A New Deep-Water Epilithic Green Alga, Ulvella lacustris, from an Alpine Brackish Lake in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Culture
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Analyses of ITS2 Secondary Structure
3. Results
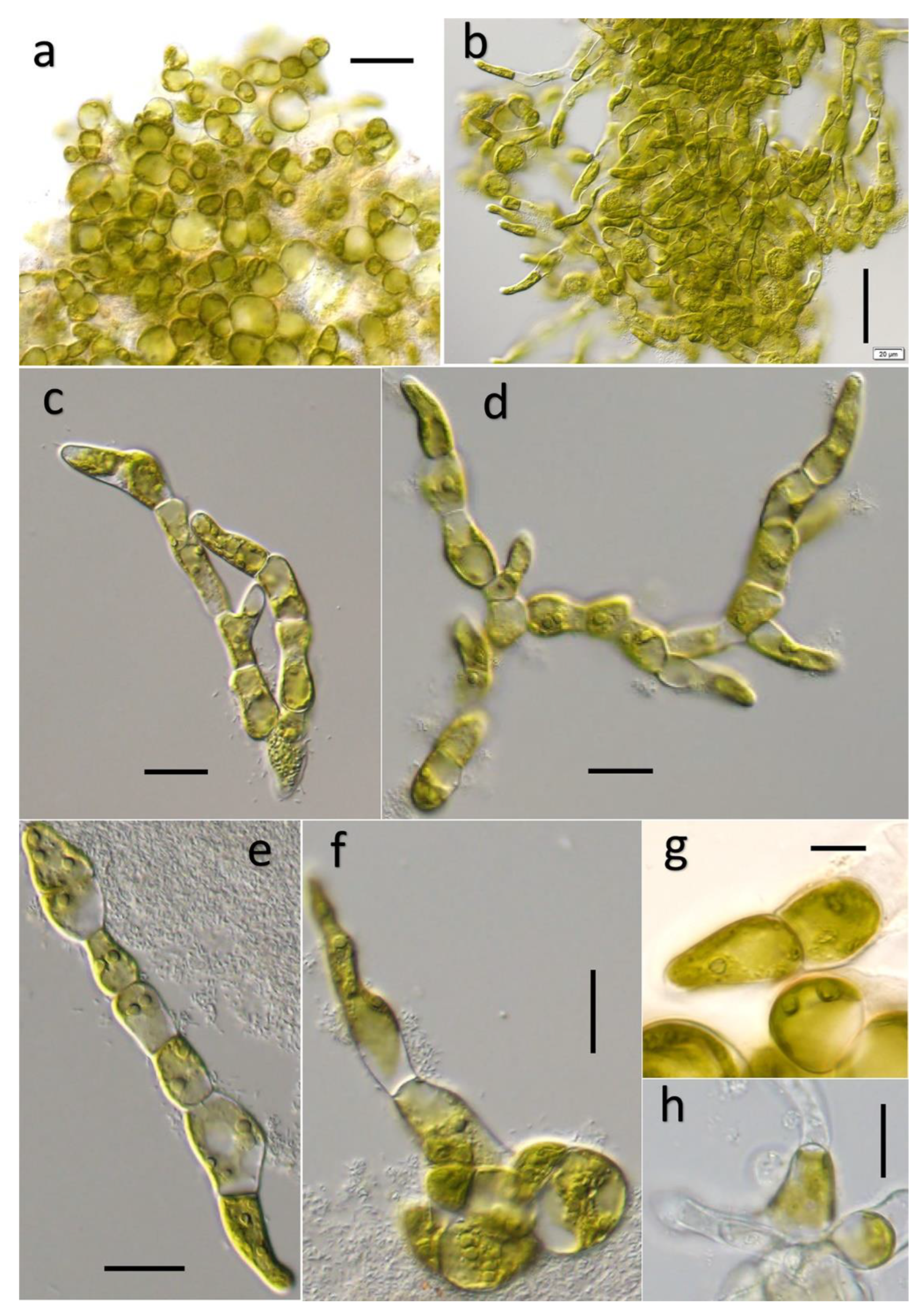
3.1. Ulvella lacustris Q. YAN et H. ZHU sp. nov.
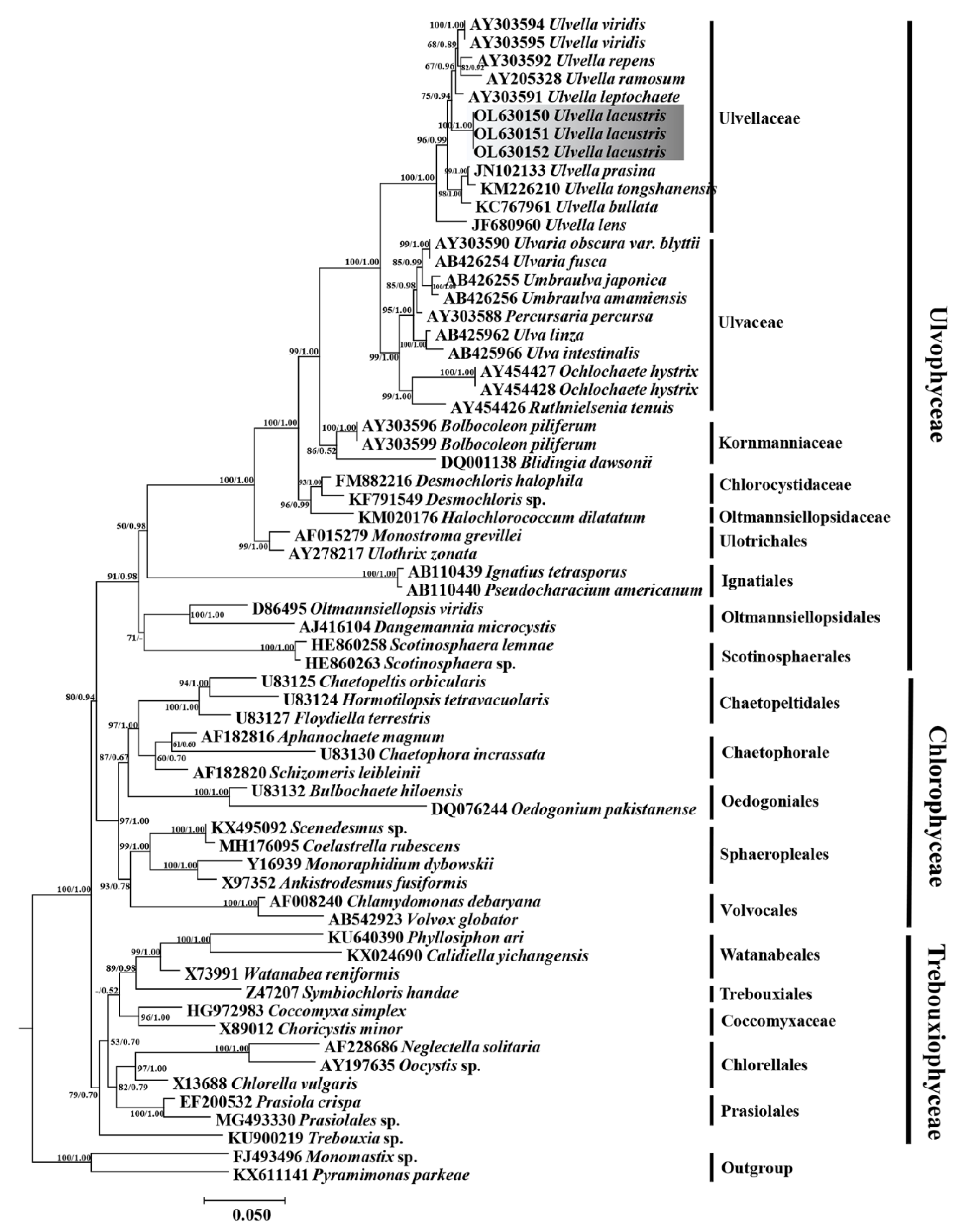
3.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
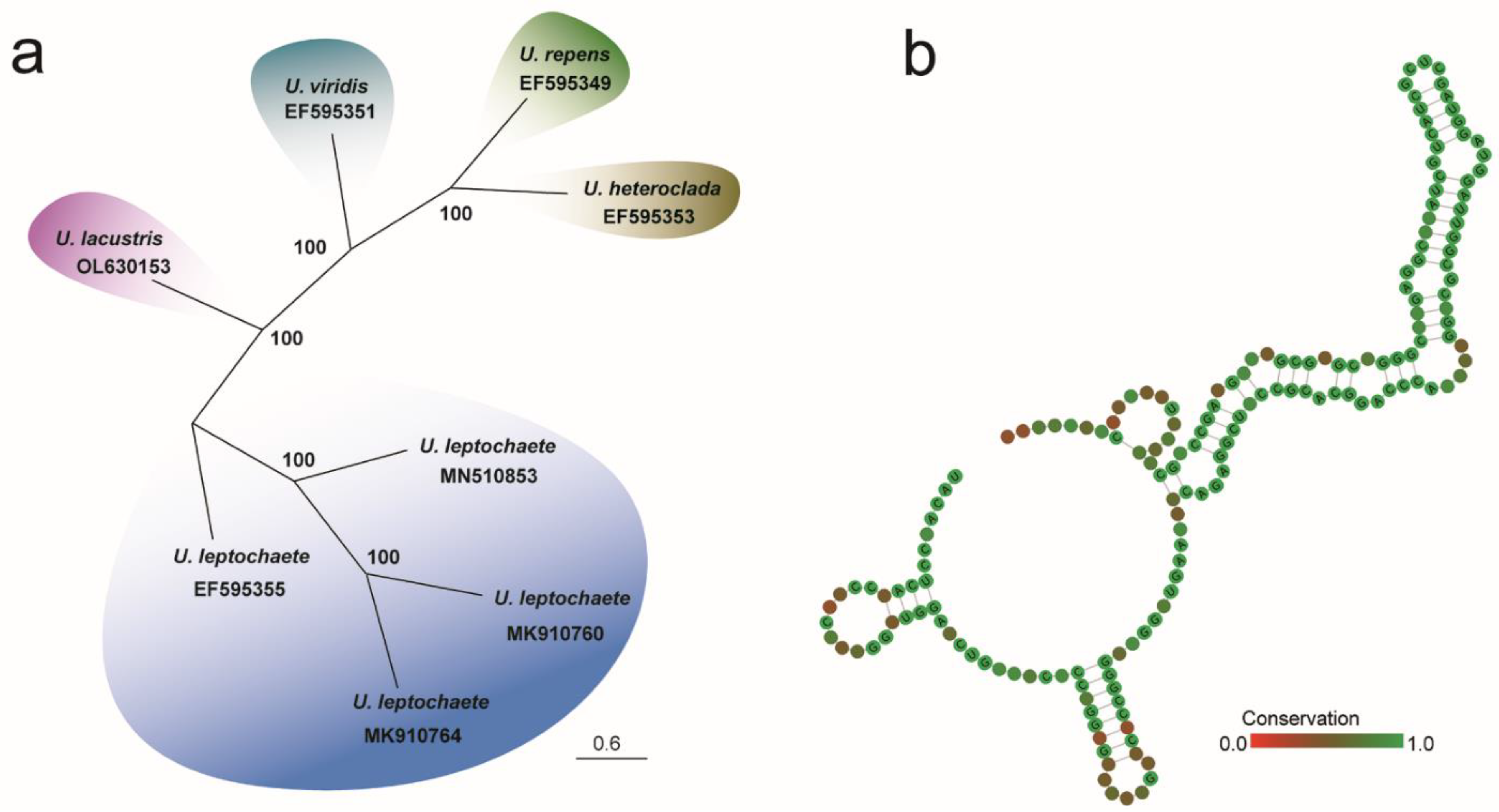
3.3. ITS2 Secondary Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedl, T. The evolution of the green algae. In Origins of Algae and Their Plastids; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1997; pp. 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Cocquyt, E.; Verbruggen, H.; Leliaert, F.; De Clerck, O. Evolution and cytological diversification of the green seaweeds (Ulvophyceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leliaert, F.; Smith, D.R.; Moreau, H.; Herron, M.D.; Verbruggen, H.; Delwiche, C.F.; De Clerck, O. Phylogeny and molecular evolution of the green algae. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2012, 31, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedeker, C.; Leliaert, F.; Zuccarello, G.C. Molecular phylogeny of the Cladophoraceae (Cladophorales, Ulvophyceae), with the resurrection of Acrocladus Nägeli and Willeella Børgesen, and the description of Lurbica gen. nov. and Pseudorhizoclonium gen. nov. J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 905–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhagen, S.; Barco, A.; Wichard, T.; Weinberger, F. Conspecificity of the model organism Ulva mutabilis and Ulva compressa (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, C.A.; Hendrixson, B.E.; Brewer, M.S.; Bond, J.E. An evaluation of sampling effects on multiple DNA barcoding methods leads to an integrative approach for delimiting species: A case study of the North American tarantula genus Aphonopelma (Araneae, Mygalomorphae, Theraphosidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 71, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlagintweit, F.; Bover-Arnal, T. The morphological adaptation of Lithocodium aggregatum Elliott (calcareous green alga) to cryptic microhabitats (Lower Aptian, Spain): An example of phenotypic plasticity. Facies 2012, 58, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škaloud, P.; Rindi, F.; Boedeker, C.; Leliaert, F. Freshwater Flora of Central Europe, Vol 13: Chlorophyta: Ulvophyceae (Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 13: Chlorophyta: Ulvophyceae) (Vol. 13); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wysor, B.; O’Kelly, C.J.; Bellows, W.K. 178 Molecular Systematics of the Ulvellaceae (Ulvales, Ulvophyceae) Inferred from Nuclear and Chloroplast DNA Sequences. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; McLachlan, J. Acrochaete marchantiae comb. nov. and Trichothyra irregularis gen. et sp. nov. with notes on other species of small filamentous green algae from St. Lucia (West Indies). Nord. J. Bot. 1986, 6, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’kelly, C.J.; Floyd, G.L. The flagellar apparatus of Entocladia viridis motile cells, and the taxonomic position of the resurrected family Ulvellaceae (Ulvales, Chlorophyta)1. J. Phycol. 1983, 19, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouan, P. Notice sur quelques especes et genres nouveaux d’algues marines de la rade de Brest. Ann. Sci. Nat. Bot. 1859, 4, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Pringsheim, N. Beiträge zur Morphologie der Meeres-Algen; Dümmler in Comm: Berlin, Germany, 1862. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, N.L. New Chlorophyceae from California; The University Press: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1909. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, W.H. Phycologia Britannica: Or a History of British Sea-Weeds, Containing Coloured Figures, Generic and Specific Characters, Synonyms, and Descriptios of All the Species of Algae Inhabiting the Shores of the British Islands; Reeve Brothers: London, UK, 1846; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, P.I.; Correa, J.A.; Cáceres, E.J. Ultrastructure and taxonomy of the genus Endophyton (Ulvales, Ulvophyceae). Eur. J. Phycol. 1997, 32, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kelly, C.J.; Wysor, B.; Bellows, W.K. Gene sequence diversity and the phylogenetic position of algae assigned to the genera Phaeophila and Ochlochaete (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta). J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; Petersen, G.; Seberg, O.; Daugbjerg, N.; Wysor, B. Revision of the genus Ulvella (Ulvellaceae, Ulvophyceae) based on morphology and tufA gene sequences of species in culture, with Acrochaete and Pringsheimiella placed in synonymy. Phycologia 2013, 52, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Leliaert, F.; Zhao, Z.J.; Xia, S.; Hu, Z.Y.; Liu, G.X. Ulvella tongshanensis (Ulvellaceae, Chlorophyta), a new freshwater species from China, and an emended morphological circumscription of the genus Ulvella. Fottea 2015, 15, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.; Guiry, G. AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication; National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, W.; Makemson, J.; Colley, S. Entocladia endozoica sp. nov., a pathogenic chlorophyte: Structure, life history, physiology, and effect on its coral host. Biol. Bull. 1984, 166, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bown, P.; Plumb, J.; Sánchez-Baracaldo, P.; Hayes, P.K.; Brodie, J. Sequence heterogeneity of green (Chlorophyta) endophytic algae associated with a population of Chondrus crispus (Gigartinaceae, Rhodophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 2003, 38, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nielsen, R.; Gunnarsson, K.; Daugbjerg, N.; Petersen, G. Description of Ulvella elegans sp. nov. and U. islandica sp. nov.(Ulvellaceae, Ulvophyceae) from Iceland–a study based on morphology of species in culture and tufA gene sequences. Eur. J. Phycol. 2014, 49, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, V.R.; Verbruggen, H. Multi-marker metabarcoding of coral skeletons reveals a rich microbiome and diverse evolutionary origins of endolithic algae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.P.; Guimaraes, S.M.; Fujii, M.T.; Batista, M.G.S.; Yoneshigue-Valentin, Y.; Yokoya, N.S. New insights on the distribution and habitat of Ulvella endozoica (Ulvellaceae, Chlorophyta) in the tropical Southwestern Atlantic, based on thallus ontogeny in culture and DNA barcoding. Mar. Biodivers. 2021, 51, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.M. Simple conditions for growth of unicellular blue-green algae on plates 1, 2. J. Phycol. 1968, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlin, L.; Elwood, H.J.; Stickel, S.; Sogin, M.L. The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene 1988, 71, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famà, P.; Wysor, B.; Kooistra, W.H.; Zuccarello, G.C. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Caulerpa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) inferred from chloroplast tufA gene. J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772. [Google Scholar]
- Manolo, G.; Stéphane, G.; Olivier, G. SeaView Version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic Tree Building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K. Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using Maximum Likelihood, evolutionary distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular ecology resources 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F.; Nielsen, R.; Bollback, J.P. Bayesian inference of phylogeny and its impact on evolutionary biology. Science 2001, 294, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibel, P.N.; Müller, T.; Dandekar, T.; Wolf, M. Synchronous visual analysis and editing of RNA sequence and secondary structure alignments using 4SALE. BMC Res. Notes 2008, 1, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Dandekar, T.; Wolf, M.; Müller, T. ProfDist: A tool for the construction of large phylogenetic trees based on profile distances. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2108–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darty, K.; Denise, A.; Ponty, Y. VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, G.W.; Kucera, H. An evaluation of rbcL, tufA, UPA, LSU and ITS as DNA barcode markers for the marine green macroalgae. Cryptogam. Algol. 2010, 31, 487. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, G.W.; McDevit, D.C. Methods for DNA barcoding photosynthetic protists emphasizing the macroalgae and diatoms. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 858, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vanormelingen, P.; Hegewald, E.; Braband, A.; Kitschke, M.; Friedl, T.; Sabbe, K.; Vyverman, W. The systematics of a small spineless desmodesmus species, d. costato-granulatus (sphaeropleales, chlorophyceae), based on ITS2 rDNA sequence analyses and cell wall morphology 1. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, C.; Paoutová, M.; Krienitz, L. Phylogenetic position of Coronastrum ellipsoideum and description of Parachlorella hussii sp. nov. Biologia 2011, 66, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, C.; Pröschold, T.; Krienitz, L. Updating the genus Dictyosphaerium and description of Mucidosphaerium gen. nov. (Trebouxiophyceae) based on morphological and molecular data. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, B.E.; Hayes, P.; Gueidan, C.; Brodie, J. A molecular phylogeny of Acrochaete and other endophytic green algae (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) 1. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
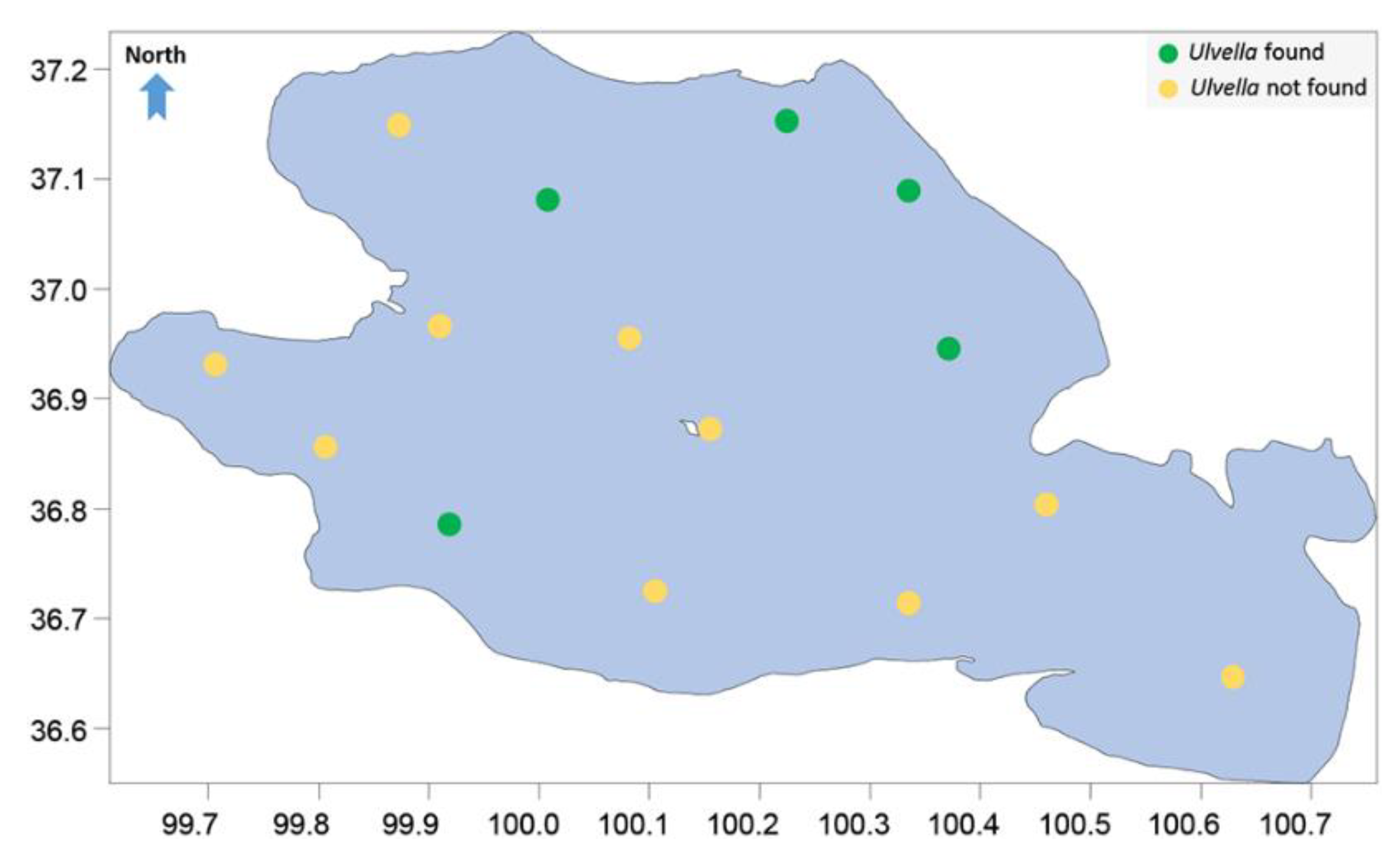


| Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Altitude (m) | DO (mg/L) | pH | Temp (°C) | EC (ms/cm) | TDS | SAL (‰) | SD (cm) | Depth (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QHH-4 | 36.9598 | 100.3865 | 3196.10 | 7.48 | 9.12 | 13.4 | 17.55 | 9.98 | 10.4 | 400 | 22.4 |
| QHH-5 | 37.1322 | 100.2354 | 3196.25 | 7.99 | 9.13 | 11.7 | 17.67 | 10.04 | 10.45 | 370 | 17.6 |
| QHH-8 | 37.0248 | 100.0906 | 3196.09 | 7.63 | 9.19 | 12.2 | 17.42 | 10.01 | 10.43 | 455 | 28.1 |
| QHH-11 | 36.7487 | 99.8509 | 3196.18 | 6.77 | 9.1 | 16 | 17.22 | 9.76 | 10.08 | 350 | 14.6 |
| QHH-15 | 37.07059 | 100.3498 | 3196.27 | 7.42 | 9.12 | 13.1 | 17.39 | 10.05 | 10.46 | 370 | 16.5 |
| Dataset | 18S | tufA |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment length Number of sequences | 1655 64 | 855 58 |
| Parsimony-informative sites | 496 | 243 |
| Invariant sites | 968 | 542 |
| Best-fit model | TN93+G+I | T92+G+I |
| Base frequency (A/C/G/T) | 0.25/0.21/0.28/0.26 | 0.32/0.12/0.35/0.21 |
| Saturation test (Iss/Iss.c) | 0.123 < 0.836 | 0.080 < 0.815 |
| U.lacustris OL630153 | U.heteroclada EF595353 | U.leptochaete EF595355 | U.repens EF595349 | U.viridis EF595351 | U.leptochaete MK910764 | U.leptochaete MK910760 | U.leptochaete MN510853 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.lacustris OL630153 | 0/0 | 2/2 | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0/2 | 4/2 | 4/2 | 1/2 |
| U.heteroclada EF595353 | 2/2 | 0/0 | 2/0 | 2/4 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 4/0 | 3/0 |
| U.leptochaete EF595355 | 1/3 | 2/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/0 |
| U.repens EF595349 | 2/3 | 2/4 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 3/1 | 3/1 | 2/1 |
| U.viridis EF595351 | 0/2 | 2/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 3/0 | 3/0 | 1/0 |
| U.leptochaete MK910764 | 4/2 | 4/0 | 0/0 | 3/1 | 3/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/0 |
| U.leptochaete MK910760 | 4/2 | 4/0 | 0/0 | 3/1 | 3/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/0 |
| U.leptochaete MN510853 | 1/2 | 3/0 | 1/0 | 2/1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 0/0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Q.; Dai, Q.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Zhu, H. A New Deep-Water Epilithic Green Alga, Ulvella lacustris, from an Alpine Brackish Lake in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Diversity 2022, 14, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080594
Yan Q, Dai Q, Liu B, Liu G, Zhu H. A New Deep-Water Epilithic Green Alga, Ulvella lacustris, from an Alpine Brackish Lake in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Diversity. 2022; 14(8):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080594
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Qiufeng, Qingyu Dai, Benwen Liu, Guoxiang Liu, and Huan Zhu. 2022. "A New Deep-Water Epilithic Green Alga, Ulvella lacustris, from an Alpine Brackish Lake in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau" Diversity 14, no. 8: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080594
APA StyleYan, Q., Dai, Q., Liu, B., Liu, G., & Zhu, H. (2022). A New Deep-Water Epilithic Green Alga, Ulvella lacustris, from an Alpine Brackish Lake in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Diversity, 14(8), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080594






