Effect of Cothurnia variabilis and Epistylis gammari (Ciliophora: Peritrichia) on Metabolic Rate of the Crayfish Cambarellus (Cambarellus) montezumae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Oxygen Consumption
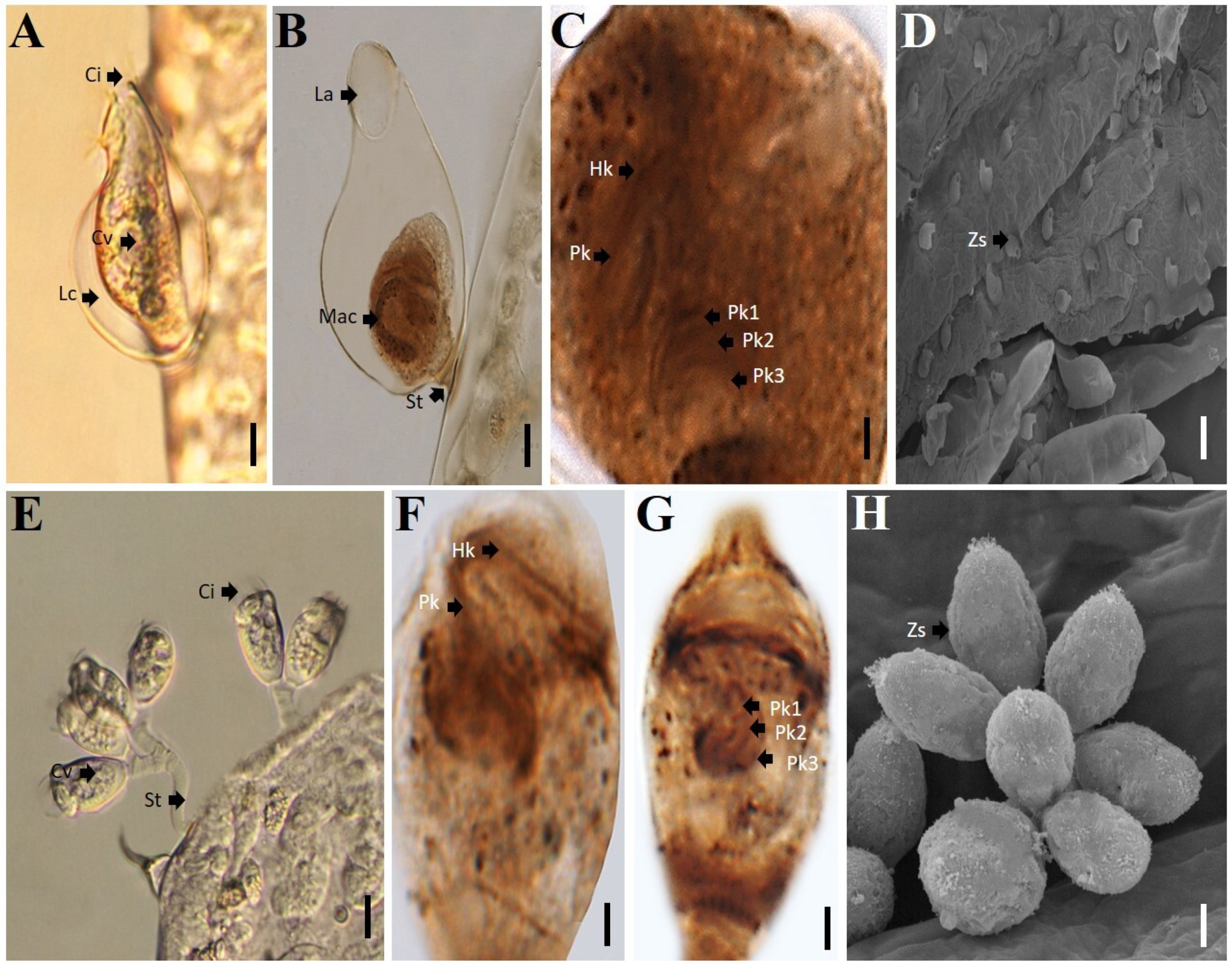
2.3. Identification of Ciliates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
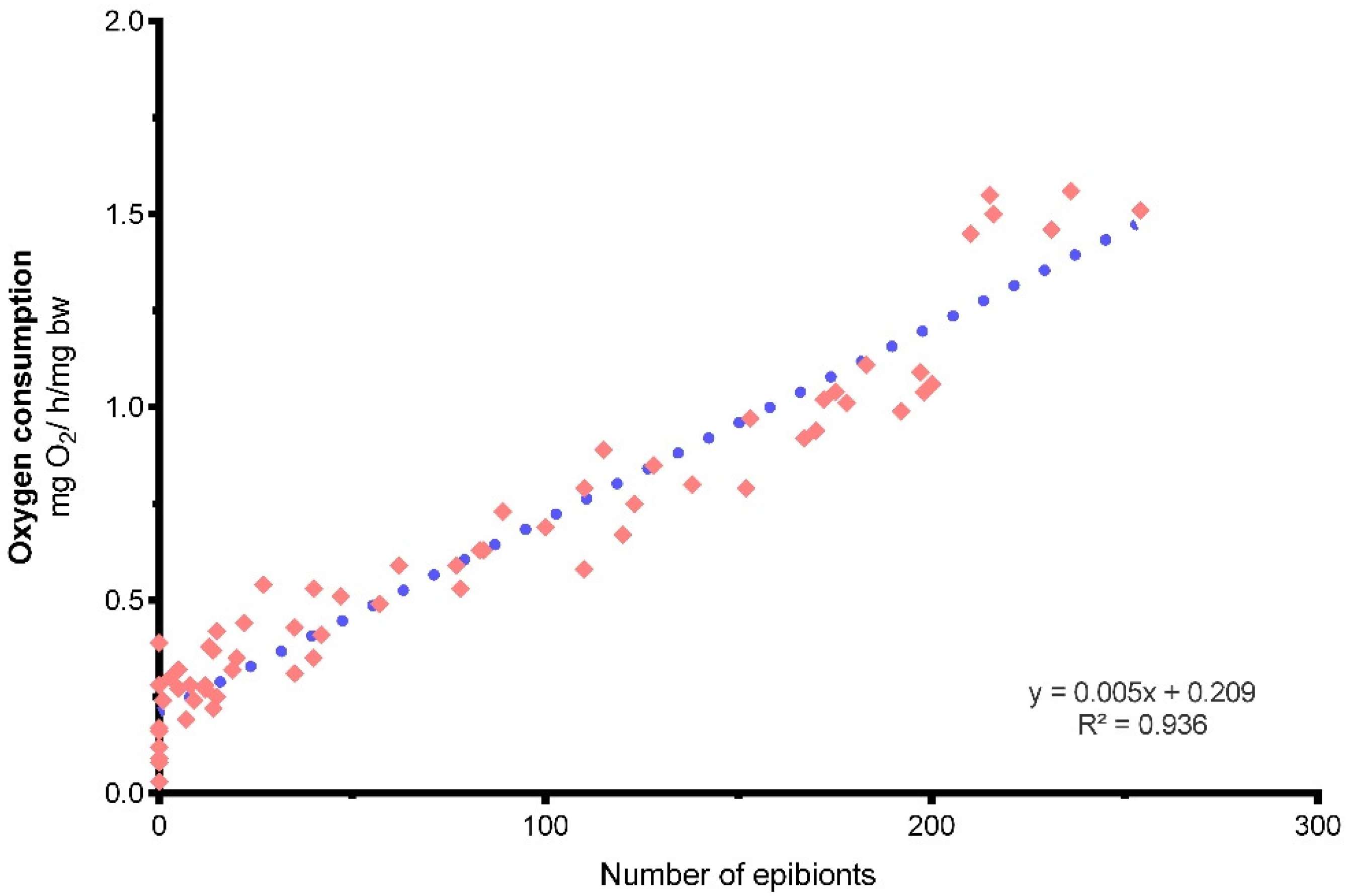
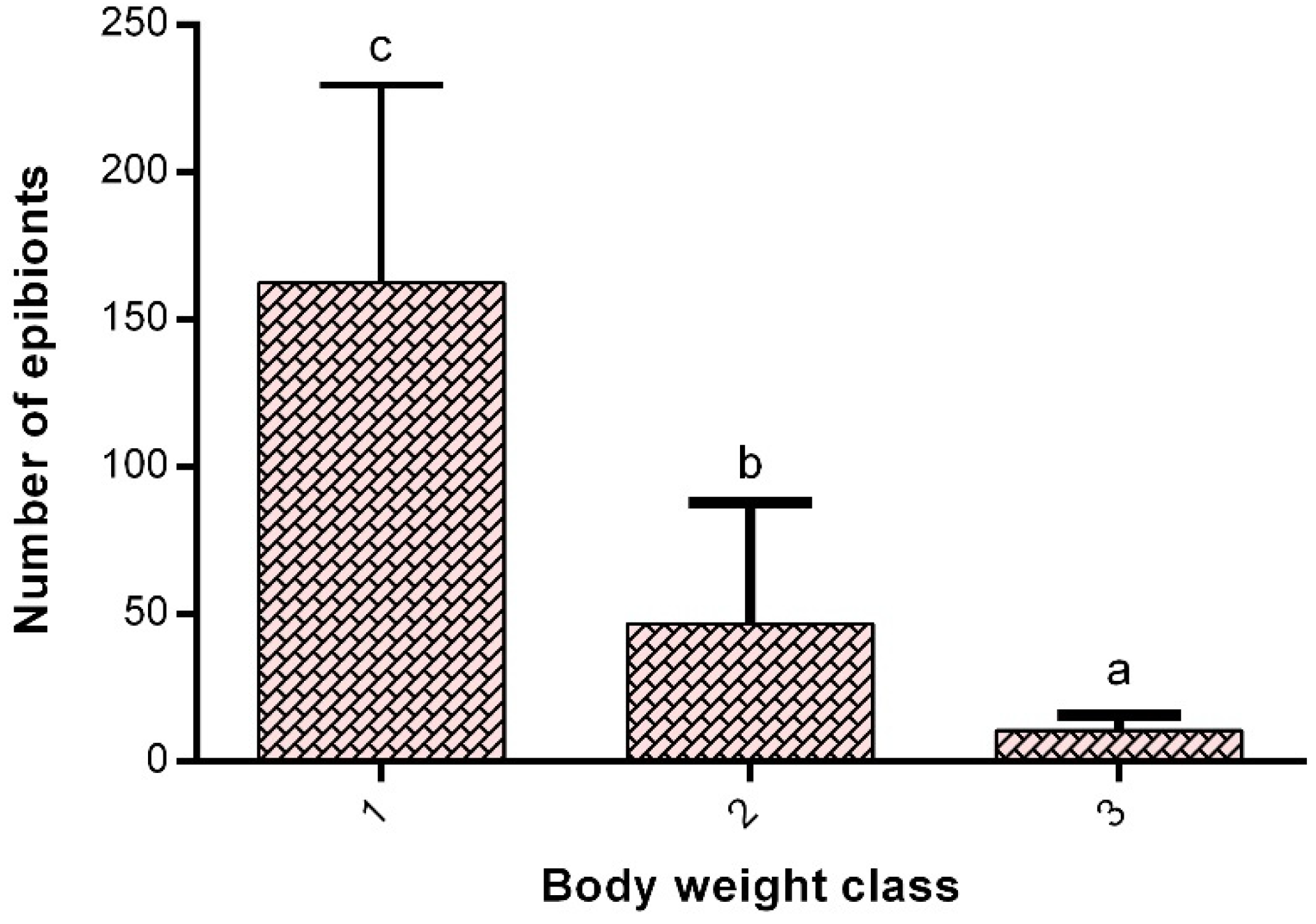
Oxygen Consumption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olson, R.J.; Young, J.W.; Ménard, F.; Potier, M.; Allain, V.; Goñi, N.; Logan, J.M.; Galván-Magaña, F. Bioenergetics, trophic ecology, and niche separation of tuna. In Advances in Marine Biology; Curry, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 74, pp. 199–344. ISBN 9780128036075. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, T.; Patoka, J. Gill morphology and formulae of crayfishes (Decapoda: Astacidea: Parastacidae) from New Guinea and New Zealand and a comparison with other selected species of crayfishes. J. Crust. Biol. 2021, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Salman, D.; Abdul-Hussain, Y. Oxygen consumption of the freshwater crab Elamenopsis kempi (Chopra and Das, 1930) from the Garmat Ali river, Iraq. Sci. Mar. 2000, 64, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Villareal, H.; Hernández-Llamas, A.; Hewitt, R. Effect of salinity on growth, survival and oxygen consumption of juvenile brown shrimp Farfantepenaeus californiensis (Holmes). Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.; Chimal, M.; Rosas, C. Effect of salinity in survival, growth, and osmotic capacity of early juveniles of Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis (Decapoda: Penaeidae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 244, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvato, B.; Cuomo, V.; Di Muro, P.; Beltramini, M. Effects of environmental parameters on the oxygen consumption of four marine invertebrates: A comparative factorial study. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.P. Pragmatic perspective on aerobic scope: Peaking, plummeting, pejus and apportioning. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 322–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M. Ecological lever and interface ecology: Epibiosis modulate the interactions between host and environment. Biofouling 2008, 24, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ďuriš, Z.; Horká, I.; Petrusek, A. Invasive zebra mussel colonisation of invasive crayfish: A case study. Hydrobiologia 2007, 590, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, T. Marine epibiosis: Concepts, ecological consequences, and host defense. In Marine and Industrial Biofouling; Flemming, H., Sriyutha, P., Venkatesan, R., Cooksey, K., Eds.; Springer: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 219–232. ISBN 978-3-540-69796-1. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, J.; Doak, S.; Leornard, M.; Creed, P.; Brown, L. The rules for symbionts community assembly change along a mutualism-parasitism continuum. J. Anim. Ecol. 2016, 85, 543–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V. Diseases of cultured penaeid shrimps. In Handbook of Mariculture, Crustacean Aquaculture, 2nd ed.; McVey, J.P., Moore, J.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; Volume 1, pp. 289–320. ISBN 9780849302558. [Google Scholar]
- Overstreet, R.M. Parasites of some penaeid shrimp with emphasis on reared hosts. Aquaculture 1973, 2, 105–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo-Figueroa, J.L.; Ponce-Palafox, J.; Hernández-Ocampo, D.; Rodríguez-Chávez, G.; Benítez-Mandujano, M. Aspectos básicos del cultivo del acocil Cambarellus (Cambarellus) montezumae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Cambaridae) en condiciones controladas. Ind. Acuícola. Acuacultura Neg. México 2015, 2, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S. The Welfare of Crustaceans at Slaughter. Impacts on Farm Animals 4. 2008. Available online: https://www.wellbeingintlstudiesrepository.org/hsus_reps_impacts_on_animals/4 (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- Foissner, W. Basic light and electron microscopic methods for taxonomic studies of ciliated protozoa. Eur. J. Protistol. 1991, 27, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrivas de Lozano, V.; Morales, A.; Yañez, J. Principios y Práctica de la Microscopía Electrónica, 1st ed.; UAT-CONICET: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2014; ISBN 978-987-43-4752-7.
- Henry, R.; Lucu, C.; Onken, H.; Weihrauch, D. Multiple functions of the crustacean gill: Osmotic/ionic regulation, acid-base balance, ammonia excretion, and bioaccumulation of toxic metals. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R. Gill-cleaning mechanisms of the crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Astacidea: Cambaridae): Experimental testing of setobranch function. Invertebr. Biol. 1998, 117, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, J.; Grell, M.; Høeg, T.; Olesen, J. Morphology of grooming limbs in species of Petrolisthes and Pachycheles (Crustacea: Decapoda: Anomura: Porcellanidae): A scanning electron microscopy study. Mar. Biol. 1992, 113, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, D.H. Ciliophora. In Handbook of the Protists; Archibald, J.M., Simpson, A.G.B., Slamovits, C.H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 679–730. ISBN 978-3-319-28148-3. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelbein, E.; Thune, R. Ultrastructural features of three ectocommensal protozoa attached to the gills of the red swamp crawfish, Procambarus clarkii (Crustacea: Decapoda). J. Protozool. 1988, 35, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, J.A. A New Species of Lagenophrys (Ciliatea: Peritrichida: Lagenophryidae) from a marine crab, Callinectes sapidus. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1967, 86, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messick, G. Diseases, parasites, and symbionts of blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) dredged from Chesapeake Bay. J. Crust. Biol. 1998, 18, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Vogan, C.; Rowley, A. Effect of the copepod parasite Nicothoë astaci on haemolymph chemistry of the European lobster Homarus gammarus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2015, 113, 169–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, R.; Alvarez, F.; Alcaraz, G. Oxygen consumption of the crab Callinectes rathbunae parasitized by the rhizocephalan barnacle Loxothylacus texanus as a function of salinity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 235, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poulter, R.; Oliver, P.G.; Hauton, C.; Sanders, T.; Ciotti, B. Infestation of shore crab gills by a free-living mussel species. Mar. Biodiv. 2018, 48, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelaar-Bonga, S.E. The stress response in fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 591–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortham, J.; Pascual, S. Grooming behaviors and gill fouling in the commercially important blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) and stone crab (Menippe mercenaria). Nauplius 2017, 25, e2017028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Wahl, M. Behaviour patterns as natural antifouling mechanisms of tropical marine crabs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 203, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbuena, R.; Cruz, P. Efecto del peso corporal y temperatura del agua sobre el consumo de oxígeno de tilapia roja (Oreochromis sp). Orinoquia 2006, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.L.; Creed, R.P.; Skelton, J.; Rollins, M.A.; Farrell, K.J. The fine line between mutualism and parasitism: Complex effects in a cleaning symbiosis demonstrated by multiple field experiments. Oecologia 2012, 170, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utz, L.; Coats, W. Telotroch formation, survival, and attachment in the epibiotic peritrich Zoothamnium intermedium 318 (Ciliophora, Oligohymenophorea). Invertebr. Biol. 2008, 127, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Leborans, G. Epibiosis in Crustacea: An overview. Crustaceana 2010, 83, 549–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiperth, A.; Gál, B.; Kuříková, P.; Bláha, M.; Kouba, A.; Patoka, J. Cambarellus patzcuarensis in Hungary: The first dwarf crayfish established outside of North America. Biología 2017, 72, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Coefficients | Estimate | Std. Error | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.177 | 0.036 | 4.856 | 0.000 |
| Nunber of zooids | 0.005 | 0.000 | 29.274 | 0.000 |
| Crayfish weight | 0.060 | 0.037 | 1.615 | 0.110 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Ballesteros, M.; Cárdenas-Vázquez, R.; Lugo-Vázquez, A.; Mayén-Estrada, R. Effect of Cothurnia variabilis and Epistylis gammari (Ciliophora: Peritrichia) on Metabolic Rate of the Crayfish Cambarellus (Cambarellus) montezumae. Diversity 2021, 13, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070333
Ramírez-Ballesteros M, Cárdenas-Vázquez R, Lugo-Vázquez A, Mayén-Estrada R. Effect of Cothurnia variabilis and Epistylis gammari (Ciliophora: Peritrichia) on Metabolic Rate of the Crayfish Cambarellus (Cambarellus) montezumae. Diversity. 2021; 13(7):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070333
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Ballesteros, Mireya, René Cárdenas-Vázquez, Alfonso Lugo-Vázquez, and Rosaura Mayén-Estrada. 2021. "Effect of Cothurnia variabilis and Epistylis gammari (Ciliophora: Peritrichia) on Metabolic Rate of the Crayfish Cambarellus (Cambarellus) montezumae" Diversity 13, no. 7: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070333
APA StyleRamírez-Ballesteros, M., Cárdenas-Vázquez, R., Lugo-Vázquez, A., & Mayén-Estrada, R. (2021). Effect of Cothurnia variabilis and Epistylis gammari (Ciliophora: Peritrichia) on Metabolic Rate of the Crayfish Cambarellus (Cambarellus) montezumae. Diversity, 13(7), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070333





