tert-Butyl (6-(3-(3-Fluorophenyl)ureido)hexyl)carbamate
Abstract
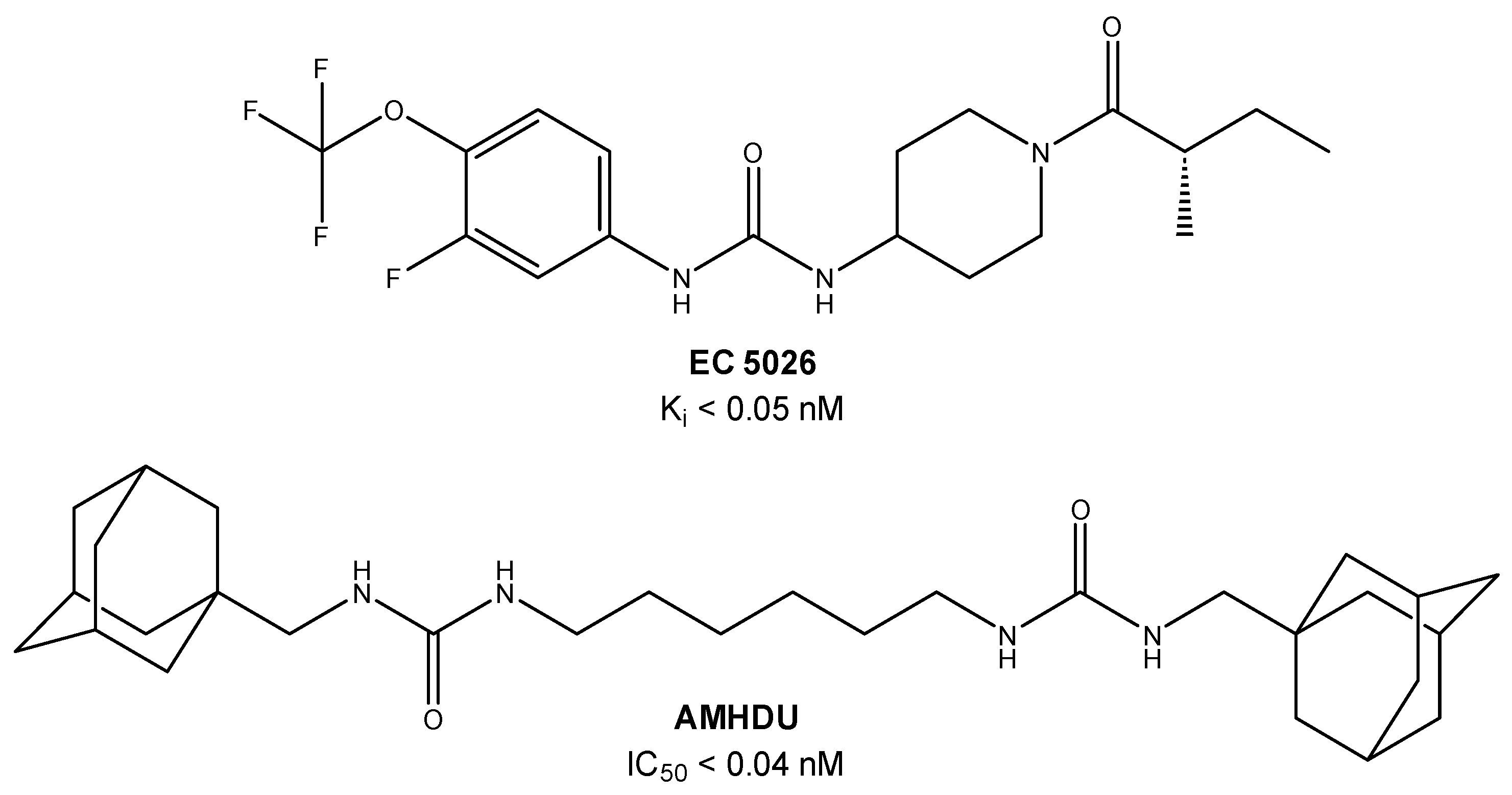
1. Introduction
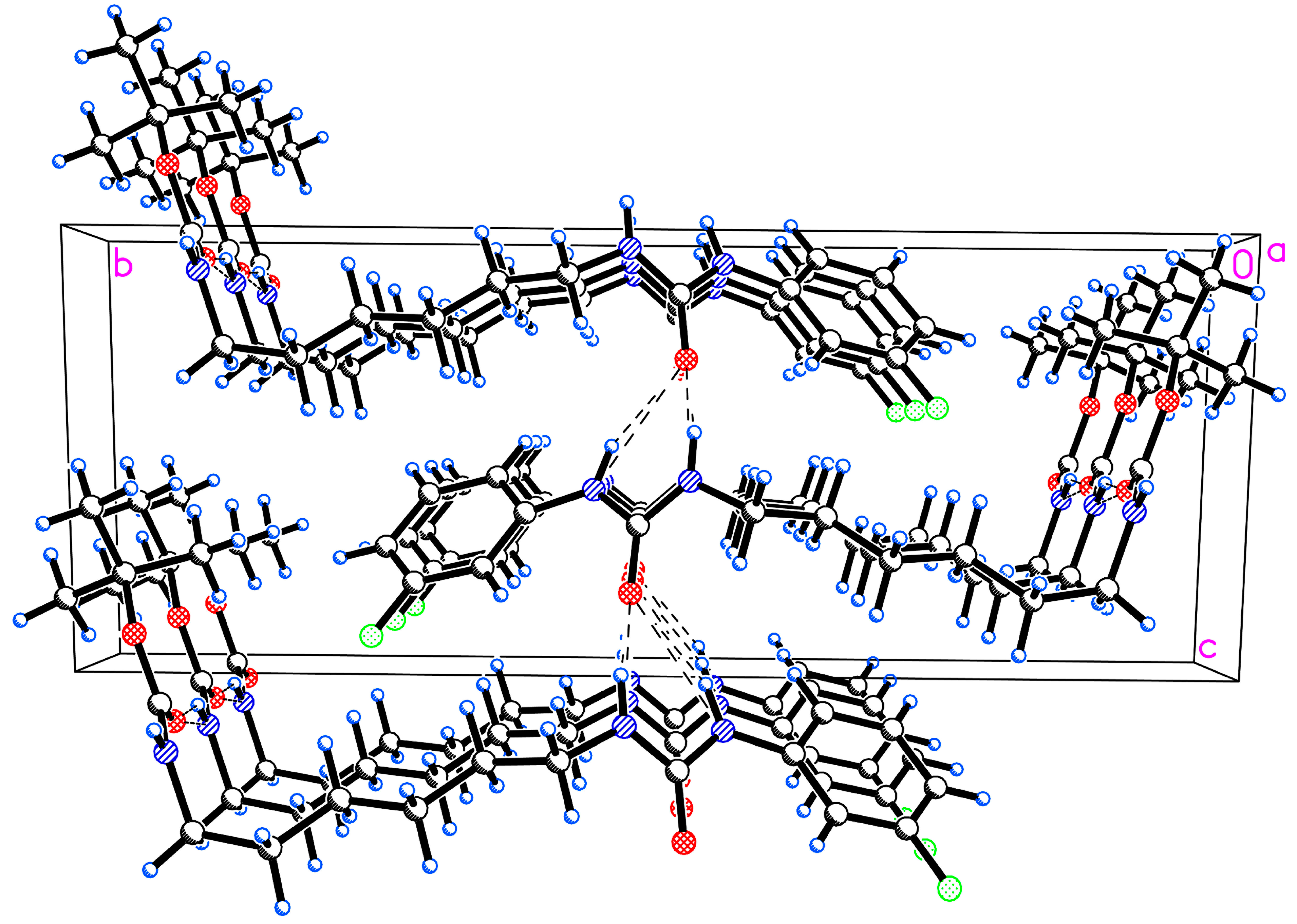
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. X-Ray Crystallography
3.2. Synthesis of tert-Butyl (6-(3-(3-Fluorophenyl)ureido)hexyl)carbamate (3)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, A.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; McReynolds, C.B.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; He, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. The soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor TPPU improves comorbidity of chronic pain and depression via the AHR and TSPO signaling. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codony, S.; Entrena, J.M.; Calvó-Tusell, C.; Jora, B.; González-Cano, R.; Osuna, S.; Corpas, R.; Morisseau, C.; Pérez, B.; Barniol-Xicota, M.; et al. Synthesis, In Vitro Profiling, and In Vivo Evaluation of Benzohomoadamantane-Based Ureas for Visceral Pain: A New Indication for Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 13660–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wagner, K.M.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of the Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase as an An-algesic Strategy: A Review of Preclinical Evidence. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Morisseau, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Hammock, B.D.; Ma, X.-C. Discovery of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors from Chemical Synthesis and Natural Products. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 184–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McReynolds, C.B.; Yang, J.; Guedes, A.; Morisseau, C.; Garcia, R.; Knych, H.; Tearney, C.; Hamamoto, B.; Hwang, S.H.; Wagner, K.; et al. Species Differences in Metabolism of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor, EC1728, Highlight the Importance of Clinically Relevant Screening Mechanisms in Drug Development. Molecules 2021, 26, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammock, B.D.; McReynolds, C.B.; Wagner, K.; Buckpitt, A.; Cortes-Puch, I.; Croston, G.; Lee, K.S.S.; Yang, J.; Schmidt, W.K.; Hwang, S.H. Movement to the Clinic of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor EC5026 as an Analgesic for Neuropathic Pain and for Use as a Nonaddictive Opioid Alternative. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1856–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babkov, D.; Eliseeva, N.; Adzhienko, K.; Bagmetova, V.; Danilov, D.; McReynolds, C.B.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Burmistrov, V. Preclinical Evaluation of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor AMHDU against Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmistrov, V.V.; Morisseau, C.; Danilov, D.V.; Gladkikh, B.P.; D’yachenko, V.S.; Zefirov, N.A.; Zefirova, O.N.; Butov, G.M.; Hammock, B.D. Fluorine and chlorine substituted adamantyl-urea as molecular tools for inhibition of human soluble epoxide hydrolase with picomolar efficacy. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2274797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Qiu, Z. Concise Syntheses and Antitumor Activities of A-Hydroxy(Mercapto)Amide Derivatives. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 3219–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, L.A.; Gulam, R.; Mueller, A.; O’Connell, M.A.; Searcey, M. Design and Synthesis of Threading Intercalators to Target DNA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6956–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of Silver and Molybdenum Microfocus X-Ray Sources for Single-Crystal Structure Determination. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallographica. Sect. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallographica. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapravdina, D.; Eremeev, K.; Yakushev, I.A.; Maksimova, A.; Bynerie, J.; Burmistrov, V. tert-Butyl (6-(3-(3-Fluorophenyl)ureido)hexyl)carbamate. Molbank 2025, 2025, M1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1984
Zapravdina D, Eremeev K, Yakushev IA, Maksimova A, Bynerie J, Burmistrov V. tert-Butyl (6-(3-(3-Fluorophenyl)ureido)hexyl)carbamate. Molbank. 2025; 2025(2):M1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1984
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapravdina, Daria, Konstantin Eremeev, Ilya A. Yakushev, Anna Maksimova, Jourdan Bynerie, and Vladimir Burmistrov. 2025. "tert-Butyl (6-(3-(3-Fluorophenyl)ureido)hexyl)carbamate" Molbank 2025, no. 2: M1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1984
APA StyleZapravdina, D., Eremeev, K., Yakushev, I. A., Maksimova, A., Bynerie, J., & Burmistrov, V. (2025). tert-Butyl (6-(3-(3-Fluorophenyl)ureido)hexyl)carbamate. Molbank, 2025(2), M1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1984






