Abstract
The Snezhnaya (=Snow) Cave System (depth −1760 m; total length 40.8 km), located in the West Caucasus, is inhabited by distinctly troglomorphic collembolan species from several families. Two new species of the family Arrhopalitidae occur in the deep parts of the system. Both are highly morphologically specialized; however, they evolved into different troglobiont life forms. Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. with extremely long claws, lamellate mucro, and an enlarged sensory organ of third antennal segment lives exclusively in hygropetric and epineustonic habitats, whereas Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov., with greatly elongated and multi-subsegmentated antennae and long legs, prefers open terrestrial spaces. The troglomorphy, as well as ecological life forms of the obligate cave-dwelling Arrhopalitidae, in general, are discussed and classified as neustonic-hygropetric, atmobiont, intrasubstrate, and intermediate troglomorphs.
Keywords:
Arrhopalites; Pygmarrhopalites; springtails; taxonomy; biospeleology; deep caves; life form; troglobiont; West Caucasus 1. Introduction
The West Caucasus could be considered an important hotspot of the subterranean biodiversity on the southern border of Europe and Asia, which holds numerous terrestrial and aquatic obligate cave-dwelling invertebrates—troglobionts and stygobionts (e.g., [1,2,3])—but it is still insufficiently investigated.
Our biospeleological samplings in this region show that Collembola, presumably, is the most diverse group among the terrestrial arthropod cave dwellers in the Caucasus, with an average of about ten species per well-sampled cave and reaching up to thirty species per cave at maximum limits (unpublished data). However, this fauna remains poorly known. Especially enigmatic are the fauna of the two high-mountainous limestone massifs in Abkhazia (Arabika and Bzyb massifs) with classic plateaus karst of Alpine type and hundreds of caves, including nine abysses exceeding 1 km in depth and two of the world’s deepest caves over 2 km in depth. Hitherto, six collembolan species have been known from these massifs. Four species were described from the currently second world deepest Krubera Cave in the Arabika Massif: Anurida stereoodorata (Jordana and Baquero, 2012), Deuteraphorura kruberaensis (Jordana and Baquero, 2012), Schaefferia profundissima (Jordana and Baquero, 2012), and Plutomurus ortobalaganensis (Jordana and Baquero, 2012) [4]. In the outstanding Snezhnaya Cave System (Bzyb Massif), two genuine troglomorphic species have been described: Typhlogastrura morozovi (Babenko, 1987) [5] and the yet monotypic Troglaphorura gladiator (Vargovitsh, 2019) [6]; several other troglobionts, among seventeen sampled in this cave morpho-species (unpublished), are awaiting taxonomic investigation.
Up to date, five obligate cave-dwelling species of the family Arrhopalitidae, belonging to three genera, are known from the Caucasus: Arrhopalites abchasicus (Vargovitsh, 2013), A. macronyx (Vargovitsh, 2012), Pygmarrhopalites dbari (Vargovitsh, 2017), P. kovali (Vargovitsh, 2017), and the monotypic Troglopalites stygios (Vargovitsh, 2012) [7,8,9]. Besides, troglophilous A. caecus (Tullberg, 1871), P. principalis (Stach, 1945), and P. pygmaeus (Wankel, 1860) were listed from Georgian caves [10].
Here, I describe two more highly specialized species of the genera Arrhopalites (Börner, 1906) and Pygmarrhopalites (Vargovitsh, 2009), with both inhabiting the same deep parts of Snezhnaya Cave but representing different life forms correlated with delicate microhabitat preferences.
In the final part of this work, the troglomorphic features of the family Arrhopalitidae are listed and discussed, and ecological life forms of troglobionts are defined and classified.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Locality
Snezhnaya Cave and Souvenir Cave: the Khipsta karst massif on the Bzyb Mountain Range, Gudauta District, Abkhazia (Figure 1A).
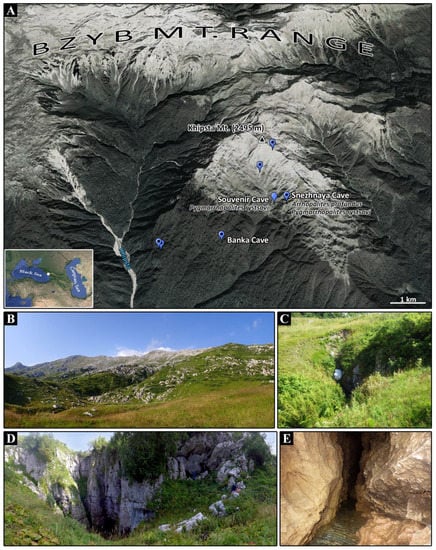
Figure 1.
Type locality of Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. and Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov. (A)—Map with locations of the six entrances of the Snezhnaya Cave System (blue marks with black spot) and Souvenir Cave; (B)—Landscape in the Khipsta Massif of the Bzyb Mt Range; (C)—Entrance to Souvenir Cave; (D)—Entrance to Snezhnaya Cave; (E)—Fragment of Crystal Meander (−1100 m) in Snezhnaya Cave—a type habitat of A. profundus sp. nov. and P. rystsovi sp. nov.
The Bzyb (or Bzybsky) Massif is a fragment of a belt of limestone karst relief, stretching along the edge of the southern macroslope of the West Caucasus, with over 400 caves explored [11]. Late Quaternary glaciation existed here, and together with adjacent Arabika Massif, it can be considered classical mid and high-mountain karst [12]. The Khipsta karst massif (156 km2) (Figure 1A,B) with the three highest mountains, around 2500 m a.s.l., is located on the southern slope of the Bzyb Mountain Range, between the rivers Khipsta and Aapsta. At altitudes of 400–500 m a.s.l. in the south, the massif borders on the Colchis Lowland. Up to an altitude of 1700–1800 m, it comprises a belt of mountain-forest vegetation and a belt of mountain-meadow vegetation at higher altitudes. The Khipsta Massif is composed of Jurassic, Cretaceous, and Paleocene rocks, and it comprises karst of naked, covered, and green (within the forest zone) types [12,13].
The Snezhnaya Cave System is located in the southern slope of the Khipsta Massif and consists of six interconnected caves with entrances exposed at different altitudes in the meadow (2389 m, 2015 m, 1970 m) and forest (1505 m, 1329 m, 1318 m) zones (Figure 1A). It is a branched, tree-like river system fed by numerous sub-vertical channels. A total spatial development of the system is 40,840 m, and a total vertical amplitude is 1760 m [14], which ranges it as the fourth deepest in the world and the longest in the Caucasus. The system is developed in a large anticlinal fold in limestones, dolomitized limestones, and dolomites of Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous carbonate rocks. Its upper parts are sub-vertical, whereas lower parts are mainly sub-horizontal with running waters. It contains an underground river with the average discharge of about 500 L/s, but it drastically increases during seasonal floods. The air and water temperature in the cave system gradually increases, with depth, from 0–2 °C to 6.5 °C, and relative air humidity along the system is close to 100% [15].
Souvenir Cave: With 1464 m length and −408 m depth, it is also located in the Khipsta Massif, with an entrance exposed at 1850 m a.s.l. (Figure 1C), south to the Khipsta Mountain, at a distance 0.4 km west to the huge entrance of Snezhnaya Cave (Figure 1D). Flowing streams and three siphons start from about −300 m, descending to the bottom part. Hydrologically, Souvenir Cave obviously belongs to the Snezhnaya Cave System [13], but terrestrial connection is yet unknown. Air and water temperature along the cave, in August 2018 and 2019, ranged from 2.8 °C to 5.7 °C.
2.2. Sampling
Springtails were sampled in two ways: (a) using the mouth aspirator on the water surface of small pools, usually scattered on the walls along the cave river and on rocks, near water (Figure 1E); (b) using Barber’s traps [16] installed at a distance, from several to tens of meters, from water. Fixation and preservation: in 96% alcohol.
2.3. Microscopic Study
Specimens were mounted on permanent slides using Hoyer’s medium [17] (p. 38), and they were studied under the light microscope Zeiss Axio Imager M1 (Center of collective using of scientific equipment “Animalia” at Schmalhausen Institute of Zoology). Figures were designed and adjusted with the help of Helicon Focus Pro v. 7.6.6 (Kharkiv, Ukraine), CorelDRAW v. 23 (Ottawa, Canada) and Adobe Photoshop v. 21 (San Jose, CA, USA) software.
2.4. Measurements
Mounted body and its parts were measured from microscope (Zeiss Axio Imager M1, Jena, Germany) photographs using AxioVision SE64 Rel. 4.9.1 software. Claws were measured from the most basal proximal point of the outer margin to the tip. Measurements of adult specimens are given in Table 1, and the length ratios between selected structures are in Table 2. Body/claw ratio is considered an index of the claw’s troglomorphy [6].

Table 1.
Lengths (in µm) and angles for body parts of adult types of Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. and Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov.

Table 2.
Proportions (mean in females) for some body parts of adult types of Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. and Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov.
2.5. Chaetotaxy Nomenclature
Chaetotaxy nomenclatures are used following Betsch and Waller [18] for the head, Fjellberg [19] for the mouthparts, Vargovitsh [9,20] for the great abdomen, Bretfeld [21] for the fifth abdominal segment and partly for great abdomen, Betsch [22] for the sixth abdominal segment, and Nayrolles [23,24,25] for appendages.
Based on the Nayrolles [23] system, I use, here, a simple tibiotarsal formula, which looks visually convenient for taxonomical purposes in Arrhopalitidae with number of setae in the whorl I, II, III, IV, V, region F (e.g., 9, 8, 8, 8, 7, 4).
2.6. Abbreviations
Ant—antennal segment, Th—thoracic segment, Abd—abdominal segment, a.s.l.—above sea level. The setae, setal rows and whorls are marked in bold in the text.
3. Results
Taxonomy
Family Arrhopalitidae Stach, 1956.
3.1. Genus Arrhopalites Börner, 1906
Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov.
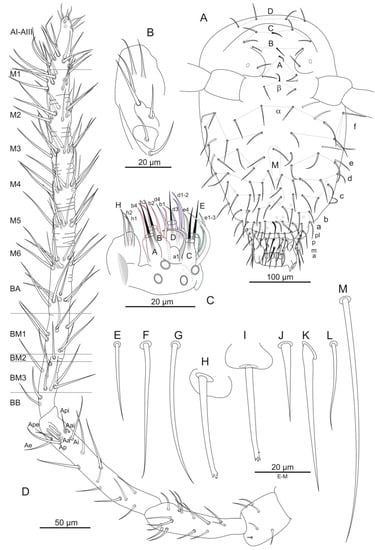
Figure 2.
Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. (A)—Chaetotaxy of head; (B)—Maxillary outer lobe; (C)—Chaetotaxy of labial palp; (D)—Chaetotaxy of antenna; (E)—Seta of head vertex; (F)—seta ms1 of Abd VI; (G)—Seta mps2 of Abd VI; (H,I)—Appendices anales; (J)—Seta Ie of dens; (K)—Seta Ia of dens; (L)—Seta m1 of mesothorax; (M)—Seta dIII-1 of great abdomen. Nomenclatures of setae in (A): after [18], (C): [19], (D): [25], (F,G): [22], (J,K): [24], (L,M): [20].
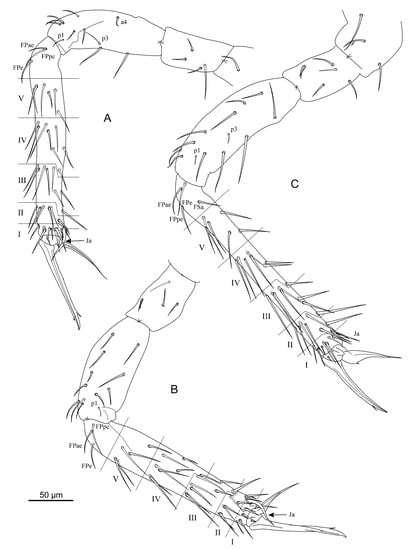
Figure 3.
Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. (A)—Chaetotaxy of foreleg; (B)—Chaetotaxy of midleg; (C)—Chaetotaxy of hindleg. Nomenclature of setae in (A–C): after [23].
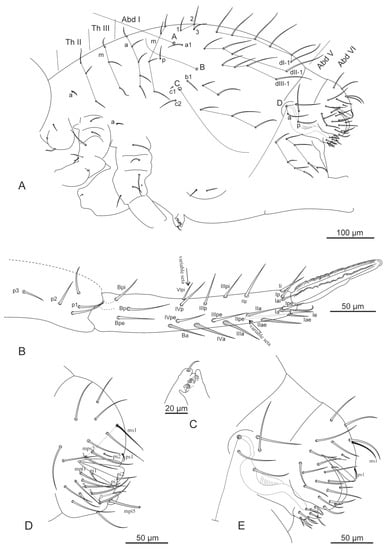
Figure 4.
Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. (A)—Chaetotaxy of great abdomen; (B)—Chaetotaxy of furca; (C)—Tenaculum; (D)—Chaetotaxy of female Abd VI; (E)—Chaetotaxy of male Abd V–VI. Nomenclatures of setae in (A): after [9,20], (B): [24], (D,E): [22].
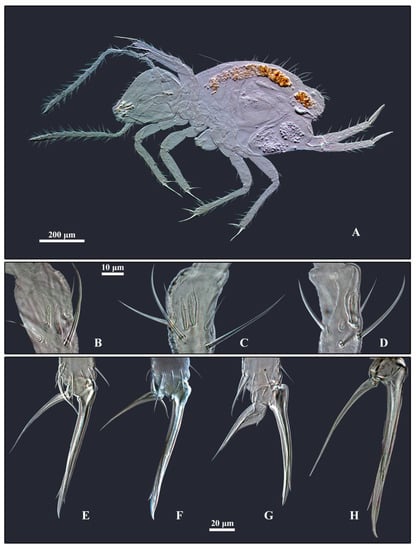
Figure 5.
Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. (A)—Habitus of mounted male; (B–D)—Antennal III organ: (B)—Female; (C)—Male, right antenna; (D)—Male, left antenna; (E–H)—Foot complex: (E)—Foreleg, male; (F)—Midleg, male; (G)—Hindleg, male; (H)—Foreleg, female.
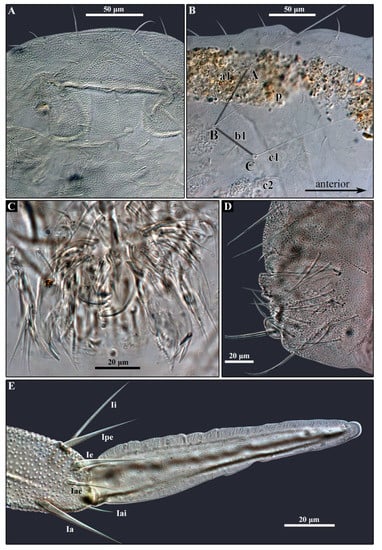
Figure 6.
Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. (A)—Head dorsum; (B)—Chaetotaxy of trichobothrial complex; (C)—Mouthparts; (D)—Female Abd VI, lateral view; (E)—Mucro and distal part of dens. Nomenclatures of setae in (B): after [20], (E): [24].
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:FA9937AE-1E30-4F47-9716-C8A4E2C7111F
Diagnosis
Body unpigmented, about 1 mm long. Eyes 1 + 1. Setae of head dorsum are slender. Antenna 2× of head; Ant III with a large sensory organ about 0.8× of segment width; Ant IV subdivided into seven, more or less distinct, subsegments often separated from each other by several annuli, with 14 whorls of setae. Trochanter I, II, and III with 4, 4, 5 setae. Femur I, II, III with 11, 12, 13 setae. Tibiotarsus I, II, III with 42, 41, 43 setae. Claws are slender and extremely elongated, without tunica, I and II with tiny inner tooth, III without inner tooth. Empodia are short, I and II without and III with a distinct corner tooth. Manubrium with 5 + 5 setae. Dens without spines, posterior side with 14 and anterior side with 3, 2, 1, 1, 1 setae. Mucro with a small spoon-like apex, edges of posterior lamellae without separated teeth. Trichobothria ABC form an angle close to a right. Posterior setae of great abdomen about 3× longer than anterior. Sixth abdominal segment with ordinary smooth unbroadened circumanal setae; dorsal valve with 10 + 2 + 10 setae; appendices anales are rod-like with apical denticulation. Belongs to Arrhopalites caecus group of species s. str. [7].
Type material
Holotype: female, dissected and mounted on two slides (head with antennae and forelegs on one slide, body with midlegs and hindlegs on another slide): W Caucasus, Abkhazia, Bzyb Mountain Range, Khipsta Massif, Snezhnaya Cave, N 43°15′53.3″; E 40°43′05.6″; 1970 m elevation, Crystal Meander, −1100 m, water surface, 27.viii.2018, R.S. Vargovitsh leg.
Paratypes: There is 1 female, 1 specimen of unknown sex (fragment of adult), and 1 juvenile, with the same data as for holotype; 1 male (Figure 5A): 22.viii.2017, same locality and collector.
Holotype (female on slides C-1136-9-1 and C-1136-9-2) and 4 paratypes (male on slide C-1059a-1; damaged fragment of juvenile on slide C-1059a-2; damaged fragment of adult specimen on slide C-1059d-1; female on slide C-1136-8) are kept in the collection of the Schmalhausen Institute of Zoology, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv.
Description
Female. Body length about 1 mm, unpigmented.
Head (Figure 2A). Eyes 1 + 1, 5.5 μm in diameter, unpigmented, sometimes hardly noticeable. Clypeal area includes six rows, a to f, and median region M with three setae. Interantennal area: row α: 2 + 2, row β: 1 + axial + 1. Dorsal area (rows A to D): axial seta present in rows A, B, and C; all setae of head dorsum are slender (Figure 2E and Figure 6A). Chaetotaxy of the head posterior side, as in Figure 2A (dashed circles).
Chaetotaxy of mouth region. Labrum (Figure 2A): labral/prelabral chaetotaxy: 4 5 5/6.
Labium: submentum with 4 setae, mentum with 5 setae; labial palp (Figure 2C and Figure 6C) with 5 proximal setae, 5 papillae (A, B, C, D, E) with deeply inserted setae, with 13 associated guard setae (a1, b1–4, d1–4, e1–4 of which a1 is blunt and strongly curved), and 3 hypostomal setae (H, h1, h2). Maxilla as in Figure 6C. Maxillary outer lobe as in Figure 2B: apical seta of the maxillary outer lobe, with short and thin, hardly noticeable branch at the base, sublobal plate with three sublobal hairs. Oral fold with two setae.
Antenna (Figure 2D) about 2× of head. Length ratio of antennal segments I/II/III/IV = 1/2.1/3.4/8.3. Ant I with 6 setae, p as microseta (6 μm). Ant II with 14 setae, one of which is about 2× longer than others. Ant III without swelling, with the following chaetotaxy: 15 simple setae of which Api and Ape are especially thin, two large sense rods (15 μm) in shallow pits and Aai as small (4 μm) bent and blunt sensillum (Figure 2D and Figure 5B–D). Ant IV subdivided into 7 subsegments or pseudosubsegments (almost indistinct in female and more distinct in male), often separated from each other by 0–4 weakly developed and hardly visible annuli. (Pseudo)subsegmental formula: 1 + 5 + 1. Ant IV bears 14 whorls of setae: 4 on apical subsegment (AI–AIII + M1), 5 on median subsegments (M2–M6), and 5 on basal subsegment (BA + BM1–BM3 + BB).
Legs. Foreleg (Figure 3A): precoxa 1 and 2 and coxa with 1, 0, 1 seta, respectively (Figure 4A). Trochanter with 3 anterior and 1 posterior setae. Femur with 11 setae, a4 turned perpendicularly to the longitudinal axis of the segment. Tibiotarsus with 42 setae, tibiotarsal formula: 9, 8, 8, 8, 6, 3; seta Ja of distal whorl I, curved and distinctly spine-like; whorl V without ai and pi setae; region F with primary setae e, ae, pe. Pretarsus with 1 anterior and 1 posterior setulae. Foot complex (Figure 5E,H). Claw: slender and much elongated (up to 148 μm), without tunica, with tiny inner tooth and a pair of long subapical lateral teeth; about 2× shorter than tibiotarsus. Empodium: thin, without corner tooth; 1.6× shorter than claw; tip of empodial filament not reaching tip of claw.
Midleg (Figure 3B): precoxa 1 and 2 with 1, 1 seta, respectively, precoxal process present, coxa with 3 setae and microsensillum (Figure 4A). Trochanter with 4 setae: anterior trochanteral organ, 2 anterior and 1 posterior simple setae. Femur with 12 setae. Tibiotarsus with 41 setae (9, 8, 8, 8, 5, 3); Ja, curved and distinctly spine-like, whorl V without ai and pi setae; region F with primary setae e, ae, pe. Pretarsus with 1 anterior and 1 posterior setulae. Foot complex (Figure 5F). Claw: slender and much elongated (up to 146 μm), without tunica, with tiny inner tooth (sometimes unnoticed) and a pair of long subapical lateral teeth; about 2× shorter than tibiotarsus. Empodium: thin, without a corner tooth; 1.7× shorter than claw; tip of empodial filament not reaching tip of claw.
Hindleg (Figure 3C): precoxa 1 and 2 with 1, 1 seta, respectively, process on precoxa 1 present, coxa with 3 setae and microsensillum (Figure 4A). Trochanter with 5 setae: anterior trochanteral organ, 3 anterior and 1 posterior simple setae. Femur with 13 setae, 2 posterior ones as microsetae. Tibiotarsus with 43 setae (9, 8, 8, 8, 6, 4); Ja of whorl I as simple seta, whorl V without ai seta, region F with primary setae e, ae, pe and secondary seta FSa. Pretarsus with 1 anterior and 1 posterior setulae. Foot complex (Figure 5G). Claw: slender and elongated (up to 131 μm) but shorter than claw I and II, without tunica, without inner tooth, but with pair of long subapical lateral teeth; about 2.7× shorter than tibiotarsus. Empodium: broad, with a distinct corner tooth; 1.7× shorter than claw; tip of empodial filament not reaching tip of claw.
Lengths ratio of tibiotarsi I/II/III = 1/1/1.2. Tibiotarsus I about 1.3× shorter than head.
Ventral tube with 1 + 1 subapical microsetae.
Tenaculum (Figure 4C): each ramus with three teeth and basal process; anterior lobe with 1 apical seta.
Furca (Figure 4B). Manubrium with 5 + 5 posterior setae. Dens with 22–23 setae (8 anterior and 14–15 posterior). There are 3, 2, 1, 1, 1 setae on the anterior side, Ia–IVa, Ba, and IIae are thick, but Ia is not spine-like (Figure 2K). The posterior side is without spine-like setae; however, Ie, Ipe, and Ii are somewhat thickened (Figure 2J and Figure 6E). Mucro (Figure 6E): posterior lamellae with teeth usually accreted together, so margins look rather wavy; anterior lamella smooth and well-developed; tip rounded or spoon-like but not broadened. Dens about 2× as long as mucro.
Great abdomen (Figure 4A). Segments Th II and III bearing single short (13–15 μm) and bent sensillum in row a and three setae in row m with m1 (Figure 2L) about three times shorter than most posterior setae (dI–dIII)-1 of posterior dorsal complex (Figure 2M). Abd I bears single row with 5 setae. Trichobothrial complex (Figure 6B): ABC form an angle close to right (96–97°), and AB is 1.3–1.5× longer than BC; seta p is located above the level of trichobothrium B; seta b1 lies on line BC, a little closer to C; microseta c1 (11 μm) lies in front of trichobothrium C and seta c2—below C. Posterior lateral complex with five setae in two rows (2 + 3) and furca base complex with eight setae in two rows, neosminthuroid seta is absent. Central dorsal complex with the three usual setae. Posterior dorsal complex, with about 14 long setae arranged in 3 longitudinal rows, the longest of which (the most posterior setae of rows dI–dIII) = 85–88 μm but shorter than hind claw (Table 1). Ventral complex with 1–2 setae.
Small abdomen. The fifth abdominal segment (Figure 4A), with two setae and trichobothrium D in row a, as well as two setae in row p. Genital field with 3 + 3 microsetae along the anterior margin of the genital opening.
The sixth abdominal segment (Figure 4D and Figure 6D) without any cuticular spines. Dorsal valve with 10 + 2 axial + 10 setae. Each of the lateral valves bears 15 setae. Setae of the circumanal row are slender and not modified, with the longest = 47–56 μm, which is 1.7× shorter than posterior setae of the great abdomen (Figure 2F,G). Appendices anales (Figure 2H,I) (34–37 μm) rod-like, laterally smooth, apically not broadened, and denticulated; sitting on globular basal papilla.
Male. Body 0.9 mm long (Figure 5A), a little smaller than females. Subsegmentation of Ant IV is clearer than in female, with more distinct annulation (Figure 2D). Apex of Ant IV with 11 small setae. Dens without seta IIpe (in Figure 4B, marked as variable). Dorsal anal valve of Abd VI with 7 + 2 axial +7 setae, genital opening surrounded by about 10 short setae per side (Figure 4E). Otherwise, male chaetotaxy corresponds to that of females.
Variability
Dens setae IIpe (in male) and IVpi (in female) missing. Apical whorl of Ant IV with 12 small setae (in female) or 11 (in male). In male seta of left coxa II forked (Figure 4A). Inner tooth of claw I and II very small, sometimes looks absent.
Bionomy and distribution
Specimens of Arrhopalites profundus sp. nov. were found exclusively on the water surface in small pools along the cave river at the depth of 1100 m in Snezhnaya Cave (Figure 1E). The air temperature in the sampling locality was 5.8 °C in August 2017 and 6.2 °C in August 2018, and water temperature 5.2 °C (in 2017) and 4.8 °C (in 2018). They co-occur with highly troglomorphic T. gladiator.
Etymology
The species name is a Latin adjective ‘profundus’ in meaning ‘deep, obscure’, referring to considerable cave depth at which Arrhopalites species was recorded for the first time.
Taxonomic remarks
The new species belongs to A. caecus species group s. str. with 3, 2, 1, 1, 1 setae on the anterior side of dens. It resembles two highly troglomorphic species with extremely elongated claws—A. macronyx from the West Caucasian Anukhvinskaya Cave [9] and A. gul Yosii, 1966 from three Japanese caves [26]. Apart elongated claws all these species share the absence of distinctly spine-like setae on dens, short empodia not reaching the tip of corresponding claw, long antennae with 7 subsegments on Ant IV with several annuli between neighboring subsegments, long posterior setae of great abdomen (3× longer than anterior setae).
From A. gul the new species differs by shorter antennae (2× of head in A. profundus sp. nov. vs. 3× in A. gul), enlarged sense rods of antennal III organ (1.5× shorter than segment width vs. 3× shorter in A. gul), thin setae on head dorsum (stout in A. gul), thin and smooth setae on female Abd VI (broadened and barbered near the basis in A. gul), presence of corner tooth on empodium III (absent in A. gul), absence of teeth on posterior lamellae of mucro (present in A. gul), unbroadened tip of mucro (distinctly broadened in A. gul).
Very close to the new species is A. macronyx with which, apart from those mentioned above, it shares important similarities. It also shares enlarged antennal III organ, the same antenna/head ratio, absence of spine-like setae on head dorsum, mucro with large anterior lamella and with unbroadened tip, etc. A. profundus sp. nov. differs from it by: slender and smooth circumanal setae (broadened and basally serrated in A. macronyx), appendices anales with apical denticulation (smooth and acuminated tip in A. macronyx), posterior lamellae of mucro without teeth (teeth partly but not completely accreted in A. macronyx), and the presence of very small inner tooth on claw I and II (absent in A. macronyx). Some details of chaetotaxy are also different: Ant III with 18 setae, including 3 sensilla (vs. 20 in A. macronyx); femur III with 13 setae (vs. 12 in A. macronyx); setae Vai and Vpi of tibiotarsi I and II absent (vs. variable in A. macronyx); seta 3 of central dorsal complex of great abdomen is of normal length (vs. microseta in A. macronyx); lateral valves of Abd VI with 15 setae each (vs. 17 in A. macronyx).
3.2. Genus Pygmarrhopalites Vargovitsh, 2009
Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov.
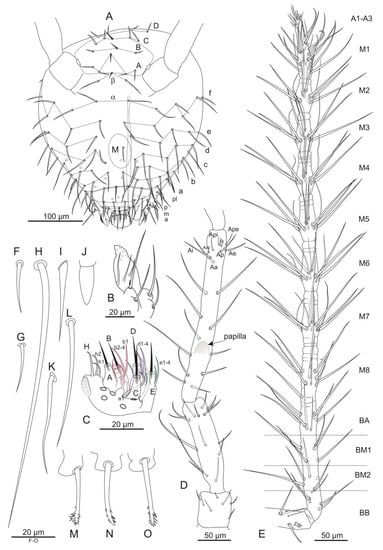
Figure 7.
Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov. (A)—Chaetotaxy of head; (B)—Maxillary outer lobe; (C)—Chaetotaxy of labial palp; (D)—Chaetotaxy of antennal segments I–III; (E)—Chaetotaxy of antennal segment IV; (F–O)—Shape of setae: (F)—Seta of head vertex; (G)—m1 of mesothorax; (H)—dIII-1 of great abdomen; (I)—Ii of dens; (J)—Ie of dens; (K)—ms1 of Abd VI; (L)—mps2 of abd VI; (M–O)—Appendices anales. Nomenclatures of setae in (A): after [18], (C): [19], (D,E): [25], (G,H): [20], (I,J): [24], (K,L): [22].
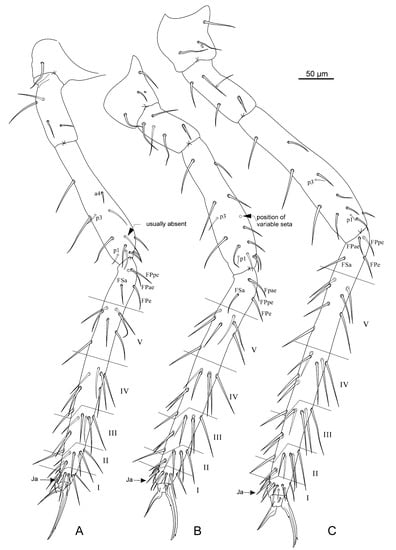
Figure 8.
Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov. (A)—Chaetotaxy of foreleg; (B)—Chaetotaxy of midleg; (C)—Chaetotaxy of hindleg. Nomenclature of setae in (A–C): after [23].
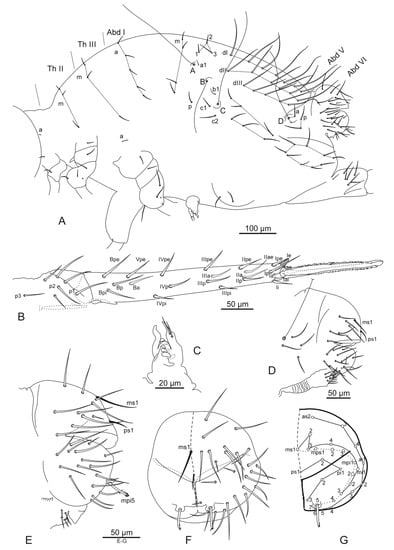
Figure 9.
Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov. (A)—Chaetotaxy of great abdomen; (B)—Chaetotaxy of furca; (C)—Tenaculum; (D)—Chaetotaxy of male Abd V–VI; (E–G)—Chaetotaxy of female Abd VI: (E)—Lateral view; (F)—Posterior view; (G)—The same as (F) but schematic with setae labeling. Nomenclatures of setae in (A): after [9,20], (B): [24], (D–G): [22].
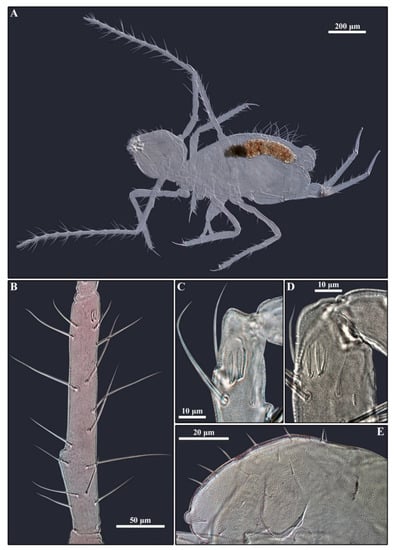
Figure 10.
Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov. (A)—Habitus of mounted female; (B)—Antennal segment III with subbasal papilla; (C–D)—Antennal III organ: (C)—Female; (D)—Male; (E)—Head dorsum.
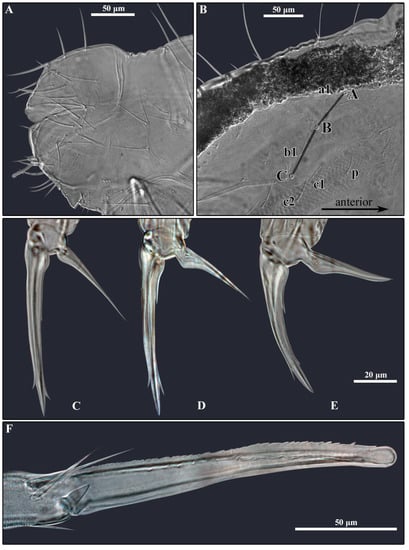
Figure 11.
Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov. (A)—Female small abdomen; (B)—Chaetotaxy of trichobothrial complex; (C–E)—Foot complex: (C)—Foreleg; (D)—Midleg; (E)—Hindleg; (F)—Mucro and distal part of dens. Nomenclature of setae in (B): after [20].
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:5282117D-D944-4F1F-AD6F-D40F8039E3FF
Diagnosis
Body unpigmented, about 1.1 mm long, possessing 1 + 1 eyes without pigmentation. Setae of head dorsum slender. Antenna 3.5× of head; Ant III with subbasal papilla; Ant IV subdivided into 9–10 subsegments with several annulations between them and with 15 whorls of setae. Trochanter I, II, III with 4, 5, 5 setae. Femur I, II, III with 12, 13/14, 12 setae. Each tibiotarsus with 44 setae (9, 8, 8, 8, 7, 4). Claws slender and elongated, without tunica, claw I with tiny (or unnoticeable) and II–III with distinct small inner tooth. Empodia are short, with tips not reaching corresponding claw’s tip, and without corner tooth. Manubrium with 7 + 7 setae. Dens posterior side with 16 setae, of which Ie as spine and IIIpe and Ii weakly spine-like near basis; anterior side with 3, 2, 1, 1 setae. Mucro, with broadened tip and about 30 teeth on inner, and partly accreted teeth on outer posterior lamella. Trichobothria ABC form an angle about 160° and AB < BC. Sixth abdominal segment with unbroadened circumanal setae; dorsal valve with 10 + 2 + 10 setae (ms5 absent); appendices anales apically tapered with lateral subapical fringes or weakly palmated. Intermediate between Pygmarrhopalites principalis and pygmaeus group of species [27] (p. 66).
Type material
Holotype: female on slide: W Caucasus, Abkhazia, Bzyb Mt. Range, massif of Khipsta Mt., Snezhnaya Cave (N 43°15′53.3″; E 40°43′05.6″; 1970 m elevation), Crystal Meander, −1100 m, 27.viii.2018, R.S. Vargovitsh leg.
Paratypes: There are 4 females and 1 juvenile, with the same data as for holotype; 1 male, W Caucasus, Abkhazia, Bzyb Mt. Range, massif of Khipsta Mt., Snezhnaya Cave, −800 m, 7th Choke (Ozhidaniya Hall), traps, 27.ii.-9.iii.2011, V.V. Rystsov leg.; 1 female, W Caucasus, Abkhazia, Bzyb Mt. Range, massif of Khipsta Mt., Souvenir Cave, −60 m, on trap surface, 24.viii.2019, R.S. Vargovitsh leg.
Holotype (female on slide: C-1136-1) and 7 paratypes (male on 4 slides: C-766-1, C-766-2, C-766-3, C-766-4; female on 3 slides: C-1136-2-1, C-1136-2-2, C-1136-2-3; female on slide: C-1136-3; female on 2 slides: C-1136-4-1, C-1136-4-2; female on slide: C-1136-5; juvenile on slide: C-1136-6; female on slide: C-1216) are kept in the collection of the Schmalhausen Institute of Zoology, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv.
Description
Female. Length about 1.1 mm, unpigmented.
Head (Figure 7A). Eyes 1 + 1, cornea well-marked, about 13 μm in diameter, unpigmented. Clypeal area includes six rows a to f: row a: 4 + axial + 4 setae, rows b, c, and e with 5 + 5 setae each, rows d and f with 6 + 6 setae each; median region M with 1 seta.
Interantennal area: row α: 2 + 2, row β: 1 + axial + 1. Dorsal area (rows A to D): axial seta is present in rows A, B, and C; all setae of head dorsum are slender and relatively short (Figure 7F and Figure 10E). Chaetotaxy of the head posterior side, as in Figure 7A (dashed circles).
Chaetotaxy of mouth region. Labrum (Figure 7A): labral/prelabral chaetotaxy: 4 5 5/6.
Labium: submentum with 4 setae, mentum with 5 setae; labial palp (Figure 7C) with 6 proximal setae, 5 papillae (A, B, C, D, E) with deeply inserted setae, and with 13 associated guard setae (a1, b1–4, d1–4, e1–4 of which a1 is strongly curved) and 3 hypostomal setae (H, h1, h2). Maxillary outer lobe, as in Figure 7B: apical seta with a short and thin subparallel branch at the base, sublobal plate with three sublobal hairs. Oral fold with two setae.
Antenna (Figure 7D,E) about 3.5× of head, subequal or longer than body. Length ratio of antennal segments I/II/III/IV = 1/2.8/4.9/13.8. Ant I with seven setae, p as microseta (6 μm). Ant II with 15 setae, 2 of which are over 2× longer than others. Ant III with subbasal papilla (Figure 10B), with following chaetotaxy: 17 simple setae of which Api and Ape especially thin, as well as 2 relatively large (11 μm) sense rods with 2 longitudinal ribs each in common pit, and Aai as small (5 μm) blunt sensillum (Figure 7D and Figure 10C,D). Ant IV subdivided into 9–10 subsegments, separated from each other by small intercalar pseudosubsegment, without setae or/and by 2–4 annuli (Figure 7E). Subsegmental formula: 1 + 7(8) + 1. Ant IV bears 15 whorls of setae: 4 on apical subsegment (AI–AIII + M1), 7 on median subsegments (M2–M8), and 4 on basal subsegment (BA + BM1–BM2 + BB).
Legs (Figure 8). Foreleg (Figure 8A): precoxa 1 and 2 and coxa with 1, 0, 1 seta, respectively (Figure 9A). Trochanter with three anterior and one posterior setae, two of which in the basal part of the segment are longer and stronger than those in subapical. Femur with 12 (in one case in male, asymmetrically 13 setae: variable seta marked in Figure 8A), a4 thin, not modified and usually not turned perpendicularly to the longitudinal axis of the segment. Tibiotarsus with 44 setae, tibiotarsal formula: 9, 8, 8, 8, 7, 4. Seta Ja in distal whorl I, weakly curved and slightly thickened but not spine-like; anterior secondary seta Sa in region F present. Pretarsus with one anterior and one posterior setulae. Foot complex (Figure 11C). Claw: slender and elongated, without tunica, with (sometimes without) tiny inner tooth and a pair of well-marked subapical lateral teeth; about 4.2× shorter than tibiotarsus. Empodium: thin, without corner tooth; smoothly shaped in the broadest part; 2× shorter than claw; empodial tip not reaching the tip of the claw.
Midleg (Figure 8B): precoxa 1 and 2 with 1, 1 setae, respectively, precoxal process present, coxa with 3 setae and microsensillum (Figure 9A). Trochanter with five setae: anterior trochanteral organ, three anterior, and one posterior simple setae. Femur with 13 (usually) or 14 setae (asymmetrically in 2 specimens: position of variable seta marked in Figure 8B). Tibiotarsus with 44 setae (9, 8, 8, 8, 7, 4) as in foreleg. Seta Ja in distal whorl I is not modified. Pretarsus with one anterior and one posterior setulae. Foot complex (Figure 11D). Claw: slender and elongated, without tunica, with small inner tooth and a pair of well-marked subapical lateral teeth; about 4.2× shorter than tibiotarsus. Empodium: without a corner tooth, but the widest part is angular shaped; 1.9× shorter than claw; tip of empodium not reaching tip of the claw.
Hindleg (Figure 8C): precoxa 1 and 2, with 1, 1 setae, respectively, process on precoxa 1 present, coxa with 3 setae and microsensillum (Figure 9A). Trochanter with five setae: anterior trochanteral organ, three anterior, and one posterior simple setae. Femur with 12 setae, 2 posterior ones as microsetae. Tibiotarsus with 44 setae (9, 8, 8, 8, 7, 4) and Ja of whorl I as simple seta. Pretarsus with one anterior and one posterior setulae. Foot complex (Figure 11E). Claw: slender and elongated, without tunica, with a small inner tooth and a pair of well-marked subapical lateral teeth; about 5.8× shorter than tibiotarsus. Empodium: broad, untoothed, and the widest part smoothly shaped; 1.7× shorter than claw; with very short apical filament, not reaching the tip of the claw.
Lengths ratio of tibiotarsi I/II/III = 1/1/1.2. Tibiotarsus I as long as the head.
Ventral tube (Figure 9A) with 1 + 1 subapical microsetae.
Tenaculum (Figure 9C): each ramus with three teeth and a basal process; anterior lobe with two apical setae.
Furca (Figure 9B). Manubrium with 7 + 7 posterior setae. Dens with 23 setae (7 anterior and 16 posterior). There are 3, 2, 1, 1 setae on the anterior side. Posterior side with Ie as relatively small spine (Figure 7J), IIpe and Ii are thickened in the basal part (Figure 7I). Mucro (Figure 11F): posterior lamellae with free or somewhat accreted teeth: inner lamella with about 30–35 teeth, outer with less teeth; anterior lamella smooth and moderately developed; tip spoon-like. Dens about 2× as long as mucro.
Great abdomen (Figure 9A). Segments Th II and III bearing single sensillum in row a (7 μm in Th II and 16 μm in Th III) and 3 setae in row m, with m1 (Figure 7G) not modified and about 6–7 times shorter than most posterior setae of posterior dorsal complex (Figure 7H). Abd I bears a single row with five setae. Trichobothrial complex (Figure 11B): ABC form a very obtuse angle (about 160°), and AB is about 1.4× shorter than BC; seta p is located below the level of trichobothrium B; seta b1 lies on line BC, a little closer to C; c1 as normal seta (35 μm, not microseta) lies in front of trichobothrium C and seta c2—below C. Trichobothrium B shorter than others. Posterior lateral complex, with six setae in two rows (3 + 3), and furca base complex, with 9 setae in two rows (5 + 4), neosminthuroid seta is absent. Central dorsal complex, with seta 3 distinctly longer than 1 and 2 (Figure 9A). Posterior dorsal complex with about 18 long setae, arranged in 3 longitudinal rows (dI: 7 setae, dII: 6, dIII: 5), the longest of which (the most posterior setae of rows dI–dIII) = 127–136 μm, which is about 1.8× longer than hind claw (Figure 7H and Table 2). Ventral complex is usually with two setae.
Small abdomen. Fifth abdominal segment (Figure 9A), with two setae and trichobothrium D in row a and two setae in row p. Genital field with 5 + 5 (also 4 + 4, 4 + 5 or 4 + 6) microsetae along the anterior margin of the genital opening.
Sixth abdominal segment (Figure 9E–G and Figure 11A). Dorsal valve with 10 + 2 axial + 10 setae, ms5 absent. Each lateral valves bears 18 setae. Setae of circumanal row (ms1, mps1–3 and mpi1–3) slightly stronger than others but not broadened (thinner than posterior setae of great abdomen) and relatively short (the longest = 43–58 μm, which is about 2.5× shorter than longest posterior seta of great abdomen) (Figure 7K,L). Appendices anales (Figure 7M–O) (30 μm): rod-like apically tapering shaft, which in the distal half, slightly palmate or bears rough lateral fringes, either subequal with shaft diameter or longer; sitting on subglobular somewhat elongated basal papilla.
Male. Body 0.95 mm long, a little smaller than that of females. Chaetotaxy of head, body, and appendages are the same as in female, apart from the small abdomen (Figure 9D): Abd V, with about 10 + 10 short setae associated with the genital opening (vs. about 5 + 5 in female); dorsal anal valve of Abd VI, with 7 + 2 axial + 7 setae (vs. 10 + 2 + 10 in female) and each of lateral valves with 14 setae (vs. 18 in female).
Variability
Femur I with 12 (usually) or 13 (in one case asymmetrically) setae (Figure 8A). Femur II with 13 or 14 setae (Figure 8B). Claw I with very small inner tooth or without tooth. Female genital plate with 5 + 5 or 4 + 4 or 4 + 5 or 4 + 6 microsetae.
Bionomy and distribution
Specimens of Pygmarrhopalites rystsovi sp. nov. were found in the terrestrial habitat on rocky surfaces, at the depth of −1100 m, in Snezhnaya Cave. Additionally, some specimens were captured in pitfall traps at −800 m and −1100 m in Snezhnaya Cave, as well as at −60 m in Souvenir Cave. No specimens were observed on the water surface yet. The air temperature at the sampling localities was: in Snezhnaya Cave: 5.0 °C at −800 m [28] and 5.8–6.2 °C at −1100 m (own data); in Souvenir Cave: 3.0 °C at −60 m (own data).
Etymology
The species name is dedicated to Valentin Rystsov—the head of St. Petersburg Club of Speleologists—who has explored the Snezhnaya Cave System during 11 expeditions since 1986; in 2011, he collected the first specimen (the only male in the type series) of the new species.
Taxonomic remarks
According to Bretfeld’s [27] divisions of species groups, and due to the structure of appendices anales (fringes subequal to shaft diameter or somewhat longer), the new species occupies an intermediate position between P. pygmaeus and principalis species group. Regardless of this, P. rystsovi sp. nov. could be compared with congeners having such distinguishable characters as presence of the only spine (Ie) on dens and/or presence of subbasal papilla on the third antennal segment. Of the genus Pygmarrhopalites, 19 species possess the only spine (Ie) on dens, and 12 species have subbasal papilla on Ant III. Combination of these two characters is very rare, and within large genus Pygmarrhopalites, with about 100 described species, it occurs in only two troglobiont troglomorphic species: P. aggtelekiensis (Stach, 1930) and P. commorus (Christiansen and Bellinger, 1996) [29,30]. The impression of similarity with these species enforces the trolomorphic shape of claws (slender, elongated, without tunica, and with short empodia), unmodified (not broadened) circumanal setae, simple (not spine-like) setae on head dorsum, and long antenna, especially in P. aggtelekiensis, which also has the same number of subsegments (9–10) on the fourth antennal segment as in the new species.
From the European P. aggtelekiensis (N Hungary and S Slovakia), the new species differs by: antenna 3.5× longer than the head (vs. 2.5× in P. aggtelekiensis); presence of several annuli (sutures) between the subsegments of Ant IV (vs. only one suture between subsegments); circumanal axial seta ms1 simple (vs. bifurcated); all empodia without a corner tooth (vs. empodium I and II with tooth); appendices anales, with fringes subequal to shaft diameter or longer (vs. very short).
From the Nearctic P. commorus (USA, Virginia), the new species differs by: shorter body (~1.1 mm vs. up to 1.5 mm in P. commorus); longer antenna (3.5× of head) with 9–10 subsegments in Ant IV (vs 1.7–2.1× of head and Ant IV with 6–7 subsegments); presence of several annuli (sutures) between subsegments of Ant IV (vs. only 1 suture); empodium I without a corner tooth (vs. with clear tooth); manubrium with 7 + 7 setae (vs. 4 + 4 setae); appendices anales with distinct lateral and apical fringes (vs. subcylindrical with finely ciliated apex).
4. Discussion
Although inhabiting the same underground realm at considerable depth and sharing basic subterranean abiotic factors, each of the species described above has its own micro-environmental preferences, which obviously led to the evolution into two different troglobiont life forms with subsequently common and different troglomorphic traits.
Below, I consider some aspects of troglomorphy, as well as life forms for the troglobionts of the family Arrhopalitidae, and particularly for the new species described above.
4.1. Reasons of Different Troglomorphy Level in Arrhopalitidae
Among 142 species of the family Arrhopalitidae (including the two described above) [31], 88 (or 62%) are considered troglobionts occurring exclusively in caves: 20 of 40 in genus Arrhopalites (50%), 67 of 101 in Pygmarrhopalites (66%), and 1 in the monotypic genus Troglopalites (Vargovitsh, 2012) (100%).
The level of troglomorphy in these troglobionts ranges from weakly marked to extremely high [9,26,29]. Besides, troglomorphic manifestations in highly specialized forms are different. Presumably, it depends on several reasons (drivers) that are listed below.
4.1.1. Ecological Evolutionary Trajectory of Certain Lineages
In general, epigean Arrhopalitidae inhabit dark and moist places, have a strongly reduced visual apparatus (1 + 1 ommatidia, rarely 2 + 2 or absent), and more or less reduced pigmentation. That presumes they are already preadapted to the subterranean life but differently. Particularly, the ancestors of cave-dwelling Arrhopalitidae lived either in litter, moss, etc. (as many Pygmarrhopalites species), where weak portions of light occasionally still might penetrate and space volume is not very tight, or in soil and lower litter layers (typical for most Arrhopalites), where light is completely absent and space volume between particles is tight. Correspondingly, the species of hemiedaphic ecological lineages possessed body and eye pigmentation and appendages of moderate length, whereas the species of euedaphic lineages lacked pigmentation and had shortened antennae and legs. Consequently, colonization of caves led both lineages to finer cave-depending morphological adaptations or troglomorphies. These adaptations involve parallel or convergent evolution of different lineages [32]. However, morphological signs of past epigean life remain traceable in cave dwellers to a certain extent. This is manifested in the remnants of pigmentation and the relative length of the appendages. Thus, troglobiont species of the genus Arrhopalites are usually (but not always) unpigmented and have shorter antennae and appendages than Pygmarrhopalites species. Diversification within each of these genera is also observed.
4.1.2. Evolutionary Age of Troglobiont Species
The level of troglomorphy correlates with the evolutionary age of the species, as well as time when colonization of subterranean (cave) habitats occurred. Thus, in Holarctic, the ‘old’ troglobionts—Tertiary thermophile relicts—are considered highly troglomorphic, whereas the ‘young’ troglobionts—Quaternary glacial and hydrophilic relicts—are weakly to moderately troglomorphic [33,34]. Normally, in addition to regressive evolutionary features like pigment and eye reduction, the ‘old’ troglobionts possess well-developed progressive troglomorphisms, such as appendage and claw elongation and the modification of sensory structures (e.g., Japanese A. gul, Carpathian P. aggtelekiensis, several Caucasian species).
4.1.3. Habitat Preferences of Species in Subterranean Realm
Cave-dwelling Arrhopalitidae species occupy several ecological niches regarding preferable substrates. The latter includes: (a) open terrestrial habitats such as the surface of cave walls, stones, floor, clay, and speleothems; (b) water surface of underground pools, rimstones, lakes, or siphons, as well as rocky surfaces with a thin water layer; (c) closed places such as under stones, in piles of bat guano, or inside other substrates. Using of these niches may be particularly overlapped by the same species, but the most specialized forms, apparently, are strictly determined (e.g., as observed in the Caucasian A. macronyx, A. profundus sp. nov. and T. stygios) [9].
4.2. Troglomorphic Features in Arrhopalitidae
Like in other cave animals, both regressive (reduction or loss of morphological structures) and progressive (adaptive development of morphological structures) evolutionary features associated with cave life [32] are present in Arrhopalitidae.
Regressive features. Given that, in Arrhopalitidae, the eye reduction or microphthalmy is not a cave-dependent feature because it was already present in epigean ancestors, the reduction/loss of pigmentation in certain species probably remains the only feature of regressive evolution in troglobionts of this family. Several patterns of this reduction, with combinations of different body and eye pigmentation, could be mentioned: (a) black or dark eyes in combination with light grayish (e.g., Pygmarrhopalites kristiani (Vargovich, 2005)) [35], brownish (P. pseudoprincipalis (Vargovitsh, 2009)) [20], or unpigmented (P. ruseki (Nosek, 1975)) [36] body in ‘young’ troglobionts; (b) unpigmented eyes with reddish (P. dbari) [8] or unpigmented (P. tauricus (Vargovitsh, 2009)) [20] body in ‘old’ troglobionts, as well as in preadapted ‘young’ troglobionts (Arrhopalites loczyi (Loksa, 1960) [37], A. karabiensis (Vargovitsh, 2009) [20])—the descendants of soil-dwelling lineages. It is interesting that reddish diffuse pigmentation, as well as complete depigmentation may occur even in highly troglomorphic species (e.g., P. aggtelekiensis, T. stygios). Unusual combinations may also happen: black eyes and light grayish body together, with the highly troglomorphic slender and distinctly elongated claws in P. kristiani [35].
Progressive features. Progressive or constructive troglomorphy is clearly affected by the cave environment [32].
In Arrhopalitidae, the troglomorphic (cave-dependent) features are: elongation of appendages (antennae, legs, furca), neustonic-hygropetric morphological adaptations (slendering and elongation of claws, modification of mucronal lamellae), and development of sensorial structures (enlarged antennal III organ, elongated and thinned setae, etc.) [8,9,20]. They are listed below.
4.2.1. Elongated Antennae with Multi-Subdivided Fourth Antennal Segment
In non-cave-dwelling species of the genus Arrhopalites (living in the soil, lower-litter layer, under the bark of trees) antennae are short, usually 1.3–1.5 times longer than the head; besides, Ant IV of these species is not subdivided or it is unclearly subdivided, e.g., [38,39,40]. The similar pattern is also known in non or weakly troglomorphic cave-dwelling Arrhopalites species (e.g., in A. karabiensis, A. glabrofasciatus (Zeppelini, Brito, and Lima, 2018)) [20,41]. In moderately or strictly cave-dependent forms, the antennae are usually distinctly longer, about 2× the size of the head (e.g., in the Caucasian A. abchasicus, A. macronyx and A. profundus sp. nov.), or reaching even about 2.9× the size of the head in the Japanese A. gul [7,9,26]. Subdivision of Ant IV becomes more developed and reaches up to 6–8 subsegments, usually with several annuli between them.
In most epigean species of the genus Pygmarrhopalites, antennae are usually about 1.6–1.8× the size of the head, with 5–6 subsegments on Ant IV. In weakly troglomorphic or non-troglomorphic cave dwellers the pattern is similar (e.g., P. pseudoprincipalis, P. ruseki, P. slovacicus (Nosek, 1975)) [20,36,42]. In more specialized species, antenna/head ratio reaches about 2.5× (P. aggtelekiensis, P. kaprusi (Vargovitsh, 2009), P. tauricus) or even 3–4× in most troglomorphic forms (P. dbari: 3×; P. rystsovi sp. nov.: 3.5×; P. uenoi (Yosii, 1956): 4×). Subdivision of Ant IV reaches 9–10 (P. aggtelekiensis, P. delamarei (Nosek and Paoletti, 1984), P. altus (Christiansen, 1966), P. tauricus) or even 15 subsegments (P. uenoi) [8,20,29,43,44].
In the monotypic T. stygios, this feature is also highly troglomorphic: antenna/head ratio is 3×, and Ant IV bears 13 subsegments [9].
4.2.2. Elongated Legs
Relative length of legs in cave-dwelling Arrhopalitidae varies from not elongated, as in epigean relatives, to distinctly elongated in highly specialized species. However, sometimes, leg segments are relatively short in highly troglomorphic—but strictly neustonic-hygropetric—forms. Particularly, this could be seen from comparison of body/tibiotarus III length ratio (2.6× in P. rystsovi sp. nov.—distinctly elongated; 3.3× in T. stygios and A. profundus sp. nov., and 4.3× in A. macronyx—not elongated) [9]. For comparison, in soil-dwelling Arrhopalites species, the body/tibiotarsus III ratio is about 4.5–5×, e.g., [39,40].
4.2.3. Elongated and Slender Claws
This character is a classical manifestation of troglomorphy, which convergently evolved in cave dwellers of several collembolan families [6,45,46,47,48,49], and the family Arrhopalitidae is among them. Only a few species of the genus Arrhopalites possess distinctly elongated claws, but in the two Caucasian species, the character is spectacular. The index of claws troglomorphy (body/claw I length ratio) in A. macronyx and A. profundus sp. nov. is about 7, representing the highest level of claw troglomorphy among Symphypleona. For comparison, in soil-dwelling and epigean species (e.g., A. persicus (Vargovitsh and Kahrarian, 2020), A. potapovi (Vargovitsh, 2015), A. prutensis (Vargovitsh and Busmachiu, 2015)), the body/claw I length ratio is about 25–30×, which is prominently different from highly troglomorphic ones [38,39,40]. The slender elongated claws in Arrhopalitidae are usually accompanied by relatively short empodia, far from reaching the tip of the corresponding claw.
4.2.4. Elongated Furca and Modified Lamellae of Mucro
In troglomorphic Arrhopalitidae, the mean body/furca length ratio is about 1.9× (in A. macronyx), 1.7× (T. stygios), 1.6× (A. profundus sp. nov.), and 1.5× (P. rystsovi sp. nov.), whereas in soil-dwelling and epigean Arrhopalites species, this ratio is about 2.3–2.7×, which means the furca in troglomorphic species is relatively longer. Besides, accreted teeth on lateral lamellae, as well as well-developed ventral lamella on mucro, are exclusive features of the highly troglomorphic water-dependent species (A. macronyx, A. profundus sp. nov., T. stygios) [9].
4.2.5. Enlarged Sensory Organ of the Third Antennal Segment
Antennal III organ in Arrhopalitidae consists of two sense rods, accompanying setae, and a short sensillum. It is especially well-developed in highly troglomorphic species, which are strongly associated with the surface of water [9]. Particularly, in A. profundus sp. nov., the length of each sense rod is about 15 μm, which is about three times larger than in soil-dwelling/epigean congeners of the same body size.
4.2.6. Thinning of the Spine-like Setae on Head and Dens
The shape of spiny setae, in weakly or moderately troglomorphic Arrhopalitidae, is similar to their homologues in epigean relatives. In highly troglomorphic species, a tendency towards attenuation and thinning of the spine-like setae is evident, especially on the head dorsum and the dens of the furca. Thus, epigean species of Pygmarrhopalites basically possess two strong external and three internal spine-like setae on the posterior surface of dens. Unlike them, highly troglomorphic species bear only one weakened external spine and thinned spine-like setae, or even ordinary setae, instead of other spiny ones (e.g., P. kaprusi, P. tauricus, P. aggtelekiensis, P. boneti (Stach, 1945), P. uenoi, P. hungaricus (Loksa, 1967), etc.) [20,29,44,50]. Simultaneously, these Pygmarrhopalites species possess thin setae on the head dorsum. In most troglomorphic water-depending Arrhopalites species (A. macronyx, A. profundus sp. nov.) and T. stygios, all spines on the dens and head dorsum are replaced with ordinary setae [9]. Probably, this replacement could mean switching the protective or supporting function (spines) to the sensitive function (setae), which is possibly preferred in cave habitats.
4.2.7. Elongated Setae of Posterior Dorsal Complex
In soil-dwelling and epigean Arrhopalites species (e.g., A. potapovi, A. persicus, A. prutensis), the body/posterior seta dI-1 of great abdomen length ratio is about 24–31× [38,39,40]. In highly troglomorphic A. macronyx, this ratio is about 15× [9], in A. profundus sp. nov. about 11×, and in P. rystsovi sp. nov. even about 8×. This comparison indicates a distinct elongation of the posterior abdominal setae in specialized cave dwellers.
4.3. Life Forms in Cave-Dwelling Arrhopalitidae
The cave environment [51], in addition to darkness, high humidity, and relatively constant temperature, provides cave-dwelling Collembola with a large open space in combination with often wet, rocky, and clay surfaces, water film, as well as spaces with small diameters within substrates.
In his ecological classification of collembolan life forms, Christiansen [52,53] defined category troglomorphs for cave dwellers with features: “elongate antennae and body form of the atmobios plan, the eyeless, pigmentless characteristics of the euedaphon, and the elongate or modified ungues of the aquatic form”.
Depending on the confinement to certain habitats inside caves, and taking for a basis the Christiansen’s [52,53] definition of troglomorph life form, the following specific life forms (or sub-forms) of troglobiont Arrhopalitidae can be distinguished.
4.3.1. Neustonic-Hygropetric Troglomorphs (Cave Water & Wet-Stone Walkers)
Preferable habitats: surface of cave water bodies (pools, lakes, rimstones, streams) and cave hygropetric (walls with thin water films moving down in mostly laminar flow [54]. Specific traits in Arrhopalitidae are: (a) slender and significantly elongated claws with a reduced/absent inner tooth—the main indicative adaptation—while other segments of the legs are not elongated; (b) enlarged antennal III organ; (c) spine-like setae on dens are replaced with attenuated setae; (d) lateral lamellae of mucro are with partly or completely accreted teeth, and ventral mucronal lamella is well-developed. Examples: A. macronyx, A. profundus sp. nov., T. stygios [9]. These species are strongly associated with water-surface habitats, have not been found remote from water, and failed to be caught by terrestrial Barber’s pitfall traps.
4.3.2. Atmobiont Troglomorphs (Cave Terrestrial Walkers)
Preferable habitats: open terrestrial substrates—walls, rocks, clay, speleothems, etc., but they may also occur on water surfaces. Specific traits in Arrhopalitidae: (a) elongated antennae and legs, while claws might not be elongated or only slightly elongated; (b) lateral lamellae of mucro are with normal teeth, and ventral lamella is not enlarged; (c) antennal III organ is not hypertrophied; (d) spine-like setae on dens are not much thinned or are moderately thinned. Examples: P. kaprusi, P. skelicus (Vargovitsh, 2009), P. carpathicus (Vargovich, 1999) [20,55]. Normally, these species can be easily caught using Barber’s traps.
4.3.3. Intermediate Troglomorphs (Cave Terrestrial & Water Walkers)
The pure neustonic-hygropetric and atmobiont troglomorphs are rather rare. Most of troglobiont Arrhopalitidae species regularly occur in search of food, both in open terrestrial and water-surface habitats. Consequently, their morphological adaptations show combined or intermediate states. Traits from both life forms, determined by shared abiotic factors and developed to varying degrees each, are: elongated antennae with an enlarged number of Ant IV subsegments, elongated legs, slender and moderately elongated claws, elongated abdominal setae, etc. Examples: A. abchasicus, A. peculiaris (Vargovitsh, 2009), P. aggtelekiensis, P. dbari, P. tauricus, P. rystsovi sp. nov. [7,8,20,29] It is probably the most diverse life (sub)form among the cave Arrhopalitidae. Unlike strict water walkers, these species can be caught using terrestrial pitfall traps.
4.3.4. Intrasubstrate Troglomorphs (Cave-Dwelling within-Substrate Inhabitants)
Preferable habitats: substrates with small space diameter, such as inside bat guano piles or other organic substrates, under stones, etc. Hypothetically, such a life form should exist among the Arrhopalitidae, and its appearance should be similar to that of an edaphic life form (relatively small body with short antennae, legs, furca, and unmodified foot complex). Probably, several Neotropic cave-dwelling Arrhopalites species described by Zeppelini (e.g., [56]) belong to this group.
5. Conclusions
The deep caves of the Bzyb Massif in the West Caucasus are inhabited by a highly specialized relictual and strictly endemic speleofauna, including collembolans of the family Arrhopalitidae.
To date, the findings of new species described from Snezhnaya Cave, A. profundus sp. nov. and P. rystsovi sp. nov., are the deepest (up to −1100 m) records of cave-dwelling Arrhopalitidae. Besides, both new species are among the most troglomorphic members of the family, but they represent different life forms.
Progressive troglomorphic (cave-dependent) features, differently exposed in Arrhopalitidae species, depending on habitat, include: (a) elongation of antennae with additional subdivision of the fourth antennal segment; (b) elongation of legs and furca; (c) thinning and elongation of claws with reduction in its inner tooth; (d) lammelization of mucro; (e) enlargement of sensory organ of third antennal segment; (f) attenuation of spiny setae on dens and head dorsum; (g) elongation of abdominal dorsal posterior setae.
Adaptation to the certain habitats inside caves led to the development of specific morphological features, indicating the presence of several life forms in cave-dwelling Arrhopalitidae: (a) neustonic-hygropetric troglomorphs preferably inhabiting the surface of cave water bodies and wet walls; (b) atmobiont troglomorphs preferably inhabiting open terrestrial substrates; (c) intermediate troglomorphs equally sharing both neustonic-hygropetric and open terrestrial habitats; (d) intrasubstrate troglomorphs preferably inhabiting substrates with small space diameter.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
I am obliged to Alexander Koval (St. Petersburg), Illya Turbanov (Sevastopol), Eugeny Romanov (Sevastopol), Igor Pelkin† (Sochi), Sergey Yashin (Sochi) and Oleg Merkurev (Sochi) for invaluable help during fieldworks in the Snezhnaya Cave System and Souvenir Cave in 2017–2019, and to Roman Dbar (Sukhum) for the administrative support during expeditions in Abkhazia.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Antić, D.Ž.; Makarov, S.E. The Caucasus as a major hotspot of biodiversity: Evidence from the millipede family Anthroleucosomatidae (Diplopoda, Chordeumatida). Zootaxa 2016, 4211, 1–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiera, C.; Arbea, J.I.; Vargovitsh, R.S.; Barjadze, S. A synthesis on troglobitic springtails in Europe. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2021, 59, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbanov, I.S.; Palatov, D.M.; Golovatch, S.I. The state of the art of biospeleology in Russia and other countries of the former Soviet Union: A review of the cave (endogean) invertebrate fauna. 2. Arachnida—Acknowledgments. Entomol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1297–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordana, R.; Baquero, E.; Reboleira, S.; Sendra, A. Reviews of the genera Schaefferia Absolon, 1900, Deuteraphorura Absolon, 1901, Plutomurus Yosii, 1956 and the Anurida Laboulbène, 1865 species group without eyes, with the description of four new species of cave springtails (Collembola) from Krubera-Voronya cave, Arabika Massif, Abkhazia. Terr. Arthropod Rev. 2012, 5, 35–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, A.B. New species of springtails of the genus Typhlogastrura (Collembola, Hypogastruridae) from caves of the USSR. Zool. Zh. 1987, 66, 463–472. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vargovitsh, R.S. Cave water walker: An extremely troglomorphic Troglaphorura gladiator gen. et sp. nov. (Collembola, Onychiuridae) from Snezhnaya Cave in the Caucasus. Zootaxa 2019, 4619, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargovitsh, R.S. Cavernicolous Arrhopalites abchasicus sp. nov. (Collembola: Symphypleona: Arrhopalitidae) from the West Caucasus with a key to the World species of the genus. Zootaxa 2013, 3666, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargovitsh, R.S. Two new troglobiont Pygmarrhopalites species of the principalis group (Collembola: Arrhopalitidae) from the West Caucasus. Zootaxa 2017, 4250, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargovitsh, R.S. New troglomorphic Arrhopalitidae (Collembola: Symphypleona) from the Western Caucasus. Zootaxa 2012, 3174, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjadze, S.; Djanashvili, R. Checklist of the springtails (Collembola) of Georgia. Caucasian Entomol. Bull. 2008, 4, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchouk, A. Caucasus, Georgia. In Encyclopedia of Caves and Karst Science; Gunn, J., Ed.; Fitzroy Dearborn: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Vakhrushev, B.A.; Dublyansky, V.N.; Amelichev, G.N. Karst of the Bzybsky Ridge. The Western Caucasus; Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia: Moscow, Russia, 2001; pp. 1–165. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gusev, A.S. Hydrology of underground water of Khipsta Massif (Abkhazia). Probl. Geogr. 2018, 147, 107–133. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mavlyudov, B.R.; Shelepin, A.L. Systema Snezhnaya. In Atlas of Caves of Russia; Shelepin, A.L., Ed.; Russian Geographical Society: Moscow, Russia, 2019; pp. 751–762. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mavlyudov, B.R. The Snezhnaya-Mezhennogo-Illyuziya cave system in the western Caucasus. Bol. Geol. Min. 2016, 127, 219–235. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, H.S. Traps for cave-inhabiting insects. J. Elisha Mitchell Sci. Soc. 1931, 46, 259–267. [Google Scholar]
- Mercet, R.G. Los enemigos de los parásitos de las plantas. Trab. Mus. Nac. Ci. Nat. 1912, 6, 1–306. [Google Scholar]
- Betsch, J.-M.; Waller, A. Chaetotaxic nomenclature of the head, thorax and abdomen in Symphypleona (Insecta, Collembola). Acta Zool. Fenn. 1994, 195, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fjellberg, A. The labial palp in Collembola. Zool. Anz. 1999, 237, 309–330. [Google Scholar]
- Vargovitsh, R.S. New cave Arrhopalitidae (Collembola: Symphypleona) from the Crimea (Ukraine). Zootaxa 2009, 2047, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretfeld, G. The chaetotaxy of the small abdomen of the Symphypleona (Insecta, Collembola) and its phylogenetic interpretation. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1994, 195, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Betsch, J.-M. An ontogenetically focused chaetotaxical scheme in Symphypleona (Collembola): The 6th abdominal segment. Pedobiologia 1997, 41, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Nayrolles, P. Chétotaxie tibiotarsale des Collemboles Symphypléones. Trav. Lab. Ecobiol. Arthrop. Edaph. Toulouse 1988, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nayrolles, P. Chétotaxie furcale des Collemboles Symphypléones. Trav. Lab. Ecobiol. Arthrop. Edaph. Toulouse 1990, 6, 27–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nayrolles, P. La chétotaxie antennaire des Collemboles Symphypléones. Trav. Lab. Ecobiol. Arthrop. Edaph. Toulouse 1991, 6, 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yosii, R. Results of the speleological survey in South Korea 1966. IV. Cave Collembola of South Korea. Bull. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo 1966, 9, 541–561. [Google Scholar]
- Bretfeld, G. Synopses on Palaearctic Collembola: Symphypleona; Staatliches Museum für Naturkunde Görlitz: Görlitz, Germany, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1–318. [Google Scholar]
- Mazina, S.E.; Bazarova, E.P.; Bashirov, A.M.; Gabbasova, E.R.; Gusev, A.S.; Kopachevskiy, Y.Y.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Savinov, V.P.; Shadrin, V.O. Abiotic Components of an Ecosystem of a Snezhnaya (Illyuzia-Mezhonnogo-Snezhnaya) Cave: A Condition and Problems of Research. In Mineralogy of Technogenesis–2011; Potapov, S.S., Ed.; IMin UrO RAS: Miass, Russia, 2011; pp. 219–238. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Stach, J. The species of the genus Arrhopalites occurring in European caves. Act. Mus. Hist. Nat. Acad. Polon. Litt. Sci. 1945, 1, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, K.; Bellinger, P. Cave Arrhopalites new to science. J. Cave Karst Stud. 1996, 58, 168–180. [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger, P.F.; Christiansen, K.A.; Janssens, F. Checklist of the Collembola of the World (1996–2022). Available online: http://www.collembola.org (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Christiansen, K. Morphological Adaptations. In Encyclopedia of Caves; Culver, D.C., White, W., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 386–397. [Google Scholar]
- Vandel, A. Biospeleology. The Biology of Cavernicolous Animals; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1965; pp. 1–524. [Google Scholar]
- Kováč, Ľ.; Parimuchová, A.; Miklisová, D. Distributional patterns of cave Collembola (Hexapoda) in association with habitat conditions, geography and subterranean refugia in the Western Carpathians. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 119, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargovich, R.S. Arrhopalites kristiani sp. n. (Collembola: Symphypleona: Arrhopalitidae) from a cave in Eastern Carpathians. Vestn. Zool. 2005, 39, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Nosek, J. A new springtail from the caves of the Moravský kras (Moravian Karst) Arrhopalites ruseki sp. n. Speleol. Vĕstn. 1975, 6, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Loksa, I. Faunistisch-systematische und ökologische Untersuchungen in der Lóczy-Höhle bei Balatonfüred (Biospeologica Hungarica, XI). Ann. Univ. Sci. Bp. Rolando Eötvös Nomin. Sect. Biol. 1960, 3, 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Vargovitsh, R.S. Arrhopalites potapovi sp. nov. (Collembola, Symphypleona) from Russia. Zootaxa 2015, 3955, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargovitsh, R.S.; Buşmachiu, G. A new species and new records of Arrhopalitidae (Collembola: Symphypleona) from the Republic of Moldova. Zootaxa 2015, 3973, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vargovitsh, R.S.; Kahrarian, M. A new species of Arrhopalites Börner, 1906 (Collembola, Symphypleona, Arrhopalitidae) from Iran with an updated key to A. diversus group of species. Zootaxa 2020, 4759, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppelini, D.; Brito, R.A.; Lima, E.C.A. Three new species of Collembola (Arthropoda: Hexapoda) from Central Brazilian shallow caves: Side effects of long term application of environmental law on conservation. Zootaxa 2018, 4500, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosek, J. Arrhopalites slovacicus a new species of Collembola from the Domica Cave. Rev. Suisse Zool. 1975, 82, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, K. The genus Arrhopalites in the United States and Canada. Int. J. Speleol. 1966, 2, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosii, R. Monographie zur Höhlencollembolen Japans; Contributions from the Biological Laboratory Kyoto University: Kyoto, Japan, 1956; Volume 3, pp. 1–109. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, K. Convergence and parallelism in cave Entomobryinae. Evolution 1961, 15, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaud, J.-M.; Massoud, Z. Un nouveau genre d’insectes collemboles Hypogastruridae cavernicole du Pays Basque. Mém. Biospéol. 1983, 10, 317–319. [Google Scholar]
- Deharveng, L. Collemboles cavernicoles VIII. Contribution a l’etude des Oncopoduridae. Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 1988, 92, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deharveng, L.; Thibaud, J.-M. Bessoniella procera n. g., n. sp., nouvel Orchesellidae cavernicole relictuel des Pyrénées (Insecta, Collembola). Bull. Mus. Natl. Hist. Nat. Sér. 4 1989, 11, 397–405. [Google Scholar]
- Lukić, M.; Houssin, C.; Deharveng, L. A new relictual and highly troglomorphic species of Tomoceridae (Collembola) from a deep Croatian cave. ZooKeys 2010, 69, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loksa, I. Vier neue Höhlencollembolen aus Ungarn (Biospeologica Hungarica, XXIII). Opusc. Zool. Bp. 1967, 6, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, F.G.; Moldovan, O.T. Where Cave Animals Live. In Cave Ecology; Ecological Studies; Moldovan, O., Kováč, Ľ., Halse, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 235, pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, K. Proposition pour la classification des animaux cavernicoles. Spelunca 1962, 2, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, K. Bionomics of Collembola. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1964, 9, 147–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sket, B. The cave hygropetric—A little known habitat and its inhabitants. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2004, 160, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargovich, R.S. A new species of Collembola of the genus Arrhopalites (Entognatha, Hexapoda) from a cave in Eastern Carpathians. Vestn. Zool. 1999, 33, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zeppelini, D. The genus Arrhopalites Börner, 1906 (Collembola, Appendiciphora, Arrhopalitidae) in the Neotropical Region, with description of four new cave species from Brazil. Zootaxa 2006, 1124, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).