How Many Mammals Are Killed on Brazilian Roads? Assessing Impacts and Conservation Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
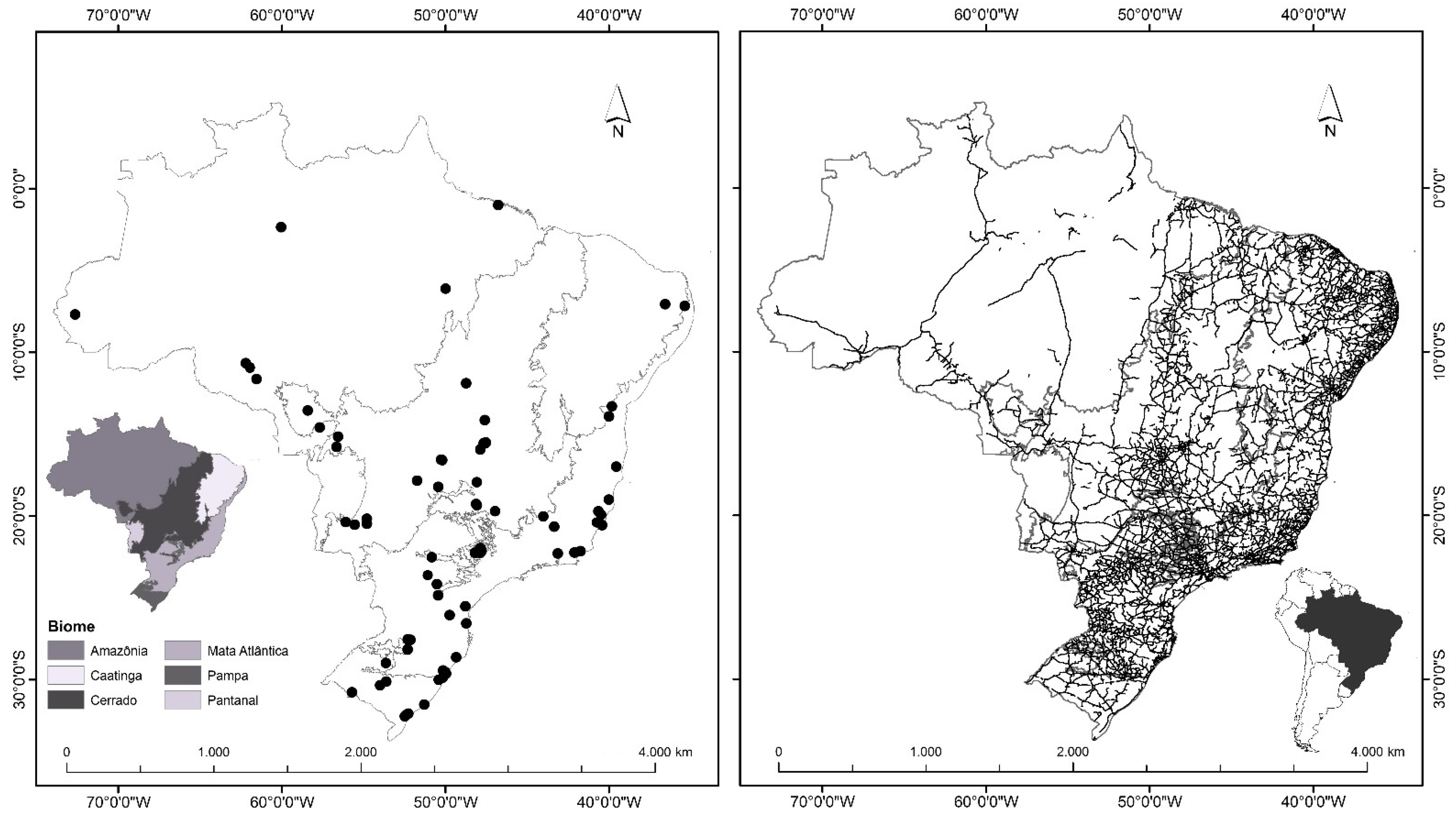
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. State of Mammal Road-Kill and Quantification of Annual Mortality
2.3. Species Conservation Status and Taxonomic Names
3. Results
3.1. State of Mammal Road-Kill and Quantification of Annual Mortality
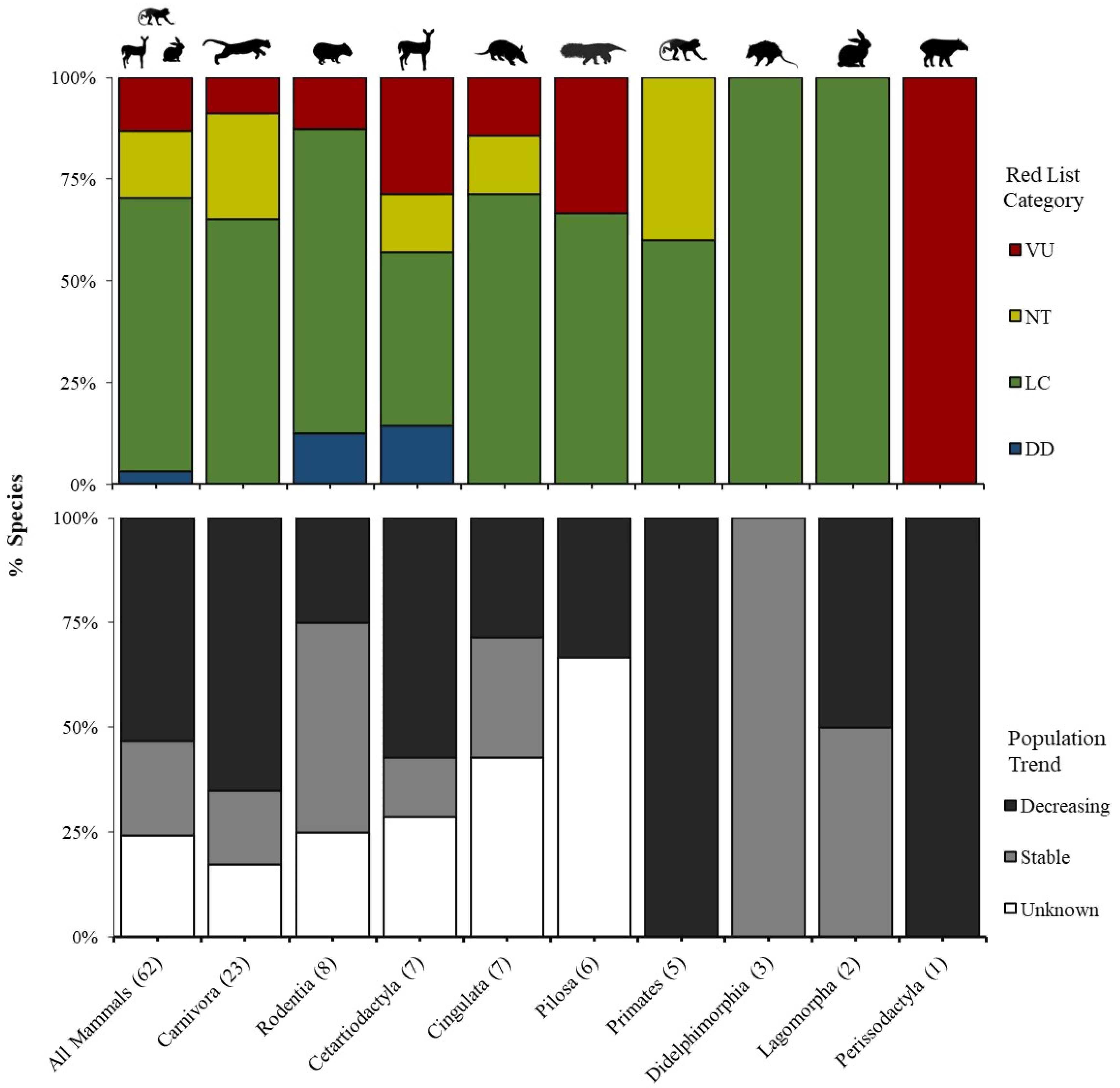
3.2. Conservation Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alamgir, M.; Campbell, M.J.; Sloan, S.; Goosem, M.; Clements, G.R.; Mahmoud, M.I.; Laurance, W.F. Economic, Socio-Political and Environmental Risks of Road Development in the Tropics. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1130–R1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Arrea, I.B. Roads to riches or ruin? Science 2017, 358, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascensão, F.; Fahrig, L.; Clevenger, A.P.; Corlett, R.T.; Jaeger, J.A.G.; Laurance, W.F.; Pereira, H.M. Environmental challenges for the Belt and Road Initiative. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Goosem, M.; Laurance, S.G.W. Impacts of roads and linear clearings on tropical forests. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, K.R.; Burdett, C.L.; Theobald, D.M.; King, S.R.B.; Di Marco, M.; Rondinini, C.; Boitani, L. Quantification of habitat fragmentation reveals extinction risk in terrestrial mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7635–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Koprowski, J.L. Barrier effects of roads on an endangered forest obligate: Influences of traffic, road edges, and gaps. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 199, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, R.; Steyaert, S.M.J.G.; Kindberg, J. Caught in the mesh: Roads and their network-scale impediment to animal movement. Ecography 2017, 40, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwinski, T.; Fahrig, L. The Impacts of Roads and Traffic on Terrestrial Animal Populations. Handb. Road Ecol. 2015, 2015, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Ree, R.; Smith, D.J.; Grilo, C. The Ecological Effects of Linear Infrastructure and Traffic: Challenges and Opportunities of Rapid Global Growth. In Handbook of Road Ecology; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: London, UK, 2005; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyn, K.; Lin, T.E.; Chen, Y.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Fitzgerald, L.A. The magnitude of roadkill in Taiwan: Patterns and consequences revealed by citizen science. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 237, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.L.W.; Shilling, F.M.; Perkins, S.E. The value of monitoring wildlife roadkill. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2020, 66, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.A.G.; Bowman, J.; Brennan, J.; Fahrig, L.; Bert, D.; Bouchard, J.; Charbonneau, N.; Frank, K.; Gruber, B.; Von Toschanowitz, K.T. Predicting when animal populations are at risk from roads: An interactive model of road avoidance behavior. Ecol. Modell. 2005, 185, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L.; Rytwinski, T. Effects of Roads on Animal Abundance: An Empirical Review and Synthesis. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwinski, T.; Fahrig, L. Do species life history traits explain population responses to roads? A meta-analysis. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 147, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.F.; Brito, D. Threats to and viability of the giant anteater, Myrmecophaga tridactyla (Pilosa: Myrmecophagidae), in a protected Cerrado remnant encroached by urban expansion in central Brazil. Zoologia 2013, 30, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grilo, C.; Borda-de-Água, L.; Beja, P.; Goolsby, E.; Soanes, K.; le Roux, A.; Koroleva, E.; Ferreira, F.Z.; Gagné, S.A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Conservation threats from roadkill in the global road network. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNT. Anuário CNT do Transporte 2021. Confederação Nacional do Transporte. 2021. Available online: https://anuariodotransporte.cnt.org.br/2021/Inicial (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Lupinetti-Cunha, A.; Cirino, D.W.; Vale, M.M.; Freitas, S.R. Roadless areas in Brazil: Land cover, land use, and conservation status. Reg. Environ. Change 2022, 22, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, C.; Coimbra, M.R.; Cerqueira, R.C.; Barbosa, P.; Dornas, R.A.P.; Gonçalves, L.O.; Teixeira, F.Z.; Coelho, I.P.; Schmidt, B.R.; Pacheco, D.L.K.; et al. BRAZIL ROAD-KILL: A data set of wildlife terrestrial vertebrate road-kills. Ecology 2018, 99, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, R.C.; Leonard, P.B.; da Silva, L.G.; Bager, A.; Clevenger, A.P.; Jaeger, J.A.G.; Grilo, C. Potential Movement Corridors and High Road-Kill Likelihood do not Spatially Coincide for Felids in Brazil: Implications for Road Mitigation. Environ. Manag. 2021, 67, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, C.; Koroleva, E.; Andrášik, R.; Bíl, M.; González-Suárez, M. Roadkill risk and population vulnerability in European birds and mammals. Front. Ecol. Environ. Cdv. 2020, 18, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Suárez, M.; Zanchetta Ferreira, F.; Grilo, C. Spatial and species-level predictions of road mortality risk using trait data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abra, F.D.; Huijser, M.P.; Magioli, M.; Bovo, A.A.A.; de Ferraz, K.M.P.M.B. An estimate of wild mammal roadkill in São Paulo state, Brazil. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Almasieh, K.; Clevenger, A.P.; Fatemizadeh, F.; Rezaei, A.; Jowkar, H.; Kaboli, M. Road expansion: A challenge to conservation of mammals, with particular emphasis on the endangered Asiatic cheetah in Iran. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 43, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poot, C.; Clevenger, A.P. Reducing Vehicle Collisions with the Central American Tapir in Central Belize District, Belize. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2018, 11, 1940082918789827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abra, F.D.; Granziera, B.M.; Huijser, M.P.; De Barros Ferraz, K.M.P.M.; Haddad, C.M.; Paolino, R.M. Pay or prevent? Human safety, costs to society and legal perspectives on animal-vehicle collisions in São Paulo state, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissonette, J.A.; Kassar, C.A.; Cook, L.J. Assessment of costs associated with deer—Vehicle collisions: Human death and injury, vehicle damage. Hum.–Wildl. Interact. 2008, 2, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huijser, M.P.; Duffield, J.W.; Clevenger, A.P.; Ament, R.J.; McGowen, P.T. Cost-benefit analyses of mitigation measures aimed at reducing collisions with large ungulates in the united states and canada: A decision support tool. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela, F.M.; Rosa, C.A.; Feijó, A. Updated and annotated checklist of recent mammals from Brazil. Biol. Sci. 2020, 92, e20191004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Jones, K.E.; Bielby, J.; Cardillo, M.; Fritz, S.A.; O’Dell, J.; Orme, C.D.L.; Safi, K.; Sechrest, W.; Boakes, E.H.; Carbone, C.; et al. PanTHERIA: A species-level database of life history, ecology, and geography of extant and recently extinct mammals. Ecology 2009, 90, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.A.; Lyons, S.K.; Ernest, S.K.M.; Jones, K.E.; Kaufman, D.M.; Dayan, T.; Marquet, P.A.; Brown, J.H.; Haskell, J.P. Body mass of late quaternary mammals. Ecology 2003, 84, 87131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.A.S.; Clevenger, A.P.; Grilo, C. Effects of roads on terrestrial vertebrate species in Latin America. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 81, 106337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.V.P.; Coelho, I.P.; Teixeira, F.Z.; Kindel, A. Siriema: Road Mortality Software. User’s Manual V. 2.0. NERF, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, Brazil. 2014. Available online: https://github.com/nerf-ufrgs/siriema (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- IBGE. BCIM: Continuous Cartographic Base of Brazil to the Millionth Scale. 2016. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/ (accessed on 26 May 2020).
- Ruedas, L.; Smith, A.T. 2019. Sylvilagus brasiliensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: E.T87491102A45191186. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T87491102A45191186.en (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Balčiauskas, L.; Stratford, J.; Balčiauskienė, L.; Kučas, A. Roadkills as a method to monitor raccoon dog populations. Animals 2021, 11, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.E.S.; Umetsu, R.K.; de Melo, F.R.; Melo, F.C.S.A.; Pereira, K.F.; Oliveira, S.R. Roadkill in the Brazilian cerrado savanna: Comparing five highways in southwestern Goiás. Oecologia Aust. 2017, 21, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffaci, A.C.; da Silva, V.P.; Hartmann, M.T.; Hartmann, P.A. Diversidade de aves, mamíferos e répteis atropelados em região de floresta subtropical no sul do brasil. Ciência Nat. 2016, 38, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano-Vizcaíno, P.; Grilo, C.; Pinto, F.A.S.; Carvalho, W.D.; Melinski, R.D.; Schultz, E.D.; González-Suárez, M. Roadkill patterns in Latin American birds and mammals. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2022, 31, 1756–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.M.C.; Ferreira, M.S.; Mourão, C.L.B.; Bueno, C. Spatial patterns of carnivore roadkill in a high-traffic-volume highway in the endangered Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Mamm. Biol. 2022, 102, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceia-Hasse, A.; Borda-de-Água, L.; Grilo, C.; Pereira, H.M. Global exposure of carnivores to roads. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.Z.; Kindel, A.; Hartz, S.M.; Mitchell, S.; Fahrig, L. When road-kill hotspots do not indicate the best sites for road-kill mitigation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalva, P.; Palomares, F. A continental approach to jaguar extirpation: A tradeoff between anthropic and intrinsic causes. J. Nat. Conserv. 2020, 66, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, L.R.; Vieira, E.M. Attracted to death. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 20, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.S.; Graham, B.; Rebelo, H.; Bocksberger, G.; Meyer, C.F.; Wich, S.; Kühl, H.S. A global risk assessment of primates under climate and land use/cover scenarios. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3163–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascensão, F.; D’Amico, M.; Barrientos, R. No Planet for Apes? Assessing Global Priority Areas and Species Affected by Linear Infrastructures. Int. J. Primatol. 2021, 43, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittermeier, R.A.; Reuter, K.E.; Rylands, A.B.; Jerusalinsky, L.; Schwitzer, C.; Strier, K.B.; Ratsimbazafy, J.; Humle, T. (Eds.) Primates in Peril: The World’s 25 Most Endangered Primates 2022–2023; IUCN SSC Primate Specialist Group; International Primatological Society; Re:Wild: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; 163p. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, F.D.O.; Culot, L.; de Carvalho, R.E.W.F.; Rocha, V.J. Functionality of two canopy bridge designs: Successful trials for the endangered black lion tamarin and other arboreal species. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2022, 68, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canevari, M.; Vaccaro, O. Guía de Mamíferos del Sur de América del Sur; Lola Editora: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brum, T.R.; Santos-Filho, M.; Canales, G.R.; Ignacio, R.A. Effects of roads on the vertebrates diversity of the Indigenous Territory Paresi and its surrounding. Braz. J. Biol. 2017, 78, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, N.C.; Bordignon, M.O.; Shapiro, J.T. Fast and furious: A look at thedeath of animals on the highway MS-080, Southwestern Brazil. Iheringia. Sér. Zool. 2014, 104, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sousa, J.C.; Cunha, V.P.; Markwith, S.H. Spatiotemporal variation in human-wildlife conflicts along highway BR-262 in the Brazilian Pantanal. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 227–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.F.; Brito, D. Protected areas effectiveness in maintaining viable giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) populations in an agricultural frontier. Nat. Conserv. 2015, 13, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ascensão, F.; Desbiez, A.L.J. Assessing the impact of roadkill on the persistence of wildlife populations: A case study on the giant anteater. Perspect Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 20, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.A.S.; Bager, A.; Clevenger, A.P.; Grilo, P. Giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) conservation in Brazil: Analysing the relative effects of fragmentation and mortality due to roads. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 228, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.; Faustino, M.T.; Freitas, S.R. Influence of landscape characteristics on capybara road-kill on highway BR-040, Southeastern Brazil. Oecologia Aust. 2013, 17, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijser, M.P.; Delborgo Abra, F.; Duffield, J.W. Mammal Road Mortality and Cost–Benefit Analyses of Mitigation Measures Aimed at Reducing Collisions with Capybara (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris) in São Paulo State, Brazil. Oecologia Aust. 2013, 17, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte, J.C.; Tavares-Filho, J.A. Diet of the yellow armadillo, Euphractus sexcinctus, in South-Central Brazil. Edentata 2004, 6, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Ramírez, L.; González-Gallina, A.; Soto, V.; Pacheco-Figueroa, C.J.; Pech-Canchém, J.M. Comparison of road-killed mammals on roads of different types of jurisdictions and traffic volume in Veracruz, México. Therya Notes 2022, 3, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros Ferraz, K.M.P.M.; De Siqueira, M.F.; Martin, P.S.; Esteves, C.F.; Do Couto, H.T.Z. Assessment of Cerdocyon thous distribution in an agricultural mosaic, southeastern Brazil. Mammalia 2010, 74, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, D.W.; Lupinetti-Cunha, A.; Freitas, C.H.; de Freitas, S.R. Do the roadkills of different mammal species respond the same way to habitat and matrix? Nat. Conserv. 2022, 47, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, D.W.; Freitas, S.R. Quais são os mamíferos silvestres mais atropelados no Brasil. In Anais do 5 Workshop de Evolução e Diversidade; Santos: Paulo, Brazil, 2018; pp. 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Borda-de-Água, L.; Grilo, C.; Pereira, H.M. Modeling the impact of road mortality on barn owl (Tyto alba) populations using age-structured models. Ecol. Modell. 2014, 276, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.; Schumaker, N.H.; Brandon, K.R.; Bager, A.; Grilo, C. Simulating the consequences of roads for wildlife population dynamics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 193, 103672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascensão, F.; Desbiez, A.L.J.; Medici, E.P.; Bager, A. Spatial patterns of road mortality of medium–large mammals in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Wildl. Res. 2017, 44, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Maciel, F.; Rufo, D.A.; Keuroghlian, A.; Russo, A.C.; Brandt, N.M.; Vieira, N.F.; da Nóbrega, B.M.; Nava, A.; Nardi, M.S.; de Jácomo, A.T.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of white-lipped peccaries (Tayassu pecari) in the Pantanal, Cerrado and Atlantic Forest from Brazil. Mamm. Biol. 2019, 95, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocheti, G.; de Assis, J.C.; Ribeiro, J.W.; Ribeiro, M.C. Highway widening and underpass effects on vertebrate road mortality. Biotropica 2017, 49, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abra, F.D.; Canena, A.C.; Garbino, G.S.T.; Medici, E.P. Use of unfenced Highway underpasses by lowland tapirs and other medium and large mammals in central-western Brazil. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 18, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braçança, D.; Menegassi, D. How Brazil Is Working to Save the Rare Lion Tamarins of the Atlantic Forest. Mongabay Report. 2022. Available online: https://news.mongabay.com/2022/06/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Abrantes, M.M.R.; da Nóbrega Carreiro, A.; de Araújo, D.V.F.; de Souza, J.G.; de Lima, J.P.R.; de Araújo Cezar, H.R.; Leite, L.S.; Abrantes, S.H.F. Vertebrados silvestres atropelados na rodovia BR-230, Paraíba, Brasil. Pubvet 2017, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, D.R.; Ribeiro, P.; Teles, L.T. Can human demographic or biological factors influence mammal roadkill? A case study in the GO-060 highway. Oecologia Aust. 2019, 23, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista Turci, L.C.; Bernarde, P.S. Vertebrados atropelados na Rodovia Estadual 383 em Rondônia. Brasil. Biotemas 2009, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belão, M.; Bóçon, R.; Christo, S.W.; de Souza, M.A.M.; de Souza Júnior, J.L. Incidentes De Mamíferos Na Rodovia Br-277, Paraná—Brasil. Publicatio UEPG. Cienc. Biol. Saude 2014, 20, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Braz, V.; França, F.G.R. Wild vertebrate roadkill in the Chapada dos Veadeiros National Park, Central Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 2016, 16, e0182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.; Sousa, C.O.M.; Freitas, S.R. Habitat or matrix: Which is more relevant to predict road-kill of vertebrates? Braz. J. Biol. 2015, 75, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, N.C. Biological characteristics influence mammal road kill in an Atlantic Forest-Cerrado interface in south-western Brazil. Ital. J. Zool. 2011, 78, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caires, H.S.; Souza, C.R.; Lobato, D.N.C.; Fernandes, M.N.S.; Damasceno, J.S. Roadkilled mammals in the northern amazon region and comparisons with roadways in other regions of Brazil. Iheringia Ser. Zool. 2019, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.F.; Custódio, A.E.I.; Junior, O.M. Wild vertebrates roadkill aggregations on the BR-050 highway, state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Biosci. J. 2015, 31, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, I.P.; Kindel, A.; Coelho, A.V.P. Roadkills of vertebrate species on two highways through the Atlantic Forest Biosphere Reserve, southern Brazil. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, L.L.C.; Silva, D.E.; de Oliveira, S.V.; Finger, J.V.G.; dos Santos, C.R.; Petry, M.V. Vertebrate road kill survey on a highway in southern Brazil. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2017, 39, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Costa, L.S. Survey of wild mammals small and medium-size run over in BR 101, stretch between the municipalities of joinville and piçarras, state of Santa Catarina [Levantamento de mamíferos silvestres de pequeno e médio porte atropelados na BR 101, entre os município. Biosci. J. 2011, 27, 666–672. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, R.R.G.F.; Dias, L.A. Mortalidade de vertebrados por atropelamento em um trecho da GO-164, no sudoeste goiano. Rev. Biotecnol. Ciência 2013, 2, 58–74. [Google Scholar]
- Da Cunha, H.F.; Moreira, F.G.A.; Silva, S.D.S. Roadkill of wild vertebrates along the GO-060 road between Goiânia and Iporá, Goiás State, Brazil. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2010, 32, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreguetti, A.C.; Graciano, J.M.; Luppi, A.P.; Pereira-Ribeiro, J.; Rocha, C.F.D.; Bergallo, H.G. Roadkill of medium to large mammals along a Brazilian road (BR-262) in Southeastern Brazil: Spatial distribution and seasonal variation. Stud. Neotropical Fauna Environ. 2020, 55, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.M.M.; de Aquino Ribas, A.C.; Casella, J.; Mendes, S.L. Variação espacial de atropelamentos de mamíferos em área de restinga no estado do Espírito Santo, Brasil. Neotrop. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 9, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, I.C.; Gonçalves, L.O.; Kindel, A.; Trigo, T.C. Mammalian fatalities on roads: How sampling errors affect road prioritization and dominant species influence spatiotemporal patterns. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2021, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.H.; Justino, C.S.; Setz, E.Z.F. Road-kills of the giant anteater in south-eastern Brazil: 10 years monitoring spatial and temporal determinants. Wildl. Res. 2014, 41, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.R.; de Oliveira, A.N.; Ciocheti, G.; Vieira, M.V.; da Silva Matos, D.M. How landscape features influence road-kill of three species of mammals in the Brazilian savanna? Oecologia Aust. 2015, 18, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, C.; de Resende Cardoso, T.; Solar, R.; Bager, A. Do the size and shape of spatial units jeopardize the road mortality-risk factors estimates? Nat. Conserv. 2016, 14, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumier-Costa, F.; Sperber, C.F. Roadkills of vertebrates in Carajas National Forest, Para, Brazil. Acta Amazon 2009, 39, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegel, C.G.Z. Mamíferos Silvestres Atropelados Na Rodovia Rs-135 E Entorno. Biotemas 2012, 25, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hengemühle, A.; Cademartori, C. Levantamento de mortes de vertebrados silvestres devido a atropelamento em um trecho da Estrada do Mar (RS-389). Biodivers. Pampeana 2008, 6, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- IBRAM. Public Data. 2017. Available online: http://www.ibram.df.gov.br/component/content/article/261.html (accessed on 15 March 2017).
- Martinelli, M.M.; Volpi, T.A. Mamíferos atropelados na Rodovia Armando Martinelli (ES-080), Espírito Santo, Brasil. Nat. On Line 2011, 9, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, E.S.; Santos-Filho, M. Efeitos da BR-070 na Província Serrana de Cáceres, Mato Grosso, sobre a comunidade de vertebrados silvestres. Rev. Bras. Zoociências 2007, 9, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Meneguetti, D.U.O.; Meneguetti, N.F.S.P.; Trevisan, O. Georreferenciamento e reavaliação da mortalidade por atropelamento de animais silvestres na linha 200 entre os municipios de Ouro Preto do Oeste e Vale do Paraíso–RO. Rev. Científic. Fac. Educ. Meio Ambiente 2010, 1, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Milli, M.S.; Passamani, M. Impacto da Rodovia Josil Espíndula Agostini (ES-259) sobre a mortalidade de animais silvestres (Vertebrata) por atropelamento. Nat. On Line 2006, 4, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D.; Oliveira, S.; Martins, V.; Silva, D. Vertebrados silvestres atropelados na BR 158, RS, Brasil. Rev. Biotemas 2012, 25, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omena Junior, R.; Pantoja Lima, J.; Wendt Santos, A.L.; Aguiar Ribeiro, G.A.; Rocha Aride, P.H. Caracterizacion de fauna vertebrada atropellada en la via BR-174;Amazonas Brasil. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Anim. 2012, 4, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, C.M.; Povaluk, M. Atropelamento de animais silvestres na rodovia federal br-116, trecho administrado pela concessionária autopista planalto sul 1. Saúde Meio Ambiente Rev. Interdiscip. 2012, 1, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.G.; Atanaena, F.; Andrade, G.; Marcus, I.; Fernandes, E.B. Dois anos de monitoramento dos atropelamentos de mamíferos na rodovia PA-458, Bragança, Pará Two-year monitoring of mammal roadkill on the PA-458 highway in Bragança. Pará 2006, 1, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.; de Londrina, U.E.; Hideki, M.; Yabu, S.; Geller, I.V.; de Londrina, U.E.; Lehn, C.R. Don’t speed up, speed kills: Mammal roadkills on highway sections of PR-445 in the south of Brazil. Oecologia Aust. 2020, 25, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, B.F.; Turci, L.C.B. Vertebrados atropelados na estrada da Variante (BR-307), Cruzeiro do Sul, Acre, Brasil. Nat. On Line 2013, 11, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, T.X. Diagnóstico dos Pontos Mais Críticos de Atropelamento de Mamíferos Silvestres no Trecho da BR 293, Que Corta a Área de Proteção Ambiental (APA) do Ibirapuitã, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil; Final thesis for graduation in Biology; Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, E.C.; Silva, J.; e Silva, P.M.; do Vale, V.S.; Araújo, M.D.S. Atropelamentos de tatu-canastra Priodontes maximus (Kerr, 1792) em uma rodovia no Cerrado goiano e sua relação com a paisagem do entorno. Multi-Sci. J. 2018, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Castro, K.G.; Ciocheti, G.; Ribeiro, J.W.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Galetti, P.M. Using DNA barcode to relate landscape attributes to small vertebrate roadkill. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roel, C.F.C.; Iannini-Custódio, A.E.; Marçal Júnior, O. Do roadkill aggregations of wild and domestic mammals overlap? Rev. Biol. Trop. 2019, 67, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranholi, B.H.; Bergel, M.M.; Ruffino, P.H.P.; Rodriguez-C, K.G.; Ramazzotto, L.A.; de Freitas, P.D.; Galetti, P.M., Jr. Roadkill hotspots in a protected area of Cerrado in Brazil: Planning actions to conservation. Revista MVZ Córdoba 2016, 21, 5441–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sássi, C.M.; Nascimento, A.A.T.; Miranda, R.F.P.; Carvalho, G.D. Survey of road-killed wild animals in stretch of the highway BR482. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária e Zootec. 2013, 65, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silva, D.E.; Corrêa, L.L.C.; Oliveira, S.V.; Cappellari, L.H. Monitoring of road-killed vertebrates in two highway sections in the central region of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Rev. Ciências Ambient. 2013, 7, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.A.N.; Miranda, P.C. Terrestrial mammals found road kills in br-230/PB between Campina Grande and João Pessoa. Rev. Biol. Farm. 2010, 4, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, F.Z.; Kindel, A. Atropelamentos de animais silvestres na Rota do Sol: Como minimizar esse conflito e salvar vidas? Rodrigo Cambará Printes. (Org.). In Gestão Ambiental e Negociação de Conflitos em Unidades de Conservação do Nordeste do Rio Grande do Sul; CORAG: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2012; pp. 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, F.Z.; Coelho, A.V.P.; Esperandio, I.B.; Kindel, A. Vertebrate road mortality estimates: Effects of sampling methods and carcass removal. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 157, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadão, G. Atropelamentos de vertebrados silvestres em quatro rodovias no cerrado, mato grosso, brasil. Multi-Sci. J. 2018, 1, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weiss, L.P.; Vianna, V.O. A study of the impact of federal roads BR-376, BR-373 and BR- 277 roads, Apucarana and Curitiba, Paraná stretch on the run over of wild animals. Ciência Biol. Saúde 2012, 18, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Zanzini, A.C.; Machado, F.S.; de Oliveira, J.E.; de Oliveira, E.C.M. Roadkills of medium and large-sized mammals on highway BR-242, midwest Brazil: A proposal of new indexes for evaluating animal roadkill rates. Oecologia Aust. 2018, 22, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Family | Scientific Name | Average-Estimate (ind./Year) in Brazil | Average-Mortality Rate (ind./Day/100 km) | Average Total Roadkilled Biomass (kg/Year) | IUCN Red List Category | IUCN Population Trend | IUCN Threats: Transportation and Service Corridors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Didelphidae | Didelphis albiventris | 221,381.6 | 0.4385 | 228,127.1 | Least Concern | Stable | |
| Chlamyphoridae | Dasypus septemcinctus | 194,008.7 | 0.3808 | 296,181.5 | Least Concern | Unknown | |
| Canidae | Cerdocyon thous | 124,679.2 | 0.2043 | 715,865.7 | Least Concern | Stable | |
| Mephitidae | Conepatus chinga | 112,069.5 | 0.5354 | 214,893.3 | Least Concern | Decreasing | |
| Chlamyphoridae | Euphractus sexcinctus | 82,219.5 | 0.1328 | 388,993.4 | Least Concern | Stable | |
| Caviidae | Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | 65,846.7 | 0.1040 | 3,170,184.5 | Least Concern | Stable | |
| Myrmecophagidae | Tamandua tetradactyla | 60,400.3 | 0.0953 | 289,921.4 | Least Concern | Unknown | Roads and railroads |
| Procyonidae | Procyon cancrivorus | 43,482.8 | 0.0685 | 301,410.8 | Least Concern | Decreasing | |
| Chlamyphoridae | Dasypus novemcinctus | 42,510.7 | 0.0670 | 167,875.3 | Least Concern | Stable | |
| Tayassuidae | Tayassu pecari | 40,473.0 | 0.0908 | 1,286,987.7 | Vulnerable | Decreasing | |
| Myrmecophagidae | Myrmecophaga tridactyla | 29,520.6 | 0.0668 | 871,796.5 | Vulnerable | Decreasing | Roads and railroads |
| Mustelidae | Galictis cuja | 23,735.4 | 0.0409 | 23,735.4 | Least Concern | Unknown | Roads and railroads |
| Didelphidae | Didelphis aurita | 22,488.1 | 0.0714 | 24,869.2 | Least Concern | Stable | |
| Cervidae | Mazama gouazoubira | 19,223.8 | 0.0345 | 319,751.9 | Least Concern | Decreasing | Roads and railroads |
| Procyonidae | Nasua nasua | 17,371.1 | 0.0380 | 65,584.7 | Least Concern | Decreasing |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, F.A.S.; Cirino, D.W.; Cerqueira, R.C.; Rosa, C.; Freitas, S.R. How Many Mammals Are Killed on Brazilian Roads? Assessing Impacts and Conservation Implications. Diversity 2022, 14, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100835
Pinto FAS, Cirino DW, Cerqueira RC, Rosa C, Freitas SR. How Many Mammals Are Killed on Brazilian Roads? Assessing Impacts and Conservation Implications. Diversity. 2022; 14(10):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100835
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Fernando Antônio Silva, Douglas William Cirino, Rafaela Cobucci Cerqueira, Clarissa Rosa, and Simone Rodrigues Freitas. 2022. "How Many Mammals Are Killed on Brazilian Roads? Assessing Impacts and Conservation Implications" Diversity 14, no. 10: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100835
APA StylePinto, F. A. S., Cirino, D. W., Cerqueira, R. C., Rosa, C., & Freitas, S. R. (2022). How Many Mammals Are Killed on Brazilian Roads? Assessing Impacts and Conservation Implications. Diversity, 14(10), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100835







