Unraveling the Biosynthesis of Quinolizidine Alkaloids Using the Genetic and Chemical Diversity of Mexican Lupins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seed Harvest
2.2. Disinfestation and Scarification of Seeds
2.3. Seed Germination and Plant Growth
2.4. Quinolizidine Alkaloids Extraction
2.5. Identification and Quantification of Quinolizidine Alkaloids by GLC–MS
3. Results
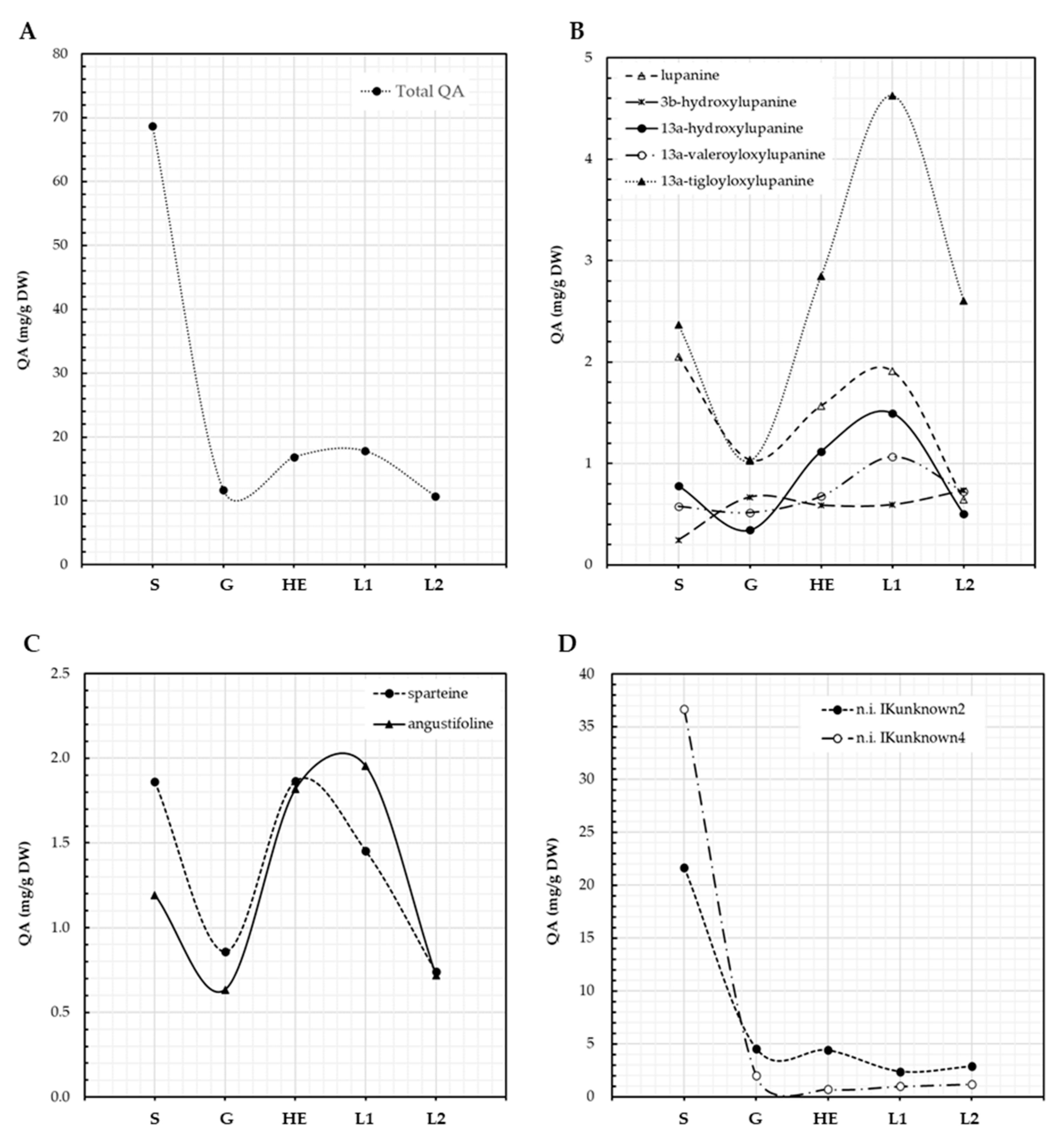
3.1. QA Patterns of Lupinus aschenbornii Seeds and Plantlets
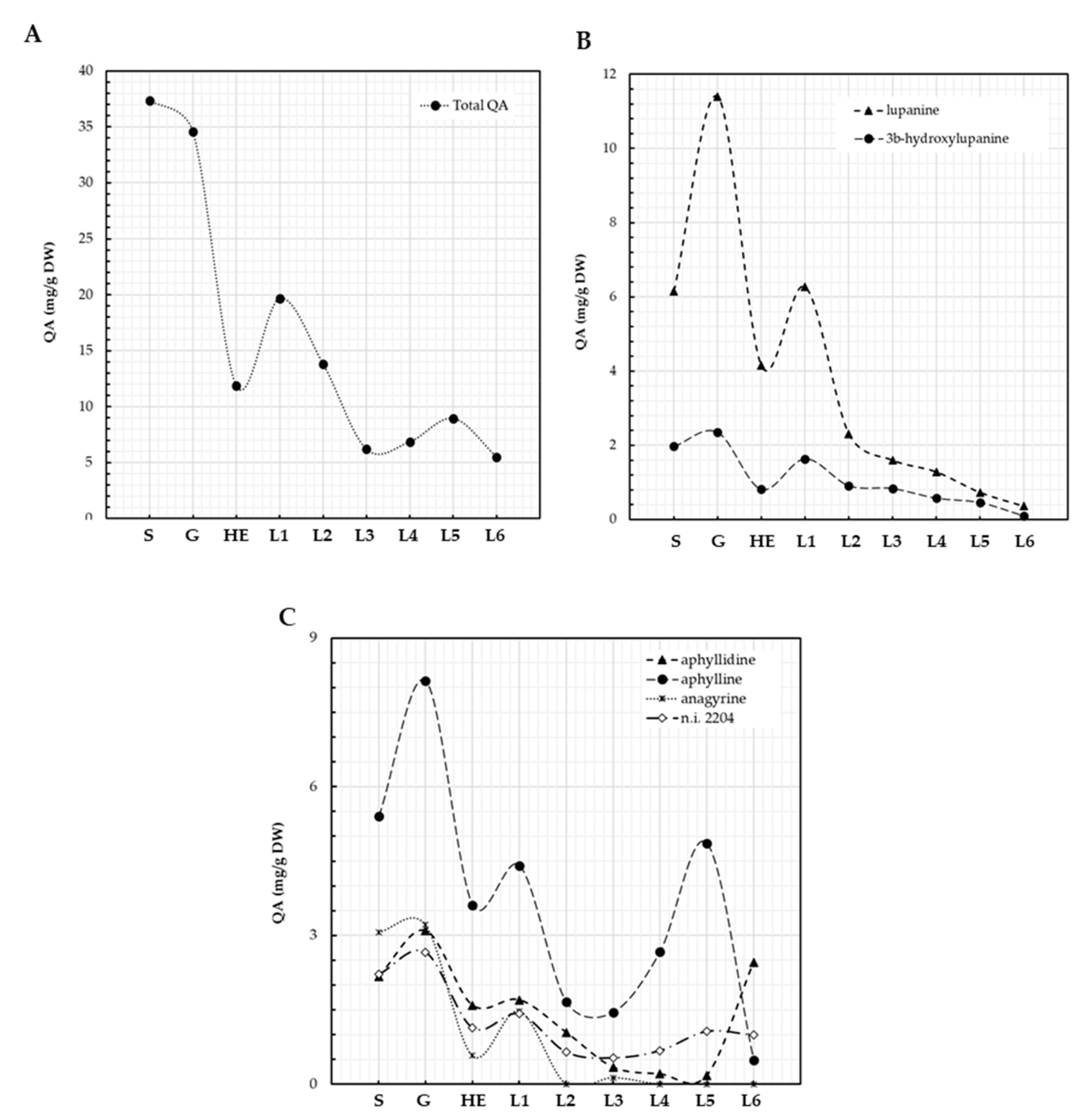
3.2. QA Patterns of Lupinus bilineatus Seeds and Plantlets
3.3. QA Patterns of Lupinus montanus Seeds and Plantlets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, C.; Eastwood, R. Island radiation on a continental scale: Exceptional rates of plant diversification after uplift of the Andes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10334–10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M.; Meißner, C.; Witte, L. Patterns of quinolizidine alkaloids in 56 species of the genus Lupinus. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Torres, K.; Ferval, M.; Hernández-Sánchez, A.M.; Tei, A.; Gers, C.; Wink, M.; Legal, L. Molecular and Chemical Markers to Illustrate the Complex Diversity of the Genus Lupinus (Fabaceae). Diversity 2021, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitoza, R.B.B.; Lima, H.R.P. Chemosystematic and evolutionary trends of the genistoid clade sensu stricto (Papilionoideae, Fabaceae). Phytochemistry 2021, 183, 112616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wink, M. The role of Quinolizidine Alkaloids in Plant-Insect Interactions. In Plant Insect Interactions; Bernays, E.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992; pp. 131–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe, D.; Hintze, F.; Tebben, P.; Paetow, M.; Ahrens, H.; Schwerdtfeger, J.; Sommerfeld, P.; Haller, J.; Guarnierp, W.; Kolczewsk, S.; et al. Enantioselective synthesis via sparteine induced asymmetric deprotonation. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeller, T.; Sauerwein, M.; Sporer, F.; Wink, M.; Müller, W.E. Binding of quinolizidine alkaloids to nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O′Brien, P. Basic instinct: Design, synthesis and evaluation of (+)-sparteine surrogates for asymmetric synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2008, 1, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, R.; Palma, A.; Rebolledo, R.; Aguilera, A. Effect of an infusion of canelo and bitter lupin on Aegorhinus superciliosus adults. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2011, 38, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalpando-Vargas, F.; Medina-Ceja, L. Sparteine as an anticonvulsant drug: Evidence and possible mechanism of action. Seizure 2016, 39, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, O.; Allanic, C.; Charvet, C.L.; Guégnard, F.; Février, H.; Théry-Koné, I.; Cortet, J.; Koch, C.; Bouvier, F.; Fassier, T.; et al. Lupin (Lupinus spp.) seeds exert anthelmintic activity associated with their alkaloid content. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.C.; Dai, W.F.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.J.; Jiang, M.Y.; Rao, K.R.; Li, R.T.; Li, H.M. Quinolizidine alkaloids from Sophora alopecuroides with anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 110, 104781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, L. Quinolizidine alkaloids derivatives from Sophora alopecuroides Linn: Bioactivities, structure-activity relationships and preliminary molecular mechanisms. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 188, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhao, L.; Yi, P.; An, Q.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Lou, H.; Yuan, C.; Gu, W.; Huang, L.; et al. Quinolizidine Alkaloids with Antiviral and Insecticidal Activities from the Seeds of Sophora tonkinensis Gagnep. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15015–15026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.H.; Elissawy, A.M.; Allam, A.E.; Farag, S.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Elshanawany, M.A.; Singab, A.N.B. New quinolizidine alkaloid and insecticidal activity of Sophora secundiflora and Sophora tomentosa against Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M. Wounding-Induced Increase of Quinolizidine Alkaloid Accumulation in Lupin Leaves. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C J. Biosci. 1983, 38, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, K.M.; Foley, R.C.; Kamphuis, L.G.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Garg, G.; Singh, K.B. Characterization of the genetic factors affecting quinolizidine alkaloid biosynthesis and its response to abiotic stress in narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2155–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otterbach, S.L.; Yang, T.; Kato, L.; Janfelt, C.; Geu-Flores, F.; Hancock, R. Quinolizidine alkaloids are transported to seeds of bitter narrow-leafed lupin. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5799–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wink, M.; Hartmann, T. Localization of the Enzymes of Quinolizidine Alkaloid Biosynthesis in Leaf Chloroplasts of Lupinus polyphyllus. Plant Physiol. 1982, 70, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M.; Hartmann, T. Enzymatic synthesis of quinolizidine alkaloid esters: A tigloyl-CoA: 13-hydroxylupanine O-tigloyltransferase from Lupinus albus L. Planta 1982, 156, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czepiel, K.; Krajewski, P.; Wilczura, P.; Bielecka, P.; Święcicki, W.; Kroc, M. Expression profiles of alkaloid-related genes across the organs of narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) and in response to anthracnose infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M.; Witte, L. Quinolizidine Alkaloids as Nitrogen Source for Lupin Seedlings and Cell Cultures. Verl. Z. Naturforsch. 1985, 40, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altares, P.; Pedrosa, M.M.; Burbano, C.; Cuadrado, C.; Goyoaga, C.; Muzquiz, M.; Jim, C.; Gloria, D. Alkaloid variation during germination in different lupin species. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsupa, S.; Katayama, K.; Ikeura, E.; Oikawa, A.; Toyooka, K.; Saito, K.; Yamazakia, M. Lysine decarboxylase catalyzes the first step of quinolizidine alkaloid biosynthesis and coevolved with alkaloid production in leguminosae. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Nagy, I.; Mancinotti, D.; Otterbach, S.L.; Andersen, T.B.; Motawia, M.S.; Asp, T.; Geu-Flores, F. Transcript profiling of a bitter variety of narrow-leafed lupin to discover alkaloid biosynthetic genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5527–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Hirai, M.Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yamazaki, M.; Saito, K. Molecular characterization of a novel quinolizidine alkaloid O-tigloyltransferase: cDNA cloning, catalytic activity of recombinant protein and expression analysis in Lupinus plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroc, M.; Koczyk, G.; Kamel, K.A.; Czepiel, K.; Fedorowicz-Strońska, O.; Krajewski, P.; Kosińska, J.; Podkowiński, J.; Wilczura, P.; Święcicki, W. Transcriptome-derived investigation of biosynthesis of quinolizidine alkaloids in narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) highlights candidate genes linked to iucundus locus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, C.S. Diversification of Lupinus (Leguminosae) in the western New World: Derived evolution of perennial life history and colonization of montane habitats. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.M.; Delgado, A.S. Leguminosas mexicanas: Fitogeografía, endemismo y orígenes. In Diversidad biológica de México: Orígenes y Distribución; Ramamoorthy, T.P., Bye, R., Lot, A., Fa, J., Eds.; Instituto de Biología, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Ciudad de México, México, 1998; pp. 449–500. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, D.B.; Lupinus, L. Flora Fanerogámica del Valle de México; Calderón de Rzedowski, G., Rzedowski, J., Eds.; Instituto de Ecología: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2005; pp. 290–300. ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez-Torres, K.; Martínez Herrera, J.; Figueroa Brito, R.; Wink, M.; Legal, L. Activity of quinolizidine alkaloids from three Mexican Lupinus against the lepidopteran crop pest Spodoptera frugiperda. BioControl 2009, 54, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz López, M.; García López, P.; Rodríguez Macías, R.; Zamora Natera, J.; Isaac Virgen, M.; Múzquiz, M. Mexican wild lupines as a source of quinolizidine alkaloids of economic potential. Polibotánica 2010, 29, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Montes-Hernández, E.; Corona-Rangel, M.L.; Encarnación-Corona, A.; Cantor del Angel, J.A.; Sánchez-López, J.A.; Sporer, F.; Wink, M.; Bermúdez-Torres, K. Quinolizidine alkaloid composition in different organs of Lupinus aschenbornii. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2011, 21, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Torres, K.; Robledo-Quintos, N.; Barrera-Necha, L.L.; Wink, M. Alkaloid Profile of Leaves and Seeds of Lupinus hintonii C.P. Smith. Z. Naturforsch 2002, 57, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Torres, K.; Robledo-Quintos, N.; Martínez-Herrera, J.; Tei, A.; Wink, M. Patrón de acumulación de alcaloides en hojas y semillas de Lupinus aschenbornii crecidos en México. Rev. Latinoam. Química 2000, 27, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ferval, M.; Legal, L.; Gers, C.; Pelissier, C.; Winterton, P. When island-like populations at high elevation show genetic divergence despite no morphological variability: The case of Lupinus montanus in Central Mexico. Turk. J. Bot. 2013, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ferretis, E.; Rivera-Meléndez, R.K.; Ramos-Herrera, O.J.; Salinas-Pérez, F.C.; Rodríguez-Monroy, M.; Bermúdez-Torres, K. Effect of scarification treatments on germination of Lupinus montanus HBK seeds. In Lupinus for Health and Wealth. Proceedings of the 12th International Lupin Conference, Fremantle, Australia, 14–18 September 2008; Palta, J.A., Berger, J.B., Eds.; International Lupin Association: Canterbury, New Zealand, 2008; pp. 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa-Rodríguez, M.I. Efecto de Especies Nativas y Silvestres de Lupinus sobre la Fertilidad del suelo Agrícola. Master Thesis, Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- NIST/EPA/NIH. Mass spectral library. In Mass Spectral Library with Search Program (Data Version: NIST05, Software Version 2.0); U.S. Department of Commerce, Technology Administration, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Standard Reference Data Program: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gresta, F.; Wink, M.; Prins, U.; Abberton, M.; Capraro, J.; Scarafoni, A.; Hill, G. Lupins in European cropping systems. Legum. Crop. Syst. 2017, 88–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.M.; Robins, D.J. Incorporation of chiral [1-2H]cadaverines into the quinolizidine alkaloids sparteine, lupanine, and angustifoline. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.H.; Ling, S.; Tian, F.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X. Interference mechanism of Sophora alopecuroides L. alkaloids extract on host finding and selection of the Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wink, M. Evolution of secondary metabolites in legumes (Fabaceae). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 89, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | Population | Altitude (m) | Latitude (N) | Longitude (W) | Voucher Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. aschenbornii | LIP1asch | 3906 | 98°39′02″ | 19°39′18″ | 1297311 |
| L. bilineatus | LIP4camp | 2781 | 98°42′59″ | 19°04′41″ | 1297301 |
| L. montanus | LIP2mon | 3889 | 98°38′54″ | 19°08′27″ | 1297279 |
| Alkaloid | KI | M+ | Characteristic Ions (Abundance %) | A | B | C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n.i. 1439 | 1439 | 168 | 55(100) | 83(73) | 97(50) | 111(25) | 168(7) | x | ||
| Gramine | 1635 | 174 | 130(100) | 131(39) | 174(16) | 77(11) | 103(8) | x | ||
| α-Isosparteine | 1682 | 234 | 98(100) | 137(55) | 136(29) | 234(28) | 110(19) | x | ||
| Sparteine | 1807 | 234 | 137(100) | 98(92) | 193(44) | 110(26) | 234(26) | x | x | x |
| n.i. 1880 | 1880 | 256 | 55(100) | 129(61) | 83(56) | 213(45) | 256(41) | x | ||
| Aphyllidine | 2052 | 246 | 98(100) | 246(80) | 97(65) | 134(22) | 163(19) | x | x | |
| 17-Oxosparteine | 2061 | 248 | 97(100) | 98(83) | 110(68) | 136(42) | 248(37) | x | ||
| Tetrahydrorhombifoline | 2067 | 248 | 207(100) | 58(39) | 112(18) | 108(10) | 248(0.8) | x | x | |
| Aphylline | 2075 | 248 | 136(100) | 97(37) | 220(36) | 248(29) | 191(20) | x | x | x |
| n.i. 2086 | 2086 | 244 | 244(100) | 96(71) | 106(40) | 207(23) | 134(21) | x | ||
| 5,6-Dehydrolupanine | 2145 | 246 | 98(100) | 97(38) | 246(20) | 134(11) | 84(10) | x | ||
| Angustifoline | 2278 | 234 | 193(100) | 112(58) | 150(16) | 41(15) | 55(14) | x | ||
| n.i. 2204 | 2204 | 246 | 246(100) | 136(57) | 96(31) | 80(18) | 55(17) | x | x | |
| Anagyrine | 2210 | 244 | 98(100) | 244(54) | 146(11) | 128(12) | 264(<1) | x | x | |
| Hydroxytetrahydrorhombifoline | 2210 | 264 | 223(100) | 58(34) | 108(31) | 41(16) | 96(14) | x | ||
| Lupanine | 2229 | 248 | 136(100) | 149(54) | 248(42) | 150(40) | 55(32) | x | x | x |
| n.i. 2248 | 2248 | 262 | 244(100) | 262(99) | 114(82) | 205(73) | 55(61) | x | ||
| 11,12-seco-12,13-Didehydromultiflorine | 2263 | 246 | 205(100) | 58(83) | 94(34) | 110(25) | 2460(8) | x | ||
| n.i. 2263 | 2263 | 246 | 246(100) | 136(61) | 96(29) | 55(27) | 207(18) | x | ||
| 3β-Hydroxylupanine | 2277 | 264 | 264(100) | 136(78) | 134(54) | 150(39) | 263(36) | x | x | x |
| n.i. 2281 | 2281 | 262 | 262(100) | 98(99) | 136(32) | 245(21) | 122(18) | x | ||
| 17-Oxolupanine | 2352 | 262 | 150(100) | 262(65) | 112(55) | 207(47) | 94(45) | x | ||
| Multiflorine | 2418 | 246 | 134(100) | 246(70) | 148(35) | 110(26) | 217(6) | x | x | x |
| n.i. 2441 | 2441 | 263 | 98(100) | 246(73) | 136(24) | 189(10) | 263(9) | x | ||
| 13α-Hydroxylupanine | 2469 | 264 | 152(100) | 246(70) | 264(51) | 165(46) | 134(39) | x | x | x |
| n.i. 2471 | 2471 | 279 | 149(100) | 167(33) | 279(10) | 112(8) | 207(1) | x | x | |
| 13α-Valeroyloxylupanine | 2684 | 348 | 246(100) | 134(30) | 148(18) | 112(12) | 348(6) | x | ||
| 13α-Tigloyloxylupanine | N.D. | 346 | 246(100) | 134(24) | 148(13) | 112(12) | 346(<1) | x | ||
| n.i. IKunknown1 | N.D. | - | 207(100) | 245(62) | 281(45) | 112(23) | 355(14) | x | ||
| n.i. IKunknown2 | N.D. | - | 245(100) | 263(78) | 112(33) | 55(19) | 149(17) | x | ||
| n.i. IKunknown3 | N.D. | - | 262(100) | 134(44) | 207(40) | 264(10) | 393(8) | x | ||
| n.i. IKunknown4 | N.D. | - | 245(100) | 55(23) | 262(19) | 207(17) | 112(13) | x | ||
| n.i. IKunknown5 | N.D. | - | 207(100) | 281(46) | 355(15) | 147(11) | 429(5) | x | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Betancourt, A.; Hernández-Sánchez, A.M.; Salcedo-Morales, G.; Ventura-Zapata, E.; Robledo, N.; Wink, M.; Bermúdez-Torres, K. Unraveling the Biosynthesis of Quinolizidine Alkaloids Using the Genetic and Chemical Diversity of Mexican Lupins. Diversity 2021, 13, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080375
Ramírez-Betancourt A, Hernández-Sánchez AM, Salcedo-Morales G, Ventura-Zapata E, Robledo N, Wink M, Bermúdez-Torres K. Unraveling the Biosynthesis of Quinolizidine Alkaloids Using the Genetic and Chemical Diversity of Mexican Lupins. Diversity. 2021; 13(8):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080375
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Betancourt, Astrid, Arianna Michelle Hernández-Sánchez, Guadalupe Salcedo-Morales, Elsa Ventura-Zapata, Norma Robledo, Michael Wink, and Kalina Bermúdez-Torres. 2021. "Unraveling the Biosynthesis of Quinolizidine Alkaloids Using the Genetic and Chemical Diversity of Mexican Lupins" Diversity 13, no. 8: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080375
APA StyleRamírez-Betancourt, A., Hernández-Sánchez, A. M., Salcedo-Morales, G., Ventura-Zapata, E., Robledo, N., Wink, M., & Bermúdez-Torres, K. (2021). Unraveling the Biosynthesis of Quinolizidine Alkaloids Using the Genetic and Chemical Diversity of Mexican Lupins. Diversity, 13(8), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080375











