Characterization of Terrihabitans soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel 0.2 μm-Filterable Soil Bacterium Belonging to a Widely Distributed Lineage of Hyphomicrobiales (Rhizobiales)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phylogenetic and Phylogenomic Analysis
2.2. Metagenomic Database Search for Potential Habitat Prediction
2.3. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Characterization
2.4. Chemotaxonomic Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
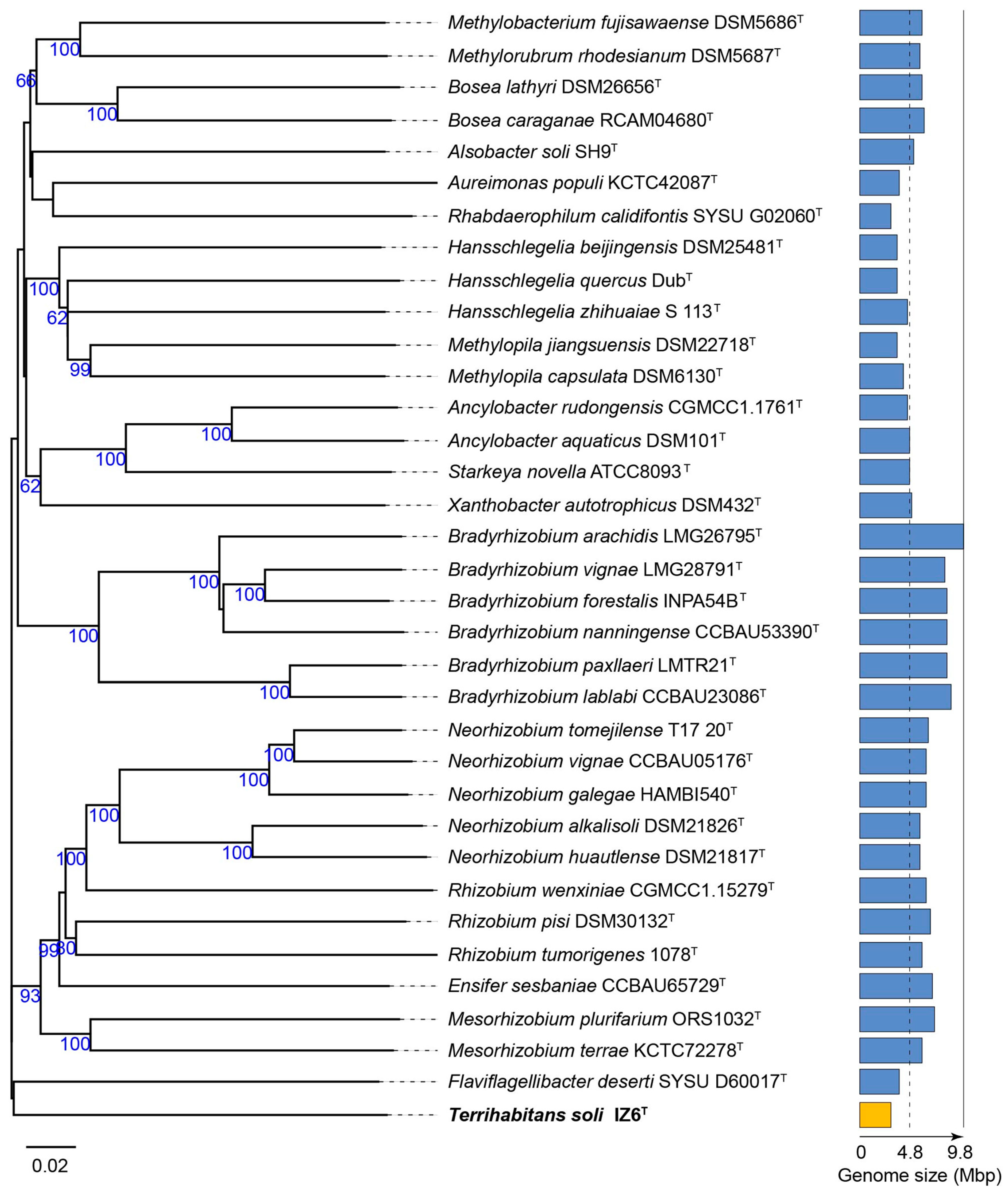
3.1. Phylogenetic Affiliation and Phylogenomic Placement of Strain IZ6T
3.2. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Characteristics of Strain IZ6T
3.3. Chemotaxonomic Characteristics of Strain IZ6T
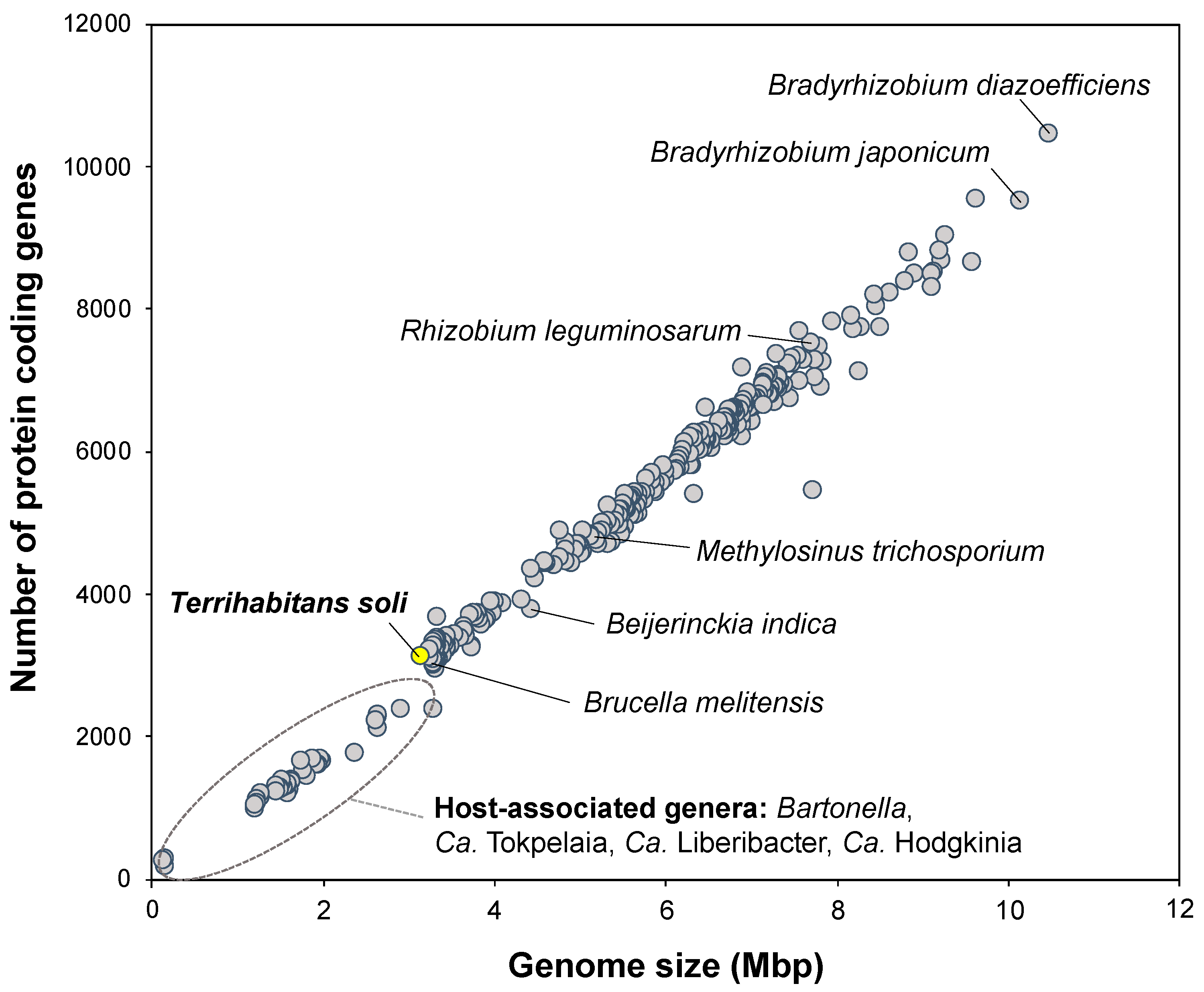
3.4. Potential Distribution and Habitability of Close Relatives of Strain IZ6T
3.5. Proposal of a Novel Genus and Species for Strain IZ6T
Description of Terrihabitans gen. nov.
Description of Terrihabitans soli sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levy, R.V.; Jornitz, M.W. Types of filtration. In Sterile Filtration; Jornitz, M.W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W. Broad Diversity of Viable Bacteria in ‘Sterile’ (0.2 μm) Filtered Water. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, V.I.; Suzina, N.E.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Boronin, A.M. Ultramicrobacteria: Formation of the Concept and Contribution of Ultramicrobacteria to Biology. Microbiology 2012, 81, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuneim, L.-A.J.; Jones, D.L.; Golyshin, P.N.; Golyshina, O.V. Nano-Sized and Filterable Bacteria and Archaea: Biodiversity and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R. Size Matters: Ultra-Small and Filterable Microorganisms in the Environment. Microbes Environ. 2020, 35, ME20025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, M.C.; Leff, J.W.; Lauber, C.L.; Fierer, N. Cell Size Distributions of Soil Bacterial and Archaeal Taxa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7610–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.H.; Schuhmann, A.; Mörschel, E.; Rainey, F.A. Novel Anaerobic Ultramicrobacteria Belonging to the Verrucomicrobiales Lineage of Bacterial Descent Isolated by Dilution Culture from Anoxic Rice Paddy Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R.; Shibuya, E.; Justel, A.; Rico, E.; Quesada, A.; Kobayashi, F.; Iwasaka, Y.; Shi, G.-Y.; Amano, Y.; Iwatsuki, T.; et al. Phylogeographic Analysis of Filterable Bacteria with Special Reference to Rhizobiales Strains That Occur in Cryospheric Habitats. Antarct. Sci. 2013, 25, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R.; Naganuma, T.; Tazato, N.; Morohoshi, S.; Koide, T. Cell Plasticity and Genomic Structure of a Novel Filterable Rhizobiales Bacterium That Belongs to a Widely Distributed Lineage. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hördt, A.; López, M.G.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Schleuning, M.; Weinhold, L.-M.; Tindall, B.J.; Gronow, S.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Woyke, T.; Göker, M. Analysis of 1,000+ Type-Strain Genomes Substantially Improves Taxonomic Classification of Alphaproteobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpiano, C.G.; Sant’Anna, F.H.; Ambrosini, A.; de São José, J.F.B.; Beneduzi, A.; Whitman, W.B.; de Souza, E.M.; Lisboa, B.B.; Vargas, L.K.; Passaglia, L.M.P. Genomic Metrics Applied to Rhizobiales (Hyphomicrobiales): Species Reclassification, Identification of Unauthentic Genomes and False Type Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A Large-Scale Evaluation of Algorithms to Calculate Average Nucleotide Identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, N.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Ivanova, N.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Mavrommatis, K.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Pati, A. Microbial Species Delineation Using Whole Genome Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 6761–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R., L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The Enveomics Collection: A Toolbox for Specialized Analyses of Microbial Genomes and Metagenomes. PeerJ Prepr. 2016, 4, e1900v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS Is an Automated High-Throughput Platform for State-of-the-Art Genome-Based Taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Genome Sequence-Based Species Delimitation with Confidence Intervals and Improved Distance Functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, V.; Desper, R.; Gascuel, O. FastME 2.0: A Comprehensive, Accurate, and Fast Distance-Based Phylogeny Inference Program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2798–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, J.S. Estimating Phylogenetic Trees from Distance Matrices. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 645–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreft, Ł.; Botzki, A.; Coppens, F.; Vandepoele, K.; Van Bel, M. PhyD3: A Phylogenetic Tree Viewer with Extended PhyloXML Support for Functional Genomics Data Visualization. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2946–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Joseph, D.; Kapfhammer, M.; Giritli, S.; Horn, M.; Haller, D.; Clavel, T. IMNGS: A Comprehensive Open Resource of Processed 16S rRNA Microbial Profiles for Ecology and Diversity Studies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mise, K.; Iwasaki, W. Environmental Atlas of Prokaryotes Enables Powerful and Intuitive Habitat-Based Analysis of Community Structures. iScience 2020, 23, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, G.I.; Feltham, R.K.A. Cowan and Steel’s Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kang, K.; Ahn, T.-Y. Chthonobacter Albigriseus Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., Isolated from Grass-Field Soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Sato, Y.; Fujimura, R.; Ohta, H. Alsobacter Metallidurans Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Thallium-Tolerant Soil Bacterium in the Order Rhizobiales. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A Rapid Method of Total Lipid Extraction and Purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaoka, J.; Katayama-Fujimura, Y.; Kuraishi, H. Analysis of Bacterial Menaquinone Mixtures by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1983, 54, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R.; Baba, T.; Niki, H.; Nishijima, M.; Naganuma, T. Aurantimicrobium Minutum Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Ultramicrobacterium of the Family Microbacteriaceae, Isolated from River Water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Han, M.-X.; Wang, D.; Liu, F.; Asem, M.D.; Jiao, J.-Y.; Xiao, M.; Salam, N.; Li, W.-J. Flaviflagellibacter Deserti Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Member of the Order Rhizobiales Isolated from a Desert Soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, R.A.; Garrity, G.M.; Scott, J.J.; Amend, J.P.; Nealson, K.H.; Emerson, D.; Giovannoni Stephen, J. A Genus Definition for Bacteria and Archaea Based on a Standard Genome Relatedness Index. mBio 2020, 11, e02475-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Rodriguez-R., L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. MyTaxa: An Advanced Taxonomic Classifier for Genomic and Metagenomic Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, S.J. SAR11 Bacteria: The Most Abundant Plankton in the Oceans. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W.; Scheuerl, T.; Jezberová, J.; Koll, U.; Jezbera, J.; Šimek, K.; Vannini, C.; Petroni, G.; Wu, Q.L. The Passive Yet Successful Way of Planktonic Life: Genomic and Experimental Analysis of the Ecology of a Free-Living Polynucleobacter Population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, I.-M.A.; Chu, K.; Palaniappan, K.; Ratner, A.; Huang, J.; Huntemann, M.; Hajek, P.; Ritter, S.; Varghese, N.; Seshadri, R.; et al. The IMG/M Data Management and Analysis System v.6.0: New Tools and Advanced Capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D751–D763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Stamatis, D.; Bertsch, J.; Ovchinnikova, G.; Sundaramurthi, J.C.; Lee, J.; Kandimalla, M.; Chen, I.-M.A.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Reddy, T.B.K. Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.8: Overview and Updates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D723–D733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.K.; Ng, H.J.; Ivanova, E.P. The Family Methylocystaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, R.H.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Kim, J. Pinisolibacter Ravus Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., Isolated from Pine Forest Soil and Allocation of the Genera Ancalomicrobium and Pinisolibacter to the Family Ancalomicrobiaceae Fam. Nov., and Emendation of the Genus Ancalomicrobium Staley 1968. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Tian, W.-Y.; He, W.-H.; Chen, G.-C.; An, M.-L.; Jia, B.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.-J. Methylopila Henanense Sp. Nov., a Novel Methylotrophic Bacterium Isolated from Tribenuron Methyl-Contaminated Wheat Soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronina, N.V.; Trotsenko, Y.A. Incertae Sedis IV. Methylopila. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Rainey, F., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, M., Chun, J., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Dedysh, S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, E.K.; D’Imperio, S.; Miller, A.R.; VanEngelen, M.R.; Gerlach, R.; Lee, B.D.; Apel, W.A.; Peyton, B.M. Application of Molecular Techniques to Elucidate the Influence of Cellulosic Waste on the Bacterial Community Structure at a Simulated Low-Level-Radioactive-Waste Site. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3106–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Williamson, K.E.; Kan, J.; Polson, S.W.; Williamson, S.J. Optimizing the Indirect Extraction of Prokaryotic DNA from Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, G.M.; Bell, J.A.; Lilburn, T. Alphaproteobacteria class. nov. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Rainey, F., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, M., Chun, J., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Dedysh, S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, G.M.; Bell, J.A.; Lilburn, T. Proteobacteria phyl. nov. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Rainey, F., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, M., Chun, J., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Dedysh, S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation source | Forest soil | Desert soil | Forest soil | Wheat soil |
| Motility | Nonmotile | Motile | Nonmotile | Motile |
| Growth at/in the presence of: | ||||
| 4 °C | − | + | − | − |
| 37 °C | − | + | + | + |
| pH 9 | + | − | + | − |
| 1.5% (w/v) NaCl | − | + | − | − |
| Assimilation of glucose | − | + | + | + |
| Enzymatic activities: | ||||
| Lipase (C14) | − | + | − | − |
| Leucine arylamidase | − | + | + | − |
| Valine arylamidase | − | + | + | − |
| Cystine arylamidase | − | + | + | − |
| Trypsin | − | + | + | − |
| Characteristic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major fatty acids | C18:1ω7c/C18:1ω6c | C19:0ω8c cyclo, C18:1ω7c/C18:1ω6c | C18:1ω7c/C18:1ω6c, C16:1ω7c/C16:1ω6c, C16:0 | C18:1ω7 |
| Main quinone | Q-10 | Q-10 | Q-10 | Q-10 |
| Polar lipids | DPG, PC, PE, PG, UL | DPG, PC, PE, PG, UL | DPG, PC, PE, PG, PME, UL | PC, PE |
| G + C content (mol%) | 62.2 | 63.8 | 68.4 | 66–70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakai, R.; Naganuma, T.; Tazato, N.; Kunihiro, T.; Morohoshi, S.; Koide, T.; Kusada, H.; Tamaki, H.; Narihiro, T. Characterization of Terrihabitans soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel 0.2 μm-Filterable Soil Bacterium Belonging to a Widely Distributed Lineage of Hyphomicrobiales (Rhizobiales). Diversity 2021, 13, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13090422
Nakai R, Naganuma T, Tazato N, Kunihiro T, Morohoshi S, Koide T, Kusada H, Tamaki H, Narihiro T. Characterization of Terrihabitans soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel 0.2 μm-Filterable Soil Bacterium Belonging to a Widely Distributed Lineage of Hyphomicrobiales (Rhizobiales). Diversity. 2021; 13(9):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13090422
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakai, Ryosuke, Takeshi Naganuma, Nozomi Tazato, Tadao Kunihiro, Sho Morohoshi, Tomomi Koide, Hiroyuki Kusada, Hideyuki Tamaki, and Takashi Narihiro. 2021. "Characterization of Terrihabitans soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel 0.2 μm-Filterable Soil Bacterium Belonging to a Widely Distributed Lineage of Hyphomicrobiales (Rhizobiales)" Diversity 13, no. 9: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13090422
APA StyleNakai, R., Naganuma, T., Tazato, N., Kunihiro, T., Morohoshi, S., Koide, T., Kusada, H., Tamaki, H., & Narihiro, T. (2021). Characterization of Terrihabitans soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a Novel 0.2 μm-Filterable Soil Bacterium Belonging to a Widely Distributed Lineage of Hyphomicrobiales (Rhizobiales). Diversity, 13(9), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13090422







