Risk of Infection, Local Prevalence and Seasonal Changes in an Avian Malaria Community Associated with Game Bird Releases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Populations and Field Procedure
2.2. Avian Malaria Diagnosis
2.3. Defining Parasite Lineages
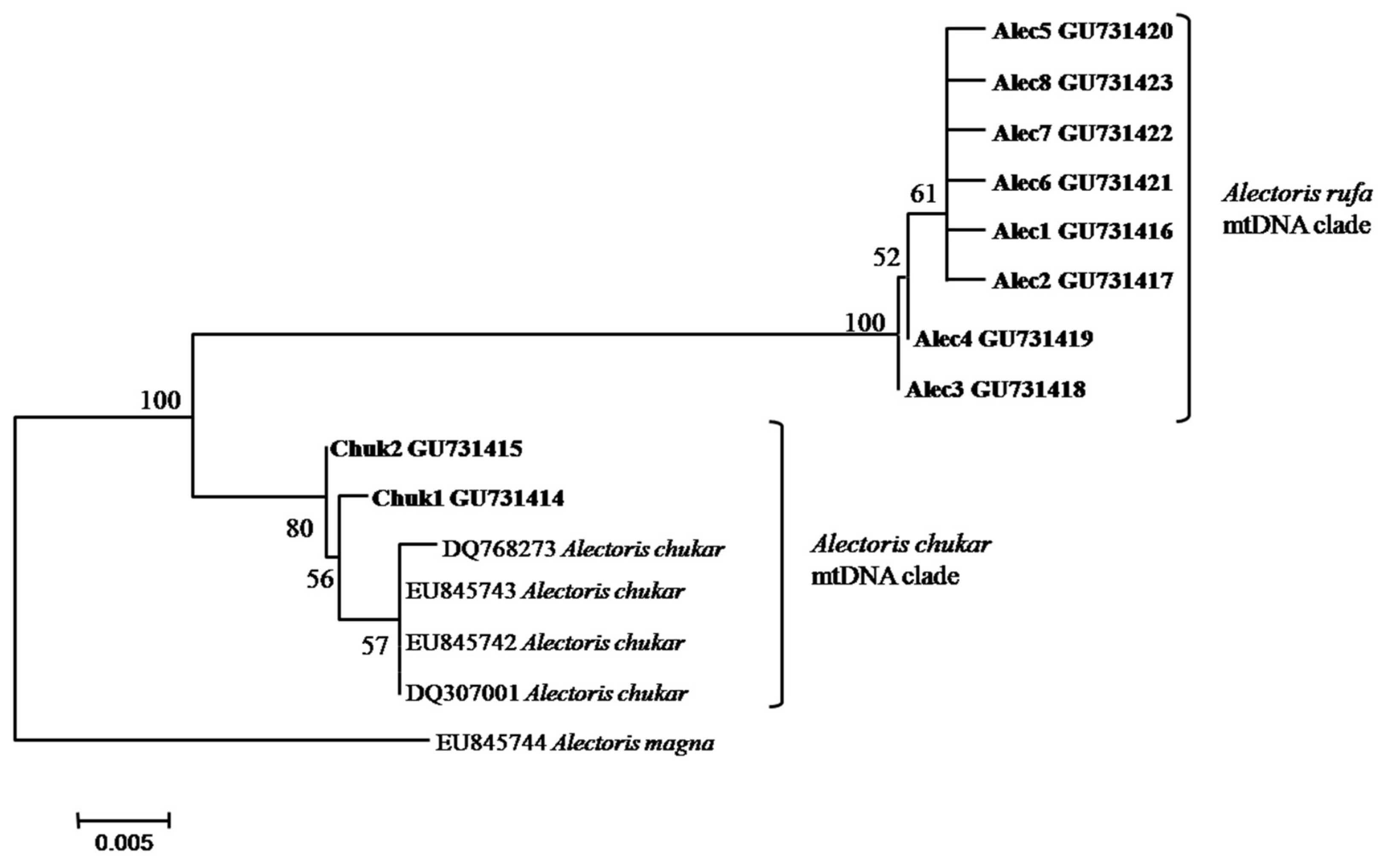
2.4. Host Mitochondrial Lineages
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Releasing Activity and Distribution of Host Genotypes
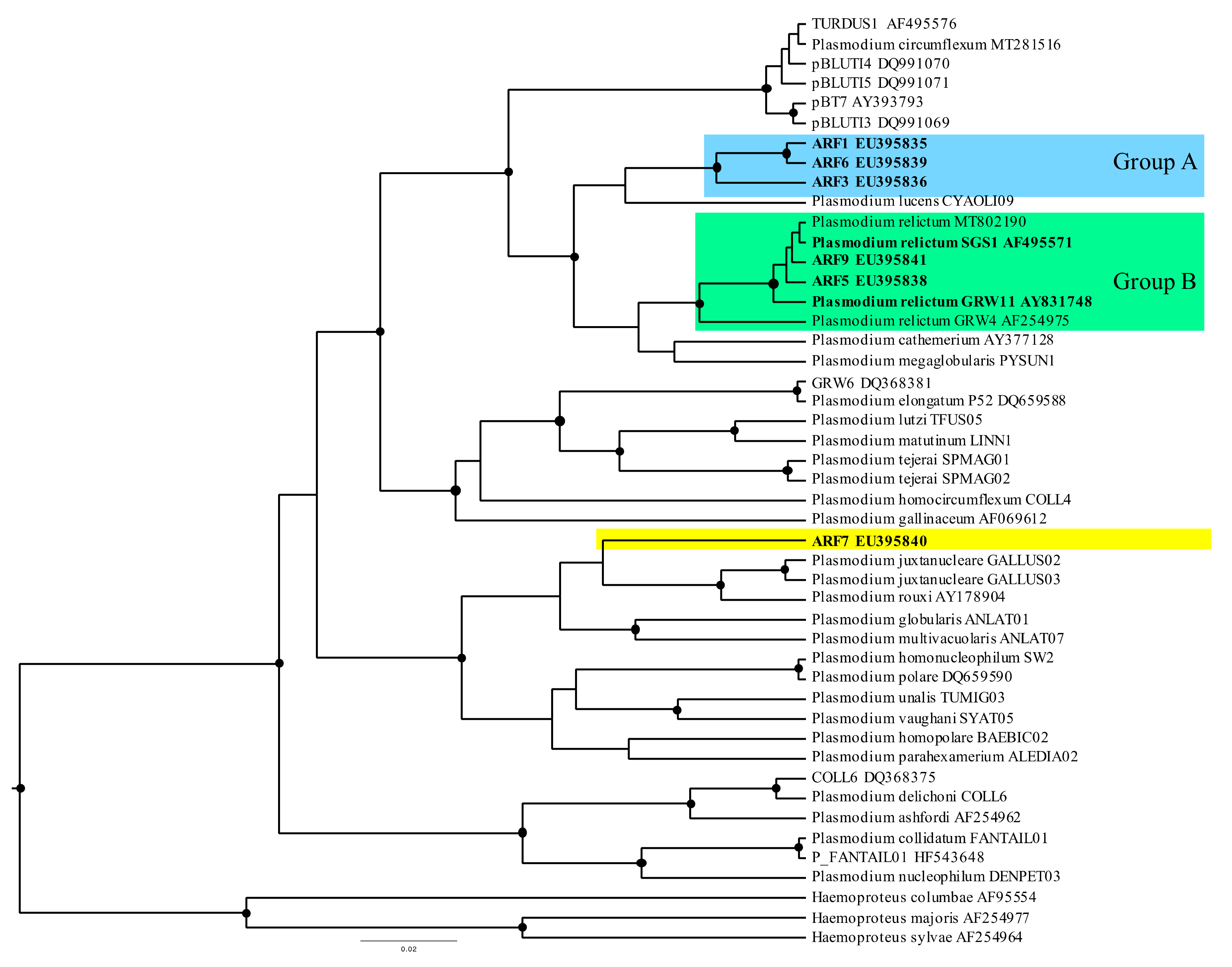
3.2. Avian Malaria Lineages of Red-Legged Partridges
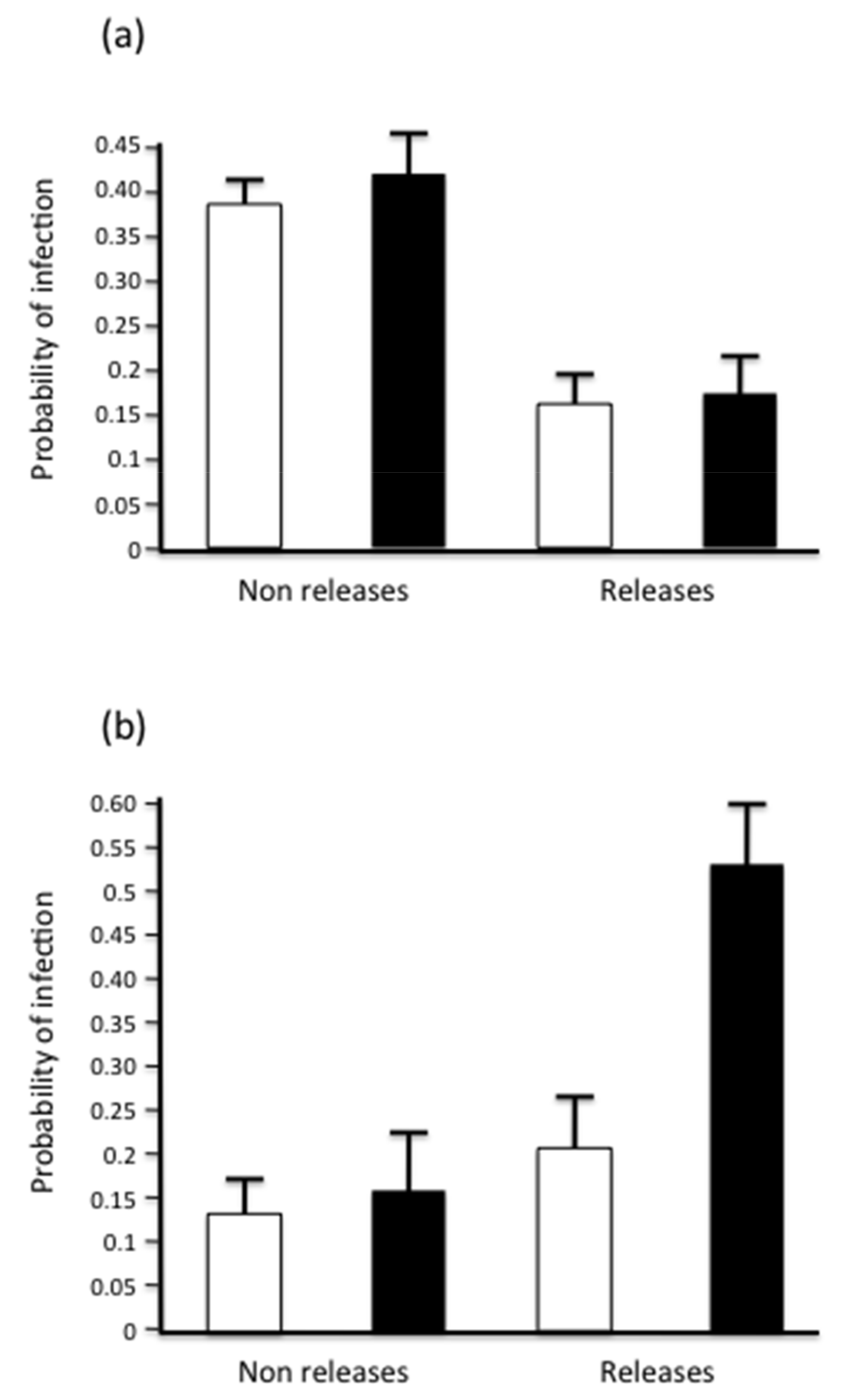
3.3. Seasonal Distribution of Parasites and Releasing Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palumbi, S.R. Humans as the World’s Greatest Evolutionary Force. Science 2001, 293, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.; Collins, S. Adaptation, Extinction and Global Change. Evol. Appl. 2008, 1, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cable, J.; Barber, I.; Boag, B.; Ellison, A.R.; Morgan, E.R.; Murray, K.; Pascoe, E.L.; Sait, S.M.; Wilson, A.J.; Booth, M. Global Change, Parasite Transmission and Disease Control: Lessons from Ecology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodosopoulos, A.N.; Grabenstein, K.C.; Bensch, S.; Taylor, S.A. A Highly Invasive Malaria Parasite Has Expanded Its Range to Non-Migratory Birds in North America. Biol. Lett. 2021, 17, 20210271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A. Disease Risks of Wildlife Translocations. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessl, B.; Kleindorfer, S.; Tebbich, S. An Experimental Study on the Effects of an Introduced Parasite in Darwin’s Finches. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 127, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, O.; Torchin, M.; Kuris, A.; Hechinger, R.; Chiba, S. Introduced Cryptic Species of Parasites Exhibit Different Invasion Pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakman, E.; Kinzelbach, R.; Trilles, J.; Bariche, M. First Occurrence of Native Cymothoids Parasites on Introduced Rabbitfishes in the Mediterranean Sea. Acta Parasitol. 2009, 54, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Moriones, A.M.; Casas, F.; Höfle, U. Prevalence of Escherichia Coli, Salmonella sp. and Campylobacter sp. in the Intestinal Flora of Farm-Reared, Restocked and Wild Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa): Is Restocking Using Farm-Reared Birds a Risk? Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2012, 58, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welchman, D. Diseases in Gamebirds: An Update. Practice 2016, 38, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszak, P.; Cunningham, A.; Hyatt, A. Emerging Infectious Diseases of Wildlife—Threats to Biodiversity and Human Health. Science 2000, 287, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.A.; Daszak, P.; Wood, J.L. One Health, Emerging Infectious Diseases and Wildlife: Two Decades of Progress? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J. Historical Survey of Disease in Birds. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1993, 24, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Burdon, J.; Thrall, P. Pathogen Evolution across the Agro-Ecological Interface: Implications for Disease Management. Evol. Appl. 2008, 1, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, P.; Wagner, D. Humans and Evolutionary and Ecological Forces Shaped the Phylogeography of Recently Emerged Diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keatts, L.O.; Robards, M.; Olson, S.H.; Hueffer, K.; Insley, S.J.; Joly, D.O.; Kutz, S.; Lee, D.S.; Chetkiewicz, C.-L.B.; Lair, S.; et al. Implications of Zoonoses from Hunting and Use of Wildlife in North American Arctic and Boreal Biomes: Pandemic Potential, Monitoring, and Mitigation. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, A. Restoring Island Ecosystems: The Potential of Parasites to Control Introduced Mammals. Conserv. Biol. 1988, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchin, M.; Lafferty, K.; Kuris, A. Release from Parasites as Natural Enemies: Increased Performance of a Globally Introduced Marine Crab. Biol. Invasions 2001, 3, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchin, M.E.; Lafferty, K.D.; Dobson, A.P.; McKenzie, V.J.; Kuris, A.M. Introduced Species and Their Missing Parasites. Nature 2003, 421, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Carpenter, S. Potential Spread of Introduced Black Rat (Rattus rattus) Parasites to Endemic Deer Mice (Peromyscus maniculatus) on the California Channel Islands. Divers. Distrib. 2006, 12, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, J.F.; Grace, D. The Consequences of Human Actions on Risks for Infectious Diseases: A Review. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 30048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, C.; van Riper, C., III. Pathogenicity and Epizootiology of Avian Haematozoa: Plasmodium, Leucocytozoon, and Haemoproteus. In Bird-Parasite Interactions. Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1991; pp. 19–48. [Google Scholar]
- Valkiunas, G. Pathogenic Influence of Haemosporidians and Trypanosomes on Wild Birds in the Field Conditions: Facts and Hypotheses. Ekologija 1993, 1, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, S.; Moreno, J.; Sanz, J.; Arriero, E. Are Avian Blood Parasites Pathogenic in the Wild? A Medication Experiment in Blue Tits (Parus caeruleus). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadam, D.; Robinson, R.A.; Clements, A.; Peach, W.J.; Bennett, M.; Rowcliffe, J.M.; Cunningham, A.A. Avian Malaria-Mediated Population Decline of a Widespread Iconic Bird Species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 182197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkman, C.; Siepielski, A.; Parchman, T. The Local Introduction of Strongly Interacting Species and the Loss of Geographic Variation in Species and Species Interactions. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.; Bernatchez, L. Evolutionary Change in Human-Altered Environments. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanua, D.; Perez-Rodriguez, L.; Casas, F.; Alzaga, V.; Acevedo, P.; Vinuela, J.; Gortazar, C. Sanitary Risks of Red-Legged Partridge Releases: Introduction of Parasites. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, J.; Gortazar, C.; Villafuerte, R. A Comparison of the Helminth Faunas of Wild and Farm-Reared Red-Legged Partridge. J. Wildl. Manag. 2004, 68, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J. Diseases of the Red-Legged Partridge (Alectoris rufa L.): A Review. Wildl. Biol. Pract. 2009, 5, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortázar, C.; Acevedo, P.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Vicente, J. Disease Risks and Overabundance of Game Species. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2006, 52, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco Aguiar, J.; Gonzalez-Jara, P.; Ferrero, M.; Sanchez Barbudo, I.; Virgós, E.; Villafuerte, R.; Dávila, J. Assessment of Game Restocking Contributions to Anthropogenic Hybridization: The Case of the Iberian Red Legged Partridge. Anim. Conserv. 2008, 11, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randi, E. Detecting Hybridization between Wild Species and Their Domesticated Relatives. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbanera, F.; Pergams, O.R.W.; Guerrini, M.; Forcina, G.; Panayides, P.; Dini, F. Genetic Consequences of Intensive Management in Game Birds. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfán, M.A.; Duarte, J.; Meriggi, L.R.; Viñuela, J.V.; Vargas, J.M. The red-legged Partridge: A historical overview on distribution, status, research and hunting. In The Future of the Red-Legged Partridge: Science, Hunting and Conservation; Wildlife Research Monographs; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Aebischer, N.; Potts, G. Red-Legged Partridge (Alectoris rufa). In Birds in Europe: Their Conservation Status; BirdLife International: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- BirdLife International. Birdlife Species Factsheet: Alectoris rufa. Available online: http://www.birdlife.org (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Garrido, J.L. Capturas de Perdiz Roja (Economía Inducida Por La Caza de Perdiz). In Aportaciones a la Gestión Sostenible de la Caza; Fedenca: Madrid, Spain, 2002; Volume I, pp. 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, J.; Vargas, J. Field Interbreeding of Released Farm-Reared Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa) with Wild Ones. Game Wildl. Sci. 2004, 21, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gortázar, C.; Villafuerte, R.; Martín, M. Success of Traditional Restocking of Red-Legged Partridge for Hunting Purposes in Areas of Low Density of Northeast Spain Aragón. Z. Jagdwiss. 2000, 46, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Pèrez, J.; Gaudioso, V.; Diez, C.; Prieto, R. Study of Survival, Dispersal and Home Range of Autumn-Released Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa). Br. Poult. Sci. 2005, 46, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, C.; Sokos, C.; Santilli, F.; Ponce, F.; Sagel, R.B.; Bro, E.; Buner, F.D. Enough Reared Red-Legs for Today, but Fewer Wild Ones for Tomorrow? The Dilemma of Gamebird Rearing and Releasing. In The Future of the Red-Legged Partridge: Science, Hunting and Conservation; Wildlife Research Monographs; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, H.; Kirkemo, A.-M.; Handeland, K. Wildlife as Source of Zoonotic Infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, J.; Torres, M.; Godoy, J. RAPD Analysis for Detection and Eradication of Hybrid Partridges (Alectoris rufa A. Graeca) in Spain. Biol. Conserv. 2001, 98, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, F.; Mougeot, F.; Ferrero, M.E.; Sánchez-Barbudo, I.; Dávila, J.A.; Viñuela, J. Phenotypic Differences in Body Size, Body Condition and Circulating Carotenoids between Hybrid and “Pure” Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa) in the Wild. J. Ornithol. 2013, 154, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogojević, M.S.; Merdić, E.; Bogdanović, T. The Flight Distances of Floodwater Mosquitoes (Aedes vexans, Ochlerotatus sticticus and Ochlerotatus caspius) in Osijek, Eastern Croatia. Biologia 2011, 66, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, F.; Viñuela, J. Agricultural Practices or Game Management: Which Is the Key to Improve Red-Legged Partridge Nesting Success in Agricultural Landscapes? Environ. Conserv. 2010, 37, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Waldenström, J.; Bensch, S.; Hasselquist, D.; Östman, Ö. A New Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction Method Very Efficient in Detecting Plasmodium and Haemoproteus Infections from Avian Blood. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the Sensitivity of Progressive Multiple Sequence Alignment through Sequence Weighting, Position-Specific Gap Penalties and Weight Matrix Choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bensch, S.; Pèarez-Tris, J.; Waldenströum, J.; Hellgren, O. Linkage between Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Sequences in Avian Malaria Parasites: Multiple Cases of Cryptic Speciation? Evolution 2004, 58, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Tris, J.; Bensch, S. Diagnosing Genetically Diverse Avian Malarial Infections Using Mixed-Sequence Analysis and TA-Cloning. Parasitology 2005, 131, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciloglu, A.; Ellis, V.A.; Bernotienė, R.; Valkiūnas, G.; Bensch, S. A New One-Step Multiplex PCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection and Identification of Avian Haemosporidian Parasites. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldenström, J.; Bensch, S.; Kiboi, S.; Hasselquist, D.; Ottosson, U. Cross-Species Infection of Blood Parasites between Resident and Migratory Songbirds in Africa. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njabo, K.Y.; Cornel, A.J.; Bonneaud, C.; Toffelmier, E.; Sehgal, R.N.M.; Valkiūnas, G.; Russell, A.F.; Smith, T.B. Nonspecific Patterns of Vector, Host and Avian Malaria Parasite Associations in a Central African Rainforest. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, S.; Hellgren, O.; Pérez-Tris, J. MalAvi: A Public Database of Malaria Parasites and Related Haemosporidians in Avian Hosts Based on Mitochondrial Cytochrome b Lineages. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An Advanced Software Platform for Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More Models, New Heuristics and Parallel Computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. LogCombiner, Version 2.3.0; Part of the BEAST Package; University of Auckland: Auckland, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A. TreeAnnotator, version 2.4.3; BEAST Package. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson, M.; Ast, J.; Dimcheff, D.; Yuri, T.; Mindell, D. Primers for a PCR-Based Approach to Mitochondrial Genome Sequencing in Birds and Other Vertebrates. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 1999, 12, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods), version 4; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- StatSoft Inc. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System), version 8.0; StatSoft: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, N.J.; Drovetski, S.V.; Voelker, G. Robust Geographical Determinants of Infection Prevalence and a Contrasting Latitudinal Diversity Gradient for Haemosporidian Parasites in Western Palearctic Birds. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 3131–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel, J.; Marzal, A.; Magallanes, S.; García-Longoria, L.; Suarez-Rubio, M.; Bates, P.J.; Lin, H.H.; Soe, A.N.; Oo, K.S.; Aye, A.A.; et al. Prevalence and Diversity of Avian Haemosporidians May Vary with Anthropogenic Disturbance in Tropical Habitats in Myanmar. Diversity 2021, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, I.; Ilahiane, L.; Boano, G.; Cucco, M.; Pavia, M.; Prestridge, H.L.; Voelker, G. Avian Haemosporidian Diversity on Sardinia: A First General Assessment for the Insular Mediterranean. Diversity 2021, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, Y.R.; Bakaloudis, D.; Barboutis, C.; Cecere, J.G.; Eraud, C.; Fischer, D.; Hering, J.; Hillerich, K.; Lormée, H.; Mader, V.; et al. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Avian Haemosporidian Parasites in Wild Bird Species of the Order Columbiformes. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Peñuela, J.; Ferraguti, M.; Martínez-de la Puente, J.; Soriguer, R.C.; Figuerola, J. Urbanization Effects on Temporal Variations of Avian Haemosporidian Infections. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Höfle, U.; Villanúa, D.; Gortázar, C. Health Monitoring and Disease Control in Red-Legged Partridges. In The Future of the Red-Legged Partridge: Science, Hunting and Conservation; Wildlife Research Monographs; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Encinas, A. Plasmodium relictum y P. cathemerium en aves del area salmantina. Rev. Ibérica Parasitol. 1982, 42, 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Millán, J.; Gortazar, C.; Villafuerte, R. First Record of Haemoproteus sp. Parasiting Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa). In Proceedings of the European Association of Zoo and Wildlife Veterinarians (EAZWV) 4th Scientific Meeting, Joint with the Annual Meeting of the European Wildlife Disease Association (EWDA), Heidelberg, Germany, 8–12 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tizzani, P.; Fanelli, A.; Negri, E.; Silvano, F.; Menzano, A.; Molinar, A.; Meneguz, P.G. Haemoparasites in Red-Legged Partridge (Alectoris rufa): First Record of Haemoproteus sp. in Italy? J. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 44, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecchio, A.; Clark, N.J.; Bell, J.A.; Skeen, H.R.; Lutz, H.L.; De La Torre, G.M.; Vaughan, J.A.; Tkach, V.V.; Schunck, F.; Ferreira, F.C.; et al. Global Drivers of Avian Haemosporidian Infections Vary across Zoogeographical Regions. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 2393–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Abraín, A.; Esparza, B.; Oro, D. Lack of Blood Parasites in Bird Species: Does Absence of Blood Parasite Vectors Explain It All? Ardeola 2004, 51, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Bernotienė, R.; Palinauskas, V.; Iezhova, T.; Murauskaitė, D.; Valkiūnas, G. Avian Haemosporidian Parasites (Haemosporida): A Comparative Analysis of Different Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays in Detection of Mixed Infections. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 163, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, F.; Arroyo, B.; Viñuela, J.; Guzmán, J.L.; Mougeot, F. Are Farm-Reared Red-Legged Partridge Releases Increasing Hunting Pressure on Wild Breeding Partridges in Central Spain? Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2016, 62, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanúa, D.; Casas, F.; Viñuela, J.; Gortázar, C.; de la Morena, E.L.G.; Morales, M. First Occurrence of Eucoleus contortus in a Little Bustard Tetrax tetrax: Negative Effect of Red-Legged Partridge Alectoris rufa Releases on Steppe Bird Conservation? Ibis 2007, 149, 405–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortázar, C.; Ferroglio, E.; Höfle, U.; Frölich, K.; Vicente, J. Diseases Shared between Wildlife and Livestock: A European Perspective. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2007, 53, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, J.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; Vicente, J.; Arroyo, B. A Quantitative Assessment of the Release of Farm-Reared Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa) for Shooting in Central Spain. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellgren, O.; Kriûanauskiene, A.; Valkiūnas, G.; Bensch, S. Diversity and Phylogeny of Mitochondrial Cytochrome B Lineages from Six Morphospecies of Avian Haemoproteus (Haemosporida: Haemoproteidae). J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beadell, J.; Ishtiaq, F.; Covas, R.; Melo, M.; Warren, B.; Atkinson, C.; Bensch, S.; Graves, G.; Jhala, Y.; Peirce, M.; et al. Global Phylogeographic Limits of Hawaii’s Avian Malaria. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.; Zehtindjiev, P.; Bensch, S. Genetic Diversity of Avian Blood Parasites in SE Europe: Cytochrome B Lineages of the Genera Plasmodium and Haemoproteus (Haemosporida) from Bulgaria. Acta Parasitol. 2010, 55, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jönsson, J.; Bensch, S. Persistence of Avian Haemosporidians in the Wild: A Case Study to Illustrate Seasonal Infection Patterns in Relation to Host Life Stages. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, C.; Wood, M.; Day, K.; Sheldon, B. Seasonal Variation in Plasmodium Prevalence in a Population of Blue Tits Cyanistes caeruleus. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkiunas, G. Avian Malaria Parasites and Other Haemosporidia; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-415-30097-5. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, J.M.; Mellinger, S.; Halupka, L.; Marzal, A.; Zehtindjiev, P.; Westerdahl, H. Seasonal Dynamics of Haemosporidian (Apicomplexa, Haemosporida) Parasites in House Sparrows Passer domesticus at Four European Sites: Comparison between Lineages and the Importance of Screening Methods. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roode, J.; Read, A. Evolution and Ecology, after the Malaria Genomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, K.M.; Fleischer, R.C.; Kilpatrick, A.M. The Role of Native and Introduced Birds in Transmission of Avian Malaria in Hawaii. Ecology 2020, 101, e03038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, F.; Mougeot, F.; Sánchez-Barbudo, I.; Dávila, J.A.; Viñuela, J. Fitness consequences of anthropogenic hybridization in wild red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa, Phasianidae) populations. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, A.; Brooke, M.; McGowan, P. Correlates of Extinction Risk and Hunting Pressure in Gamebirds (Galliformes). Biol. Conserv. 2005, 126, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñuela, J.; Arroyo, B. Gamebird Hunting and Biodiversity Conservation: Synthesis, Recommendations and Future Research Priorities; CSIC-UCLM-Instituto de Investigación en Recursos Cinegéticos (IREC): Brussels, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mustin, K.; Arroyo, B.; Beja, P.; Newey, S.; Irivine, R.J.; Kestler, J.; Redpath, S.M. Consequences of Game Bird Management for Non-game Species in Europe. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Game Estate | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site A | Site B | Site C | Site D | Total | ||||||||
| Parasite Taxon | Lineage | GenBank | AT | SP | AT | SP | AT | SP | AT | SP | AT | SP |
| Plasmodium sp. | ARF1 | EU395835 | 10 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | 11 | 29.4 | 51.9 |
| P. relictum | SGS1 | AF495571 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | - | 1 | 31.4 | 25.0 |
| Plasmodium sp. | ARF3 | EU395836 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 1 | 0.0 | 1.9 |
| Plasmodium sp. | ARF5 | EU395838 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 3.9 | 1.9 |
| Plasmodium sp. | ARF6 | EU395839 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | - | 2 | 11.8 | 9.6 |
| Plasmodium sp. | ARF7 | EU395840 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| P. relictum | GRW11 | AY831748 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | - | 0 | 15.7 | 5.8 |
| Plasmodium sp. | ARF9 | EU395841 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | - | 0 | 5.9 | 1.9 |
| N° of samples | 31 | 39 | 25 | 35 | 21 | 9 | - | 29 | 77 | 112 | ||
| N° of infections | 19 | 21 | 17 | 9 | 15 | 7 | - | 15 | 51 | 52 | ||
| Prevalence | 61.2 | 53.8 | 68 | 25.7 | 71.4 | 77.7 | - | 51.7 | 66.2 | 46.4 | ||
| Wald χ2 | d.f. | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Parasites Pooled | |||
| Period | 7.77 | 1 | 0.005 |
| Management | 0.24 | 1 | 0.6 |
| Period x Management | 2.76 | 2 | 0.1 |
| Parasites of Group A | |||
| Period | 0.13 | 1 | 0.71 |
| Management | 12.12 | 1 | 0.0004 |
| Period x Management | 0.04 | 2 | 0.95 |
| Parasites of Group B | |||
| Period | 4.51 | 0.033 | |
| Management | 9.04 | 1 | 0.0026 |
| Period x Management | 2.57 | 0.11 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García, J.T.; Viñuela, J.; Calero-Riestra, M.; Sánchez-Barbudo, I.S.; Villanúa, D.; Casas, F. Risk of Infection, Local Prevalence and Seasonal Changes in an Avian Malaria Community Associated with Game Bird Releases. Diversity 2021, 13, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120657
García JT, Viñuela J, Calero-Riestra M, Sánchez-Barbudo IS, Villanúa D, Casas F. Risk of Infection, Local Prevalence and Seasonal Changes in an Avian Malaria Community Associated with Game Bird Releases. Diversity. 2021; 13(12):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120657
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía, Jesús T., Javier Viñuela, María Calero-Riestra, Inés S. Sánchez-Barbudo, Diego Villanúa, and Fabián Casas. 2021. "Risk of Infection, Local Prevalence and Seasonal Changes in an Avian Malaria Community Associated with Game Bird Releases" Diversity 13, no. 12: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120657
APA StyleGarcía, J. T., Viñuela, J., Calero-Riestra, M., Sánchez-Barbudo, I. S., Villanúa, D., & Casas, F. (2021). Risk of Infection, Local Prevalence and Seasonal Changes in an Avian Malaria Community Associated with Game Bird Releases. Diversity, 13(12), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120657







