The Reef Coral Coscinaraea marshae Is Not a High-Latitude Endemic
Abstract
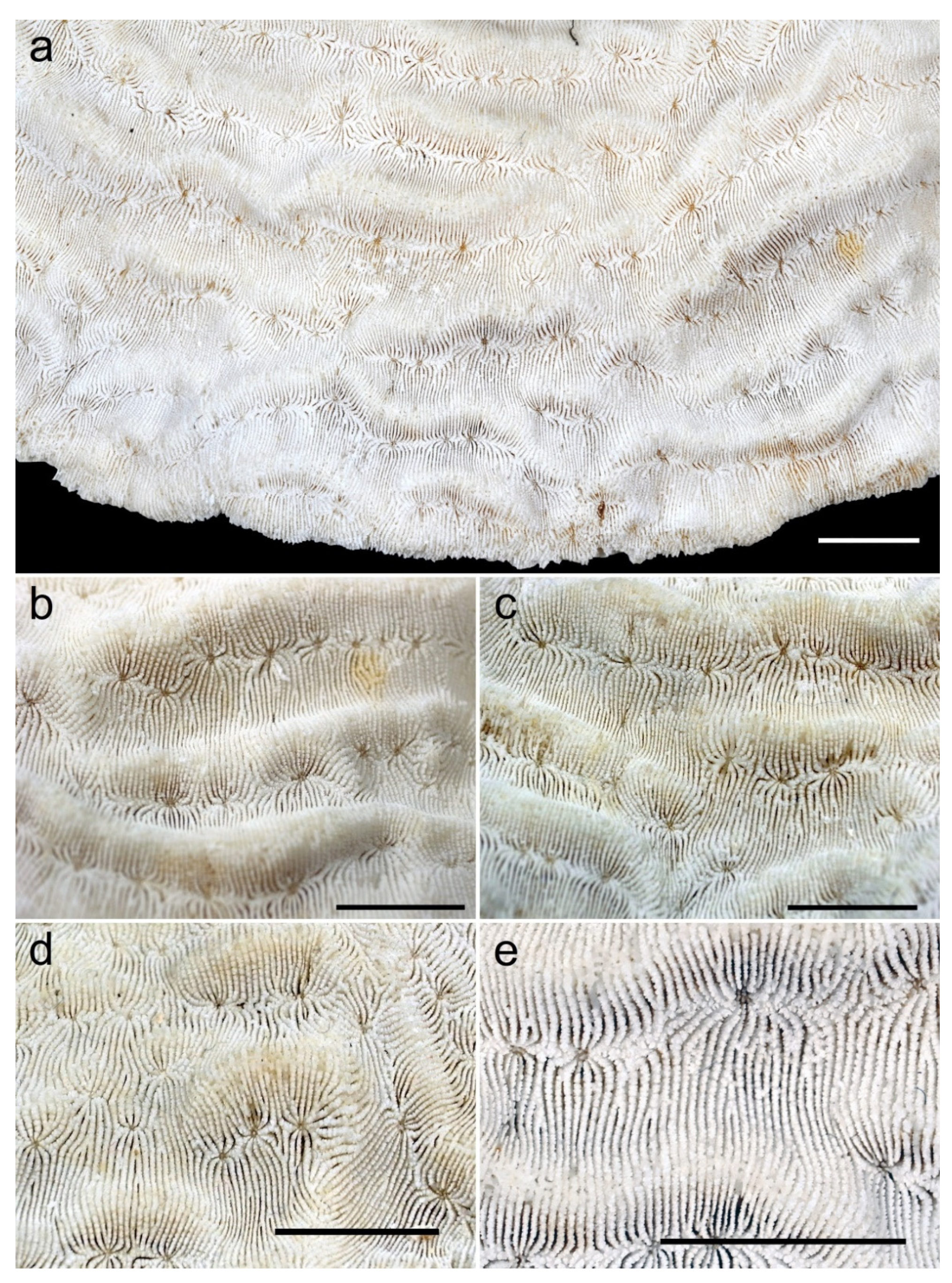
:1. Introduction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoogenboom, M.O.; Frank, G.E.; Blowes, S.A.; Chase, T.J.; Zawada, K.J.A.; Dornelas, M. Disparity between projected geographic ranges of rare species: A case study of Echinomorpha nishihirai (Scleractinia). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2015, 8, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswambharan, D.; Sreenath, K.; Jasmine, S.; Joshi, K.K.; Sheeraj, C.R.; Mohan, S.; Rohit, P. Occurrence of the supposedly endemic Australian azooxanthellate coral Astrangia woodsi Wells, 1955 in the eastern Arabian Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2021, 51, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, M.; Rouzé, H.; Barathieu, G.; Konieczny, O.; Adjeroud, M.; Thomassin, B. Extension of the known distribution of the scleractinian coral Leptoseris troglodyta to the southwestern Indian Ocean: New record from mesophotic submarine caves in Mayotte. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2020, 96, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenison-Woods, J.E. On the extratropical corals of Australia. Proc. Linn. Soc. N.S.W. 1878, 2, 292–341, pls. 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Veron, J.E.N. Corals in Space and Time. The Biogeography & Evolution of the Scleractinia; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1995; p. 321. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, S.D.; Parker, S.A. Review of the recent Scleractinia (stony corals) of South Australia, Victoria and Tasmania. Rec. S. Austr. Mus. Monogr. Ser. 1992, 3, 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rowlett, J. Indo-Pacific Corals; Joe Rowlett, Self-Published. 2020, p. 809.
- Wells, J.W. Two new scleractinian corals from Australia. Rec. Austr. Mus. 1962, 25, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veron, J.E.N. Corals of the World. Volume 2; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Townsville, Australia, 2000; p. 429. [Google Scholar]
- Veron, J.E.N.; Marsh, L.M. Hermatypic corals of Western Australia: Records and annotated species list. Rec. West. Austr. Mus. Suppl. 1988, 29, 1–136. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, Z.; Kirkendale, L.; Moore, G.; Hosie, A.; Huisman, J.; Bryce, M.; Marsh, L.; Bryce, C.; Hara, A.; Wilson, N.; et al. Marine biodiversity in temperate Western Australia: Multi-taxon surveys of Minden and Roe Reefs. Diversity 2016, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, D.P.; Bearham, D.; Graham, F.; Eagle, J.V. High latitude, deeper water coral bleaching at Rottnest Island, Western Australia. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bessell-Browne, P.; Stat, M.; Thomson, D. Coscinaraea marshae corals that have survived prolonged bleaching exhibit signs of increased heterotrophic feeding. Coral Reefs 2014, 33, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckett, C.A.; de Bettignies, T.; Fromont, J.; Wernberg, T. Expansion of corals on temperate reefs: Direct and indirect effects of marine heatwaves. Coral Reefs 2017, 36, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longhurst, A.R.; Pauly, D. Ecology of Tropical Oceans; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987; p. 407. [Google Scholar]
- Kunzmann, A. The coral reefs of West Sumatra. In The Ecology of the Indonesian Seas, Part II; Tomasick, T., Mah, A.J., Nontji, A., Moosa, M.K., Eds.; Periplus: Singapore, 1979; pp. 1249–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Kunzmann, A. On the way to management of West Sumatra’s coastal ecosystems. Naga ICLARM Quat. 2002, 25, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Abram, N.J.; Gagan, M.K.; McCulloch, M.T.; Chappell, J.; Hantoro, W.S. Coral reef death during the 1997 Indian Ocean dipole linked to Indonesian wildfires. Science 2003, 301, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Cleary, D.F.R. The sudden death of a coral reef. Science 2004, 303, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizerek, T.L.; Madin, J.S.; Benzoin, F.; Huang, D.; Luiz, O.J.; Mera, H.; Schmidt-Roach, S.; Smith, S.D.A.; Sommer, B.; Baird, A.H. No evidence for tropicalization of coral assemblages in a subtropical climate change hot spot. Coral Reefs 2021, 40, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.L.; French, B.; Lester, E.K.; Wilson, S.K.; Day, P.B.; Taylor, M.D.; Barrett, N. Coral communities on marginal high-latitude reefs in West Australian marine parks. Diversity 2021, 13, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Moka, W. Species assemblages and ecomorph variation of mushroom corals (Scleractinia: Fungiidae) related to reef habitats in the Flores Sea. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1989, 23, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoeksema, B.W.; Johan, O.; Kunzmann, A. The Reef Coral Coscinaraea marshae Is Not a High-Latitude Endemic. Diversity 2021, 13, 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120681
Hoeksema BW, Johan O, Kunzmann A. The Reef Coral Coscinaraea marshae Is Not a High-Latitude Endemic. Diversity. 2021; 13(12):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120681
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoeksema, Bert W., Ofri Johan, and Andreas Kunzmann. 2021. "The Reef Coral Coscinaraea marshae Is Not a High-Latitude Endemic" Diversity 13, no. 12: 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120681
APA StyleHoeksema, B. W., Johan, O., & Kunzmann, A. (2021). The Reef Coral Coscinaraea marshae Is Not a High-Latitude Endemic. Diversity, 13(12), 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120681







