Stripes Matter: Integrative Systematics of Coryphellina rubrolineata Species Complex (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) from Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
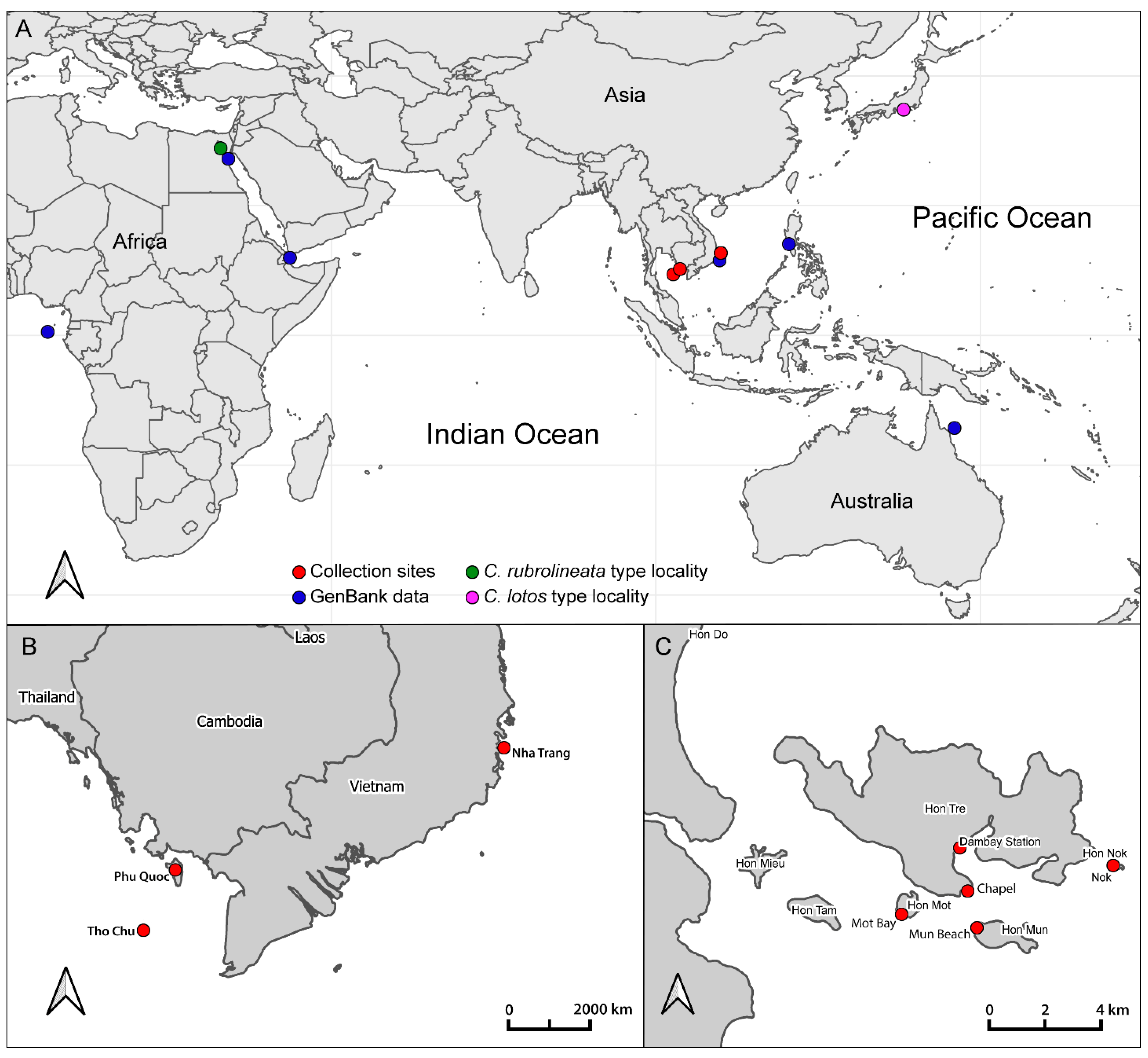
2.1. Collection Data and Community Descriptions
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Data Processing and Phylogenetic Reconstruction
2.4. Species Delimitation
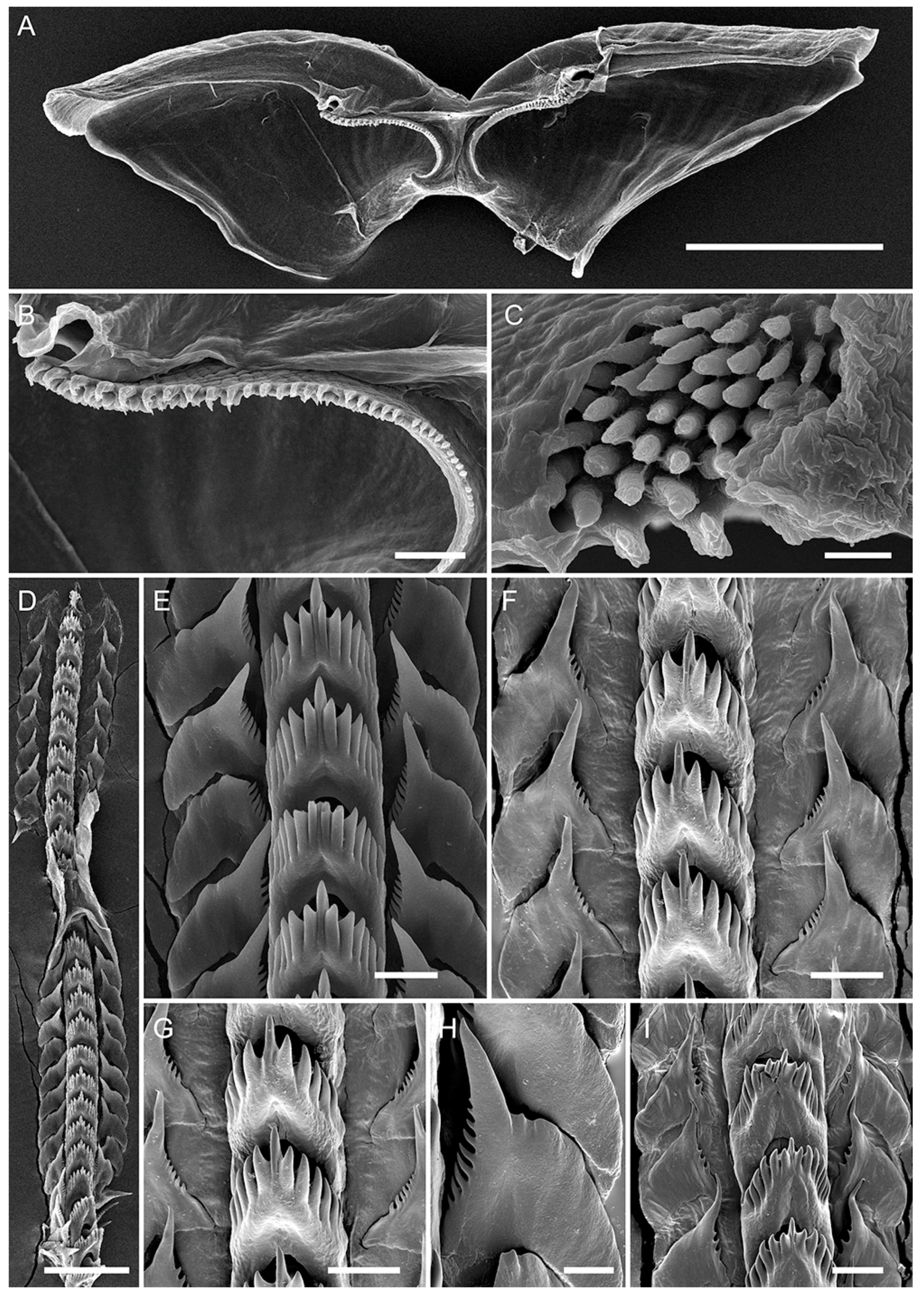
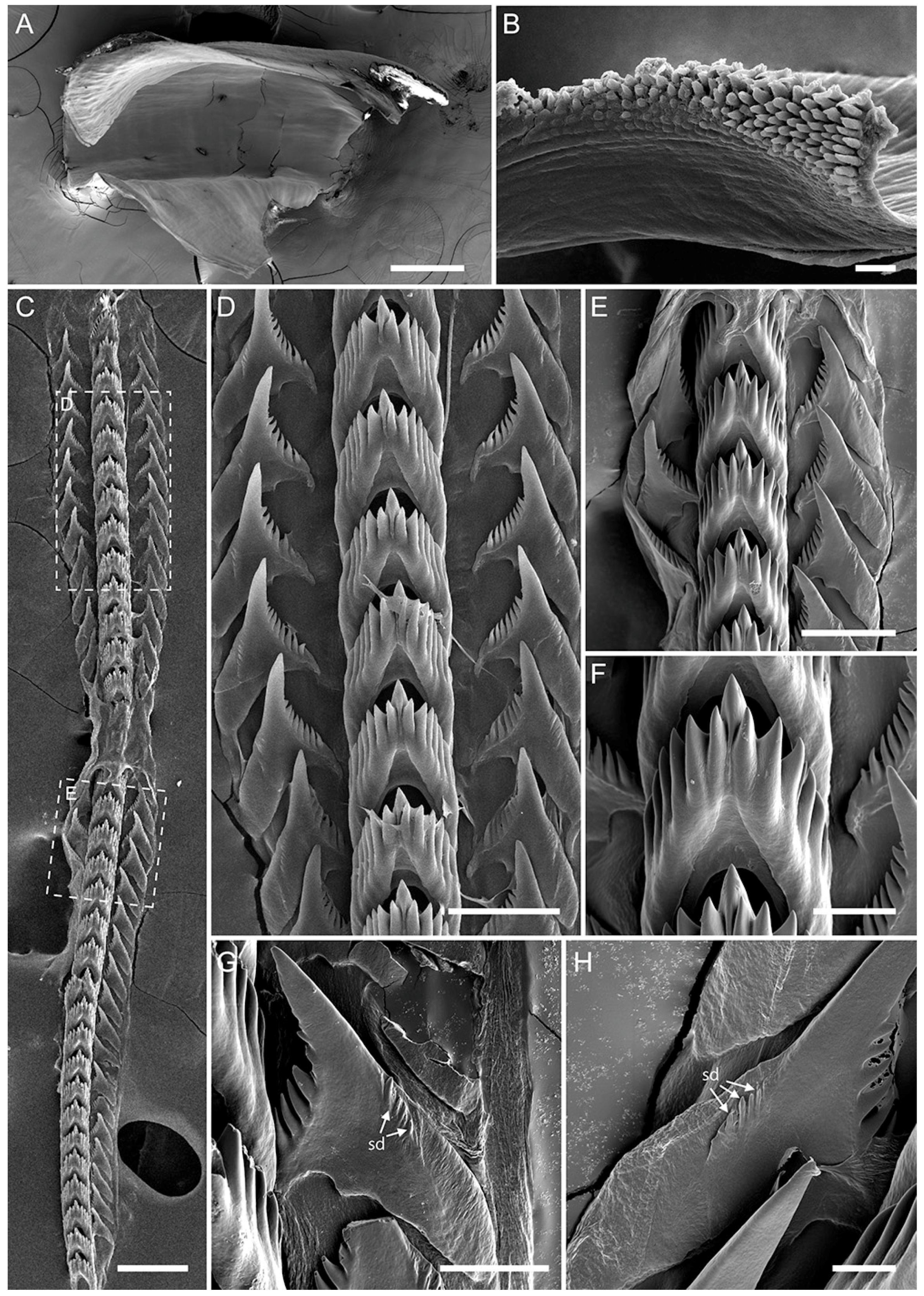
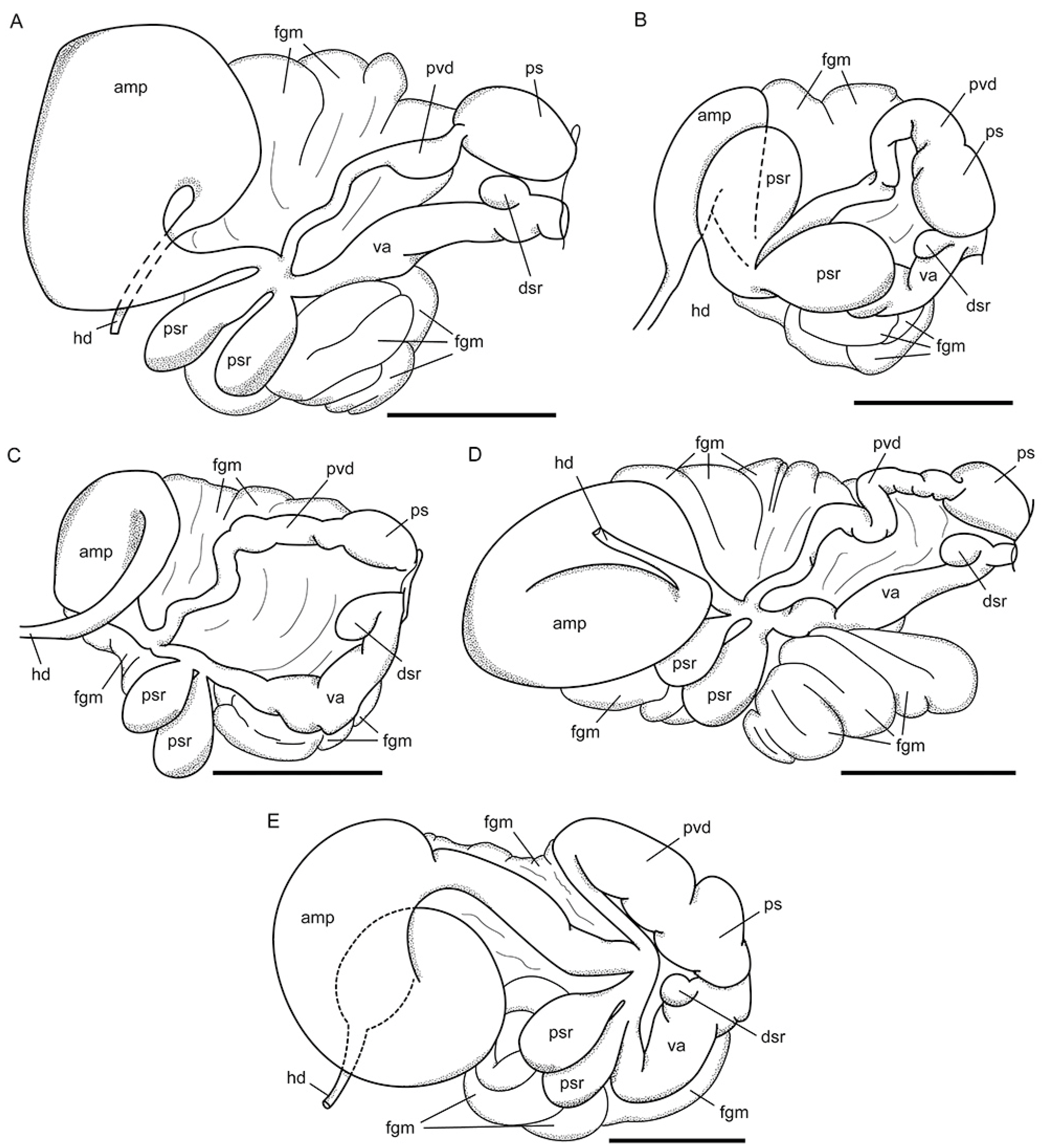
2.5. Morphological Studies
2.6. Nomenclatural Acts
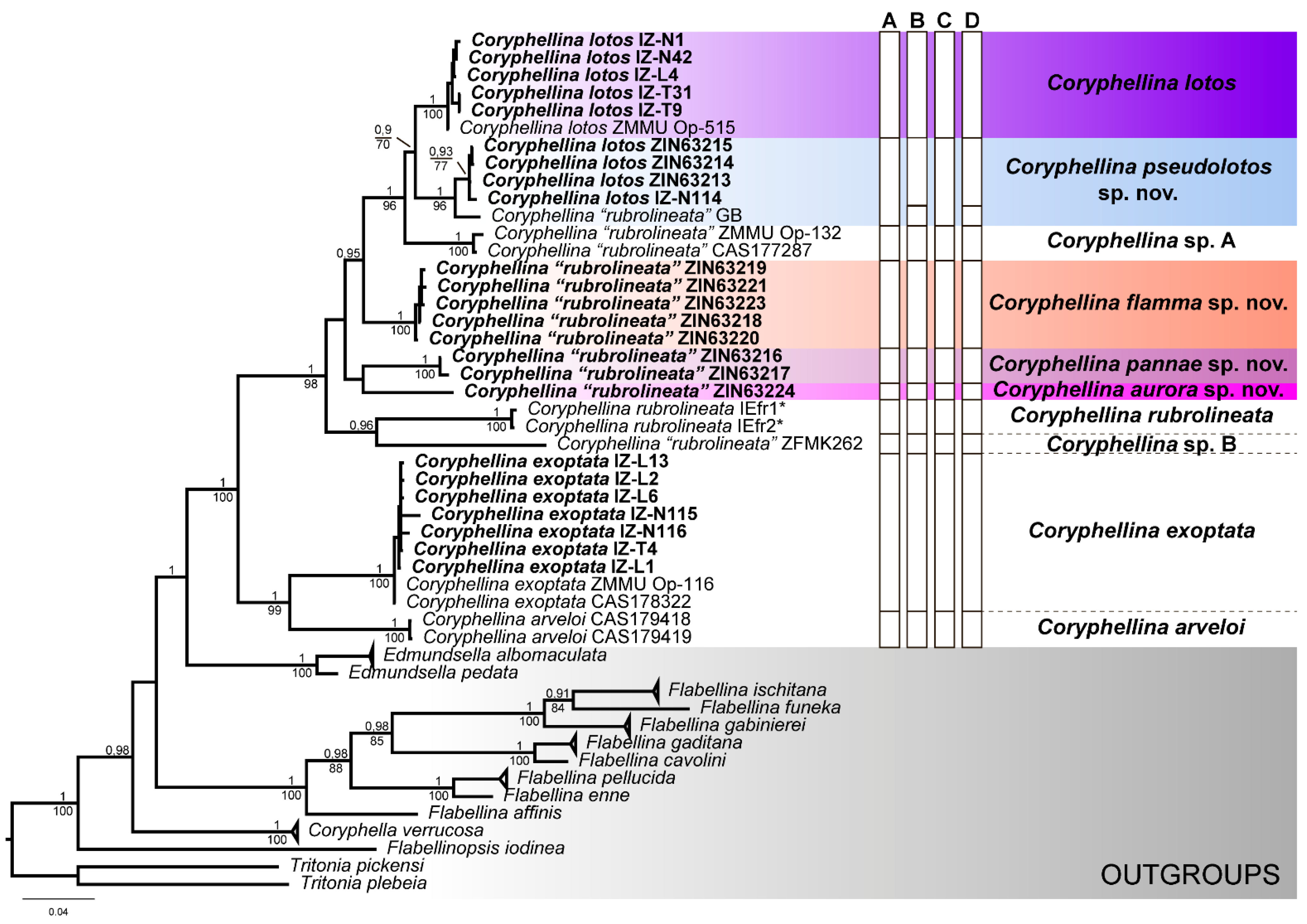
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2. Species Delimitation
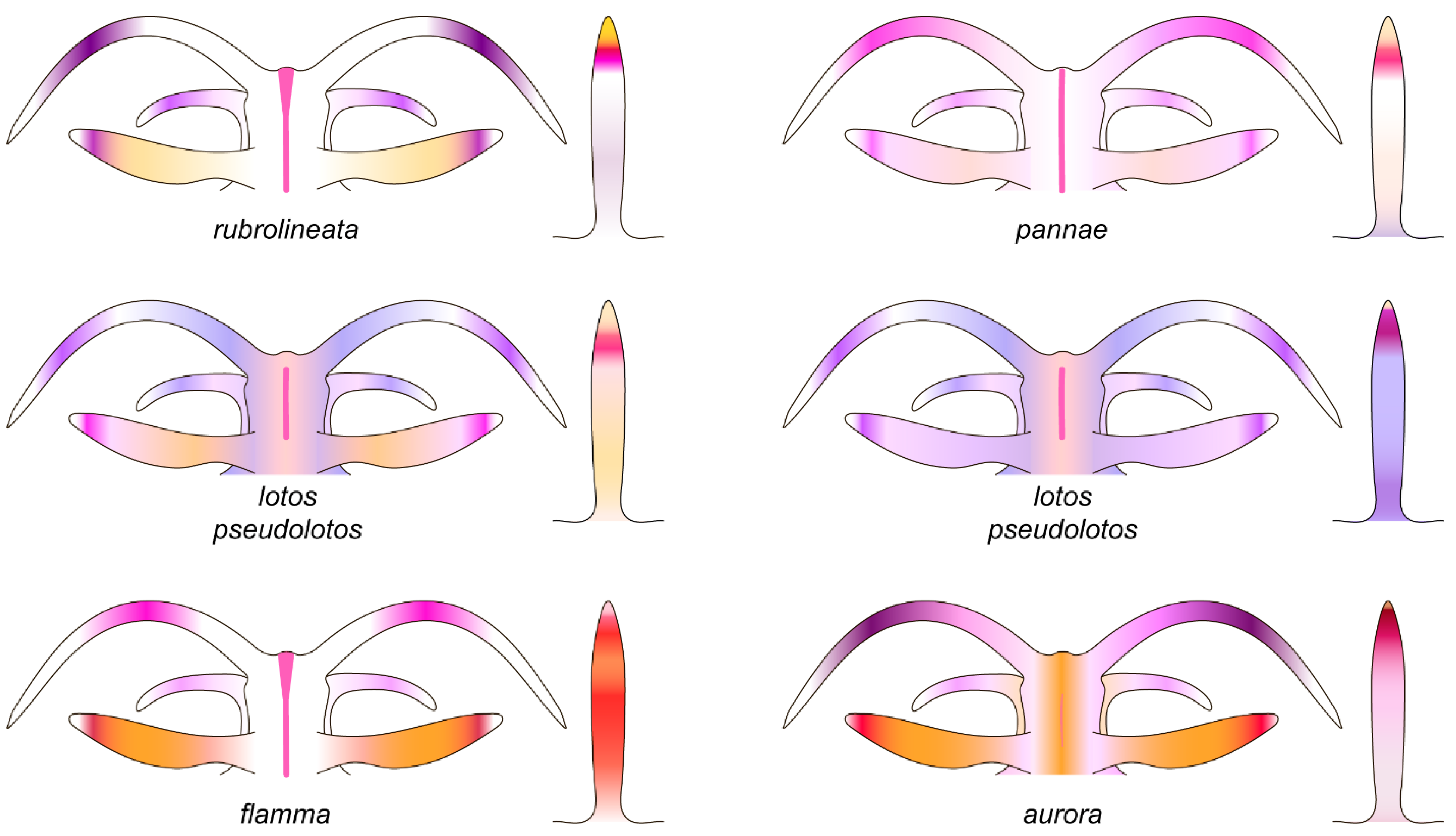
3.3. Systematics
3.3.1. Coryphellina lotos Korshunova, Martynov, Bakken, Evertsen, Fletcher, Mudianta, Saito, Lundin, Schrödl, and Picton, 2017
3.3.2. Coryphellina pseudolotos sp. nov.

3.3.3. Coryphellina pannae sp. nov.
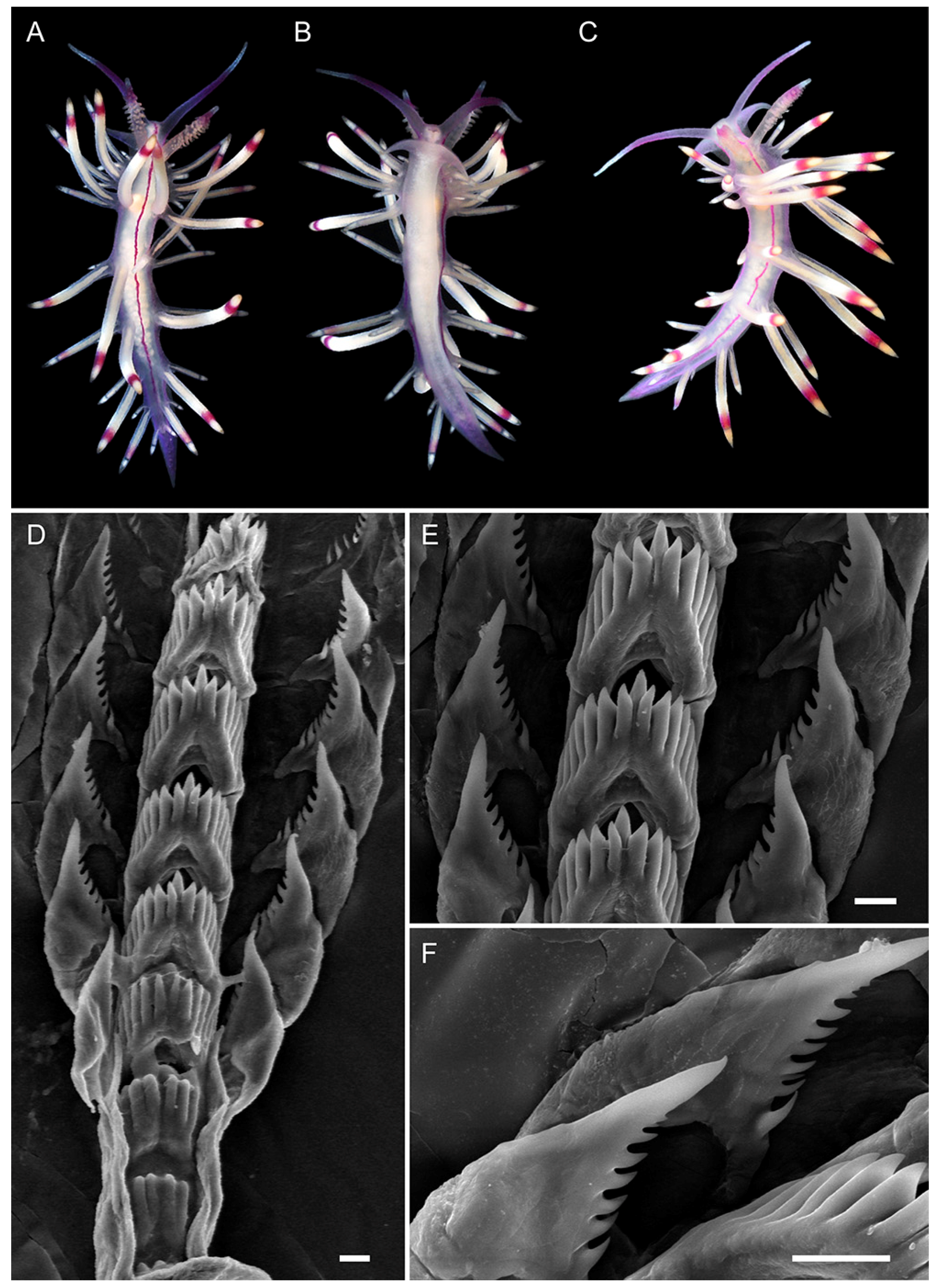
3.3.4. Coryphellina flamma sp. nov.
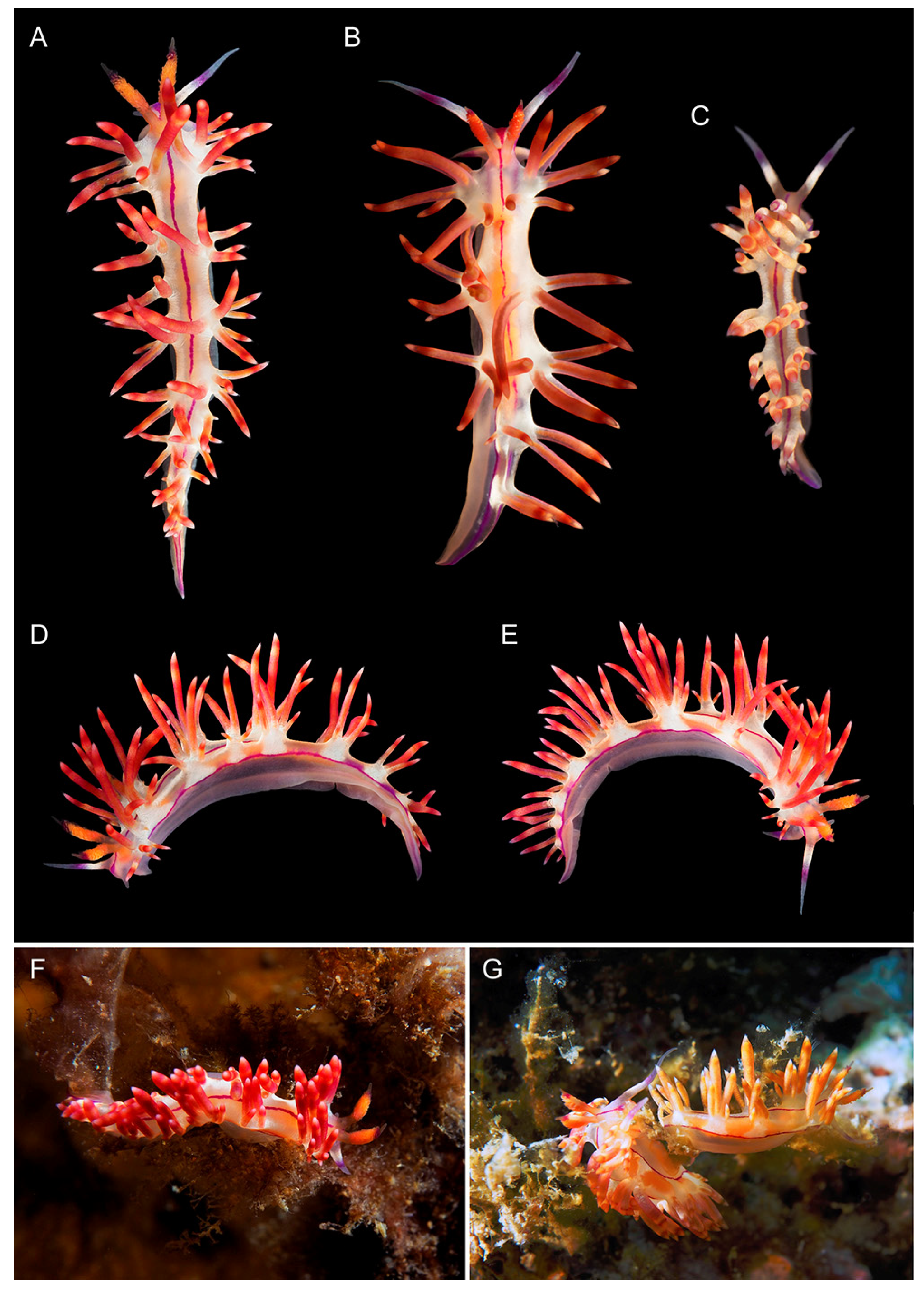

3.3.5. Coryphellina aurora sp. nov.

4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knowlton, N. Sibling species in the sea. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1993, 24, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.L.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Ingram, K.K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The barcode of life data system (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauvel, P. Classes des annélides polychètes. Distribution géographique. Trait. de Zool. 1959, 5, 163–165. [Google Scholar]
- Laakkonen, H.M.; Strelkov, P.; Väinölä, R. Molecular lineage diversity and inter oceanic biogeographical history in Hiatella (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Zool. Scr. 2015, 44, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienberger, K.; Carmona, L.; Pola, M.; Padula, V.; Gosliner, T.M.; Cervera, J.L. Aeolidia papillosa (Linnaeus, 1761) (Mollusca: Heterobranchia: Nudibranchia), single species or a cryptic species complex? A morphological and molecular study. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 2016, 177, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layton, K.K.; Martel, A.L.; Hebert, P.D. Geographic patterns of genetic diversity in two species complexes of Canadian marine bivalves. J. Mollus. Stud. 2016, 82, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.B.; Krug, P.J.; Valdés, Á. Integrative systematics of Placida cremoniana (Trinchese, 1892) (Gastropoda, Heterobranchia, Sacoglossa) reveals multiple pseudocryptic species. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekimova, I.; Valdés, Á.; Chichvarkhin, A.; Antokhina, T.; Lindsay, T.; Schepetov, D. Diet–driven ecological radiation and allopatric speciation result in high species diversity in a temperate-cold water marine genus Dendronotus (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 141, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekimova, I.A.; Mikhlina, A.L.; Vorobyeva, O.A.; Antokhina, T.I.; Tambovtseva, V.G.; Schepetov, D.M. Young but distinct: Description of Eubranchus malakhovi sp. n. a new, recently diverged nudibranch species (Gastropoda: Heterobranchia) from the Sea of Japan. Invertbr. Zool. 2021, 18, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, S.; Rützler, K. Ecological speciation in a Caribbean marine sponge. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, C.K.; Valdés, Á.; Foighil, D.Ó. Molecular and morphological systematics of neustonic nudibranchs (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Glaucidae: Glaucus), with descriptions of three new cryptic species. Invertebr. Syst. 2014, 28, 174–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, P.J.; Vendetti, J.E.; Valdés, A. Molecular and morphological systematics of Elysia Risso, 1818 (Heterobranchia: Sacoglossa) from the Caribbean region. Zootaxa 2016, 4148, 1–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygren, A.; Parapar, J.; Pons, J.; Meißner, K.; Bakken, T.; Kongsrud, J.A.; Oug, E.; Gaeva, D.; Sikorski, A.; Johansen, R.A.; et al. A mega-cryptic species complex hidden among one of the most common annelids in the North East Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, P.J. Patterns of speciation in marine gastropods: A review of the phylogenetic evidence for localized radiations in the sea. Am. Malacol. Bull. 2011, 29, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts-Penniman, A.L.; Gosliner, T.M.; Mahardika, G.N.; Barber, P.H. Cryptic ecological and geographic diversification in coral-associated nudibranchs. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 144, 106698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, C.H. Report on the Opisthobranchia. XXXVIII. Zoological results of the Cambridge Expedition to the Suez Canal. Trans. Zool. Soc. Lon. 1929, 22, 713–841. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, G. Flabellina rubrolineata (O’Donoghue) and Phidiana indica (Bergh) (Nudibranchia: Aeolidoidea), two new Lessepsian immigrants in the Eastern Mediterranean. J. Mollus. Stud. 1993, 59, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokes, B.; Rudman, W.B. Lessepsian opisthobranchs from southwestern coast of Turkey: Five new records for Mediterranean. Rapp. Comm. Int. Explor. Mer Méditerranée 2004, 37, 557. [Google Scholar]
- Yonow, N. Red Sea Opisthobranchia 4: The orders Cephalaspidea, Anaspidea, Notaspidea and Nudibranchia: Dendronotacea and Aeolidacea. Fauna Arab. 2000, 18, 87–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yonow, N. Opisthobranchs of the Gulf of Eilat and the Red Sea: An Account of Similarities and Differences. In Aqaba–Eilat, the Improbable Gulf: Environment, Biodiversity and Preservation; Por, F.D., Ed.; Hebrew University Magnes Press: Jerusalem, Israel, 2008; pp. 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, S. New records of nudibranchs (Gastropoda: Heterobranchia) from the coast of Pakistan (Northern Arabian Sea). Festivus 2019, 51, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeraj, C.R.; Sivaperuman, C.; Raghunathan, C. Addition to the opisthobranchiate (Opisthobranchia, Mollusca) fauna of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Galaxea 2012, 14, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sreeraj, C.R.; Sivaperuman, C.; Raghunathan, C. An annotated checklist of opisthobranch fauna (Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia) of the Nicobar Islands, India. J. Threat. Tax 2012, 4, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeraj, C.R.; Sivaperuman, C.; Raghunathan, C. Species Diversity and Abundance of Opisthobranch Molluscs (Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia) in the Coral Reef Environments of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. In Ecology and Conservation of Tropical Marine Faunal Communities; Venkataraman, K., Sivaperuman, C., Raghunathan, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 81–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tibiriçá, Y.; Pola, M.; Cervera, J.L. Astonishing diversity revealed: An annotated and illustrated inventory of Nudipleura (Gastropoda: Heterobranchia) from Mozambique. Zootaxa 2017, 4359, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosliner, T.M.; Kuzirian, A. Two new species of Flabellinidae (Opisthobranchia: Aeolidacea) from Baja California. Proc. Cal. Acad. Sci. 1990, 47, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gosliner, T.M.; Willan, R.C. Review of the Flabellinidae (Nudibranchia: Aeolidacea) from the tropical Indo–Pacific, with descriptions of five new species. Veliger 1991, 34, 97–133. [Google Scholar]
- Martynov, A.V.; Korshunova, T.A. Opisthobranch molluscs of Vietnam (Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia). In Benthic Fauna of the Bay of Nhatrang, Southern Vietnam; Britayev, T.A., Pavlov, D.S., Eds.; KMK Scientific Press: Moscow, Russia, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 142–257. [Google Scholar]
- Yonow, N. Results of the Rumphius Biohistorical Expedition to Ambon (1990). Part 16. The Nudibranchia—Dendronotina, Arminina, Aeolidina, and Doridina (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Heterobranchia). Arch. Für Molluskenkd. 2017, 146, 135–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papu, A.; Undap, N.; Martinez, N.A.; Segre, M.R.; Kuada, R.R.; Perin, M.; Yonow, N.; Wägele, H. First Study on Marine Heterobranchia (Gastropoda, Mollusca) in Bangka Archipelago, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Diversity 2020, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Park, J.K. First report of an aeolid nudibranch Flabellina athadona and an identification key for the genus Flabellina from Korea. Korean J. Malacol. 2015, 31, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baba, K. Opisthobranchia of Sagami Bay; Iwanami Shoten: Tokyo, Japan, 1955; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, F.E.; Bryce, C.W. Sea Slugs of Western Australia; Western Australian Museum: Perth, Australia, 1993; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Burn, R. A checklist and bibliography of the Opisthobranchia (Mollusca: Gastropoda) of Victoria and the Bass Strait area, south–eastern Australia. Mus. Vict. Sci. Rep. 2006, 10, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.F.; Smith, S.D.; Willan, R.C.; Davis, T.R. Diel and seasonal variation in heterobranch sea slug assemblages within an embayment in temperate eastern Australia. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosliner, T.M.; Behrens, D.W.; Valdés, Á. Indo–Pacific Nudibranchs and Sea Slugs: A Field Guide to The World’s Most Diverse Fauna; Sea Challengers Natural History Books; California Academy of Sciences: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008; p. 426. [Google Scholar]
- Korshunova, T.; Martynov, A.; Bakken, T.; Evertsen, J.; Fletcher, K.; Mudianta, I.W.; Saito, H.; Lundin, K.; Schroedl, M.; Picton, B. Polyphyly of the traditional family Flabellinidae affects a major group of Nudibranchia: Aeolidacean taxonomic reassessment with descriptions of several new families, genera, and species (Mollusca, Gastropoda). ZooKeys 2017, 717, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekimova, I.A.; Antokhina, T.I.; Schepetov, D.M. Molecular data and updated morphological description of Flabellina rubrolineata (Nudibranchia: Flabellinidae) from the Red and Arabian seas. Ruthenica 2020, 30, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosliner, T.M.; Valdés, Á.; Behrens, D.W. Nudibranch & Sea Slug Identification: Indo–Pacific, 2nd ed.; New World Publications: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2018; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Goodheart, J.A.; Bazinet, A.L.; Valdés, Á.; Collins, A.G.; Cummings, M.P. Prey preference follows phylogeny: Evolutionary dietary patterns within the marine gastropod group Cladobranchia (Gastropoda: Heterobranchia: Nudibranchia). BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, Á.; Lundsten, L.; Wilson, N.G. Five new deep-sea species of nudibranchs (Gastropoda: Heterobranchia: Cladobranchia) from the Northeast Pacific. Zootaxa 2018, 4526, 401–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekimova, I.A.; Antokhina, T.I.; Schepetov, D.M. “Invasion” in the Russian Arctic: Is global Climate Change a real driver? A remarkable case of two nudibranch species. Ruthenica 2019, 29, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ekimova, I.; Valdés, Á.; Malaquias, M.A.E.; Rauch, C.; Chichvarkhin, A.; Mikhlina, A.; Antokhina, T.; Chichvarkhina, O.; Schepetov, D. High-level taxonomic splitting in allopatric taxa causes confusion downstream: A revision of the nudibranch family Coryphellidae. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 2022, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furfaro, G.; Salvi, D.; Trainito, E.; Vitale, F.; Mariottini, P. When morphology does not match phylogeny: The puzzling case of two sibling nudibranchs (Gastropoda). Zool. Scr. 2021, 50, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekimova, I.A. A new species of the genus Coryphella (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) from the Kuril Islands. Ruthenica 2022, 32, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Dewaard, J.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. An inexpensive, automation-friendly proto-col for recovering high-quality DNA. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterburg, H.H.; Allen, J.K.; Finch, C.E. The use of ammonium acetate in the precipitation of ribonucleic acid. Biochem. J. 1975, 147, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palumbi, S.; Martin, A.; Romano, S.; McMillan, W.O.; Stice, L.; Grabowski, G. The Simple Fool’s Guide to PCR; Version 2.0; University of Hawaii: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Puslednik, L.; Serb, J.M. Molecular phylogenetics of the Pectinidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia) and effect of increased taxon sampling and outgroup selection on tree topology. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgan, D.J.; McLauchlan, A.; Wilson, G.D.F.; Livingston, S.P.; Edgecombe, G.D.; Macaranas, J.; Gray, M.R. Histone H3 and U2 snRNA DNA sequences and arthropod molecular evolution. Aust. J. Zool. 1998, 46, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, H.L.; Lecointre, G.; Perasso, R. A 28S rRNA-based phylogeny of the gnathostomes: First steps in the analysis of conflict and congruence with morphologically based cladograms. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1993, 2, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Drummond, A. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, E.M.; Ekimova, I.A.; Schepetov, D.M.; Chernyshev, A.V. Meloscaphander grandis (Heterobranchia: Cephalaspidea), a deep-water species from the North Pacific: Redescription and taxonomic remarks. Zootaxa 2019, 4646, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Posada, D.; Kozlov, A.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Morel, B.; Flouri, T. ModelTest-NG: A new and scalable tool for the selection of DNA and protein evolutionary models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flouri, T.; Izquierdo-Carrasco, F.; Darriba, D.; Aberer, A.J.; Nguyen, L.T.; Minh, B.Q.; von Haeseler, A.; Stamatakis, A. The Phylogenetic Likelihood Library. Syst. Biol. 2014, 64, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. B Bio. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A.P. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting species using single-locus data and the Generalized Mixed Yule Coalescent approach: A revised method and evaluation on simulated data sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar]
- Furfaro, G.; Salvi, D.; Mancini, E.; Mariottini, P. A multilocus view on Mediterranean aeolid nudibranchs (Mollusca): Systematics and cryptic diversity of Flabellinidae and Piseinotecidae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 118, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.G.; Burghardt, I. Here be dragons-phylogeography of Pteraeolidia ianthina (Angas, 1864) reveals multiple species of photosynthetic nudibranchs (Aeolidina: Nudibranchia). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 2015, 175, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunova, T.; Mehrotra, R.; Arnold, S.; Lundin, K.; Picton, B.; Martynov, A. The formerly enigmatic Unidentiidae in the limelight again: A new species of the genus Unidentia from Thailand (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia). Zootaxa 2019, 4551, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.B.; Gosliner, T.M. Glossing over cryptic species: Descriptions of four new species of Glossodoris and three new species of Doriprismatica (Nudibranchia: Chromodorididae). Zootaxa 2018, 4444, 501–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soong, G.Y.; Bonomo, L.J.; Reimer, J.D.; Gosliner, T.M. Battle of the bands: Systematics and phylogeny of the white Goniobranchus nudibranchs with marginal bands (Nudibranchia, Chromodorididae). ZooKeys 2022, 1083, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.G.; Willan, R.C. Nudibranchs of Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999; p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Herve, J.-F. Guide des Nudibranches de Nouvelle-Caledonie et autres Opisthobranches; Editions Catherine Ledru: Noumea, France, 2010; p. 403. [Google Scholar]
- Cheney, K.L.; Cortesi, F.; How, M.J.; Wilson, N.G.; Blomberg, S.P.; Winters, A.E.; Marshall, N.J. Conspicuous visual signals do not coevolve with increased body size in marine sea slugs. J. Evolut. Biol. 2014, 27, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Marker | Primers | PCR Conditions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I | LCO1490 GGT CAA CAA ATC ATA AAG ATA TTG G HCO2198 TAA ACT TCA GGG TGA CCA AAA AAT CA | 5 min—94 °C, 35 × [15 s—95 °C, 45 s—45 °C, 1 min—72 °C], 7 min—72 °C | [49] |
| 16S rRNA | 16Sar-L CGC CTG TTT ATC AAA AAC AT 16S R CCG RTY TGA ACT CAG CTC ACG | 5 min—94 °C, 35 × [20 s—95 °C, 30 s—52 °C, 45 s—72 °C], 7 min—72 °C | [50,51] |
| Histone H3 | H3AF ATG GCT CGT ACC AAG CAG ACV GC H3AR ATA TCC TTR GGC ATR ATR GTG AC | 5 min—94 °C, 35 × [15 s—94 °C, 30 s—50 °C, 45 s—72 °C], 7 min—72 °C | [52] |
| 28S rRNA | 28SC1 ACC CGC TGA ATT TAA GCA T 28SC2 TGA ACT CTC TCT TCA AAG TTC TTT TC | 5 min—94 °C, 35 × [15 s—94 °C, 30 s—50 °C, 45 s—72 °C], 7 min—72 °C | [53] |
| Trait | C. rubrolineata O’Donoghue, 1929 | C. lotos Korshunova et al., 2017 | C. pseudolotos sp. nov. | C. pannae sp. nov. | C. flamma sp. nov. | C. aurora sp. nov. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximal length | 12 mm | 23 mm (preserved) | 15 mm (preserved) | 6 mm (preserved) | 13 mm (preserved) | 27 mm (preserved) |
| OT vs. RH length | 2–3 times longer | 1.5–2 | 2 | 1.5–2 | 1.5 | 1.2–1.5 |
| Groups of cerata | Up to 7 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5–7 | 9 |
| Cerata in first group | 8–12 | 9–13 | 9–12 | 8–9 | 8–10 | Up to 23 |
| Cerata in second group | 5 | 4–5 | 3–5 | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| DG volume in cerata | 1/2–1/3 | 1/3–1/4 | 1/3–1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2–1/3 | 1/4–1/5 |
| Background color | Translucent to milky-white | Translucent white to purple | Translucent | Translucent white to light lilac | Translucent white with opaque white patches on ceratal groups | Translucent violet |
| OT color | White opalescent powder with lilac subapical rings | White to purple with intensive pink to purple subapical ring, translucent tip | Pink to violet, more intensive in middle, white or translucent tip | Translucent violet more intensive to tip, white tips | White opalescent powder with lilac subapical rings and translucent tips | Translucent violet more intensive to tip, white tips |
| Rhinophores color | Lilac tips and light-orange patches underneath them | Same color as body or apricot, purple subapical rings | Same color as body or light yellow, violet or purple subapical rings | Light pink, purple subapical rings, white tips | Translucent white, orange papillae, violet-red subapical rings | Intensive pink with orange papillae |
| Cerata color | White to violet, orange pigment on cnidosac area, purple subapical rings | Peachy to purple, red to violet subapical rings, peachy cnidosac area | Translucent white to peachy, red to violet subapical rings, white to peachy cnidosac area | Milky-white, white to yellow cnidosac area, red subapical rings | Two rings of salmon pink and peachy orange or brown, light-pink tips | Pink to lilac, violet-red subapical rings, peachy tips |
| Dorsal line | Continuous, purple, thickened on head and tail | Discontinuous, pink, thickened on head, on body indistinct | Discontinuous, pink, on body indistinct | Continuous, pink | Continuous to 2/3 of body length, then discontinuous, pink | Only on head, indistinct |
| Dorsolateral lines | Continuous, purple | Discontinuous, lilac | Discontinuous, lilac | Continuous, pink | Continuous, pink | Absent |
| Jaw masticatory border | 8 rows | 5 rows | 6 rows | 4 rows | 7 rows | 10 rows |
| Rows of teeth (radula) | 27–34 | 27–35 | 17–22 | 15 | 23–25 | 36 |
| Denticles on rachidian tooth (one side) | 5–8 | 5–7 | 6 | 6–7 | 6–9 | 6–7 |
| Denticles on laterals | 8–11 | 8–11 | 4–7 | 7–9 | 8–12 | 7–8 |
| Ampulla | Sausage-shaped | Sausage-shaped, widened in middle | Large, sausage-shaped | Large, sausage-shaped | Sausage-shaped, bent in midline | Sausage-shaped, coiled |
| Prostatic vas deference | With loops | Slightly widens | Slightly widens | With loops | Gradually widens | narrow Proximally, bent and expanded distally |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ekimova, I.; Deart, Y.; Antokhina, T.; Mikhlina, A.; Schepetov, D. Stripes Matter: Integrative Systematics of Coryphellina rubrolineata Species Complex (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) from Vietnam. Diversity 2022, 14, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14040294
Ekimova I, Deart Y, Antokhina T, Mikhlina A, Schepetov D. Stripes Matter: Integrative Systematics of Coryphellina rubrolineata Species Complex (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) from Vietnam. Diversity. 2022; 14(4):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14040294
Chicago/Turabian StyleEkimova, Irina, Yury Deart, Tatiana Antokhina, Anna Mikhlina, and Dimitry Schepetov. 2022. "Stripes Matter: Integrative Systematics of Coryphellina rubrolineata Species Complex (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) from Vietnam" Diversity 14, no. 4: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14040294
APA StyleEkimova, I., Deart, Y., Antokhina, T., Mikhlina, A., & Schepetov, D. (2022). Stripes Matter: Integrative Systematics of Coryphellina rubrolineata Species Complex (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) from Vietnam. Diversity, 14(4), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14040294








