Stochastic Processes Drive Plant Community Assembly in Alpine Grassland during the Restoration Period
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Study Sites
2.2. Measurement of Species Richness and Coverage of Each Species
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
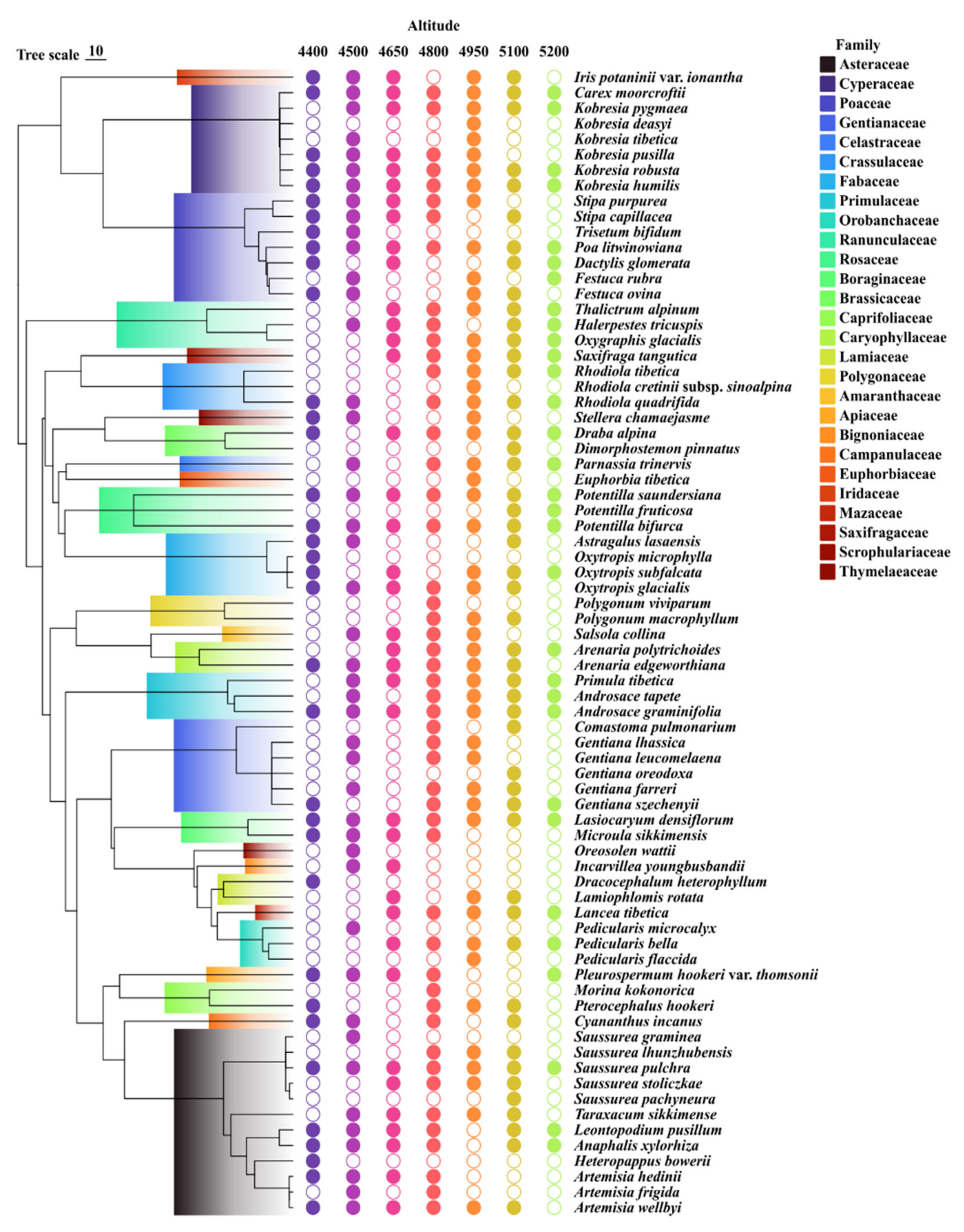
3.1. The Overview of the Community Structure
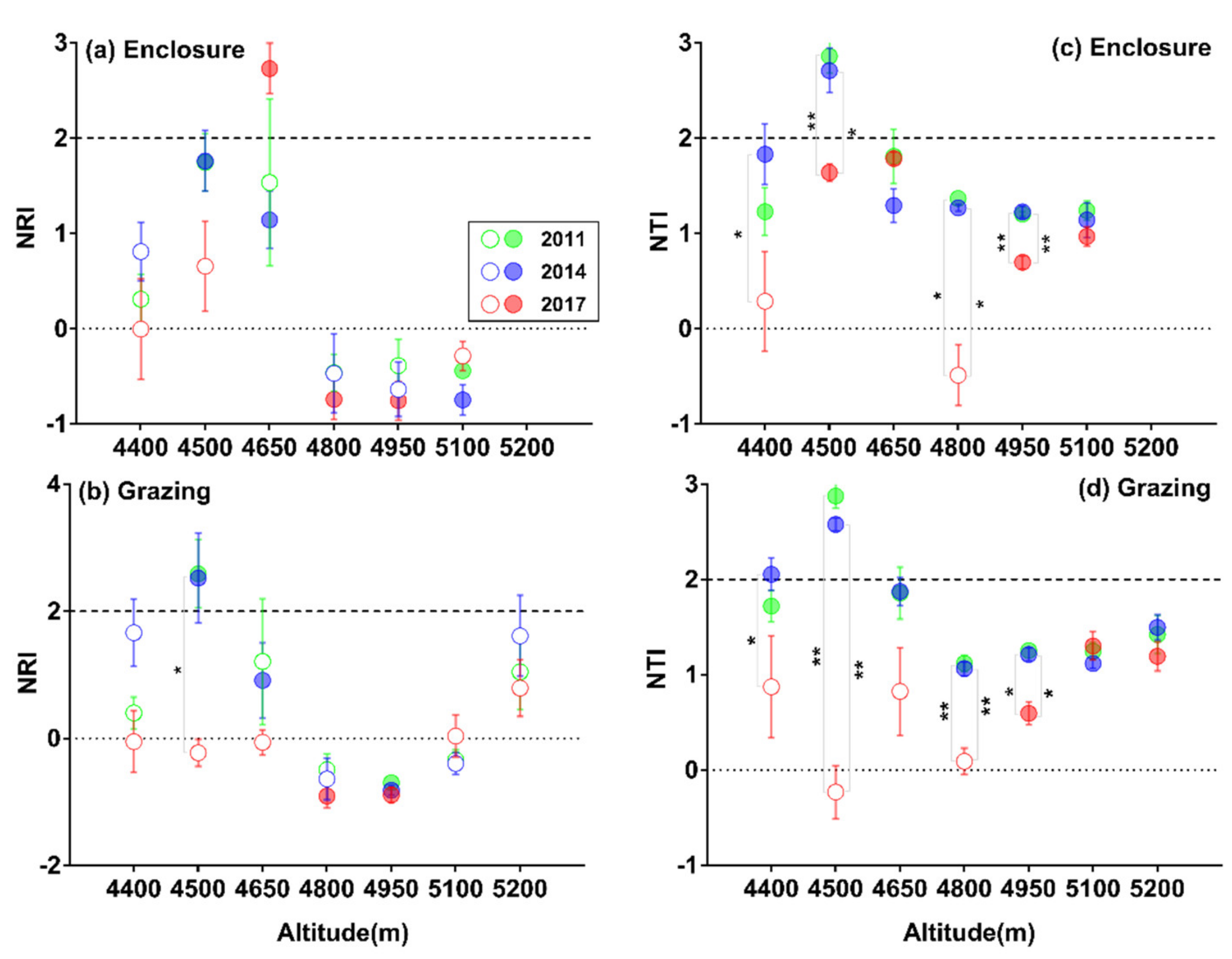
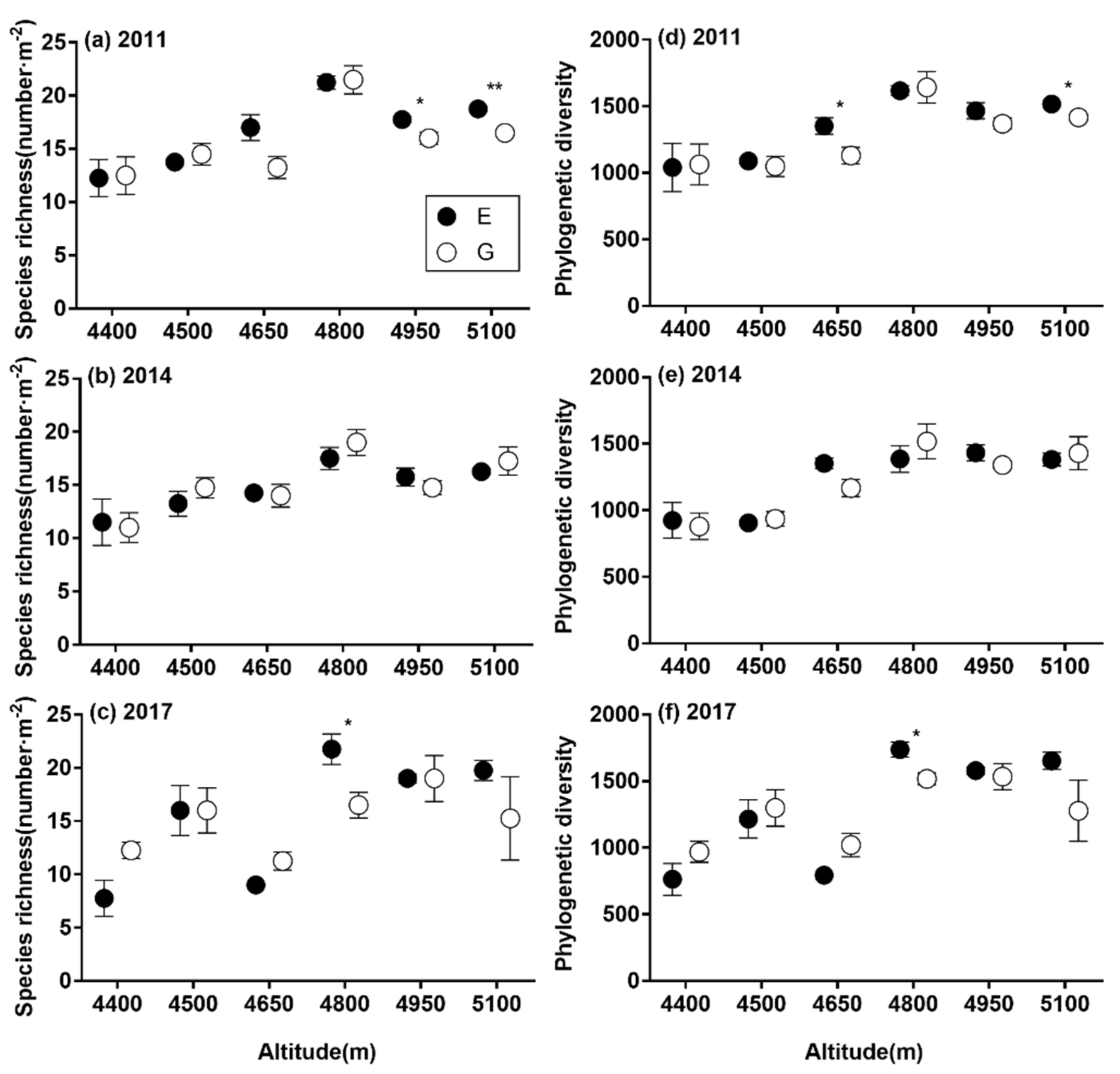
3.2. Patterns of SR and α-phylogenetic Indices
3.3. The Relative Impacts of Grazing Management, Duration of Enclosure and Environmental Factors on SR and α-phylogenetic Indices
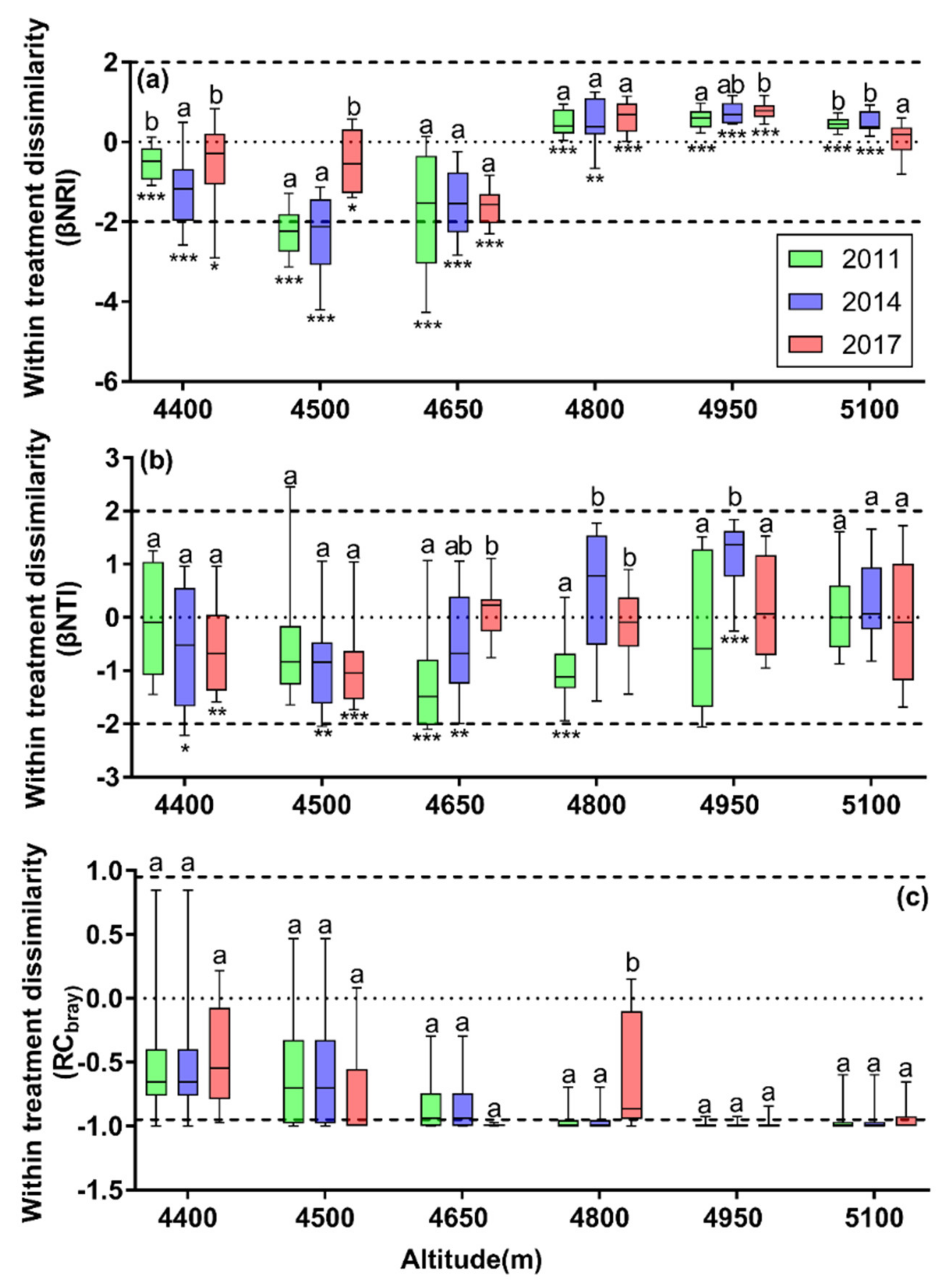
3.4. Patterns of β-phylogenetic Indices between Enclosure and Grazing Plots
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kraft, N.J.; Cornwell, W.K.; Webb, C.O.; Ackerly, D.D. Trait evolution, community assembly, and the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities. Am. Nat. 2007, 170, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnillas, C.A.; Borer, E.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Alberti, J.; Baez, S.; Bakker, J.D.; Boughton, E.H.; Buckley, Y.M.; Bugalho, M.N.; Donohue, I.; et al. Opposing community assembly patterns for dominant and nondominant plant species in herbaceous ecosystems globally. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 17744–17761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, H.A. The Individualistic Concept of the Plant Association. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1926, 53, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, C.S. The Ecology of Animals; Methuen: London, UK, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- Sale, P.F. Maintenance of High Diversity in Coral Reef Fish Communities. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, P.L.; Warner, R.R. Environmental variability promotes coexistence in lottery competitive systems. Am. Nat. 1981, 117, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, P. Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, P.B.; Hillerislambers, J.; Levine, J.M. A niche for neutrality. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosindell, J.; Hubbell, S.P.; He, F.; Harmon, L.J.; Etienne, R.S. The case for ecological neutral theory. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembel, S.W. Disentangling niche and neutral influences on community assembly: Assessing the performance of community phylogenetic structure tests. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.S.; Cadotte, M.W.; MacDonald, A.A.; Marushia, R.G.; Mirotchnick, N. Phylogenetic diversity and the functioning of ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Stegen, J.C.; Kim, M.; Dong, K.; Adams, J.M.; Lee, Y.K. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, V.G.; Bordenave, C.D.; Nieva, A.S.; Llames, M.E.; Colavolpe, M.B.; Gárriz, A.; Ruiz, O.A. Soil bacterial and fungal community structure of a rice monoculture and rice-pasture rotation systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 151, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnai, M.; Trindade, D.P.F.; Thierry, M.; Kaushik, K.; Hrček, J.; Götzenberger, L. Environment and space drive the community assembly of Atlantic European grasslands: Insights from multiple facets. J. Biogeogr. 2022, 49, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, D.; Canham, C.D.; Beaudet, M.; Messier, C. Reconciling niche and neutrality: The continuum hypothesis. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; Myers, J.A. Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellend, M. Conceptual synthesis in community ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 2010, 85, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic Community Assembly: Does It Matter in Microbial Ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Crist, T.O.; Chase, J.M.; Vellend, M.; Inouye, B.D.; Freestone, A.L.; Sanders, N.J.; Cornell, H.V.; Comita, L.S.; Davies, K.F.; et al. Navigating the multiple meanings of beta diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Martiny, J.B. Beyond biogeographic patterns: Processes shaping the microbial landscape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, T. Historical contingency in community assembly: Integrating niches, species pools, and priority effects. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2015, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Yuan, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Arkin, A.P.; Firestone, M.K.; Zhou, J. A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Peng, F.; Xue, X.; You, Q.; Lai, C.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, Y. Productivity and quality of alpine grassland vary with soil water availability under experimental warming. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bullock, J.M.; Lavorel, S.; Manning, P.; Schaffner, U.; Ostle, N.; Chomel, M.; Durigan, G.; Fry, E.L.; Johnson, D.; et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, G.; Luo, Y. Quantitative evaluation of the effect of prohibiting grazing policy on grassland desertification reversal in northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Kang, W.; David, M. Several challenges in monitoring and assessing desertification. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7561–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Shi, P.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Wu, F. Current condition and protection strategies of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecological security barrier. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Ri, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, T. Responses of CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes to livestock exclosure in an alpine steppe on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Plant Soil 2012, 359, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.M.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wu, G.L.; Shi, J.J.; Ren, G.H. A review of formation mechanism and restoration measures of “black-soil-type” degraded grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2359–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mi, Z.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhu, B.; Cao, G.; et al. Shifting plant species composition in response to climate change stabilizes grassland primary production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4051–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Long, R. Formation causes and recovery of the “Black Soil Type” degraded alpine grassland in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Agri. China 2007, 1, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-L.; Du, G.-Z.; Liu, Z.-H.; Thirgood, S. Effect of fencing and grazing on a Kobresia-dominated meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 2009, 319, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Ren, Z.; Luo, M. Effects of animal grazing on vegetation biomass and soil moisture on a typical steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, R.A.; Facelli, J.M. Effects of sheep exclusion on the soil seed bank and annual vegetation in chenopod shrublands of South Australia. J. Arid Environ. 1999, 42, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.A.; Farrell, A.K.; Blackburn, R.C.; Bauer, J.T.; Groves, A.M.; Brudvig, L.A.; Jones, H.P.; Gibson, D. Grassland restoration characteristics influence phylogenetic and taxonomic structure of plant communities and suggest assembly mechanisms. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, J.; Bakker, E.S.; van Klink, R.; Olff, H.; Smit, C. Herbivore exclusion promotes a more stochastic plant community assembly in a natural grassland. Ecology 2017, 98, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Yang, N.; Dong, K.; Xu, Y.; Ding, X.; Shi, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, N.; Gao, Y. Shrub-encroached grassland as an alternative stable state in semiarid steppe regions: Evidence from community stability and assembly. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3142–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, G. Effects of grazing on plant species and phylogenetic diversity in alpine grasslands, Northern Tibet. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 170, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Shen, R.; Chen, N.; Yang, X. Species turnover drives grassland community to phylogenetic clustering over long-term grazing disturbance. J. Plant. Ecol. 2020, 13, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; Li, R.; Tang, Y.; Du, M. Causes for the unimodal pattern of biomass and productivity in alpine grasslands along a large altitudinal gradient in semi-arid regions. J. Veg. Sci. 2013, 24, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.X.; Luo, T.X.; Li, R.C.; Wei, H.X.; Li, X.; Du, M.Y.; Tang, Y.H. Precipitation alters temperature effects on ecosystem respiration in Tibetan alpine meadows. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 252, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Liu, B.; Liu, S.; Feng, Z.H.; Jiang, K.W. Plantlist: Looking Up the Status of Plant Scientific Names based on The Plant List Database. R package version 0.7.2. Available online: https://github.com/helixcn/plantlist/ (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, D.; Bell, T.; Barbera, C.; Combe, M.; Pommier, T.; Mouquet, N. Phylogenetic constraints on ecosystem functioning. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, F.; Grenyer, R.; Rouget, M.; Davies, T.J.; Cowling, R.M.; Faith, D.P.; Balmford, A.; Manning, J.C.; Procheş, Ş.; van der Bank, M.; et al. Preserving the evolutionary potential of floras in biodiversity hotspots. Nature 2007, 445, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherson, R.A.; Faith, D.P. Phylogenetic Diversity: Applications and Challenges in Biodiversity Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.T.; Jolley-Rogers, G.; Mishler, B.D.; Thornhill, A.H. Phylogenetic diversity is a better measure of biodiversity than taxon counting. J. Syst. Evol. 2018, 56, 663–667.54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.O.; Ackerly, D.D.; McPeek, M.A.; Donoghue, M.J. Phylogenies and community ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 475–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamosi, S.M.; Heard, S.B.; Vamosi, J.C.; Webb, C.O. Emerging patterns in the comparative analysis of phylogenetic community structure. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 572–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.O. Exploring the Phylogenetic Structure of Ecological Communities: An Example for Rain Forest Trees. Am. Nat. 2000, 156, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Deng, Y.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhou, J. A general framework for quantitatively assessing ecological stochasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16892–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Ouyang, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Zhou, W. The diversity and community assembly process of wetland plants from lakeshores on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Diversity 2021, 13, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopping, K.A.; Knapp, A.K.; Dorji, T.; Klein, J.A. Warming and land use change concurrently erode ecosystem services in Tibet. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5534–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.A.; Koch, A.M.; Forsythe, J.; Johnson, N.C.; Tilman, D.; Klironomos, J. Resistance of soil biota and plant growth to disturbance increases with plant diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyashevska, O.; Farnsworth, K.D. How many dimensions of biodiversity do we need? Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoine, S.; Bonsall, M.B. Measuring biodiversity to explain community assembly: A unified approach. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2011, 86, 792–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, N.G. The role of evolutionary processes in producing biodiversity patterns, and the interrelationships between taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic biodiversity. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Jin, Y.; Ricklefs, R.E. Phylogenetic diversity anomaly in angiosperms between eastern Asia and eastern North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11452–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firincioglu, H.K.; Seefeldt, S.S.; Sahin, B. The effects of long-term grazing exclosures on range plants in the Central Anatolian Region of Turkey. Environ. Manag. 2007, 39, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, X. Precipitation and species composition primarily determine the diversity–productivity relationship of alpine grasslands on the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Alpine. Bot. 2014, 124, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, M.; Fiedler, S.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tietjen, B. Impacts of grazing exclusion on productivity partitioning along regional plant diversity and climatic gradients in Tibetan alpine grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, W.; Paul, K. Ecological Assembly Rules Perspectives, Advances, Retreats; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kraft, N.J.B.; Adler, P.B.; Godoy, O.; James, E.C.; Fuller, S.; Levine, J.M.; Fox, J. Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering metaphor. Funct. Ecol. 2015, 29, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Partitioning diversity into independent alpha and beta components. Ecology 2007, 88, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Hsieh, T.C.; Sander, E.L.; Ma, K.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Ellison, A.M. Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: A framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecol. Monogr. 2014, 84, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmandrier, L.; Munkemuller, T.; Lavergne, S.; Thuiller, W. Effects of species’ similarity and dominance on the functional and phylogenetic structure of a plant meta-community. Ecology 2015, 96, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, H.; Ma, Z. Phylogenetic structure of alpine steppe plant communities along a precipitation and temperature gradient on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C. Alpine Plant Life; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- González-Caro, S.; Duivenvoorden, J.F.; Balslev, H.; Cavelier, J.; Grández, C.; Macía, M.J.; Romero-Saltos, H.; Sánchez, M.; Valencia, R.; Duque, Á.; et al. Scale-dependent drivers of the phylogenetic structure and similarity of tree communities in northwestern Amazonia. J. Ecol. 2020, 109, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.T.; Farine, D.R.; Trisos, C.H. Phylogenetic community structure metrics and null models: A review with new methods and software. Ecography 2017, 40, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Fang, J.; Chi, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, W.; Mohhamot, A.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gaston, K.J. Geography, environment, and spatial turnover of species in China’s grasslands. Ecography 2012, 35, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odriozola, I.; García-Baquero, G.; Etxeberria, A.; Aldezabal, A. Patterns of species relatedness created by competitive exclusion depend on species niche differences: Evidence from Iberian Atlantic grasslands. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 28, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; John, R.; Liu, K.; Qi, W.; Long, W. Using functional trait diversity patterns to disentangle the processes influencing the recovery of subalpine grasslands following abandonment of agricultural use. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, O.; Schmid, B.C.; Sykes, M.T.; Poschlod, P.; Michalski, S.G.; Durka, W.; Kühn, I.; Winter, M.; Prentice, H.C.; Fridley, J. Contrasting changes in taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional diversity during a long-term succession: Insights into assembly processes. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liang, C.; Li, F.Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, W.; Wang, L.; Wen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; et al. Community phylogenetic structure of grasslands and its relationship with environmental factors on the Mongolian Plateau. J. Arid Land 2019, 11, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.N.; Hiiesalu, I.; Gerhold, P.; Partel, M. Small-scale grassland assembly patterns differ above and below the soil surface. Ecology 2012, 93, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynard, C.N.; Lavergne, S.; Boulangeat, I.; Garraud, L.; Van Es, J.; Mouquet, N.; Thuiller, W. Disentangling the drivers of metacommunity structure across spatial scales. J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, G. Stochastic and deterministic processes together determine alpine meadow plant community composition on the Tibetan Plateau. Oecologia 2013, 171, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradi, T.; Temperton, V.M.; Kollmann, J. Resource availability determines the importance of niche-based versus stochastic community assembly in grasslands. Oikos 2017, 126, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Luarte, C.; Escobedo, V.M.; Stotz, G.C.; Rios, R.S.; Arancio, G.; Gianoli, E. Goat grazing reduces diversity and leads to functional, taxonomic, and phylogenetic homogenization in an arid shrubland. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J.D.; Poff, N.L. Toward a mechanistic understanding and prediction of biotic homogenization. Am. Nat. 2003, 162, 442–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.L.; Cheng, G.; Liu, Z.I.; Yan, Z.J.; Chu, X.H. VOR and CVOR index for health evaluation of typical steppe in Inner Mongolia. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2012, 20, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Soliveres, S.; Torices, R.; Maestre, F.T. Environmental conditions and biotic interactions acting together promote phylogenetic randomness in semi-arid plant communities: New methods help to avoid misleading conclusions. J. Veg. Sci. 2012, 23, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Guo, Y.; Luo, T.; Zhang, L. Stochastic Processes Drive Plant Community Assembly in Alpine Grassland during the Restoration Period. Diversity 2022, 14, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100832
Deng Z, Zhao J, Wang Z, Li R, Guo Y, Luo T, Zhang L. Stochastic Processes Drive Plant Community Assembly in Alpine Grassland during the Restoration Period. Diversity. 2022; 14(10):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100832
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zhaoheng, Jingxue Zhao, Zhong Wang, Ruicheng Li, Ying Guo, Tianxiang Luo, and Lin Zhang. 2022. "Stochastic Processes Drive Plant Community Assembly in Alpine Grassland during the Restoration Period" Diversity 14, no. 10: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100832
APA StyleDeng, Z., Zhao, J., Wang, Z., Li, R., Guo, Y., Luo, T., & Zhang, L. (2022). Stochastic Processes Drive Plant Community Assembly in Alpine Grassland during the Restoration Period. Diversity, 14(10), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100832






