A Review of Coastal Anthropogenic Impacts on Mytilid Mussel Beds: Effects on Mussels and Their Associated Assemblages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Selection
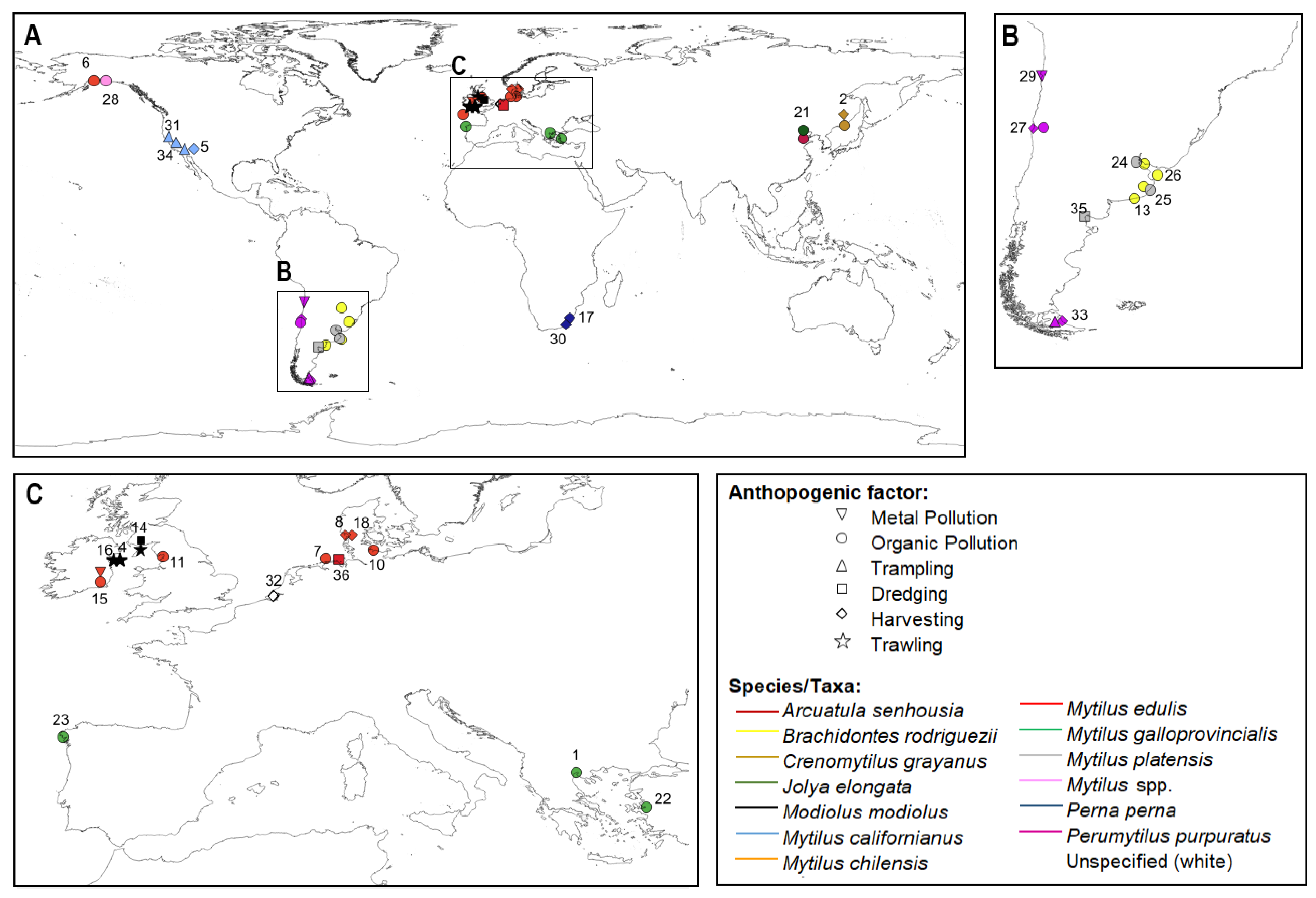
3. Geographic Area and Taxa
4. Anthropogenic Perturbations
4.1. Pollution Impacts
4.1.1. Organic Compounds
4.1.2. Heavy Metals
4.2. Small- to Medium-Scale Physical Impacts
4.2.1. Harvesting
4.2.2. Trampling
4.3. Large-Scale Physical Impacts
4.3.1. Dredging
4.3.2. Trawling
5. Synthesis and Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antoniadou, C.; Sarantidis, S.; Chintiroglou, C. Small-scale spatial variability of zoobenthic communities in a commercial Mediterranean port. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2011, 91, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galysheva, Y.A. Current state and long-term changes of the Crenomytilus grayanus community in Vostok Bay, Sea of Japan. Russ. J. Ecol. 2008, 39, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, P.; Ramos-Oliveira, C.; Sampaio, L.; Rubal, M. The role of urbanisation in affecting Mytilus galloprovincialis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariñas-Franco, J.M.; Allcock, A.L.; Roberts, D. Protection alone may not promote natural recovery of biogenic habitats of high biodiversity damaged by mobile fishing gears. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 135, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; Fong, P.; Ambrose, R.F. The Impacts of Human Visitation on Mussel Bed Communities Along the California Coast: Are Regulatory Marine Reserves Effective in Protecting These Communities? Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, D.C.; Houghton, J.P.; Driskell, W.B. Effects of shoreline treatment methods on intertidal biota in Prince William Sound. In Proceedings of the International Oil Spill Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 29 March–1 April 1993; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 1993, pp. 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Reichert, K.; Buchholz, F. Changes in the macrozoobenthos of the intertidal zone at Helgoland (German Bight, North Sea): A survey of 1984 repeated in 2002. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2006, 60, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesen, W.; Reise, K. Macrobenthos of the subtidal Wadden Sea: Revisited after 55 years. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1982, 35, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestoso, I.; Arenas, F.; Rubal, M.; Veiga, P.; Peña, M.; Olabarria, C. Shifts from native to non-indigenous mussels: Enhanced habitat complexity and its effects on faunal assemblages. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 90, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, K. On the influence of sewage pollution on inshore benthic communities in the South of Kiel Bay. Helgoländer Wiss. Meeresunters. 1975, 27, 408–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, T.P.; Smith, E.L.; Donkin, P.; Barnaby, D.L.; Rowland, S.J. Measurements of sublethal effects on individual organisms indicate community-level impacts of pollution. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 41, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintino, V.; Azevedo, A.; Magalhães, L.; Sampaio, L.; Freitas, R.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Elliott, M. Indices, multispecies and synthesis descriptors in benthic assessments: Intertidal organic enrichment from oyster farming. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 110, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elías, R.; Rivero, M.S.; Palacios, J.R.; Vallarino, E.A. Sewage-induced disturbance on polychaetes inhabiting intertidal mussel beds of Brachidontes rodriguezii off Mar del Plata (SW Atlantic, Argentina). Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.; Fariñas-Franco, J.M.; Gell, F.R.; Holt, R.H.F.; Holt, T.; Lindenbaum, C.; Porter, J.S.; Seed, R.; Skates, L.R.; Stringell, T.B.; et al. The Substantial First Impact of Bottom Fishing on Rare Biodiversity Hotspots: A Dilemma for Evidence-Based Conservation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Brooks, P.R.; Clough, R.; Fisher, A.S.; Pinto, M.M.; Crowe, T.P. Simulating regimes of chemical disturbance and testing impacts in the ecosystem using a novel programmable dosing system. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 7, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magorrian, B.H.; Service, M. Analysis of underwater visual data to identify the impact of physical disturbance on horse mussel (Modiolus modiolus) beds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 36, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, V.J.; McQuaid, C.D.; Nakin, M.D.V. Marine protected areas export larvae of infauna, but not of bioengineering mussels to adjacent areas. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saier, B. Subtidal and intertidal mussel beds (Mytilus edulis L.) in the Wadden Sea: Diversity differences of associated epifauna. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2002, 56, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Register of Marine Species. At VLIZ. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Cárdenas, L.; Leclerc, J.-C.; Bruning, P.; Garrido, I.; Détrée, C.; Figueroa, A.; Astorga, M.; Navarro, J.M.; Johnson, L.E.; Carlton, J.T.; et al. First mussel settlement observed in Antarctica reveals the potential for future invasions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.N.; Liu, X.S.; Tu, L.H.; Yu, Z.S. Changes in the shelf macrobenthic community over large temporal and spatial scales in the Bohai Sea, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 67, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çinar, M.E.; Katagan, T.; Koçak, F.; Öztürk, B.; Ergen, Z.; Kocatas, A.; Önen, M.; Kirkim, F.; Bakir, K.; Kurt, G.; et al. Faunal assemblages of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in and around Alsancak Harbour (Izmir Bay, eastern Mediterranean) with special emphasis on alien species. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 71, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Regueira, X.; Tato, R.; Moreira, J.; Urgorri, V. Temporal evolution of polychaete assemblages on intertidal hard substrata at two localities of the Galician coast after the ‘Prestige’ oil spill. Thalassas 2010, 26, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Adami, M.L.; Tablado, A.; Gappa, J.L. Spatial and temporal variability in intertidal assemblages dominated by the mussel Brachidontes rodriguezii (d’Orbigny, 1846). Hydrobiologia 2004, 520, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallarino, E.A.; Rivero, M.S.; Gravina, M.C.; Elías, R. The community-level response to sewage impact in intertidal mytilid beds of the Southwestern Atlantic, and the use of the Shannon index to assess pollution. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanog. 2002, 37, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.A.; Jaubet, M.L.; Garaffo, G.V.; Elías, R. Spatial and long-term analyses of reference and sewage-impacted sites in the SW Atlantic (38° S, 57° W) for the assessment of sensitive and tolerant polychaetes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia, N.; Thiel, M. Effects of point-source nutrient addition and mussel removal on epibiotic assemblages in Perumytilus purpuratus beds. J. Sea Res. 2006, 56, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Houghton, J.P.; Fukuyama, A.K.; Lees, D.C.; Driskell, W.B.; Shigenaka, G.; Mearns, A.J. Impacts on Intertidal Epibiota: Exxon Valdez Spill and Subsequent Cleanup. In Proceedings of the International Oil Spill Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 29 March–1 April 1993; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 1993, pp. 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo, J.; Orellana, I.F.; Guiñez, R. Evaluación experimental de la toxicidad de cobre in situ sobre la fauna asociada a Perumytilus purpuratus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae), un ingeniero ecosistémico. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanog. 2010, 45, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasiak, T.A.; Field, J.G. Community-level attributes of exploited and non-exploited rocky infratidal macrofaunal assemblages in Transkei. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995, 185, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, K.A.; Gowing, M.M. A quantitative assessment of human trampling effects on a rocky intertidal community. Mar. Environ. Res. 1982, 7, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meire, P.M.; Dereu, J. Use of the Abundance/Biomass Comparison Method for Detecting Environmental Stress: Some Considerations Based on Intertidal Macrozoobenthos and Bird Communities. J. Appl. Ecol. 1990, 27, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, J.A.; Curelovich, J.N.; Fernandez, V.M.; Thatje, S.; Lovrich, G.A. Effects of physical disturbance on a sub-Antarctic middle intertidal bivalve assemblage. Mar. Biol. Res. 2012, 8, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Werfhorst, L.C.; Pearse, J.S. Trampling in the rocky intertidal of central California: A follow-up study. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2007, 81, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Morsan, E.M. Impact on biodiversity of scallop dredging in San Matías Gulf, northern Patagonia (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 2009, 619, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhs, F.; Riese, K. Epibenthic fauna dredged from tidal channels in the Wadden Sea of Schleswig-Holstein: Spatial patterns and a long-term decline. Helgolander Meeresun. 1997, 51, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amoroso, R.O.; Pitcher, C.R.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; McConnaughey, R.A.; Parma, A.M.; Suuronen, P.; Eigaard, O.R.; Bastardie, F.; Hintzen, N.T.; Althaus, F.; et al. Bottom trawl fishing footprints on the world’s continental shelves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10275–E10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.D.; Stenberg, C.; Støttrup, J.G.; Poulsen, L.K.; Christensen, H.T.; Dolmer, P.; Røjbek, M.; Thorsen, S.W.; Holmer, M.; Deurs, M.V.; et al. Establishment of blue mussel beds to enhance fish habitats. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 783–798. [Google Scholar]
| Article | Mussel Species | Habitat | Disturbance | Sampling Period | Metazoan Taxa | Mussel Response | Impact on Fauna | Indices and Statistics | Other Measures | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | Mytilus galloprovincialis | Intertidal, Subtidal: Rock, Sand | Organic pollution (hydrocarbons and sewage) | 2004 | 88 spp. [only mussel beds]: Arthropoda (20.5%); Echinodermata (1.1%), Mollusca (18.2%), Annelida (36.4%), Other (23.8%) | (+) | Moderate impact | N, S, H, J, ANOVA, ANOSIM, nMDS | - | Thermaikos Gulf, Northern Aegean Sea, Greece |
| [2] | Crenomytilus grayanus | Subtidal: Rock, Sand | Organic pollution (sewage), Harvesting | 2000–2004 | 138 spp.: Arthropoda (11.6%), Echinodermata (11.6%), Mollusca (23.2%), Annelida (32.6%), Other (21.0%) | (−) | High impact | N, S, H, J | Biomass, trophic guilds | Vostok Bay, Sea of Japan, Russia |
| [4] | Modiolus modiolus | Subtidal: Mud, Rock, Shells | Trawling | 2010 | 273 spp.: Annelida (34.1%), Arthropoda (17.9%), Echinodermata (6.2%), Mollusca (17.2%), Other (24.6%) | (−) | High impact | N, S, H, J, Margalef, PERMANOVA, PERMDISP, SIMPER | - | Strangford Lough, Ireland |
| [5] | Mytilus californianus | Intertidal: Rock | Harvesting, Trampling | not specified | 22 spp. [highest species richness in a site]: not specified | (−) | Low impact | N, S, H, J, t-test | Biomass, cover, size, thickness | CA, USA |
| [6] | Mytilus edulis | Intertidal: Rock | Organic pollution (hydrocarbons) | 1989 | 18 spp. [highest species richness in a site]: not specified | (−) | High impact | N, S | Cover | Prince William Sound, AK, USA |
| [7] | Mytilus edulis | Intertidal: Rock | Unspecified pollutants Alien species | 2002 | 154 spp.: Annelida (18.2%), Arthropoda (27.9%), Echinodermata (1.9%), Mollusca (18.2%), Other (33.8%) | - | Moderate impact | S, Conspicuousness, Cluster Analysis, nMDS | - | Helgoland, German Bight, North Sea |
| [8] | Mytilus edulis | Subtidal: Gravel, Mud, Rock, Sand, Shell | Human interference: Harvesting (Ostrea edulis), | 1980 | 89 spp.: not specified | (+) | High impact | N, S, Cluster Analysis, Linear Regression | - | Island of Sylt, German Bight, North Sea |
| [10] | Mytilus edulis | Subtidal: Mud, Sand | Organic pollution (sewage) | 1971, 1972 | 38 spp. [only mussel beds]: Annelida (44.7%), Arthropoda (28.9%); Mollusca (21.1%), Echinodermata (2.6%), Other (2.6%) | (-) | Moderate impact | N, S, H, J, Simpson | Biomass | Kiel Bay, Baltic Sea |
| [11] | Mytilus edulis | Intertidal: Rock, Sand, Shells | Organic pollution (hydrocarbons) | 1999 | 57 spp.: Annelida (22.8%), Arthropoda (35.1%), Mollusca (31.6%), Other (10.5%) | (−) | Moderate impact | S, H, BIOENV, MANOVA, nMDS, SIMPER | - | West Coast of UK |
| [13] | Brachidontes rodriguezii | Intertidal: Rock, Sand | Organic pollution (sewage) | 1997–2000 | 12 spp.: only Polychaeta | (−) | Moderate impact | ANOSIM, SIMPER | - | Mar del Plata, Argentina |
| [14] | Modiolus modiolus | Subtidal: Rock | Dredging, Trawling | 2007–2009, 2012 | 29 spp.: not specified | (−) | High impact | N, S, H, J, Margalef, ANOVA, nMDS, PERMANOVA, PERMDISP, SIMPER | - | Isle of Man and Wales, UK |
| [15] | Mytilus edulis | Subtidal: Artificial structures | Metal and Organic pollution (experimental) | 2010 | not specified | (−) | High impact | ANOVA | - | Malahide Marina, Ireland |
| [16] | Modiolus modiolus | Subtidal: Mud, Rock, Shells | Trawling | not specified | not specified | (−) | High impact | Cluster Analysis, DECORANA | - | Strangford Lough, Ireland |
| [17] | Perna perna | Intertidal: Rock | Harvesting | 2008 | not specified | (−) | Moderate impact | N, S, PERMANOVA | Cover | Transkei, South Africa |
| [18] | Mytilus edulis | Intertidal, Subtidal: Rock | Harvesting (subtidal) | 1997, 1998 | 19 spp. [Intertidal], 22 spp. [Subtidal]: not specified | (−) | Moderate impact | N, S, H, J, Sørensen’s index, Renkon’s index, ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney U-Test | - | Island of Sylt, German Bight, North Sea |
| [21] | Arcuatula senhousia, Jolya elongata | Subtidal: Mud, Sand | Organic pollution (unspecified), | 1985–1987, 1997–1999 | 460 spp.: not specified | (−) | Moderate impact | N, S, H, J, ANOSIM, nMDS | - | Bohai Sea, China |
| [22] | Mytilus galloprovincialis | Intertidal: Artificial structures | Organic pollution (unspecified) | 2004 | 155 spp.: Annelida (43.2%); Arthropoda (18.1%) Echinodermata (0.6%), Mollusca (9.7%), Other (28.4%) | (+) | Moderate impact | N, S, H, J, Margalef, ANOVA, ANOSIM, BIOENV, nMDS, SIMPER | Biomass | Izmir Bay, Eastern Mediterranean, Turkey |
| [23] | Mytilus galloprovincialis | Intertidal: Rock | Organic pollution (hydrocarbons) | 2004, 2005 | 104 spp.: only Annelida | - | Moderate impact | N, S, H, nMDS | - | Caldebarcos and O Segaño, Galicia, Spain |
| [24] | Brachidontes rodriguezii, Mytilus platensis | Intertidal: Rock, Sand | Organic pollution (sewage) | 1999, 2000 | 24 spp.: Annelida (33.3%), Arthropoda (29.2%), Mollusca (20,8%), Other (16.7%) | (+) | Moderate impact | S, H, Margalef, ANOVA, ANOSIM, nMDS | Biomass | Quequén and Necoche, Argentina |
| [25] | Brachidontes rodriguezii, Mytilus platensis | Intertidal: Rock, Sand | Organic pollution (sewage) | 1997 | 43 spp.: not specified | (−) | Moderate impact | N, S, H, J, Jack-Knife test | - | Mar del Plata, Argentina |
| [27] | Perumytilus purpuratus | Intertidal: Rock | Harvesting, Organic enrichment (experimental) | 2004 | 45 spp.: Annelida (17.8%), Arthropoda (31.1%), Mollusca (35.6%), Echinodermata (4.4%) Other (11.1%) | - | Moderate impact | N, S, ANOVA, ANOSIM, SIMPER | Trophic guilds | Bahía Totoralillo, Northern-Central Chile |
| [28] | Mytilus sp. | Intertidal: Rock, Heterogenous sediment | Organic pollution (hydrocarbons), | 1990, 1991 | 42 spp. [highest species richness in a site]: not specified | (−) | High impact | N, S, H, ANOVA | Cover | Prince William Sound, AK, USA |
| [29] | Perumytilus purpuratus | Intertidal: Rock | Metal pollution (experimental) | 2007 | 46 spp.: Annelida (30.4%), Arthropoda (19.6%), Echinodermata (8.7%), Mollusca (23.9), Other (17.4%) | null | Moderate impact | S, H, J | - | Bahia San Jorge, Northern Chile |
| [30] | Perna perna | Intertidal: Rock | Harvesting | not specified | not specified | (−) | Low impact | N. S, H, nMDS | Biomass, trophic guilds | Transkei, South Africa |
| [31] | Mytilus californianus | Intertidal: Rock | Trampling | 1977, 1978 | 67 spp.: not specified | null | Low impact | N, S, H, Dominance curves, Kruskall-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney U-Test | - | Santa Cruz, CA, USA |
| [32] | unspecified | Intertidal: Mud, Sand | Harvesting | 1981–1984, 1987 | 44 spp. [unpolluted site]: Annelida (50.0%), Arthropoda (20.4%), Echinodermata (3.7%), Mollusca (25.9%) | (−) | Moderate impact | ABC K-Dominance curves | - | Netherlands and Belgium |
| [33] | Perumytilus purpuratus, Mytilus chilensis | Intertidal: Mud, Rock, Sand | Harvesting, Trampling (experimental) | 2001 | not specified | (−) | Moderate impact | ANOVA, Mann-Whitney U-Test | Biomass, cover, size | Rio Grande, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina |
| [34] | Mytilus californianus | Intertidal: Rock | Trampling | 1995 | 20 spp. [highest species richness in a site]: not specified | (−) | Low impact | S, H, ANOVA, ANCOVA, t-test | Cover | Santa Cruz, CA, USA |
| [35] | Mytilus platensis | Subtidal: Gravel, Mud, Sand, Shells | Dredging | 1986–1997 | 46 spp. [highest species richness in a site]: not specified | (−) | Moderate impact | S, ANOSIM, MDS | - | Golfo de San Matías, Argentina |
| [36] | Mytilus edulis | Subtidal: Gravel, Sand, Shells | Dredging | 1988, 1992 | 42 spp.: Arthropoda (23.8%), Echinodermata (4.8%), Mollusca (21.4%), Annelida (4.8%), Other (45.2%) | (+) | High impact | Mann-Whitney U-Test | - | Schleswig-Holstein, Wadden Sea, North Sea |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sampaio, L.; Moreira, J.; Rubal, M.; Guerrero-Meseguer, L.; Veiga, P. A Review of Coastal Anthropogenic Impacts on Mytilid Mussel Beds: Effects on Mussels and Their Associated Assemblages. Diversity 2022, 14, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050409
Sampaio L, Moreira J, Rubal M, Guerrero-Meseguer L, Veiga P. A Review of Coastal Anthropogenic Impacts on Mytilid Mussel Beds: Effects on Mussels and Their Associated Assemblages. Diversity. 2022; 14(5):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050409
Chicago/Turabian StyleSampaio, Leandro, Juan Moreira, Marcos Rubal, Laura Guerrero-Meseguer, and Puri Veiga. 2022. "A Review of Coastal Anthropogenic Impacts on Mytilid Mussel Beds: Effects on Mussels and Their Associated Assemblages" Diversity 14, no. 5: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050409
APA StyleSampaio, L., Moreira, J., Rubal, M., Guerrero-Meseguer, L., & Veiga, P. (2022). A Review of Coastal Anthropogenic Impacts on Mytilid Mussel Beds: Effects on Mussels and Their Associated Assemblages. Diversity, 14(5), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050409









