Abstract
Annelida is a ubiquitous, common and diverse group of organisms, found in terrestrial, fresh waters and marine environments. Despite the large efforts put into resolving the evolutionary relationships of these and other Lophotrochozoa, and the delineation of the basal nodes within the group, these are still unanswered. Annelida holds an enormous diversity of forms and biological strategies alongside a large number of species, following Arthropoda, Mollusca, Vertebrata and perhaps Platyhelminthes, among the species most rich in phyla within Metazoa. The number of currently accepted annelid species changes rapidly when taxonomic groups are revised due to synonymies and descriptions of a new species. The group is also experiencing a recent increase in species numbers as a consequence of the use of molecular taxonomy methods, which allows the delineation of the entities within species complexes. This review aims at succinctly reviewing the state-of-the-art of annelid diversity and summarizing the main systematic revisions carried out in the group. Moreover, it should be considered as the introduction to the papers that form this Special Issue on Systematics and Biodiversity of Annelids.
1. Introduction
We entered the 21st century with a view about Annelida very different to what we have today, only twenty years later. In those days, we thought that the classification of the group was suffering a revolution because early molecular analyses placed clitellates within polychaetes [1,2,3]. Although there were also some indications that several of the then considered phyla, such as Sipuncula, Myzostomida, Vestimentifera, Pogonophora and Echiura, had annelid affinities (e.g., [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]), it was not until the advent of the phylogenomic methods that we were provided with strong enough evidence to consider these taxa within Annelida (e.g., [12,13,14,15]). This expansion of the Annelida concept greatly increased the diversity within the group, including aspects such as body plan, anatomy, reproductive biology, life history, feeding strategies, and species richness.
The fossil record evidenced that early annelids, provided with head appendages, birramous parapodia and simple chaetae were already present in the Early Cambrian [16] (although molecular clocks date the origin of annelids even earlier, e.g., [17]). These taxa do seem closely related to the extant annelid groups, which in most cases diversified rapidly during the Late Cambrian—Ordovician [16]. The deep relationships in the annelid radiation remain poorly resolved, in part due to the short basal branches as a consequence of this rapid diversification, but also due to the analysis of artifacts such as the long branch attraction of some groups [12,15,18,19,20,21]. Sister group relationships of Annelida are still being debated, but its placement within Lophotrochozoa and monophyly are now widely accepted (e.g., [12,13,14,15,22,23].
There have been several revisions of Annelida in the last 20 years. The volume Polychaetes & Allies The Southern Synthesis [24] (no longer in print but pdfs are available on the ABRS website, http://www.environment.gov.au/science/abrs/publications/fauna-of-australia/fauna-4a (accessed on 17 March 2021)), known as the red book, included an historical overview of not just polychaetes, but also of sipunculans, echiuroids, myzostomes and pogonophorans and, while oligochaetes were also originally to be included, this unfortunately did not happen. Its chapters include information on the biology and ecology of annelids, the higher classification based on the most recently available cladistics analysis by Rouse and Fauchald [4] and a chapter on each family then recognized with standardized content on morphology, diversity, physiology, reproduction, distribution, including how many species were present in Australian waters. While the title suggests it is Australia focused, the book is relevant to all parts of the world, as almost all polychaete families occur worldwide.
Shortly after the publication of Polychaetes & Allies, Rouse and Pleijel [8] published Polychaetes, also known as the black book. This book, whilst dealing with the anatomy, biology and ecology of polychaetes, it also focused on the phylogenetic relationships of the different clades and taxa. After the publication of these two books thorough reviews, some dramatic changes in the understanding of the systematics and classification of the annelids have taken place (e.g., [12,13,14,15]. Since 2014, an ambitious project aiming at updating the prestigious Handbook of Zoology [25,26,27,28] has gathered the interest of many Annelida experts with the aim of producing a comprehensive overview on different annelid groups, including updated information regarding the systematics, morphology, physiology, behavior, ecology and applied zoological research. The Handbook of Zoology, Annelida [29,30,31] appeared first online and later in book form, and it will eventually cover all clades and taxonomic annelid groups. It represents the third 21st century “must have” book series for annelid workers. In these volumes, it is highlighted the enormous efforts that have been put into resolving the phylogenetic relationships and the description of the diversity of forms and biological strategies exhibited within the group.
However, besides these comprehensive reviews, it is clear that further work is needed in order to pursue a better understanding of the diversification patterns in Annelida, to evaluate the current awareness on the species’ richness, its distribution patterns and highlight where the major gaps of knowledge are in the different taxa.
Annelids are critically important in most marine ecosystems because of their diversity and abundance, especially in soft sediments from the intertidal to the deep-sea, as well as encrusting or attached to hard substrates. They exhibit a variety of feeding strategies ranging from deposit feeders, filter feeders, carnivores, herbivores and parasites, thus occupying all levels within the food chain. Some groups of polychaetes, fundamentally earthworms, are important bioturbators, turning over the sediment as well as breaking down organic matter. These mud swallowing feeders may also accumulate heavy metals and other contaminants in their body, and they are able to transfer these to other members of the trophic webs. Annelids are a major component of the marine benthos and terrestrial realm, and they comprise species with different tolerances to stress. Consequently, they have been considered as good bioindicators in environmental monitoring (e.g., [32,33,34]) and surrogates for marine biodiversity [35,36] biomarkers (e.g., [37,38,39,40]).
Annelids also exhibit a tremendous range of reproductive strategies ranging from mass spawning, brooding, laying of egg capsules as well as asexual reproduction [41]. Life spans range from a few weeks to many years, with some species spawning annually, whereas others only breed once and then die. Thus, while the biomass of polychaetes may not be high, in benthic communities they typically have a high productivity which is readily available to a wide range of organisms. Some species of annelids are widely collected as bait for recreational fishing (e.g., [42]), and some species are used as food for aquaculture practices, or are collected during the annual mass spawning associated with phases of the moon for human consumption. Annelid bioactive compounds are being used after showing properties compatible with anesthetics, fluorescent probes and even antibiotics and pesticides [43,44]. Negative ecological and economic impacts have also been reported because of annelids. For instance, an invasive species can cause problems such as blocking intake pipes to power stations, impact commercial value of mollusks by boring into shells, or modifying benthic habitats [45,46,47].
Until late in the last century, several polychaete workers assumed many polychaetes were widely distributed (e.g., [48,49,50,51,52]). Consequently, taxonomists and ecologists from around the world identified polychaetes using comprehensive and well-illustrated monographs such as those used by Fauvel [53,54] and Day [51,52], even though these were focused on the polychaete fauna of France and South Africa, respectively. The concept of “cosmopolitan” species was widely accepted with well-known examples such as Capitella capitata (Fabricius 1780), Marphysa sanguinea (Montagu, 1813), Terebellides stroemii Sars, 1835, Owenia fusiformis Delle Chiaje, 1844 or Chaetozone setosa Malmgren, 1867. However, the validity of this concept was questioned around the 1980s as detailed morphological studies, as well as molecular analyses, proved that “cosmopolitan species” were in fact siblings or cryptic species (e.g., [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63]). As recently synthesized by several authors [64,65,66], most species natural distributions is discrete (although a few species from shallow waters and more from pelagic deep sea environments have been shown to exhibit wide distribution patterns), and these can be delimited with appropriate microscopic imagining techniques or molecular analyses. However, the number of translocated species (intentionally or unintentionally transported by anthropogenic means) outside of their natural range expands as we increase our surveys. Anthropogenic environments are more susceptible for the establishment of non-indigenous species, both in terrestrial [67] and in coastal areas, especially in ports and estuaries. Most recorded non-indigenous or invasive polychaete species are within the Serpulidae, Sabellidae and Spionidae [68].
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Systematics
Since 1866 annelids (although not including clitellates) were divided in two groups: Annelidae erraticae and Annelidae sedentariae [69]. The terms Errantia and Sedentaria were widely used afterwards to refer to the more mobile or vagile forms and the tubiculous or sedentary forms, respectively. This division was originally made based on the type of segmentation: polychaetes with homonymous segmentation (with all segments similar) were placed in Errantia, and those with heteronomous segmentation (segments are grouped in morphology distinct series each with a different function) in Sedentaria. This was not strictly followed later on, and some annelid families were moved around between these two groups (e.g., [51,52,53,54,70,71,72,73]). Since the 1960s, a different classification system, where families were gathered in orders, started to be widely used (e.g., [74,75,76,77,78]). Some of these “orders” were shown to be natural clusters when cladistic analyses started to be implemented on annelids [79]. However, some of the early phylogenetic hypotheses of Annelida were conflicting, especially at interpreting the basal relationships. While some of the classifications, based on analyses of morphological data, divided Annelida into Clitellata and Polychaeta, and the later further split into Scolecida (parapodia with similar rami and the possession of two or more pairs of pygidial cirri) and Palpata (with palps and peristomium limited to the lips) [8,41,79,80], other studies contradicted this view based on methodological discrepancies (e.g., [81,82]). Later molecular phylogenies corroborated that clitellates, echiurids, myzostomids and sipunculids, were within the polychaetes and recovered some of the earlier considered taxa within Palpata (that is Canalipalpata) closely related to Scolecida, returning to the earlier concept of Errantia (see Figure 1) and Sedentaria (including Clitellata) (see Figure 2) (e.g., [12,13,14,15,83,84,85]). There is, however, a series of heterogeneous and basally branching annelids previously considered among the sedentarians or errants. These are the Palaeoannelida, Chaetopteridae, Amphinomida and Sipuncula (e.g., [13,14,15], Figure 1).
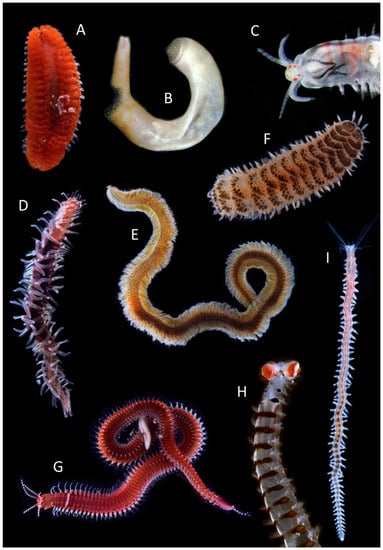
Figure 1.
Small selection of some basal annelids (A,B) and Errantia (C–I). (A). Euphrosine foliosa Audouin & H Milne Edwards, 1833 (Amphinomida); (B). Aspidosiphon muelleri Diesing, 1851 (Sipuncula); C. Dorvillea similis (Crossland, 1924) (Eunicida); (D). Amphiduros fuscescens (Marenzeller, 1875) (Phyllodocida); (E). Phyllodoce sp. (Phyllodocida); (F). Harmothoe areolata (Grube, 1860) (Phyllodocida); (G). Eunice cf. dubitata Fauchald, 1974 (Eunicida); (H). Vanadis Formosa Claparède, 1870 (Phyllodocida); Nereis sp. (Phyllodocida). Photos: (A,D–I) by Xavier Salvador Costa; (B) by Daniel Martin; (C) by Alexander Semenov.

Figure 2.
Small selection of the diversity encountered in Sedentaria. (A). Amphictene auricoma (O.F. Müller, 1776) (Terebelliformia); (B). Maxmuelleria gigas (M. Müller, 1852) (Echiura); (C). Maldanidae (Capitellida); (D). Escalibregma sp. (Scalibregmatidae); (E). Armandia polyophthalma Kükenthal, 1887 (Opheliida), (F). Dasybranchus gajolae Eisig, 1887 (Capitellida); (G). Acromegalomma sp. (Sabellida); (H). Loimia tuberculata Nogueira, Hutchings & Carrerette, 2015 (Terebelliformia). Photos: (A,C,E,F) by Xavier Salvador Costa; (D) by Dani Martin, (G,H) by Alexander Semenov.
2.2. Annelid Diversity
The current ranges of valid nominal species in the literature go from 14,000 to 20,000 [7,86,87,88], and databases such as WoRMS currently considers 23,774 accepted species of extant annelids [89]. Recounting the number of species after the latest revisions, such as the Handbook of Zoology chapters [29,30,31] and the present special issue ([90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101]), there seems to be around 20,000 currently accepted nominal species (Figure 3). There is a continuous documentation of new species and diversity patterns as new taxonomic surveys are carried out in poorly explored geographic areas and localities, in new environments, such as the deep-sea and, surprisingly, also in apparently well-known zones when using different collecting gear, sorting methods or identification techniques, such as SEM and molecular taxonomy.
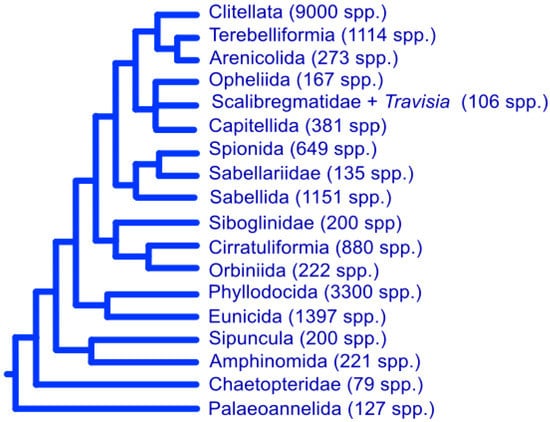
Figure 3.
Metatree (based in [88,102]). The estimates for currently valid species were obtained from following studies or experts, although some minor groups are missing in the tree.; Clitellata, Erséus and Martinsson, pers. com. [94]; Terebelliformia [93]; Arenicolidae [89]; Opheliidae [90], Salibregmatidae and Travisia [89,90]; Capitellida [89]; Spionida [103,104,105,106]; Sabellariidae [89,107]; Sabellida [99]; Siboglinidae [108]; Cirratuliformia [89,100]; Orbiniida [95]; Phyllodocida [101]; Eunicida [91]; Sipuncula [97]; Amphinomida [89].
There are several factors influencing the discrepancy in the total numbers of annelid species considered as currently valid:
- Literature thorough scrutiny, including old and obscure publications. It is not uncommon to see how some taxonomic and nomenclatural mistakes have been passed on to most recent publications. Many annelid genera and families require a thorough follow up of synonyms (species that may have been synonymized with others or moved to a different genus or taxonomic group), and also way to rescue some old names that have been lost in most recent taxonomic lists. Of course, databases such as WoRMS are of invaluable help, but as much as they try to keep updated with taxonomic progress there is often a lag [109].
- Some groups require an exhaustive taxonomic revision that includes the examination of type material. This has become more difficult lately as shipping of preserved specimens has become an extremely regulated process, and unaffordable (for economic or time-related reasons) for some museums. Travelling to museums where the type specimens of a genus are housed is also challenging as these may be spread around the globe.
- Taxonomists too often have a partial understanding of their group because we tend to specialize in particular families, genera, environments or geographic areas. This may lead to a non-confident or tentative perception of the overall diversity of larger groups.
- When referring to the total number of a species we generally mean that the currently accepted binomial names are based on morphologically recognizable entities. Taxonomists often hold knowledge of a wider number of morphospecies that are new but not formerly described. In fact, the average time it takes from the first collection of a specimen of a new species to its formal naming and description in a scientific paper is 21 years [110]. The reason for this may be the need for more specimens to account for intraspecific variability or to be preserved in a specific manner, revisions/examination of similar or related species are needed, the group requires a revision, a lack of funding or the need for collaboration with other (often lacking) experts in the group, e.g., taxonomic impediment, etc. [110,111]. Moreover, when the lines of evidence for delineating species are molecular (e.g., DNA sequences), these newly recognized lineages are not often accompanied by formal descriptions [112]. In these situations (no formal binomials), species will be missing from species lists in most cases.
- Cryptic species. The number of complexes of annelid species accounted for in recent years has vastly increased due to the use of molecular data. This has an impact in the real overall diversity present in the group. Although this is not necessary reflected in the total number of species accounted for, and this is because species delineated by molecular mean are often not accompanied by a formal species description (as discussed by Goldstein et al. [112] and exemplified by [61,113,114,115,116]).
According to some predictions, there are potentially still 13,000 to 24,000 of annelid species awaiting to be discovered and described [86].
2.3. Gaps of Knowledge and Future Perspectives
In this special issue, a considerable number of researchers have participated towards providing a summary of the current knowledge about the biology, systematics and diversity in a broad range of annelid taxonomic groups. Most of them acknowledge the improvement in the assessment of internal relationships within the groups after molecular phylogenetic analyses have been performed. However, they also indicate that these are still not fully settled in most cases, and the analyses require further data, analytical considerations or a combination of sources of information. Robust phylogenies with comprehensive taxon coverage are crucial for stablishing the backbone of classification and to trace the evolution. The review papers in this special issue point to some of the main gaps in the knowledge on each of the taxonomic groups they deal with, but there are large similarities between all of them. It seems clear that there are some geographic areas that have been scarcely studied. In the marine realm, these include the North Indo-Pacific, South America, polar waters, but mainly the African coastline. In the terrestrial and limnic realms, South America, Africa and Asia are in need of further taxonomic surveys (Figure 4, but see papers in this Special Issue for more information). Our knowledge about habitats such as extreme environments [92] and the deep sea is also very limited (e.g., [117]).
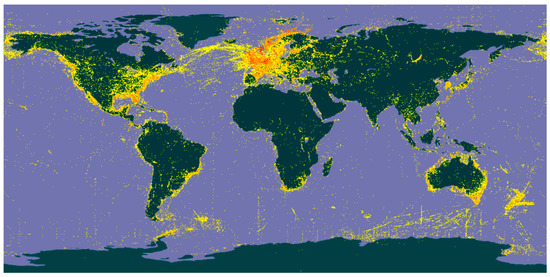
Figure 4.
Occurrence data from Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) with 813,947 georeferenced records for Annelida in the marine and terrestrial environments. In red and orange, hotspots of occurrences, in yellow sites with one occurrence. This map does not show the real knowledge about annelid records, but those uploaded in this platform. However, it can be used as a proxy of the current number of undertaken surveys.
In the papers within this Special Issue, there are suggestions as to how to proceed in the future if we want to progress at a steady and efficient manner towards increasing our knowledge about Annelida and in discovering the real diversity held in this phylum. These can be summarized as follows:
- An increase in field work in the areas that have been poorly surveyed. There is also a large amount of material, specially coming from deep sea expeditions, that is awaiting to be studied in natural history museums. Therefore, only diving in poorly studied geographic areas, in extreme environments and in museum collections will provide us with a good understanding about the diversity of annelids.
- Most of the knowledge about the biology, anatomy and behavior of annelid groups is based on a limited number of species for each family. This is more obvious in modern biology that mainly focuses on model organisms, especially in the fields of comparative physiology and morphology. Studies based on a larger number of taxa and including some of the microscopic modern technics (phase contrast, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, confocal laser scanning microscopy, tomography and 3D reconstructions) are needed.
- It is recommended to undertake an integrative approach for delimiting and documenting species. This includes the combination of morphological, molecular and biological data. For several groups of annelids, understanding the reproductive and developmental features has also shown to be helpful for species delimitation.
- Species descriptions or re-description often requires re-examination of type specimens for species comparisons. Ideally, a thorough examination of specimens from different geographical areas and ecological features is needed in order to establish species boundaries and to assess intraspecific variability.
- Obtaining genetic information for at least the type species (preferably from type locality) of each genus is needed, as this would allow generic revisions. Specimens for genetic analysis should be collected from the type localities and vouchers deposited.
- For species with wide geographical or bathymetric distribution, population genetic studies are necessary to reveal potential cryptic species. In this line, the advent of high-throughput sequencing methods has a lot to offer for the generation of species delimitation datasets.
- Molecular taxonomy is revealing hidden diversity at a high speed, but formal taxonomic descriptions are lagging behind the molecular work. Therefore, we should increase the efforts made in describing the species encountered after molecular methods. Only trained taxonomist can undertake the development of a proper account and documentation of these lineages, as these activities often require revision of genera, revision of old literature, synonymies and varying terminology, re-examination of museum types, etc.
- Policy should take care of biodiversity, and governments should invest in systems and in training the next generation of taxonomists. The taxonomic work has been neglected for decades and we are suffering a loss of taxonomic knowledge. This has a direct impact on the speed with which species are described, but also on the quality of the biodiversity assessments and the studies based on those. We need to train and sustain more systematists able to discover, describe, identify and classify species.
- We need to promote, care and engage with museum collections and public databases. It is imperative that the type material (holotype, type series, additional specimens showing intraspecific variability, and DNA extractions) is always deposited in properly curated permanent museum collection(s) where it is maintained in optimal conditions. Museums and researchers need to commit to open-access databases such as World Register of Marine Species—WoRMS, Ocean Biodiversity Information System—OBIS, National Center for Biotechnology Information—Genbank, or the Global Biodiversity Information Facility—GBIF, that offer invaluable information for research projects.
2.4. This Special Issue
For the present special issue, we aimed at gathering updated information and discuss the recent advances in different diversity aspects and in recent systematic revisions of some of the major Annelida clades, including Palaeoannelida, Sipuncula, Phyllodocida, Eunicida, Orbiniida, Cirratuliformia, Sabellida, Opheliida and Scalibregmatidae, Terebelliformia, and Clitellata [90,91,93,94,95,96,97,99,100,101]. Other chapters take a more ecological approach, for example the papers on extreme or interstitial annelids [92,98]. By gathering this information, we aim to highlight the importance of annelids in biodiversity assessments and ecosystem functioning, to recapitulate differing diversity aspects about selected groups of annelids, and highlight the bridge between the written literature and the public databases and platforms regarding taxonomy, occurrence data and DNA sequences (e.g., WoRMS, GBIF, GenBank or DriloBASE Taxo). We also aim at revealing where the gaps of knowledge are and where the efforts should be concentrated if we want to progress towards a deeper understanding of the annelid diversity inhabiting our planet. We need to increase efforts in exploring understudied areas and in revisiting museum collections, in reviewing some neglected taxonomic groups, training the next generations of taxonomists and systematists, uncover hidden diversity, embrace methods for speeding up diversity assessments and taxonomic surveys, connect the updated taxonomic results with the more applied approach of ecology and pay special attention to the large number of species that have been translocated (e.g., [66]).
We have gathered 46 colleagues from 16 countries and 37 institutions at different stages in their careers, stressing the importance of collaboration (every chapter is multiauthored and multi-international), an amalgamation of different perspectives and sources of data, aiming at mentoring the next generation of annelid workers and highlighting the international and collaborative annelid community. Unfortunately, and due to different reasons, this special issue is not complete, and some relevant annelid groups and environments have not been included.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C. and P.H.; writing—original draft preparation, review and editing, M.C. and P.H.; visualization, M.C. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.C. was funded by the Ramón y Cajal program (RYC-2016-20799) funded by Spanish MINECO, Agencia Estatal de Investigación, Comunidad Autónoma de las Islas Baleares and the European Social Fund.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dani Martin, Xavier Salvador and Alexander Semenov for allowing us to use the photographs to show the diversity of worms among annelids. It has been a privilege to be able to bring together this group of colleagues from all over the world gather some basic and updated knowledge about the diversity of Annelida. We are grateful to four anonymous reviewers for providing useful comments for the improvement of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kojima, S. Paraphyletic Status of Polychaeta Suggested by Phylogenetic Analysis Based on the Amino Acid Sequences of Elongation Factor-1 Alpha. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 1998, 9, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P. On the Origin of the Hirudinea and the Demise of the Oligochaeta. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2001, 268, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.; Rouse, G.; Hutchings, P.; Colgan, D. Assessing the Usefulness of Histone H3, U2 SnRNA and 28S RDNA in Analyses of Polychaete Relationships. Aust. J. Zool. 1999, 47, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W.; Fauchald, K. Cladistics and Polychaetes. Zool. Scr. 1997, 26, 139–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, D. Molecular Evidence That Echiurans and Pogonophorans Are Derived Annelids. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8006–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, D. Molecular Phylogeny of the Annelida. Can. J. Zool. 2000, 78, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, G.; Hessling, R.; Westheide, W. The Phylogenetic Position of the Clitellata and the Echiura-on the Problematic Assessment of Absent Characters. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2000, 38, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W.; Pleijel, F. Polychaetes; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2001; pp. 1–354. [Google Scholar]
- Bleidorn, C.; Vogt, L.; Bartolomaeus, T. New Insights into Polychaete Phylogeny (Annelida) Inferred from 18S RDNA Sequences. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 29, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleidorn, C.; Vogt, L.; Bartolomaeus, T. A Contribution to Sedentary Polychaete Phylogeny Using 18S RRNA Sequence Data. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2003, 41, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, V.; Rouse, G.W.; Siddall, M.E.; Tillier, A.; Pleijel, F. The Phylogenetic Position of Siboglinidae (Annelida) Inferred from 18S RRNA, 28S RRNA and Morphological Data. Cladistics 2004, 20, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, T.H.; Paul, C.; Hill, N.; Hartmann, S.; Hösel, C.; Kube, M.; Lieb, B.; Meyer, A.; Tiedemann, R.; Purschke, G.; et al. Phylogenomic Analyses Unravel Annelid Evolution. Nature 2011, 471, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struck, T.H.; Golombek, A.; Weigert, A.; Franke, F.A.; Westheide, W.; Purschke, G.; Bleidorn, C.; Halanych, K.M. The Evolution of Annelids Reveals Two Adaptive Routes to the Interstitial Realm. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigert, A.; Helm, C.; Meyer, M.; Nickel, B.; Arendt, D.; Hausdorf, B.; Santos, S.R.; Halanych, K.M.; Purschke, G.; Bleidorn, C.; et al. Illuminating the Base of the Annelid Tree Using Transcriptomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, S.C.S.; Novo, M.; Kawauchi, G.Y.; Worsaae, K.; Pleijel, F.; Giribet, G.; Rouse, G.W. Articulating “Archiannelids”: Phylogenomics and Annelid Relationships, with Emphasis on Meiofaunal Taxa. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2860–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, L.; Tanner, A.; Vinther, J. The Origin of Annelids. Palaeontology 2014, 57, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.J.; Cotton, J.A.; Gehling, J.G.; Pisani, D. The Ediacaran Emergence of Bilaterians: Congruence between the Genetic and the Geological Fossil Records. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Kaygorodova, I.; Sherbakov, D.Y.; Verheyen, E. Rapidly Evolving Lineages Impede the Resolution of Phylogenetic Relationships among Clitellata (Annelida). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2000, 15, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleidorn, C.; Eeckhaut, I.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Schult, N.; McHugh, D.; Halanych, K.M.; Milinkovitch, M.C.; Tiedemann, R. Mitochondrial Genome and Nuclear Sequence Data Support Myzostomida as Part of the Annelid Radiation. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 24, 1690–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleidorn, C.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Zhong, M.; Eeckhaut, I.; Hartmann, S.; Halanych, K.M.; Tiedemann, R. On the Phylogenetic Position of Myzostomida: Can 77 Genes Get It Wrong? BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, T.H. The Impact of Paralogy on Phylogenomic Studies—A Case Study on Annelid Relationships. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, A.; Golombek, A.; Gerth, M.; Schwarz, F.; Struck, T.H.; Bleidorn, C. Evolution of Mitochondrial Gene Order in Annelida. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2016, 94, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumer, C.E.; Bekkouche, N.; Kerbl, A.; Goetz, F.; Neves, R.C.; Sørensen, M.V.; Kristensen, R.M.; Hejnol, A.; Dunn, C.W.; Giribet, G.; et al. Spiralian Phylogeny Informs the Evolution of Microscopic Lineages. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, P.L.; Ross, G.J.B.; Glasby, C.J. Polychaetes & Allies: The Southern Synthesis. Fauna of Australia. Polychaeta, Myzostomida, Pogonophora, Echiura, Sipuncula; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2000; Volume 44, pp. 1–465. [Google Scholar]
- Reisinger, E. Zweiter Unterstamm der Vermes Polymera. Allgemeine Einleitung zur Naturgeschichte der Vermes Polymera. In Handbuch der Zoologie; Part 6, Vermes Polymera; DeGruyter & Co.: Leipzig/Berlin, Germany, 1928; Volume 2.2, pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hempelmann, F. Erste und Zweite Klasse der Vermes Polymera (Annelida). Archiannelida = UrRingelwürmer und Polychaeta = Borstenwürmer. In Handbuch der Zoologie; Part 7, Vermes Polymera; Kükenthal, W., Krumbach, T., Eds.; DeGruyter & Co.: Leipzig/Berlin, Germany, 1928; Volume 2.2, pp. 1–212. [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen, W. Dritte Klasse der Vermes Polymera (Annelida). Clitellata = Gürtelwürmer. 1. Ordnung der Clitellata: Oligochaeta = Regenwürmer und Verwandte. In Handbuch der Zoologie; Part 8, Vermes Polymera; Kükenthal, W., Krumbach, T., Eds.; DeGruyter & Co.: Leipzig/Berlin, Germany, 1928; Volume 2.2, pp. 1–118. [Google Scholar]
- Scriban, I.A.; Autrum, H. 2. Ordnung Der Clitellata: Hirudinea = Egel. In Handbuch der Zoologie; Part 8, Vermes Polymera; Kükenthal, W., Krumbach, T., Eds.; DeGruyter & Co.: Leipzig/Berlin, Germany, 1928; Volume 2.2, pp. 119–352. [Google Scholar]
- Purschke, G.; Böggemann, M.; Westheide, W. Basal Groups and Pleistoannelica, Sedentaria. In Handbook of Zoology; Annelida; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1–472. [Google Scholar]
- Purschke, G.; Böggemann, B.; Westheide, W. Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria II. In Handbook of Zoology; Annelida; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 1–465. [Google Scholar]
- Purschke, G.; Böggemann, B.; Westheide, W. Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria III and Errantia I. In Handbook of Zoology; Annelida; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 3, pp. 1–480. [Google Scholar]
- Belan, T.A. Marine Environmental Quality Assessment Using Polychaete Taxocene Characteristics in Vancouver Harbour. Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 57, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surugiu, V. The Use of Polychaetes as Indicators of Eutrophication and Organic Enrichment of Coastal Waters: A Study Case–Romanian Black Sea Coast. An. Ştiinţifice ale Univ. “Al.I. Cuza” Iaşi s. Biol. Anim. 2005, 51, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Fründ, H.-C.; Graefe, U.; Tischer, S. Earthworms as Bioindicators of Soil Quality. In Biology of Earthworms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 261–278. [Google Scholar]
- Olsgard, F.; Brattegard, T.; Holthe, T. Polychaetes as Surrogates for Marine Biodiversity: Lower Taxonomic Resolution and Indicator Groups. Biodiv. Conserv. 2003, 12, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, W.; Murray, B.R.; Hutchings, P. Promising yet Variable Performance of Cross-Taxon Biodiversity Surrogates: A Test in Two Marine Habitats at Multiple Times. Biodiv. Conserv. 2020, 29, 3067–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchetti, R.; Fattorini, D.; Gambi, M.; Regoli, F. Trace Metal Concentrations and Susceptibility to Oxidative Stress in the Polychaete Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin)(Sabellidae): Potential Role of Antioxidants in Revealing Stressful Environmental Conditions in the Mediterranean. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, L.; Berthet, B.; Amiard, J.-C.; Jeantet, A.-Y.; Amiard-Triquet, C. A Suitable Model for the Biomonitoring of Trace Metal Bioavailabilities in Estuarine Sediments: The Annelid Polychaete Nereis diversicolor. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2006, 86, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, H.K. The Use of Polychaetes (Annelida) as Indicator Species of Marine Pollution: A Review. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2008, 56, 11–38. [Google Scholar]
- Unrine, J.M.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Tsyusko, O.V.; Rao, W.; Shoults-Wilson, W.A.; Bertsch, P.M. Evidence for Bioavailability of Au Nanoparticles from Soil and Biodistribution within Earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8308–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, B.G.M.; Rouse, G.W.; Pleijel, F. Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Annelida; Science Publishers: Enfield, UK, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 1–698. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, V.J.; Chick, R.C.; Hutchings, P.A. A Review of Global Fisheries for Polychaete Worms as a Resource for Recreational Fishers: Diversity, Sustainability and Research Needs. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2018, 28, 543–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, D.; Talapatra, S.N.; Swarnakar, S. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Invertebrates for Potential Medicines-an Overview. Int. Let. Nat. Sci. 2015, 7, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, A.P.; Costa, P.M. The Hidden Biotechnological Potential of Marine Invertebrates: The Polychaeta Case Study. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, N.; Williamson, A.; Aguero, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Geeves, W. Marine Invasive Alien Species: A Threat to Global Biodiversity. Mar. Pol. 2003, 27, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Çinar, M.; Pancucci-Papadopoulou, M.; Harmelin, J.; Furnari, G.; Andaloro, F.; Bellou, N.; Streftaris, N.; Zibrowius, H. Annotated List of Marine Alien Species in the Mediterranean with Records of the Worst Invasive Species. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2005, 6, 63–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, J.L.; Gamboa, R.L.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M.D. Assessing the Global Threat of Invasive Species to Marine Biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, S. Zoogeography of the Sea; Sidgwick & Jackson, Ltd.: London, UK, 1953; Volume 6, pp. 1–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, G. The Distribution of Polychaetes within the Indo-Pacific. In Proceedings of the 8th Pacific Science Congress, Quezon City, Philippines, 16–28 November 1953; National Research Council of the Philippines: Quezon City, Philippines, 1957; Volume 3, pp. 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, O. Catalogue of the Polychaeta Annelids of the World. Allan Hancock Found. Publ. 1959, 23, 1–628. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.H. A Monograph on the Polychaeta of Southern Africa. Part 1. Errantia; British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1967; pp. 1–458. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.H. A Monograph on the Polychaeta of Southern Africa. Part II. Sedentaria; British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1967; pp. 459–878. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, P. Polychète Errantes. Faune Fr. 1923, 5, 1–488. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, P. Polychètes Sédentaires. Addenda Aux Errantes, Archiannélides, Myzostomaires. Faune Fr. 1927, 16, 1–494. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, S.J. The Status of Terebellides stroemi (Polychaeta; Trichobranchidae) as a Cosmopolitan Species, Based on a Worldwide Morphological Survey, Including Description of New Species. In Proceedings of the First International Polychaete Conference, Sydney, Australia, 4–9 July 1983; pp. 118–142. [Google Scholar]
- Eckelbarger, K.; Grassle, J. Spermatogenesis, Sperm Storage and Comparative Sperm Morphology in Nine Species of Capitella, Capitomastus and Capitellides (Polychaeta: Capitellidae). Mar. Biol. 1987, 95, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, S.J.; Woodham, A. A New Species of Chaetozone (Polychaeta: Cirratulidae) from Deep Water in the Northeast Atlantic, with Comments on the Diversity of the Genus in Cold Northern Waters. Hydrobiologia 2003, 496, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, P.; Karageorgopoulos, P. Designation of a Neotype of Marphysa sanguinea (Montagu, 1813) and a Description of a New Species of Marphysa from Eastern Australia. Hydrobiologia 2003, 496, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, B.S.; Bhaud, M.R.; Jirkov, I.A. Two New Species of Owenia (Annelida: Polychaeta) in the Northern Part of the North Atlantic Ocean and Remarks on Previously Erected Species from the Same Area. Sarsia 2003, 88, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.; Hutchings, P. An Analysis of Morphological Characters of Owenia Useful to Distinguish Species: Description of Three New Species of Owenia (Oweniidae: Polychaeta) from Australian Waters. Mar. Ecol. 2005, 26, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, A.; Parapar, J.; Pons, J.; Meißner, K.; Bakken, T.; Kongsrud, J.A.; Oug, E.; Gaeva, D.; Sikorski, A.; Johansen, R.A.; et al. A Mega-Cryptic Species Complex Hidden among One of the Most Common Annelids in the North East Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, M.; Bakken, T.; Nygren, A.; Kongsrud, J.A.; Capa, M. Species Delimitation Analyses of NE Atlantic Chaetozone (Annelida, Cirratulidae) Reveals Hidden Diversity among a Common and Abundant Marine Annelid. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2020, 149, 106852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapar, J.; Capa, M.; Nygren, A.; Moreira, J. To Name but a Few: Descriptions of Five New Species of Terebellides (Annelida, Trichobranchidae) from the North East Atlantic. ZooKeys 2020, 992, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, A. Cryptic Polychaete Diversity: A Review. Zool. Scr. 2014, 43, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, P.; Kupriyanova, E. Cosmopolitan Polychaetes–Fact or Fiction? Personal and Historical Perspectives. Invertebr. Syst. 2018, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, P.; Lavesque, N. I Know Who You Are, but Do Others Know? Why Correct Scientific Names Are so Important for the Biological Sciences. Zoosymposia 2020, 19, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, P.F.; Callaham Jr, M.A.; Drake, J.M.; Huang, C.-Y.; James, S.W.; Snyder, B.A.; Zhang, W. Pandora’s Box Contained Bait: The Global Problem of Introduced Earthworms. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 593–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çinar, M.E. Alien Polychaete Species Worldwide: Current Status and Their Impacts. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2013, 93, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Quatrefages, A. Histoire Naturelle Des Annéles Marine et d’eau Douce. Annélides et Géphyriens; Librarie Encyclopédique de Roret: Paris, France, 1866; Volume 2, pp. 1–588. [Google Scholar]
- Uschakov, P.V. Polychaeta of the Far Eastern Seas of the U.S.S.R. Keys to the Fauna of the USSR. No. 56; Zoological Institute of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR: Moscow, Russia, 1955; pp. 1–433. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, O. Atlas of the Errantiate Polychaetous Annelids from California; Allan Hancock Foundation, University of Southern California: Los Angeles, LA, USA, 1968; pp. 1–828. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, O. Atlas of the Sedentariate Polychaetous Annelids from California; Allan Hancock Foundation, University of Southern California: Los Angeles LA, USA, 1969; pp. 1–812. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Annelida, Borstenwürmer, Polychaeta. Tierwelt Dtschl. 1971, 58, 1–594. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, R.P. Annelids; Hutchinson University Library: London, UK, 1963; pp. 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, R.P. The polychaete stomodeum and phylogeny. In Essays on Polychaetous Annelids in Memory of Dr. Olga Hartman; Reish, D.J., Fauchald, K., Eds.; Allan Hancock Foundation, University of Southern California: Los Angeles, LA, USA, 1977; pp. 525–546. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, K. The Polychaete Worms. Definitions and Keys to the Orders, Families and Genera. Nat. Hist. Mus. Los Angeles Cty. Sci. Ser. 1977, 28, 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Pettibone, M.H. Annelida. In Synopsis and Classification of living Organisms; Parker, S.P., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Co: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 2, pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Annelida, Borstenwürmer, Polychaeta. In Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der Angrenzenden Meeresteile; 2nd revised ed.; Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1996; pp. 1–648. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, K.; Rouse, G. Polychaete Systematics: Past and Present. Zool. Scr. 1997, 26, 71–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W.; Pleijel, F. Current Problems in Polychaete Systematics. Hydrobiologia 2003, 496, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibye-Jacobsen, D.; Nielsen, C. The Rearticulation of Annelids. Zool. Scr. 1996, 25, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomaeus, T.; Purschke, G.; Hausen, H. Polychaete Phylogeny Based on Morphological Data–a Comparison of Current Attempts. Hydrobiologia 2005, 535, 341–356. [Google Scholar]
- Struck, T.H.; Schult, N.; Kusen, T.; Hickman, E.; Bleidorn, C.; McHugh, D.; Halanych, K.M. Annelida phylogeny and the status of Sipuncula and Echiura. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, T.H.; Nesnidal, M.P.; Purschke, G.; Halanych, K.M. Detecting Possibly Saturated Positions in 18S and 28S Sequences and Their Influence on Phylogenetic Reconstruction of Annelida (Lophotrochozoa). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 48, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zrzavý, J.; Říha, P.; Piálek, L.; Janouškovec, J. Phylogeny of Annelida (Lophotrochozoa): Total-Evidence Analysis of Morphology and Six Genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appeltans, W.; Ahyong, S.T.; Anderson, G.; Angel, M.V.; Artois, T.; Bailly, N.; Bamber, R.; Barber, A.; Bartsch, I.; Berta, A. The Magnitude of Global Marine Species Diversity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, M.; Capa, M.; Oceguera-Figueroa, A.; Rouse, G. Annelida. In The Tree of Life: Evolution and Classification of Living Organisms; Vargas, P., Zardoya, R., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 254–269. [Google Scholar]
- Weigert, A.; Bleidorn, C. Current Status of Annelid Phylogeny. Org. Divers. Evol. 2016, 16, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WoRMS Annelida. 2021. Available online: http://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=882 (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Parapar, J.; Martínez, A.; Moreira, J. On the Systematics and Biodiversity of the Opheliidae and Scalibregmatidae. Diversity 2021, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanol, J.; Carrera-Parra, L.F.; Steiner, T.M.; Amaral, A.C.Z.; Wiklund, H.; Ravara, A.; Budaeva, N. The Current State of Eunicida (Annelida) Systematics and Biodiversity. Diversity 2021, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasby, C.J.; Erséus, C.; Martin, P. Annelids in Extreme Aquatic Environments: Diversity, Adaptations and Evolution. Diversity 2021, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, P.; Carrerette, O.; Nogueira, J.M.; Hourdez, S.; Lavesque, N. The Terebelliformia-Recent Developments and Future Directions. Diversity 2021, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsson, S.; Erséus, C. Cryptic Clitellata: Molecular Species Delimitation of Clitellate Worms (Annelida): An Overview. Diversity 2021, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meca, M.A.; Zhadan, A.; Struck, T.H. The Early Branching Group of Orbiniida Sensu Struck et al., 2015: Parergodrilidae and Orbiniidae. Diversity 2021, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapar, J.; Mortimer, K.; Capa, M.; Moreira, J. On the Systematics and Biodiversity of the Palaeoannelida. Diversity 2021, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Kawauchi, G.Y. How Many Sipunculan Species Are Hiding in Our Oceans? Diversity 2021, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsaae, K.; Kerbl, A.; Domenico, M.D.; Gonzalez, B.C.; Bekkouche, N.; Martínez, A. Interstitial Annelida. Diversity 2021, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capa, M.; Kupriyanova, E.; Nogueira, J.M.M.; Bick, A.; Tovar-Hernández, M.A. Fanworms: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow. Diversity 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Grosse, M.; Zhadan, A.; Langeneck, J.; Fiege, D.; Martínez, A. Still Digging: Advances and Perspectives in the Study of the Diversity of Several Sedentarian Annelid Families. Diversity 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.; Aguado, M.T.; Fernández Alamo, M.A.; Britayev, T.; Böggemann, M.; Capa, M.; Faulwetter, S.; Fukuda, M.V.; Helm, C.; Petti, M.A.V.; et al. An Approach to the Diversity of Phyllodocida (Annelida: Errantia), with a Focus on Glyceridae, Goniadidae, Nephtyidae, Polynoidae, Sphaerodoridae, Syllidae and the Holoplanktonic Families. Diversity 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Struck, T. Phylogeny. Annelida, Basal Groups: Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria I. In Handbook of Zoology; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 37–68. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, J.A.; Maciolek, N.J.; Meissner, K. Spionidae Grube, 1850. In Handbook of Zoology; Annelida; Volume 2: Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria II; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, J.A.; Maciolek, N.J. Poecilochaetidae Hannerz, 1956. In Handbook of Zoology; Annelida; Volume 2: Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria II; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 103–119. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, J.A.; Maciolek, N.J. Uncispionidae Green, 1982. In Handbook of Zoology; Annelida; Volume 2: Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria II; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, J.A.; Maciolek, N.J. Trochochaetidae Pettibone,1963. In Handbook of Zoology; Annelida; Volume 2: Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria II.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 120–135. [Google Scholar]
- Capa, M.; Hutchings, P. Sabellariidae. In Hanbook of Zoology; Volume 2: Pleistoannelida, Sedentaria II; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 144–163. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kocot, K.M.; Whelan, N.V.; Santos, S.R.; Waits, D.S.; Thornhill, D.J.; Halanych, K.M. Phylogenomics of Tubeworms (Siboglinidae, Annelida) and Comparative Performance of Different Reconstruction Methods. Zool. Scr. 2017, 46, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J.; Wilson, S.; Houlding, B. Predicting Total Global Species Richness Using Rates of Species Description and Estimates of Taxonomic Effort. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, B.; Perrard, A.; Bouchet, P. 21 Years of Shelf Life between Discovery and Description of New Species. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R943–R944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, P.A. Major Issues Facing Taxonomy—A Personal Perspective. Megataxa 2020, 1, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, P.Z.; DeSalle, R. Integrating DNA Barcode Data and Taxonomic Practice: Determination, Discovery, and Description. Bioessays 2011, 33, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capa, M.; Pons, J.; Hutchings, P. Cryptic Diversity, Intraspecific Phenetic Plasticity and Recent Geographical Translocations in Branchiomma (Sabellidae, Annelida). Zol. Scr. 2013, 42, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, V.C.; Zanol, J.; Magalhães, W.F.; Paiva, P.C. Genetic Diversity of Timarete punctata (Annelida: Cirratulidae): Detection of Pseudo-Cryptic Species and a Potential Biological Invader. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2017, 197, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsson, S.; Erséus, C. Cryptic Diversity in Supposedly Species-Poor Genera of Enchytraeidae (Annelida: Clitellata). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 183, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchán, D.F.; Fernández, R.; Domínguez, J.; Díaz Cosín, D.J.; Novo, M. Genome-Informed Integrative Taxonomic Description of Three Cryptic Species in the Earthworm Genus Carpetania (Oligochaeta, Hormogastridae). Syst. Biodivers. 2020, 18, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunton, L.M.; Kupriyanova, E.K.; Alvestad, T.; Avery, L.; Blake, J.A.; Biriukova, O.; Böggemann, M.; Borisova, P.; Budaeva, N.; Burghardt, I.; et al. Annelids of the Eastern Australian Abyss Collected by the 2017 RV ‘Investigator’ Voyage. Zookeys 2021, 1020, 1–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).