Abstract
The leafy liverwort Nowellia curvifolia is a widespread Holarctic species belonging to the family Cephaloziaceae. It is made up of a newly sequenced, assembled and annotated organellar genomes of two European specimens, which revealed the structure typical for liverworts, but also provided new insights into its microevolution. The plastome of N. curvifolia is the second smallest among photosynthetic liverworts, with the shortest known inverted repeats. Moreover, it is the smallest liverwort genome with a complete gene set, since two smaller genomes of Aneura mirabilis and Cololejeunea lanciloba are missing six and four protein-coding genes respectively. The reduction of plastome size in leafy liverworts seems to be mainly impacted by deletion within specific region between psbA and psbD genes. The comparative intraspecific analysis revealed single SNPs difference among European individuals and a low number of 35 mutations differentiating European and North American specimens. However, the genetic resources of Asian specimen enabled to identify 1335 SNPs in plastic protein-coding genes suggesting an advanced cryptic speciation within N. curvifolia or the presence of undescribed morphospecies in Asia. Newly sequenced mitogenomes from European specimens revealed identical gene content and structure to previously published and low intercontinental differentiation limited to one substitution and three indels. The RNA-seq based RNA editing analysis revealed 17 and 127 edited sites in plastome and mitogenome respectively including one non-canonical editing event in plastid chiL gene. The U to C editing is common in non-seed plants, but in liverwort plastome is reported for the first time.
1. Introduction
Organellar genomes of early land plants are known from their stable structure and almost identical gene order present in all main evolutionary lineages [1,2,3,4,5], which include complex thalloids, simply thalloids, leafy and early divergent leafy liverworts from the order Treubiales and Haplomitriales. Despite the fact that the organellar genomes of model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha were among first sequenced plant plastomes [6] and mitogenomes [7], the number of complete genomes sequences was very limited, till the end of the second decade of XXI century, when several paper were published significantly expanding our knowledge about evolutionary dynamics of these molecules [2,3,4,5]. The current genomic resources comprise 61 mitogenomes and 59 plastomes complete sequences, but many liverwort families do not have their representatives.
Among all known liverwort chloroplast genomes, the typical structure is present including large single copy unit (LSC) and small single copy unit (SSC), which are separated by two inverted repeats (IRs), however the plastome size and GC content differ among lineages.
The smallest plastome (108,007 bp) was found in mycoheterotrophic Aneura mirabilis [8], while the largest one (128,728 bp) in the early divergent Haplomitrium blumei [4]. The plastome of the latter species also shows the highest GC-content, with 44.4%, whereas the lowest GC-content (28.2%) was found in the plastid genome of the complex thalloid Conocephalum salebrosum [9].
The structural changes of plastomes are mainly limited to small rearrangements at borders of inverted repeats and single copy regions, which lead to IR expansion [4,7] or losing of six genes by a pseudogenization in mycoheterotrophic species [6]. The gene content of plastome units is conserved in almost all known liverworts, with exception of Conocephalum conicum where two genes, rps7 and rps12 were transferred from LSC to IR [9].
Apart from vascular plants the liverwort mitogenomes are structurally stable, with only one known exception of Gymnomitrion concinnatum, where two recombination events appear [10]. This stability seems to be associated with the lack of a repetitive sequence in the mitogenomes of early land plants, which are common in seed plants [1]. However, in the case of the species mentioned above, the number of repeats is lower than in other liverworts. The other differences in liverwort mitogenome structures include changes of an intron content in leafy liverwort lineage [3,11] and presence of the nad7 gene in early divergent Treubiales and Haplomitriales [3,12].
The leafy liverwort Nowellia curvifolia (Dicks.) Mitt. belongs to the family Cephaloziaceae, which includes 17 genera. The genus Nowellia has been resolved by phylogenetic studies as a sister to Cephalozia [13]. Nowellia is a small genus, which includes only two species: N. curvifolia widespread in Holarctic and N. wrightii endemic to Cuba. N. curvifolia grows on rotting logs in forests and produces up to 20 mm long shoots, which are green in the shade and red in the sunny condition. The morphology of N. curvifolia is very charateric by its inflated leaves with two long, narrow, incurved lobes ended with long, slender teeth [14]. The well-developed morphological features are one of the reason of overlooked cryptic diversity, which often lead to description of new species [15,16,17]. Despite recent publication of several papers dealing with liverwort plastomes [4,5,9,10,18], the GenBank entries didn’t include any representative of the Cephaloziaceae family.
In the present study, we sequenced, assembled and characterized organellar genomes of two N. curvifolia specimens from Europe. Obtained genomes were compared to close relatives of Nowellia and to shed some light on intraspecific variation of these molecules. We also report the first complete plastome sequences of a member of the Cephaloziaceae family.
2. Materials and Methods
The specimen details, including herbarium number and locality are given in Supplementary Table S1. The DNA was extracted using the Qiagen Plant Mini-kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) from a fresh material from two European locality collected in silica gel bags. One branched individual was ground with silica beds in a MiniBead-Beater homogenizer for 50 s and subsequently processed according to the manufacturer protocol. DNA quantity was estimated using the Qubit fluorometer and Qubit™ dsDNA BR Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Carsbad, NM, USA). DNA quality was checked by electrophoresis in 0.5% agarose gel stained with Euryx Simple Safe (Eurx, Gdańsk, Poland).
The genomic libraries were constructed with Qiagen FX DNA kit (Qiagen) and were sequenced using HiSeqX (Illumina) to generate 150 bp paired-end reads at Macrogen Inc. (Seoul, Korea) with 350 bp insert in size between paired-ends. Afterwards, sequencing reads were cleaned by removing the adaptor sequences and low quality reads with Trimmomatic v0.36 [19]. Trimmed reads were assembled using NOVOplasty 4.2 [20] with previously published Nowellia curvifolia (MK230952) mitochondrial, and Calypogeia integristipula chloroplast (MK293997) reference genomes, respectively. The GeSeq software was used for annotation of organellar genomes [21] and genome maps were drawn using OGDRaw web server [22]. The junctions between chloroplast inverted repeats and single copy regions were visualized using IRscope software [23]. To assemble the third plastome of the individual used for MK230952 assembly, SSR8246023 archive was used. The specimens details, including GenBank accession numbers of newly assembled genomes are given in Supplementary Table S1.
As the backbone of phylogenetic analysis we used plastid CDS alignment from studies on Ptilidiales [24]. Existing dataset, which includes a set of plastid Nowellia curvifolia genes from Asian specimens, was expanded by adding CDS from three newly assembled plastomes (two from Europe and one form North America). To keep a congruence with a previous study, we applied Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian inference methods using RAxML [25] and MrBayes [26] with parameters used during studies on Ptilidiales [19].
The RNA-seq library of Nowelia curvifolia (Accession number SRR8202183) was mapped onto organellar genomes using Geneious 2020 software [27] and the alignment mismatches with variant frequency >0.50 were subsequently compared with the RNA editing sites predicted by PREPACT 3.12.0 [28].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Characteristics of Nowellia curvifolia Plastome
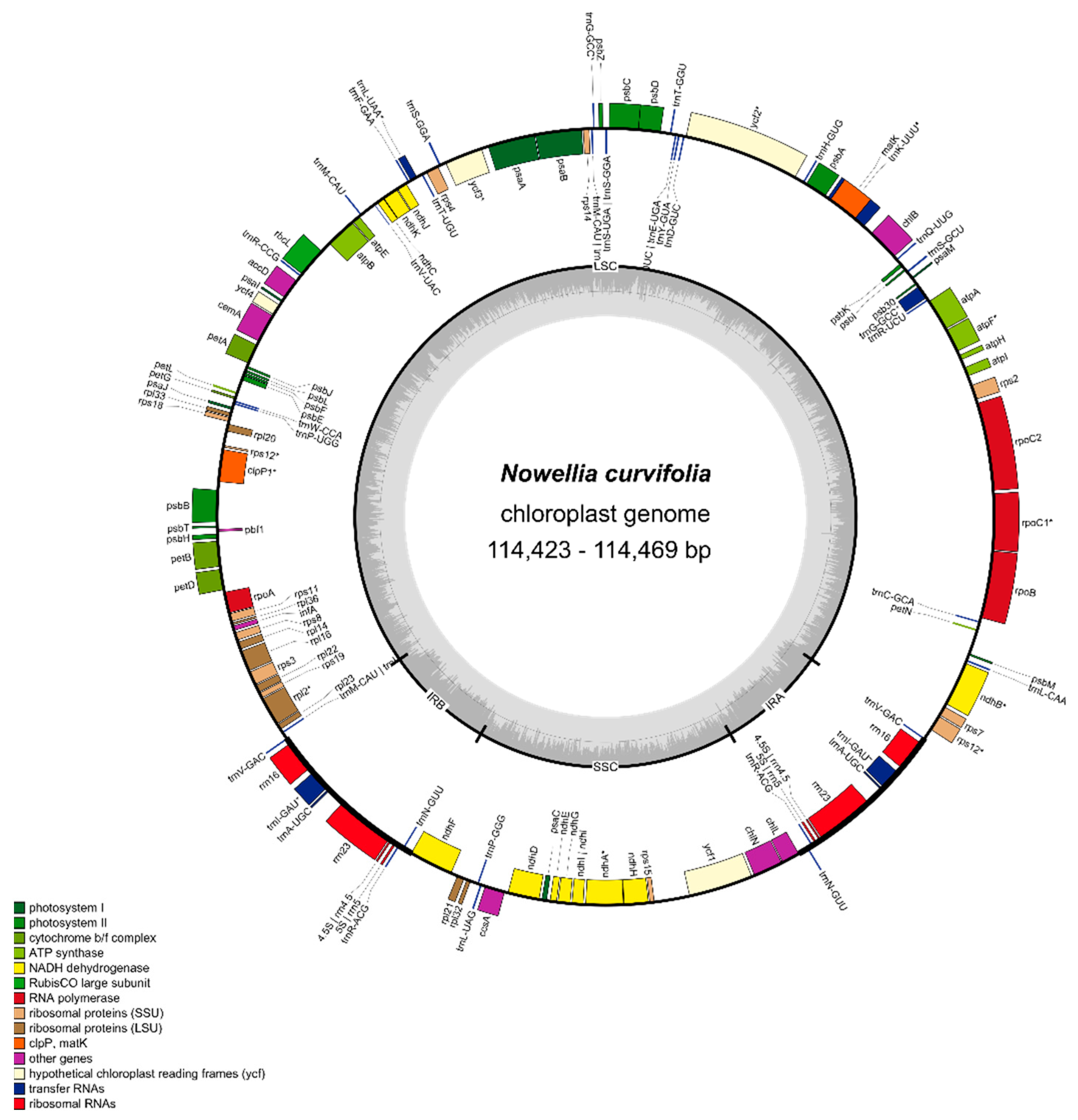
Newly sequenced and assembled plastomes are 114,423-114,469 bp long and their structure is typical for other known liverwort genomes (Figure 1). The overall length of Nowellia curvifolia plastome is the shortest among its closest relatives with known complete genome sequences: Scapania ampliata (NC_051002.1: 118,026 bp) and Douinia plicata (NC_051003.1: 118,797 bp).
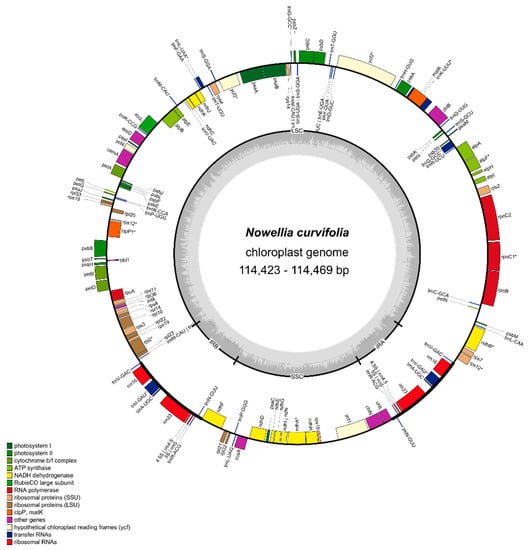
Figure 1.
Gene map of the chloroplast genome of Nowellia curvifolia. Genes inside and outside the outer circle are transcribed in counterclockwise and clockwise directions, respectively. The genes are color-coded based on their function. The inner circle visualizes the G/C content.
The reduction of plastome length is splitted among all four regions (Supplementary Figure S1): detected IRs were 8,086 bp (8,870 bp and 9,022 bp in Scapania, and Douinia, respectively), LSC is 79,341-79,293 bp (80,850 bp and 81,142 bp in Scapania and Douinia respectively) and SSC is 18,956 (19,436 bp and 19,611 bp in Scapania, and Douinia, respectively). Considering all known complete liverwort plastome sequences, Nowellia chloroplast genome is the third smallest one, with Cololejeunea lanciloba second (108,674 bp) and mycoheterotrophic Aneura mirabilis with the smallest genome among liverworts (108,007 bp). The biggest difference among these three species is the length of SSC, which is 13,974 bp and 14,268 bp in A. mirabilis and C. lanciloba respectively, in the latter caused by the deletion of the ndhF-ccsA region. The differences in LSC length are much smaller (77,553 bp in A. mirabilis and 78,204 bp in C. lanciloba), but the IRs of N. curvifolia plastome are the shortest among known liverwort chloroplast sequences, passing C. lanciloba by 15 bp.
The reduction of plastome length in leafy liverworts is often caused by deletions around the ycf2 gene [10]. The region between psbA and psbD genes contains, besides the previously mentioned ycf2 gene, four tRNAs: trnH-GUG, trnD-GUC, trnY-GUA and trnE-UCC, and in the case of Nowellia and Scapania this region is 1797 bp shorter in the former. Keeping in mind that the total difference in LSC length between these species is 1509 bp, the role of this region in plastome length reduction is leading.
As in the closest known relatives with a plastome sequence mentioned above, the plastome of N. curvifolia consists of 121 unique genes, including 81 protein-coding genes, 6 genes of unknown function (ycf genes), 4 ribosomal RNAs and 30 transfer RNAs (Supplementary Table S2). The gene order and content seem to be stable in the most of leafy and simple thalloid liverworts [4,5,10,18,29,30], with some exceptional gene deletions as in the mentioned above Cololejeunea lanciloba [4] or mycoheterotrophic A. mirabilis [8].
3.2. The Characteristics of Nowellia curvifolia Mitogenome
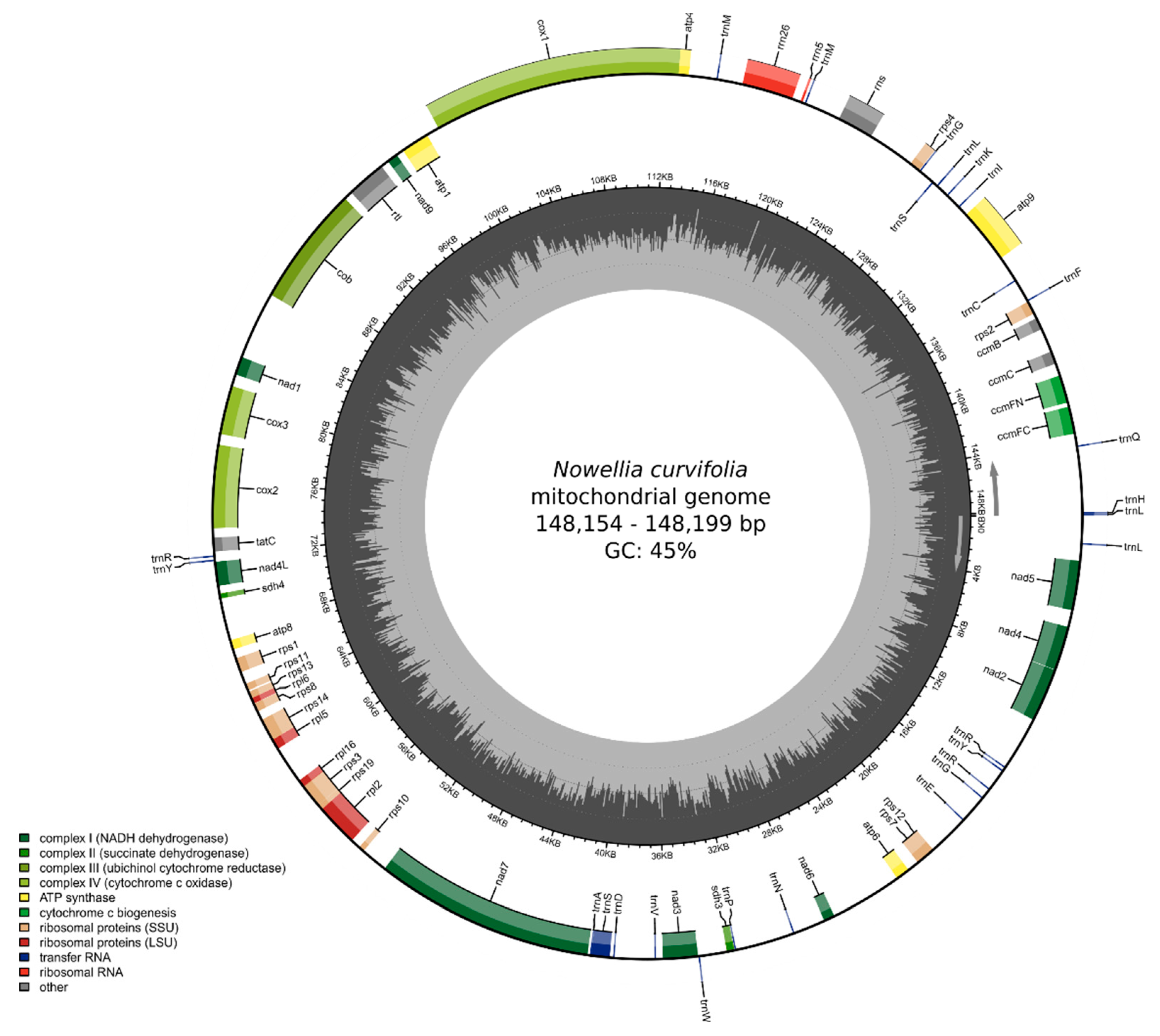
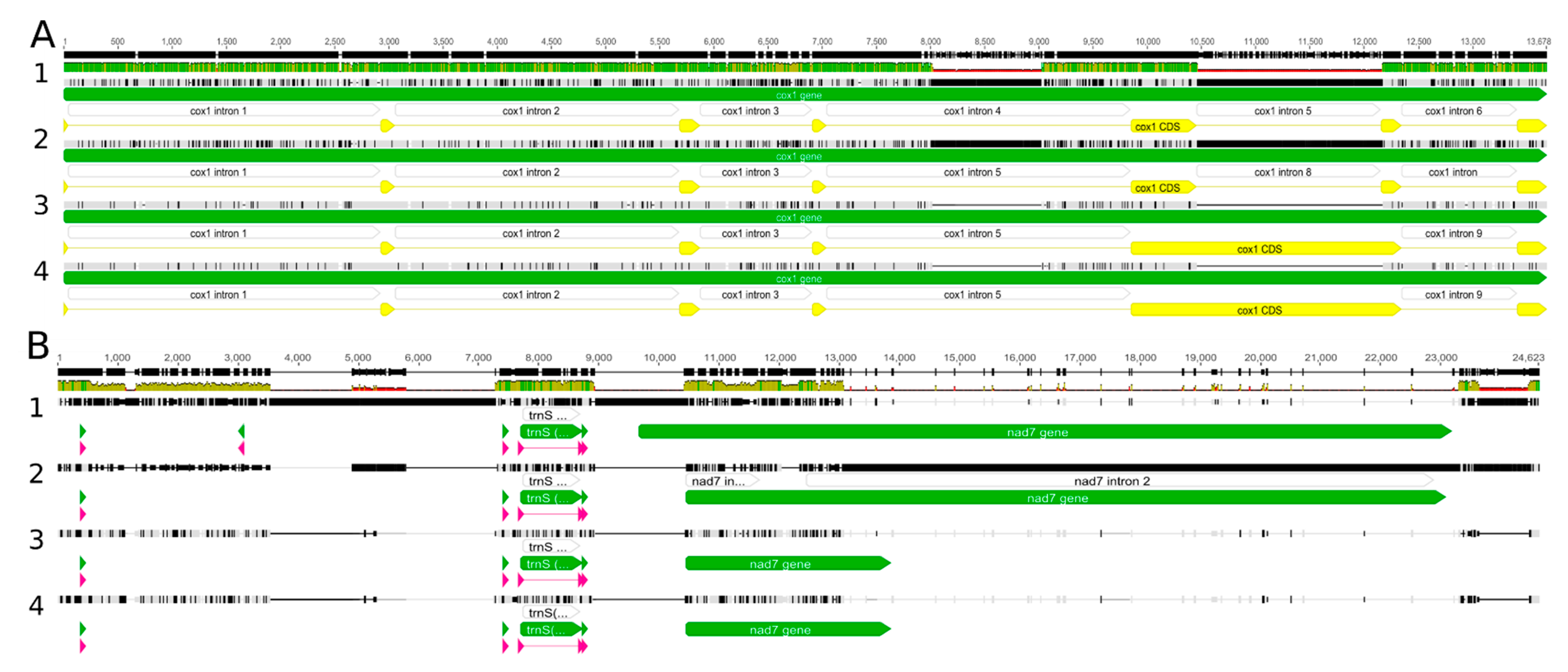
The newly sequenced Nowelia curvifolia mitogenomes are 148,199 bp long (Figure 2) and are slightly longer than the closest related species with a known mitogenome structure: Scapania ampliata (143,664 bp) and Scapania ornithopodioides (142,992 bp). Both mitogenomes contain a typical liverwort set of genes, including 42 protein-coding genes, 25 tRNA and three rRNA genes. The gene order and intron content is the same as in Calypogeia species, but the closest relatives with known mitogenome sequences - representatives of the genus Scapania (S. ampliata and S. ornithopodioides) lack intron 8 (cox1i1116g1) of cox1 gene (Figure 3). The losses of introns in leafy liverworts lineage seem to be common and it is probably done via retroprocessing [3,11].
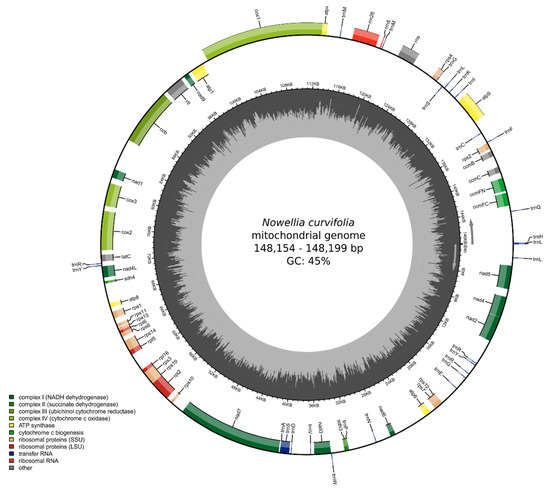
Figure 2.
Gene map of the mitochondrion of Nowellia curvifolia. Genes inside and outside the outer circle are transcribed in counterclockwise and clockwise directions, respectively. The genes are color-coded based on their function. The inner circle visualizes the G/C content.
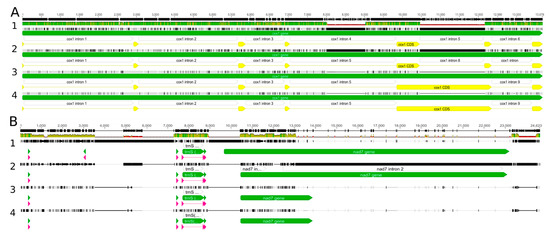
Figure 3.
The main sources of mitogenome length variation among Nowellia and its close relatives: 1—Calypogeia integristipula, 2—Nowellia curvifolia, 3—Scapania ornithopodioides, 4—Scapania ampliata. (A)—intron reductions in cox1 gene; (B)—deletion in region between nad3 and rpl10.
However, the loss of an intron alone does not explain the almost 5k bp-difference in mitogenome length between Nowellia and Scapania, since the size of the intron cox1i1116g1 ranges 1.6–1.8 kb in Jungermanniales. The reduction or increase of mitogenome length in leafy liverworts is often caused by deletions between genes nad3 and rpl10. This region contains the pseudogenized nad7 gene and four tRNAs: trnV-UAC, trnD-GUC, trnS-GCU and is a main source of mitogenome size variation among in Nowellia and its relatives. In Nowellia mitogenome the distance between nad3 and rpl10 gene is 17,620 bp and in Scapania species ranged from 8350 bp to 8364 bp. Moreover, the length of this region in Nowellia is even longer than in the genus Calypogeia (ca. 14.5 kb), which mitogenomes are significantly bigger with ca. 163 kb [11]. The described patterns are similar to those found in results of comparative analysis of Nowellia and its close relatives.
3.3. Intraspecific Variation of Nowellia curvifolia Organellar Genomes
The variation of organellar genomes among tested European samples was low. The mitogenomes and plastomes of both sequenced samples were almost identical and differed in only one SNP in the intergenic spacer atp1-cox1 (mitochondrial) and rps4-trnM-CAU (plastid). Newly sequenced mitogenomes were longer than mitogenome of North American sample available in Genbank (accession number MK230952) due to three indels: 2 bp long in trnN-GUU and trnP-UGG spacer, 42 bp long in spacer between rps14 and rps8, 1 bp long in intron 2 of cob gene. Only one substitution was found in atp1-cox1 spacer in the case of the NCU specimen.
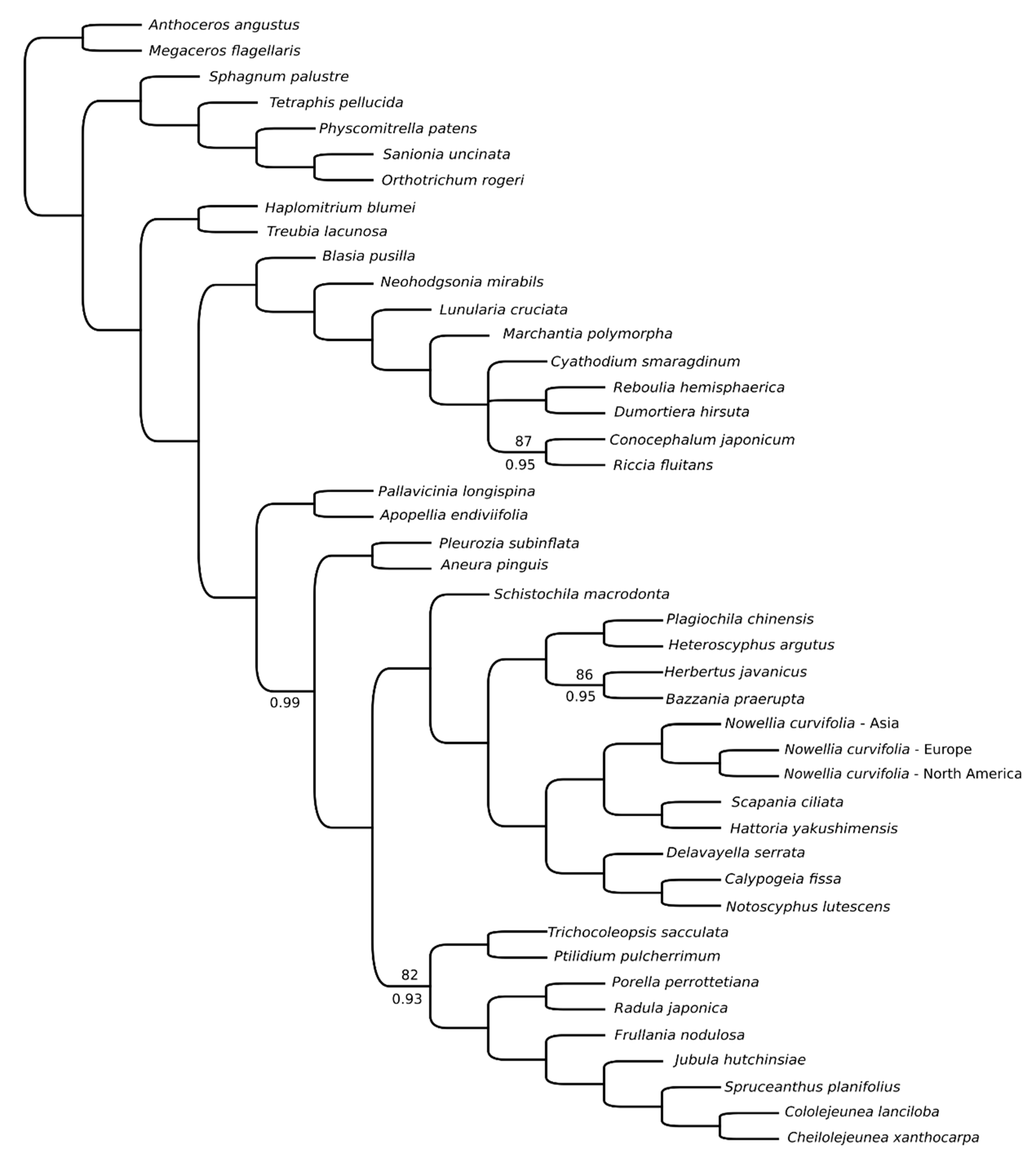
Comparative analyses of European and North American plastomes revealed presence of 35 SNPs and one 41bp long indel between ndhJ and ndhK genes. Almost half of detected SNPs were found in 12 protein-coding genes (Supplementary Table S2), but with exception of ycf2 (4 SNPs), rps7 (2 SNPs) and chiL (2 SNPs) remaining genes differed by single substitution. Since no Asian complete plastome was available, the comparative analysis of CDS revealed presence of 1335 SNPs unique for this sample (Supplementary Table S2). Top-five most variable genes include rpoB (98 SNPs), ycf2 (81 SNPs), ycf1 (51), ndhD (51), ndhF (46) and ndhB (46). Four of these genes (ycf1, ycf2, ndhB, ndhD) were among most variable plastid genes of the leafy liverwort genus Calypogeia [5] and ycf1 and ycf2 were the most variable genes of simple thalloid Aneura pinguis complex [18]. Both ycf genes are often considered as promising barcodes in many taxa of vascular plants [31,32,33,34]. The phylogenetic position of Asian specimens reflects their divergence from European and North American specimens (Figure 4), but it does not impact a general tree layout as it is congruent with previously published one [24].
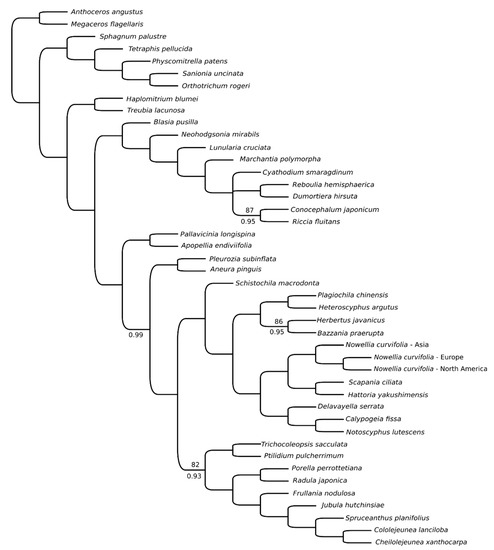
Figure 4.
Phylogenetics relationships of 44 bryophyte species based on protein-coding sequences obtained using ML analysis. Bootstrap values lower than 100 are given at the nodes. Bayesian inference resulted in a tree with congruent topology and PP values lower than 1 are given below branches.
The comparative data for genus or species levels are very limited, since most sequenced genera consist of genome sequence of single species [4,10,29,30]. The number of SNPs between closely related Calypogeia species (C. muelleriana and C. integristipula) detected for the whole genome was one third of the amount detected for CDS for Nowellia specimens, and the intraspecific differentiation was limited to few SNPs, however all the samples had European origin [5]. Lower genetic differentiation was also detected at inter- and intraspecific level of complex thalloid liverwort genera Marchantia and Conocephalum [9], but this lineage is known from low genetic differentiation and slow evolutionary rate of organellar genomes [35]. The level of CDS polymorphism found among remaining Asian specimens is similar to those found among cryptic lineages of A. pinguis complex [18,36,37].
The numbers of detected SNPs reflect the genetic identity which amounted to 99.98% among European and North American samples, and 97.49% among Asian and European/North American ones. This value is rather characteristic for interspecific values, as mean genetic identity among ten Calypogeia species was 97.50% and 99.81% at infraspecific level [5]. Similar genetic identity were found among complex thalloid Conocephalum species with 97.67% at interspecific and 99.98% at infraspecific levels [9]. The high genetic differentiation could be explained by population origin or could suggest a cryptic speciation. The morphological differentiation in easily delimited liverwort taxa is often overlooked, especially if well-established features, like characteristic macromorphology or unique micromorphological characters, are present. With very characteristic morphology, N. curvifolia falls within this group of species. Detailed studies based on wide material collection often lead to description of new species [16,38].
Intraspecific differentiation of N. curvifolia was not studied using morphological or molecular methods, but genetic distances between European and Asian samples suggest presence of geographical races or cryptic species, which are known in liverworts [17,36,39]. Application of integrative taxonomy approach enabled description of new species within genera like Conocephalum [15], Calypogeia [16] and Marsupella [40]. However in some cryptic species morphological characters are too blurry despite strong molecular, physiological and environmental differentiation, but this concerns mainly simple thalloids [37,41,42].
3.4. RNA Editing in Organellar Genomes
RNA editing alters the identity of nucleotides in an RNA sequence so that the mature transcript differs from the template defined in the genome. This process has been observed in chloroplasts and mitochondria of both seed and early land plants, including liverworts. In plant organellar genomes two types of RNA edition are known: typical C to U and reverse U to C [43].
The RNA editing in liverwort plastomes is poorly explored, especially with direct use of RNA-seq data. In plastome of Nowellia curvifolia 17 RNA editing sites were confirmed by RNA sequencing (Table S3). Single nucleotide edition was confirmed for dehydrogenases (ndhB, ndhC, ndhF, ndhG, ndhI), genes of photosystem I and II (psaI, psbH, psbZ) and other like: rpoB, petB, ycf4, ycf66. Two edited nucleotides were found in genes petD and atpI, and one edition in the latter is obligatory to create a start codon. Among 16 typical C-U editing events, that are common in plant plastomes and mitogenomes, the reverse edition U-C was found in the plastid chiL gene. The reverse U-to-C RNA editing appears to be restricted to hornworts, some lycophytes, and ferns [44], but has not been confirmed in liverwort plastomes up to the date. The robust reverse editing was predicted for plastome of Gymnomitrion concinnatum [10], but in silico prediction tools seem to be incorrect in the case of U to C ending in the early land plants [2].
The RNA editing within mitochondrial transcripts was more frequent with 127 edited sites along 23 genes, but all of them were canonical C-U events (Supplementary Table S3). Among most edited were genes ccmC (15), cox1 (10), atp6, ccmB and ccmFN (9). The disproportion between editing events in plastome and mitogenome is bigger than an average for liverworts, where usually RNA edition is three times more frequent in mitogenome than plastome, but in few species from genera Bazzania, Lepidozia and Odonthoschizma edition in plastid transcript is more frequent than in mitochondrial transcript [45]. Overall RNA editing frequency of Nowellia curvifolia organellar genes is lower than the average for Jungermanniales (210).
4. Conclusions
Recently published papers significantly expand our knowledge of liverworts organellar genomes, but their infra-specific variation remained almost unexplored. The newly assembled plastomes of Nowellia curvifolia revealed the smallest size among species with a complete set of genes and the shortest IRs among all liverworts. However, the size reduction was not equally distributed along the genome, but mostly focused in the region between psbA and psbD genes. The comparative analysis of chloroplast genes enables identification of significant amounts of SNPs between American, European and Asian specimens suggesting advanced cryptic speciation in this morphologically defined species. However, further studies are required to better understand this process in Nowellia, including wider sampling and morphological studies with special focus on Asian populations. Detailed analysis of RNA-editing revealed one example of non-canonical, reverse editing in chloroplast chiL gene, which was not reported in liverworts to date. The previous studies reported the possibility of reverse editing, but RNA-seq datasets didn’t confirm U to C edition in plastid genomes of liverworts, which is quite common in other non-seed plants lineages.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1424-2818/13/2/81/s1, Figure S1: The comparison of Nowellia plastome with close relatives and two liverworts with smaller genomes with reduced gene sets (Aneura mirablis and Cololejeunea lanciloba), Table S1: Specimens details, Table S2: Number of SNPs detected in chloroplast CDS, Table S3: Number of edited sites in plastid and mitochondrial transcripts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: J.S., M.S., writing: J.S., K.K., M.Ś., M.S., laboratory analyses: M.Ś., M.S., resources: J.S., M.S., data validation: K.K., J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The sequencing of liverwort organellar genomes was financially supported by The National Science Center Kraków, Poland: Grant No. 2015/19/B/NZ8/03970.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The newly sequenced organellar genomes sequenced are submitted to GenBank database.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, Y.; Medina, R.; Goffinet, B. 350 My of Mitochondrial Genome Stasis in Mosses, an Early Land Plant Lineage. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2586–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszczyński, K.; Ślipiko, M.; Sawicki, J. Potential of Transcript Editing Across Mitogenomes of Early Land Plants Shows Novel and Familiar Trends. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhu, R.; Jia, Y.; Goffinet, B.; Liu, Y. Mitochondrial genomes of the early land plant lineage liverworts (Marchantiophyta): Conserved genome structure, and ongoing low frequency recombination. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Ma, W.; Pressel, S.; Wu, Y.; Schneider, H. Exploring the plastid genome disparity of liverworts. J. Syst. Evol. 2019, 57, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślipiko, M.; Myszczyński, K.; Buczkowska, K.; Bączkiewicz, A.; Szczecińska, M.; Sawicki, J. Molecular delimitation of European leafy liverworts of the genus Calypogeia based on plastid super-barcodes. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, K.; Fukuzawa, H.; Kohchi, T.; Sano, T.; Sano, S.; Shirai, H.; Umesono, K.; Shiki, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Aota, Z.C.S.-I.; et al. Structure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome. J. Mol. Biol. 1988, 203, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Yamato, K.; Ohta, E.; Nakamura, Y.; Takemura, M.; Nozato, N.; Akashi, K.; Kanegae, T.; Ogura, Y.; Kohchi, T.; et al. Gene organization deduced from the complete sequence of liverwort Marchantia polymorpha mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 223, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickett, N.J.; Zhang, Y.; Hansen, S.K.; Roper, J.M.; Kuehl, J.V.; Plock, S.A.; Wolf, P.G.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Boore, J.L.; Goffinet, B. Functional Gene Losses Occur with Minimal Size Reduction in the Plastid Genome of the Parasitic Liverwort Aneura mirabilis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, J.; Bączkiewicz, A.; Buczkowska, K.; Górski, P.; Krawczyk, K.; Mizia, P.; Myszczyński, K.; Ślipiko, M.; Szczecińska, M. The Increase of Simple Sequence Repeats during Diversification of Marchantiidae, An Early Land Plant Lineage, Leads to the First Known Expansion of Inverted Repeats in the Evolutionarily-Stable Structure of Liverwort Plastomes. Genes 2020, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myszczyński, K.; Górski, P.; Ślipiko, M.; Sawicki, J. Sequencing of organellar genomes of Gymnomitrion concinnatum (Jungermanniales) revealed the first exception in the structure and gene order of evolutionary stable liverworts mitogenomes. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ślipiko, M.; Myszczyński, K.; Buczkowska-Chmielewska, K.; Bączkiewicz, A.; Szczecińska, M.; Sawicki, J. Comparative Analysis of Four Calypogeia Species Revealed Unexpected Change in Evolutionarily-Stable Liverwort Mitogenomes. Genes 2017, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, J.-Y.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Qiu, Y.-L. The Mitochondrial Genomes of the Early Land Plants Treubia lacunosa and Anomodon rugelii: Dynamic and Conservative Evolution. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldberg, K.; Váňa, J.; Krusche, J.; Kretschmann, J.; Patzak, S.D.F.; Pérez-Escobar, O.A.; Rudolf, N.R.; Seefelder, N.; Schäfer-Verwimp, A.; Long, D.G.; et al. A phylogeny of Cephaloziaceae (Jungermanniopsida) based on nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers. Org. Divers. Evol. 2016, 16, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, M. Liverworts of New England; Memoirs of the New York Botanical Garden; Botanical Garden Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 99. [Google Scholar]
- Szweykowski, J.; Buczkowska, K.; Odrzykoski, I.J. Conocephalum salebrosum (Marchantiopsida, Conocephalaceae)—A new Holarctic liverwort species. Plant Syst. Evol. 2005, 253, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowska, K.; Bakalin, V.; Bączkiewicz, A.; Aguero, B.; Gonera, P.; Ślipiko, M.; Szczecińska, M.; Sawicki, J. Does Calypogeia azurea (Calypogeiaceae, Marchantiophyta) occur outside Europe? Molecular and morphological evidence. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs, J.; Hentschel, J.; Bombosch, A.; Fiebig, A.; Reise, J.; Edelmann, M.; Kreier, H.-P.; Schäfer-Verwimp, A.; Caspari, S.; Schmidt, A.R.; et al. One species or at least eight? Delimitation and distribution of Frullania tamarisci (L.) Dumort. s. l. (Jungermanniopsida, Porellales) inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2010, 56, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszczyński, K.; Bączkiewicz, A.; Buczkowska, K.; Ślipiko, M.; Szczecińska, M.; Sawicki, J. The extraordinary variation of the organellar genomes of the Aneura pinguis revealed advanced cryptic speciation of the early land plants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty:de novoassembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Vand accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, W.; Pressel, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Schneider, H. Chloroplast phylogenomics of liverworts: A reappraisal of the backbone phylogeny of liverworts with emphasis on Ptilidiales. Cladistics 2020, 36, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, H.; Knoop, V. PREPACT 2.0: Predicting C-to-U and U-to-C RNA Editing in Organelle Genome Sequences with Multiple References and Curated RNA Editing Annotation. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, L.L.; Wickett, N.J.; Cox, C.J.; Goffinet, B. Deep sequencing of Ptilidium (Ptilidiaceae) suggests evolutionary stasis in liverwort plastid genome structure. Plant Ecol. Evol. 2011, 144, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosche, C.; Funk, H.T.; Maier, U.G.; Zauner, S. The Chloroplast Genome of Pellia endiviifolia: Gene Content, RNA-Editing Pattern, and the Origin of Chloroplast Editing. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Highly Variable Chloroplast Markers for Evaluating Plant Phylogeny at Low Taxonomic Levels and for DNA Barcoding. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Xu, C.; Li, C.; Sun, J.; Zuo, Y.; Shi, S.; Cheng, T.; Guo, J.; Zhou, S. ycf1, the most promising plastid DNA barcode of land plants. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczecińska, M.; Sawicki, J. Genomic Resources of Three Pulsatilla Species Reveal Evolutionary Hotspots, Species-Specific Sites and Variable Plastid Structure in the Family Ranunculaceae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22258–22279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Peng, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z. Determination of the evolutionary pressure on Camellia oleiferaon Hainan Island using the complete chloroplast genome sequence. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, A.J.C.; Crandall-Stotler, B.J.; Hart, M.L.; Long, D.G.; Forrest, L.L. Divergence times and the evolution of morphological complexity in an early land plant lineage (Marchantiopsida) with a slow molecular rate. New Phytol. 2015, 209, 1734–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bączkiewicz, A.; Sawicki, J.; Buczkowska, K.; Polok, K.; Zieliński, R. Application of Different DNA Markers in Studies on Cryptic Species of Aneura Pinguis (Jungermanniopsida, Metzgeriales). Cryptogam. Bryol. 2008, 29, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bączkiewicz, A.; Szczecinska, M.; Sawicki, J.; Stebel, A.; Buczkowska, K. DNA barcoding, ecology and geography of the cryptic species of Aneura pinguis and their relationships with Aneura maxima and Aneura mirabilis (Metzgeriales, Marchantiophyta). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakalin, V.; Vilnet, A.; Klimova, K.; Nguyen, V.S. Calypogeia vietnamica sp. nov. (Calypogeiaceae, Hepaticae) from North Vietnam and Diversification in Calypogeia Taxa with Blue Oil Bodies. Herzogia 2019, 32, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldberg, K.; Groth, H.; Wilson, R.; Heinrichs, J. Cryptic speciation in Herbertus (Herbertaceae, Jungermanniopsida): Range and morphology of Herbertus sendtneri inferred from nrITS sequences. Plant Syst. Evol. 2004, 249, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalin, V.A.; Fedosov, V.E.; Fedorova, A.V.; Nguyen, V.S. Integrative Taxonomic Revision of Marsupella (Gymnomitriaceae, Hepaticae) Reveals Neglected Diversity in Pacific Asia. Cryptogam. Bryol. 2019, 40, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedorow, P.; Odrzykoski, I.; Szweykowski, J.; Szweykowska-Kulińska, Z. Phylogeny of the European species of the genus Pellia (Hepaticae; Metzgeriales) based on the molecular data from nuclear tRNA Leu CAA intergenic sequences. Gene 2001, 262, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diatta, J.; Bączkiewicz, A.; Drapikowska, M.; Rodkiewicz, P.; Sawicki, J.; Szczecinńska, M.; Buczkowska, K. Geochemical Al-kalinity and Acidity as Preferential Site-Specific for Three Liverwort Lineages of Aneura Pinguis Cryptic Species A. Sci. Rep. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Knoop, V. When you can’t trust the DNA: RNA editing changes transcript sequences. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 68, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knie, N.; Grewe, F.; Fischer, S.; Knoop, V. Reverse U-to-C editing exceeds C-to-U RNA editing in some ferns—A monilophyte-wide comparison of chloroplast and mitochondrial RNA editing suggests independent evolution of the two processes in both organelles. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Mu, W.; Wei, T.; Li, N.; Wan, T.; Liu, H.; Cui, J.; et al. The Amount of RNA Editing Sites in Liverwort Organellar Genes Is Correlated with GC Content and Nuclear PPR Protein Diversity. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 3233–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).