Artificial Wetlands as Breeding Habitats for Colonial Waterbirds within Central Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
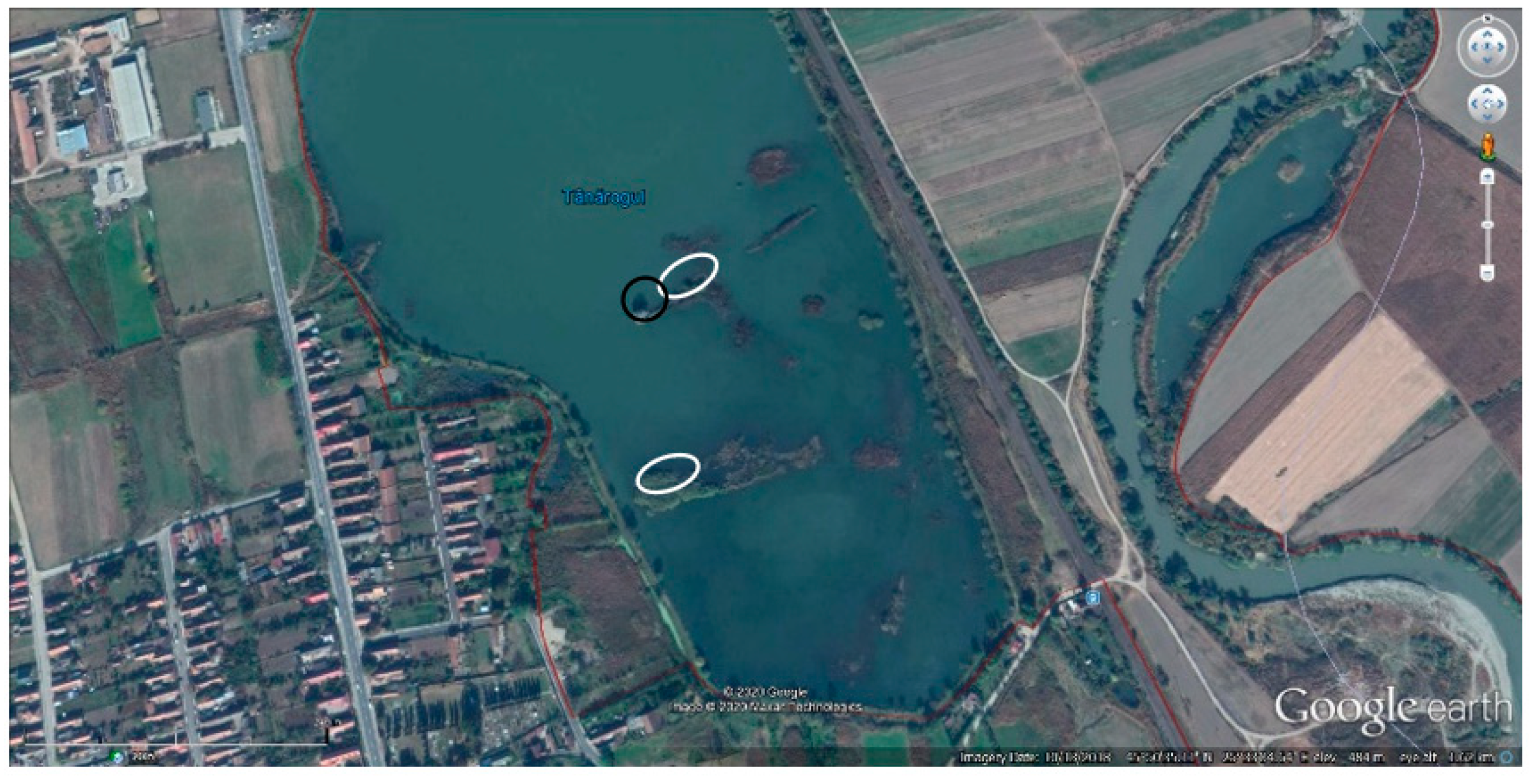
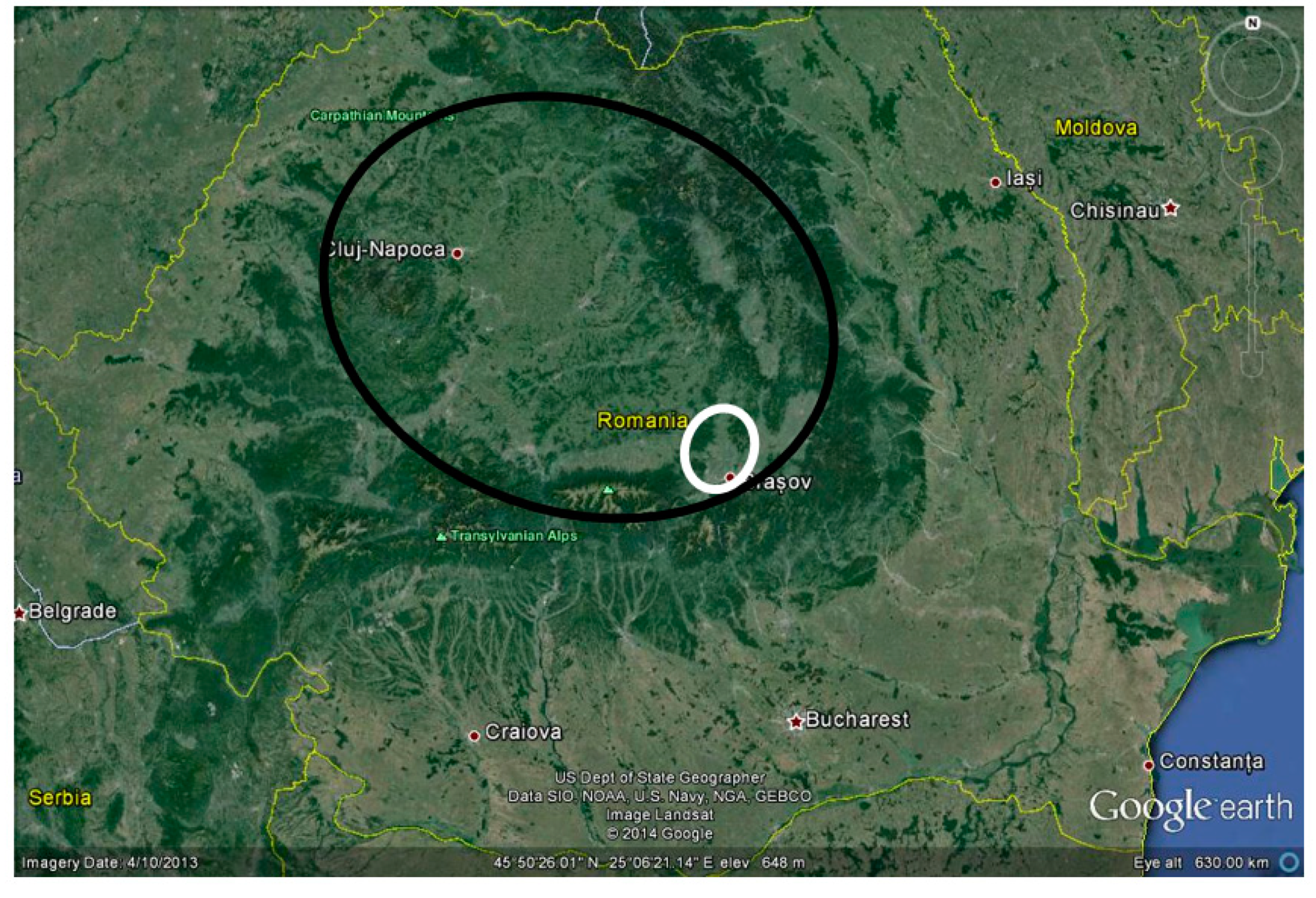
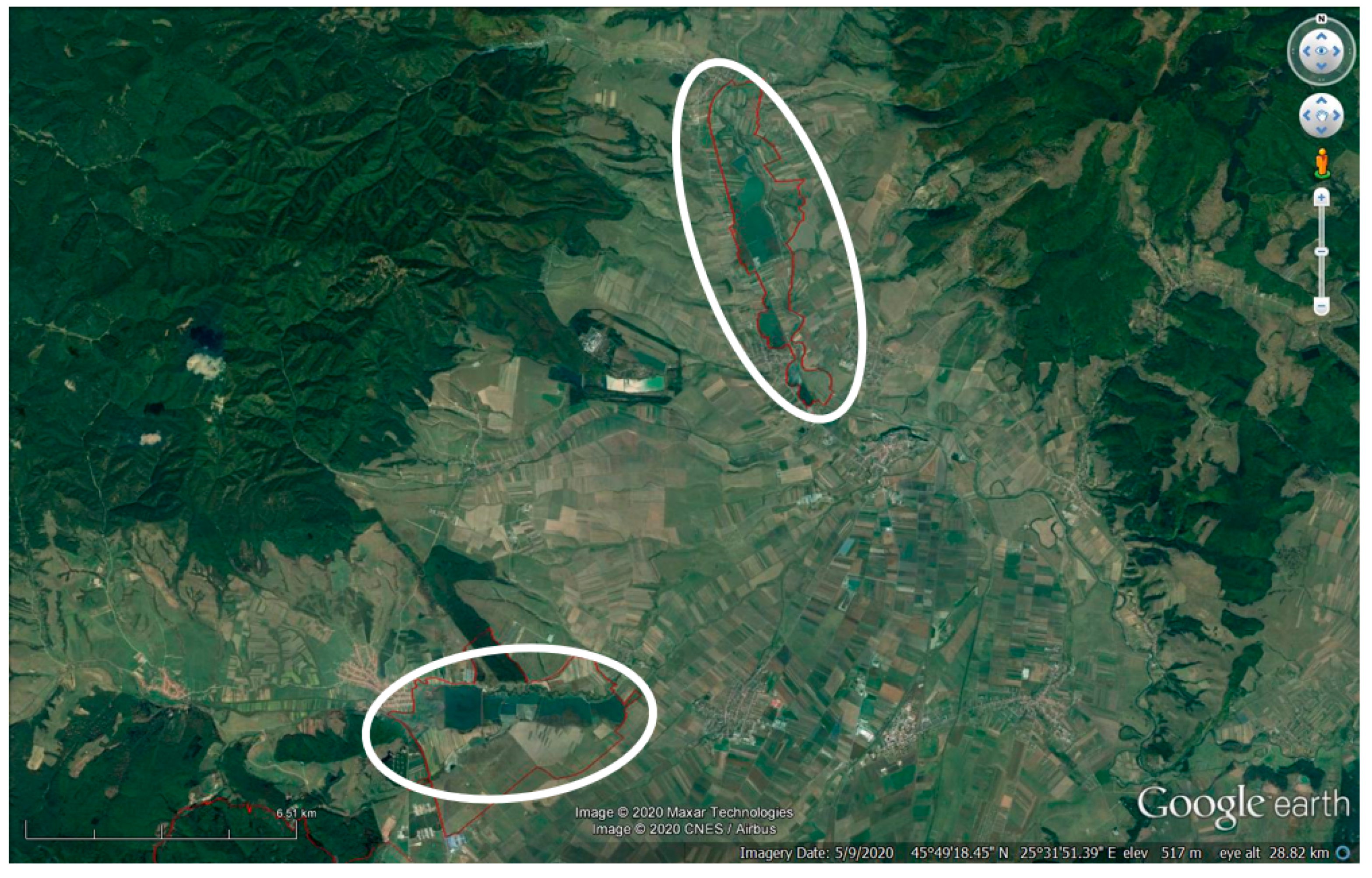
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Colony Types
- —
- Monospecific, for the following species: Phalacrocorax carbo, Ardea cinerea, Ardea purpurea, and Ardea alba. All of them can also form mixed colonies, and some can also breed in isolated pairs (Ardea cinerea, Ardea purpurea, Ardea alba).
- —
- Only mixed for the following species: Microcarbo pygmaeus, Egretta garzetta, Nycticorax nycticorax, and Ardeola ralloides. The most stable type of mixed colony was formed by all four of these species, with Ardea cinerea at Dumbrăvița (since 2012) and the other three species at Rotbav (since 2016).
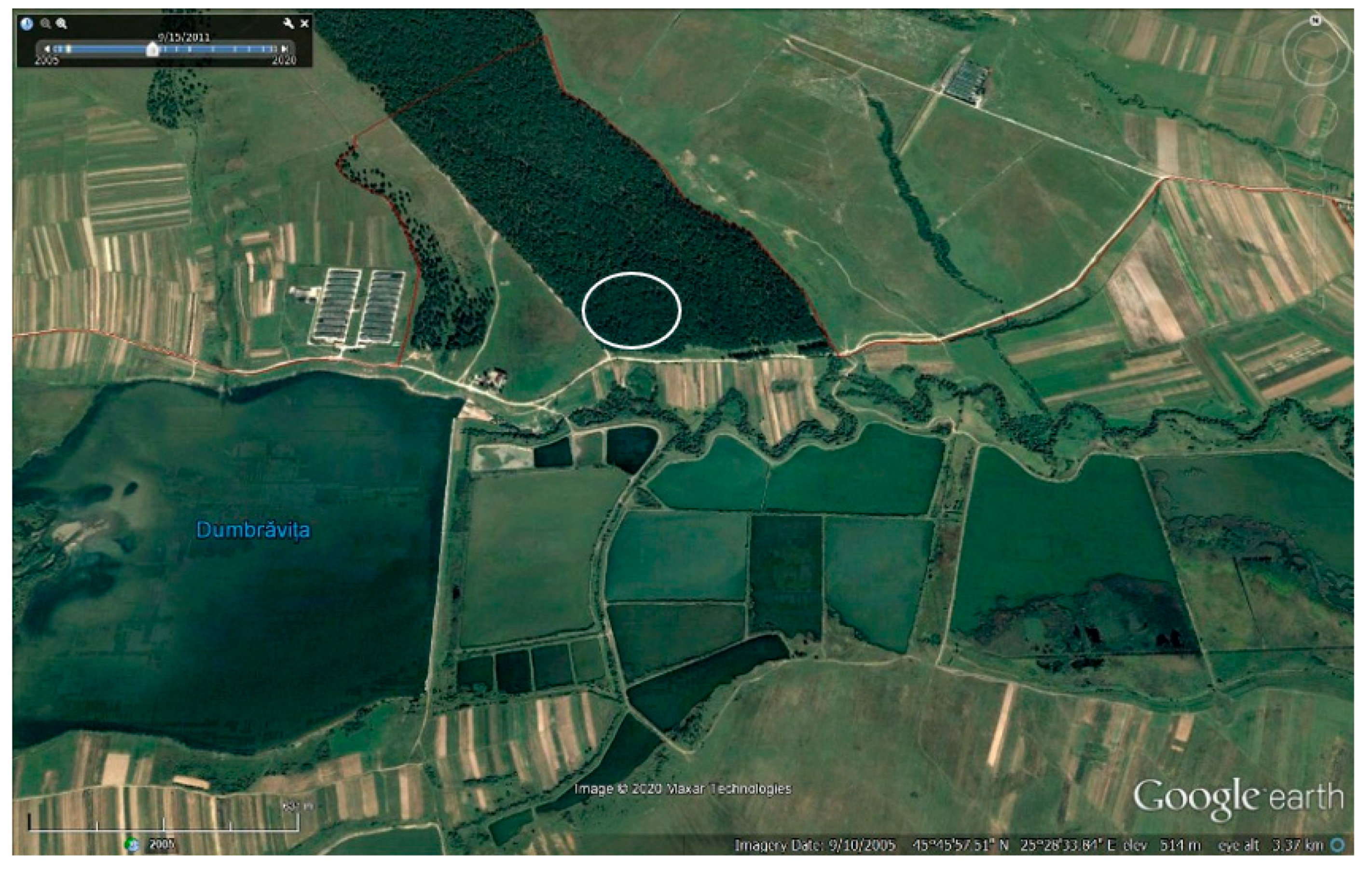
3.2. Breeding Habitat Types/Nest Locations
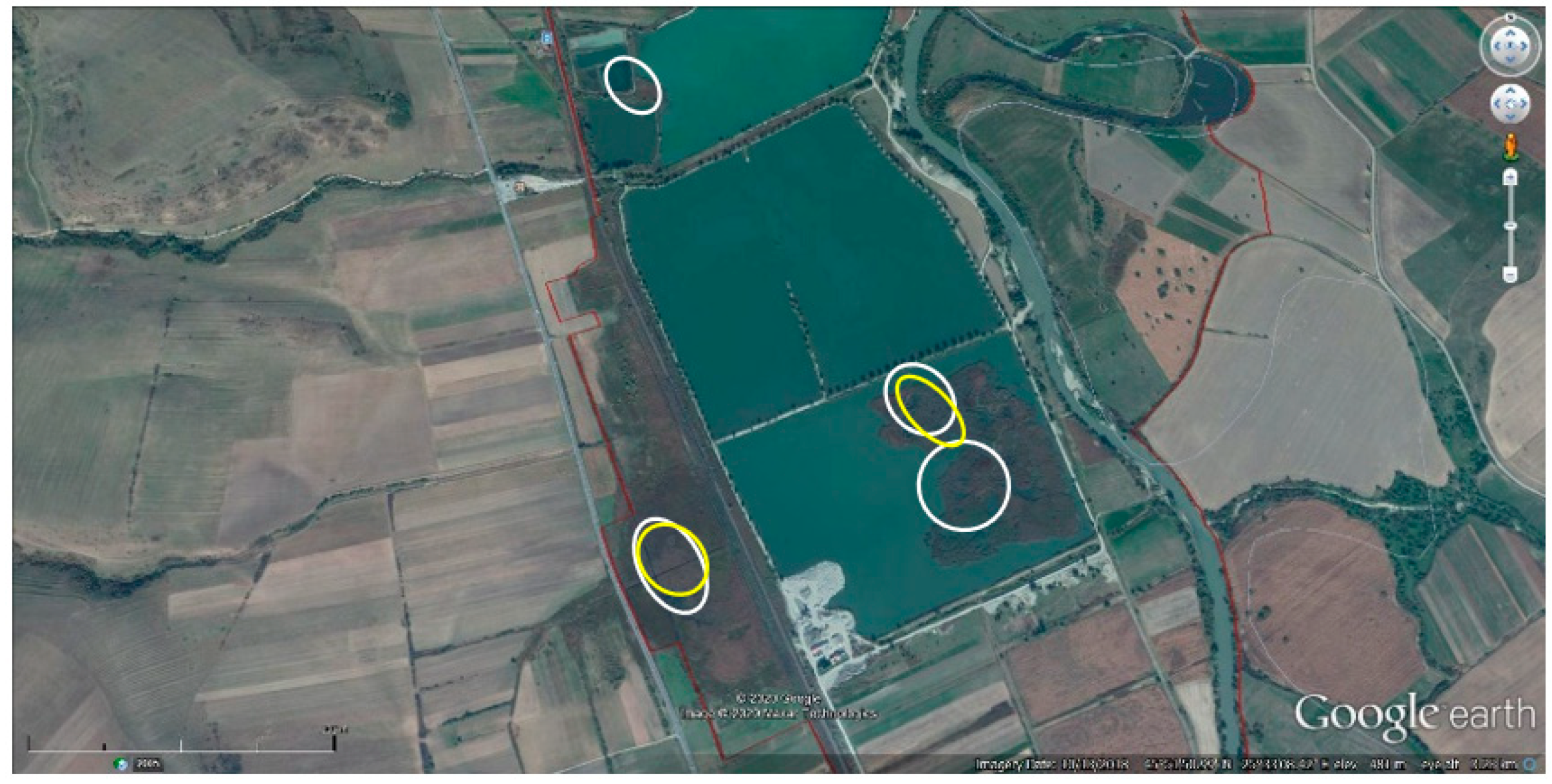
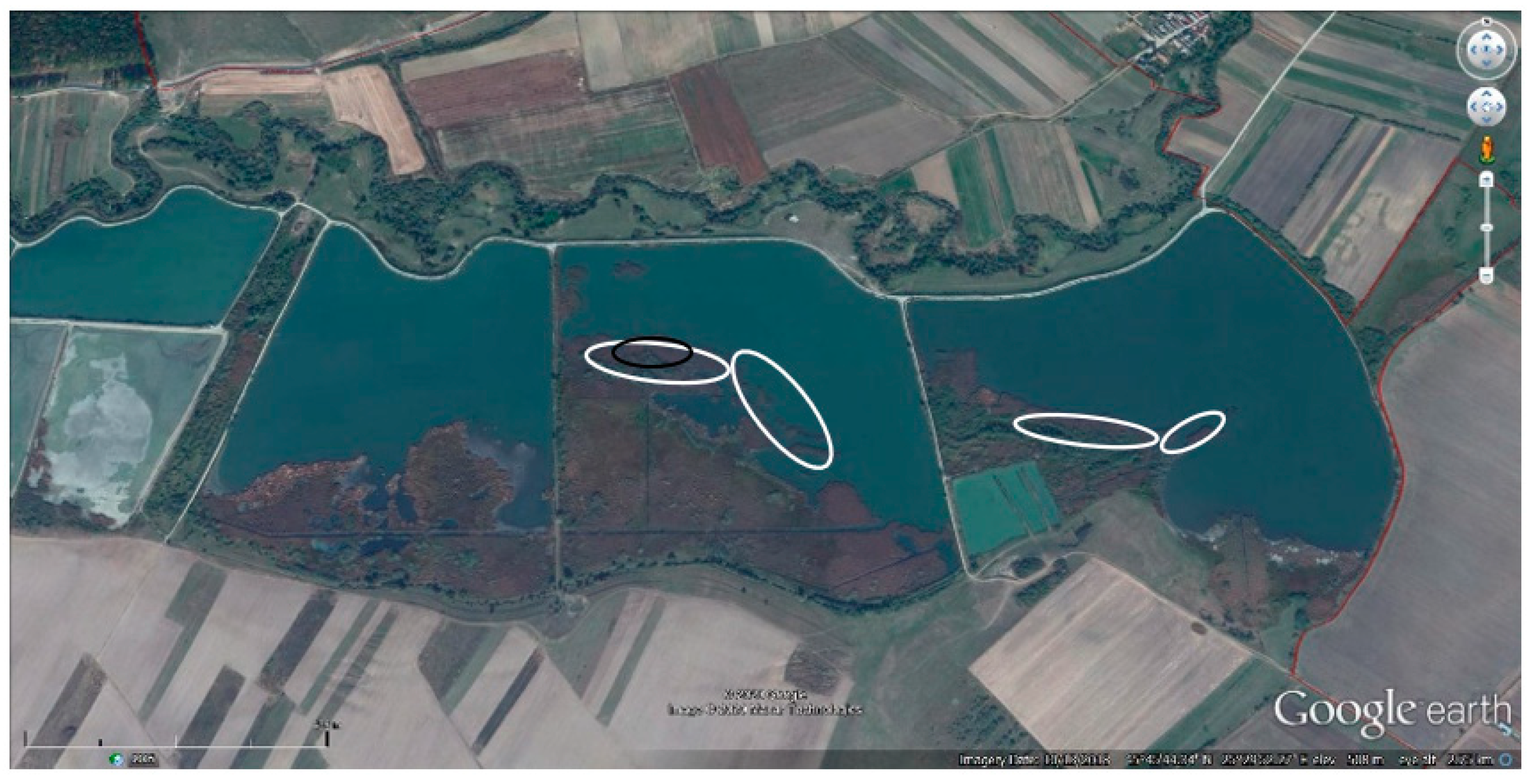
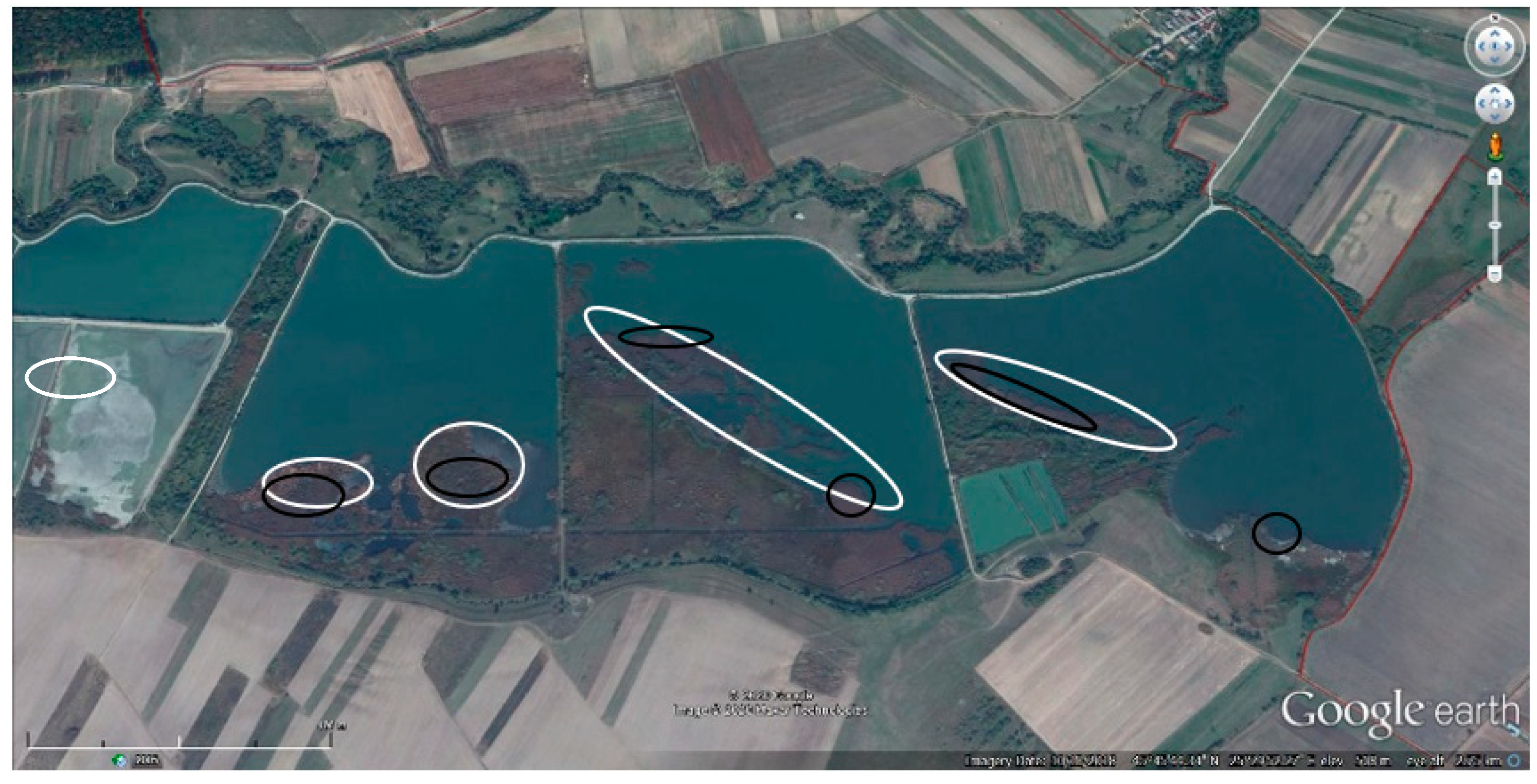
3.3. Colony Distribution within Study Area
3.4. Colony Characteristics/Elements
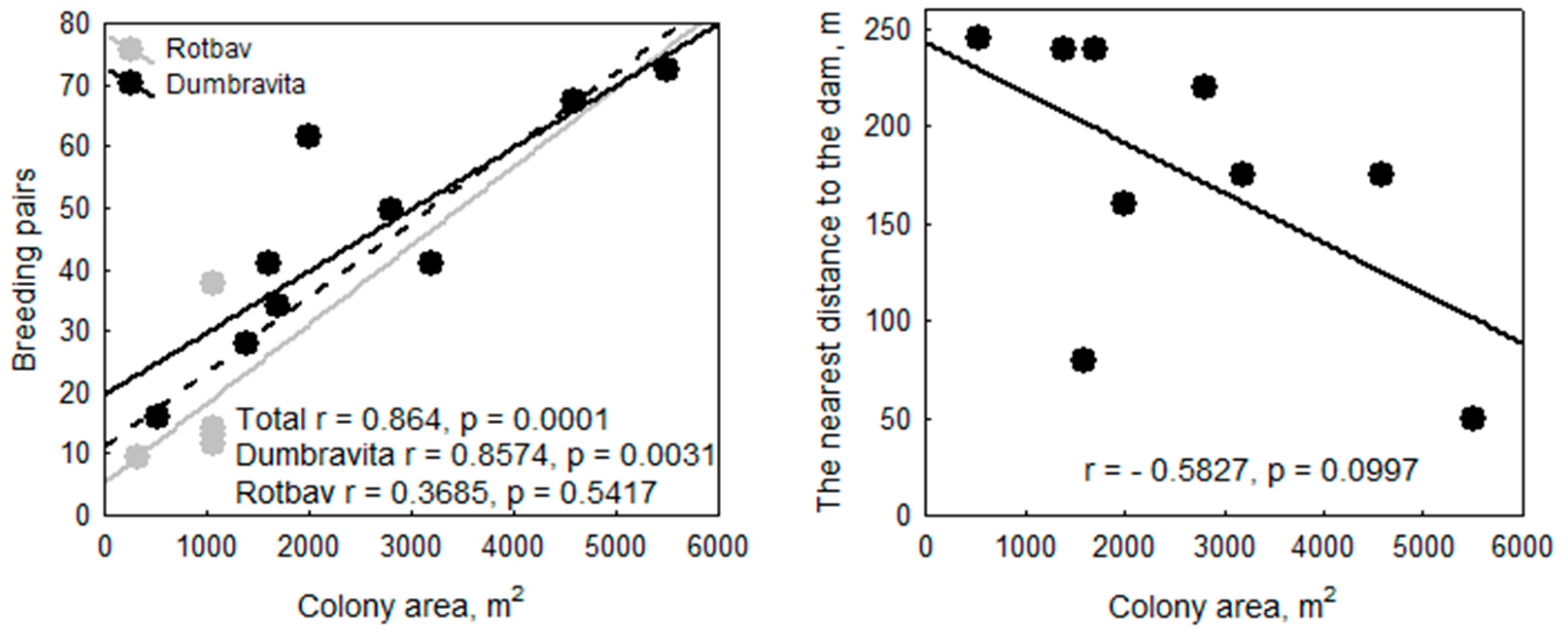
3.4.1. Areas Occupied by Colonies during Monitoring Period
3.4.2. Nearest Distance from Colony Edge to Terrestrial Habitats and Human Constructions (Dams, Roads, or Buildings)
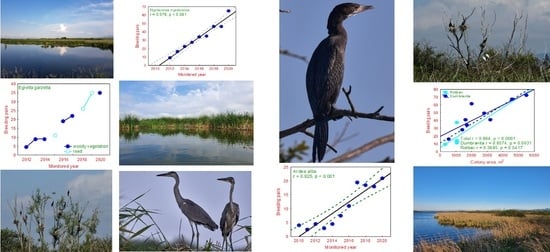
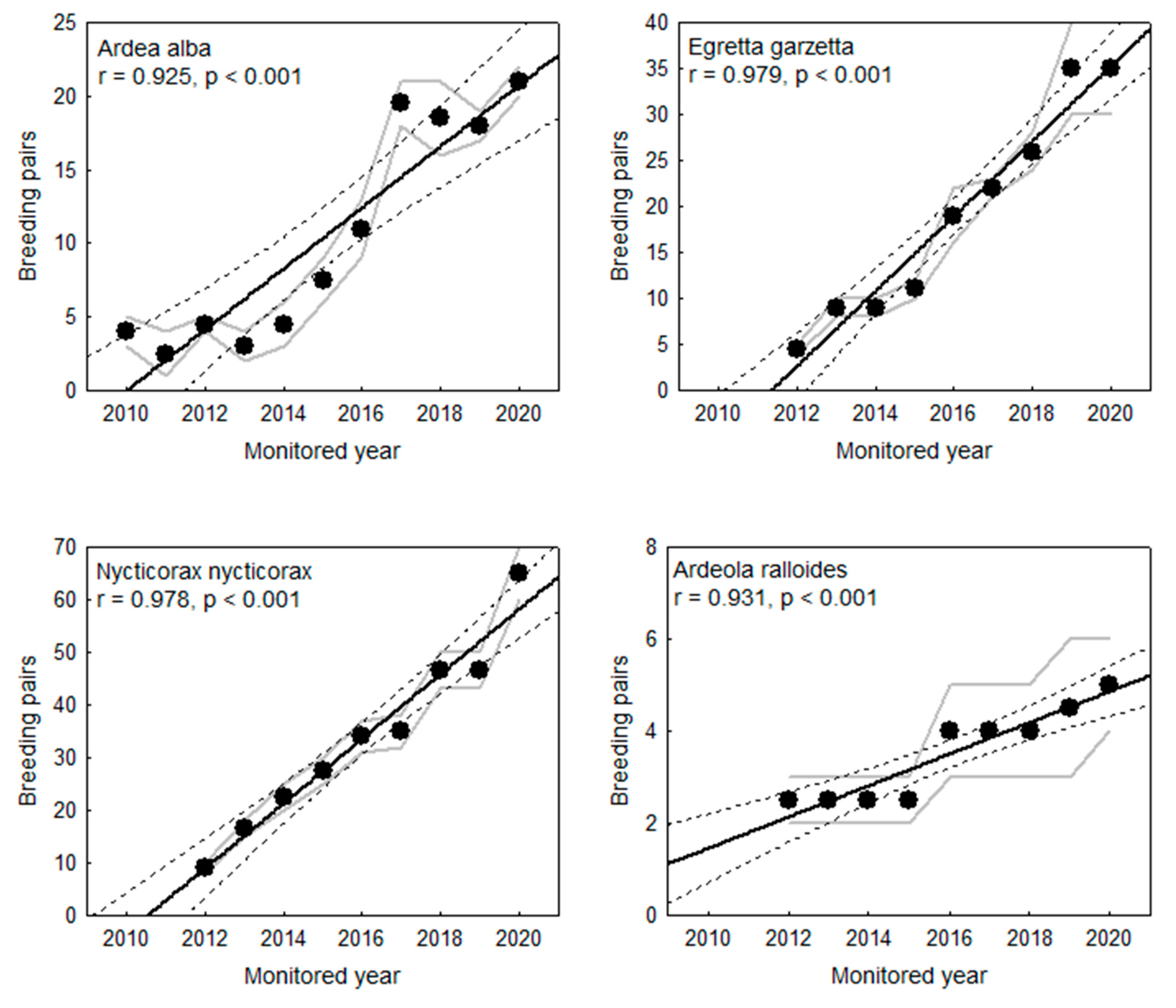
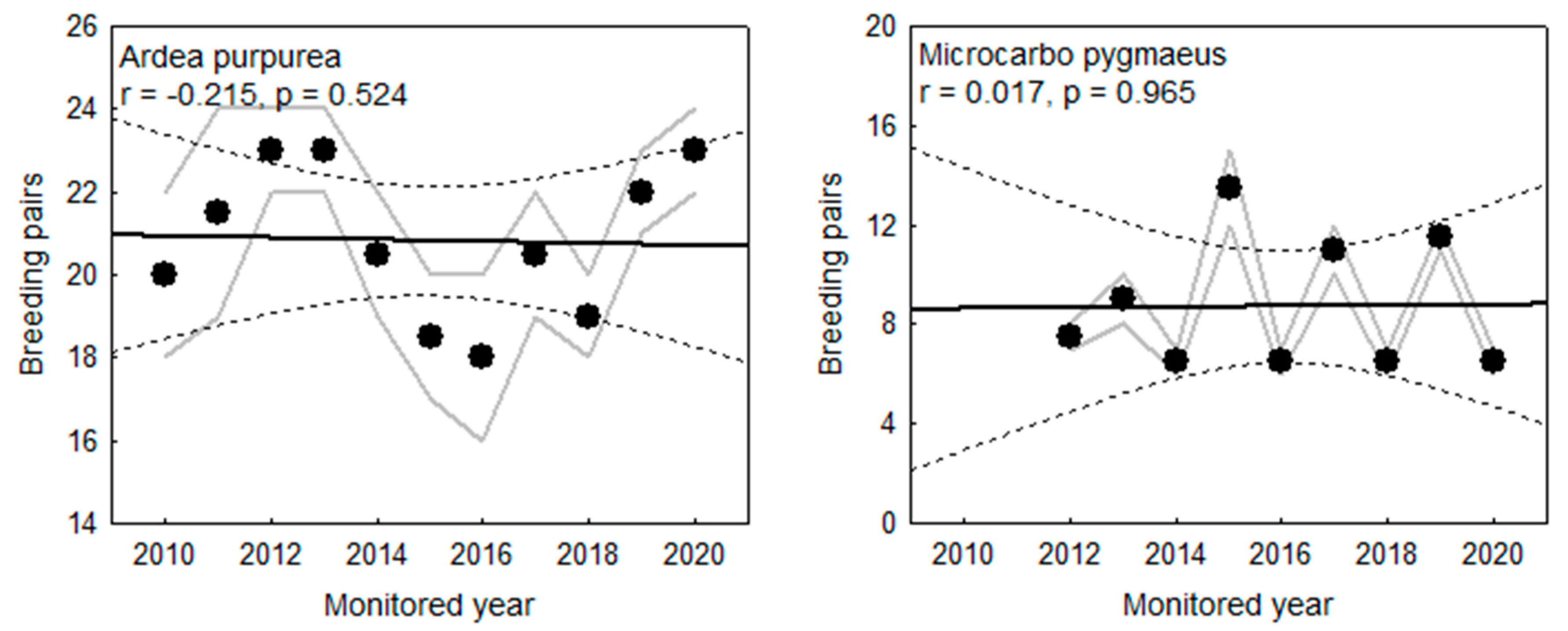
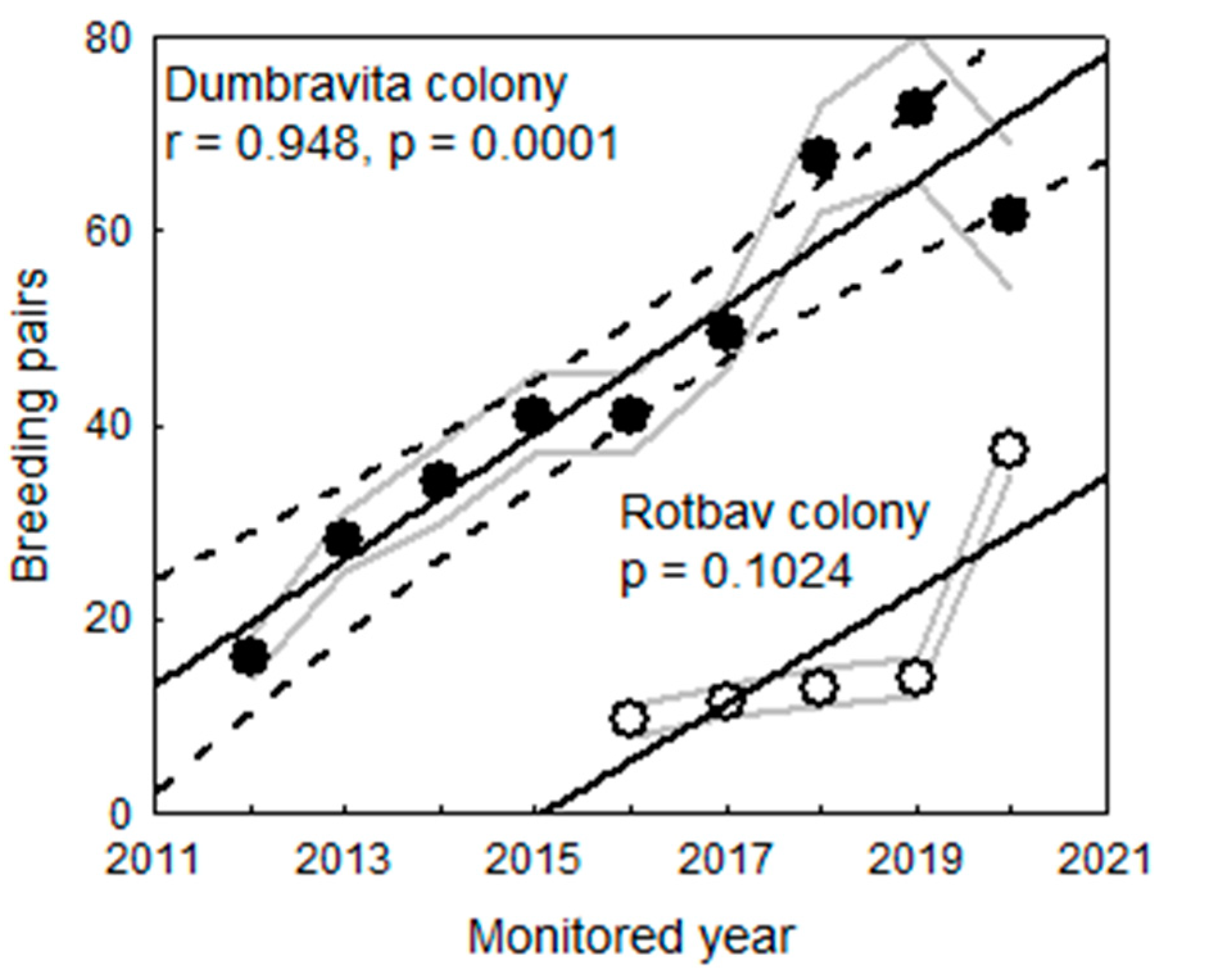
3.5. Population Size/Number of Pairs and Trends
4. Discussion
4.1. Use of Habitat Type or Nesting Location in Relation to Natural and Human Factors
4.2. Nearest Distance from Colony Edge to Terrestrial Habitats and Human Contructions
4.3. Species Occurrence, and Their Distribution and Population Size
4.3.1. Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo)
4.3.2. Pygmy Cormorant (Microcarbo pygmaeus)
4.3.3. Grey Heron (Ardea cinerea)
4.3.4. Purple Heron (Ardea purpurea)
4.3.5. Black-Crowned Night Heron (Nycticorax nycticorax)
4.3.6. Squacco Heron (Ardeola ralloides)
4.3.7. Little Egret (Egretta garzetta)
4.3.8. Great White Egret (Ardea alba)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoiculescu, D.C. Ecological Reconstruction from the Easily Flooded Region of the Romanian Danube; WWF: Dunăre-Carpați, București, România, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, D.T.; Popescu, V.; Iordache, D. Data concerning the designation of Dumbrăvița (Romania) Complex as Ramsar Site. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2008, 6, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Munteanu, D.; Papadopol, A.; Weber, P. Atlasul păsărilor clocitoare din România, 2nd ed.; Romanian Ornithological Socety: Cluj-Napoca, România, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Munteanu, D.; Chișamera, G.; David, A.; Simon, D.; Onea, N.; Petrescu, A.; Sevianu, E.; Stermin, A.N. Fauna României, Aves, Galliformes, Ciconiiformes, 15th ed.; Academiei Române: Bucuresti, Romania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas al Speciilor de Păsări de Interes Comunitar din România; Ministerul Mediului, Apelor și Pădurilor: București, Romania, 2015.
- Birds Report. Available online: http://cdr.eionet.europa.eu/ro/eu/art12/envxtwkg/RO_birds_reports_20200727-125003.xml/manage_document (accessed on 3 August 2020).
- Ramsar Sites Information Service. Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/RISapp/section.php?idSection=25&part=62&idvris=53484791&action=view (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Papp, T.; Fântână, C. (Eds.) Important Bird Areas in Romania; Romanian Ornithological Socety and Association, “Milvus Group”: Târgu-Mureș, Romania, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Domșa, C.; Hulea, D.; Todorov, E.; Răducescu, L.; Szabó, D.Z.; Komáromi, I.; Fântână, C.; Veres-Szászka, J.; Bugariu, S.; Damoc, D.; et al. Ghid Standard de Monitorizare a Speciilor de Păsări de Interes Comunitar din România. Coordonatori: Societatea Ornitologică Română și Asociația pentru Protecția Păsărilor și a Naturii “Grupul Milvus”; Ministerul Mediului și Schimbărilor Climatice-Direcția Dezvoltare Durabilă și Protecția Naturii: București, Romania, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- The Birds Directive. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/nature/legislation/birdsdirective/index_en.htm (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Doniţă, N.; Popescu, A.; Paucă-Comănescu, M.; Mihăilescu, S.; Biriş, I.V. Habitatele din România; Ed. Tehnică-Silvică: Bucureşti, Romania, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- David, A. Cercetări Faunistice, Biologice și Ecologice Asupra Populațiilor de Păsări din Câmpia Fizeșului. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitatea Babeș-Bolyai, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sandor, D.A. Heronry in a Pine Forest (Colonia de Stârci de la Miheșu de Câmpie); Milvus: Targu Mures, Romania, 1998; Volume 4–5, pp. 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Fasola, M.; Rubolini, D.; Merli, E.; Boncompagni, E.; Bressan, U. Long-term trends of heron and egret populations in Italy, and the effects of climate, human-induced mortality, and habitat on population dynamics. Popul. Ecol. 2009, 52, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzidis, S.; Goutner, V.; Pyrovetsi, M.; Sinis, A. Comparative nest site selection and breeding success in 2 sympatric Ardeids, Black-crowned Night Heron (Nycticorax nycticorax) and Little Egret (Egretta garzetta) in the Axios Delta, Macedonia, Greece. Colonial Waterbirds J. 1997, 20, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schogolev, I.V. Fluctuations and Trends in Breeding Populations of Colonial Waterbirds in the Dnestr Delta, Ukraine, Black Sea. Colonial Waterbirds J. 1996, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbraud, C.; Lepley, M.; Mathevet, R.; Mauchamp, A. Reedbed selection and colony size of breeding Purple Herons Ardea purpurea in southern France. Ibis 2002, 144, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deerenberg, C.; Hafner, H. Fluctuation in population size and colony dynamics in the Purple Heron Ardea purpurea in Mediteraneean France. Ardea 1999, 87, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Grull, A.; Ranner, A. Populations of the Great Egret and Purple Heron in Relation to Ecological Factors in the Reed Belt of the Neusiedler See. Colonial Waterbirds J. 1998, 21, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Schuster, A. Spatial and temporal variation of habitat and prey utilization in the Great White Egret Ardea alba alba at Neusedler Lake, Austria. Birds Study 2005, 52, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignat, A.E. Aspecte Privind Biologia Stârcilor, Lopătarilor și Țigănușilor din Zona Central a Bazinului Românesc al Prutului; Ed. Univ. “Alexandru Ioan Cuza”: Iași, Romania, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.P.; Pratt, H.M.; Greene, P.L. The Distribution, Reproductive Success, and Habitat Characteristics of Heron and Egret Breeding Colonies in the San Francisco Bay Area. Colonial Waterbirds J. 1993, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.; Black, J.M. Waterfowl Ecology; Blackie: Glasgow, UK; London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Musil, P.; Cepák, J.; Hudec, K.; Zárybnický, J. The long-Term Trends in the Breeding Waterfowl Populations in the Czech Republic; OMPO and Institute of Applied Ecology: Kostelec nad Černými lesy, Czech Republic, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Management Plan for Natura 2000 Site ROSPA0037 Dumbrăvița-Rotbav-Măgura Codlei. 2016. Available online: http://www.anpm.ro/documents/15795/2964930/PLAN+MANAGEMENT+Dumbravita-Rotbav-Magura+Codlea.pdf/8b94f816-11b3-427a-b08e-5d96d7a91533 (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Kristiansen, J.N. Egg predation in reedbed nesting Greylag Geese Anser anser. Ardea 1998, 86, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rašajski, J.; Kiss, A. Ptice Banata Die Vögel Banats, Gradski Musej Vršac; Ed. Triton: Timișoara, Romania, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Salmen, H. Die Ornis Siebenburgens; Bohlau Verlag: Wien, Austria; Koln, Austria, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, W.; Kohl, Ș.T. Die Ornis Siebenburgens; Bohlau Verlag: Wien, Austria, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ciochia, V. Păsările clocitoare din România; Ed. Ştiinţifică: Bucureşti, Romania, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, P. Atlasul Provizoriu al Păsărilor Clocitoare din România; Publ. Societăţii Ornitologice Române: Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeijer, E.J.M.; Blair, M.J. (Eds.) The EBCC Atlas of European Breeding Birds: Their Distribution and Abundance; T&AD Poyser: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bábos, K.; Sándor, D.A. Költésbiológiai megfigyelések a Mezö-Méhesi gémtelepen; Studii și Comunicări: Satu Mare, Romania, 1998–1999; Volume XV–XVI, pp. 680–696.
- Formularul Standard Natura 2020. Available online: http://www.mmediu.ro/app/webroot/uploads/files/Formulare_standard_SPA.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Marinov, M.; Doroșencu, A.; Alexe, V.; Bolboacă, L.E.; Kiss, J.B.; Nanu, C.; Tosic, K.; Tudor, M. Recent data concerning colonial waterbirds in Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve (Romania). J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2019, 20, 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, D.T.; Iordache, D.; Popescu, V. New breeding bird species of community interest within wetlands from the central side of Romania. In Proc. of the Biennial International Symposium Forest and Sustainable Development; Tranilvania Univeristy Publishing House: Brasov, Romania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, D.T. The Great Egret (Casmerodius albus) as a breeding species in the central part of Romania (Transylvania). Bull. Transilv. Uni. Bv. 2007, 14, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, M.F.; Evans, M.I. (Eds.) Important Bird Areas in Europe: Priority Sites for Conservation; BirdLife International Publ.: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Švažas, S.; Kozulin, A. Waterbirds of Large fishponds of Belarus and Lithuania; OMPO Special Publication and Lithuanian Institute of Ecology: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2002. [Google Scholar]



| No. | Species | Habitat Type | Nests on | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emergent Vegetation | Woody Vegetation | |||
| 1 | Phalacrocorax carbo | Trees in wetlands; artificial land islands with woody vegetation. | - | Salix babylonica (Rotbav) and S. fragilis (dead trees, Dumbrăvița). |
| 2 | Microcarbo pygmaeus * | Shrubs in wetlands. | - | Salix cinerea. |
| 3 | Ardea cinerea | Reed/reedmace beds; shrubs or trees in wetlands; mature pure oak forest. | Phragmites australis, Typha sp. | Salix cinerea, S. fragilis, Quercus robur. |
| 4 | Ardea purpurea * | Reed/reedmace beds. | Phragmites australis, Typha sp. | - |
| 5 | Ardea alba * | Reedbed; shrubs or trees in wetlands. | Phragmites australis. | Salix cinerea. |
| 6 | Egretta garzetta * | Reedbed; shrubs or trees in wetlands; artificial land islands with woody vegetation. | Phragmites australis. | Salix cinerea. |
| 7 | Nycticorax nycticorax * | Reedbed; shrubs or trees in wetlands; artificial land islands with woody vegetation. | Phragmites australis. | Salix cinerea, Prunus cerasifera, Sambucus nigra. |
| 8 | Ardeola ralloides * | Reedbed; shrubs or trees in wetlands; artificial land islands with woody vegetation. | Phragmites australis. | Salix cinerea. |
| Colony Type | Location | Nearest Distance (m) from Edge of Colony to: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | D | Dam | Building | National Road (DN13) | Local Road (DJ 112C) | Cement Factory | |
| Mixed | x | 25 | 130 | 260 | |||
| Ardea purpurea (fish farm) | x | 30 | 350 | 480 | |||
| Ardea purpurea (marsh) | x | 90 | 225 | ||||
| Ardea alba (marsh) | x | 110 | 250 | ||||
| Mixed | x | 50 | 780 | 800 | |||
| Ardea alba | x | 40 | 880 | ||||
| Ardea cinerea (oak forest) | x | 330 | 60 | ||||
| Phalacrocorax carbo | x | 105 | 175 | 300 | |||
| Phalacrocorax carbo | x | 150 | 880 | ||||
| Species | No. of Pairs/Decade within Study Area | No. of Pairs on National Level [5] (Period: 2008–2013) | Percentage of National Population (%) [5] | No. of Pairs on National Level [6] (Period: 2013–2018) | Percentage of National Population (%, 2020) [6] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| Phalacrocorax carbo | 10 | 10 | 12,000 | 20,000 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 12,000 | 20,000 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| Microcarbo pygmaeus | 5 | 15 | 9400 | 10,500 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 9400 | 10,500 | 0.05 | 0.14 |
| Ardea cinerea | 40 | 60 | 4500 | 6000 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 4500 | 10,000 | 0.88 | 0.60 |
| Ardea purpurea | 16 | 24 | 850 | 1500 | 1.88 | 1.60 | 1797 | 7830 | 0.89 | 0.30 |
| Ardea alba | 1 | 21 | 210 | 370 | 0.47 | 5.67 | 400 | 1000 | 0.25 | 2.10 |
| Egretta garzetta | 4 | 40 | 4000 | 8000 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 4000 | 8000 | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| Nycticorax nycticorax | 8 | 70 | 4000 | 8000 | 0.20 | 0.87 | 4000 | 8000 | 0.20 | 0.87 |
| Ardeola ralloides | 2 | 6 | 2500 | 5500 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 2700 | 6000 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ionescu, D.T.; Hodor, C.V.; Petritan, I.C. Artificial Wetlands as Breeding Habitats for Colonial Waterbirds within Central Romania. Diversity 2020, 12, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100371
Ionescu DT, Hodor CV, Petritan IC. Artificial Wetlands as Breeding Habitats for Colonial Waterbirds within Central Romania. Diversity. 2020; 12(10):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100371
Chicago/Turabian StyleIonescu, Dan Traian, Călin Vasile Hodor, and Ion Cătălin Petritan. 2020. "Artificial Wetlands as Breeding Habitats for Colonial Waterbirds within Central Romania" Diversity 12, no. 10: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100371
APA StyleIonescu, D. T., Hodor, C. V., & Petritan, I. C. (2020). Artificial Wetlands as Breeding Habitats for Colonial Waterbirds within Central Romania. Diversity, 12(10), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100371