The Myeloid Biomarker MS4A6A Drives an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma via Activation of the PGE2 Signaling Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
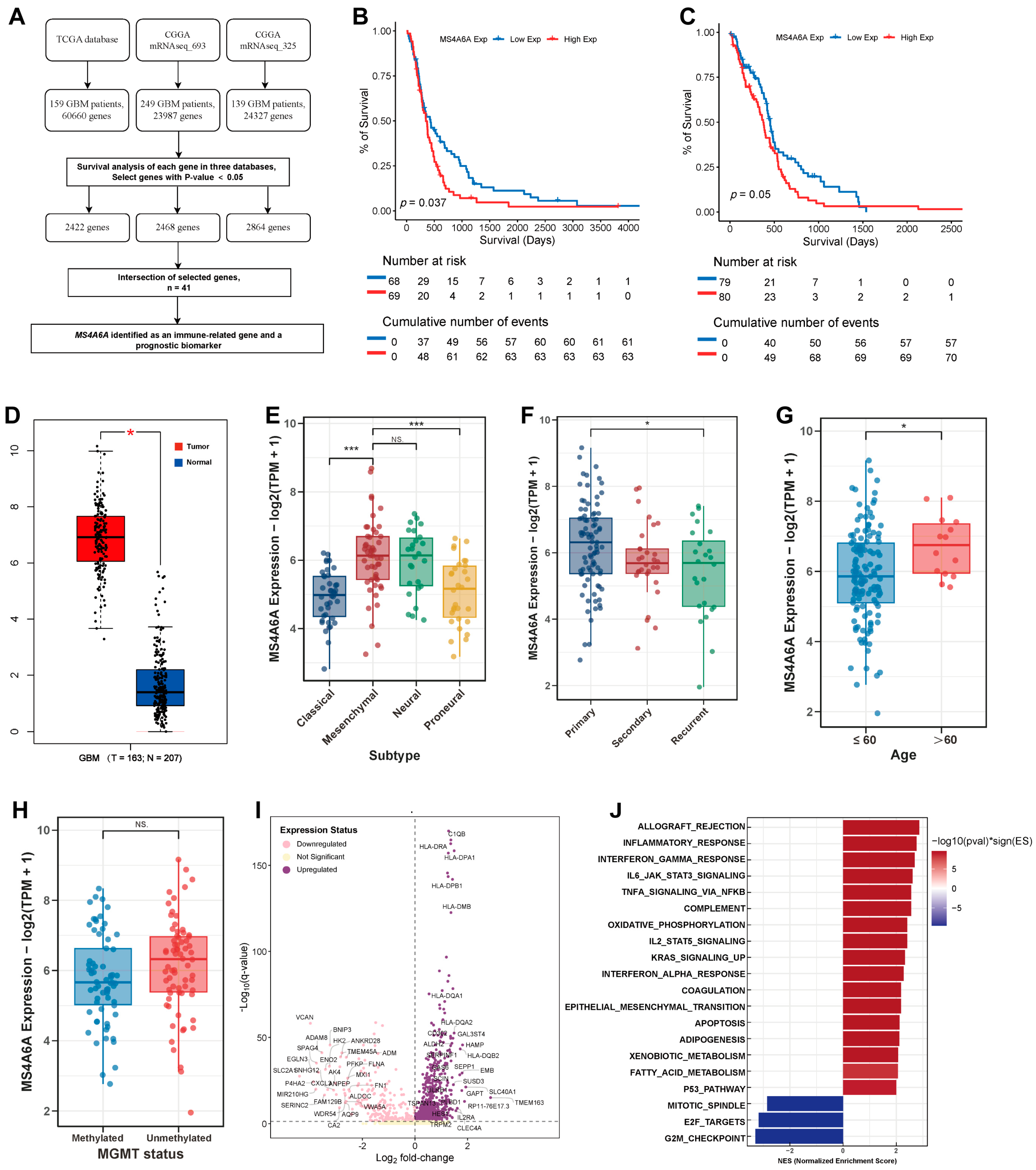
2.1. Identification of MS4A6A as an Immune-Related Prognostic Biomarker in GBM
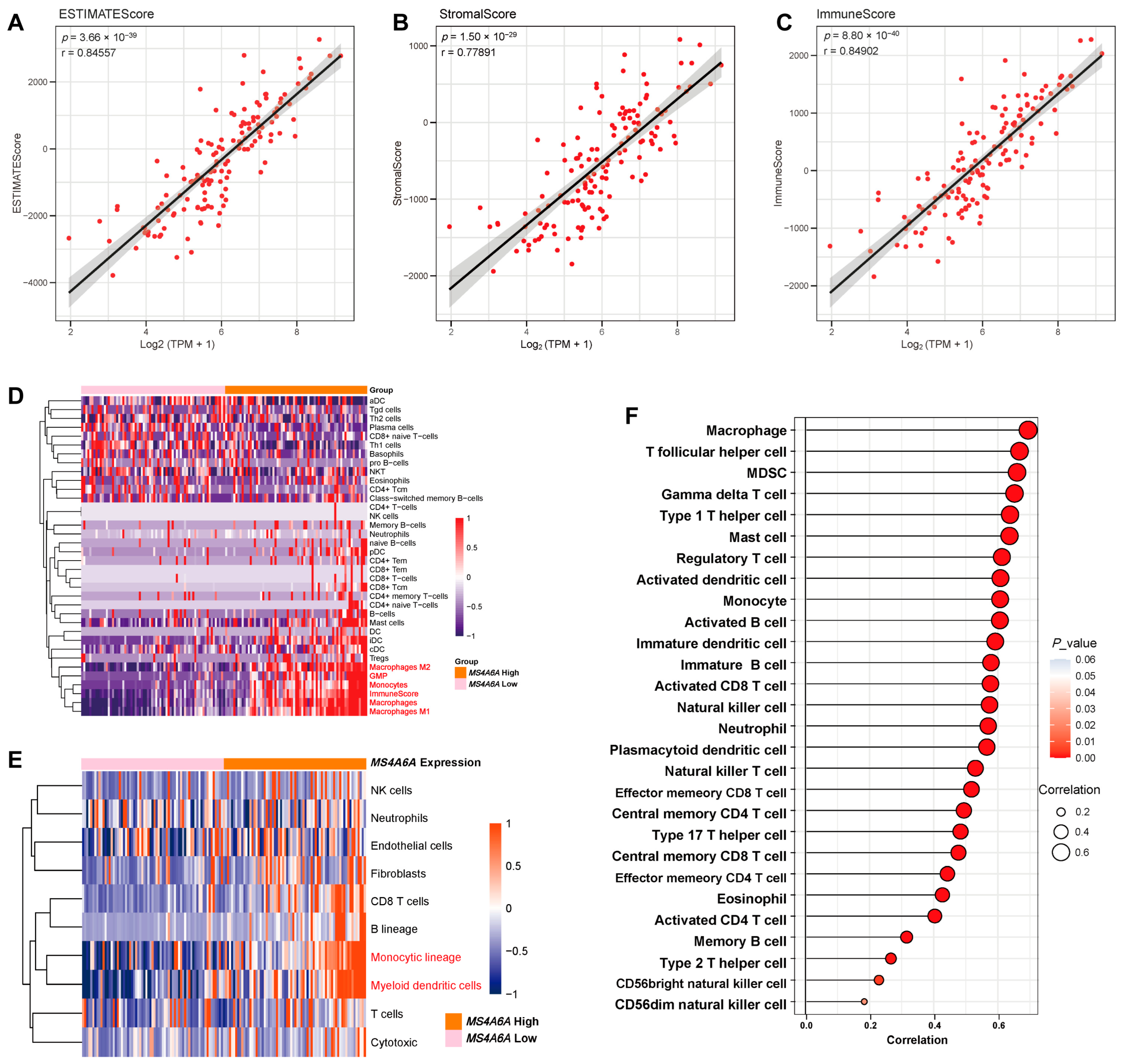
2.2. MS4A6A Associates with Immune and Stromal Enrichment in the GBM Microenvironment
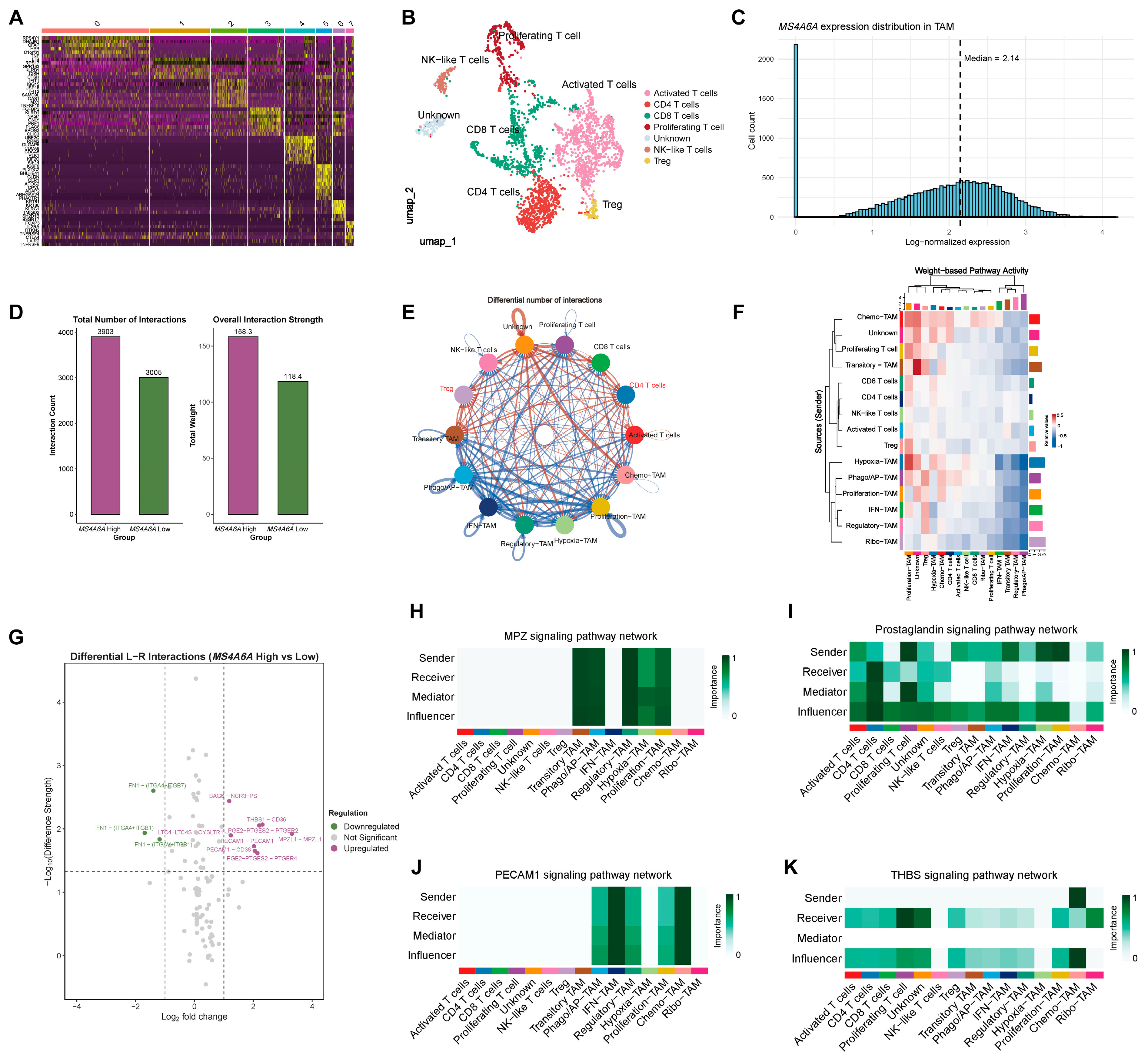
2.3. Single-Cell Atlas Localizes MS4A6A to TAMs and Reveals State-Specific Biological Programs
2.4. T-Cell Atlas and CellChat Highlight Strengthened Myeloid–T-Cell Communication in the MS4A6A-High Condition
2.5. Spatial Enrichment in Vascular Niches and Nomination of Pathway-Targeted Vulnerabilities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
4.2. Differential Expression and Survival Analysis of MS4A6A
4.3. Functional Enrichment, Immune Infiltration, and GSEA/Correlation Analyses
4.4. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis and Cell-Type Annotation
4.5. Single-Cell Resolution Analysis of MS4A6A in TAM Subpopulations
4.6. Cell–Cell Communication Analysis
4.7. Spatial Transcriptomic Localization and Drug Sensitivity Prediction
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaff, L.R.; Mellinghoff, I.K. Glioblastoma and Other Primary Brain Malignancies in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K.; et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients With Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, M.; Ding, F.; Zheng, X.; Sun, S.; Du, J. Exploring tumor-associated macrophages in glioblastoma: From diversity to therapy. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhong, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Tong, A.; Zhou, L. Tumor-associated microglia and macrophages in glioblastoma: From basic insights to therapeutic opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 964898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Pang, L.; Dunterman, M.; Lesniak, M.S.; Heimberger, A.B.; Chen, P. Macrophages and microglia in glioblastoma: Heterogeneity, plasticity, and therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e163446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Berglund, A.E.; Macaulay, R.J.; Mule, J.J.; Etame, A.B. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Glioblastoma: Mechanisms of Tumor Progression and Therapeutic Strategies. Cells 2025, 14, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wu, H.; Colt, M.; Guo, X.; Pluimer, B.; Zeng, J.; Dong, S.; Zhao, Z. Microglia and its Genetics in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2021, 18, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunez, C.; Boada, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Gayan, J.; Ramirez-Lorca, R.; Marin, J.; Hernandez, I.; Moreno-Rey, C.; Moron, F.J.; Lopez-Arrieta, J.; et al. The membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A (MS4A) gene cluster contains a common variant associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Med. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jun, G.R.; Chung, J.; Zhang, X.; Kunkle, B.W.; Naj, A.C.; White, C.C.; Bennett, D.A.; De Jager, P.L.; Alzheimer’s Disease Genetics Consortium; et al. CpG-related SNPs in the MS4A region have a dose-dependent effect on risk of late–onset Alzheimer disease. Aging Cell. 2019, 18, e12964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, K.P.; Snijders, G.J.L.; Humphrey, J.; Allan, A.; Sneeboer, M.A.M.; Navarro, E.; Schilder, B.M.; Vialle, R.A.; Parks, M.; Missall, R.; et al. Genetic analysis of the human microglial transcriptome across brain regions, aging and disease pathologies. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.S.; Ge, Y.J.; Huang, L.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, B.S.; Lian, P.P.; Hao, Y.N.; Han, S.S.; Li, Y.T.; Wu, K.M.; et al. MS4A6A/Ms4a6d deficiency disrupts neuroprotective microglia functions and promotes inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease model. Mol. Neurodegener. 2025, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-W.; Zhuang, Q.-Z.; Zhao, J.-J.; Lai, B.-C.; Ke, P.-F.; Wu, X.-B.; Luo, Y.-F.; Kang, C.-M.; Huang, X.-Z. MS4A6A regulates ox-LDL-induced endothelial dysfunction and monocyte adhesion in atherosclerosis via the IKK/NF-kappaB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 152, 114404. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, D.; Liu, H.; Hu, B. Exploring the prognostic value and potential therapeutic strategies of MS4A6A in glioblastoma: A comprehensive analysis of single-cell and multi-omics data. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Lin, S.; Zuo, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y. Involvement of microglia-expressed MS4A6A in the onset of glioblastoma. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2024, 59, 2836–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Berglund, A.E.; Macaulay, R.J.; Mule, J.J.; Etame, A.B. RNF135 Expression Marks Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand-Enriched Macrophage-Tumor Interactions in the Glioblastoma Microenvironment. Cancers 2025, 17, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, J.; Song, Y.H.; Li, Y. Ribosome biogenesis in disease: New players and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punyawatthananukool, S.; Matsuura, R.; Wongchang, T.; Katsurada, N.; Tsuruyama, T.; Tajima, M.; Enomoto, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Kawashima, M.; Toi, M.; et al. Prostaglandin E(2)-EP2/EP4 signaling induces immunosuppression in human cancer by impairing bioenergetics and ribosome biogenesis in immune cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qu, L.; Yan, S. Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes tumor growth and suppresses tumor immunity. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinski, P. Regulation of Immune Responses by Prostaglandin E2. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Zarredar, H.; Zafari, V.; Soleimani, Z.; Saeedi, H.; Caner, A.; Shanehbandi, D. Immune Features of Tumor Microenvironment: A Genetic Spotlight. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, R.B.; Shah, N.; Miller, J.; Dalley, R.; Nomura, S.R.; Yoon, J.G.; Smith, K.A.; Lankerovich, M.; Bertagnolli, D.; Bickley, K.; et al. An anatomic transcriptional atlas of human glioblastoma. Science 2018, 360, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, P.K.; Liu, X.; Wong, M.D.; Lin, L.T. The Roles of RNA-Binding Proteins in Vasculogenic Mimicry Regulation in Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, K.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Jia, B.; Hu, G. PPARgamma/mTOR Regulates the Synthesis and Release of Prostaglandins in Ovine Trophoblast Cells in Early Pregnancy. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Moreira, L.; Soares, V.C.; Dias, S.; Bozza, P.T. Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Modulate Lipid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Biogenesis via AKT/mTOR-PPARgamma Signalling in Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.; Watson, U.; Vasudevan, L.; Saini, D.K. ERK Activation Pathways Downstream of GPCRs. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 338, 79–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Georgiev, P.; Singh, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Grein, J.; Zhang, C.; Muise, E.S.; Sloman, D.L. Combination of EP4 antagonist MF-766 and anti-PD-1 promotes anti-tumor efficacy by modulating both lymphocytes and myeloid cells. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1896643. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, K.N.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Chai, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; et al. Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA): A Comprehensive Resource with Functional Genomic Data from Chinese Glioma Patients. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vlaminck, K.; Van Hove, H.; Kancheva, D.; Scheyltjens, I.; Pombo Antunes, A.R.; Bastos, J.; Vara-Perez, M.; Ali, L.; Mampay, M.; Deneyer, L.; et al. Differential plasticity and fate of brain-resident and recruited macrophages during the onset and resolution of neuroinflammation. Immunity 2022, 55, 2085–2102.e2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Stuart, T.; Kowalski, M.H.; Choudhary, S.; Hoffman, P.; Hartman, A.; Srivastava, A.; Molla, G.; Madad, S.; Fernandez-Granda, C.; et al. Dictionary learning for integrative, multimodal and scalable single-cell analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitprez, F.; Levy, S.; Sun, C.M.; Meylan, M.; Linhard, C.; Becht, E.; Elarouci, N.; Tavel, D.; Roumenina, L.T.; Ayadi, M.; et al. The murine Microenvironment Cell Population counter method to estimate abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations in murine samples using gene expression. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, D.; Hu, Z.; Butte, A.J. xCell: Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martinez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Trevino, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbie, D.A.; Tamayo, P.; Boehm, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Moody, S.E.; Dunn, I.F.; Schinzel, A.C.; Sandy, P.; Meylan, E.; Scholl, C.; et al. Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature 2009, 462, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukawa, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shiohara, T. In vivo dynamics of intraepidermal CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells during the evolution of fixed drug eruption. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, M.C.; Parnes, J.R. Role of CD4 and CD8 in T cell activation and differentiation. Adv. Immunol. 1993, 53, 59–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeser, D.; Gruener, R.F.; Huang, R.S. oncoPredict: An R package for predicting in vivo or cancer patient drug response and biomarkers from cell line screening data. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Bodycombe, N.E.; Cheah, J.H.; Price, E.V.; Liu, K.; Schaefer, G.I.; Ebright, R.Y.; Stewart, M.L.; Ito, D.; Wang, S.; et al. An interactive resource to identify cancer genetic and lineage dependencies targeted by small molecules. Cell 2013, 154, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Potash, J.B.; Han, S. COMBAT: A Combined Association Test for Genes Using Summary Statistics. Genetics 2017, 207, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Berglund, A.E.; Macaulay, R.J.; Mulé, J.J.; Etame, A.B. The Myeloid Biomarker MS4A6A Drives an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma via Activation of the PGE2 Signaling Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010058
Chen J, Wu Q, Berglund AE, Macaulay RJ, Mulé JJ, Etame AB. The Myeloid Biomarker MS4A6A Drives an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma via Activation of the PGE2 Signaling Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jianan, Qiong Wu, Anders E. Berglund, Robert J. Macaulay, James J. Mulé, and Arnold B. Etame. 2026. "The Myeloid Biomarker MS4A6A Drives an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma via Activation of the PGE2 Signaling Axis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010058
APA StyleChen, J., Wu, Q., Berglund, A. E., Macaulay, R. J., Mulé, J. J., & Etame, A. B. (2026). The Myeloid Biomarker MS4A6A Drives an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma via Activation of the PGE2 Signaling Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010058




