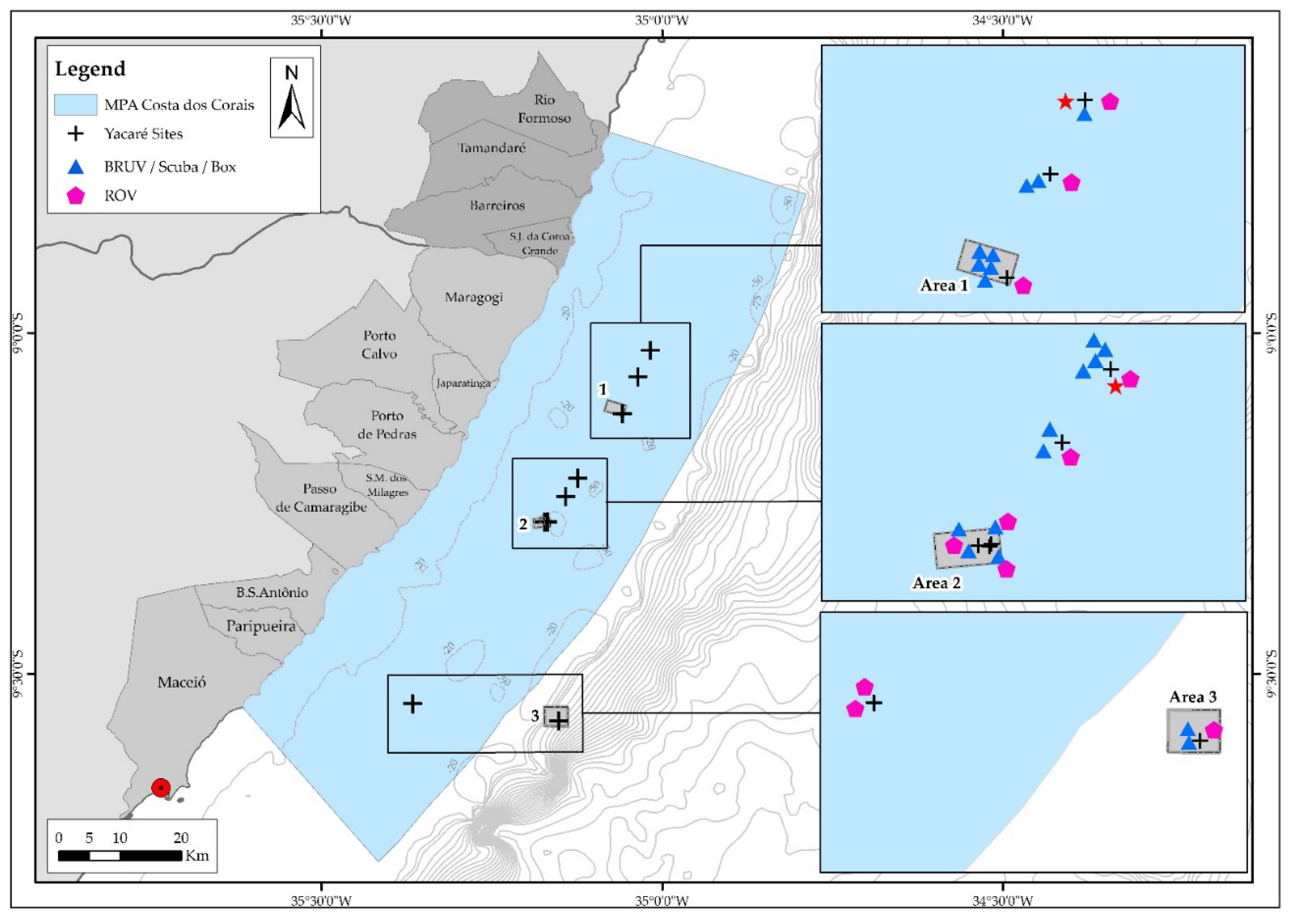
2.2. Sampling Design and Field Measurements
2.3. Data Analyses
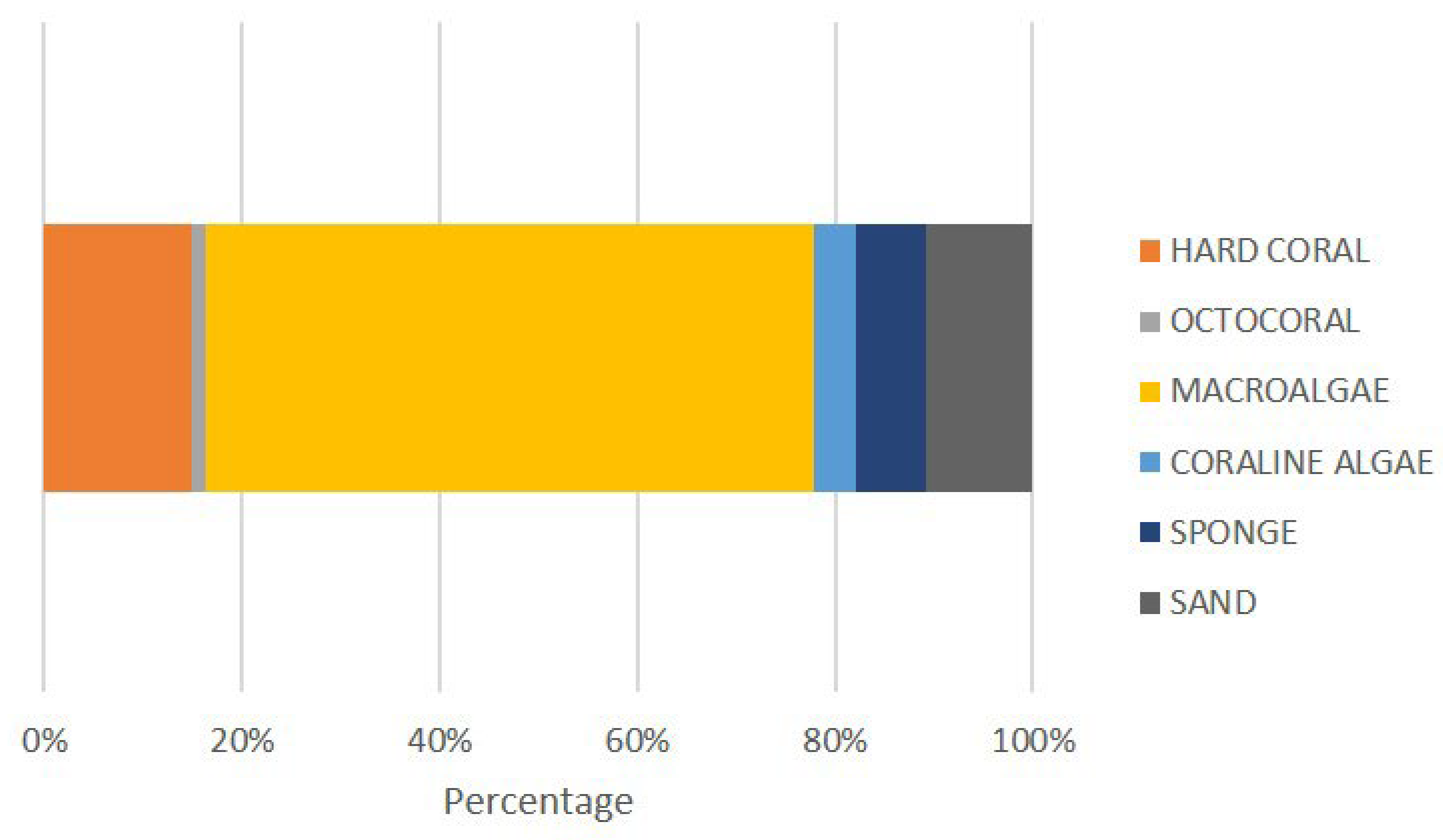
3. Results
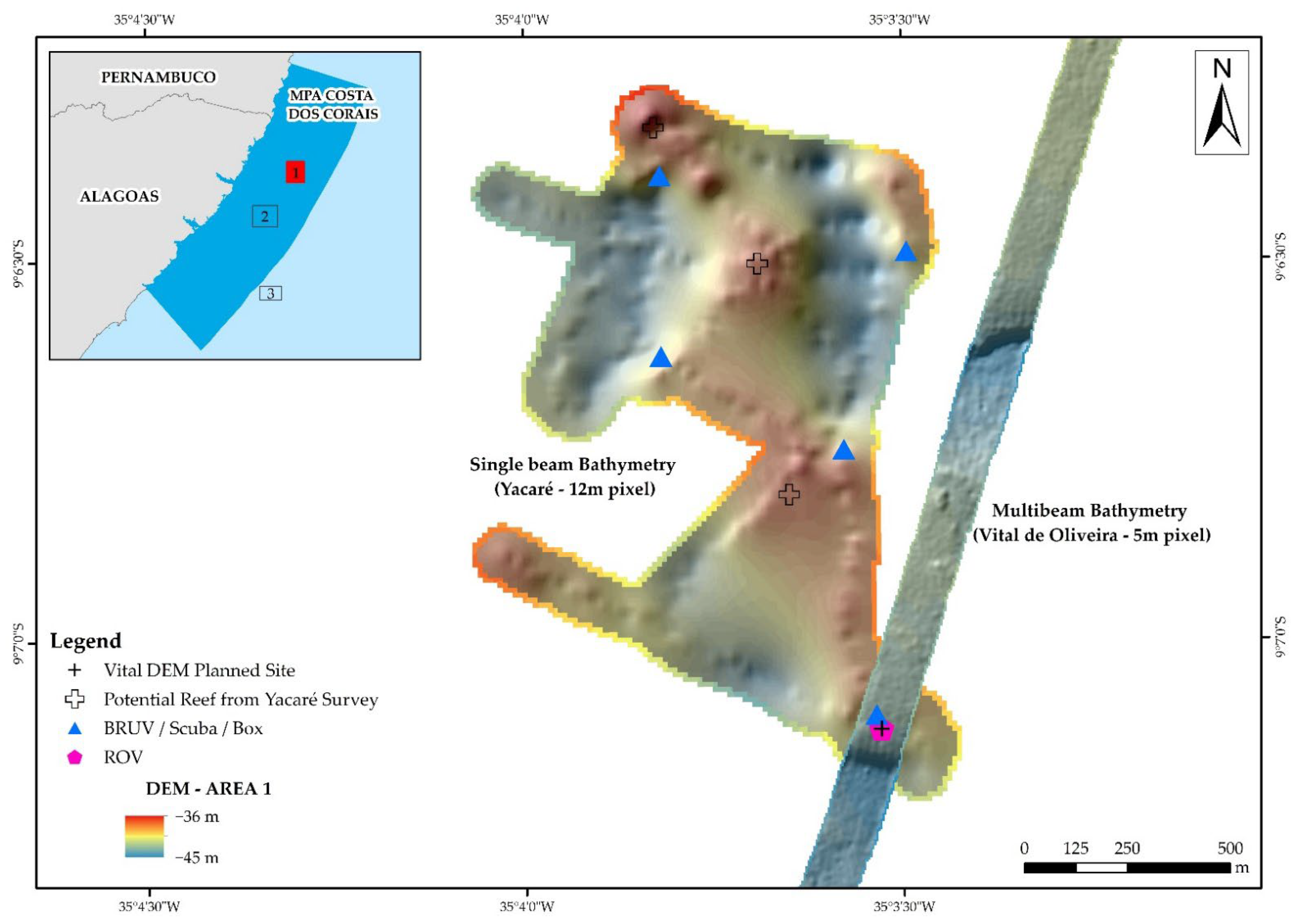
3.1. Digital Bathymetry Model
3.1.1. Area 1 (Point 3)
3.1.2. Area 2 (Points 7 and 8)
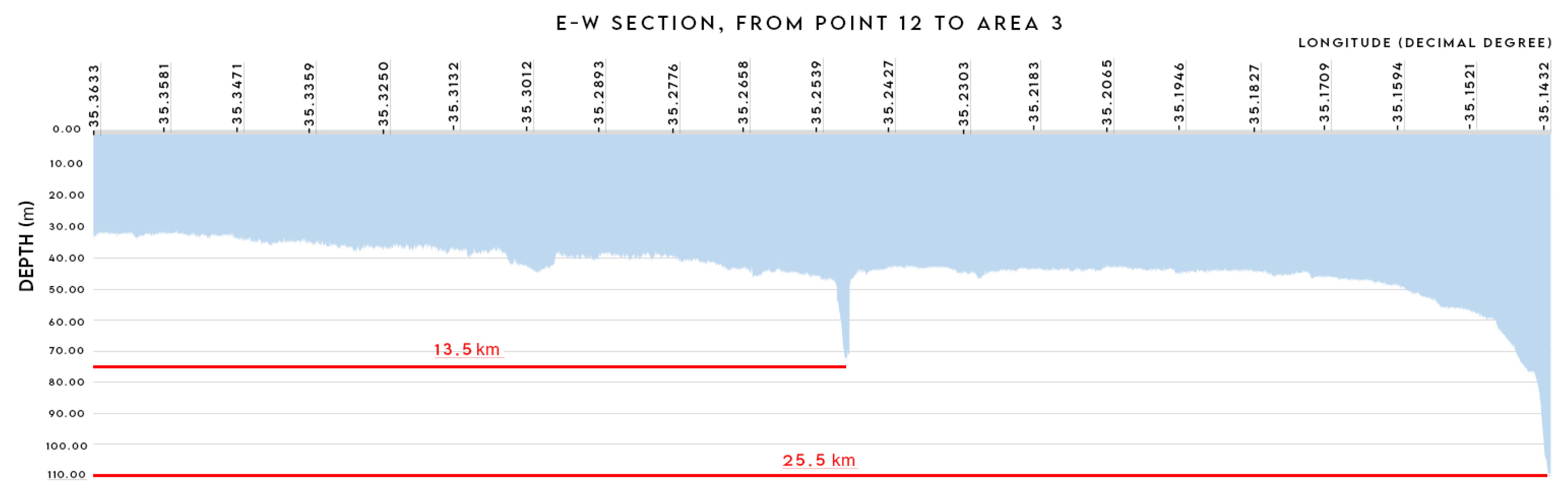
3.1.3. Area 3 (Break of Continental Shelf)
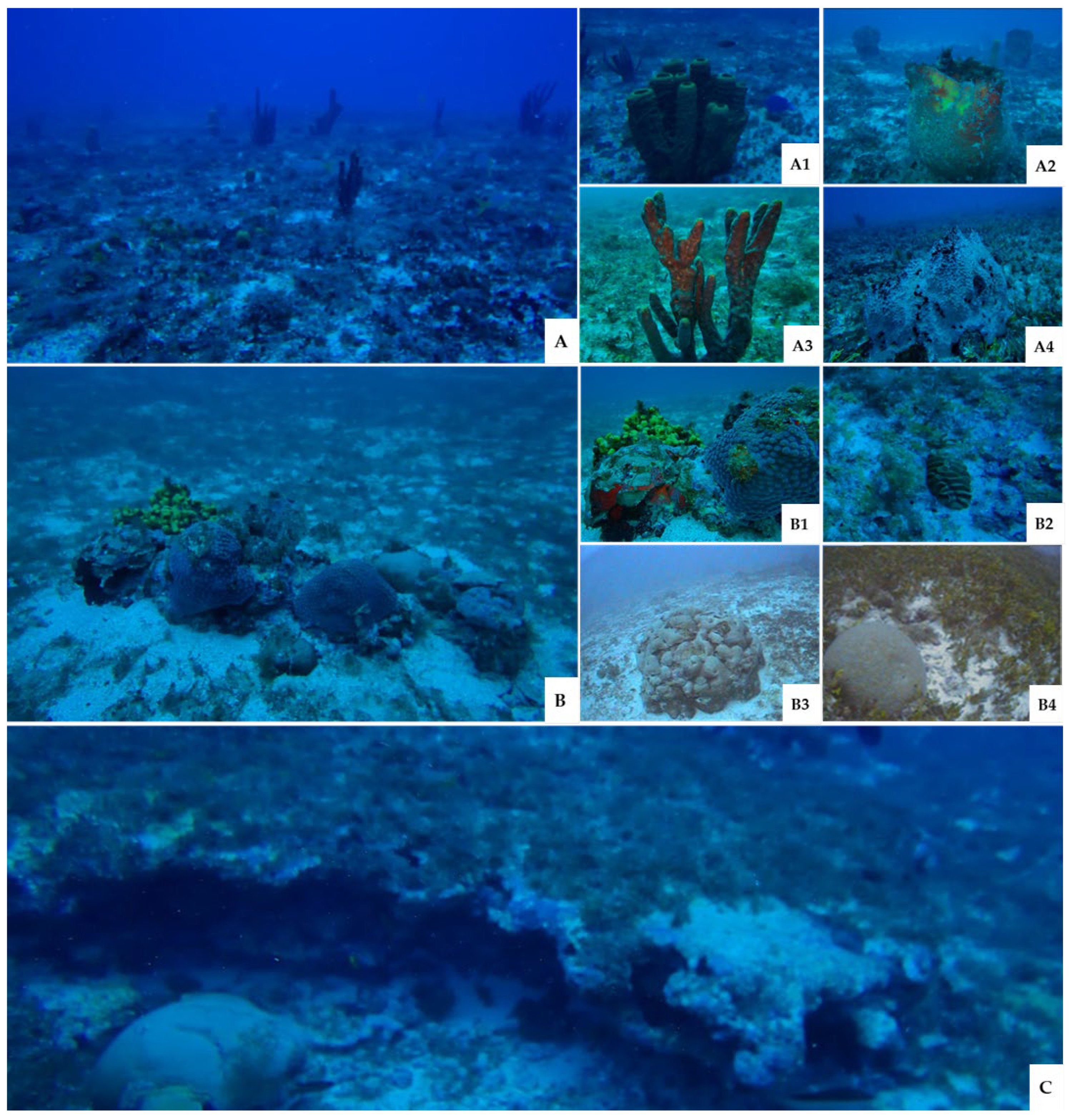
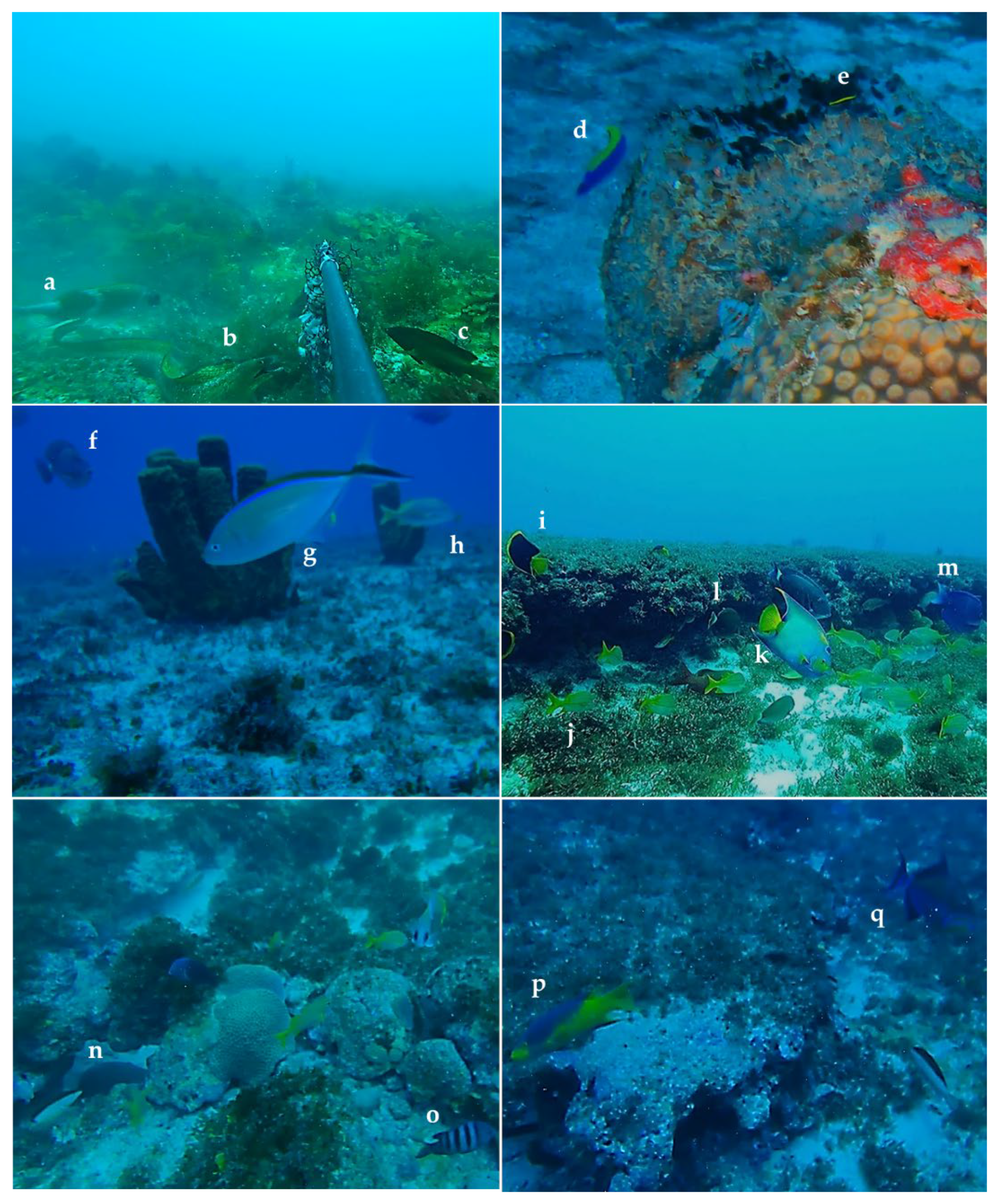
3.2. Biodiversity
3.2.1. Benthic Community
3.2.2. Fish Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Olympic Committee. IOC Capacity Development Strategy 2015–2021; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Hoey, A.S.; Choat, J.H. Limited Functional Redundancy in High Diversity Systems: Resilience and Ecosystem Function on Coral Reefs. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long-Term Region-Wide Declines in Caribbean Corals. Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.1086050 (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Bellwood, D.R.; Hughes, T.P.; Folke, C.; Nyström, M. Confronting the Coral Reef Crisis. Nature 2004, 429, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Álvarez-Noriega, M.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Anderson, K.D.; Baird, A.H.; Babcock, R.C.; Beger, M.; Bellwood, D.R.; Berkelmans, R.; et al. Global Warming and Recurrent Mass Bleaching of Corals. Nature 2017, 543, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, A.M.; Bahr, K.D. The Coral Conservation Crisis: Interacting Local and Global Stressors Reduce Reef Resiliency and Create Challenges for Conservation Solutions. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, K.R.N.; Helmstedt, K.J.; Bay, L.K.; Fidelman, P.; Hussey, K.E.; Lundgren, P.; Mead, D.; McLeod, I.M.; Mumby, P.J.; Newlands, M. Interventions to Help Coral Reefs under Global Change—A Complex Decision Challenge. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236399. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0236399 (accessed on 6 July 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyle, R. Exploring Deep Coral Reefs: How Much Biodiversity Are We Missing? Glob. Biodivers. 1996, 6, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brokovich, E.; Einbinder, S.; Shashar, N.; Kiflawi, M.; Kark, S. Descending to the Twilight-Zone: Changes in Coral Reef Fish Assemblages along a Depth Gradient down to 65 m. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 371, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglise, K.A.; Hinderstein, L.M.; Marr, J.C.A.; Dowgiallo, M.J.; Martinez, F.A. Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems Research Strategy: International Workshop to Prioritize Research and Management Needs for Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems, Jupiter, Florida, 12–15 July 2008. 2009. Available online: http://aquaticcommons.org/id/eprint/14943 (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Eyal, G.; Pinheiro, H.T. Mesophotic Ecosystems: The Link between Shallow and Deep-Sea Habitats. Diversity 2020, 12, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Soares, M.; Tavares, T.C.L.; de Macêdo Carneiro, P.B. Mesophotic Ecosystems: Distribution, Impacts and Conservation in the South Atlantic. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francini-Filho, R.B.; Velásquez, V.M.; da Silva, M.B.; Rosa, M.R.; Sumida, P.Y.G.; Pinheiro, H.T.; Rocha, L.A.; Ferreira, C.E.L.; Francini, C.L.B.; de Souza Rosa, R. Brazil. In Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems; Loya, Y., Puglise, K.A., Bridge, T.C.L., Eds.; Coral Reefs of the World; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 163–198. ISBN 978-3-319-92735-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.J.; Micaroni, V.; Harris, B.; Strano, F.; Broadribb, M.; Rogers, A. Global Status, Impacts, and Management of Rocky Temperate Mesophotic Ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 2022, e13945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellan, G.; Angeletti, L.; Montagna, P.; Taviani, M. Drawing the Borders of the Mesophotic Zone of the Mediterranean Sea Using Satellite Data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinderstein, L.M.; Marr, J.C.A.; Martinez, F.A.; Dowgiallo, M.J.; Puglise, K.A.; Pyle, R.L.; Zawada, D.G.; Appeldoorn, R. Theme Section on “Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems: Characterization, Ecology, and Management”. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 247–251. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00338-010-0614-5 (accessed on 6 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kahng, S.E.; Garcia-Sais, J.R.; Spalding, H.L.; Brokovich, E.; Wagner, D.; Weil, E.; Hinderstein, L.; Toonen, R.J. Community Ecology of Mesophotic Coral Reef Ecosystems. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 255–275. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00338-010-0593-6 (accessed on 6 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kahng, S.; Copus, J.; Wagner, D. Recent Advances in the Ecology of Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems (MCEs). Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 7, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, C.; Kosaki, R.K.; Wagner, D. High Levels of Mesophotic Reef Fish Endemism in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2014, 90, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaki, R.K.; Pyle, R.L.; Leonard, J.C.; Hauk, B.B.; Whitton, R.K.; Wagner, D. 100% Endemism in Mesophotic Reef Fish Assemblages at Kure Atoll, Hawaiian Islands. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, A.H.; DeMartini, E.E.; Brodziak, J.; Nichols, R.S.; Humphreys, R.L. A Long-Lived Life History for a Tropical, Deepwater Snapper (Pristipomoides Filamentosus): Bomb Radiocarbon and Lead–Radium Dating as Extensions of Daily Increment Analyses in Otoliths. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1850–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.H.C.; Macedo, C.H.; Nunes, J.D.A.C.C.; de Barros Marangoni, L.F.; Bianchini, A. Effects of Depth on Reef Fish Communities: Insights of a “Deep Refuge Hypothesis” from Southwestern Atlantic Reefs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanoudis, P.V.; Gress, E.; Pitt, J.M.; Smith, S.R.; Kincaid, T.; Rivers, M.; Andradi-Brown, D.A.; Rowlands, G.; Woodall, L.C.; Rogers, A.D. Depth-Dependent Structuring of Reef Fish Assemblages From the Shallows to the Rariphotic Zone. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirman, D.; Gracias, N.R.; Gintert, B.E.; Gleason, A.C.R.; Reid, R.P.; Negahdaripour, S.; Kramer, P. Development and Application of a Video-Mosaic Survey Technology to Document the Status of Coral Reef Communities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 125, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, A.C.R.; Gracias, N.; Lirman, D.; Gintert, B.E.; Smith, T.B.; Dick, M.C.; Reid, R.P. Landscape Video Mosaic from a Mesophotic Coral Reef. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laverick, J.H.; Piango, S.; Andradi-Brown, D.A.; Exton, D.A.; Bongaerts, P.; Bridge, T.C.L.; Lesser, M.P.; Pyle, R.L.; Slattery, M.; Wagner, D.; et al. To What Extent Do Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems and Shallow Reefs Share Species of Conservation Interest? A Systematic Review. Environ. Evid. 2018, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongaerts, P. Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R345–R346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eduardo, L.N.; Frédou, T.; Lira, A.S.; Ferreira, B.P.; Bertrand, A.; Ménard, F.; Frédou, F.L. Identifying Key Habitat and Spatial Patterns of Fish Biodiversity in the Tropical Brazilian Continental Shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 166, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Soares, M.; de Araújo, J.T.; Ferreira, S.M.C.; Santos, B.A.; Boavida, J.R.H.; Costantini, F.; Rossi, S. Why Do Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems Have to Be Protected? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, C.B.L.; Reuss Strenzel, G.M.; Maida, M.; Ferreira, B.P. Pushing Satellite Imagery to New Depths: Seascape Feature Mapping in a Tropical Shelf. Remote Sens. Appl. 2020, 19, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SciELO (Brasil). Mesophotic Ecosystems at Fernando de Noronha Archipelago, Brazil (South-Western Atlantic), Reveal Unique Ichthyofauna and Need for Conservation Mesophotic Ecosystems at Fernando de Noronha Archipelago, Brazil (South-Western Atlantic), Reveal Unique Ichthyofauna and Need for Conservation. Available online: https://www.scielo.br/j/ni/a/VT6myX65FvzZhNtCWrynXWK/?lang=en (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Lesser, M.P.; Slattery, M. Mesophotic Coral Reef Community Structure: The Constraints of Imagery Collected by Unmanned Vehicles. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 663, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maida, M.; Ferreira, B. Coral Reefs of Brazil: Overview and Field Guide. In Proceedings of the 8th International Coral Reef Symposium, Panama City, Panama, 24–29 June 1996; Volume 1, pp. 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, B.; Maida, M.; Cava, F.C. Características e Perspectivas Para o Manejo Da Pesca Na APA Marinha Costa Dos Corais. In Proceedings of the Congresso Brasileiro de Unidades de Conservação, Campo Grande, Brazil, 18 July 2000; pp. 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, H.T.; Rocha, L.A.; Macieira, R.M.; Carvalho-Filho, A.; Anderson, A.B.; Bender, M.G.; Di Dario, F.; Ferreira, C.E.L.; Figueiredo-Filho, J.; Francini-Filho, R.; et al. South-Western Atlantic Reef Fishes: Zoogeographical Patterns and Ecological Drivers Reveal a Secondary Biodiversity Centre in the Atlantic Ocean. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.H.C.; Côrtes, L.G.F.; Lima, G.V.; Gomes, E.; Pontes, A.V.F.; Mattos, F.; Araújo, M.E.; Ferreira-Junior, F.; Sampaio, C.L.S. Reef Fishes Biodiversity and Conservation at the Largest Brazilian Coastal Marine Protected Area (MPA Costa Dos Corais). Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2021, 19, e210071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centro de Hidrografia Da Marinha. De Cabedelo a Maceio. Available online: https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-segnav-cartas-raster/de-cabedelo-maceio (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Teledyne Geospatial. HIPS and SIPS. Available online: https://www.teledynecaris.com/en/products/hips-and-sips/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Hutchinson, M.F.; Gallant, J.C. Representation of terrain. In Geographical Information Systems: Principles, Technical Issues, Management Issues and Applications, 2nd ed.; Longley, P.A., Goodchild, M.F., Maguire, D.J., Rhind, D.W., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Chapter 9; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, M.F.; Gallant, J.C. Digital elevation models and representation of terrain shape. In Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; Wilson, J.P., Gallant, J.C., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Chapter 2; pp. 29–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, M.F. Adding the Z-dimension. In Handbook of Geographic Information Science; Wilson, J.P., Fotheringham, A.S., Eds.; Blackwell: London, UK, 2008; pp. 144–168. [Google Scholar]
- Geoprocessamento Em Projetos Ambientais. Available online: http://www.dpi.inpe.br/gilberto/tutoriais/gis_ambiente/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- de Almeida Silveira, T.; Portugal, J.L.; de Sá, L.A.C.M.; de Oliveira Vitalo, S.R. Análise estatística espacial aplicada a construção de superfícies batimétricas. Geosci. Geociências 2014, 33, 596–615. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, C. Interpolating Surfaces in ArcGIS Spatial. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Interpolating-Surfaces-in-ArcGIS-Spatial-Childs/944f410c2ac7456fe951b726f63c2f41466b9f67 (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Buckley, A. Create Amazing Hillshade Effects Quickly and Easily in Arcgis PRO. Arcuser. 2018. Available online: https://www.esri.com/about/newsroom/arcuser/create-amazing-hillshade-effects-quickly-and-easily-in-arcgis-pro/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Hill, J.; Wilkinson, C. Methods for Ecological Monitoring of Coral Reefs; Version 1; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Townsville, Australia, 2004; pp. 1–116. [Google Scholar]
- Leão, Z.M.A.N.; Kikuchi, R.K.P.; Ferreira, B.P.; Neves, E.G.; Sovierzoski, H.H.; Oliveira, M.D.M.; Maida, M.; Correia, M.D.; Johnsson, R. Brazilian Coral Reefs in a Period of Global Change: A Synthesis. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2016, 64, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappo, M.; Speare, P.; De’ath, G. Comparison of Baited Remote Underwater Video Stations (BRUVS) and Prawn (Shrimp) Trawls for Assessments of Fish Biodiversity in Inter-Reefal Areas of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 302, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, K.; Reis-Filho, J.A.; Harvey, E.; Giarrizzo, T. Baited Remote Underwater Video as a Promising Nondestructive Tool to Assess Fish Assemblages in Clearwater Amazonian Rivers: Testing the Effect of Bait and Habitat Type. Hydrobiologia 2017, 784, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1118342336. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Laan, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Fricke, R. Family-Group Names of Recent Fishes. Zootaxa 2014, 3882, 1–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westneat, M.W.; Alfaro, M.E. Phylogenetic Relationships and Evolutionary History of the Reef Fish Family Labridae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 36, 370–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/en (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Livro Vermelho Da Fauna Brasileira Ameaçada de Extinção 2018—Português (Brasil). Available online: https://www.gov.br/icmbio/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/publicacoes-diversas/livro-vermelho/livro-vermelho-da-fauna-brasileira-ameacada-de-extincao-2018 (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Emslie, M.; Logan, M.; Williamson, D.; Ayling, A.; MacNeil, M.; Ceccarelli, D.; Cheal, A.; Evans, R.; Johns, K.; Jonker, M.; et al. Expectations and Outcomes of Reserve Network Performance Following Re-Zoning of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 983–992. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960982215001372 (accessed on 11 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S. The Impact of Marine Reserves: Do Reserves Work and Does Reserve Size Matter? Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, E.R.; Brown, C.J.; Araújo, T.C. Geomorphological Classification of the Benthic Structures on a Tropical Continental Shelf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, D.P.T.; Gomes, M.P.; Longo, G.O. Underwater Valley at the Continental Shelf Structures Benthic and Fish Assemblages of Biogenic Reefs. Estuarine. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 224, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.P.; Vital, H.; Nascimento Silva, L.L.; Eichler, P.B.; Rovira, D.; Longo, G.O. Nature and Condition of Outer Shelf Habitats on the Drowned Açu Reef, Northeast Brazil. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 571–585. ISBN 978-0-12-814960-7. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, K.L.; Holt, R.; Endrino, I.P.; Stewart, H. When the Species Is Also a Habitat: Comparing the Predictively Modelled Distributions of Lophelia Pertusa and the Reef Habitat It Forms. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, S.N.; Bastos, A.C.; Quaresma, V.S.; Vieira, F.V.; Pinheiro, H.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; De Moura, R.L.; Teixeira, J.B. Seabed Morphology and Sedimentary Regimes Defining Fishing Grounds along the Eastern Brazilian Shelf. Geosciences 2018, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.A.; Pinheiro, H.T.; Shepherd, B.; Papastamatiou, Y.P.; Luiz, O.J.; Pyle, R.L.; Bongaerts, P. Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems Are Threatened and Ecologically Distinct from Shallow Water Reefs. Science 2018, 361, 281–284. Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.aaq1614 (accessed on 8 July 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neves, E.G.; Andrade, S.C.S.; da Silveira, F.L.; Solferini, V.N. Genetic Variation and Population Structuring in Two Brooding Coral Species (Siderastrea Stellata and Siderastrea Radians) from Brazil. Genetica 2008, 132, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, R.L.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Moraes, F.C.; Brasileiro, P.S.; Salomon, P.S.; Mahiques, M.M.; Bastos, A.C.; Almeida, M.G.; Silva, J.M.; Araujo, B.F.; et al. An Extensive Reef System at the Amazon River Mouth. Science 2016, 2, e1501252. Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.1501252 (accessed on 8 July 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, M.; Aguilar, R.; Bannister, R.J.; Bell, J.J.; Conway, K.W.; Dayton, P.K.; Díaz, C.; Gutt, J.; Kelly, M.; Kenchington, E.L.R.; et al. Sponge Grounds as Key Marine Habitats: A Synthetic Review of Types, Structure, Functional Roles, and Conservation Concerns. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., del Valle, C.O.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–39. ISBN 978-3-319-17001-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, Y.-Y.; Prince, J.; Kendrick, G.; Abdul Wahab, M.A. Sponges in Shallow Tropical and Temperate Reefs Are Important Habitats for Marine Invertebrate Biodiversity. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.H.C.; Ternes, M.L.F.; Nunes, J.A.C.C.; Giglio, V.J. Overexploitation and Behavioral Changes of the Largest South Atlantic Parrotfish (Scarus Trispinosus): Evidence from Fishers’ Knowledge. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 254, 108940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.G.; Machado, G.R.; Silva, P.J.D.; Floeter, S.R.; Monteiro-Netto, C.; Luiz, O.J.; Ferreira, C.E.L. Local Ecological Knowledge and Scientific Data Reveal Overexploitation by Multigear Artisanal Fisheries in the Southwestern Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110332. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0110332 (accessed on 8 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Guabiroba, H.C.; Santos, M.E.A.; Pinheiro, H.T.; Simon, T.; Pimentel, C.R.; Vilar, C.C.; Joyeux, J.-C. Trends in Recreational Fisheries and Reef Fish Community Structure Indicate Decline in Target Species Population in an Isolated Tropical Oceanic Island. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 191, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, H.T.; Nunes, J.A.C.C.; Coni, E.O.C.; Almeida, E.C.G.; Sampaio, C.L.S.; Ferreira, C.E.L.; Meirelles, P.M.; Hostim-Silva, M.; Pereira, P.H.C.; Giglio, V.J.; et al. An Inverted Management Strategy for the Fishery of Endangered Marine Species. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.H.C.; Araujo, J.C.; Lima, G.V.; Côrtes, L.G.F.; Gomes, E.; Magris, R.A. Effectiveness of Management Zones for Recovering Parrotfish Species within the Largest Coastal Marine Protected Area in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.J.; Pinto, T.K.O.; Lopes, R.V.R.; Santos, J.W.; Sampaio, C.L.S.; Santos, R.G.; Pereira, P.H.C.; Cardoso, A.T.C.; Malhado, A.C.M.; Ladle, R.J. Oil Spill Disaster in Southwest Atlantic Coast: An Evaluation of Short-Term Effects on Coral Reef Benthic Assemblages. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2022, 94, e20210401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.H.C.; Lima, G.V.; Pontes, A.V.F.; Côrtes, L.G.F.; Gomes, E.; Sampaio, C.L.S.; Pinto, T.K.; Miranda, R.J.; Cardoso, A.T.C.; Araujo, J.C.; et al. Unprecedented Coral Mortality on Southwestern Atlantic Coral Reefs Following Major Thermal Stress. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlesinger, T.; Grinblat, M.; Rapuano, H.; Amit, T.; Loya, Y. Can Mesophotic Reefs Replenish Shallow Reefs? Reduced Coral Reproductive Performance Casts a Doubt. Ecology 2018, 99, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papastamatiou, Y.; Meyer, C.; Kosaki, R.; Wallsgrove, N.; Popp, B. Movements and Foraging of Predators Associated with Mesophotic Coral Reefs and Their Potential for Linking Ecological Habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 521, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UN. The SDGS in Action. 2022. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals?c_src=CENTRAL&c_src2=GSR (accessed on 8 July 2022).




| Type | Species | Max Depth (m) | IUCN | ICMBio | SWA Endemic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coral | Scleractinia | ||||
| Agaricia agaricites | 75 | LC | ? | no | |
| Favia gravida | ? | LC | LC | yes | |
| Madracis decactis | 125 | LC | LC | no | |
| Meandrina braziliensis | 100 | DD | DD | yes | |
| Montastraea cavernosa | 180 | LC | LC | no | |
| Mussismilia hispida | 92 | DD | LC | yes | |
| Porites astreoides | 70 | LC | LC | no | |
| Siderastrea spp. | 90 | DD | DD | no | |
| Sponge | Haplosclerida | ||||
| Xestospongia muta | 100 | NE | LC | no | |
| Verongiida | |||||
| Aiolochroia crassa | 135 | NE | LC | no | |
| Aplysina fistularis | 120 | NE | LC | no | |
| Aplysina fulva | 100 | NE | LC | no | |
| Aplysina sp. | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Dictyoceratida | |||||
| Ircinia strobilina | 731 | NE | LC | no | |
| Ircinia sp. | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Clionaida | |||||
| Cliona sp. | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Family | Species | Max Depth (m) | Trophic Guild | Targeted Species | IUCN | ICMBio | SWA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginglymostomatidae | Ginglymostoma cirratum | 130 | MCAR | yes | NT | VU | no |
| Dasyatidae | Hypanus berthalutzae | 65 | MINV | yes | VU | DD | yes |
| Myliobatidae | Aetobatus narinari | 80 | MCAR | yes | EN | DD | no |
| Albulidae | Albula vulpes | 84 | MINV | yes | NT | DD | no |
| Muraenidae | Gymnothorax moringa | 200 | MCAR | yes | LC | DD | no |
| Gymnothorax vicinus | 85 | MCAR | yes | LC | DD | no | |
| Clupeidae | Harengula clupeola | 50 | PLANK | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Holocentridae | Holocentrus adscensionis | 200 | MINV | no | LC | LC | no |
| Fistulariidae | Fistularia tabacaria | 200 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Serranidae | Cephalopholis fulva | 218 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Epinephelus adscensionis | 189 | MCAR | yes | LC | DD | no | |
| Serranus baldwini | 80 | MINV | no | LC | LC | no | |
| Malacanthidae | Malacanthus plumieri | 153 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Carangidae | Caranx bartholomaei | 70 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Caranx crysos | 100 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Caranx lugubris | 350 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Caranx ruber | 106 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Decapterus punctatus | 90 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus alexandrei | 54 | MCAR | yes | NE | LC | yes |
| Lutjanus cyanopterus | 55 | MCAR | yes | VU | VU | no | |
| Lutjanus jocu | 70 | MCAR | yes | NT | NT | no | |
| Ocyurus chrysurus | 180 | MCAR | yes | DD | NT | no | |
| Haemulidae | Anisotremus virginicus | 40 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Anisotremus surinamensis | 60 | MINV | yes | DD | DD | no | |
| Haemulon aurolineatum | 70 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Haemulon parra | 60 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Haemulon plumierii | 70 | MINV | yes | LC | DD | no | |
| Haemulon squamipinna | 40 | MINV | yes | NE | LC | yes | |
| Sciaenidae | Equetus lanceolatus | 60 | MINV | no | LC | LC | no |
| Sparidae | Calamus penna | 87 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Calamus pennatula | 85 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Mullidae | Mulloidichthys martinicus | 66 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Pseudupeneus maculatus | 90 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Chaetodontidae | Chaetodon ocellatus | 30 | SINV | no | LC | DD | no |
| Chaetodon striatus | 65 | SINV | no | LC | LC | no | |
| Pomacanthidae | Holacanthus ciliaris | 120 | SINV | yes | LC | DD | no |
| Holacanthus tricolor | 92 | SINV | yes | LC | DD | no | |
| Pomacanthus paru | 100 | SINV | yes | LC | DD | no | |
| Kyphosidae | Kyphosus sectatrix | 55 | HERB | yes | LC | NE | no |
| Pomacentridae | Abudefduf saxatilis | 20 | OMNI | no | LC | LC | no |
| Azurina multilineata | 84 | PLANK | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Chromis multilineata | 60 | PLANK | no | LC | LC | no | |
| Stegastes fuscus | 55 | HERB | no | LC | LC | yes | |
| Stegastes pictus | 85 | HERB | no | NE | LC | yes | |
| Stegastes variabilis | 30 | HERB | no | NE | LC | yes | |
| Labridae | Bodianus rufus | 70 | MINV | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Clepticus brasiliensis | 62 | PLANK | no | LC | LC | yes | |
| Halichoeres brasiliensis | 60 | MINV | no | DD | LC | yes | |
| Halichoeres dimidiatus | 71 | MINV | no | LC | LC | yes | |
| Halichoeres poeyi | 71 | MINV | no | LC | LC | no | |
| Labridae-Scarinae | Cryptotomus roseus | 66 | HERB | no | LC | LC | no |
| Scarus zelindae | 55 | HERB | yes | DD | VU | yes | |
| Sparisoma amplum | 57 | HERB | yes | LC | NT | yes | |
| Sparisoma axillare | 45 | HERB | yes | DD | VU | yes | |
| Sparisoma frondosum | 45 | HERB | yes | DD | VU | yes | |
| Sparisoma radians | 12 | HERB | no | LC | LC | no | |
| Gobiidae | Elacatinus figaro | 70 | MINV | yes | VU | VU | yes |
| Ptereleotris randalli | 60 | PLANK | no | LC | LC | yes | |
| Acanthuridae | Acanthurus bahianus | 71 | HERB | yes | LC | LC | yes |
| Acanthurus chirurgus | 70 | HERB | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Acanthurus coeruleus | 71 | HERB | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Scombridae | Scomberomorus brasiliensis | 33 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no |
| Scomberomorus regalis | 20 | MCAR | yes | LC | LC | no | |
| Balistidae | Balistes vetula | 111 | MINV | yes | NT | NT | no |
| Monacanthidae | Cantherhines pullus | 57 | OMNI | no | LC | LC | no |
| Stephanolepis hispida | 293 | OMNI | no | LC | LC | no | |
| Ostraciidae | Acanthostracion polygonius | 80 | OMNI | no | LC | LC | no |
| Acanthostracion quadricornis | 80 | OMNI | no | LC | LC | no |
| Family | Species | Min Depth (m) | Maragogi | Japaratinga | Porto de Pedras | São Miguel dos Milagres | Barra de Santo Antônio | Parede |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corals | ||||||||
| Agariciidae | Agaricia agaricites | R | ||||||
| Faviidae | Favia gravida | 36.5 | S | |||||
| Pocilloporidae | Madracis decactis | 36.5 | R | S | ||||
| Meandrinidae | Meandrina braziliensis | R | ||||||
| Montastraeidae | Montastrea cavernosa | 31 | R | R, S | R, S | |||
| Mussidae | Mussismilia hispida | 36.5 | S | |||||
| Plexaurellidae | Plexaurella grandiflora | 36.5 | S | |||||
| Siderastreidae | Siderastrea spp. | 31 | R | R, S | R, S | R | ||
| Sponges | ||||||||
| Aplysinidae | Aiolochroia crassa | 31 | R | R | S | |||
| Aplysina fistularis | 31 | R | S | S | R | |||
| Aplysina fulva | 31 | S | R, S | |||||
| Aplysina sp. | 31 | S | R, S | R | ||||
| Clionaidae | Cliona sp. | R | R | |||||
| Irciniidae | Ircinia sp. | 31 | R | S | ||||
| Ircinia strobilina | 31 | R | R, S | R | R | |||
| Petrosiidae | Xestospongia muta | 31 | R | S | ||||
| Family | Species | Min Depth (m) | Maragogi | Japaratinga | Porto de Pedras | São Miguel dos Milagres | Barra de Santo Antônio | Parede | Personal Observation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginglymostomatidae | Ginglymostoma cirratum | R | |||||||
| Dasyatidae | Hypanus berthalutzae | 35 | B | ||||||
| Myliobatidae | Aetobatus narinari | X | |||||||
| Albulidae | Albula vulpes | 35 | B | ||||||
| Muraenidae | Gymnothorax moringa | 35 | B | ||||||
| Gymnothorax vicinus | 35 | B | |||||||
| Clupeidae | Harengula clupeola | 31 | B | ||||||
| Holocentridae | Holocentrus adscensionis | 31 | R, B | R, S | R, S, B | R, B | R | R, B | |
| Fistulariidae | Fistularia tabacaria | 31 | B | ||||||
| Serranidae | Cephalopholis fulva | 31 | R | R, S, B | R, S, B | R, B | R | ||
| Epinephelus adscensionis | 34 | B | R | ||||||
| Serranus baldwini | X | ||||||||
| Malacanthidae | Malacanthus plumieri | 31 | R | B | |||||
| Carangidae | Caranx bartholomaei | 31 | R, B | B | R | R, B | |||
| Caranx crysos | 35 | R | B | ||||||
| Caranx lugubris | 31 | B | |||||||
| Caranx ruber | R | ||||||||
| Decapterus punctatus | R | R | |||||||
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus alexandrei | R | R | R | |||||
| Lutjanus cyanopterus | R | ||||||||
| Lutjanus jocu | R | ||||||||
| Ocyurus chrysurus | 31 | R, B | R, B | R, B | R, B | ||||
| Haemulidae | Anisotremus virginicus | 34 | R | R, B | |||||
| Anisotremus surinamensis | R | R | |||||||
| Haemulon aurolineatum | R | R | |||||||
| Haemulon parra | 31 | R | R, B | ||||||
| Haemulon plumierii | 31 | R | R, B | ||||||
| Haemulon squamipinna | 35 | R, B | R, B | ||||||
| Sciaenidae | Equetus lanceolatus | R | |||||||
| Sparidae | Calamus penna | 31 | B | B | B | B | |||
| Calamus pennatula | 31 | R, B | R | R, B | R | ||||
| Mullidae | Mulloidichthys martinicus | R | R | ||||||
| Pseudupeneus maculatus | 31 | R | R, B | R | R | ||||
| Chaetodontidae | Chaetodon ocellatus | X | |||||||
| Chaetodon striatus | 32 | S | R, S, B | R, B | |||||
| Pomacanthidae | Holacanthus ciliaris | R | |||||||
| Holacanthus tricolor | 31 | R | S | R, S | R | R | |||
| Pomacanthus paru | R | ||||||||
| Kyphosidae | Kyphosus sectatrix | X | |||||||
| Pomacentridae | Abudefduf saxatilis | R | R | ||||||
| Azurina multilineata | X | ||||||||
| Chromis multilineata | R | ||||||||
| Stegastes fuscus | 36,5 | S | |||||||
| Stegastes pictus | R | ||||||||
| Stegastes variabilis | 36,5 | S | |||||||
| Labridae | Bodianus rufus | 31 | R | S | R, S | R | R | ||
| Clepticus brasiliensis | R | R | |||||||
| Halichoeres brasiliensis | X | ||||||||
| Halichoeres dimidiatus | 31 | R | R, S | R, S | R | ||||
| Halichoeres poeyi | 31 | B | R, S, B | R, S, B | R, B | ||||
| Labridae-Scarinae | Cryptotomus roseus | R | |||||||
| Scarus zelindae | 31 | S | |||||||
| Sparisoma amplum | 34 | B | |||||||
| Sparisoma axillare | 36,5 | S | R | R | |||||
| Sparisoma frondosum | 34 | B | R | ||||||
| Sparisoma radians | 34 | S, B | |||||||
| Gobiidae | Elacatinus figaro | 31 | R | R, S | R, S | B | |||
| Ptereleotris randalli | 36,5 | S | |||||||
| Acanthuridae | Acanthurus bahianus | 35 | R | B, R | R | B, R | |||
| Acanthurus chirurgus | 31 | R | S | S | R | ||||
| Acanthurus coeruleus | 31 | R | R, S | R | |||||
| Scombridae | Scomberomorus brasiliensis | 35 | B | ||||||
| Scomberomorus regalis | R | ||||||||
| Balistidae | Balistes vetula | 31 | R, B | R, S, B | R, B | R, B | |||
| Monacanthidae | Cantherhines pullus | R | R | ||||||
| Stephanolepis hispidus | 34 | B | |||||||
| Ostraciidae | Acanthostracion polygonius | 34 | B | B | |||||
| Acanthostracion quadricornis | R |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, P.H.C.; Lima, G.V.; Araujo, J.C.; Gomes, E.; Côrtes, L.G.F.; Pontes, A.V.; Recinos, R.; Cardoso, A.; Seoane, J.C.; Brito, C.C.P. Mesophotic Reefs of the Largest Brazilian Coastal Protected Area: Mapping, Characterization and Biodiversity. Diversity 2022, 14, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090760
Pereira PHC, Lima GV, Araujo JC, Gomes E, Côrtes LGF, Pontes AV, Recinos R, Cardoso A, Seoane JC, Brito CCP. Mesophotic Reefs of the Largest Brazilian Coastal Protected Area: Mapping, Characterization and Biodiversity. Diversity. 2022; 14(9):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090760
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Pedro H. C., Gislaine V. Lima, Julia C. Araujo, Erandy Gomes, Luís G. F. Côrtes, Antonio V. Pontes, Radharanne Recinos, Andrei Cardoso, José C. Seoane, and Camila C. P. Brito. 2022. "Mesophotic Reefs of the Largest Brazilian Coastal Protected Area: Mapping, Characterization and Biodiversity" Diversity 14, no. 9: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090760
APA StylePereira, P. H. C., Lima, G. V., Araujo, J. C., Gomes, E., Côrtes, L. G. F., Pontes, A. V., Recinos, R., Cardoso, A., Seoane, J. C., & Brito, C. C. P. (2022). Mesophotic Reefs of the Largest Brazilian Coastal Protected Area: Mapping, Characterization and Biodiversity. Diversity, 14(9), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090760








