Distinguishing Long-Discussed Cryptic Species of the Epibiotic Goose-Neck Barnacle of the Genus Conchoderma (Thoracicalcarea: Lepadidae) with Integrative Taxonomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collections
2.2. Morphological Examination
2.3. Molecular Analysis
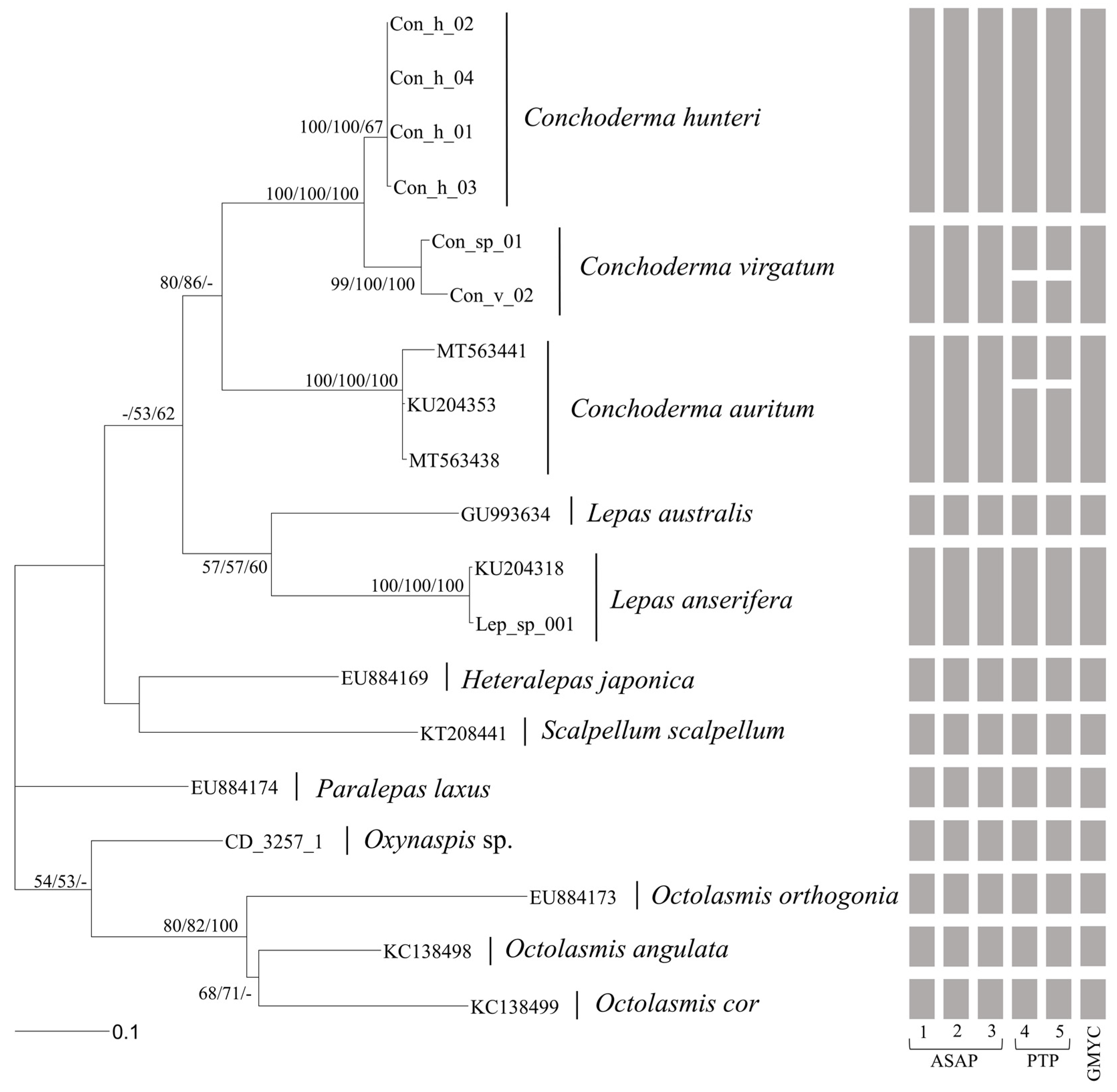
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
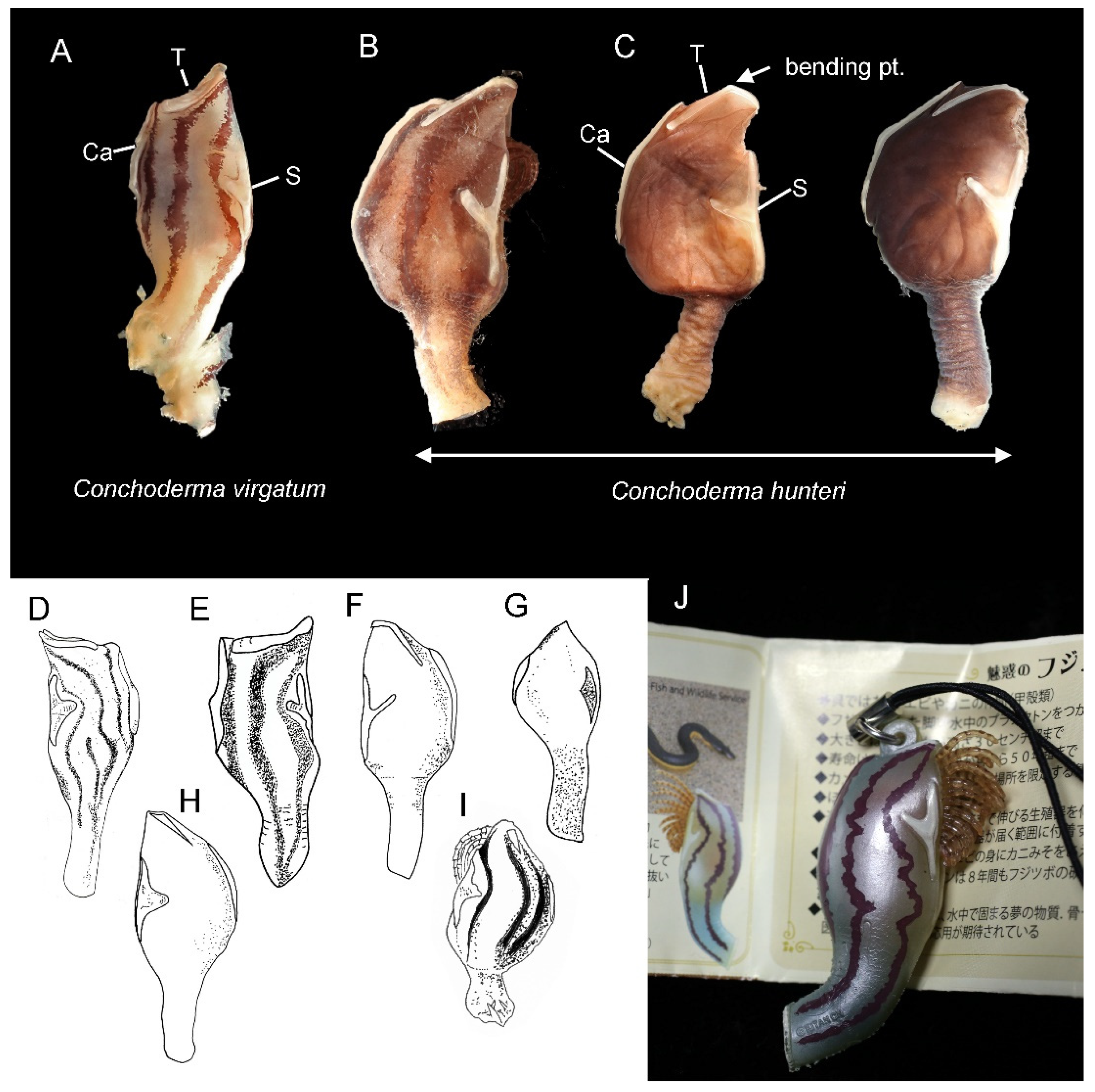
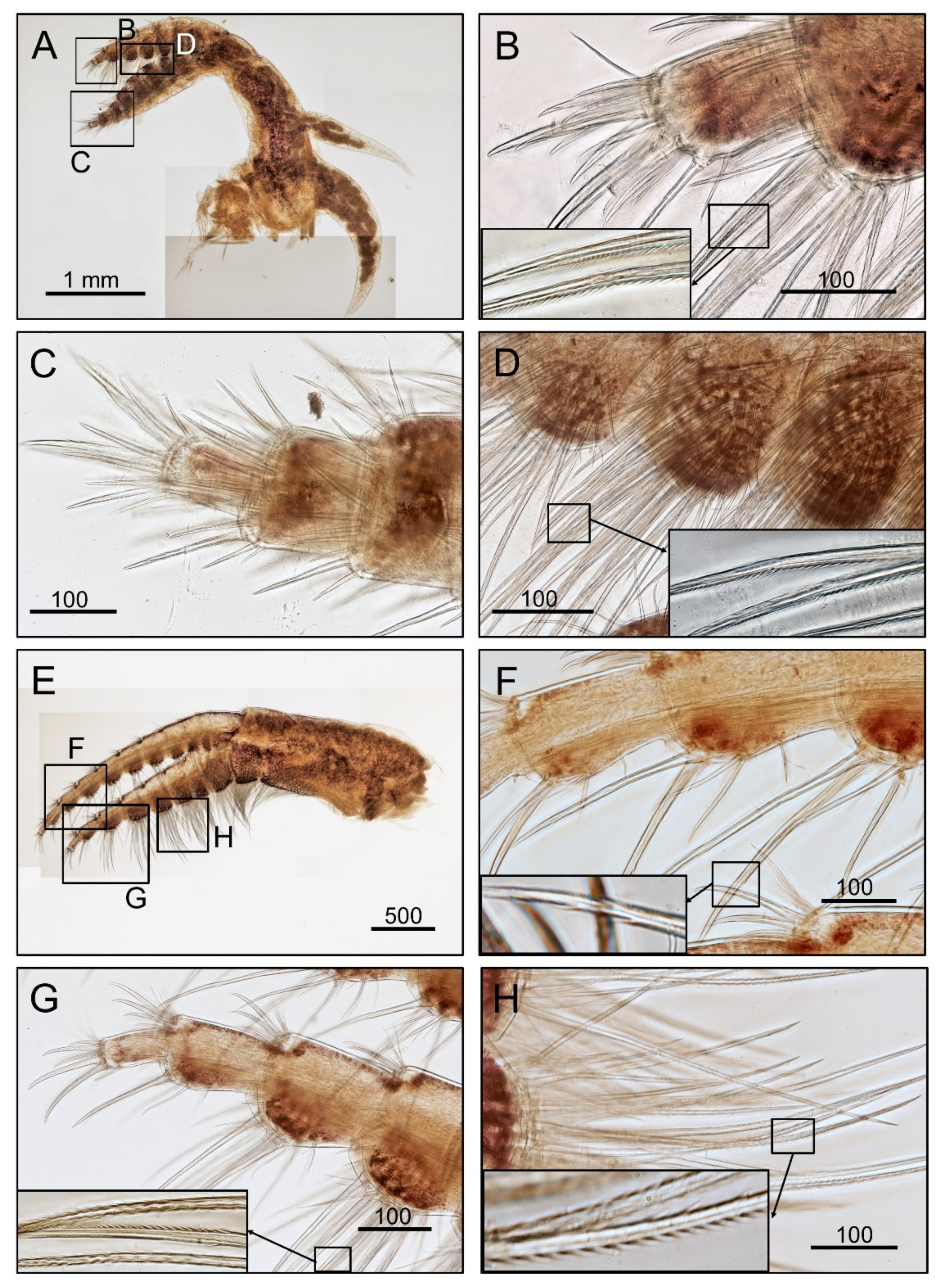
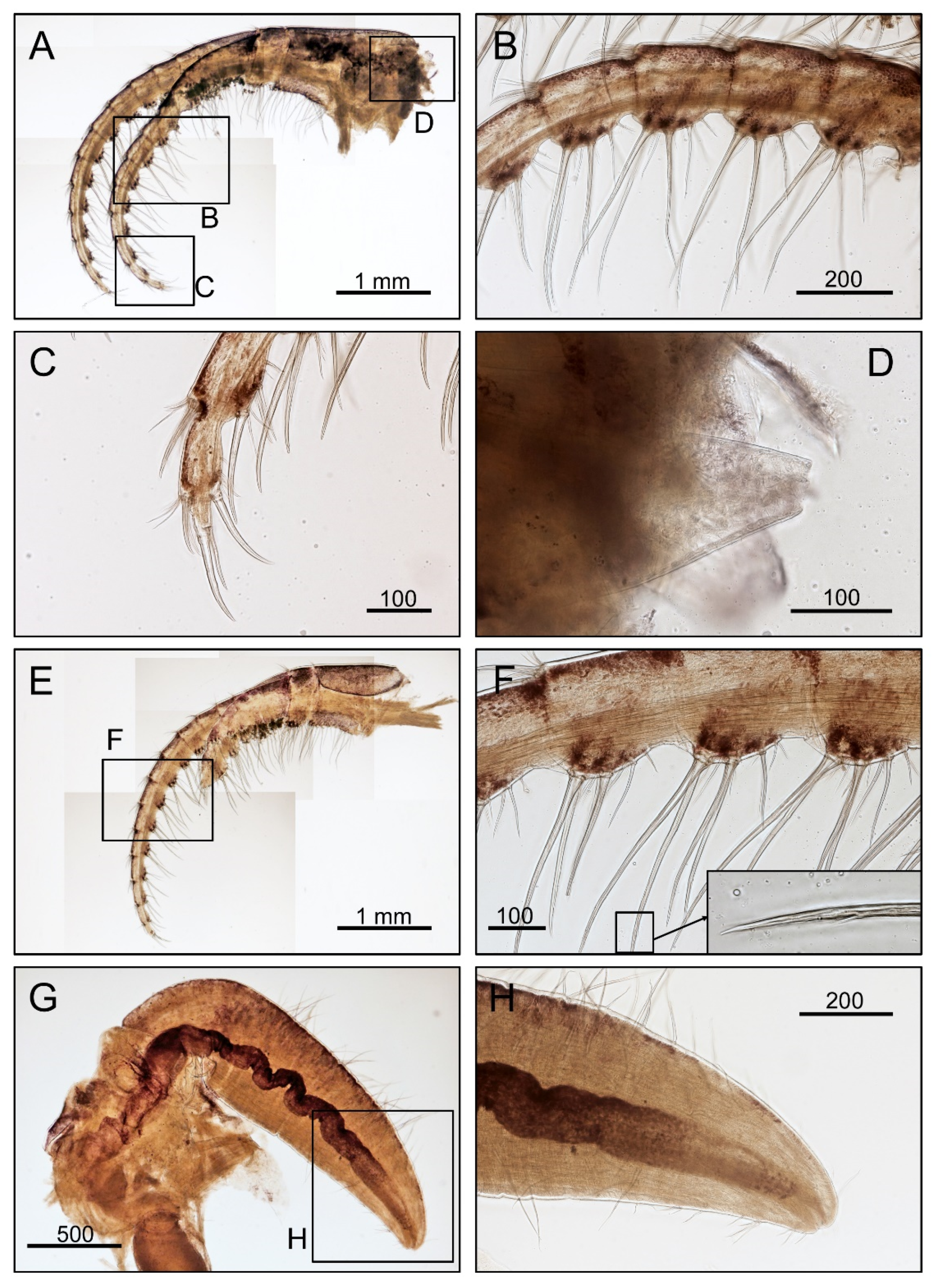
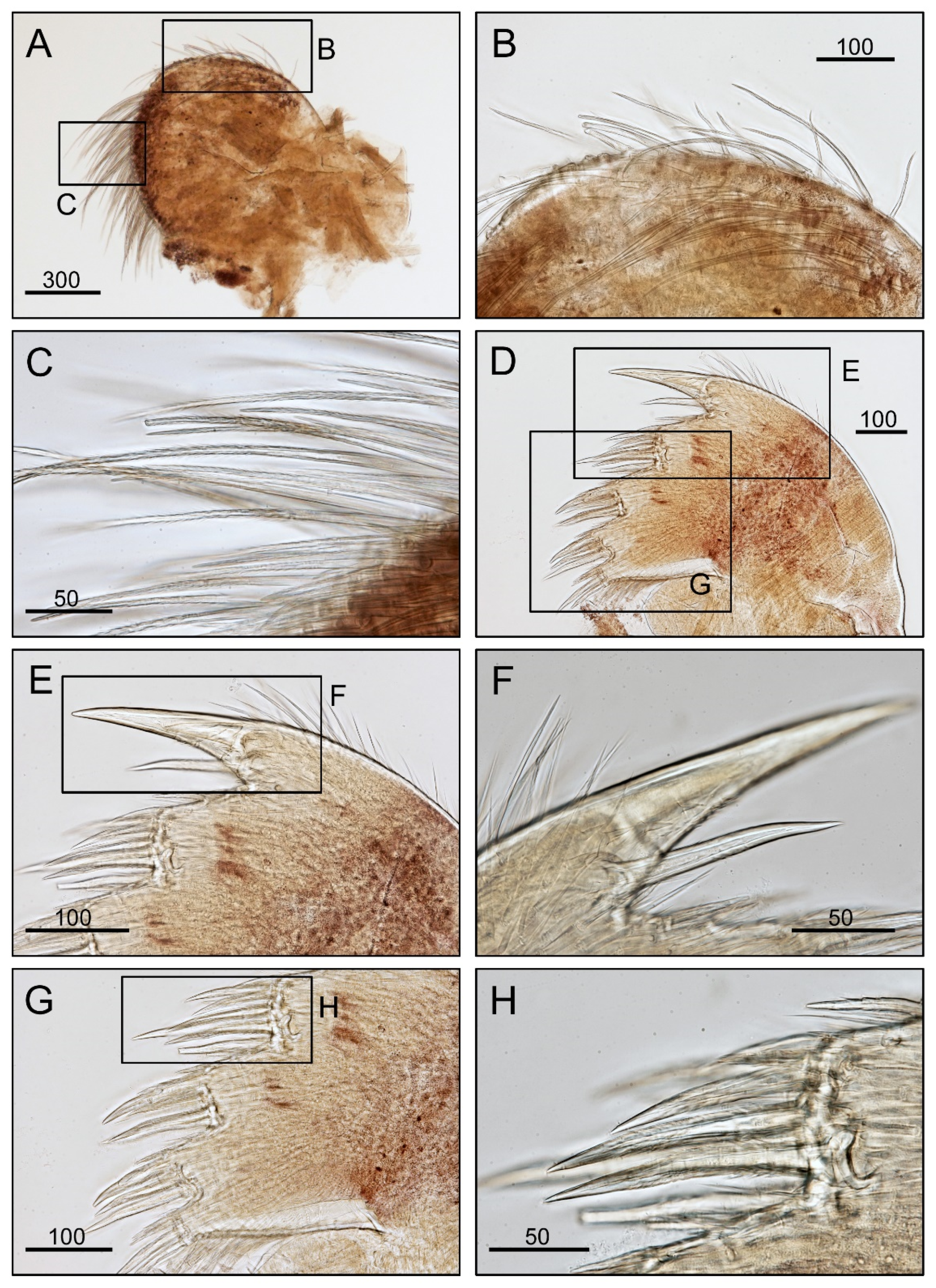
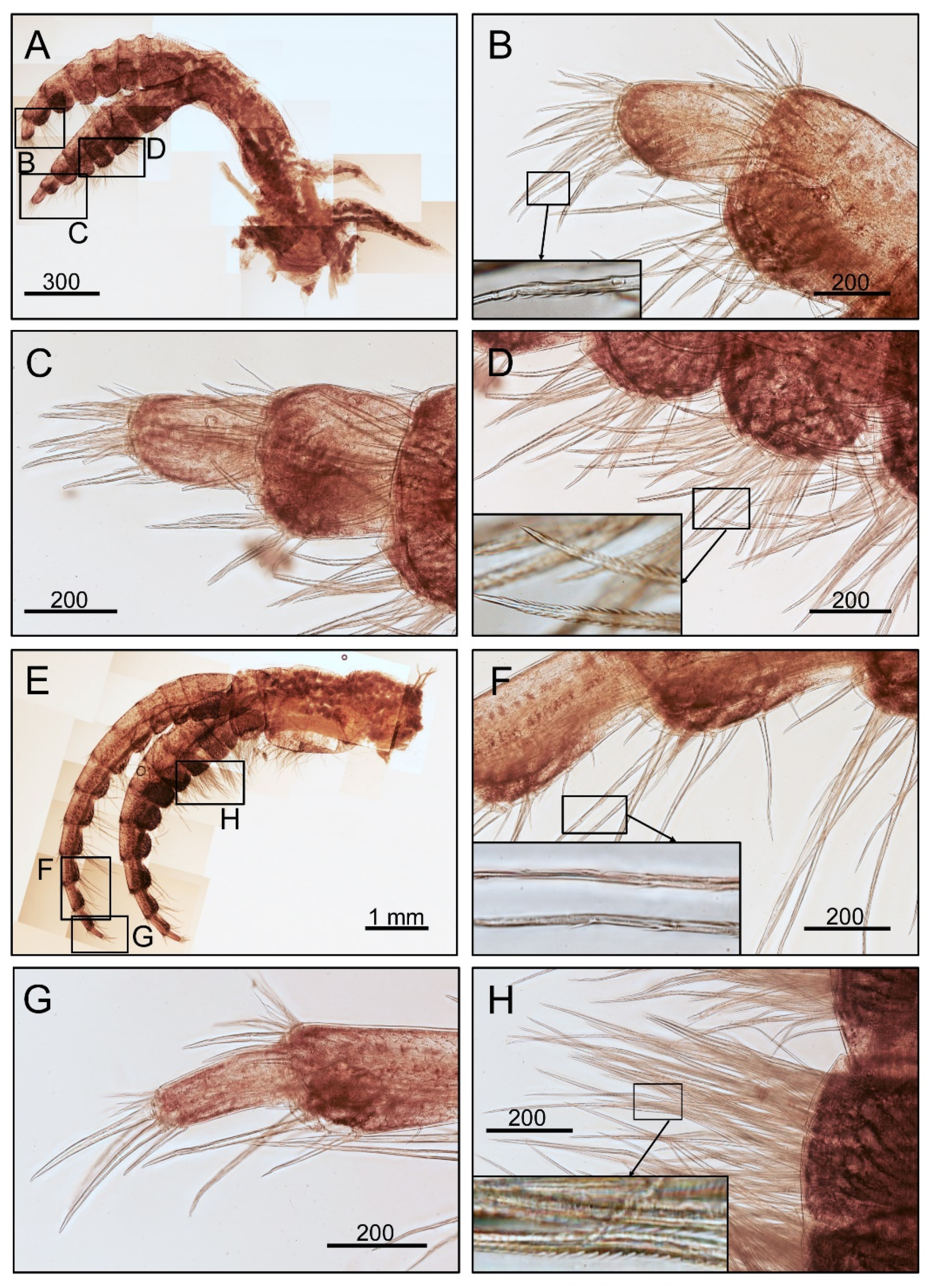
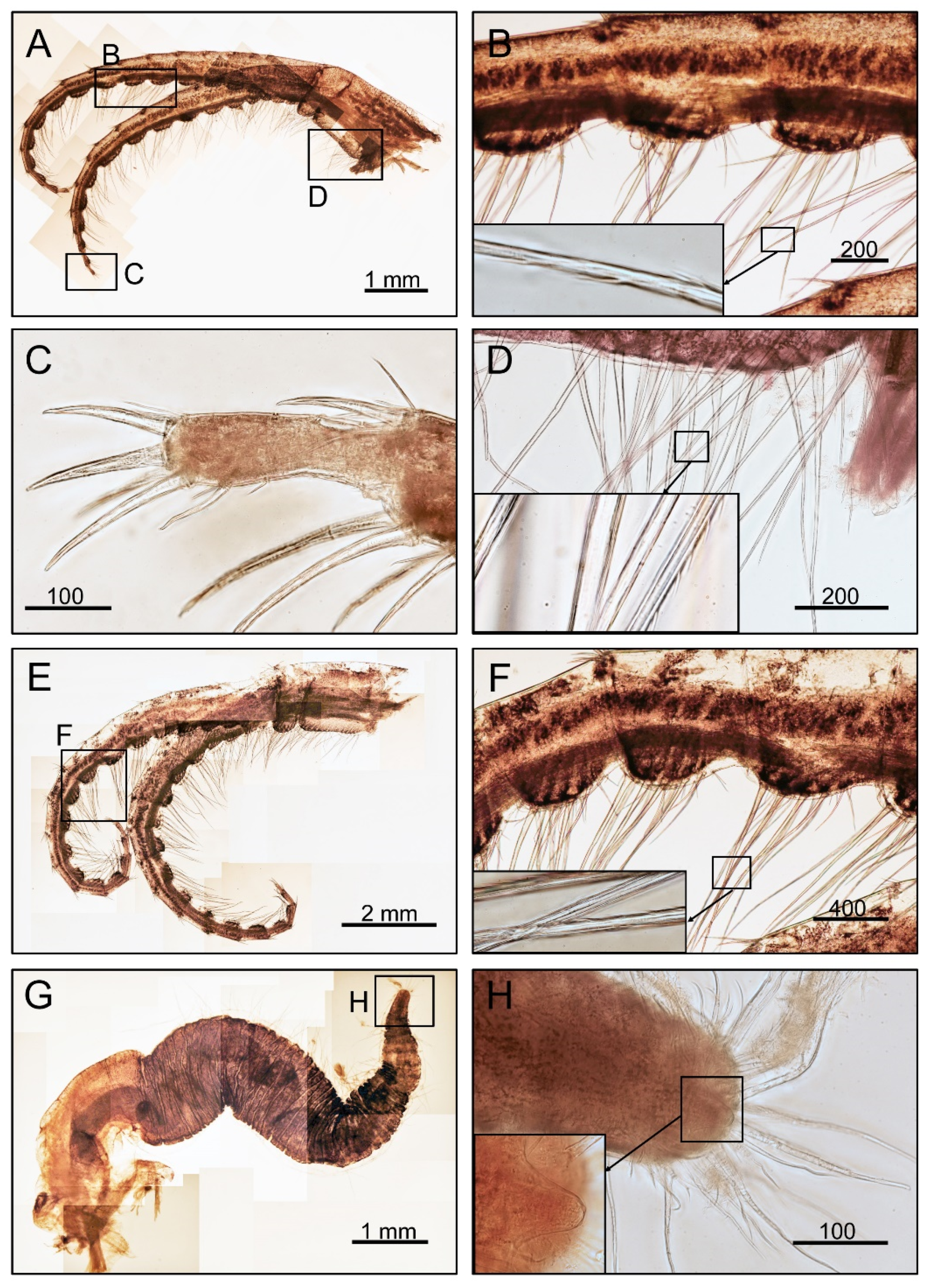
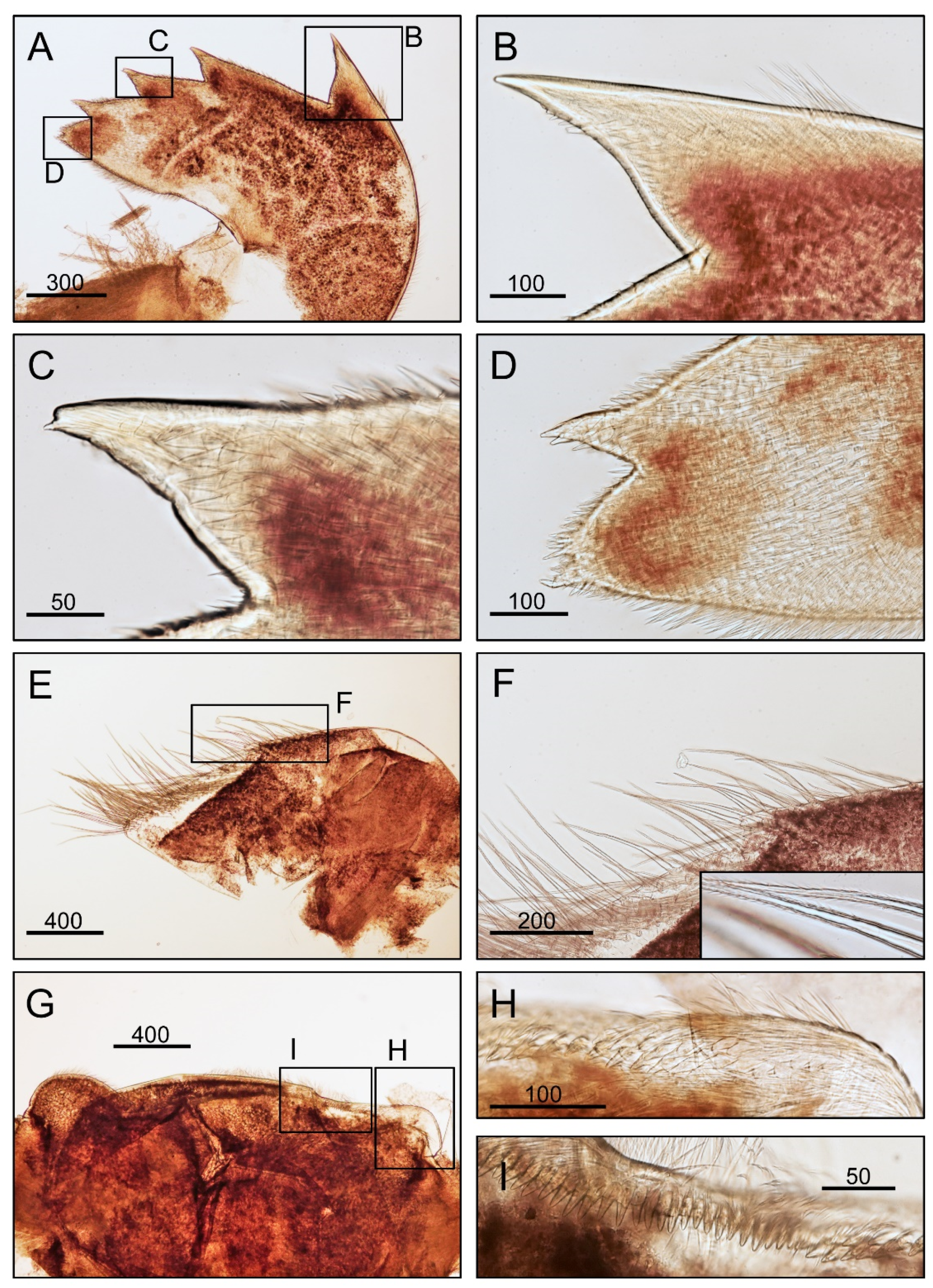
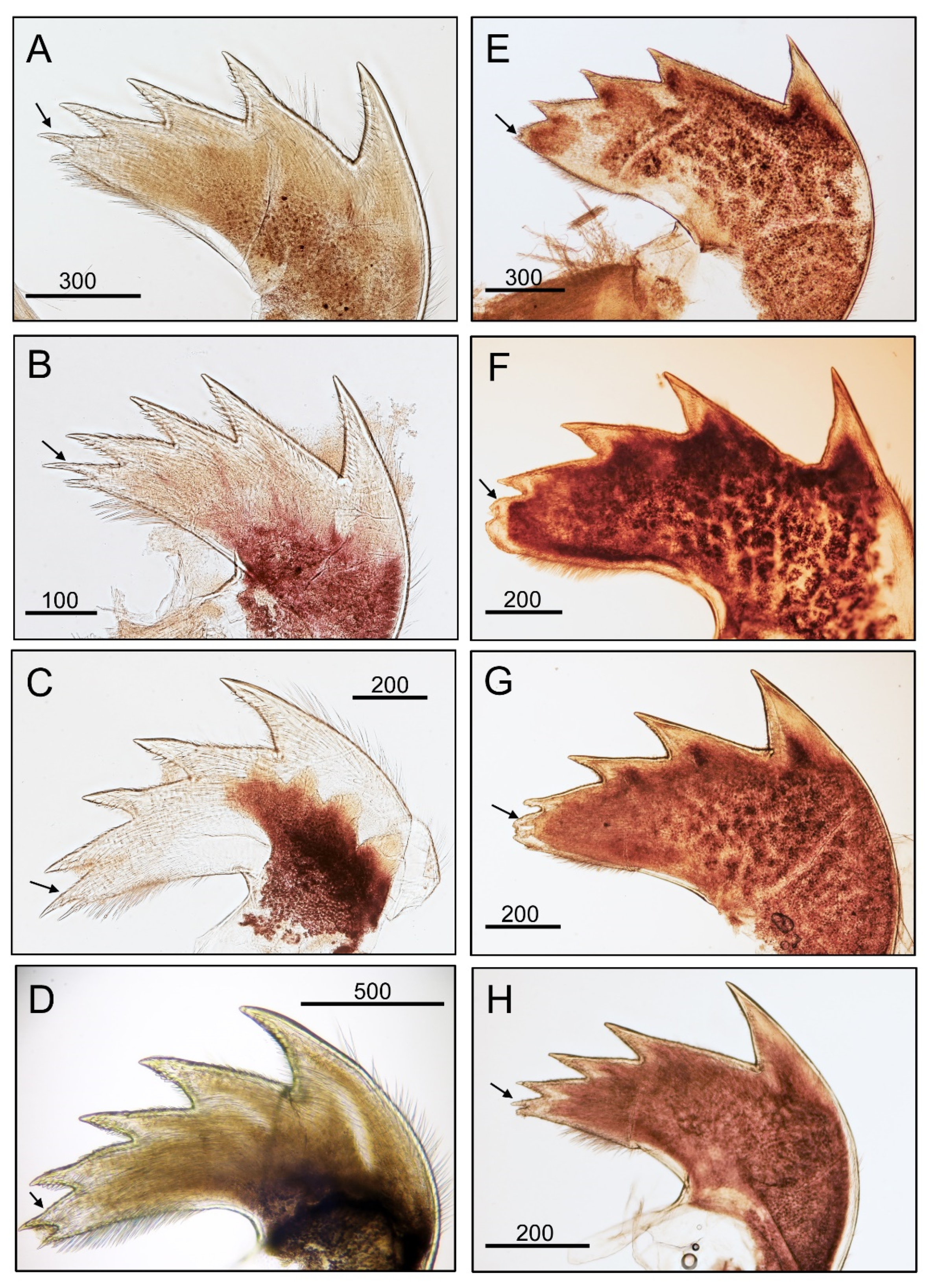
3.1. Taxonomy
3.2. Molecular Analysis
4. Discussion
- (1)
- With ear-like extension in the capitulum…………………Conchoderma auritum
- (2)
- Without ear-like extension in capitulum…………………………………..………(3)
- (3)
- 2nd cirri with filamentary appendages……………………Conchoderma indicum
- (4)
- 2nd cirri without filamentary appendages………………………………………(5)
- (5)
- Tergum bended at 1/3 distal portion………………………Conchoderma hunteri
- (6)
- Tergum not bended………………………………………………….…………(7)
- (7)
- Live on sea turtles……………………………………Conchoderma chelonophilum
- (8)
- Live on other marine substratum/organism……………Conchoderma virgatum
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, B.K.K.; Dreyer, N.; Glenner, H.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Ewers-Saucedo, C.; Gale, A.; Kolbasov, G.A.; Crandall, K.; Høeg, J.T. The evolutionary diversity of barnacles and a classification of fossil and living forms. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, 193, 789–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, W.A.; Ross, A. Antarctic Cirripedia. AGU Antarct. Res. Ser. 1971, 14, 1–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, R.W. The barnacle, Conchoderma virgatum (Spengler), in association with the isopod, Nerocila acuminata (Schioedte and Meinert), and the orange filefish, Alutera schoepfi (Walbaum). Crustaceana 1972, 22, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamato, S.; Yusa, Y.; Tanase, H. Distribution of two species of Conchoderma (Cirripedia: Thoracica) over the body of a sea snake, Laticauda semifasciata (Reinwardt), from the Kii Peninsula, Southwestern Japan. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1996, 37, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yorisue, T.; Hayashi, R.; Ikeguchi, S. Distribution and orientation of the pedunculated barnacle Conchoderma sp. on the swimming crab Portunus tribuerculatus (Miers, 1876). Crustaceana 2016, 89, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Chan, B.K.K.; Kang, C.B.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, W. How do whale barnacles live on their hosts? Functional morphology and mating-group sizes of Conchoderma diadema (Linnaeus, 1767) and Conchoderma auritum (Linnaeus, 1767) (Cirripedia: Thoracicalcarea). J. Crustac. Biol. 2020, 40, 808–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin, C. A Monograph on the Sub-Class Cirripedia, with Figures of All the Species. The Lepadidae; or, Pedunculated Cirripedes; Ray Society: London, UK, 1851. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Y.; Ren, X.Q. Fauna Sinica. Invertebrata. Vol. 42 Crustacea Cirripedia Thoracica; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Spengler, L. Beskrivelse og Oplysing over den hidindtil lidet udarbeide Slaegt af mangeskallede Konchylier, som Linnaes har daldet Lepas, med tilfoiede nye og ubeskrevne Arter. (Om. Conchylie-Slaegten Lepas). Skr. Naturhist.-Selsk 1790, 1, 158–212. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, R. Invertebrate Part I.; Catalogue of the Contents of the Museum of the Royal College of Surgeons of London: London, UK, 1830. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, W.E. Narrative of an Expedition to Explore the River Zaire, usually Called the Congo, in South Africa, in 1816, under the Direction of Captain J. K. Tuckey, R.N., to Which is Added, the Journal of Professor Smith; and Some General Observations on the Country and Its Inhabitants; Murray, J., Ed.; William B. Gilley Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Daniel, A. Conchoderma indicum n.sp. a pedunculated cirripede from Krusadi Islands. J. Zool. Soc. India 1953, 3, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hiro, F. Studies on cirripedian fauna of Japan. II. Cirripeds found in the vicinity of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory. Mem. Coll. Sci. Kyoto Imp. Univ. Ser. B 1937, 12, 385–478. [Google Scholar]
- WoRMS. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=211416. (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Pilsbry, H.A. The barnacles (Cirripedia) contained in the collections in the U. S. National Museum. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1907, 60, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, P.P.C. Report on the Cirripedia collected by H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873–1876. Rep. Sci. Results Explor. Voyag. H.M.S. Chall. Zool. 1883, 8, 1–169. [Google Scholar]
- Annandale, N. An account of the Indian Cirripedia Pedunculata. Part I. Family Lepadidae. Mem. Indian Mus. 1909, 2, 60–138, pis. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zevina, G.B. Barnacles of the Suborder Lepadomorpha (Cirripedia, Thoracica) of the world Oceans II. Fauna SSSR 1982, 133, 1–223. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Y.; Ren, X.Q. Studies on Chinese Cirripedia (Crustacea) VI. Suborder Lepadomorpha. Studia Mar. Sin. 1985, 25, 179–281. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–297. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. J. Bioinform. 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A.P. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting Species Using Single-Locus Data and the Generalized Mixed Yule Coalescent Approach: A Revised Method and Evaluation on Simulated Data Sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarisation in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R-Forge. Available online: https://r-forge.r-project.org/projects/splits/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.V.; Davidson, I.C.; Geller, J.; Ruiz, G.M. Disentangling the biogeography of ship biofouling: Barnacles in the Northeast Pacific. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.J.; Barco, A.; Steinke, D.; Beermann, J.; Laakmann, S.; Mohrbeck, I.; Neumann, H.; Kihara, T.C.; Pointner, K.; Radulovici, A.; et al. The application of DNA barcodes for the identification of marine crustaceans from the North Sea and adjacent regions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.N.; Høeg, J.T.; Chan, B.K.K. Morphometric and molecular identification of individual barnacle cyprids from wild plankton: An approach to detecting fouling and invasive barnacle species. Biofouling 2013, 29, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.K.; Tsang, L.M.; Shih, F.L. Morphological and genetic differentiations of the stalked barnacle Heteralepas japonica Aurivillius, 1892, with description of a new species of Heteralepas Pilsbry 1907 from the Philippines. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2009, 20, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.C.; Høeg, J.T.; Yusa, Y.; Chan, B.K.K. The origins and evolution of dwarf males and habitat use in thoracican barnacles. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, A.S. Origin and phylogeny of the thoracican cirripede family Stramentidae. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 2015, 14, 653–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buckeridge, J.S.; Newman, W.A. A revison of the Iblidae and the stalked barnacles (Crustacea: Cirripedia: Thoracica), including new ordinal, familial and generic taxa, and two new species from New Zealand and Tasmanian waters. Zootaxa 2006, 1136, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Olfers, F. Ueber die Linneischen Gattungen Chiton und Lepas. Ges. Naturf. Freunde Berl. Mag. Neuesten Entdeck. Gesammten Nat. 1814, 8, 163–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zevina, G.B. A new classification of Lepadomorpha (Cirripedia). Zool. Zhurnal 1980, 59, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Gruvel, A. Monographie des Cirrhipèdes ou Thecostracés.; Masson et Cie: Paris, France, 1905. [Google Scholar]
- Gruvel, A. Cirrhipédes provenant des campagnes Scientifiques de S. A. S. le Prince de Monaco (1855–1913). Result. Des Camp. Sci. Accompl. Sur Son Yacht Par Albert Ier Prince Souver. De Monaco 1920, 53, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing, T.R.R. General catalogue of South African Crustacea. Ann. S. Afr. Mus. 1910, 6, 563–575. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, L.S. Art. III. Revision of the Cirripedia of New Zealand. Trans. Proc. N. Z. Inst. 1918, 50, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Cantell, C.A. Cirripeden-Studien. Zur Kenntnis der Biologie, Antomie und Systematic dieser Gruppe. Zool. Bidr. Fran Upps. 1921, 7, 75–390. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Cantell, C.A. Studies on cirripeds in the British Museum. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1928, 10, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson-Cantell, C.A. Thoracic cirripedes collected in 1925–1927. Discover. Rep. 1930, 2, 223–260. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Cantell, C.A. Thoracic Cirripeds collected in 1925–1936. Discover. Rep. 1939, 18, 223–238. [Google Scholar]
- Broch, H. Cirripedia Thoracica von Norwegen und dem Norwegischen Nordmeere: Eine Systemarische und biologisch-Tiergeographische studie. Videnskapsselsk. Skrifter. I. Mat.-Naturv. kl. 1924, 17, 1–121. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, K.H. Contributions to the crustacean fauna of South Africa 7. Cirripedia. Ann. S. Afr. Mus 1924, 20, 197–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, D.P. Cirripedia Thoracica der Danischen Gewasser. Vidensk. Meddel. Naturhist. Foren. Kjøbenhavn Vidensk. Meddel. Dansk Naturhist. Foren. Kjøbenhavn 1927, 84, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hiro, F. Report on the cirripedia collected in the Malayan waters by the ship ‘Zuiho-maru’. Jpn. J. Zool. 1936, 6, 621–636. [Google Scholar]
- Hiro, F. Order Thoracica, I. (Cirripedia Pedunculata) Subclass Cirripedia (Class Crustacea). Fauna Nippon. 1937, 9, 1–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hiro, F. Studies on the Ciripedian fauna of Japan. V. Cirripeds of the northern part of Honshu. Sci. Rep. Tohoku Imp. Univ. Ser. 4 Biol. 1939, 15, 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hiro, F. Studies on the cirripedian fauna of Japan IV. Cirripeds of Formosa (Taiwan), with some geographical and ecological remarks on the littoral forms. Mem. Coll. Sci. Kyoto Imp. Univ. Ser. B Biol. 1939, 15, 245–284. [Google Scholar]
- Utinomi, H. Studies on the cirripedian fauna of Japan. 9. Distributional survey of the thoracic cirripeds in the southeastern part of Japan Sea. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1970, 17, 339–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, K.P. Observations on the occurrence of Conchoderma virgatum (Spengler) (Cirripedia) on Diodon hystrix Linnaeus (Pisces). Crustaceana 1969, 16, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.H. Conchoderma virgatum (Spengler) (Cirripedia, Thoracica) in association with Dinemoura latifolia (Steenstrup and Lutken) (Copepoda, Caligidea), a parasite of the Shortfin Mako, Isurus oxyrhynchus Rafinesque (Pisces, Chodrichthyes). Crustaceana 1978, 34, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, R.; Limpus, C.J. Barnacles on turtles in Queensland waters with descriptions of three new species. Mem. Queensl. Mus. 1979, 19, 197–223. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, B.A.; Willan, R.C. Foreign barnacles transported to New Zealand on an oil platform. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1979, 13, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, K.L.; Eckert, S.A. Growth rate and reproductive condition of the barnacle Conchoderma virgatum on gravid leatherback sea turtles in Caribbean waters. J. Crustac. Biol. 1987, 7, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, L.; Estraddes, A.; Scarabino, F.; Calcagno, J. Conchoderma virgatum (Spengler, 1790) (Cirripedia: Pedunculata) associated with sea turtles in Uruguayan shallow coastal waters. Pan-Am. J. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 5, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, K.H. An addition to the faunal list of South African barnacles. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. Mus. Lond. 1955, 13, 247. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, D.P. Beitrage zur Cirripedienfauna Ostasien. Beitr. Zur Nat. Ostasiens Hrsg. Von. F. Doflein. Konglige Bayer. Akad. Der Wiss. Munich Math. Phys. Klasse. Abh. Suppl. Band 1911, 2, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Broch, H. Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen’s Pacific Expedition 1914~1916, LVI. Indomalayan Cirripedia. Vidensk. Meddel. Naturhist. Foren. Kjøbenhavn 1931, 91, 1–146. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Cantell, C.A. Cirripeds from the Indian Ocean in the collection of the Indian Museum, Calcutta. Mem. Indian Mus. 1938, 13, 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Utinomi, H. Pelagic shelf and shallow-water cirripedia from the Indo-west Pacific. Vidensk. Meddel. Naturhist. Foren. Kjøbenhavn 1968, 131, 161–186. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, J.A. An annotated checklist of Hawaiian barnacles (Class Crustacea: Subclass Cirripedia) with notes on their nomenclature, habitats and Hawaiian localities. Hawaii Inst. Mar. Biol. Tech. Rep. 1970, 19, 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.M.; Chen, Y.S.; Cai, R.X. Preliminary study on the Chinese cirripedian fauna (Crustacea). Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1980, 2, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.S. Australian barnacles (Cirripedia: Thoracica), distributions and biogeographical Affinities. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2012, 52, 366–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Species | Specimen Voucher | Locality | GenBank Accession Numbers | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lepas anserifera | KU204318 | Apra Harbor, Guam | KU204318 | [34] |
| Lep_sp_001 | Taitung, Taiwan | ON938319 | Present study | |
| Scalpellum scalpellum | KT208441 | North Sea, Taiwan | KT208441 | [35] |
| Octolasmis cor | KC138499 | Pingtung, Taiwan | KC138499 | [36] |
| Octolasmis angulata | KC138498 | Ha Long Bay, Vietnam | KC138498 | Unpublished |
| Lepas australis | GU993634 | Chile | GU993634 | Unpublished |
| Paralepas laxus | EU884174 | - | EU884174 | [37] |
| Octolasmis orthogonia | EU884173 | - | EU884173 | |
| Heteralepas japonica | EU884169 | - | EU884169 | |
| Oxynaspis sp. | CD_3257_1 | Madagascar | ON938312 | Present study |
| Conchoderma hunteri | Con_h_01 | Panglao Island, Philippines | KF484213 | [38] |
| Con_h_02 | KC138463 | |||
| Con_h_03 | Penghu, Taiwan | ON938315 | ||
| Con_h_04 | ON938315 | |||
| Conchoderma virgatum | Con_v_02 | Pingtung, Taiwan | KC138464 | [36] |
| Con_sp_01 | Kagoshima, Japan | ON938317 | ||
| Conchoderma auritum | MT563438 | - | MT563438 | Unpublished |
| MT563441 | - | MT563441 | ||
| KU204353 | Portland, USA | KU204353 | [34] |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Conchoderma hunteri | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.038 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.041 | 0.045 | 0.044 | |
| 2. Conchoderma virgatum | 0.097 | 0.030 | 0.035 | 0.042 | 0.034 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.038 | 0.042 | 0.041 | 0.040 | |
| 3. Conchoderma auritum | 0.257 | 0.242 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.042 | 0.040 | 0.049 | 0.044 | 0.046 | |
| 4. Lepas australis | 0.278 | 0.285 | 0.300 | 0.032 | 0.033 | 0.042 | 0.034 | 0.039 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.039 | |
| 5. Lepas anserifera | 0.276 | 0.339 | 0.313 | 0.257 | 0.035 | 0.051 | 0.039 | 0.044 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.044 | |
| 6. Heteralepas japonica | 0.288 | 0.282 | 0.345 | 0.258 | 0.278 | 0.031 | 0.036 | 0.035 | 0.037 | 0.041 | 0.038 | |
| 7. Salpellum scalpellum | 0.311 | 0.298 | 0.346 | 0.334 | 0.396 | 0.255 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.039 | 0.040 | 0.036 | |
| 8. Paralepas laxus | 0.279 | 0.281 | 0.336 | 0.264 | 0.320 | 0.278 | 0.278 | 0.031 | 0.042 | 0.031 | 0.039 | |
| 9. Oxynaspis sp. | 0.278 | 0.306 | 0.320 | 0.307 | 0.353 | 0.277 | 0.281 | 0.231 | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.035 | |
| 10. Octolasmis orthogonia | 0.321 | 0.336 | 0.394 | 0.337 | 0.346 | 0.307 | 0.315 | 0.350 | 0.275 | 0.030 | 0.033 | |
| 11. Octolasmis angulata | 0.350 | 0.333 | 0.363 | 0.331 | 0.343 | 0.330 | 0.321 | 0.248 | 0.235 | 0.236 | 0.029 | |
| 12. Octolasmis cor | 0.354 | 0.331 | 0.399 | 0.304 | 0.358 | 0.313 | 0.288 | 0.306 | 0.268 | 0.272 | 0.206 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, B.K.K.; Chen, Y.-H. Distinguishing Long-Discussed Cryptic Species of the Epibiotic Goose-Neck Barnacle of the Genus Conchoderma (Thoracicalcarea: Lepadidae) with Integrative Taxonomy. Diversity 2022, 14, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080593
Chan BKK, Chen Y-H. Distinguishing Long-Discussed Cryptic Species of the Epibiotic Goose-Neck Barnacle of the Genus Conchoderma (Thoracicalcarea: Lepadidae) with Integrative Taxonomy. Diversity. 2022; 14(8):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080593
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Benny K. K., and Yu-Hsuan Chen. 2022. "Distinguishing Long-Discussed Cryptic Species of the Epibiotic Goose-Neck Barnacle of the Genus Conchoderma (Thoracicalcarea: Lepadidae) with Integrative Taxonomy" Diversity 14, no. 8: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080593
APA StyleChan, B. K. K., & Chen, Y.-H. (2022). Distinguishing Long-Discussed Cryptic Species of the Epibiotic Goose-Neck Barnacle of the Genus Conchoderma (Thoracicalcarea: Lepadidae) with Integrative Taxonomy. Diversity, 14(8), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080593






