17β-Hydroxy-2-oxa-5α-androstan-3-one
Abstract
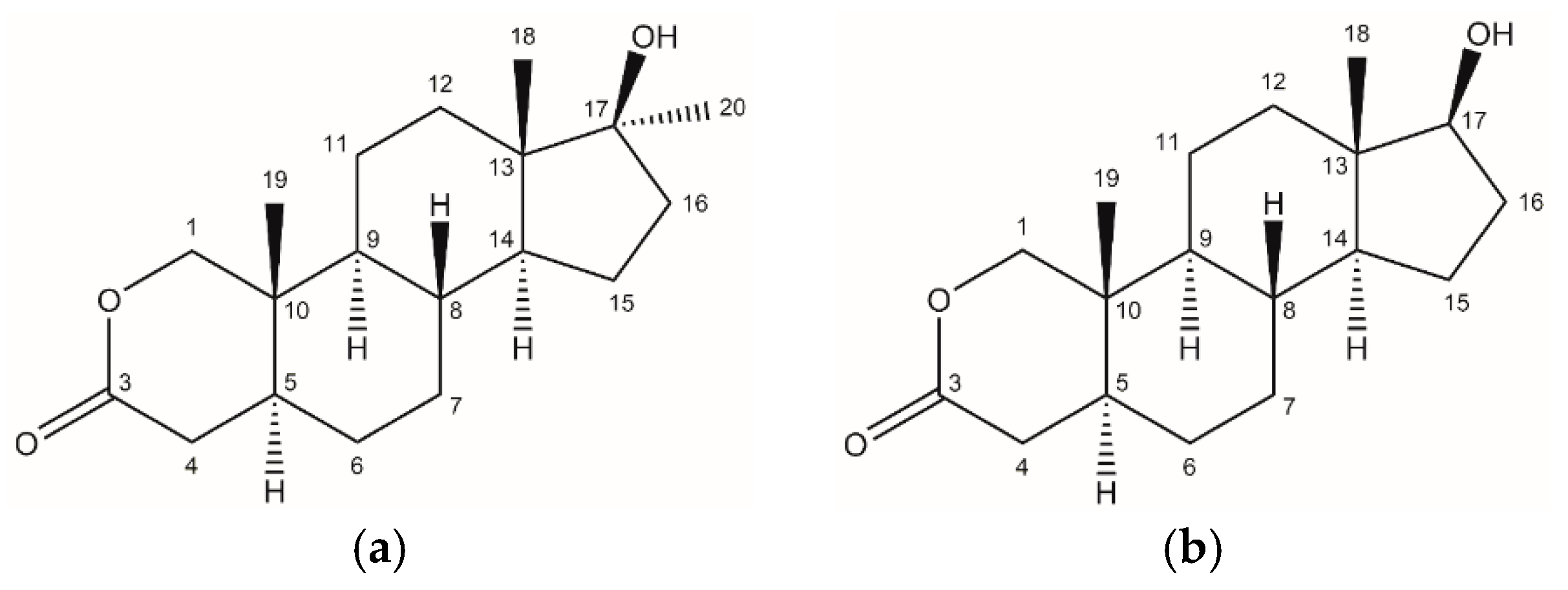
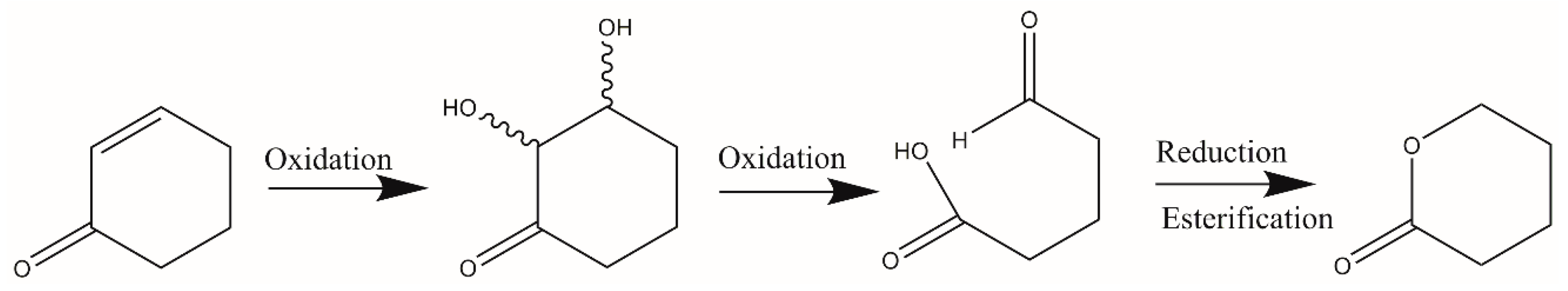
1. Introduction
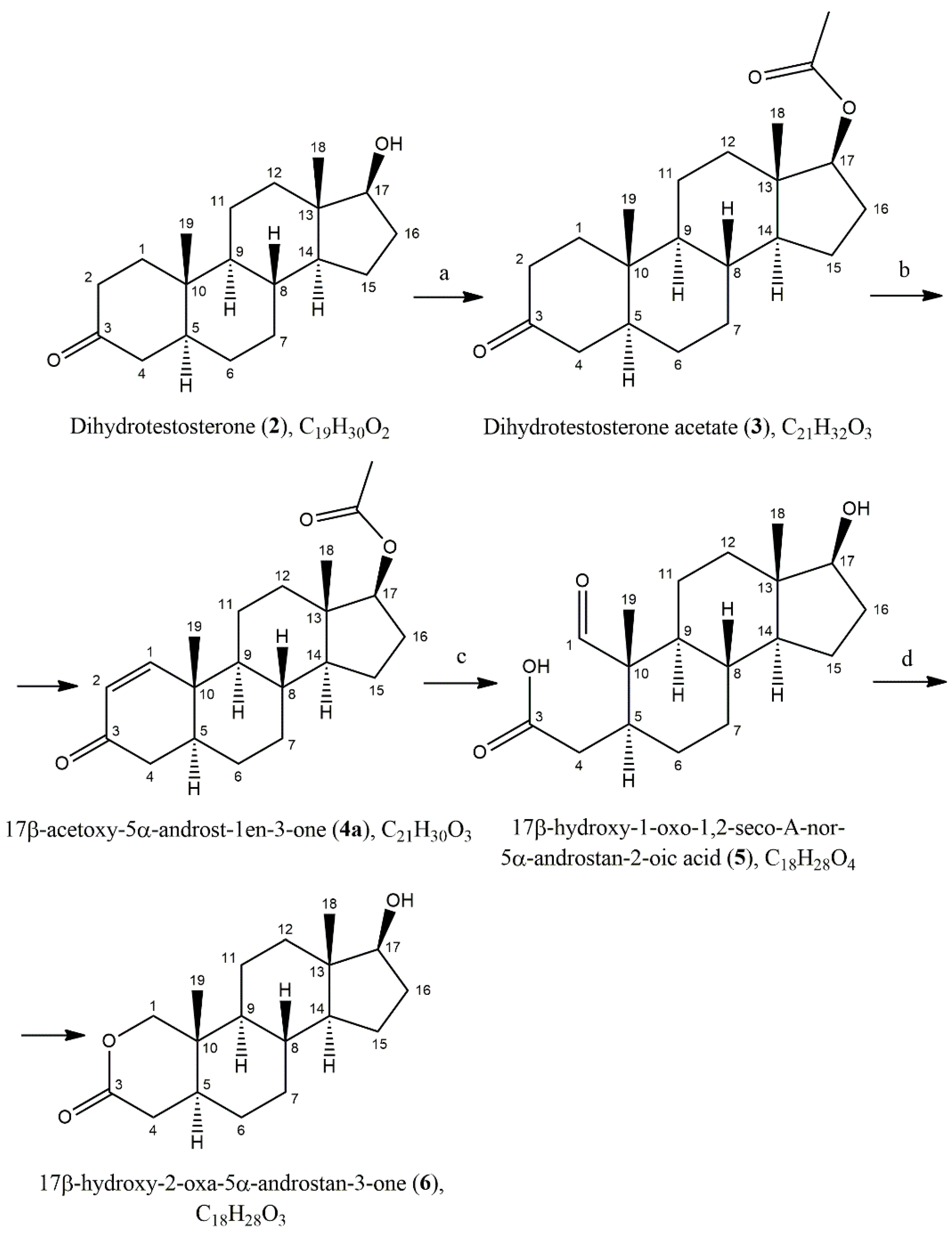
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Procedures
3.2.1. Dihydrotestosterone Acetate (3)
3.2.2. 17β-Acetoxy-5α-androst-1en-3-one (4a) and (4b)
3.2.3. 17β-Hydroxy-1-oxo-1,2-seco-A-nor-5α-androstan-2-oic Acid (5)
3.2.4. 17β-Hydroxy-2-oxa-5α-androstan-3-one (6)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charles, K. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Vida, J.A. Androgens and Anabolic Agents: Chemistry and Pharmacology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, M.; Minot, A.S.; Liddle, G.W. Oxandrolone: A potent anabolic steroid of novel chemical configuration. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1962, 22, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutting, E.; Calhoun, D. Estradienes and 2-Oxaestradienes. Potent Oral Anabolic-Androgenic Agents. Endocrinology 1969, 84, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, P.C.A.; Yarrow, M. Anabolic steroid abuse: Physiological and anaesthetic considerations. Anaesthesia 2005, 60, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, H. Effects of various 17-alpha-alkyl substitutions and structural modifications of steroids on sulfobromophthalein (BSP) retention in rabbits. Steroids 1966, 7, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappo, R.; Jung, C. 2-oxasteroids: A new class of biologically active compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 1962, 9, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S. Baeyer-Villiger Reaction of 2-Oxo-A-norsteroids. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1964, 12, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rogic, M. Reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide with six- and five-membered steroid lactones. Bull. Chem. Soc. Serb. 1964, 29, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.; Ringold, H. Applications of high-potential quinones. Part I. The mechanism of dehydrogenation of steroidal ketones by 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyanobenzoquinone. J. Chem. Soc. C 1967, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRheenen, V.; Kelly, R.; Cha, D. An improved catalytic OsO4 oxidation of olefins to cis-1,2-glycol using tertiary amine as the oxidant. Tetr. Lett. 1976, 17, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Takegawa, S.; Koizumi, N.; Yamakoshi, N.; Shimazawa, E. Antiandrogen. I. 2-azapregnane and 2-oxapregnane steroids. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pappo, R.; Allen, D.; Lemieux, R.; Johnson, W. Osmium Tetroxide-Catalyzed Periodate Oxidation of Olefinic Bonds. J. Org. Chem. 1956, 21, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, C. O-hetero-analogues of steroids. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1951, 70, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, N.; Ralls, J. 4-Oxasteroid Analogs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, K.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; You, Q.; Xiao, H.; Xiang, H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 3-oxo-4-oxa-5α-androst-17β-amide derivatives as dual 5α-reductase inhibitors and androgen receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4212–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.; Moser, B.; Mendonça, R.; Knight, J.; Hogan, F. The cephalostatins. 22. synthesis of bis-steroidal pyrazine pyrones. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foell, T.; Smith, L. 1-Fluoro Steroids. II. 1ξ-Fluoro-5α-androst-2-en-17β-ol Acetate. J. Nat. Prod. 1966, 9, 953–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukacs, G.; Neszmelyi, A. Natural anubdance 13C-13C coupling constants in a steroid. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1981, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, J.; Hampel, B. Die kernresonanzspektren von steroiden in polaren lösungsmitteln—II: Pyridin. Tetrahedron 1966, 22, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Sollman, P. 17-Oxygenated-2-Thia-5alpha-Androstanes and Derivatives Thereof. U.S. Patent US3281431A, 25 October 1966. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoyanova, S.; Dinkov, G.; Bogdanov, M.G. 17β-Hydroxy-2-oxa-5α-androstan-3-one. Molbank 2024, 2024, M1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1935
Stoyanova S, Dinkov G, Bogdanov MG. 17β-Hydroxy-2-oxa-5α-androstan-3-one. Molbank. 2024; 2024(4):M1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1935
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoyanova, Savina, Georgi Dinkov, and Milen G. Bogdanov. 2024. "17β-Hydroxy-2-oxa-5α-androstan-3-one" Molbank 2024, no. 4: M1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1935
APA StyleStoyanova, S., Dinkov, G., & Bogdanov, M. G. (2024). 17β-Hydroxy-2-oxa-5α-androstan-3-one. Molbank, 2024(4), M1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1935




