Abstract
A marine Alphaproteobacterium designated as strain NZ-96T was isolated in February 2021, from a sponge species (Demospongiae) collected in muddy sediments with boulders and old chimneys in Otago/Canterbury Slope, Pacific Ocean, New Zealand. The isolate was found to be Gram-negative, rod-shaped, aerobic, motile, and produced yellow-colored colonies. The isolate was positive for alkaline phosphatase, leucine arylamidase, trypsin, catalase, and oxidase and negative for α-galactosidase and urease. It was resistant to many antibiotics including hygromycin, trimethoprim, spectinomycin, ampicillin, oxytetracycline, cephalosporin, bacitracin, and polymyxin. The 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic analyses exhibited that strain NZ-96T belonged to the genus Qipengyuania and showed 98.3–98.8% 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity to its closest relatives. The major respiratory quinone was ubiquinone-10 (Q-10). The polar lipid profile consisted of phosphatidylcholine, sphingoglycolipid, phosphatidylglycerol, one unknown polar lipid, and three unknown glycolipids. The major fatty acids were C18:1ω12t, C16:0, C16:1ω7c, C17:1ω6c, C16:02-OH, and C14:0 2-OH. Carotenoid were produced. The crude extract showed pronounced activity against Staphylococcus aureus Newman and Bacillus subtilis DSM 10. Pairwise ANI and dDDH values of strain NZ-96T and closely related phylogenetic hits were below the threshold values of 95% and 70%, respectively. Genes for trehalose biosynthesis, aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, flagellar biosynthesis, fatty acid biosynthesis, and antibiotics resistance were present, which aids in isolate survival in a sea or ocean environment. The DNA G+C content was 60.8% (by genome). Based on data obtained by the polyphasic approach, strain NZ-96T (= DSM 112811T = NCCB 100842T) represents a novel species of the genus Qipengyuania, for which the name Qipengyuania pacifica sp. nov. is proposed.
1. Introduction
Reduction in the discovery of new antimicrobial compounds has led the scientific community to exploit underexplored and extreme ecological niches in search of novel microorganisms. This has led to a particular interest in seas and oceans, which host some of the least explored and most hostile environments on Earth [1]. Sponges (phylum Porifera) in the ocean shelter abundant and diverse symbiotic microbial communities [2]. They are ecologically productive and a treasure of novel, biotechnologically relevant natural products [3]. The study aimed at the isolation of the novel bacteria from the sea sponge led to the isolation of a strain designated as NZ-96T. Based on 16S rRNA gene sequences comparative analysis, the isolate was shown to be closely related to Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027-248T, a member of the family Erythrobacteraceae. Through phylogenomic core genes reconstruction and analyses of genome similarity, the taxonomy of the family Erythrobacteraceae was recently revised, leading to the formation of many novel genera within the family [4]. Taxonomy revision resulted in the transfer of Erythrobacter pelagi into a new genus Qipengyuania in the family Erythrobacteraceae, thus the species is called by its new name, Qipengyuania pelagi. Marine organisms [5], marine cyanobacterial mats, seawater, marine and mangrove sediments [6,7,8], solar saltern [9], ice core [10], and estuarine environments [11] have been found to contain members of the family Erythrobacteraceae. Members of the family Erythrobacteraceae are Gram-negative, have rod-shaped or pleomorphic coccidal forms and are pink, red, orange, or yellow pigmented and aerobic chemoorganotrophs [12]. The genus Qipengyuania, a member of the Erythrobacteraceae family [13], belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria, with the representation of Qipengyuania sediminis as the type of species [14]. To date, the genus Qipengyuania comprises thirteen (13) species with validly published names. https://lpsn.dsmz.de/genus/qipengyuania (accessed on 29 February 2022) [15].
The present work was carried out to determine the taxonomic status of NZ-96T using a polyphasic study involving the phenotypic and chemotaxonomic characterization, a detailed phylogenetic investigation based on 16S rRNA gene sequences, and genetic analyses of genome data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation, Cultivation, and Maintenance of Bacteria
A sponge species sample (Demospongiae) was collected in February 2017 during a collection expedition using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), located at a depth of 596 m below the ocean surface at muddy sediments with boulders and old chimneys in the Otago/Canterbury Slope (45°02′ N, 171°90′ W), Pacific Ocean, New Zealand. An artificial seawater wash was used to remove loosely bound bacterial cells and debris from the sponge for bacterial isolation. A sponge tissue sample (±1 cm3) was ground and added to 9 mL of sterile artificial seawater. The serial dilutions technique (10−2–10−6) was carried out and 0.1 mL was spread on seawater glutamate (SWG) agar medium (artificial seawater (3.9% (w/v) of sea salt from ATI Coral Ocean), 0.1% sodium glutamate, and 1.6% agar (Difco) [16] with antifungal agent cycloheximide (50 mg/L). Incubation was processed at 30 °C for 2–4 weeks and growth was checked under the stereomicroscope. The strain NZ-96T was isolated by repeated streaking on MA (Marine agar, Difco). The strain was preserved in marine broth 2216 (MB, Difco) with 50% (v/v) glycerol at −80 °C.
All characterization of the strain, unless otherwise specified, are based on cultures incubated at 30 °C for 3 days on MA or MB medium.
2.2. Morphological, Cultural, and Physiological Characterization
Over the course of 1 week, morphological observations were performed on MA 2216 medium incubated at 30 °C. Phase-contrast microscopy and electron microscopy (SEM and negative staining TEM) were used to analyze the cell morphology. A scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was carried out following the previous method with a few modifications [17]. In a nutshell, 1-day-old bacterial broth culture were fixed in aldehydes solution (2% glutaraldehyde for 30 min, followed by 5% formaldehyde for 30 min). After twice washing with TE buffer (10 mM TRIS, 1 mM EDTA, and pH 6.9), it was dehydrated in a graded series of acetone (10, 30, 50, 70, 90, and 100%). After drying the samples with liquid CO2, they were sputter-coated with gold-palladium and subsequently examined with a Zeiss Merlin field emission scanning electron microscope applying the HE-SE detector and the inlens-SE detector in a 75:25 ratio. For transmission electron microscopy (TEM), a sample drop was placed on with a thin carbon film, taken off with a grid, twice washed before being negatively stained with 4% uranyl acetate, and subsequently examined with a Zeiss Libra 120 at different magnifications.
Gram staining was carried out following the manufacturer’s instructions using a Gram stain kit (Sigma-Aldrich CA, USA). The RAL color code (https://www.ralfarben.de accessed on 29 February 2022) was used to determine the culture’s color [18]. N, N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride, and 3% (v/v) hydrogen peroxide solutions were employed to determine the oxidase and catalase activities, respectively. The strain growth under anaerobic conditions at 30 °C was evaluated on MA in an anaerobic chamber by employing the Anaerocult A, as per the manufacturer’s instructions. The hanging drop method was used for motility testing [6]. Varying temperatures (4, 15, 20, 25, 30, 37, and 44 °C) were used to determine the growth on MA medium. Growth was also observed on CY medium (Casitone 3.00 g, CaCl2 × 2.H2O 1.36 g, Yeast extract 1.00 g, Agar 16.00 g, Distilled water 1000 mL, pH 7.2) augmented with 39 g of artificial sea salts (3.9% (w/v) of sea salt from ATI Coral Ocean). The pH range 3-11 with one unit difference of pH was used to examine the growth in MB. The pH validation was performed after autoclaving. Resistance towards sodium chloride was evaluated with varying concentrations of (2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10% (w/v)) NaCl on agar medium containing (per liter) 5.9 g MgCl2, 3.24 g Na2SO4, 1.8 g CaCl2, 0.55 g KCl, 5.0 g peptone, 0.1 g ferric citrate, and 1.0 g yeast extract (pH 7.6) [19]. Biochemical and physiological properties were examined using API ZYM, API 20E, and API 20NE strips (Biomerieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France), and the Biolog Gen III Microplate system (Biolog, CA, USA) as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
A 24-well plate was used with 1% filter sterilized carbon sources (arabinose, cellulose, fructose, inositol, mannitol, raffinose, rhamnose, sucrose, and xylose) added to MA medium for carbon sources utilization. An antibiotic resistance test was performed on agar plates containing filter-sterilized antibiotics with the final concentration of 50 µg/mL−1 except for oxytetracycline ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and hygromycin. The antibiotics used were bacitracin (50 µg/mL), polymyxin (50 µg/mL), gentamicin (50 µg/mL), oxytetracycline (10 µg/mL), trimethoprim (50 µg/mL), ampicillin (100 µg/mL), chloramphenicol (30 µg/mL), spectinomycin (50 µg/mL), kanamycin (50 µg/mL), cephalosporin (50 µg/mL), fusidic acid (50 µg/mL), thiostrepton (50 µg/mL), and hygromycin (150 µg/mL) [20,21].
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
The phylogenetic analysis of the isolate was based on a 16S rRNA gene sequence. Strain NZ-96T was cultivated in MB medium for 3 days at 30 °C. A Nucleospin microbial DNA kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) was used to extract the genomic DNA. Primers 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) were used for the amplification of the 16S rRNA gene. Following analysis by the gel electrophoresis, the PCR product was purified using the Nucleospin gel and PCR clean-up kit (Macherey Nagel) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Primers F1100 (5′-CAACGAGCGCAACCC-3′), R1100 (5′-GGGTTGCGCTCGTTG-3′), and R518 (5′-CGTATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG-3′) were applied for sequencing in addition to the primers used for primary PCR, to assure that both nucleotide directions were covered. The program BioEdit (version 7.0.5.3) was used for the assembly of acquired sequences. The cap contig function of the BioEdit sequence editor (version 7.0.5.3) was used to build the consensus sequences and compared with the NCBI-BLAST nucleotide database using the FASTA search tool [20]. Phylogenies were deduced by the web server of GGDC (Meier-Kolthoff et al., 2021) available at http://ggdc.dsmz.de/ accessed on 29 February 2022 using the DSMZ phylogenomics pipeline [22] adapted to single genes. MUSCLE was used to create multiple sequence alignment [23]. Maximum likelihood (ML) and maximum parsimony (MP) trees were deduced from the RAxML [24] and TNT [25] alignments, respectively. For ML, rapid bootstrapping in connection with the autoMRE bootstopping criterion [26] and subsequent search for the best tree was used. For MP, 1000 bootstrapping replicates were carried out in conjunction with tree-bisection-and-reconnection branch swapping and ten random sequence addition replicates. The sequences were checked for a compositional bias using the Χ² test as implemented in PAUP* [27]. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain NZ-96T was deposited at Genbank under the accession no. MZ569436.
2.4. Chemotaxonomy
To study chemotaxonomic fingerprints of respiratory quinones, fatty acids, and polar lipids, freeze-dried cells were used. Cells of strain NZ-96T, Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027-248T, Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T, and Erythrobacter aureus YH-07T, were incubated for 3 days in MB at 30 °C and harvested and washed three times with sterile phosphate buffer saline prior to freeze-drying.
The polar lipids extraction was carried out by adding 6.75 mL of chloroform-methanol-0.3% aqueous sodium chloride (50-100-40 v/v) solution to 50 mg of lyophilized biomass and run overnight on a rotator. The extraction was based on the method by Minnikin et al. [28]. Separation of polar lipids was performed by a two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography (2D-TLC) on silica gel, using five TLC plates (10 × 10) per isolate. Each plate was spotted with 10 µL lipid extracts, followed by treatment with chloroform/methanol/water (65:25:4) and chloroform/methanol/acetic acid/water (80:12:15:4) by volume for the first and second dimensions, respectively. A range of reagents were used for the detection of polar lipids with varying functional groups [29]. Phosphomolybdic acid was applied on the first plate to detect all polar lipids. Aminolipids detection was performed by staining the second plate with ninhydrin, followed by the application of molybdenum blue to the same plate for the detection of phospholipids. To detect glycolipids, the third plate was stained with α-naphthol [28]. Anisaldehyde and Dragendorff’s reagents were applied to the fourth and fifth plates, respectively. Polar lipids were visualized by heating all the stained plates at 100–120 °C, except the molybdenum blue and Dragendorff’s stained plates, which were developed at room temperature.
Extraction using a ternary solvent system of hexane/methanol/water mixture in a ratio of (2:1:1), respectively, was carried out for the presence or absence of bacteriochlorophyll a and carotenoids [30], and subsequent analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (Agilent 1260 series) equipped with diode-array detection and mass spectrometry (RP-HPLC-DAD-MS). High-resolution electron spray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS) data were generated by Maxis ESI-TOF-MS spectrometer (Bruker). The RP-HPLC system used Acquity C18 column 2.1 × 50 mm, 1.7 µm with gradient elution employing two mobile phases (solvent A: water + 0.1 formic acid and solvent B: acetonitrile + 0.1 formic acid) with the flow rate of 0.6 mL/min. The gradient system was 5% B in the first 0.5 min, increasing gradually to 100% B in 19.5 min, and finally withholding for 5 min at 100% B. Isoprenoid quinones were extracted according to the method of MinniKin et al., (1984) [28] and were analyzed by HPLC following Risdian et al. [31] with slight modifications using isocratic condition acetonitrile/isopropanol 65:35 (v/v) and flow rate 0.3 mL/min. Cellular fatty acids were extracted and methylated to yield fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) following the method of Sasser [32]. The FAME analysis was carried out using 6890N gas chromatography with a Macherey Nagel Optima 5 column (5% phenyl, 95% dimethylpolysiloxane; 50 m length; 0.32 mm inner diameter; and 0.25 µm film thickness) and equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID). Identification of FAMEs were performed by comparing them with the in-house reference standard.
2.5. Secondary Metabolites Production and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Assay
Strain NZ-96T was incubated in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask carrying 100 mL MB medium with 2% (v/v) of purified adsorbent resin XAD-16N at 30 °C with 160 rpm agitation for 4 days. The adsorbent was filtered through a sieve and collected in a flask after incubation. A total of 50 mL of acetone was added and placed at room temperature for 1 h in darkness. To remove the XAD resin the eluate was filtered (ROTH, membrane 240 mm, folded filter) after incubation. Utilizing a rotary evaporator, the acetone was removed to yield a solid residue (40 °C, 1 mb). The obtained crude extract was stored at −20 °C after being dissolved in (100:1) methanol. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) assay was conducted against a panel of microorganisms following the previous method [33]. The indicator strains used were Escherichia coli acrB JW25113, Staphylococcus aureus Newman, Citrobacter freundii DSM 30039, Candida albicans DSM 1665, Bacillus subtilis DSM 10, Escherichia coli wild type BW25113, Mycobacterium smegmatis ATCC 700084, Pseudomonas aeruginosa DSM 19882, Mucor hiemalis DSM 2656, Pichia anomala DSM 6766, and Acinetobacter baumannii DSM 30008. The strains were added to 40 mL of their respective growth medium (Mueller–Hinton Broth medium containing 0.5% casein peptone, 0.5% protease peptone, 0.1% meat extract, 0.1% yeast extract, pH 7.0 for bacteria, MYC medium containing 1.0% glucose, 1.0% phytone peptones, and 50-mM HEPES 11.9 g/L, pH 7.0 for fungi and yeasts [34]) and mixed well. Diluted cultures in a volume of 150 μL were transferred into each well of a 96-well plate (initial OD600 for the bacteria was 0.01; and for fungi and yeasts, 0.05). The first row was augmented by an additional 130 μL of indicator culture. Crude extracts (20 μL) of the strain NZ-96T were added to the first row. The extract was serially diluted (1:1) by transferring 150 μL from one well to the next in a 96-well plate. Methanol and antibiotics were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Thereafter, the microtiter plates were incubated on a microplate shaker incubator at 160 rpm at 30 or 37 °C for 24 h. Visual inspection of the indicator strain was performed after incubation. Turbidity absence in a well showed strain inhibition.
2.6. Genome Analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from a pure culture grown for 3 days on MA at 30 °C using a Nucleospin Microbial DNA kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) following the protocol from the manufacturer. Genome sequencing was conducted at the sequencing facility (HZI Braunschweig, Germany) using the Illumina MiSeq (300 bp, paired-end reads) with NexteraXT protocol for library preparation. Unicycler [35] and Prokka [36] were employed for de novo assembly and genome annotation, respectively. Draft genome sequences were submitted to NCBI Genbank and analyzed using ContEst16S (www.ezbiocloud.net/tools/contest16s, accessed on 29 August 2021) [37] to verify the purity of the genome. The whole-genome sequence of strain NZ-96T was deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession JAHWXO000000000. The guanine and cytosine (G+C) content of the genomic DNA (mol%) was calculated using genome assembly annotation 1.14.0 (https://github.com/tseemann/prokka, accessed on 1 September 2021). Rapid Annotation using Subsystem Technology (RAST) (https://rast.nmpdr.org/, accessed on 2 September 2021) [38] and antibiotics and secondary metabolite analysis shell (antiSMASH) (https://antismash.secondarymetabolites.org/, accessed on 2 September 2021) [39] were used for the analysis of metabolic reconstruction and secondary metabolite gene clusters prediction, respectively. Responsible genes for strain NZ-96T survival in the sea environment were deciphered using the RAST server. Based on the genome sequence of NZ-96T and its closely related phylogenetic neighbours, a phylogenomic tree was produced using the type (strain) genome server (TYGS) (https://tygs.dsmz.de/, accessed on 6 September 2021). For the phylogenomic inference, Genome Blast Distance Phylogeny (GBDP) was employed for all pairwise comparisons of genomes and under the algorithm ‘trimming’ as well as distance formula d5 [22]. The accurate intergenomic distances were inferred with 100 distance replicates. Using the amino acid sequences of the complete proteome, a second GBDP phylogenomic analysis was deduced, promising a better-resolved phylogeny. Pairwise average nucleotide identity (ANI) values between strain NZ-96T and its closest phylogenetic relatives were determined using the EzBiocloud server (www.ezbiocloud.net/tools/ani, accessed on 15 September 2021). Digital DNA–DNA hybridization (dDDH) values between the genome data of strain NZ-96T and its closest type strains were estimated using the Genome to Genome Distance Calculator (GGDC; version 2.1) [40].
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Morphological and Physiological Characteristics
In February 2017, Strain NZ-96T was isolated from a sponge sample obtained at a depth of 596 m below the ocean surface in Otago/Canterbury slope (45° 02/N, 171° 90/W), Pacific Ocean, New Zealand. Cells of strain NZ-96T were catalase and oxidase-positive, Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, and straight rods that occur singly and in pairs. Colonies were circular, zinc yellow-colored, and convex with entire margins (Figure 1). A scanning electron microscopy image of strain NZ-96T depicts distinctly the rod-shaped morphology (2.5–3.0 um in length and 0.5–0.6 um wide) and cell-connecting filaments that represent the bundle-forming flagella-like structure (Figure 1). Strain NZ-96T grew at 15–37 °C (optimal growth was shown at 20–30 °C). No growth was observed at 4 °C and 44 °C. Growth was displayed at pH 6–9 (optimum growth shown at pH 6). Growth was observed in the presence of 0–7.5% (w/v) NaCl with optimum growth at 2.5% (w/v) NaCl. The strain also grew on CY medium, apart from marine agar 2216 (Difco). An antibiotic susceptibility test showed that the strain was sensitive to thiostrepton (50 µg/mL), fusidic acid (50 µg/mL), kanamycin (50 µg/mL), and gentamycin (50 µg/mL). However, resistance was shown against, spectinomycin (50 µg/mL), ampicillin (100 µg/mL), oxytetracycline (10 µg/mL), trimethoprim (50 µg/mL), cephalosporin (50 µg/mL), hygromycin (150 µg/mL), bacitracin (50 µg/mL), chloramphenicol (30 µg/mL), and polymyxin (50 µg/mL).
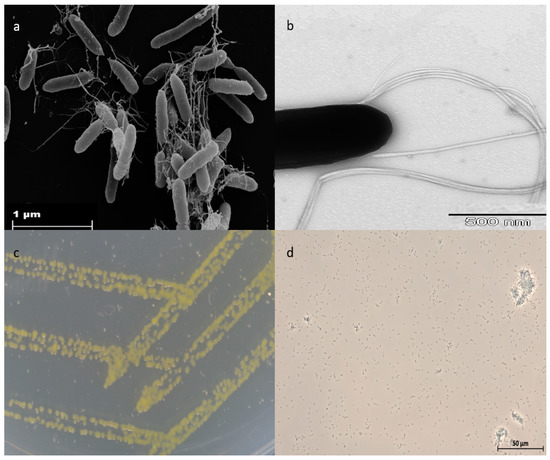
Figure 1.
(a) Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of cells grown on marine agar with the formation of cell-connecting fibers, (b) TEM of a single cell with cell-connecting fibers, (c) growth of strain NZ-96T on marine agar after 72 h, (d) phase contrast microscopy of strain NZ-96T showing rod-shaped morphology.
Biochemical and physiological properties of strain NZ-96T at 30 °C according to API ZYM (Table S1), API 20E (Table S2), API 20NE (Table S3) strips, and the Biolog Gen III Microplate system (Table S4) showed a pronounced activity for acid phosphatase, leucine arylamidase, valine arylamidase, alkaline phosphatase, trypsin, naphthol-AS-BI-phosphohydrolase, cystine arylamidase, α-glucosidase, inositol and rhamnose fermentation, arginine dihydrolase, and esculin hydrolysis. Whereas no activity was seen for β-galactosidase, β-glucuronidase, α-galactosidase, β-glucosidase, ornithine decarboxylase, β-galactosidase (ONPG), N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, α-mannosidase, α-fucosidase, urease, melibiose fermentation, and mannose assimilation. Strain NZ-96T showed activity for lysine decarboxylase and citrate utilization in comparison to Qipengyuania pelagi JCM 14468T and Qipengyuania citreus DSM 14432T which showed no activity. In contrast to Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027-248T and Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T (which reduces nitrate, strain NZ-96T was negative for the said property), cells of strain NZ-96T are motile rods; whereas Qipengyuania pelagi JCM 14468T and Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T cells are non-motile. Strain NZ-96T was positive for α-glucosidase, whereas Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T was negative for the said property. A detailed comparison of phenotypic properties and enzymatic activities among strain NZ-96T and comparative analyses strains are shown in Tables S1–S3 of Supplementary Materials.
3.2. 16S rRNA Gene-Based Phylogenetic Analysis
Sequence similarity comparisons of the 16S rRNA gene using NCBI- BLAST [41] depicted that strain NZ-96T was closely related to Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T (98.8%), Erythrobacter aureus YH-07T (98.3%), and Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027-248T (98.3%). Inference of the tree (Figure 2 maximum likelihood tree rooted by midpoint rooting) based on an almost complete 16S rRNA gene sequence (1425 nucleotides) depicted that strain NZ-96T forms a well-defined tight cluster with Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027-248T coupled with high bootstrap value. Based upon the 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities and phylogenetic analysis, Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027-248T, Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T, and Erythrobacter aureus YH-07T were designated as the reference strains for comparative analysis.
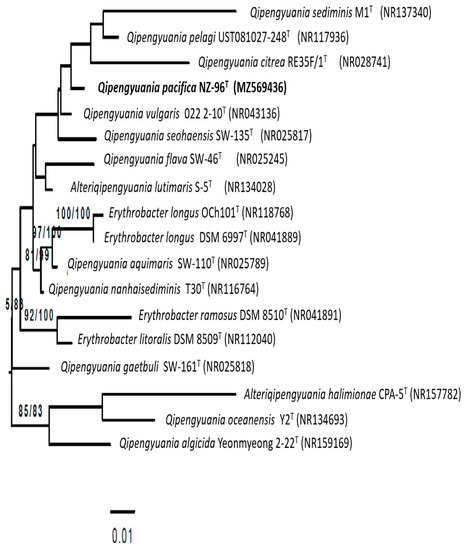
Figure 2.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree based on almost complete 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain NZ-96T and its most closely related species, inferred under the GTR+GAMMA model. The numbers above the branches are support values when larger than 60% from ML (left) and MP (right) bootstrapping. Bar 0.01 substitution per nucleotide position.
3.3. Chemotaxonomy
Analyses of the chemical composition of cell constituents of NZ-96T showed that it carries chemotaxonomic features that are in agreement with those prescribed for members of the family Erythrobacteraceae [42]. The respiratory quinone profiles consisted exclusively of ubiquinone-10 (Q-10), which is in agreement with the description of genus Qipengyuania [12]. The polar lipid profile of NZ-96T is composed of phosphatidylcholine, sphingoglycolipid, phosphatidylglycerol, one unknown polar lipid, and three unknown glycolipids (Figure 3). The major fatty acids of strain NZ-96T are C18:1ω12t (40.3%), C16:0 (11.9%), C16:1ω7c (9.9%), C17:1ω6c (9.5%), C16:02-OH (5.9%), and C14:02-OH (5.1%). The fatty acid profiles of strain NZ-96T and its closely related members were presented in Table 1. Differences in the percentages of major fatty acids C18:1ω12t, C16:0, and C16:1ω7c distinguish the strain from its close relatives. The absence of C19:0 and C17:1ω8c, and the presence of C18:0 and some other quantitative differences between the novel strain NZ-96T and closely related strains can be considered as a distinguishing characteristic for the novel species.
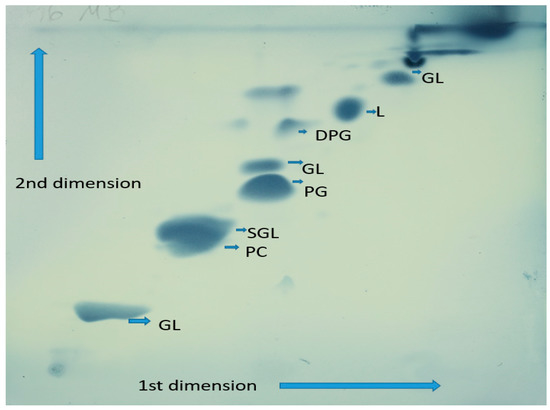
Figure 3.
Polar lipids observed in strain NZ-96T are DPG: diphosphatidylglycerol; GL1-3: unknown glycolipid; PGL: unknown phosphoglycolipid; L: Unknown polar lipid; PG: Phosphatidylglycerol; SGL: Sphingoglycolipid; PC: Phosphatidylcholine.

Table 1.
Fatty acids profiles of strain NZ-96T and the phylogenetically closest relatives. Strains 1: NZ-96T; 2: Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T; 3: Erythrobacter aureus YH-07T; and 4: Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027-248T. Values are percentages of the total fatty acids. The bold type represents the major fatty acids. -: Not detected.
BChl a was absent. The ternary solvent extract spectra exhibited peak retention time at 22.16 min with UV absorption at 425 nm (the characteristic spectra of carotenoid-like pigments).
3.4. Antimicrobial Potential
The extract of strain NZ-96T exhibited a varying degree of inhibition activity against the tested strains. A minimal inhibitory concentration of crude extracts from NZ-96T showed high activity against Gram-positive bacteria, Bacillus subtilis DSM 10, and Staphylococcus aureus Newman. Whereas only the highest concentration of NZ-96T XAD extract in the first well showed activity against tested Gram-negative bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 DSM 19882, and Escherichia coli DSM 1116. No antimicrobial activity was observed against fungal and yeast organisms such as, Pichia anomala DSM 6766, Candida albicans DSM 1665, and Mucor himalis DSM 2656 in this approach. The strain NZ-96T crude extract was fractionated through a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and subsequently tested in bioassays against the susceptible strains, i.e., Staphylococcus aureus Newman and Bacillus subtilis DSM 10 in order to determine the peak-related activities (Figure S1). The micro-fractionation was performed in 96-well plates to narrow down the active compounds of the crude extract.
3.5. Genome Analysis
The draft assembled genome of strain NZ-96T yielded 54 contigs with a total sequence length of 3,497,702 bp. Annotation resulted in 3400 coding sequences, 48 tRNA genes, 6 rRNA operons, and a single tmRNA gene. The DNA G+C content of strain NZ-96T was 60.8 mol%, a value in line with the range reported for members of genus Qipengyuania, i.e., 60.6–66.7% [4].
A RAST analysis revealed that only 28% of the annotated genes in the genome of strain NZ-96T were assigned to the subsystems category (Figure 4). Among the subsystem categories, amino acids and derivate metabolism had the highest feature counts (235), followed by protein metabolism with 190 feature counts. Then, 32 feature counts were detected for resistance to antibiotics and toxic compounds; whereas, genomes of Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T, Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027248T, and Erythrobacter aureus YH-07T contained 40, 29, and 18 feature counts, respectively. The characteristic genes and gene products present in strain NZ-96T were determined via the RAST analysis (Figure 4). Strain NZ-96T contained the proteins involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, biosynthesis of amino acids and derivatives, metabolism of fatty acids, lipids, isoprenoids, motility, and chemotaxis. Concerning ecology, gene products related to the resistance of antibiotics and toxic compounds such as copper, zinc, and chromium compounds were present. The antiSMASH server predicted three secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters displaying similarities to terpene (66%), beta lactone, lasso peptide, and hserlactone biosynthetic gene clusters (Figure S2). A genome analysis indicated the absence of the photosynthetic gene cluster (PGC) involved in the BChl a biosynthetic pathway (bch genes, puf genes, puh genes, and regulatory genes). However, strain NZ-96T harbored crt genes responsible for the biosynthesis of carotenoids.
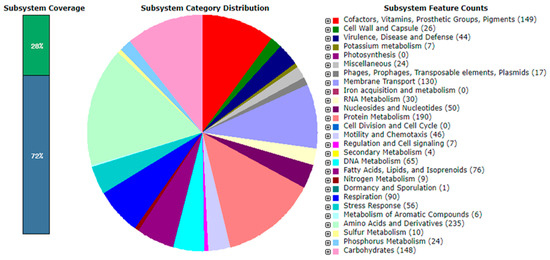
Figure 4.
Subsystem category distribution of strain NZ-96T based on RAST annotation server (https://rast.nmpdr.org/, accessed on 2 September 2021).
A phylogenomic tree (Figure S3) with low average branch support of 61.8% generated with TYGS server using genome sequence showed that the strain NZ-96T was separated from the closest phylogenetic neighbors Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027248T and Qipengyuania citrea RE35F/1T based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses. A second whole-proteome-based tree was well-supported with high average branch support of 97.8%, depicting the reliable placement of strain NZ-96T in the tree. Strain NZ-96T was placed in a group that contains members of Qipengyuania and a couple strains that are put in single quotes (Figure 5). Pairwise ANI values between genome sequence of strain NZ-96T and the closest phylogenetic hits Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T, Erthrobacter aureus YH-07T, Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027248T, and Qipengyuania seohaensis SW-135T were 79.38%, 78.93%, 75.43%, and 75.81%, respectively, values clearly below the threshold value of 95–96% that corresponds to the species boundary. The dDDH values between strain NZ-96T and strains Qipengyuania citreus RE35F/1T, Erythrobacter aureus YH-07T, Qipengyuania pelagi UST081027248T, and Qipengyuania seohaensis SW135T were 22.1%, 21.4%, 21.4%, and 19.4%, respectively (Table 2); values well-below the cut-off value of 70% (dDDH) generally used for species delineation. The ANI and DNA relatedness values warrant that strain NZ-96T represents a new species of the genus Qipengyuania. Detailed contrasting characteristics that distinguish strain NZ-96T from its closely related phylogenetic relatives are provided in Table 3.
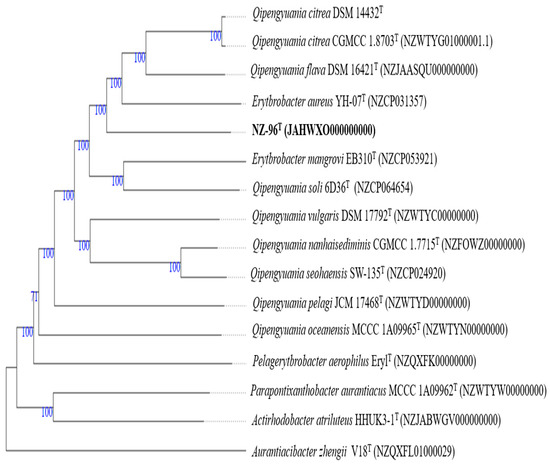
Figure 5.
Tree deduced with FastME 2.1.6.1 [43] from whole-proteome-based GBDP distances. The branch lengths are scaled via GBDP distance formula d5. Branch values are GBDP pseudo-bootstrap support values >60% from 100 replications, with average branch support of 97.8%.

Table 2.
16S, ANI, and dDDH values of NZ-96T and its closely related phylogenetic species.

Table 3.
Differential properties of strain NZ-96T and closely related type strains.
Detailed differential characteristics that distinguish strain NZ-96T from its closely related phylogenetic relatives are provided in Table 3. Given these combined chemotaxonomic, morphological, phylogenetic, and phylogenomic analyses, strain NZ-96T guarantees classification in the genus Qipengyuania. The level of DNA–DNA association and phenotypic characteristics confirmed that the strain constitutes a separate species. Therefore, based on the data presented, we propose to include strain NZ-96T in the genus Qipengyuania as Qipengyuania pacifica sp. nov.
4. Description of Qipengyuania pacifica sp. nov.
Qipengyuania pacifica (pa.ci′fi.ca. L. fem. adj. pacifica) pertains to the Pacific Ocean from where the type strain was isolated. The cells are Gram-stain-negative, motile, rod-shaped, and aerobic. Colonies on marine agar (MA) were circular, smooth, opaque, convex with entire margins, zinc-yellow colored, and 0.7–1.0 mm in diameter at 30 °C for 3 days. Flagellum was present. BChl a was not produced. Growth occurred at 15–37 °C (optimum growth at 20–30 °C), at pH 6–9 (optimum growth at pH 6), and in 0–7.5% NaCl (optimum growth at 2.5% (w/v) NaCl). Positive activity was observed for catalase and oxidase tests. No reduction in nitrate was observed. The cells were negative for the production of H2S, indole, and acetoin. The enzyme reactions for valine arylamidase, cystine arylamidase, alkaline phosphatase, leucine arylamidase, trypsin, acid phosphatase, esculin hydrolysis, naphthol-AS-BI-phosphohydrolase, α-glucosidase, and arginine dihydrolase were positive. The enzyme reactions for α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, β-glucuronidase, β-glucosidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, α-mannosidase, α-fucosidase, β-galactosidase (ONPG), ornithine decarboxylase, urease, gelatinase were negative. Dextrin, D-trehalose, cellobiose, sucrose, turanose, raffinose, α-D-lactose, β-methyl-D-glucoside, D-salicin, N-acetyl-β-d-mannosamine, N-acetyl-D-galactosamine, N-acetylneuraminic acid, D-fucose, L-fucose, L-rhamnose, D-arabitol, Myo-inositol, glycerol, D-fructose-6-PO4, L-arginine, L-aspartic acid, L-glutamic acid, L-pyroglutamic acid, lincomycin, D-galacturonic acid, L-galactonic acid lactone, D-glucose-6-PO4, D-gluconic acid, D-galactose, D-glucuronic acid, glucuronamide, mucic acid, quinic acid, D-saccharic acid, D-lactic acid methyl ester, L-lactic acid, α-keto-glutaric acid, L-malic acid, Tween 40, β-hydroxy-d, L-butyric acid, propionic acid, and acetic acid can be used as sole carbon sources. The principal fatty acids are C18:1ω12t, C16:0, C16:1ω7c, C17:1ω 6c. The polar lipids profile includes phosphatidylcholine, sphingoglycolipid, phosphatidylglycerol, one unknown polar lipid, and three unknown glycolipids. The respiratory quinone is ubiquinone-10 (Q-10). The G+C content is 60.8 mol%.
The type strain NZ-96T (=DSM 112811T = NCCB 100842T) was isolated from a sponge sample. The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the 16S rRNA gene sequence and draft genome sequence of strain NZ-96T is MZ569436 and JAHWXO000000000, respectively.
5. Conclusions
Morphological, cultural, and chemotaxonomic markers, in addition to a phylogenomic tree analysis, revealed that strain NZ-96T belongs to the genus Qipengyuania. The strain can be distinguished from the closely related type strains by several striking characteristics. Crude extracts from NZ-96T showed high activity against Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus Newman, and Bacillus subtilis DSM 10. Whereas weak activity was displayed against tested Gram-negative bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 DSM 19882, and Escherichia coli DSM 1116. No antimicrobial activity was observed against fungal and yeast organisms such as, Pichia anomala DSM 6766, Candida albicans DSM 1665, and Mucor himalis DSM 2656 in this approach. On the basis of the polyphasic approach, we propose to include strain NZ-96T in the genus Qipengyuania. as Qipengyuania pacifica sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d14040295/s1, Table S1: Physiological and biochemical characteristics of NZ-96T and reference strains on API ZYM strip system. Table S2: Physiological and biochemical characteristics of NZ-96T and reference strains on API 20E strip system. Table S3: Physiological and biochemical characteristics of NZ-96T and reference strains on API20NE strip system. Table S4: Physiological and biochemical characteristics of NZ-96T on Biolog Gen III Microplate. Figure S1: HPLC fractionation chromatogram of NZ-96T vs Staphylococcus aureus Newman. Figure S2: Predicted secondary metabolite gene cluster for strain NZ-96T identified by analysis of the NZ-96T genome sequence with the bioinformatics tool antiSMASH 5.0. Figure S3: Genome sequence-based tree of NZ-96T from TYGS.
Author Contributions
S.T.; performed experiments, data analyses, manuscript drafting. C.R.; chemotaxonomy analysis edited manuscript. M.M.; performed electron microscopy. J.W.; supervision, edited manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Strain NZ-96T is deposited at German collection of microorganisms and cell cultures (DSMZ) and Netherlands culture collection of bacteria (NCCB) under accession no. 112811 and 100842, respectively.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Stephanie Schulz and Wera Collisi for excellent technical assistance, Aileen Gollasch for recording the GC data, and Ina Schleicher for electron microscopy sample preparation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Back, C.R.; Stennett, H.L.; Williams, S.E.; Wang, L.; Ojeda Gomez, J.; Abdulle, O.M.; Duffy, T.; Neal, C.; Mantell, J.; Jepson, M.A.; et al. A New Micromonospora Strain with Antibiotic Activity Isolated from the Microbiome of a Mid-Atlantic Deep-Sea Sponge. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Taylor, M.W. Marine Sponges and Their Microbial Symbionts: Love and Other Relationships. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.; Tsai, P.; Bell, J.; Fromont, J.; Ilan, M.; Lindquist, N.; Perez, T.; Rodrigo, A.; Schupp, P.J.; Vacelet, J.; et al. Assessing the Complex Sponge Microbiota: Core, Variable and Species-Specific Bacterial Communities in Marine Sponges. ISME J. 2012, 6, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Sun, C.; Fang, C.; Oren, A.; Xu, X.W. Genomic-Based Taxonomic Classification of the Family Erythrobacteraceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 4470–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Lin, B.; Xu, L.; Li, G.; Wu, C.J.; Luo, L. Erythrobacter spongiae sp. nov., isolated from marine sponge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wu, Y.H.; Sun, C.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.; Meng, F.X.; Wang, C.S.; Xu, X.W. Erythrobacter zhengii sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from deep-sea sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denner, E.B.M.; Vybiral, D.; Koblízek, M.; Kämpfer, P.; Busse, H.-J.; Velimirov, B. Erythrobacter citreus sp. nov., a yellow-pigmented bacterium that lacks Bacteriochlorophyll a, isolated from the western mediterranean sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Xu, H.; Zheng, T. Erythrobacter luteus sp. nov., isolated from mangrove sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subhash, Y.; Tushar, L.; Sasikala, C.; Ramana, C.V.; Ch Ramana, C.V. Erythrobacter odishensis sp. nov. and Pontibacter odishensis sp. nov. isolated from dry soil of a solar saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 4524–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Xu, B.; Liu, K.; Shen, L.; Gu, Z.; Guo, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H. Erythrobacter arachoides sp. nov., isolated from ice core. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4235–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Won, S.M.; Yoon, J.H. Erythrobacter marisflavi sp. nov., isolated from estuary water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2696–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon, L.A.C.; Moreira, A.P.B.; Thompson, F. The Family Erythrobacteraceae. In The Prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 9783642301, pp. 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, T.; Simidu, U. Erythrobacter longus gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic bacterium which contains Bacteriochlorophyll a. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1982, 32, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.M.; Mo, Y.X.; Han, L.; Nogi, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Lv, J. Qipengyuania sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a Member of the Family Erythrobacteraceae Isolated from Subterrestrial Sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3658–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parte, A.C. LPSN—List of Prokaryotic Names with Standing in Nomenclature (Bacterio.Net), 20 Years On. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, S.; Arunpairojana, V.; Suwannachart, C.; Kanjana-Opas, A.; Yokota, A. Aureispira marina gen. nov., sp. nov., a gliding, Arachidonic Acid-Containing Bacterium Isolated from the Southern Coastline of Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2931–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landwehr, W.; Kämpfer, P.; Glaeser, S.P.; Rückert, C.; Kalinowski, J.; Blom, J.; Goesmann, A.; Mack, M.; Schumann, P.; Atasayar, E.; et al. Taxonomic Analyses of Members of the Streptomyces cinnabarinus Cluster, Description of Streptomyces cinnabarigriseus sp. nov. and Streptomyces davaonensis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, N.; Nouioui, I.; Mast, Y.; Zaburannyi, N.; Rohde, M.; Schumann, P.; Müller, R.; Wink, J. Kibdelosporangium persicum sp. nov., a new member of the Actinomycetes from a Hot Desert in Iran. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Lai, P.Y.; Lee, O.O.; Zhou, X.J.; Miao, L.; Wang, H.; Qian, P.Y. Erythrobacter Pelagi sp. nov., a member of the Family Erythrobacteraceae isolated from the Red Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareen, S.; Risdian, C.; Müsken, M.; Wink, J. Alteriqipengyuania Abyssalis sp. nov., a Novel Member of the Class Alphaproteobacteria Isolated from Sponge, and Emended Description of the Genus Alteriqipengyuania. Diversity 2021, 13, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, K.I.; Garcia, R.O.; Gerth, K.; Irschik, H.; Müller, R. Sandaracinus Amylolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a starch-degrading soil myxobacterium, and Description of Sandaracinaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome Sequence-Based Species Delimitation with Confidence Intervals and Improved Distance Functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A Tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Farris, J.S.; Nixon, K.C. TNT, a Free Program for Phylogenetic Analysis. Cladistics 2008, 24, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattengale, N.D.; Alipour, M.; Bininda-Emonds, O.R.P.; Moret, B.M.E.; Stamatakis, A. How Many Bootstrap Replicates Are Necessary? J. Comput. Biol. 2010, 17, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and Other Methods), Version 4.0 Beta 10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland—References—Scientific Research Publishing. 2002. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/(S(lz5mqp453edsnp55rrgjct55))/reference/ReferencesPapers.aspx?ReferenceID=1958232 (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Minnikin, D.E.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Athalye, M.; Schaal, A.; Parlett, J.H. An Integrated Procedure for the Extraction of Bacterial Isoprenoid Quinones and Polar Lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 1984, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.R.; Correa, H.; Haltli, B.A.; Kerr, R.G. Fulvivirga Aurantia sp. nov. and Xanthovirga Aplysinae gen. nov., sp. nov., Marine Bacteria Isolated from the Sponge Aplysina Fistularis, and Emended Description of the Genus Fulvivirga. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2766–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bóna-Lovász, J.; Bóna, A.; Ederer, M.; Sawodny, O.; Ghosh, R. A Rapid Method for the Extraction and Analysis of Carotenoids and Other Hydrophobic Substances Suitable for Systems Biology Studies with Photosynthetic Bacteria. Metabolites 2013, 3, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risdian, C.; Landwehr, W.; Rohde, M.; Schumann, P.; Hahnke, R.L.; Spröer, C.; Bunk, B.; Kämpfer, P.; Schupp, P.J.; Wink, J. Streptomyces Bathyalis sp. nov., an Actinobacterium Isolated from the Sponge in a Deep Sea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasser, M. Identification of Bacteria by Gas Chromatography of Cellular Fatty Acids. Technical Note # 101. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284025789_Identification_of_bacteria_by_gas_chromatography_of_cellular_fatty_acids (accessed on 29 February 2022).
- Khosravi Babadi, Z.; Ebrahimipour, G.; Wink, J.; Narmani, A.; Risdian, C. Isolation and Identification of Streptomyces sp. Act4Zk, a Good Producer of Staurosporine and Some Derivatives. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodamoradi, S.; Hahnke, R.L.; Mast, Y.; Schumann, P.; Kämpfer, P.; Steinert, M.; Rückert, C.; Surup, F.; Rohde, M.; Wink, J. Streptomonospora litoralis sp. nov., a halophilic thiopeptides producer isolated from Sand Collected at Cuxhaven Beach. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 114, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Chalita, M.; Ha, S.M.; Na, S.I.; Yoon, S.H.; Chun, J. ContEst16S: An Algorithm That Identifies Contaminated Prokaryotic Genomes Using 16S RNA Gene Sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2053–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Steinke, K.; Villebro, R.; Ziemert, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. AntiSMASH 5.0: Updates to the Secondary Metabolite Genome Mining Pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W81–W87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M.; Spröer, C.; Klenk, H.P. When Should a DDH Experiment Be Mandatory in Microbial Taxonomy? Arch. Microbiol. 2013, 195, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosako, Y.; Yabuuchi, E.; Naka, T.; Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Proposal of Sphingomonadaceae fam. Nov., Consisting of Sphingomonas Yabuuchi et Al. 1990, Erythrobacter Shiba and Shimidu 1982, Erythromicrobium Yurkov et Al. 1994, Porphyrobacter Fuerst et Al. 1993, Zymomonas Kluyver and van Niel 1936, and Sandaracinobac. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 44, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Desper, R.; Gascuel, O. FastME 2.0: A Comprehensive, Accurate, and Fast Distance-Based Phylogeny Inference Program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, T.; Sun, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Q. Erythrobacter aureus sp. nov., a plant growth-promoting bacterium isolated from sediment in the Yellow Sea, China. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).