Abstract
Sipuncula, long considered a separate phylum, are now commonly included in the Annelida based on phylogenomic analyses. The sipunculan body consists of an unsegmented trunk and a retractable introvert, usually with a set of tentacles at its anterior end. Unlike other annelids, they have no chaetae, but the introvert is often adorned with proteinaceous hooks that can be important taxonomic characters. Other external taxonomic characters include the tentacles (number, shape and arrangement), body papillae and, in some cases, hardened shields, as well as length ratios. Many species require dissection for correct identification to reveal internal characteristics, such as introvert retractor muscles, nephridia and contractile vessels. Here we summarize the state of the current knowledge of species diversity in sipunculans. We emphasize molecular studies, conducted over the past two decades, that have revealed multiple complexes of cryptic or pseudocryptic species. It has become obvious that diversity is significantly higher than the current taxonomic scheme accounts for, but formal species descriptions are lagging behind. Although the major branches in the sipunculan phylogeny have become increasingly consolidated, the internal relationships within most branches are still in flux.
1. Introduction
With their distinctive morphology, sipunculans have long been regarded as a phylum of their own (phylum Sipuncula Rafinesque, 1814). Sipuncula are commonly known by their vernacular names “peanut worms” or “star worms”. Lacking typical annelid segmentation, they are more easily confused with sea cucumbers or anemones (especially sand anemones of the genus Edwardsia) than with more closely related annelids.
The recent placement of sipunculans within the annelid radiation is based on phylogenetic and phylogenomic analyses conducted since the early 2000s [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], although this view is still not universally accepted [8]. Their fossil record is sparse, but shows that their morphology has changed little since the Cambrian [9]. As adults, sipunculans show no trace of external or internal segmentation, but there has been disagreement on whether the nervous and muscular systems of the larvae are segmented [8,10,11]. The most recent analysis based on confocal laser scanning microscopy and whole mount in situ hybridization on Themiste lageniformis concluded that their ventral nerve cord is an unsegmented medullary cord and therefore rejects the hypothesis of larval segmentation [8].
Saiz Salinas [12] summarized the history of sipunculan research since the 1500s. Sipunculans have been associated with various animal groupings in the ever-changing animal classification schemes over the centuries. One notion that survived well into the middle of the 20th century was the Gephyrea (Greek, meaning “bridge”) concept, originally proposed by de Quatrefages [13]. Apart from sipunculans, Gephyrea included taxa as diverse as holothurians, echiurans and priapulids. What all these taxa have in common is an elongated, unsegmented body with some type of appendages for food collection at the anterior end. This morphology was regarded as an intermediate form between segmented worms and echinoderms (although we recognize today that holothurians are echinoderms). Hyman [14] finally officially rejected the Gephyrea concept and, to our knowledge, the term has not been used since then, except in historical accounts.
The inclusion of Sipuncula in the Annelida may not be so surprising considering that other taxa without obvious segmentation (e.g., Siboglinidae, previously known as Pogonophora; Echiura and Myzostomida) have similarly been absorbed into the phylum Annelida. What is most baffling, however, is their inferred sister group relationship with amphinomids [6,7], or fireworms, as the two taxa starkly differ morphologically. In contrast to sipunculans, amphinomids are distinctly segmented and carry conspicuous calcareous chaetae on each segment.
The classification within the Sipuncula has also seen significant revisions over the past ~140 years. Selenka et al. in 1883 [15] proposed 10 genera, Fisher in 1952 [16] recognized 13 and Stephen in 1965 [17] 16. The two most recent monographs, Stephen & Edmonds in 1972 [18] and Cutler in 1994 [19], both recognize 17 genera, although there are some discrepancies with regard to which genera are considered valid and their definitions. The two monographs starkly differ in the number of recognized species: While Stephen and Edmonds [18] listed 320 species, Cutler [19] reduced the number to ~150 by assembling long lists of synonyms for many species. This practice of “taxonomic lumping” was based on the observations that many species have long-lived planktotrophic larval stages [20], theoretically enabling dispersal across ocean basins, leading to large geographic distribution ranges.
Since 1994, 12 additional species and one new subspecies have been described, and one previously synonymized species has been reinstated [21]. Based on morphological characters, Kawauchi and Rice [22] described two new species of Nephasoma from the western Atlantic. Hylleberg described a total of nine new species from Thailand (in the genera Sipunculus, Xenosiphon, Siphonosoma and Aspidosiphon) and Saiz Salinas described a new subspecies of Phascolion from Indian waters [23]. Relying primarily on molecular data, Silva-Morales et al. [24] described a new species of Antillesoma from the eastern Pacific.
Molecular phylogenetics has reshaped ideas about sipunculan relationships [25,26,27,28,29,30]. Although these studies, based on different sets of genes, do not necessarily agree in every aspect of the phylogeny, all strongly support the monophyly of the Sipuncula. Based on a phylogenetic tree derived from the analysis of five gene regions, Kawauchi et al. [29] established a new classification of sipunculans that recognizes 16 genera organized into six families, but no higher taxonomic ranks. Kawauchi et al.’s [29] major groupings were also confirmed in a later phylogenomic analysis of RNA Sequence data [30] (Figure 1).
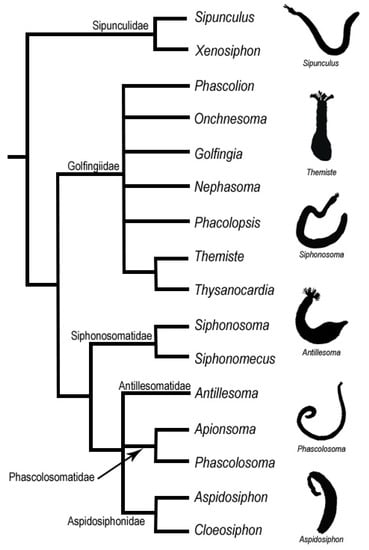
Figure 1.
Phylogeny of the Sipuncula (modified from [29]). Right, exemplar shadows representing one genus from each family.
2. External Morphology
The simple body plan of sipunculans consists of a trunk region and a thinner introvert region that can be completely retracted into the trunk (Figure 2 and Figure 3A). A number of tentacles are generally located at the anterior end of the introvert, either arranged in a circle around the mouth or in a horseshoe shape around the chemosensory nuchal organ on the dorsal margin of the oral disk. The introvert is often adorned with proteinaceous hooks. The remainder of the body wall may be smooth or covered with papillae of various shapes and sizes. Some species, particularly in the genera Aspidosiphon (Figure 2H) and Cloeosiphon, have hardened proteinaceous shields at the anterior and sometimes at the posterior end. There are no appendages, and the only more or less visible landmarks on the trunk are the dorsal anus near the anterior end and the (usually) paired openings of the nephridia on the ventral side, at roughly the same level of the anus. Many species are transparent or white without body pigmentation, while others are brown or gray in color, sometimes with black markings. A few species, especially in the genera Antillesoma (Figure 2G) and Themiste (Figure 2D), have some purple or greenish pigment on their tentacles or at the tentacle base. Sipunculans range in length from a few mm to about 30 cm.
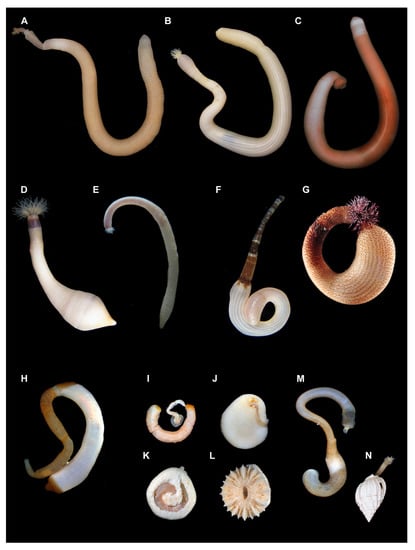
Figure 2.
Diversity of sipunculan body plans (A) Sipunculus phalloides; (B) Siphonosoma cumanense; (C) Xenosiphon branchiatus; (D) Themiste langeniformis; (E) Nephasoma pellucidum; (F) Phascolosoma perlucens; (G) Antillesoma antillarum; (H) Aspidosiphon fischeri; (I) Aspidosiphon muelleri, a commensal sipunculan living in symbiosis with a solitary coral; (J) A. mulleri introvert coming out from a whole in the base of the coral made by the worm; (K) space inside a solitary coral inhabited by A. mulleri; (L) solitary coral from the genus Heteropsammia; (M) Phascolion cryptum; (N) P. cryptum inside a gastropod shell.
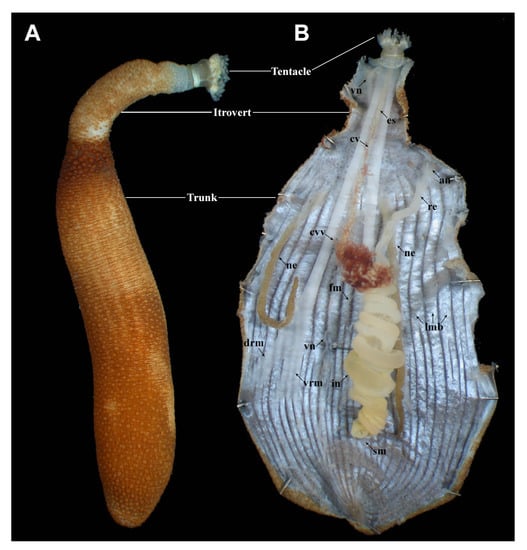
Figure 3.
Sipuncula external and internal anatomy. (A) Antillesoma antillarum: external view. (B) A. antillarum: internal view. Abbreviations: an = anus, cv = contractile vessel, cvv = contractile vessel villi, drm = dorsal retractor muscle, es = esophagus, fm = fixing muscle, in = intestine, lmb = longitudinal muscle band, ne = nephridia, re = rectum, sm = spindle muscle, vn = ventral nerve cord, vrm = ventral retractor muscle.
3. Anatomy
Anatomically, one of the most distinctive features, present in most species, is an intestine that forms a double-helix in the trunk, consisting of a descending branch that stretches from the mouth at the tip of the introvert towards the posterior end of the trunk, and an ascending branch that runs back anteriorly towards the anus (Figure 3B). Also very distinctive are the well-developed introvert retractor muscles that connect the tip of the introvert to the body wall in the trunk. Four introvert retractors, divided into a dorsal and a ventral pair, appear to be the ancestral condition [31], but in many species they have been reduced to two or one, although separate insertion points in the body may remain visible. The central nervous system consists of a dorsal cerebral ganglion at the anterior end of the esophagus, a pair of circumesophageal connectives, and a single ventral nerve cord without obvious ganglia. A large, primary coelom constitutes the main body cavity. A secondary coelom extends into the tentacles and is connected to a pair of compensatory sacs or contractile vessels. The latter extend along the esophagus and sometimes carry hairlike villi, known as contractile vessel villi. The gonads are inconspicuous and located at the insertion points of the retractor muscles in the body wall. Oocytes or spermatocytes are released into the body coelom where they mature. Shortly before spawning, they are taken up by the nephridia and are then released through the nephridiopores. The nephridial system consists of one, or more often two, elongate sacs that extend into the body coelom along the ventral side.
4. Ecology
Sipunculans are exclusively marine and benthic as adults. They inhabit all oceans, ranging from polar waters to the tropics and from the intertidal zone to the abyss. Their presence is usually not obvious on superficial inspection of a benthic habitat, as they tend to be well hidden. While some sipunculan species inhabit sand or mud, others are associated with hard substrates, such as the underside of rocks, spaces between bivalve shells, the holdfasts of submerged vegetation or submerged wood. Although two species, Phascolion psammophilum Rice, 1993, and Aspidosiphon exiguus Edmonds, 1874, have been described as meiofaunal, adults of these species are larger than the generally recognized size thresholds for meiofauna of 500 μm or 1 mm. Most sipunculans found in meiofaunal samples actually represent postlarvae or juveniles of larger species [32]. Some species contribute to the erosion of hard substrate, such as coral rubble, mollusc shells, calcareous rock or sandstone (Figure 4). Other species, particularly in the genus Phascolion, inhabit abandoned mollusc shells (Figure 2M), polychaete tubes or foraminiferan tests. One species, Phascolosoma turnerae Rice, 1985, was originally described from submerged wood but has also been reported from methane and hydrocarbon seeps [33,34,35]. Another species in the same genus, Phascolosoma saprophagicum Gibbs, 1987, has been described from a whale carcass in abyssal depths. Aspidosiphon species can also inhabit empty molluscs shells, but one in particular has an interesting relationship with a solitary coral. As a juvenile A. muelleri looks for an empty mollusc shell as a shelter. Later, a planula larva from a solitary coral from the genera Heteropsammia and Heterocyathus can settle outside the occupied shell. The coral can overgrow and absorb the shell’s material into its own tissue, leaving the sipunculan coiled inside the coral (Figure 2I–L). In this relationship the worm gains a portable shelter, and the coral benefits by being relocated if the local conditions deteriorate and by being kept upright [36]. Despite their cryptic nature, sipunculans can reach high densities. For example, Rice et al. [37] reported 8000 individuals/m2 of Phascolion cryptum (Figure 2N) in the Indian River Lagoon in Florida.
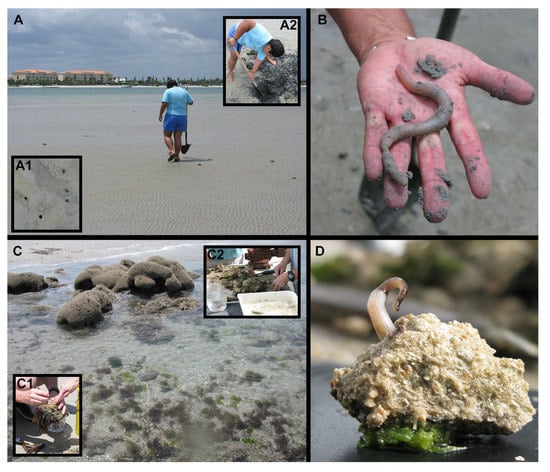

Figure 4.
Collecting Sipuncula. (A) Sand bar exposed by low tide, habitat for large sipunculans; (A1) Sipuncula holes; (A2) Digging deep into the sediment searching for sipunculans; (B) Siphonosoma cumanenses found in this habitat; (C) Beach with sabellariid mounds exposed by low tide; (C1) Pieces of polychaete colonies with sipunculans; (C2) breaking the pieces of polychaete colonies searching for sipunculans; (D) Phascolosoma perlucens found living among the polychate colony.
Sipunculan worms are either nonselective deposit feeders, surface grazers or suspension feeders [19,38,39,40,41]. As adults, they have a limited range of movement. While some species have been found burrowing up to about 1 m deep into sediment [42], not much is known about their horizontal movement, but it is most likely very limited. Many species are semi-sessile, although none physically attach to substrate.
5. Reproduction and Development
With a few exceptions [43,44,45], sipunculans are gonochoric. Reproduction is usually sexual via free-spawned gametes, although a few cases of parthenogenesis, budding and fission have been reported [45,46,47]. Embryonic and larval development has been exceptionally well-studied in some species, mostly through the work of Mary Rice on the northwest and southeast coasts of the U.S. and the Caribbean [48,49]. Sipunculan embryos undergo spiral cleavage [48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. Further development may include a trochophore larva and/or a unique larval form known as pelagosphera (Figure 5). While the trochophore larva is always lecithotrophic, the pelagosphera may be lecithotrophic or planktotrophic. Four developmental modes can be distinguished [56,57]: (I) direct development; (II) indirect development with a trochophore stage only; (III) indirect development with a trochophore and a lecithotrophic pelagosphera; and (IV) indirect development with a trochophore and a planktotrophic pelagospera. While there are still many sipunculan species for which development is unknown, it appears that the IV is the most common developmental mode.
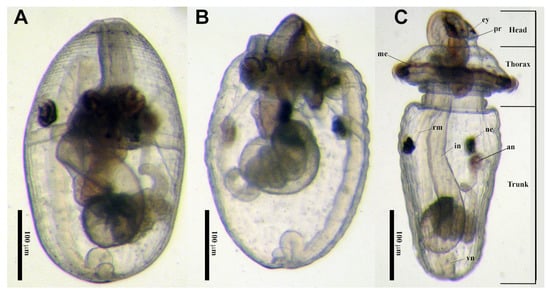
Figure 5.
Pelagosphera larvae from Sipunculus sp. (A) Pelagosphera larva with the head and thorax retracted inside the trunk; (B) Pelagosphera lateral view of a larva in the process of extending the head from the trunk; (C) Dorsal view of the pelagosphera larva showing regions of the body and external and internal structures viewed through the translucent the body wall. Abbreviations: an = anus, ey = eye, in = intestine, me = metatroch, ne = nephridia, pr = prototroch, rm = retractor muscle, vn = ventral nerve cord.
Planktotrophic pelagosphera larvae can spend several months in the plankton [20] and are considered the primary dispersal mechanism for sipunculans. The body of the pelagosphera is spherical to elongate (Figure 5), with a distinctive constriction between the trunk and the thorax and a prominent metatrochal ciliary ring on the thorax used for swimming (Figure 5C). The head and thorax, with the metatroch, can be retracted into the trunk, temporarily rendering the larva incapable of swimming (Figure 5A). There are many morphologically distinct types of pelagosphera larvae, varying in size, color, body texture and head morphology [58]. Using DNA barcoding of adults and larvae, Schulze et al. [59] matched 11 of these morphotypes to a sipunculan species, and three additional ones to genus level. When discussing overall sipunculan diversity, the developmental mode and larval stages need to be taken into consideration as well.
6. Species Complexes
Compared to more “typical” annelids, sipunculans have few morphological characters that can be used for the diagnosis of species or higher-level taxa. While the relationships among the higher taxa are becoming increasingly consolidated, many species are ill-defined morphologically and molecularly. Since the 1990s, it has become easier and more affordable to generate molecular data that can be used in addition to morphological data to delineate species boundaries. This has helped identify several complexes of “cryptic” or “pseudocryptic” species within Sipuncula. Cryptic species are here defined as species that are morphologically indistinguishable but form evolutionary distinct units based on their genetic divergence [60]; pseudocryptic species that can be identified by morphological characters after a detailed comparative study of morphological and non-morphological features [61]. While two studies on sipunculan cryptic diversity relied on genetic fingerprinting techniques [62,63], most others used DNA sequencing of one or several mitochondrial or nuclear gene markers. The most commonly used marker has been the common “DNA barcoding” sequence [64], a ~650 bp sequence of the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) gene. Another mitochondrial marker is 16S ribosomal RNA (16S). Some studies have additionally used nuclear markers such as 28S ribosomal RNA (28S) or Histone H3 (H3). If genetic distances among clades are calculated, they are most commonly reported as average Kimura 2 Parameter (K2P) distances.
6.1. Sipunculus nudus Complex
Sipunculus nudus Linnaeus, 1766, is the most popular species among this group being used as bait for recreational fishing [65] and as delicatessen food in some Asian countries [66]. Specimens from this genus can reach 50 cm in trunk length, but S. nudus varies from 5 to 15 cm long. This species was described from “Europeans waters” and has been considered cosmopolitan in tropical, subtropical and temperate waters in all oceans [19]. However, a multilocus phylogenetic analysis using nuclear (28S and H3) and mitochondrial (COI and 16S) markers has shown a higher level of genetic variation among distant populations of putative species S. nudus, and morphological analyses corroborates phylogenetic discovery [67]. Average genetic distances among clades were not reported, but based on the phylogenetic trees, it is clear that S. nudus is a case of pseudocryptic species.
6.2. Themiste pyroides/hexadactyla Complex
Themiste pyroides (Chamberlin, 1920) is an intertidal species originally described from Laguna Beach, California, and has been widely reported from the northeast Pacific (Alaska through Baja California) [48] as well as the northwest Pacific [40,68]. A morphologically similar species, Themiste hexadactyla, was described from northern Japan [69] and reported from Hokkaido [70] as well as from California [70], but Cutler and Cutler [71] declared T. hexadactyla a junior synonym to T. pyroides. However, COI and 16S sequence data indicate significant genetic differences (11.5% average K2P distance for COI) between populations from British Columbia, Canada, and the Peter the Great Bay in the Sea of Japan [72]. Additionally, major differences in developmental mode and developmental timing have been reported between the eastern and western Pacific lineages, summarized in [72]. Whereas the lineage from British Columbia develops directly (developmental mode I), the lineage from the Sea of Japan includes lecithotrophic trochophore and pelagosphera stages (developmental mode III) [73]. Based on these differences, Maiorova and Adrianov [74] and Nishikawa [75] proposed the resurrection of T. hexadactyla in the western Pacific.
6.3. Thysanocarida nigra/Golfingia pugettensis Complex
Thysanocarida nigra (Ikeda, 1904) has a relative long (up to 10 cm), smooth trunk and an introvert up to twice as long. The type locality is listed as “Japan” [18]. The morphologically similar Golfingia pugettensis was described by Fisher [16] from Puget Sound, and has been the subject of investigations on reproduction, embryology and larval development [48,76]. The two species were synonymized by Gibbs et al. [77], under Thysanocardia nigra as the valid name. Genetic studies based on 16S sequences indicate that the eastern and western Pacific populations represent separate genetic lineages (29.3% K2P for 16S); moreover, there was indication that two clades exist in the eastern Pacific [72]. Based on [48] and [73], differences between the eastern and western Pacific lineages are also apparent in reproduction, development and larval behavior, summarized in [72].
6.4. Phascolosoma agassizii Complex
Phascolosoma agassizii agassizii Keferstein, 1866, is a relatively large and common shallow-water species that is abundant on the west coast of North America as well as the Northwest Pacific. There are also records from the Indian Ocean [78], tropical South Pacific [29], Atlantic [79] and Mediterranean Sea [80]. A second subspecies, P. agassizii kurilense (Satô, 1937) was described from the Kuril Islands. Schulze et al. [72] first reported a genetic break between the populations in the eastern and western north Pacific, based on COI and 16S sequence data. This was later confirmed with a larger sample size and broader geographic sampling range [81]. The average genetic distance between the eastern and western Pacific populations was over 32% for COI. Not only were the two taxa very genetically distinct, they were not even sister taxa that were separated by several other Phascolosoma species in the phylogenetic tree. Although there were some differences in the pigmentation patterns and hook morphology between the two clades, both fit the description of P. agassizii agassizii as given in Cutler’s monograph [19]. The two specimens from the Kuril Islands included in the Johnson et al. study [81] showed no genetic divergence from other members of the western Pacific clade. Morphologically, P. agassizii kurilense differs from P. agassizii agassizii only by the presence of a small secondary lobe in the nephridia. The type locality for P. agassizii agassizii is Mendocino, California; it is therefore likely that the western Pacific represents a different, as yet undescribed species. DNA sequence data [81] and studies based on intersimple sequence repeat polymerase chain reaction (ISSR-PCR, a genetic fingerprinting technique) [63] indicated that there is slight genetic structure among the populations in the eastern Pacific and more substantial structure among the populations in the western Pacific, although there is no genetic break between the Kuril Island samples and those from the Sea of Japan. The larval development of both species has been studied extensively [48,73,82,83]. Both have planktotrophic pelagosphera larvae, which may possibly enable dispersal across the Pacific basin. Although some differences in developmental timing were observed between the larvae on both coasts [82], it is unclear whether these are examples of phenotypic plasticity or have a genetic basis.
6.5. Phascolosoma nigrescens/varians Complex
Keferstein [84] described Phascolosoma nigrescens from Fiji and P. varians from the St. Thomas in the Caribbean. The two species were synonymized with P. nigrescens as the senior synonym [19]. In addition to P. varians, Cutler [19] lists 12 other junior synonyms for P. nigrescens. However, Silva-Morales [21] recently provided morphological and molecular evidence to support the reinstatement of P. varians. The three Caribbean specimens included in their study diverged from the specimen from New Caledonia (the closest available sequence to Fiji, the type locality for P. nigrescens) by an average K2P distance of 24% for COI. They proposed that P. nigrescens (from the Indo-Pacific) and P. varians (from the Caribbean) can be distinguished by their hook morphology (rounded secondary tooth in P. varians; square in P. nigrescens), attachment of the nephridia to the body wall (partially in P. varians; fully in P. nigrescens) and the shape of the contractile vessel (simple in P. varians; with lateral sacs in P. nigrescens). Furthermore, Silva-Morales’ molecular analyses suggest that P. nigrescens might consist of at least five additional species, from Spain, Australia, New Caledonia, Israel and South Africa, respectively [21].
6.6. Phascolosoma perlucens Complex
Phascolosoma perlucens Baird, 1868, is the third of the tree circumtropical and cosmopolitan species in the genus Phascolosoma. They are found in abundance in shallow waters inside coral rubble or in crevices of calcareous rocks [85] in the Caribbean, [86,87,88], western Pacific [15,89,90,91], eastern Pacific [16], several localities in Indian Ocean, [92,93,94], and few localities from eastern Atlantic, [95]. Described originally from Jamaica [87], the species is readily distinguished from other congeners by the presence of reddish, conical posteriorly directed, pre-anal papillae at the dorsal base of the introvert, and by the secondary round tooth at the concave side of the introvert hooks [96]. Cutler [19] reduced the confusion within P. perlucens but still lists 18 synonymies, resulting in putative P. perlucens species over-lumping. Following the tendency in testing the cosmopolitanism among invertebrates with few morphological characteristics, Kawauchi & Giribet [97] examined 56 putative individuals identified as P. perlucens from 13 localities throughout the tropics, using two mitochondrial genes (COI and 16S) in phylogenetic analyses. Although genetic distances among populations were not reported, the phylogenetic trees and haplotype networks show clear genetic separation of geographically distant populations of this species. More than that, the authors analyzed hook morphology, and identified at least four different lineages, corroborating part of the genetic analysis. However, to delimit species we need an effort in analyzing a larger sample of individuals, localities and more genes before a comprehensive taxonomic revision can be achieved.
6.7. Apionsoma misakianum Complex
Apionsoma (Apionsoma) misakianum (Ikeda, 1904) is a small species, with a trunk of 3-8 mm length and a thin introvert of up to 10 times the length of the trunk. The species has been widely reported in shallow water throughout the tropics and subtropics but is generally uncommon. The trunk morphology is relatively nondescript and the extreme length of the introvert makes it difficult to preserve specimens with their introverts fully extended. As a consequence, the distal rings of introvert hooks, which have distinctive characteristics, cannot easily be visualized. It is therefore possible that some records of this species are misidentifications. Using allozyme data, Staton and Rice [62] presented evidence of a genetic split between populations of this species between populations from the Florida Keys/Bahamas and a population from Sebastian Pinnacles, off the south-central Florida Atlantic coast. Moreover, although these populations could not be distinguished morphologically (in this case the introvert hooks were carefully examined), each group had distinctive pelagosphera larvae. Described in detail by Rice et al. [58,98], the larvae from the southern population have been dubbed “white blackhead” larvae, whereas those from the northern population are known as “spotted velvet” [58]. Not only can they be distinguished by their pigmentation patterns, but also in their slightly different developmental timing [56,58,98]. DNA sequencing of larvae and adults confirmed the original findings of genetic heterogeneity within A. misakianum [59] (average distance for all A. misakianum combined: 19% K2P). In addition to the population from Sebastian Pinnacles, the “spotted velvet” clade further included one adult specimen each from the Red Sea and New Caledonia, whereas the “white blackhead” clade included an additional specimen from Belize. White blackhead larvae have also been captured in surface waters of the central Atlantic (described as “type C” or Baccaria oliva) [99], indicating that they are long-lived and have high dispersal potential. The average within-clade genetic distance for COI was 16.2% for the “spotted velvet” clade, but only 0.7% for the “white blackhead” clade [59]. Based on these data and the wide geographic distribution of the “spotted velvet” clade, we suggest that this clade likely represents multiple species, although more extensive sampling would be necessary to resolve this clade. At the minimum, we can conclude that Apionsoma misakianum includes two species, but we cannot currently determine which, if either, is the nominal species. Cutler [19] synomized three species with A. misakianum: Phascolosoma hespera Chamberlain, 1920, Golfingia (Phascolana) longirostris Wesenberg-Lund, 1959, and Golfingia (Phascolana) tenuissima Wesenberg-Lund, 1959. Careful examination of type material and/or sequencing of topotypes would be necessary to evaluate whether any of these should be resurrected. The type locality for the species is in Japan [100]; it would therefore be of particular interest to study material from the western Pacific.
6.8. Antillesoma antillarum Complex
Antillesoma antillarum (Grube & Öersted, 1858) is another common and relatively large species reported from warm shallow-water habitats worldwide. Silva-Morales et al. [24] recently described a new species of Antillesoma, A. mexicanum, from the Mexican Pacific coast. This species differs morphologically from A. antillarum by having darker pigmentation, sparser distribution of body papillae and shorter trunk length. Moreover, the average genetic distance is 21% for COI between the Mexican Pacific and Caribbean-Florida clade. Silva-Morales et al. [24] also included a COI sequence from a specimen identified as A. antillarum from Thailand in their analysis that constituted its own distinct genetic lineage, but the specimen was not examined morphologically. Given the genetic divergence, we surmise that the Thailand sample constitutes a third species of Antillesoma. Addititional morphological and molecular studies covering a broader geographic scope might reveal that more species are present worldwide.
6.9. Aspidosiphon Species Complexes
No focused studies have yet been conducted on cryptic/pseudocryptic species complexes in the genus Aspidosiphon. However, based on phylogenetic analyses that included multiple representatives of some common species from different geographic locations [28,29], it is likely that several species complexes exist. For example, several specimens each of Aspidosiphon (Paraspidosiphon) laevis de Quatrefages, 1865, Aspidosiphon (Paraspidosiphon) parvulus Gerould, 1913, and Aspidosiphon (Aspidosiphon) elegans (Chamisso and Eysenhardt, 1821) from different locations were included in multigene phylogenetic reconstructions of the phylum and the resulting trees did not support the monophyly of these species.
7. Geographic Coverage
In general, sipunculan diversity data strongly reflect the amount of taxonomic effort for geographic areas. Due to easier accessibility, shallow-water species are better known than deep sea species. For example, of the ~70 lots of sipunculans collected from deep water along the eastern Australian margin by Gunton et al. [101], only 10 could reliably be identified to the species level and represented only two species. Murina [102] stressed the lack of knowledge of sipunculans all over the word, and pointed out that Indian, Pacific, Southwest Atlantic Oceans and China coast are the most unexplored regions. More than four decades later, only a few efforts in specific parts of the world have been made to fill this gap. The absence of specialists trained to identify Sipuncula contributes to this problem.
Sipunculans in Southwest Atlantic are still poorly known. In Brazil, the collection of this organism along the coast was mainly made by oceanographic expeditions at the continental shelf [103,104,105,106]. Besides that, the benthos from the intertidal zone and beyond the continental shelf of the Brazilian coast are still poorly or completely unexplored [107]. Lana, et al. [108] acknowledge that there is more information about the Brazilian southeastern and south marine fauna, and this is true for sipunculans also, because this situation is a consequence of the high level of the oceanographic expedition in this area and the consolidated researcher groups since the 1950s.
8. Conclusions
The global diversity of the Sipuncula is still poorly understood, but multiple studies using genetic techniques in combination with morphological and/or reproductive and developmental features have revealed that more diversity is present than the current taxonomic scheme [19] accounts for. Many of the lineages that were detected with molecular tools likely represent new species or species that were previously synonymized and should be reinstated. As in many other invertebrate taxa, formal taxonomic descriptions are lagging behind the molecular work. This gap is likely going to widen in the future due to the small number of sipunculan taxonomists worldwide, as well as lack of funding and recognition for taxonomic work. Although the major clades in the Sipuncula are well supported, the internal relationships within them need to be better resolved, especially in the Golfingiidae and the clade including Phascolosomatidae, Antillesomatidae, and Aspidosiphonidae.
Author Contributions
The authors contributed the following components to the manuscript: Conceptualization, A.S. and G.Y.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S. and G.Y.K.; visualization, G.Y.K. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We thank the guest editors of this special edition, Maria Capa and Pat Hutchings, for inviting us to contribute this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Boore, J.L.; Staton, J.L. The mitochondrial genome of the sipunculid Phascolopsis gouldii supports its association with Annelida rather than Mollusca. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, M.J.; Wise, M.J.; Gowri-Shankar, V. Consideration of RNA secondary structure siginificantly improves likelihood-based estimates of phylogeny: Examples from the Bilateria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.W.; Hejnol, A.; Matus, D.Q.; Pang, K.; Browne, W.E.; Smith, S.A.; Seaver, E.; Rouse, G.W.; Obst, M.; Edgecombe, G.D.; et al. Broad phylogenomic sampling improves resolution of the animal tree of life. Nature 2008, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwinyi, A.; Meyer, A.; Bleidorn, C.; Lieb, B.; Bartolomaeus, T.; Podsiadlowski, L. Mitochondrial genome sequence and gene order of Sipunculus nudus give additional support for an inclusion of Sipuncula into Annelida. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, T.H.; Paul, C.; Hill, N.; Hartmann, S.; Hosel, C.; Kube, M.; Lieb, B.; Meyer, A.; Tiedemann, R.; Purschke, G.; et al. Phylogenomic analyses unravel annelid evolution. Nature 2011, 471, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigert, A.; Golombek, A.; Gerth, M.; Schwarz, F.; Struck, T.H.; Bleidorn, C. Evolution of mitochondrial gene order in Annelida. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 94, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigert, A.; Helm, C.; Meyer, M.; Nickel, B.; Arendt, D.; Hausdorf, B.; Santos, S.R.; Halanych, K.M.; Purschke, G.; Bleidorn, C.; et al. Illuminating the base of the annelid tree using transcriptomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Baltodano, A.M.; Boyle, M.J.; Rice, M.E.; Meyer, N.P. Developmental architecture of the nervous system in Themiste lageniformis (Sipuncula): New evidence from confocal laser scanning microscopy and gene expression. J. Morphol. 2019, 280, 1628–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Vannier, J.; Saiz Salinas, J.I. Early Cambrian sipunculan worms from southwest China. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2004, 271, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristof, A.; Wollesen, T.; Wanninger, A. Segmental mode of neural patterning in Sipuncula. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristof, A.; Wollesen, T.; Maiorova, A.S.; Wanninger, A. Cellular and muscular growth patterns during sipunculan development. J. Exp. Zool. Part. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2011, 316B, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiz Salinas, J.I. Almost five centuries of systematic study of the enigmatic sipunculan worms. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Biology of the Sipuncula; Boyle, M.J., Kawauchi, G.Y., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 219–235. [Google Scholar]
- De Quatrefages, A. Etudes sur les types inférieurs de l’embranchement des annelés. Mémoire sur l’echiure de Gaertner (Echiurus Gaertnerii NOB). Ann. Sci. Nat. Zool. (Paris) 1847, 7, 307–343. [Google Scholar]
- Hyman, L.H. Phylum Sipunculida. In Smaller Coelomate Groups; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959; Volume 5, pp. 610–690. [Google Scholar]
- Selenka, E.; de Man, J.G.; Bülow, C. Die Sipunculiden, eine systematische Monographie. Semper Reis. Archipel Phillippinen 2 1883, 4, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, W.K. The sipunculid worms of California and Baja California. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1952, 102, 371–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.C. Echiura and Sipuncula from the Isreal South Red Sea Expedition. Sea Fish. Res. Stn. Haifa Bull. 1965, 40, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, A.C.; Edmonds, S.J. The Phyla Sipuncula and Echiura; Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, E.B. The Sipuncula. Their Systematics, Biology and Evolution; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1994; p. 453. [Google Scholar]
- Scheltema, R.S.; Hall, J.R. The dispersal of pelagosphera larvae by ocean currents and the geographical distribution of sipunculans. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Biology of the Sipuncula and Echiura; Rice, M.E., Todorovic, M., Eds.; Nauçno Delo: Belgrade, Serbia, 1975; pp. 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Morales, I. Reinstatement of Phascolosoma (Phascolosoma) varians Keferstein, 1865 (Sipuncula: Phascolosomatidae) based on morphological and molecular data. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, G.Y.; Rice, M.E. Two New Species of Nephasoma (Sipuncula: Golfingiidae) from the Western Atlantic Ocean. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2009, 122, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz Salinas, J.I.; Bustamante, M.; Tajadura, J.; Vijapure, T.; Sukumaran, S. A new subspecies of Phascolion Théel, 1875 (Sipuncula: Golfingiidae) from Indian waters. Zootaxa 2015, 3931, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silva-Morales, I.; López-Aquino, M.J.; Islas-Villanueva, V.; Ruiz-Escobar, F.J.; Bastida-Zavala, R. Morphological and molecular differences between the Amphiamerican populations of Antillesoma (Sipuncula: Antillesomatidae), with the description of a new species. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2019, 67, S101–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staton, J.L. Phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene from 13 sipunculan genera: Intra-and interphylum relationships. Invertebr. Biol. 2003, 122, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxmen, A.B.; King, B.F.; Cutler, E.B.; Giribet, G. Evolutionary relationships within the protostome phylum Sipuncula; a molecular analysis of ribosomal genes and histone H3 sequence data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 27, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Cutler, E.B.; Giribet, G. Reconstructing the phylogeny of the Sipuncula. Hydrobiologia 2005, 535/536, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Cutler, E.B.; Giribet, G. Phylogeny of sipunculan worms: A combined analysis of four gene regions and morphology. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 42, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawauchi, G.Y.; Sharma, P.P.; Giribet, G. Sipunculan phylogeny based on six genes, with a new classification and the descriptions of two new families. Zool. Scr. 2012, 41, 186–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemer, S.; Kawauchi, G.Y.; Andrade, S.C.S.; González, V.L.; Boyle, M.J.; Giribet, G. Re-evaluating the phylogeny of Sipuncula through transcriptomics. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2015, 83, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Rice, M.E. Musculature in sipunculan worms: Ontogeny and ancestral states. Evol. Dev. 2009, 11, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Kawauchi, G.Y.; Migotto, A. 13 Sipuncula. In Guide to the Identification of Marine Meiofauna; Schmidt-Rhaesa, A., Ed.; Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil: Munich, Germany, 2020; pp. 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cordes, E.E.; Carney, S.L.; Hourdez, S.; Carney, R.S.; Brooks, J.M.; Fisher, C.R. Cold seeps of the deep Gulf of Mexico: Community structure and biogeographic comparisons to Atlantic equatorial belt seep communities. Deep Sea Res. Part. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2007, 54, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAvoy, S.E.; Fisher, C.R.; Carney, R.S.; Macko, S.A. Nutritional associations among fauna at hydrocarbon seep communities in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 292, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, E.E.; Hourdez, S.; Predmore, B.L.; Redding, M.L.; Fisher, C.R. Succession of hydrocarbon seep communities associated with the long-lived foundation species Lamellibrachia luymesi. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 305, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonge, C.M. A note on mutualism between sipunculans and scleractinian corals. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Biology of Sipuncula and Echiura; Rice, M.E., Todorovic, M., Eds.; Nauçno Delo: Belgrade, Serbia, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M.E.; Piraino, J.; Reichardt, H.F. Observations on the ecology and reproduction of the sipunculan Phascolion cryptus in the Indian River Lagoon. Fla. Sci. 1983, 46, 382–396. [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds, S.J. Some notes on the abundance, environment, and nutrition of Sipunculus nudus L. (Sipunculoidea) at Morgat, Brittany. Cah. Biol. Mar. III 1962, 3, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Pilger, J.F. Ultrastructure of the tentacles of Themiste lageniformis (Sipuncula). Zoomorphology 1982, 100, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianov, A.V.; Malakhov, V.V.; Maiorova, A.S. Development of the tentacular apparatus in sipunculans (Sipuncula): I. Thysanocardia nigra (Ikeda, 1904) and Themiste pyroides (Chamberlin, 1920). J. Morphol. 2006, 267, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumars, P.A.; Dorgan, K.M.; Lindsay, S.M. Diet of worms emended: An update of polychaete feeding guilds. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorova, A.S.; Adrianov, A.V. Distribution of peanut worms (Sipuncula) in the West Pacific. In Proceedings of the China-Russia Bilateral Symposium on “Comparison on Marine Biodiversity in the Northwest Pacific Ocean”, Qingdao, China, 10–11 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, G. Über Petalostoma minutum Keferstein und verwandte Arten. Jahrb. Abtheilung Anat. 1909, 29, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, P.E. Gametogenesis and spawning in a hermaphroditic population of Golfingia minuta (Sipuncula). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1975, 55, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilger, J.F. Reproductive biology and development of Themiste lageniformis, a parthenogenic sipunculan. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1987, 41, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M.E. Asexual reproduction in a sipunculan worm. Science 1970, 167, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajulu, G.S.; Krishnan, N. Occurrence of asexual reproduction by budding in Sipunculida. Nature 1969, 223, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.E. A comparative study of the development of Phascolosoma agassizii, Golfingia pugettensis, and Themiste pyroides with a discussion of developmental patterns in the Sipuncula. Ophelia 1967, 4, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.E. Observations on the development of six species of Caribbean Sipuncula with a review of development in the phylum. In Proceedings of the International Symposium of Sipuncula and Echiura; Rice, M.E., Todorovic, M., Eds.; Naucno Delo Press: Belgrade, Serbia, 1975; pp. 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- Selenka, E. Eifurchung und Larvenbildung von Phascolosoma elongatum. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1875, 25, 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Gerould, J.H. The development of Phascolosoma. Zool. Jahrb. Abtheilung Anat. 1906, 23, 77–162. [Google Scholar]
- Åkesson, B. A study of the nervous system of the sipunculoideae, with some remarks on the development of the two species Phascolion strombi Montagu and Golfingia minuta Keferstein. Unders. Över Öresund 1958, 38, 1–249. [Google Scholar]
- Åkesson, B. The development of Golfingia elongata Keferstein (Sipunculidea) with some remarks on the development of neurosecretory cells in sipunculids. Ark. Zool. 1961, 13, 511–531. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, A.; Boyle, M.J.; Kawauchi, G.Y. Chapter 6.1: Sipuncula. In Annelida; Volume 1: Annelida Basal Groups and Pleistoannelida; Sedentaria, I., Purschke, G., Böggemann, M., Westheide, W., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 177–201. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, M.J.; Seaver, E.C. Expression of FoxA and GATA transcription factors correlates with regionalized gut development in two lophotrochozoan marine worms: Chaetopterus (Annelida) and Themiste lageniformis (Sipuncula). EvoDevo 2010, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, M.E. Larvae adrift: Patterns and problems in life histories of sipunculans. Am. Zool. 1981, 21, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boyle, M.J.; Rice, M.E. Comparative development and the evolution of life history diversity in Sipuncula. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Biology of the Sipuncula; Boyle, M.J., Kawauchi, G.Y., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M.E.; Piraino, J.; Reichardt, H.F.; Boyle, M.J. Observations on oceanic pelagosphera larvae (Sipuncula): Morphology, behavior, and metamorphosis. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Biology of the Sipuncula; Boyle, M.J., Kawauchi, G.Y., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 41–81. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, A.; Hipes, J.; Borda, E.; Rice, M.E. Who’s who in the Sipuncula: Matching larvae and adults using DNA. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Biology of the Sipuncula; Boyle, M.J., Kawauchi, G.Y., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton, N. Sibling species in the sea. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1993, 24, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, A.G.; Lozano, E. Body doubles. Nature 2005, 433, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staton, J.; Rice, M.E. Genetic Differentiation despite teleplanic larval dispersal: Allozyme variation in sipunculans of the Apionsoma misakianum species complex. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1999, 65, 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, N.D.; Schulze, A. Genetic structure in two Phascolosoma species in the Pacific Ocean. Mar. Biol. Res. 2016, 12, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; DeWaard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.F.E.; Gil, J.; Passos, A.M.; Pereira, P.; Melo, P.; Batista, F.; Fonseca, L.C.D. The market features of imported nonindigenous polychaetes in Portugal and consequent ecological concerns. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, A.J. Predation on Sipuncula. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Biology of Sipuncula and Echiura; Rice, M.E., Todorovic, M., Eds.; Nauçno Delo: Belgrade, Serbia, 1975; pp. 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi, G.Y.; Giribet, G. Sipunculus nudus Linnaeus, 1766 (Sipuncula): Cosmopolitan or a group of pseudo-cryptic species? An integrated molecular and morphological approach. Mar. Ecol. 2014, 35, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianov, A.V.; Maiorova, A.S.; Malakhov, V.V. Embryonic and larval development of the peanut worm Themiste pyroides (Sipuncula: Sipunculoidea) from the Sea of Japan. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 52, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H. Report on the biological survey of Mutsu Bay. 15. Sipunculoidea. Sci. Rep. Ser. 4 Biol. 1930, 5, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, E.B.; Cutler, N.J. A reconsideration of Sipuncula named by I. Ikeda and H. Sato. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1981, 26, 51–93. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, E.B.; Cutler, N.J. A revision of the genus Themiste (Sipuncula). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1988, 101, 741–766. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, A.; Maiorova, A.; Timm, L.E.; Rice, M.E. Sipunculan larvae and “cosmopolitan” species. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2012, 52, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianov, A.; Maiorova, A. Reproduction and development of common species of peanut worms (Sipuncula) from the Sea of Japan. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2010, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorova, A.S.; Adrianov, A.V. Peanut worms of the phylum Sipuncula from the Sea of Japan with a key to species. Deep Sea Res. Part. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2013, 86–87, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T. Some comments on the taxonomy of the peanut worms (Annelida: Sipuncula) in Japanese waters toward a future revision. In Species Diversity of Animals in Japan; Motokawa, M., Kajihara, H., Eds.; Springer Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.E. Gametogenesis in three species of Sipuncula: Phascolosoma agassizii, Golfingia pugettensis, and Themiste pyroides. La Cell. 1974, 70, 295–313. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, P.E.; Cutler, E.B.; Cutler, N.J. A review of the genus Thysanocardia Fisher (Sipuncula). Zool. Scr. 1983, 12, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Haldar, B.P. Sipunculans of the Indian coast. Mem. Zool. Surv. India 1991, 17, 1–169. [Google Scholar]
- Murina, V.V. New records of Echiura and Sipuncula in the North Atlantic Ocean, with the description of a new species of Jacobia. Mar. Biol. Res. 2008, 4, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açik, Ş. Checklist of Sipuncula from the coasts of Turkey. Turk. J. Zool. 2014, 38, 723–733. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, N.D.; Sanders, C.; Maiorova, A.; Schulze, A. Cryptic species in Pacific sipunculans (Sipuncula: Phascolosomatidae): East-west divergence between non-sister taxa. Zool. Scr. 2016, 45, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianov, A.V.; Maiorova, A.S.; Malakhov, V.V. Embryonic and larval development of the peanut worm Phascolosoma agassizii (Keferstein 1867) from the Sea of Japan (Sipuncula: Phascolosomatidea). Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2011, 55, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.E. Morphology, behavior and histogenesis of the pelagosphera larva of Phascolosoma agassizii (Sipuncula). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1973, 132, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Keferstein, W. Beitrage zur anatomischen und systematischen Kenntniss der Sipunculiden. Z. Fur Wiss. Zool. 1865, 15, 404–445. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M.E. Survey of the Sipuncula of the coral and beach rock communities of the Caribbean Sea. In Proceedings of the International Symposium of Sipuncula and Echiura; Rice, M.E., Todorovic, M., Eds.; Naucno Delo Press: Belgrade, Serbia, 1975; pp. 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- tenBroeke, A. Westindische Sipunculiden und Echuiriden. Bijdr. Tot De Dierkd. 1925, 24, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, W.B. Monograph on the species of worms belonging to the subclass Gephyreae. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1868, 1868, 77–114. [Google Scholar]
- Murina, V.V. On the sipunculid fauna of the littoral of Cuba. Zool. Zhurnal 1967, 46, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Shipley, A.E. Report on the Gephyrean worms collected by Mr. J. Stanley Gardiner at Rotuma and Funafuti. J. Zool. 1898, 66, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, S.J. A revision of the systematics of Australian sipunculans (Sipuncula). Rec. South. Aust. Mus. 1980, 18, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, E.B.; Cutler, N.J.; Nishikawa, T. The Sipuncula of Japan: Their systematics and distribution. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1984, 29, 249–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W. Westindische Gephyreen. Zool. Anz. 1922, 55, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, E.B.; Kirsteuer, E. Additional notes on some Sipuncula from Madagascar. Results of the Australian Indo-West Pacific Expedition, 1959–1960. Part 12. Zool. Anz. 1968, 180, 352–356. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, E.B.; Cutler, N.J. Madagascar and Indian Ocean Sipuncula. Bull. Mus. Natl. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1979, 4, 941–990. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, A.C. Echiuroidea and Sipunculoidea from Senegal, West Africa. Bull. L’inst. Fr. D’afrique Noire 1960, 22A, 512–520. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, N.J.; Cutler, E.B. A revision of the subgenus Phascolosoma (Sipuncula, Phascolosoma). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1990, 3, 691–730. [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi, G.; Giribet, G. Are there true cosmopolitan sipunculan worms? A genetic variation study within Phascolosoma perlucens (Sipuncula, Phascolosomatidae). Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 1417–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.E. Factors influencing larval metamorphosis in Golfingia misakiana (Sipuncula). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1986, 39, 362–375. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.R.; Scheltema, R.S. Comparative morphology of open-ocean pelagosphera. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Biology of the Sipuncula and Echiura; Rice, M.E., Todorovic, M., Eds.; Nauçno Delo Press: Belgrade, Serbia, 1975; pp. 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, I. The Gephyrea of Japan. J. Coll. Sci. Imp. Univ. Tokyo 1904, 20, 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gunton, L.M.; Kupriyanova, E.; Alvestad, T.; Avery, L.; Blake, J.A.; Biriukova, O.; Böggemann, M.; Borisova, P.; Budaeva, N.; Burghardt, I.; et al. Annelids of the eastern Australian abyss collected by the 2017 RV Investigator voyage. ZooKeys, in press.
- Murina, V.V. The geographic distribution of marine worms of the phylum Sipuncula of the world ocean. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Biology of the Sipuncula and Echiura; Rice, M.E., Todorovic, M., Eds.; Nauçno Delo: Bêlgrade, Serbia, 1975; Volume 1, pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, E.B.; Cutler, N.J. Sipuncula from Southern Brazil. Bol. Inst. Oceanogr. Sao Paulo 1980, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migotto, A.E.; Ditadi, A.S.F. Aspidosiphonidae (Sipuncula) from the northern and northeastern coast of Brazil. Rev. Bras. Biol. 1988, 48, 245–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi, G.Y.; Migotto, A. Filo Sipuncula. In Biodiversidade Bentônica da Região Sudeste-Sul do Brasil; Amaral, A.C.Z., Rossi-Wongtschowski, C.L.D.B., Eds.; USP Instituto Oceanográfico: São Paulo, Brasil, 2004; pp. 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pires Vanin, A.M.S.; Corbisier, T.N.; Arasaki, E.; Möellmann, A.M. Composição e distribuição espaço-temporal da fauna bêntica no Canal de São Sebastião. Realt. Técnico Inst. Oceanogr. 1997, 41, 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Migotto, A.E.; Tiago, C.G. Síntese. In Biodiversidade do Estado de São Paulo, Brasil: Síntese do Conhecimento ao Final do Século XX, Volume 3: Invertebrados Marinhos; Migotto, A.E., Tiago, C.G., Eds.; Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, FAPESP: São Paulo, Brasil, 1999; pp. 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Lana, P.C.; Camargo, M.G.; Brogin, R.A.; Isaac, V.J. O bentos da Costa Brasileira: Avaliação Crítica e Levantamento Bibliográfico (1858–1996); FEMAR: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 1996; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).