Review of the Cyanobacterial Genus Phormidesmis (Leptolyngbyaceae) with the Description of Apatinema gen. nov.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Isolation of Strains
2.3. Morphological Characterization
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Molecular Analyses
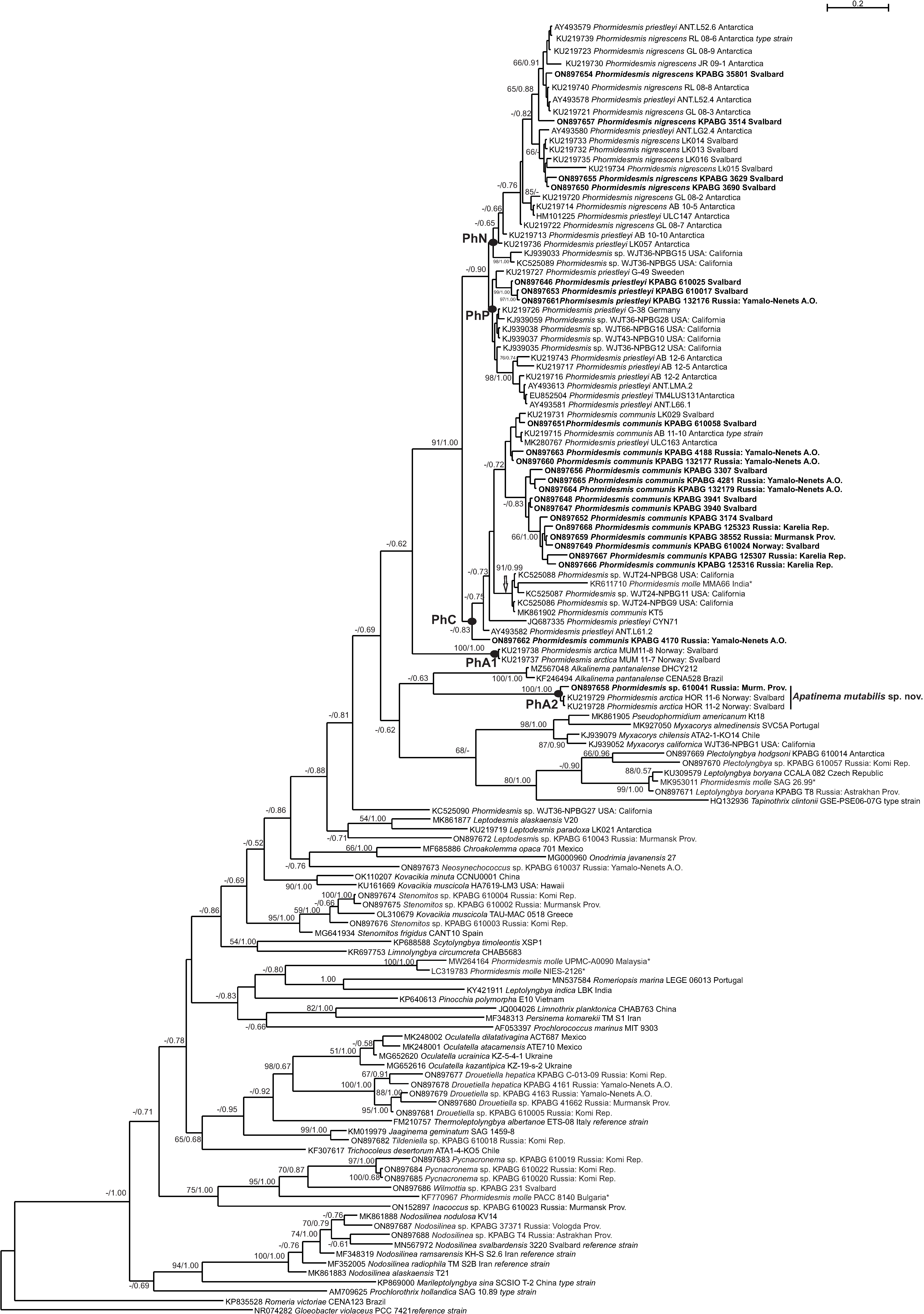
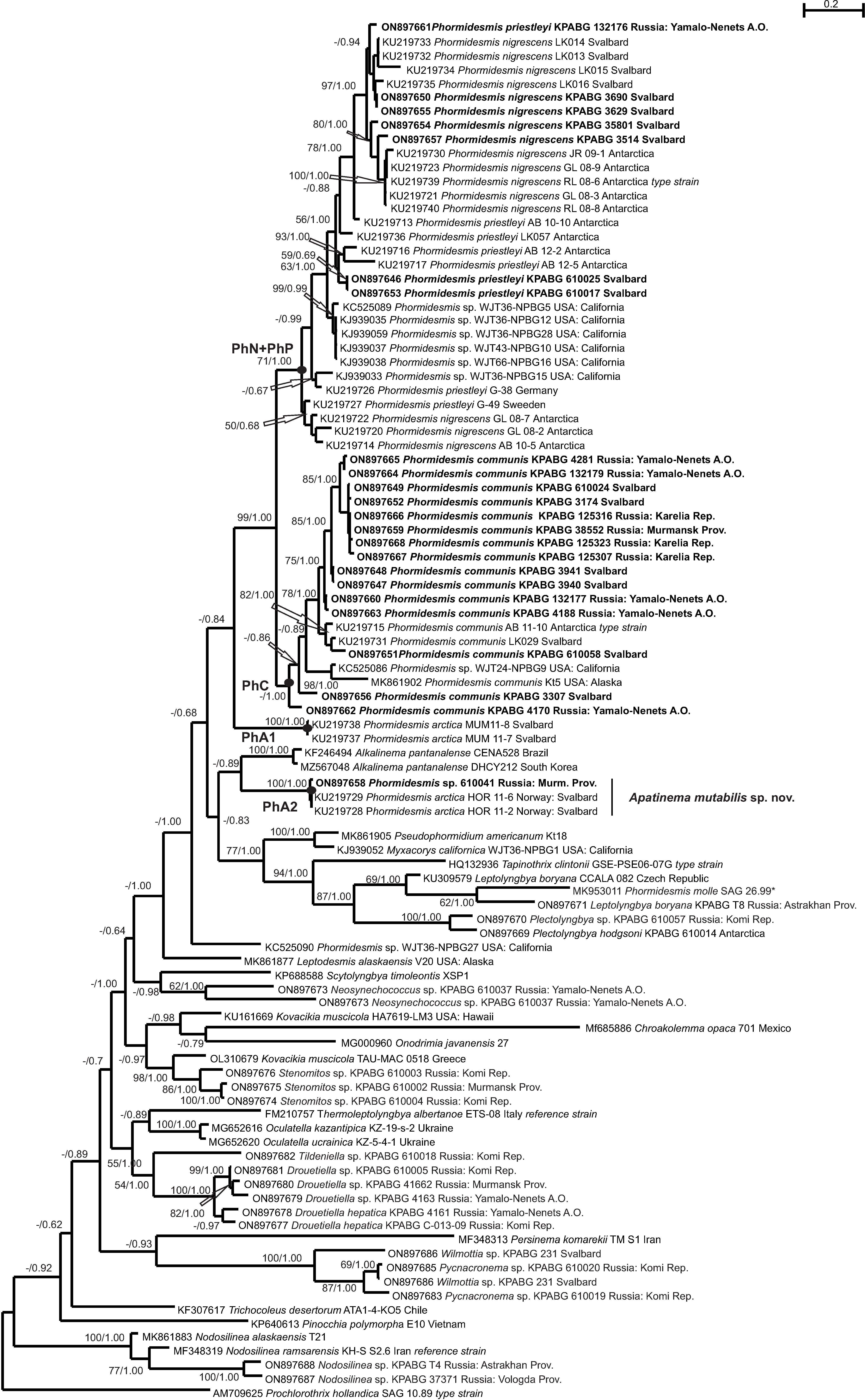
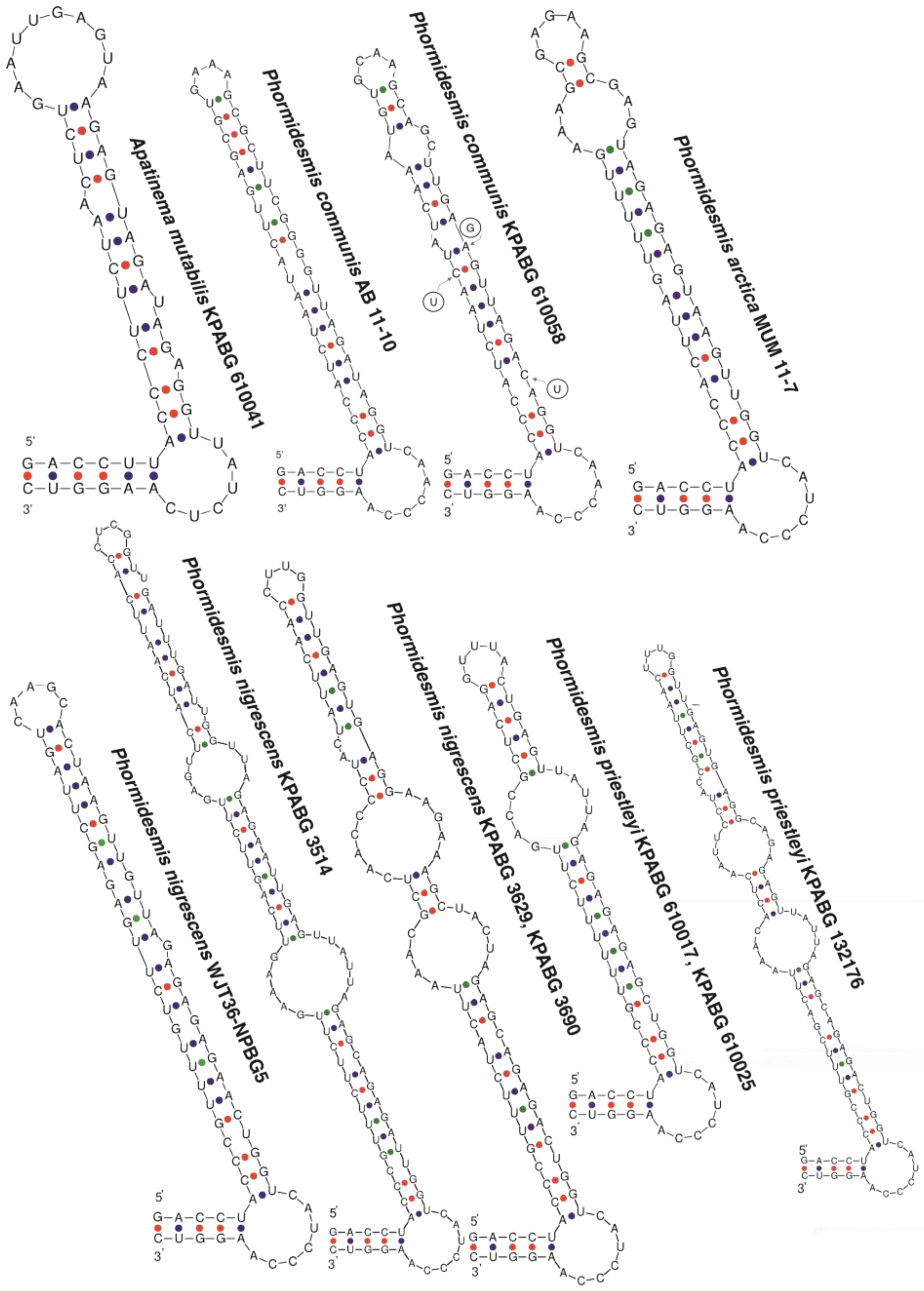
3. Results
Taxonomic Description
- Class Cyanophyceae
- Subclass Synechococcophycidae
- Order Synechococcales
- Family Leptolyngbyaceae
- Apatinema Davydov gen. nov.
4. Discussion
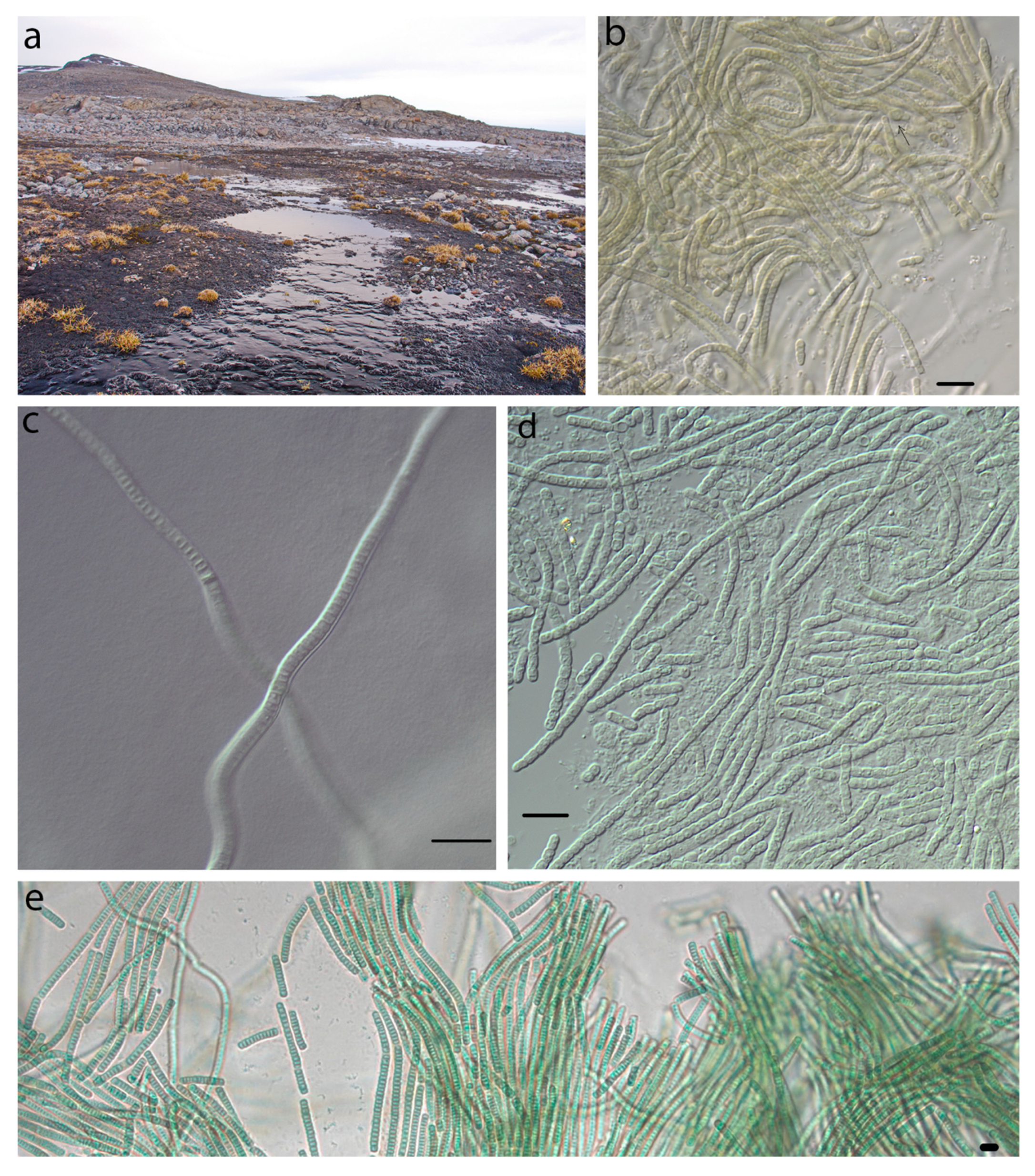
4.1. Phormidesmis molle
4.2. Phormidesmis priestleyi
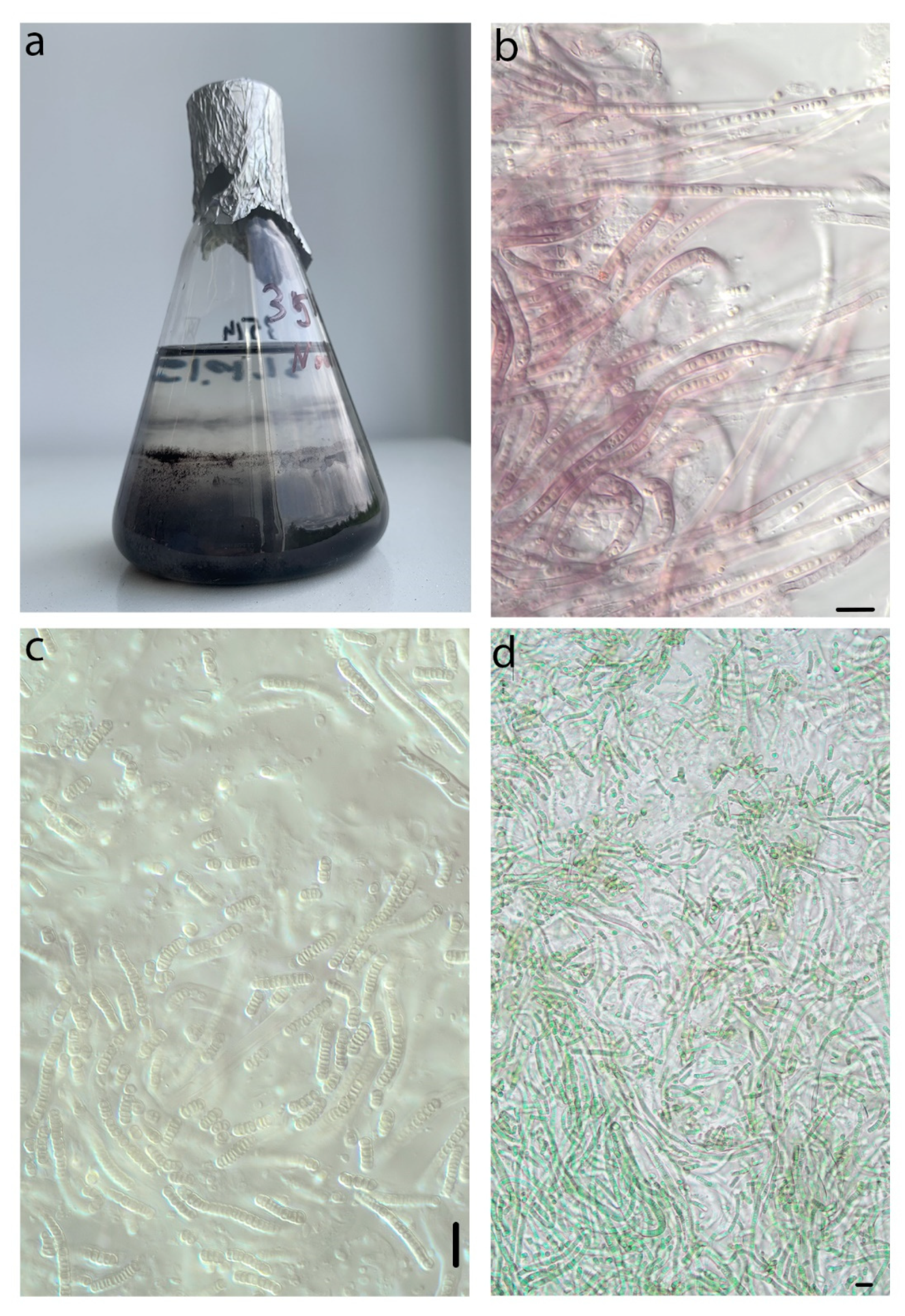
4.3. Phormidesmis nigrescens
4.4. Phormidesmis arctica
4.5. Apatinema mutabilis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Drouetiella hepatica, KPABG 4161 Russia: Yamalo-Nenets A.O., ON897678;
- Drouetiella hepatica, KPABG C-013-09, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897677;
- Drouetiella sp., KPABG 4163, Russia: Yamalo-Nenets A.O., ON897679;
- Drouetiella sp., KPABG 41662, Russia: Murmansk Prov., ON897680;
- Drouetiella sp., KPABG 610005, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897681;
- Leptodesmis sp., KPABG 610043, Russia: Murmansk Prov., ON897672;
- Leptolyngbya boryana, KPABG T8, Russia: Astrakhan Prov., ON897671;
- Neosynechococcus sp., KPABG 610037, Russia: Yamalo-Nenets A.O., ON897673;
- Nodosilinea sp., KPABG 37371, Russia: Vologda Prov., ON897687;
- Nodosilinea sp., KPABG T4, Russia: Astrakhan Prov., ON897688;
- Plectolyngbya hodgsoni, KPABG610014, Antarctica, ON897669;
- Plectolyngbya sp., KPABG 610057, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897670;
- Pycnacronema sp., KPABG 610019, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897683;
- Pycnacronema sp., KPABG 610020, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897685;
- Pycnacronema sp., KPABG 610022, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897684;
- Stenomitos sp., KPABG 610002, Russia: Murmansk Prov., ON897675;
- Stenomitos sp., KPABG 610003, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897676;
- Stenomitos sp., KPABG 610004, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897674;
- Tildeniella sp., KPABG 610018, Russia: Komi Rep., ON897682;
- Wilmottia sp., KPABG 231, Norway: Svalbard, ON897686.
References
- Davydov, D.; Patova, E. The diversity of Cyanoprokaryota from freshwater and terrestrial habitats in the Eurasian Arctic and Hypoarctic. Hydrobiologia 2018, 811, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtman, M.; Wagner, M. Microbial diversity and the genetic nature of microbial species. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, M.G.M.V.; Genuáro, D.B.; Andreote, A.P.D.; Malone, C.F.S.; Sant’Anna, C.L.; Barbiero, L.; Fiore, M.F. Pantanalinema gen. nov. and Alkalinema gen. nov.: Novel pseudanabaenacean genera (Cyanobacteria) isolated from saline-alkaline lakes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, T.; Johansen, J.R.; Pietrasiak, N.; Bohunicka, M.; Martin, M.P. Revision of the Synechococcales (Cyanobacteria) through recognition of four families including Oculatellaceae fam. nov. and Trichocoleaceae fam. nov. and six new genera containing 14 species. Phytotaxa 2018, 365, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahodářová, E.; Dvořák, P.; Hašler, P.; Holušová, K.; Poulíčková, A. Elainella gen. nov.: A new tropical cyanobacterium characterized using a complex genomic approach. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadheech, P.W.; Mahmoud, H.; Kotut, K.; Krienitz, L. Haloleptolyngbya alcalis gen. et sp. nov., a new filamentous cyanobacterium from the soda lake Nakuru, Kenya. Hydrobiologia 2012, 637, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miscoe, L.H.; Johansen, J.R.; Kociolek, J.P.; Lowe, R.L.; Vaccarino, M.A.; Pietrasiak, N.; Sherwood, A.R. Novel cyanobacteria from caves on Kauai, Hawaii. Bibl. Phycol. 2016, 120, 75–152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, R. Limnolyngbya circumcreta gen & comb. nov. (Synechococcales, Cyanobacteria) with three geographical (provincial) genoptypes in China. Phycologia 2016, 55, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrasiak, N.; Osorio-Santos, K.; Shalygin, S.; Martin, M.P.; Johansen, J.R. When Is A Lineage A Species? A Case Study in Myxacorys Gen. Nov. (Synechococcales: Cyanobacteria) with the Description of Two New Species from The Americas. J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 976–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkerson, R.B., III; Johansen, J.R.; Kovácik, L.; Brand, J.; Kastovsky, J.; Casamatta, D.A. A unique pseudanabaenalean (cyanobacteria) genus Nodosilinea gen. nov. based on morphological and molecular data. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D.; Shalygin, S.; Vilnet, A. New cyanobacterium Nodosilinea svalbardensis sp. nov. (Prochlorotrichaceae, Synechococcales) isolated from alluvium in Mimer river valley of the Svalbard archipelago. Phytotaxa 2020, 442, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, G.; Billi, D.; Albertano, P. The subaerophytic cyanobacterium Oculatella subterranea (Oscillatoriales, Cyanophyceae) gen. et sp. nov.: A cytomorphological and molecular description. Eur. J. Phycol. 2012, 47, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Santos, K.; Pietrasiak, N.; Bohunicka, M.; Laura, H.; Kovačik, L.; Martin, M.P. Seven new species of Oculatella (Pseudanabaenales, Cyanobacteria): Taxonomically recognizing cryptic diversification. Eur. J. Phycol. 2014, 49, 450–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahodářová, E.; Dvořák, P.; Hašler, P.; Poulíčková, A. Revealing hidden diversity among tropical cyanobacteria: The new genus Onodrimia (Synechococcales, Cyanobacteria) described using the polyphasic approach. Phytotaxa 2017, 329, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turicchia, S.; Ventura, S.; Komárková, J.; Komárek, J. Taxonomic evaluation of cyanobacterial microflora from alkaline marshes of northern Belize. 2. Diversity of oscillatorialean genera. Nova Hedwig. 2009, 89, 165–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabová, L.; Kovacik, L.; Elster, J.; Strunecký, O. Review of the genus Phormidesmis (Cyanobacteria) based on environmental, morphological, and molecular data with description of a new genus Leptodesmis. Phytotaxa 2019, 395, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, P.; Jahodářová, E.; Hašler, P.; Gusev, E.; Pouličková, A. A new tropical cyanobacterium Pinocchia polymorpha gen. et sp. nov. derived from the genus Pseudanabaena. Fottea 2015, 15, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taton, A.; Wilmotte, A.; Smarda, J.; Elster, J.; Komárek, J. Plectolyngbya hodgsonii: A novel filamentous cyanobacterium from Antarctic lakes. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R. Scytolyngbya timoleontis gen et sp. nov. (Leptolyngbyaceae, Cyanobacteria): A novel false branching Cyanobacteria from China. Phytotaxa 2015, 224, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalygin, S.; Shalygina, R.R.; Redkina, V.V.; Gargas, C.B.; Johansen, J.R. Description of Stenomitos kolaenensis and S. hiloensis sp. nov. (Leptolyngbyaceae, Cyanobacteria) with an emendation of the genus. Phytotaxa 2020, 440, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuto, K.; Moro, I. Detection of the new cosmopolitan genus Thermoleptolyngbya (Cyanobacteria, Leptolyngbyaceae) using the 16S rRNA gene and 16S-23S ITS region. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 105, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciuto, K.; Moschin, E.; Moro, I. Cryptic cyanobacterial diversity in the Giant Cave (Trieste, Italy): The new genus Timaviella (Leptolyngbyaceae). Cryptogam. Algol. 2017, 38, 285–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turland, N.J.; Wiersema, J.H.; Barrie, F.R.; Greuter, W.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Herendeen, P.S.; Knapp, S.; Kusber, W.-H.; Li, D.-Z.; Marhold, K.; et al. (Eds.) International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Shenzhen Code) Adopted by the Nineteenth International Botanical Congress Shenzhen, China, July 2017; Koeltz Botanical Books: Glashütten, Germany, 2018; 254p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Herdman, M.; Rippka, R. The Cyanobacterial Phylogeny and Taxonomy Reference Website, Release 13.1. Available online: http://cyanophylogeny.scienceontheweb.net/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Davydov, D. Diversity of the Cyanoprokaryota in polar deserts of Rijpfjorden east coast, North-East Land (Nordaustlandet) Island, Spitsbergen. Algol. Stud. 2013, 142, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D. Diversity of the Cyanoprokaryota in polar deserts of Innvika cove North-East Land (Nordaustlandet) Island, Spitsbergen. Czech Polar Rep. 2016, 6, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D. Diversity of the Cyanoprokaryota of the area of settlement Pyramiden, West Spitsbergen Island, Spitsbergen archipelago. Folia Cryptogam. Est. 2014, 51, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D. Cyanoprokaryotes of the west part of Oscar II Land, West Spitsbergen Island, Spitsbergen archipelago. Czech Polar Rep. 2017, 7, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D. Cyanobacterial Diversity of the Northern Polar Ural Mountains. Diversity 2021, 13, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotai, J. Instructions for preparation of modified nutrient solution Z8 for algae. In Norwegian Institute for Water Research; 11/69; Blindern: Oslo, Norway, 1972; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Waterbury, J.B. The Cyanobacteria—Isolation, purification and identification of major groups of Cyanobacteria. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melekhin, A.V.; Davydov, D.A.; Borovichev, E.A.; Shalygin, S.S.; Konstantinova, N.A. CRIS—Service for input, storage and analysis of the biodiversity data of the cryptogams. Folia Cryptogam. Est. 2019, 56, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmotte, A.; Van Der Auwera, C.; De Wachter, R. Structure of the 16S ribosomal RNA of the thermophilic cyanobacteria Chlorogloeopsis HTF (‘Mastigocladus laminosus HTF’) strain PCC7518 and phylogenetic analysis. FEBS Lett. 1993, 317, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neilan, B.A.; Jacobs, D.; Therese, D.D.; Blackall, L.L.; Hawkins, P.R.; Cox, P.T.; Goodman, A.E. rRNA Sequences and Evolutionary Relationships among Toxic and Nontoxic Cyanobacteria of the Genus Microcystis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nübel, U.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Muyzer, G. PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A fast, scalable, and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, btz305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Mark, P.; van der Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Hülsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, T.M.; Creevey, C.J.; Pentony, M.M.; Naughton, T.J.; Mclnerney, J.O. Assessment of methods for amino acid matrix selection and their use on empirical data shows that ad hoc assumptions for choice of matrix are not justified. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v1.4. 2007. Available online: http://beast.community/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Rambaut, A. FigTree Version 1.4.4. 2020. (Default Version). Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, L.W.; Schleifer, K.H.; Witman, W.B.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taton, A.; Grubisic, S.; Ertz, D.; Hodgson, D.A.; Piccardi, R.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R.; Mainini, M.; Losi, D.; Marinelli, F.; et al. Polyphasic study of Antarctic cyanobacterial strains. J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, S.L.; Flechtner, V.R.; Johansen, J.R. Is the 16S-23S rRNA Internal Transcribed Spacer Region a Good Tool for Use in Molecular Systematics and Population Genetics? A Case Study in Cyanobacteria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansen, J.R.; Kováčik, L.; Casamatta, D.A.; Fucikova, K.; Kaštovský, J. Utility of 16S-23S ITS sequence and secondary structure for recognition of intrageneric and intergeneric limits within cyanobacterial taxa: Leptolyngbya corticola sp. nov. (Pseudanabaenaceae, Cyanobacteria). Nova Hedwig. 2011, 92, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
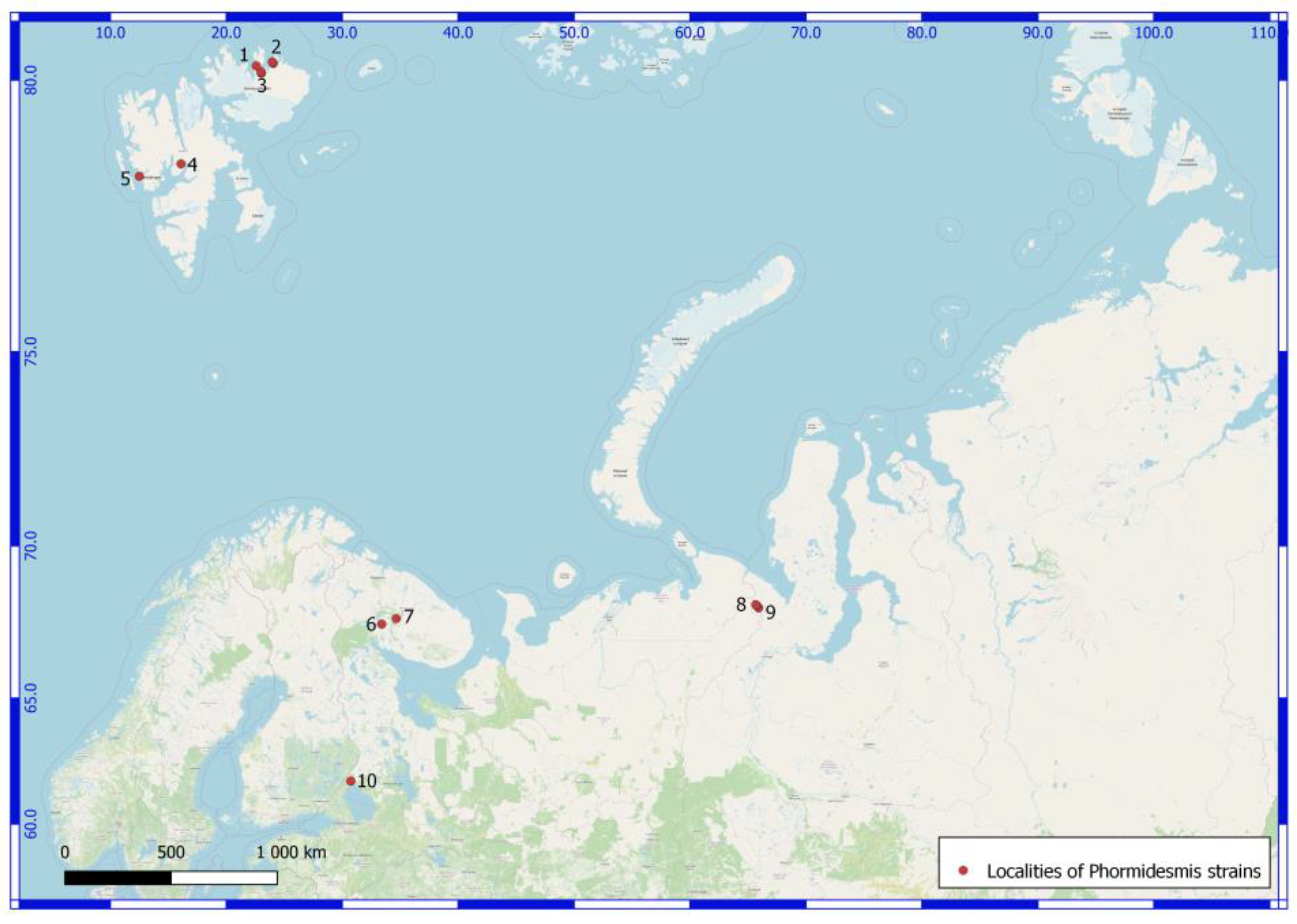
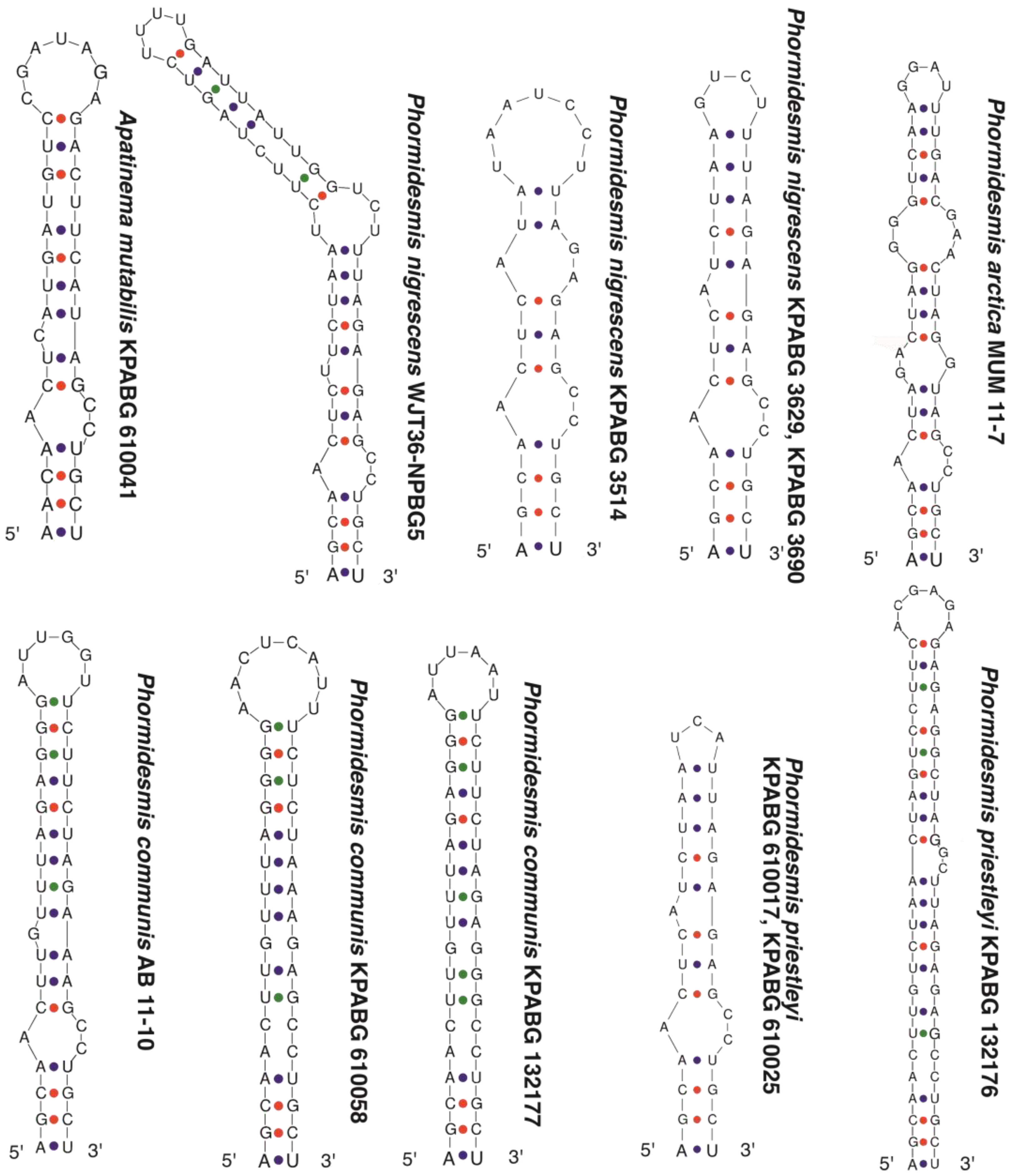
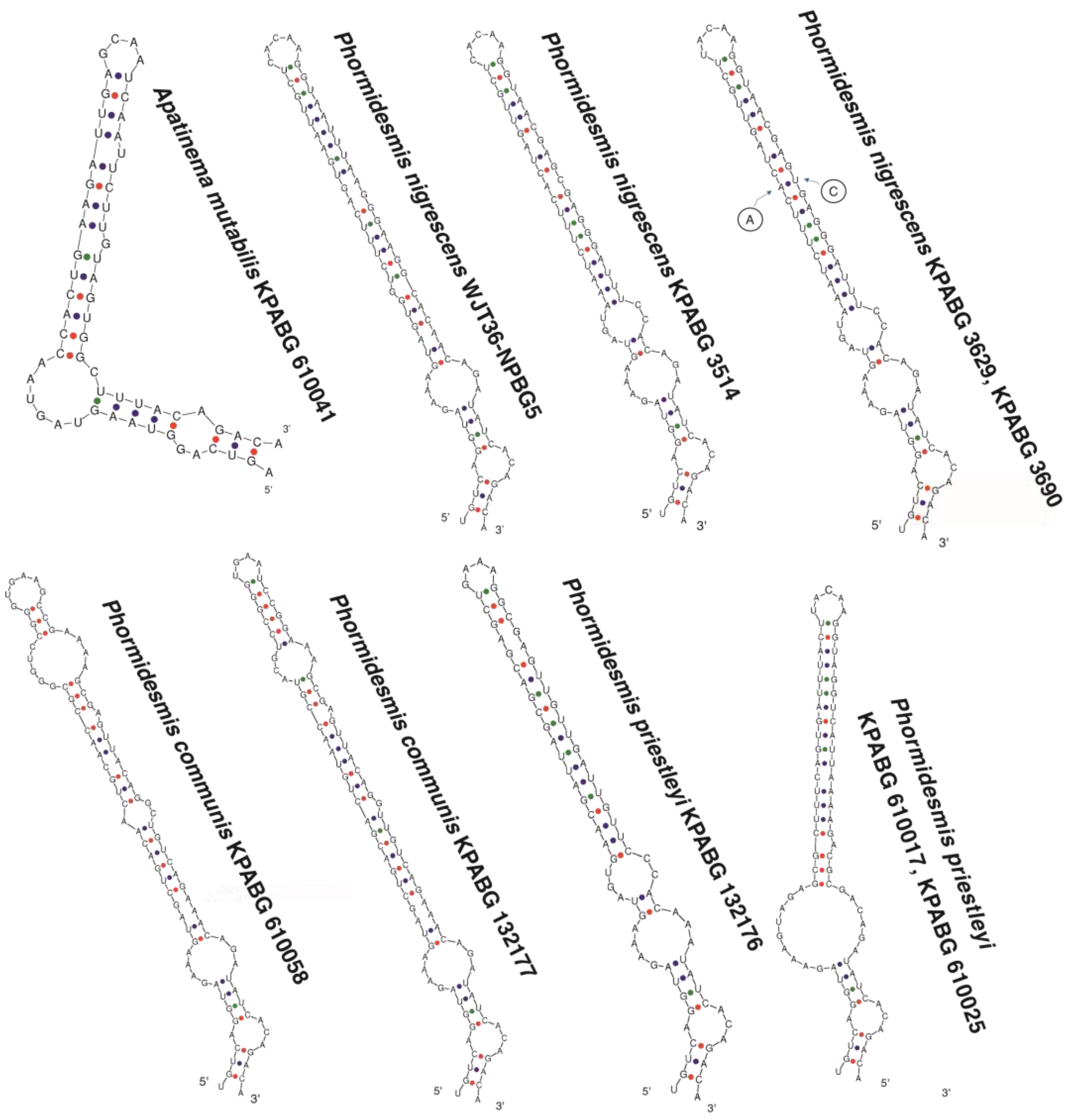
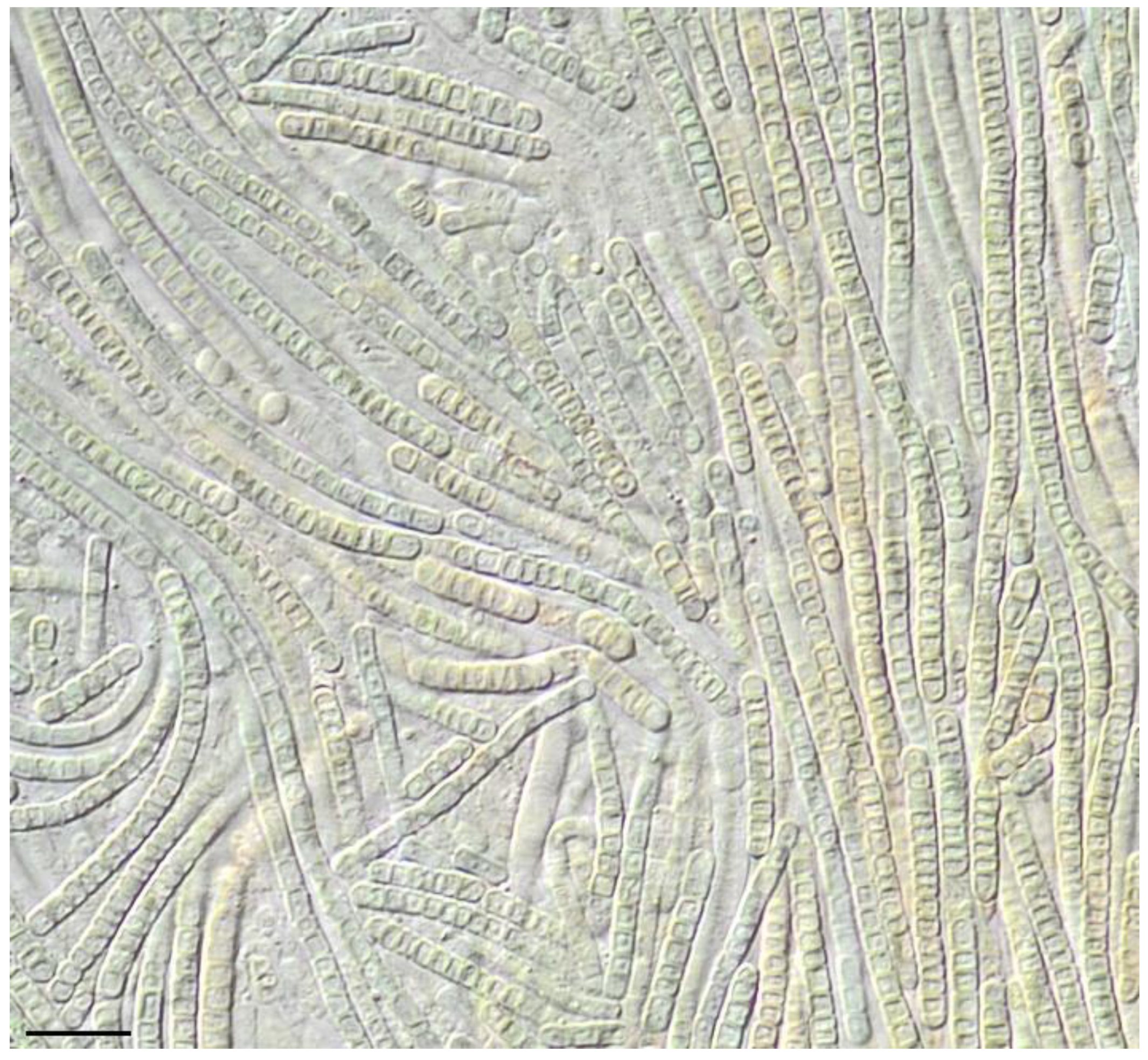
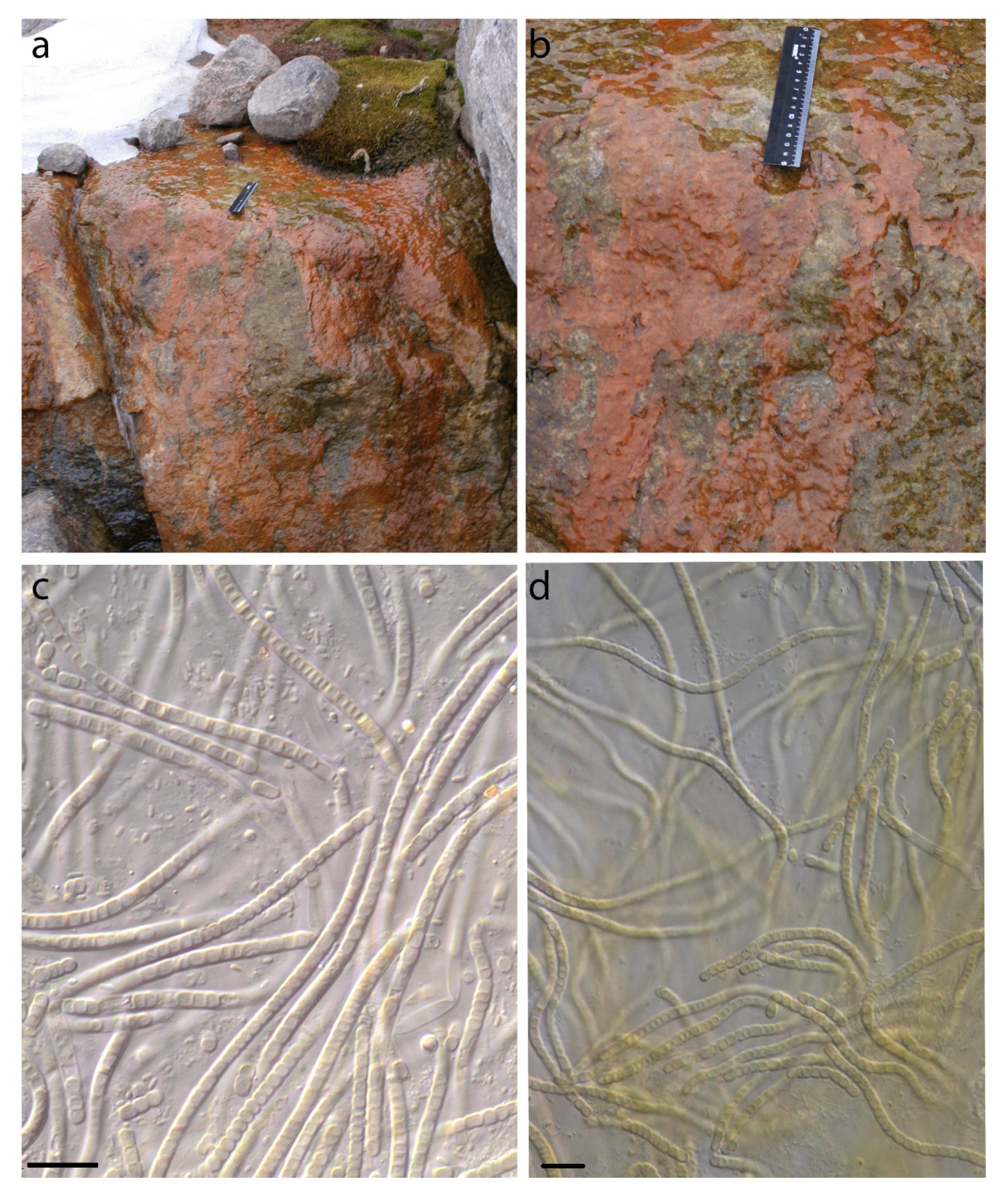
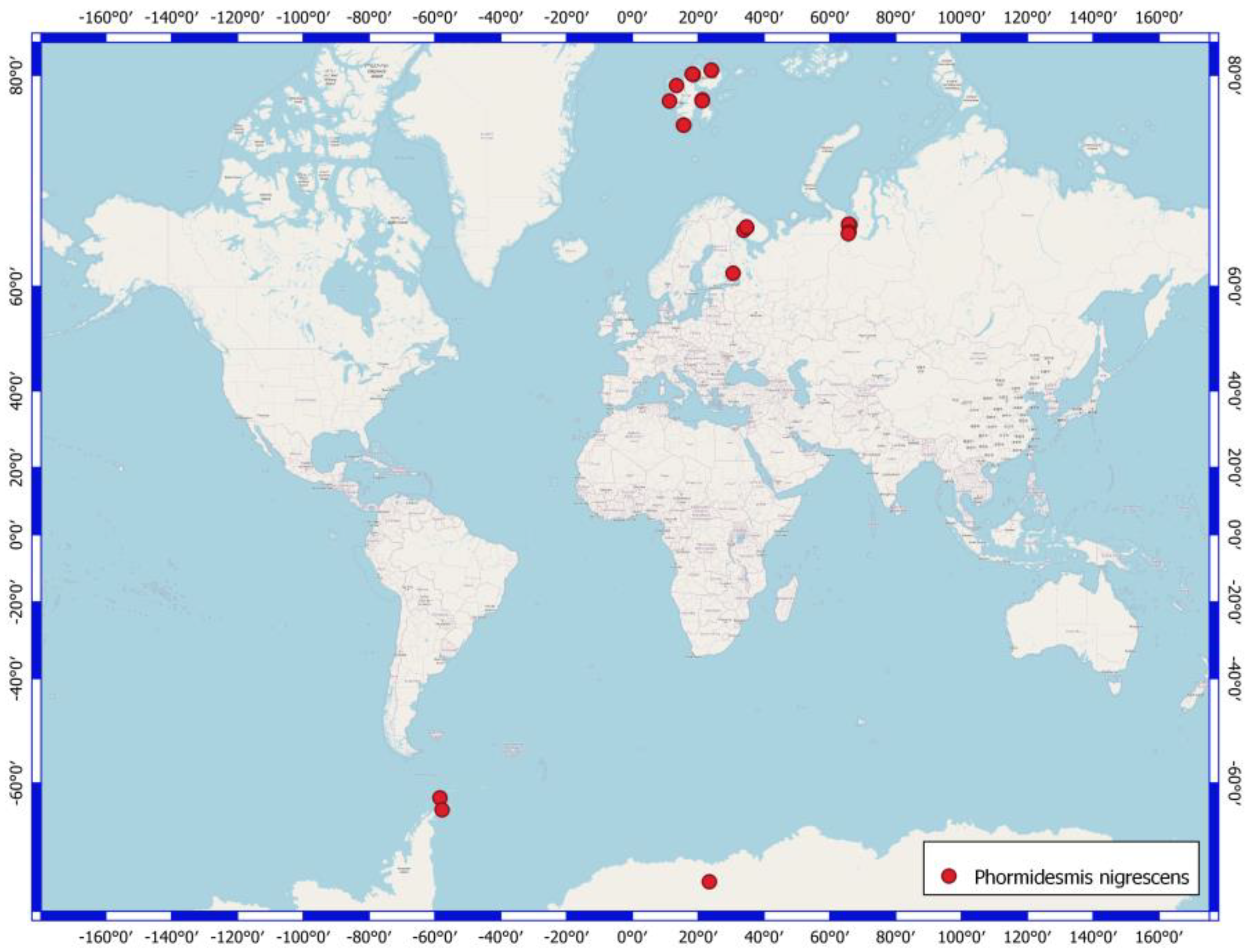
| Number of Location | Number of a Strain in Collection (GB Accession Number) | Locality | Habitats | Latitude N | Longitude E | Elev. (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Svalbard Archipelago. North East Land Island. | ||||||
| 1 | 610025 (ON897646) Phormidesmis priestleyi | Prins Oscars Land. East coast of Rijpfjorden bay. | Stony desert with spots of lichens and mosses. On the upper side of a boulder. | 80.211484 | 22.584801 | 100 |
| 2 | 3940 (ON897647) Phormidesmis communis | Orvin Land. Duvefjorden bay. Sætherbukta cove. Damflya plain. | On the shore of lake. | 80.26839 | 23.96481 | 3 |
| 2 | 3941 (ON897648) Phormidesmis communis | -//- | -//- | 80.26839 | 23.96481 | 3 |
| 2 | 610024 (ON897649) Phormidesmis communis | -//- | On pebbles in a slow stream. | 80.24648 | 24.05033 | 100 |
| 2 | 3690 (ON897650) Phormidesmis nigrescens | -//- | Seashore at 3 m from the water line. In the sand. | 80.2637 | 23.9864 | 1 |
| 3 | 610058 (ON897651) Phormidesmis communis | Prins Oscars Land. Duvefjorden bay. Innvika cove. The eastern shore Ringgåsvatnet lake. Slope of w. exposure Innvikhøgda mount. | On the horizontal surface of a rock. | 80.10297 | 23.02117 | 70 |
| 3 | 3174 (ON897652) Phormidesmis communis | Prins Oscars Land. Duvefjorden day. Innvika cove. | Seepage, mats on the bottom of local deepening. | 80.1097 | 23.02969 | 20 |
| 3 | 610017 (ON897653) Phormidesmis priestleyi | Prins Oscars Land. Duvefjorden bay. Innvika cove. The east shore of the Ringgåsvatnet lake. Vikvaktaren mountain western exposure slope. | Boulder on which the water flows melting snow. Red-brown mats. | 80.1042 | 23.024 | 34 |
| 3 | 35801 (ON897654) Phormidesmis nigrescens | Prins Oscars Land. Duvefjorden bay. Innvika cove. The north shore of Ringgåsvatnet lake, littoral. | At the bottom of the lake. | 80.1094 | 23.0199 | 22 |
| 3 | 3629 (ON897655) Phormidesmis nigrescens | Orvin Land. Duvefjorden bay. Innvika cove. Slope of a hill northern exposure. | Under the overhanging rock. | 80.12598 | 22.98589 | 71 |
| Norway. Spitsbergen Archipelago. West Spitsbergen Island. | ||||||
| 4 | 3307 (ON897656) Phormidesmis communis | Billefjorden bay. The neighborhood of settlement Pyramiden. Planteryggen Mountain of S exposition. | Cyanobacterial mats on a seepage. | 78.665 | 16.08917 | 369 |
| 5 | 3514 (ON897657) Phormidesmis nigrescens | Oscar II Land. Slope W exposure of the Svartfjella mountain. | Overhanging boulder. Wet rock outcrops. | 78.45282 | 12.50317 | 250 |
| Russia. Murmansk Region. | ||||||
| 6 | 610041 (ON897658) Apatinema mutabilis | Apatity town. Bredova st., between 17 and 19 buildings. | In the upper layer of podzol soil (AY, 5 cm) under a footpath | 67.561394 | 33.410578 | 197 |
| 7 | 38552 (ON897659) Phormidesmis communis | Lovozerskie Mountains. Valley of the river Kitkuay. | A cliff in tundra. On the wet rock. | 67.74522 | 34.65973 | 663 |
| Russia. Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The Polar Urals Mountains. | ||||||
| 8 | 132177 (ON897660) Phormidesmis communis | The left shore of the Ochetyvis river. | A stagnant pool. | 68.16459 | 65.75465 | 224 |
| 8 | 132176 (ON897661) Phormidesmis priestleyi | -//- | On a wet wall of rock, near a water line. | 68.16459 | 65.67815 | 154 |
| 8 | 4170 (ON897662) Phormidesmis communis | -//- | On boulders underwater. | 68.18995 | 65.67754 | 167 |
| 8 | 4188 (ON897663) Phormidesmis communis | -//- | A stagnant pool. | 68.16459 | 65.75466 | 225 |
| 9 | 132179 (ON897664) Phormidesmis communis | Unnamed mountain, 832.5 m alt. North exposure slope. | A slow stream on a wet rock | 68.09187 | 65.91724 | 669 |
| 9 | 4281 (ON897665) Phormidesmis communis | -//- | A slow stream on a wet rock. | -//- | -//- | -//- |
| Russia. The Karelia Republic. | ||||||
| 10 | 125316 (ON897666) Phormidesmis communis | Ristijärvi park. | On the wet granitic rock. | 61.7983143 | 30.741688 | 30 |
| 10 | 125307 (ON897667) Phormidesmis communis | -//- | -//- | -//- | -//- | -//- |
| 10 | 125323 (ON897668) Phormidesmis communis | Filina Mts museum. | On the wet granitic rock. | 61.5483418 | 30.1989323 | 30 |
| Taxon | Infraspecific Variation, 16S/ITS, % | Infrageneric Variation, 16S/ITS, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 1. P. nigrescens | 99.16/92.95 99.61/95.3 * | ||||||
| 2. P. priestley | 99.18/92.71 99.06/92.38 * | 98.58/91.54 98.50/91.01 * | |||||
| 3. P. communis | 98.88/93.32 | 97.84/87.93 97.94/87.22 * | 97.59/88.02 97.59/88.57 * | ||||
| 4. P. arctica 1 | 100/100 | 94.31/86.43 94.25/86.11 * | 94.45/87.27 94.45/87.23 * | 94.34/85.88 | |||
| 5. Apatinema mutabilis (P. arctica 2) | 99.82/100 | 92.46/84.34 92.45/84.26 * | 92.44/84.52 92.45/84.52 * | 92.45/83.25 | 94.49/83.43 | ||
| 6. Alkalinema pantanalense | 99.73/97.96 | 93.33/82.87 93.19/82.53 * | 93.55/84.01 93.60/83.88 * | 93.27/83.44 | 93.18/83.82 | 93.11/84.55 | |
| 7. Myxacorys californica | n/c/n/c | 92.12/79.70 92.04/79.24 * | 92.57/78.91 92.50/79.57 * | 93.17/80.21 | 91.73/79.06 | 90.39/78.75 | 92.5/82.6 |
| Strain Number | Cell Width, μm | Cell Length, μm | Necri-Dia | Sheaths | Granu-Les | Cells Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phormidesmis priestleyi | ||||||
| 610017 | 2.0–2.7 | 1.3–2.7 | + | colorless | + | olive-green |
| 610025 | 2.7–3.3 | 2.4–3.5 | + | colorless | + | olive-green |
| 132176 | 1.8–2.9 | 1.7–3.2(4) | + | colorless | blue-green | |
| Phormidesmis nigrescens | ||||||
| 3514 | 2.0–2.5 | 1.2–2.1 | ? | blackish, layered | pale blue-green | |
| 35801 | 1.7–2.2 | 1.5–2.5 | + | colorless | brownish | |
| 3629 | 1.8–3.1 | 1–2.1 | + | colorless/blackish | + | pale blue-green |
| 3690 | 1.6–2.3 | 1.3–2.3 | ? | colorless | blue-green | |
| Phormidesmis communis | ||||||
| 3174 | 1.6–2.2 | 1.6–2.6 | + | colorless | pale blue-green | |
| 3307 | 2.0–3.6 | 2.6–4 | + | colorless | olive-green | |
| 38552 | 1.8–2.3 | 1.3–2 | + | colorless | olive-green | |
| 3940 | (1.9)2.2–3.2 | 1.3–2.3(3) | + | colorless | pale blue-green | |
| 3941 | 2.1–3.2 | 1.4–2.3 | + | colorless | olive-green | |
| 4170 | 1.7–2.5 | 1.1–2.7 | + | colorless | ||
| 4188 | 2.5–3.4 | 1.1–2.3 | + | colorless | brownish | |
| 4281 | 1.7–2.7 | 1.5–4.3 | + | colorless | brownish | |
| 610024 | 1.9–2.9 | 1.9–2.4 | + | colorless | + | olive-green/brownish |
| 610058 | 1.5–1.7 | 1.3–1.8 | + | colorless | olive-green | |
| 125307 | 2.0–2.9 | 1.0–2.0 | + | colorless | + | olive-green |
| 125316 | 2.1–3.2 | 1.2–1.9 | + | colorless | + | blue-green |
| 125323 | 1.7–2.5 | 1.1–1.7 | + | colorless | + | olive-green |
| 132177 | 2.5–3.4 | 1.1–2.3 | + | colorless | + | blue-green |
| 132179 | 2.5–3.3 | 1.0–2.3 | + | colorless | + | brownish |
| Apatinema mutabilis | ||||||
| 610041 | 1.7–3.5(4) | 1.7–2.5(4.7) | rare | rare | + | blue-green/olive green |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davydov, D.; Vilnet, A. Review of the Cyanobacterial Genus Phormidesmis (Leptolyngbyaceae) with the Description of Apatinema gen. nov.. Diversity 2022, 14, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090731
Davydov D, Vilnet A. Review of the Cyanobacterial Genus Phormidesmis (Leptolyngbyaceae) with the Description of Apatinema gen. nov.. Diversity. 2022; 14(9):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090731
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavydov, Denis, and Anna Vilnet. 2022. "Review of the Cyanobacterial Genus Phormidesmis (Leptolyngbyaceae) with the Description of Apatinema gen. nov." Diversity 14, no. 9: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090731
APA StyleDavydov, D., & Vilnet, A. (2022). Review of the Cyanobacterial Genus Phormidesmis (Leptolyngbyaceae) with the Description of Apatinema gen. nov.. Diversity, 14(9), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14090731







