Evaluation of Systemic Injury in Calves with Rotavirus-Induced Diarrhea Using Sensitive Biomarkers and Immunopathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biochemical, Biomarker, and Clinical Examination Findings
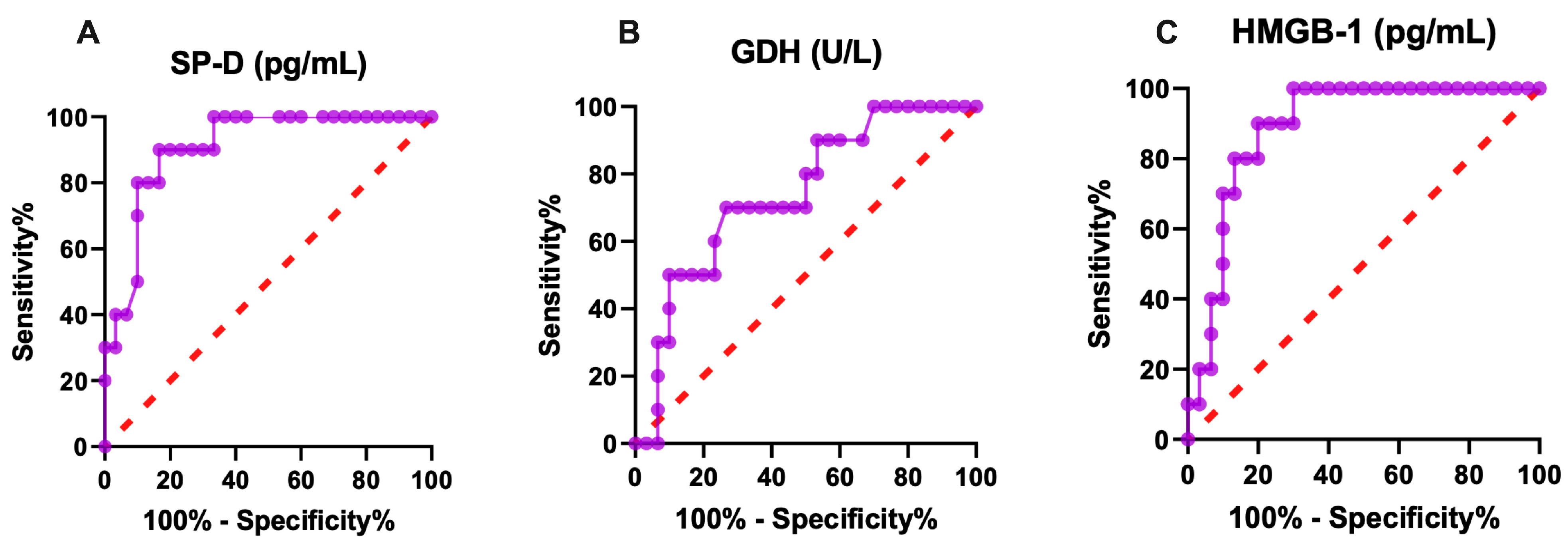
2.2. The Receiver-Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC) Analysis of Lung and Liver-Specific Biomarkers
2.3. Correlation Analysis
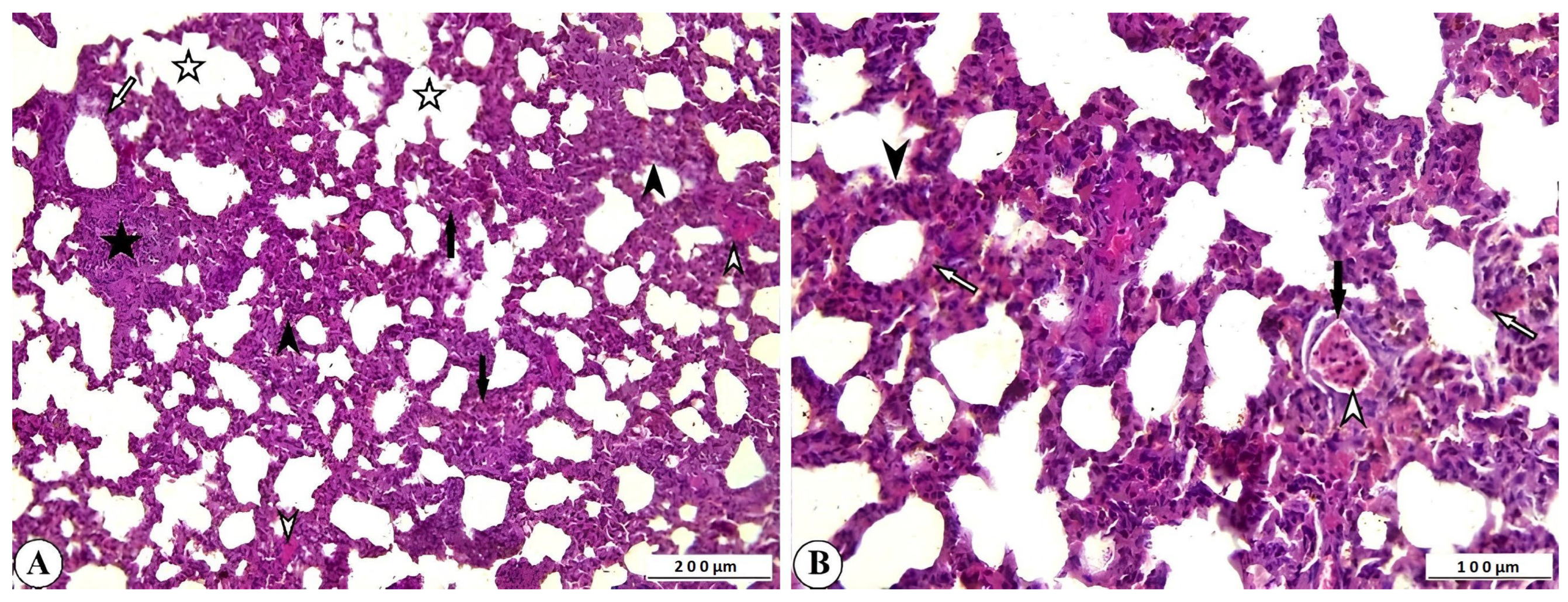
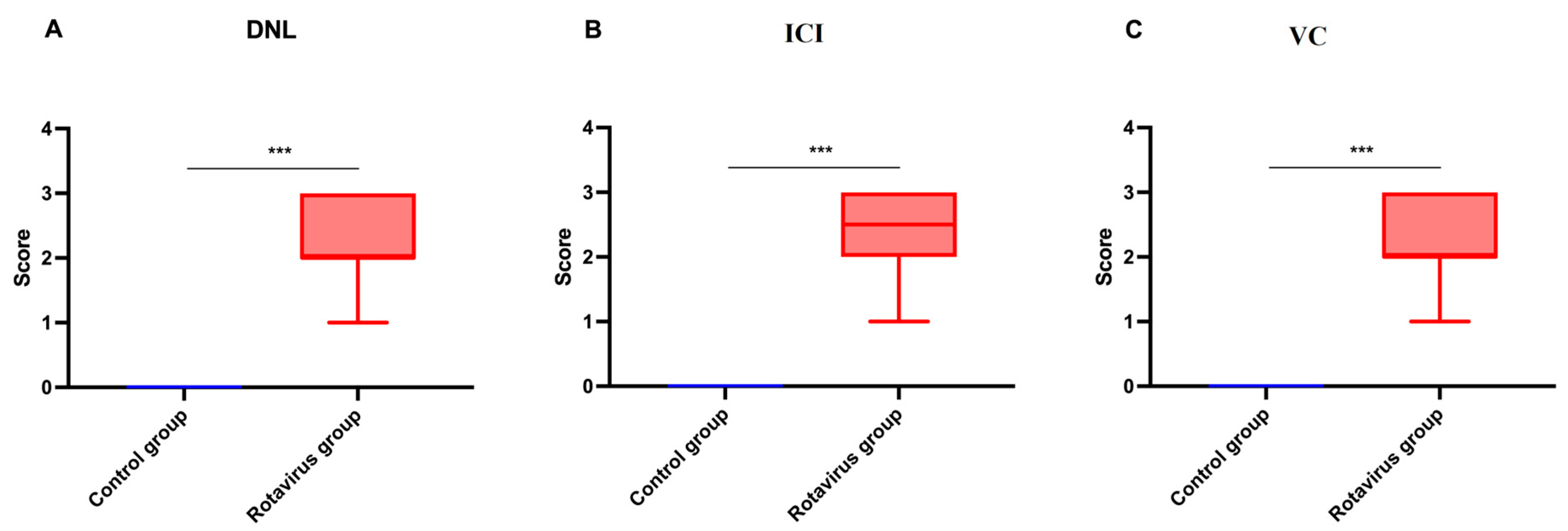
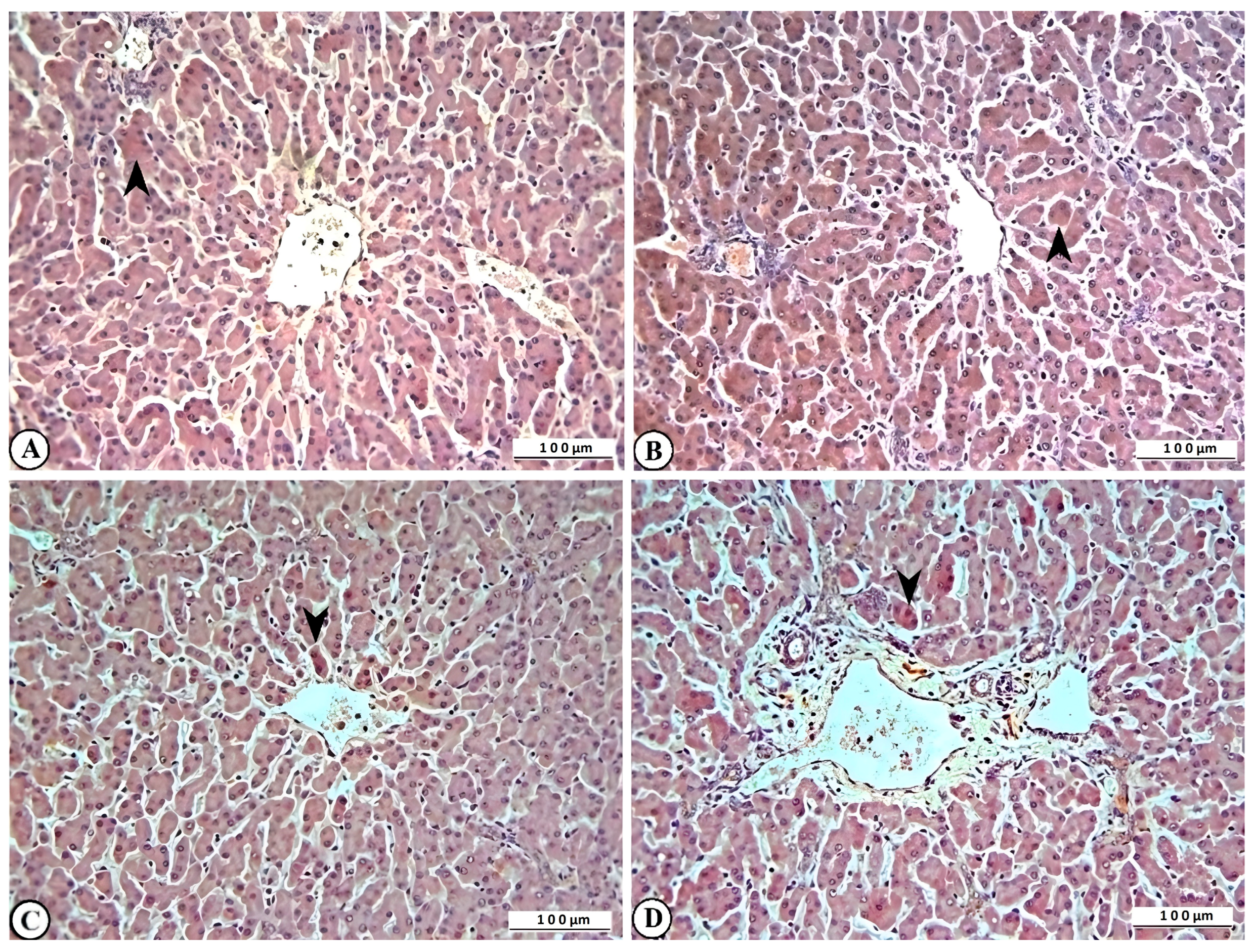
2.4. Histopathological Findings
2.5. Immunohistochemical Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Grouping
4.2. Healthy Calves Group
4.3. Rotavirus-Infected Calves Group
4.4. Sample Collection and Laboratory Analysis
4.5. Histopathological Examination
4.6. Immunohistochemical Examination
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMGB-1 | High mobility group box |
| SP-D | Surfactant Protein D |
| GDH | Glutamate dehydrogenase |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| γ-H2AX | γ-phosphorylated form of histone H2AX |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| HCT | Hematocrit |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| HSP-27 | Heat shock protein-27 |
| CASP-3 | Caspase-3 |
| ROC | Receiver-operating characteristic curve |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
References
- Uztimur, M.; Kizil, O.; Akbulut, H.H. Immunophenotyping of peripheral circulating lymphocytes and serum selenium levels in calves with neonatal diarrhea. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2024, 269, 110728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uztimur, M.; Sengul, A.E.; Unal, C.N. Evaluation of serum serotonin as a biomarker of intestinal inflammation in calves. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2025, 284, 110947, Erratum in Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2025, 285, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.I.; Yoon, K.J. An overview of calf diarrhea—Infectious etiology, diagnosis, and intervention. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehta, A.; El-Zahar, H.; Mansour, A.; Mustafa, B.; Shety, T. Clinical, hematological and some biochemical alterations during diarrhea in Friesian calves naturally infected with E. coli and Salmonella. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, M.; Yildiz, R.; Hatipoglu, F.; Baspinar, N.; Ider, M.; Uney, K.; Erturk, A.; Durgut, M.K.; Terzi, F. Use of intestine-related biomarkers for detecting intestinal epithelial damage in neonatal calves with diarrhea. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 81, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantell, L.L.; Parrish, W.R.; Ulloa, L. Hmgb-1 as a therapeutic target for infectious and inflammatory disorders. Shock 2006, 25, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, U.; Wang, H.; Palmblad, K.; Aveberger, A.C.; Bloom, O.; Erlandsson-Harris, H.; Janson, A.; Kokkola, R.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; et al. High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Svetkauskaite, D.; He, Q.; Kim, J.Y.; Strassheim, D.; Ishizaka, A.; Abraham, E. Involvement of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in cellular activation by high mobility group box 1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7370–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, M.T.; Tracey, K.J. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): Nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liao, H.; Ochani, M.; Justiniani, M.; Lin, X.; Yang, L.; Al-Abed, Y.; Wang, H.; Metz, C.; Miller, E.J.; et al. Cholinergic agonists inhibit HMGB1 release and improve survival in experimental sepsis. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bloom, O.; Zhang, M.; Vishnubhakat, J.M.; Ombrellino, M.; Che, J.; Frazier, A.; Yang, H.; Ivanova, S.; Borovikova, L.; et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 1999, 285, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, J.; Qiang, X.; Czura, C.J.; Ochani, M.; Ochani, K.; Ulloa, L.; Yang, H.; Tracey, K.J.; Wang, P.; et al. Suppression of HMGB1 release by stearoyl lysophosphatidylcholine:an additional mechanism for its therapeutic effects in experimental sepsis. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Sano, H.; Chiba, H.; Kuroki, Y. Pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D: Innate immune functions and biomarkers for lung diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Pabon, M.; Choi, A.M.K.; Siempos, I.I.; Fredenburgh, L.E.; Baron, R.M.; Jeon, K.; Chung, C.R.; Yang, J.H.; Park, C.M.; et al. Plasma surfactant protein-D as a diagnostic biomarker for acute respiratory distress syndrome: Validation in US and Korean cohorts. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peukert, K.; Seeliger, B.; Fox, M.; Feuerborn, C.; Sauer, A.; Schuss, P.; Schneider, M.; David, S.; Welte, T.; Putensen, C.; et al. SP-D Serum Levels Reveal Distinct Epithelial Damage in Direct Human ARDS. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, C.; Krotzsch, E.; Jimenez-Alvarez, L.A.; Ramirez-Martinez, G.; Marquez-Garcia, J.E.; Cruz-Lagunas, A.; Moran, J.; Hernandez, C.; Sierra-Vargas, P.; Avila-Moreno, F.; et al. Serum surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a prognostic marker of poor outcome in patients with A/H1N1 virus infection. Lung 2015, 193, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.W.; Ware, L.B.; Greene, K.E.; Nuckton, T.J.; Eisner, M.D.; Matthay, M.A. Prognostic value of surfactant proteins A and D in patients with acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, M.; Scoville, E.A.; Grant, S.; Korfhagen, T.; Brondyk, W.; Scheule, R.K.; Whitsett, J.A. Surfactant protein-D and surfactant inhibit endotoxin-induced pulmonary inflammation. Chest 2007, 132, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamber, S.S.; Bansal, P.; Sharma, S.; Singh, R.B.; Sharma, R. Biomarkers of liver diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 7815–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, R.J.; Watkins, P.B. The transformation in biomarker detection and management of drug-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulin, P.; Hornby, R.J.; Auli, M.; Nordahl, G.; Antoine, D.J.; Starkey Lewis, P.; Goldring, C.E.; Park, B.K.; Prats, N.; Glinghammar, B.; et al. A longitudinal assessment of miR-122 and GLDH as biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury in the rat. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrill, A.H.; Eaddy, J.S.; Rose, K.; Cullen, J.M.; Ramanathan, L.; Wanaski, S.; Collins, S.; Ho, Y.; Watkins, P.B.; Lecluyse, E.L. Liver biomarker and in vitro assessment confirm the hepatic origin of aminotransferase elevations lacking histopathological correlate in beagle dogs treated with GABAA receptor antagonist NP260. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 277, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.L.; Li, A.F.; Chau, G.Y.; Chi, C.W.; Wu, C.W.; Huang, C.L.; Lui, W.Y. Prognostic significance of heat shock protein-27 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and its relation to histologic grading and survival. Cancer 2000, 88, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Kaviani, E.; Vakili, O.; Taheri-Anganeh, M.; Tahamtan, M.; Savardashtaki, A. Caspase-3: Structure, function, and biotechnological aspects. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Kono, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Taniguchi, T. The IL-2 receptor complex: Its structure, function, and target genes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 11, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, V.V.; Karaolanis, G.; Katafigiotis, I.; Anastasiou, I.; Patapis, P.; Dimitroulis, D.; Perrea, D. gamma-H2AX: Can it be established as a classical cancer prognostic factor? Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317695931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaios, D.; Foukas, P.G.; Kefala, M.; Hountis, P.; Trypsianis, G.; Panayiotides, I.G.; Chatzaki, E.; Pantelidaki, E.; Bouros, D.; Karakitsos, P.; et al. gamma-H2AX expression detected by immunohistochemistry correlates with prognosis in early operable non-small cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2012, 5, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantel, H.; Lugering, A.; Poremba, C.; Lugering, N.; Held, J.; Domschke, W.; Schulze-Osthoff, K. Caspase activation correlates with the degree of inflammatory liver injury in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2001, 34, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.; Ramirez, G.A.; Sarradell, J.; Andrada, M.; Lorenzo, H. Immunohistochemical labelling of cytokines in lung lesions of pigs naturally infected with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. J. Comp. Pathol. 2004, 130, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, D.; Hisaka, T.; Horiuchi, H.; Uchida, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Kawashima, Y.; Kinugasa, T.; Nakashima, O.; Yano, H.; Okuda, K.; et al. Expression of HSP27 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2016, 36, 3775–3779. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, Y.; Wakai, T.; Kubota, M.; Osawa, M.; Takamura, M.; Yamagiwa, S.; Aoyagi, Y.; Sanpei, A.; Fujimaki, S. DNA damage sensor gamma -H2AX is increased in preneoplastic lesions of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 597095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zuo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gao, C.; Chen, K.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Ouyang, P.; Deng, J.; Geng, Y.; et al. Hepatic histopathology and apoptosis in diet-induced-obese mice under Escherichia coli pneumonia. Aging 2019, 11, 2836–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L. Emerging Roles of High-mobility Group Box-1 in Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.; Miguel, M.A.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, S.S. Analysis of Fecal Microbial Changes in Young Calves Following Bovine Rotavirus Infection. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, D.J.; Williams, D.P.; Kipar, A.; Jenkins, R.E.; Regan, S.L.; Sathish, J.G.; Kitteringham, N.R.; Park, B.K. High-mobility group box-1 protein and keratin-18, circulating serum proteins informative of acetaminophen-induced necrosis and apoptosis in vivo. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 112, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andres, P.J.; Ferreiro, S.; Flores, A.; Garcia, A.; Henriquez-Camacho, C. Histological Assessment of Respiratory Tract and Liver of BALB/c Mice Nebulized with Tocilizumab. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, S.M.; Aljuaydi, S.H.; AbuBakr, H.O.; Tahoun, E.A.; Di Cerbo, A.; Alagawany, M.; Khalil, S.R.; Farag, M.R. Astaxanthin Mitigates Thiacloprid-Induced Liver Injury and Immunotoxicity in Male Rats. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomaker, S.; Warner, R.; Bock, J.; Johnson, K.; Potter, D.; Van Winkle, J.; Aubrecht, J. Assessment of emerging biomarkers of liver injury in human subjects. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 132, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, L.M. Two viruses causing diarrhoea in infant mice. In The Problems of Laboratory Animal Disease; Harris, R.J.C., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1962; pp. 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, J.G.; Matthijnssens, J.; Lee, J.H.; Bae, Y.C.; Alfajaro, M.M.; Park, S.I.; Kang, M.I.; Cho, K.O. Intestinal and extra-intestinal pathogenicity of a bovine reassortant rotavirus in calves and piglets. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzipori, S.; Smith, M.; Halpin, C.; Makin, T.; Krautil, F. Intestinal changes associated with rotavirus and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection in calves. Vet. Microbiol. 1983, 8, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, A.; Zabel, M.; Biczysko, W.; Wysocki, J.; Adamek, A.; Spachacz, R.; Surdyk-Zasada, J. Expression of cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha, and IL-2) in chronic hepatitis C: Comparative hybridocytochemical and immunocytochemical study in children and adult patients. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 52, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, S.E.; Patel, D.G.; Cheng, E.; Berkova, Z.; Hyser, J.M.; Ciarlet, M.; Finegold, M.J.; Conner, M.E.; Estes, M.K. Rotavirus viremia and extraintestinal viral infection in the neonatal rat model. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4820–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, D.J.; Dear, J.W.; Lewis, P.S.; Platt, V.; Coyle, J.; Masson, M.; Thanacoody, R.H.; Gray, A.J.; Webb, D.J.; Moggs, J.G.; et al. Mechanistic biomarkers provide early and sensitive detection of acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury at first presentation to hospital. Hepatology 2013, 58, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persad, R.; Liu, C.; Wu, T.T.; Houlihan, P.S.; Hamilton, S.R.; Diehl, A.M.; Rashid, A. Overexpression of caspase-3 in hepatocellular carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 861–867, Erratum in Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Kucukal, E.; Liu, S.; An, R.; Goreke, U.; Wulftange, W.J.; Sekyonda, Z.; Bode, A.; Little, J.A.; Manwani, D.; et al. A microfluidic device for assessment of E-selectin-mediated neutrophil recruitment to inflamed endothelium and prediction of therapeutic response in sickle cell disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 114921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ider, M.; Naseri, A.; Ok, M.; Gulersoy, E.; Bas, T.M.; Uney, K.; Parlak, T.M.; Abdelaziz, A. Serum sRAGE and sE-selectin levels are useful biomarkers of lung injury and prediction of mortality in calves with perinatal asphyxia. Theriogenology 2022, 181, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, Y.; Nezu, Y.; Komori, S.; Hara, Y.; Tagawa, M.; Ogawa, R. Evaluation of hepatosplanchnic circulation and intestinal oxygenation in dogs with a condition that mimicked septic shock induced by continuous infusion of a low dose of lipopolysaccharide. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, C.N.; Issï, M. Investigation of the relationship between serum endocan level and interleukin-6, procalcitonin, e-selectin in calves with diarrhea, according to the etiological factor. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2025, 286, 110979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, W.; Dong, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, J. Detection of Infectious Agents Causing Neonatal Calf Diarrhea on Two Large Dairy Farms in Yangxin County, Shandong Province, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 589126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berber, E.; Canakoglu, N.; Sozdutmaz, I.; Simsek, E.; Sursal, N.; Ekinci, G.; Kokkaya, S.; Arikan, E.; Ambarcioglu, P.; Goksu, A.G.; et al. Seasonal and Age-Associated Pathogen Distribution in Newborn Calves with Diarrhea Admitted to ICU. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canelli, E.; Ferrari, L.; Borghetti, P.; Candela, F.; Abiakam, N.S.; Bianchera, A.; Buttini, F.; Magi, G.E.; Sonvico, F.; Martelli, P.; et al. Nano-adjuvanted dry powder vaccine for the mucosal immunization against airways pathogens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1116722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uztimur, M.; Dortbudak, M.B. Evaluation of brain injury in goats naturally infected with Coenurus cerebralis; brain specific biomarkers, acute inflammation, and DNA oxidation. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 165, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uztimur, M.; Unal, C.N.; Dortbudak, M.B.; Firat, R.; Ekinci, A.I. Assessment of brain injury in cattle with Theileria annulata: Neuron-specific biomarkers, inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Vet. J. 2025, 309, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, G.E.; Mariotti, F.; Pallotta, L.; Di Cerbo, A.; Venanzi, F.M. Immunohistochemical Expression of p62 in Feline Mammary Carcinoma and Non-Neoplastic Mammary Tissue. Animals 2022, 12, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, Y.; Ozturk, M.; Dortbudak, M.B.; Mariotti, F.; Magi, G.E.; Di Cerbo, A. Astaxanthin Mitigates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Variables | Rotavirus Group | Control Group | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate (beats/minute) | 136 (100–180) | 125 (92–160) | 0.751 |
| Respiratory Frequency (respiratory rate/minute) | 34.66 (20–60) a | 45 (30–56) b | <0.05 |
| Body Temperature (°C) | 38.2 (35.5–40.4) | 38 (38.4–39.2) | 0.117 |
| HCT (%) | 34.33 (24–47) | 32.7 (24.2–40) | 0.235 |
| WBC (×109) | 18.64 (5.1–43.44) a | 10.2 (6.43–13.9) b | <0.001 |
| Blood pH | 7.13 (6.69–7.44) a | 7.36 (7.28–7.4) b | <0.001 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 13.94 (7.1–25.2) a | 26.41 (19.7–29.8) b | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 4.01 (1–7.6) a | 5.09 (3.7–6.1) b | <0.05 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 1.09 (0.63–1.33) a | 1.4 (1.37–1.55) b | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 131.69 (113–146) | 139 (125–141) | 0.133 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 5.55 (3.5–8.4) a | 4.65 (4.2–5.1) b | <0.05 |
| Chlorine (mmol/L) | 105.8 (81–140) | 95 (89–101) | 0.100 |
| Total protein (mg/dL) | 8.47 (6.39–10.32) | 8.84 (6.61–9.81) | 0.126 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 3.85 (3.16–4.49) | 4.07 (2.78–4.75) | 0.180 |
| Creatin (mmol/L) | 1.57 (1.1–2.31) | 1.4 (1.2–1.67) | 0.229 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 40.56 (8.07–91.27) | 33.13 (20.02–42.21) | 0.333 |
| ALT (U/L) | 18.04 (6.16–60) a | 8.32 (6.11–12.14) b | <0.01 |
| AST (U/L) | 87.49 (29.62–491.38) a | 41.38 (32.85–70.35) b | <0.05 |
| GGT (U/L) | 210.19 (17–2691) | 73.76 (10.87–153.9) | 0.126 |
| Variables | Rotavirus Group | Control Group | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-selectin (pg/mL) | 179.52 (76.55–260.86) | 173.5 (131.82–197.77) | 0.803 |
| HMGB-1 (pg/mL) | 682.76 (154–1028.2) a | 477.94 (348–612) b | <0.001 |
| SP-D (pg/mL) | 2.32 (1.13–3.15) a | 1.36 (0.8–2.19) b | <0.001 |
| GDH (U/L) | 1.39 (0.7–2.51) a | 1.09 (0.8–1.5) b | <0.05 |
| Variables | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cut-Off Point | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP-D (pg/mL) | 0.91 | 80 | 93 | 1.955 | <0.001 |
| GDH (U/L) | 0.74 | 70 | 70 | 1.185 | <0.05 |
| HMGB-1 (pg/mL) | 0.89 | 80 | 80 | 518.8 | <0.01 |
| Histological Feature | Score | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Degenerative-necrotic lesions | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Inflammatory cell infiltration | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Vascular changes | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Emphysema | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Interalveolar thickening | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Lymphoid hyperplasia | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Fibromuscular hypertrophy | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Atelectasis | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| IL-2 | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| HSP-27 | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| CASP-3 | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| γ-H2AX | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Uztimür, M.; Ünal, C.N.; Dörtbudak, M.B.; Bisanti, D.; Di Cerbo, A. Evaluation of Systemic Injury in Calves with Rotavirus-Induced Diarrhea Using Sensitive Biomarkers and Immunopathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010065
Uztimür M, Ünal CN, Dörtbudak MB, Bisanti D, Di Cerbo A. Evaluation of Systemic Injury in Calves with Rotavirus-Induced Diarrhea Using Sensitive Biomarkers and Immunopathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleUztimür, Murat, Cennet Nur Ünal, Muhammet Bahaddin Dörtbudak, Davide Bisanti, and Alessandro Di Cerbo. 2026. "Evaluation of Systemic Injury in Calves with Rotavirus-Induced Diarrhea Using Sensitive Biomarkers and Immunopathology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010065
APA StyleUztimür, M., Ünal, C. N., Dörtbudak, M. B., Bisanti, D., & Di Cerbo, A. (2026). Evaluation of Systemic Injury in Calves with Rotavirus-Induced Diarrhea Using Sensitive Biomarkers and Immunopathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010065







