Postbiotics Combination Synergises the Antiproliferative Effects of Doxorubicin in Gastric Cancer Cells: A Cellular and Molecular Deep Dive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antiproliferative Activity of SCFA Combinations, Dox, and Their Combination Against AGS Adenocarcinoma Cells
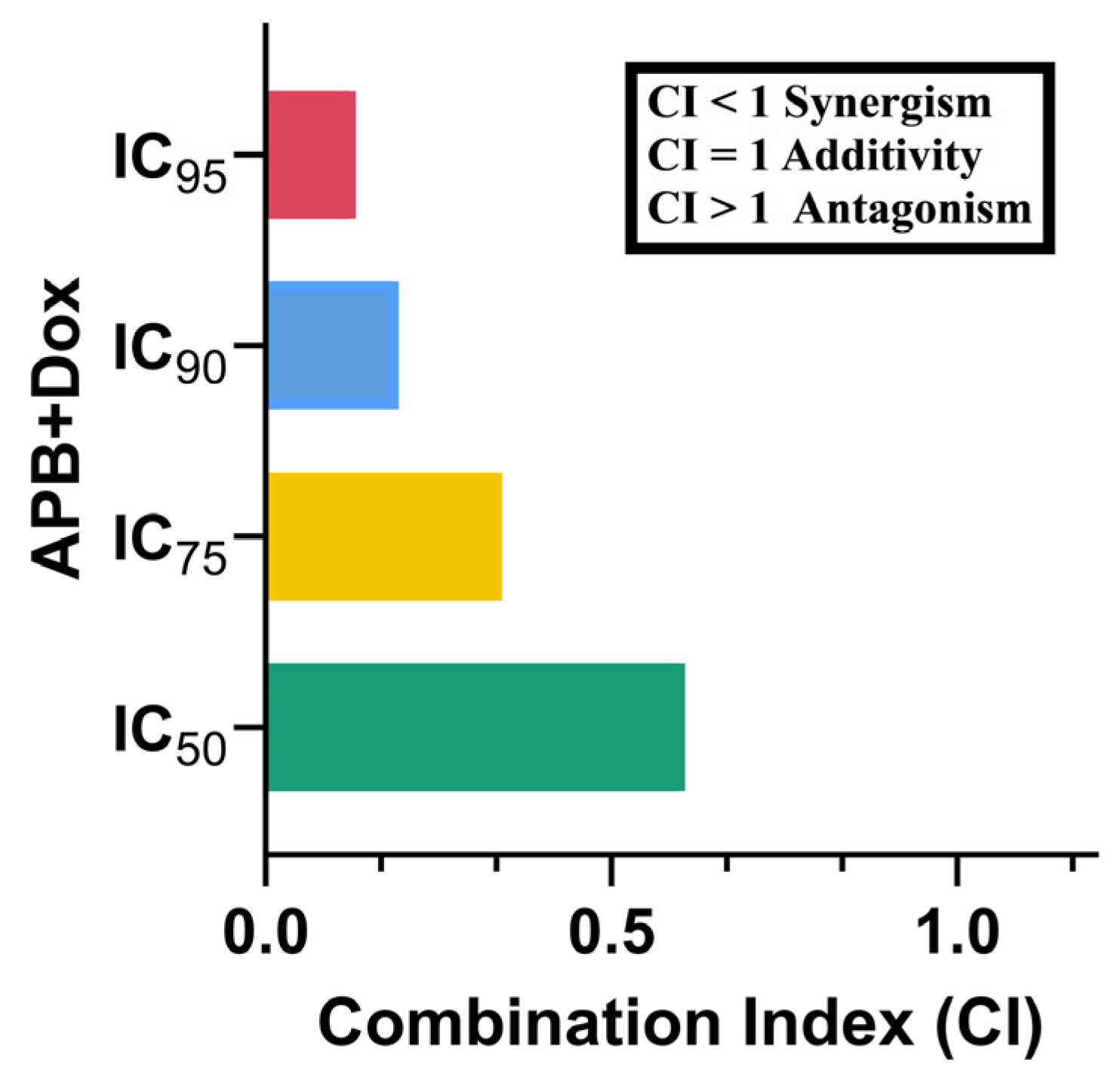
2.2. Synergistic Potential of APB with Dox Against the AGS Cells
2.3. Proteomics Study of the AGS Cells Treated with the Synergistic Combination vs. Monotreatments
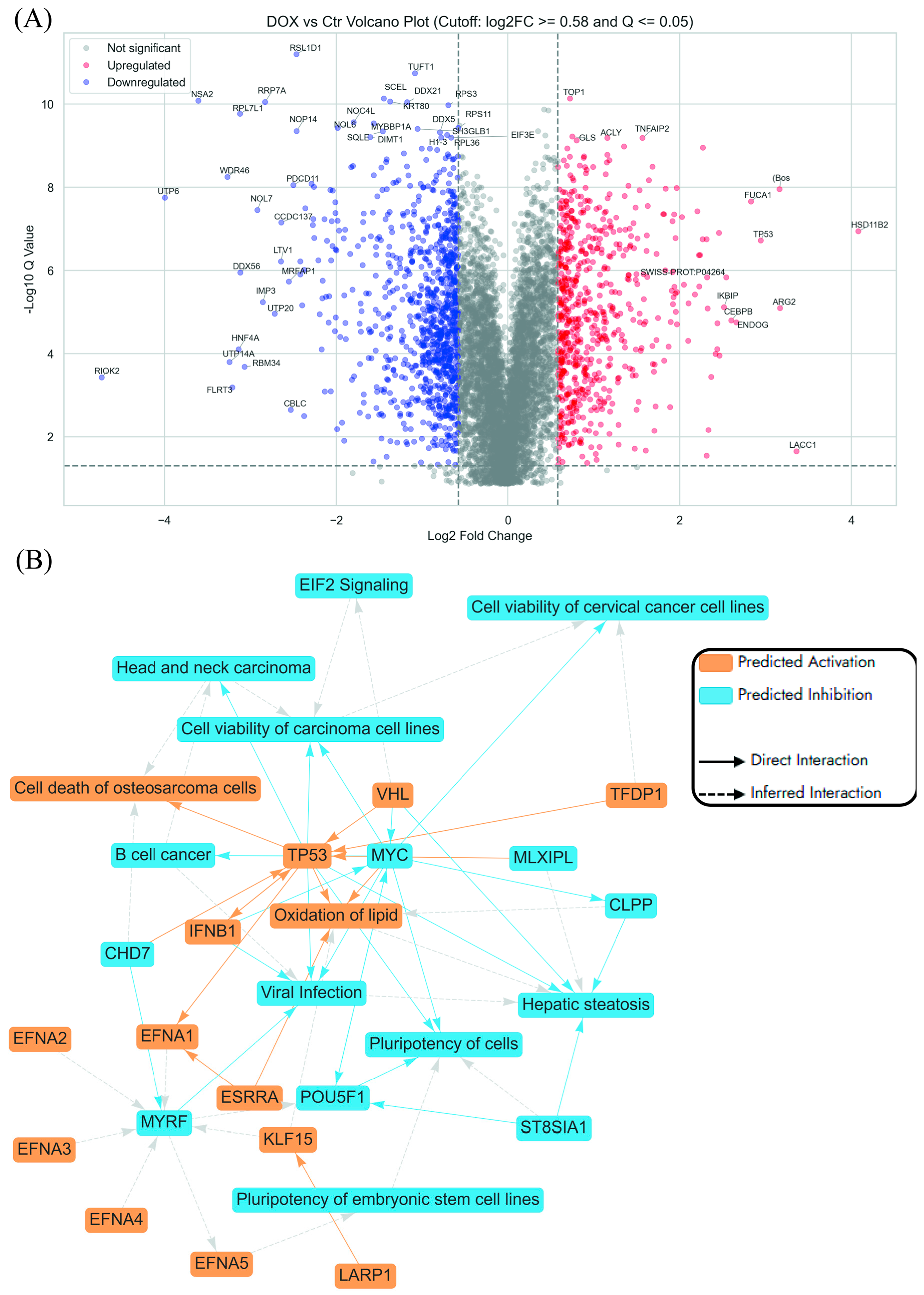
2.3.1. Enrichment Analyses of Differentially Expressed Proteins (DEPs) in Dox-Treated AGS Cells Compared to the Control Untreated Cells
- Ribosomal Protein Regulation
- DNA-related processes
- Cell Cycle
- G1/S Phase Arrest
- S Phase Disruption
- G2/M Phase Arrest
- Mitotic phase
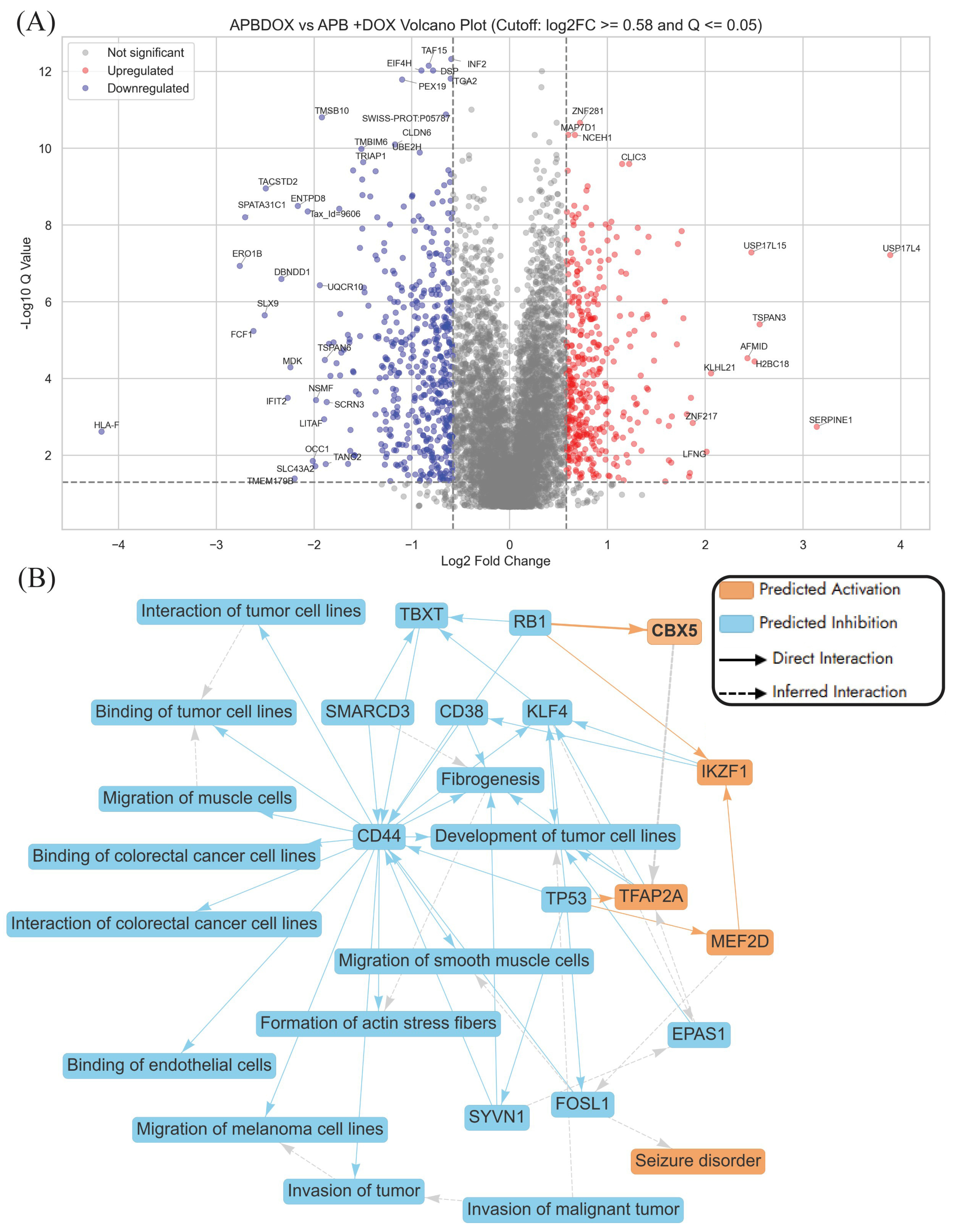
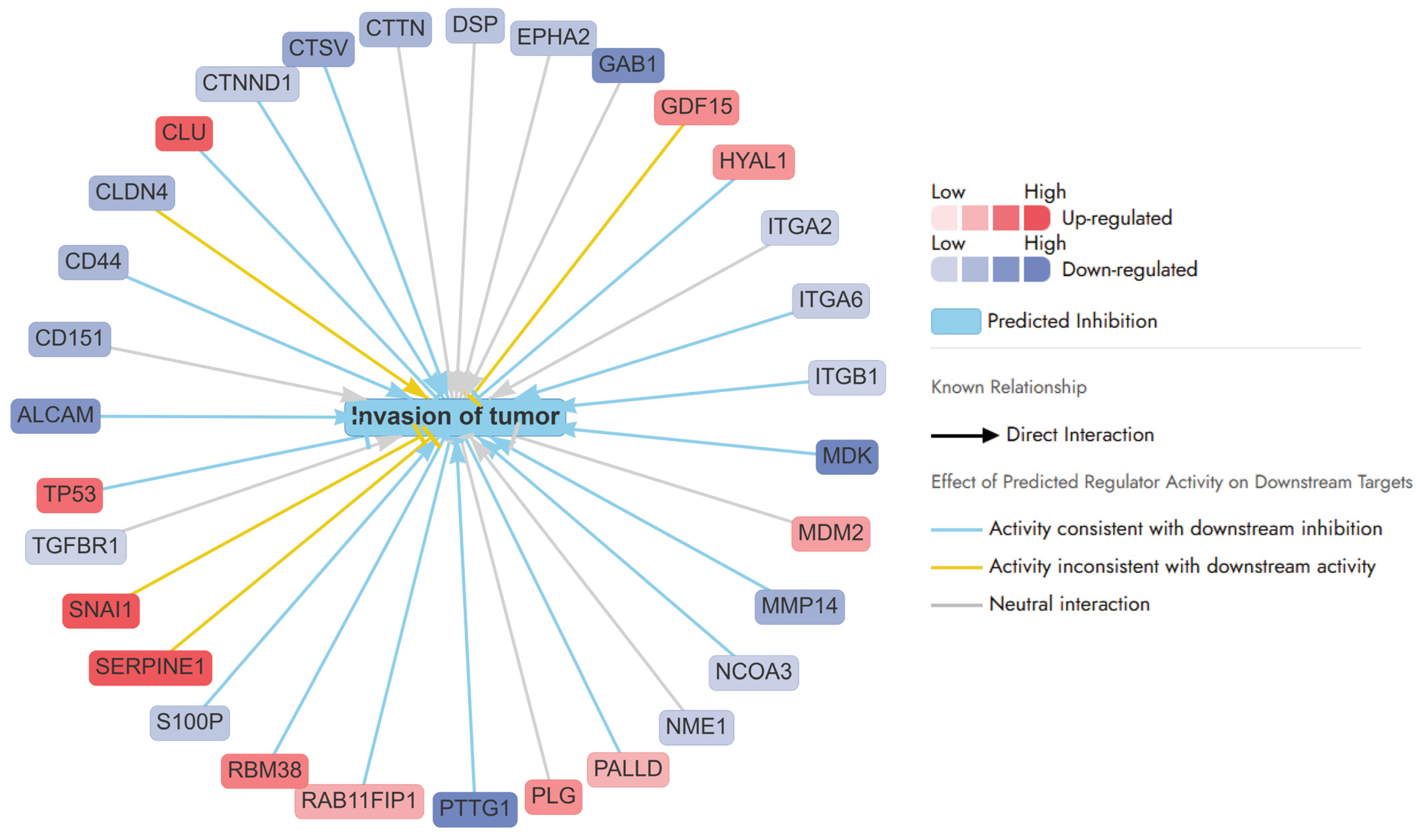
2.3.2. Enriched Pathways Using DEPs of APB+Dox Combination-Treated AGS Cells vs. Monotreatments
- Invasion of tumour pathways
- Apoptosis
- Intrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis
- Extrinsic Pathway of Apoptosis
- Crosstalk Between Pathways
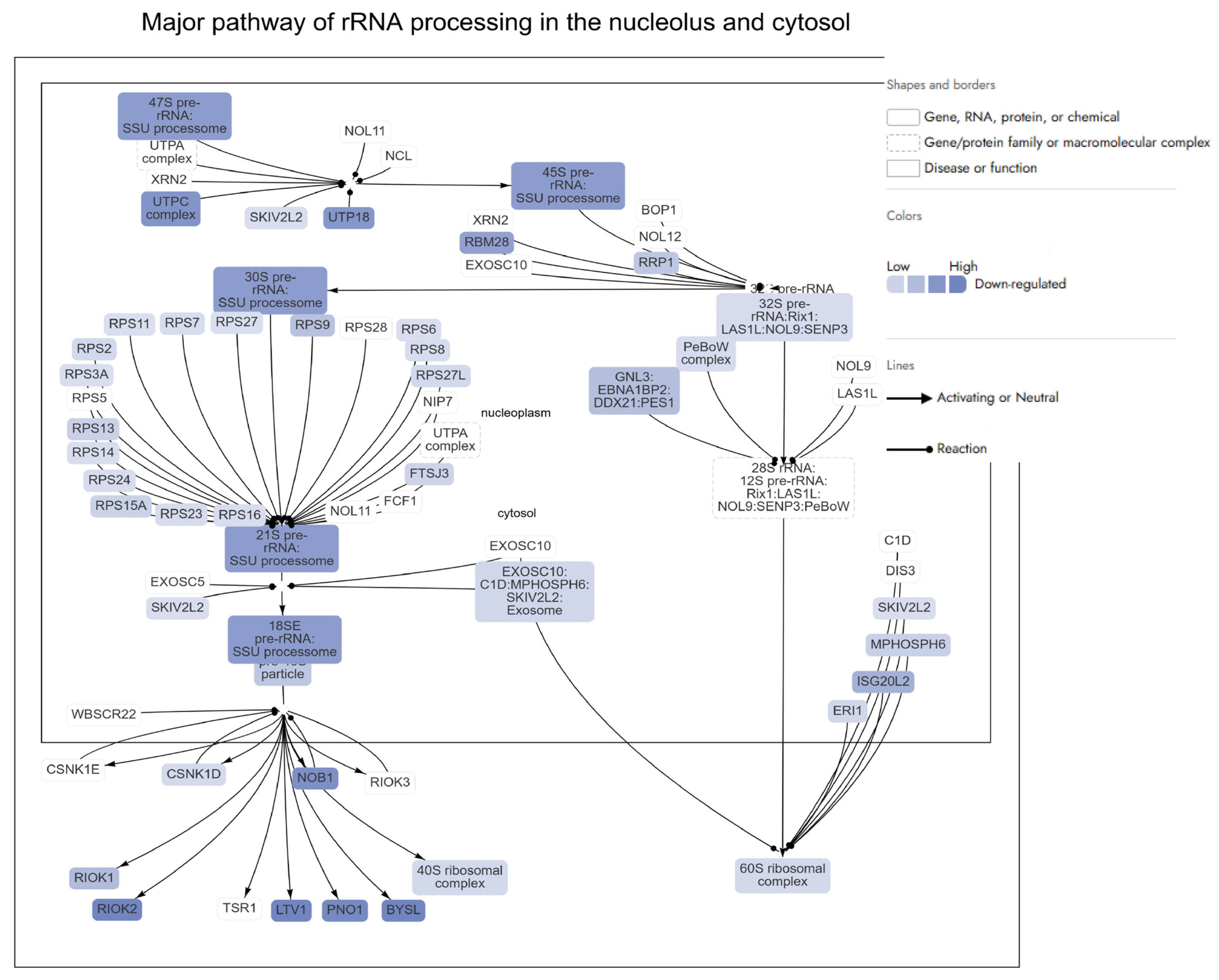
- rRNA metabolic process
- rRNA Biogenesis and Ribosomal Genes
- RNA Processing and Splicing
- Cell Cycle
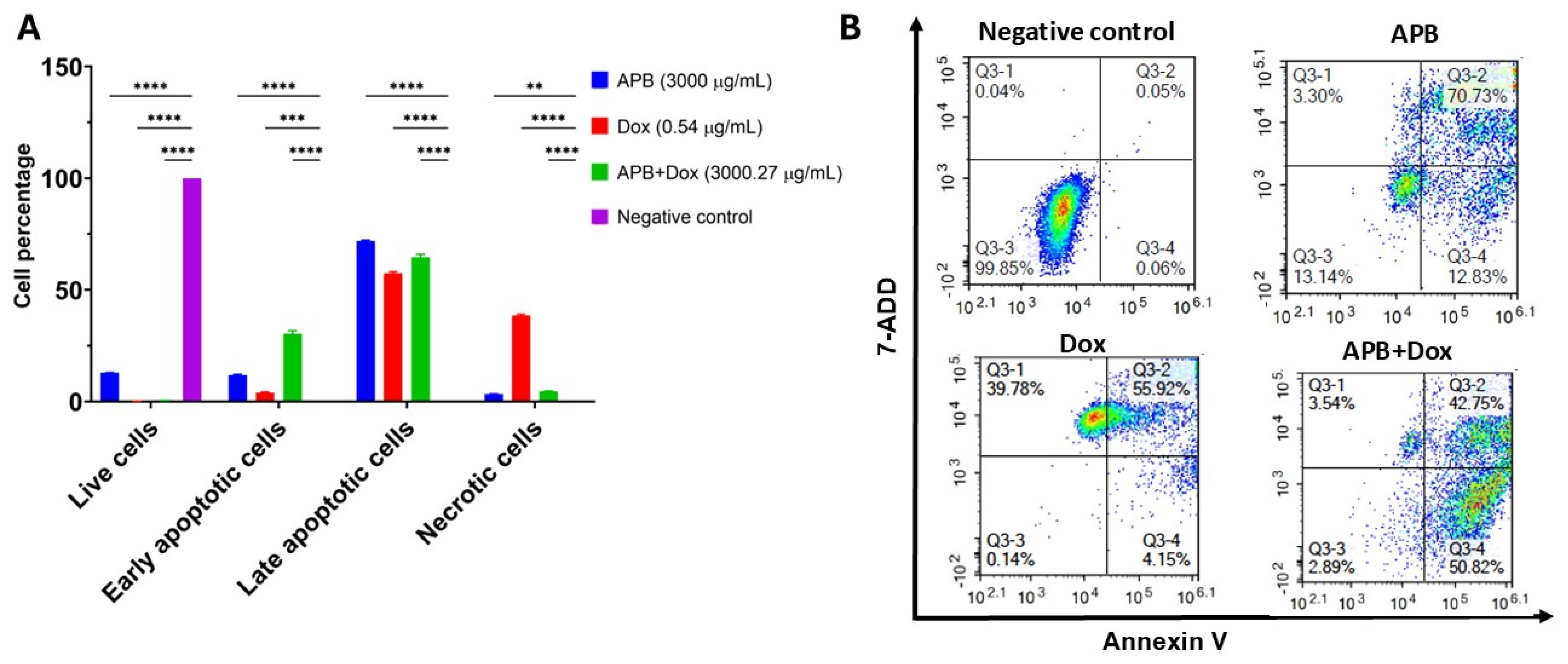
2.4. Flow Cytometric Analyses of Apoptotic Profiles of Mono and Combination Therapies
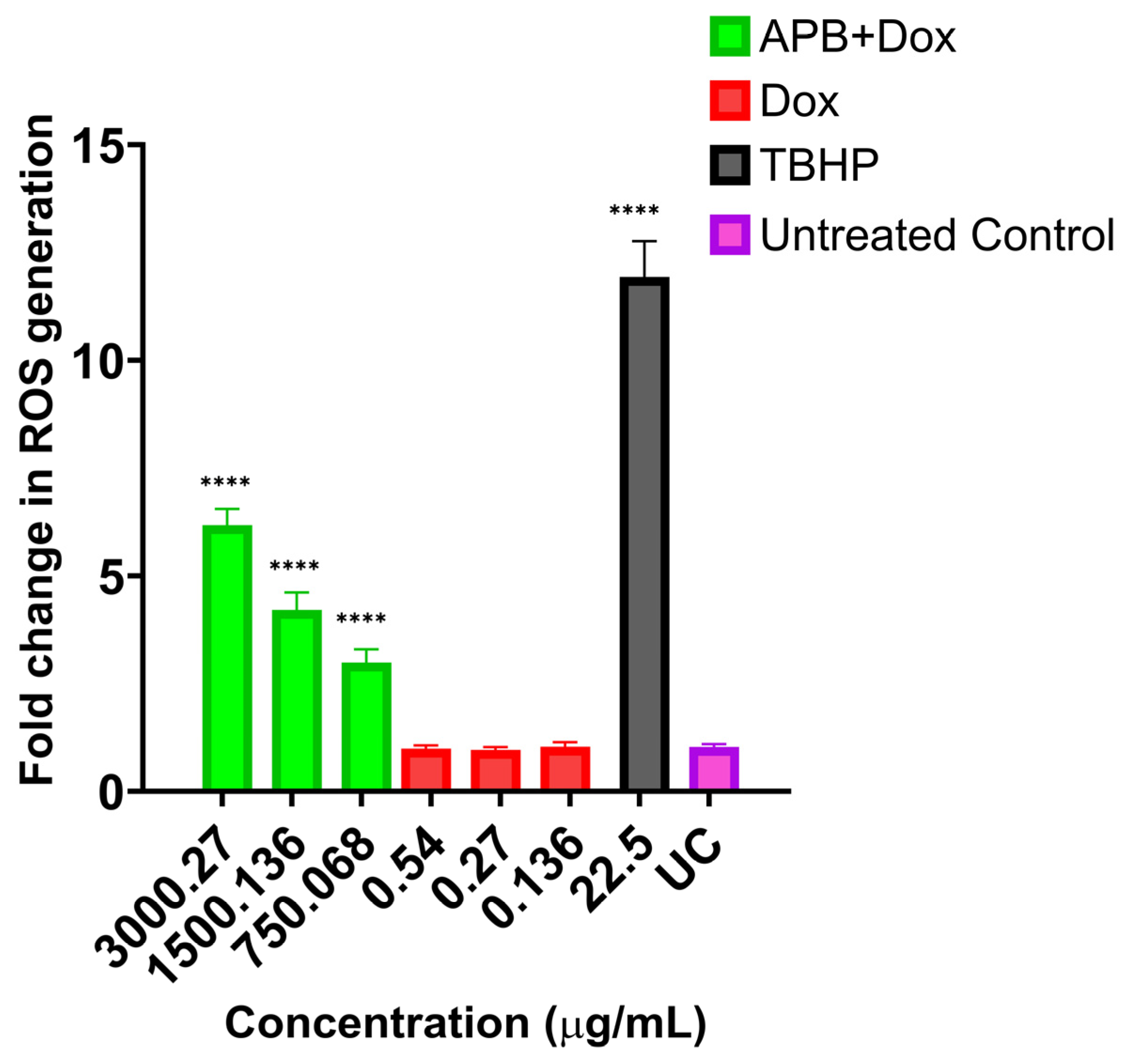
2.5. ROS Production in the AGS Cells After Treatment with Different Concentrations of APB, Dox, and APB+Dox
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Drug Preparation
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Cell Viability Assays
3.4. Synergy
3.5. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry, Label-Free Quantification Bottom-Up Proteomics
3.6. Flow Cytometry
3.7. ROS Production Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2018. Gastric Cancer 2021, 24, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.-J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Niu, H.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Ye, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Resveratrol reverses Doxorubicin resistance by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through modulating PTEN/Akt signalling pathway in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canani, R.B.; Di Costanzo, M.; Leone, L.; Pedata, M.; Meli, R.; Calignano, A. Potential beneficial effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacar, O.; Sriamornsak, P.; Dass, C.R. Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, Y. Mechanisms of drug resistance in gastric cancer. In Contemporary Approaches Toward Cure of Gastric Cancer; Maeda Shoten Co. Ltd.: Kanazawa, Japan, 1996; pp. 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Alkuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Al-Hussaniy, H.A. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Molecular mechanism and protection by conventional drugs and natural products. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Res. 2017, 2, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gianni, L.; Herman, E.H.; Lipshultz, S.E.; Minotti, G.; Sarvazyan, N.; Sawyer, D.B. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: From bench to bedside. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3777–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, A.; Tohumcu, E.; Tamai, L.; Dargenio, P.; Porcari, S.; Rondinella, D.; Venturini, I.; Maida, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G. The microbiome-driven impact of western diet in the development of noncommunicable chronic disorders. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 72, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.-W.; Yan, D.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleu, S.; Machiels, K.; Raes, J.; Verbeke, K.; Vermeire, S. Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaye, K.; Li, C.G.; Chang, D.; Bhuyan, D.J. The role of key gut microbial metabolites in the development and treatment of cancer. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2038865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’keefe, S.J. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, S.; Bertin, L.; Bonazzi, E.; Lorenzon, G.; De Barba, C.; Barberio, B.; Zingone, F.; Maniero, D.; Scarpa, M.; Ruffolo, C. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Human Health: From Metabolic Pathways to Current Therapeutic Implications. Life 2024, 14, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, G.; Van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Zang, D.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J. Butyrate as a promising therapeutic target in cancer: From pathogenesis to clinic. Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Holley, D.; Collins, L.B.; Montgomery, S.A.; Whitmore, A.C.; Hillhouse, A.; Curry, K.P.; Renner, S.W.; Greenwalt, A.; Ryan, E.P. A gnotobiotic mouse model demonstrates that dietary fiber protects against colorectal tumorigenesis in a microbiota-and butyrate-dependent manner. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, A.; Casili, G.; Scuderi, S.A.; Mannino, D.; Lanza, M.; Campolo, M.; Paterniti, I.; Capra, A.P.; Colarossi, C.; Bonasera, A. Sodium propionate contributes to tumour cell growth inhibition through PPAR-γ signalling. Cancers 2022, 15, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Afaghi, A.; Babakhani, S.; Sohrabi, M.R.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Babolhavaeji, K.; Akbari, S.K.A.; Yousefimashouf, R.; Karampoor, S. Role of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids in cancer development and prevention. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, C.; Yang, W.; Qin, Q.; Mao, A.; Tan, Q.; Lian, B.; Wei, C. Sodium butyrate combined with docetaxel for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells by targeting Gli1. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 8861–8875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, P.; Liu, Y.; Qi, M.; Dong, W. Combining sodium butyrate with cisplatin increases the apoptosis of gastric cancer in vivo and in vitro via the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 708093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.-W.; Yin, F.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Gong, X.; Yang, Y. Butyrate suppresses glucose metabolism of colorectal cancer cells via GPR109a-AKT signalling pathway and enhances chemotherapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 634874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, C.; Cuozzo, M.; Coretti, L.; Liguori, F.; Cimmino, F.; Turco, L.; Avagliano, C.; Aviello, G.; Mollica, M.; Lembo, F. Oral sodium butyrate supplementation ameliorates paclitaxel-induced behavioral and intestinal dysfunction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Qiu, J.; Ueda, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nojima, M.; Shima, H. Apoptosis of bladder cancer by sodium butyrate and cisplatin. J. Infect. Chemother. 2012, 18, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Mikami, D.; Uwada, J.; Yazawa, T.; Kamiyama, K.; Kimura, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Iwano, M. A short-chain fatty acid, propionate, enhances the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin by modulating GPR41 signalling pathways in HepG2 cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eladwy, R.A.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Chang, D.; Fares, M.; Li, C.-G.; Bhuyan, D.J. The postbiotic sodium butyrate synergizes the antiproliferative effects of dexamethasone against the AGS gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1372982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eladwy, R.A.; Fares, M.; Chang, D.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Li, C.-G.; Bhuyan, D.J. Fuelling the Fight from the Gut: Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Dexamethasone Synergise to Suppress Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancers 2025, 17, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaye, K.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Chang, D.; Li, C.-G.; Bhuyan, D.J. Mechanistic insights into the anti-proliferative action of gut microbial metabolites against breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, J.; El-Hakim, S.; Ibrahim, J.-N.; Safi, R.; Elnar, A.A.; El Boustany, C. Comparative effect of sodium butyrate and sodium propionate on proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells MCF-7. Breast Cancer 2020, 27, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qadami, G.H.; Secombe, K.R.; Subramaniam, C.B.; Wardill, H.R.; Bowen, J.M. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids: Impact on cancer treatment response and toxicities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, C.F.; Oshiro, C.; Marsh, S.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; McLeod, H.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Doxorubicin pathways: Pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsherbiny, M.A.; Radwan, I.; Moustafa, N.; Bhuyan, D.J.; El-Waisi, M.; Chang, D.; Li, C.G. Trustworthy deep neural network for inferring anticancer synergistic combinations. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 27, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, T.; Nakagawara, A. Role of p53 in cell death and human cancers. Cancers 2011, 3, 994–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterwald, C.; Alberini, C.M. Stress and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms in long-term memory: From adaptive responses to psychopathologies. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2014, 112, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Yin, G.; Xie, X.; Kong, W.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S. C/EBPβ: The structure, regulation, and its roles in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí i Líndez, A.-A.; Reith, W. Arginine-dependent immune responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 5303–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, X. Endonuclease G is an apoptotic DNase when released from mitochondria. Nature 2001, 412, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Lindbæk, L.; Krogh, N.; Doganli, C.; Keller, C.; Mönnich, M.; Gonçalves, A.B.; Sakthivel, S.; Mang, Y.; Fatima, A. RRP7A links primary microcephaly to dysfunction of ribosome biogenesis, resorption of primary cilia, and neurogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, E.; Flynn, R.A.; Martin, L.; Spitale, R.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Wysocka, J. RNA helicase DDX21 coordinates transcription and ribosomal RNA processing. Nature 2015, 518, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray Chaudhuri, A.; Nussenzweig, A. The multifaceted roles of PARP1 in DNA repair and chromatin remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, I.; Tanaka, H.; Kanakura, Y. E2F1 and c-Myc in cell growth and death. Cell Cycle 2003, 2, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, H.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Lin, P.; Li, K. Oxidative Stress and Reprogramming of Lipid Metabolism in Cancers. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathia, J.D.; Liu, H. Overview of cancer stem cells and stemness for community oncologists. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Q.; Han, Y.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liang, C. Downregulated RPL6 inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and migration and promotes cell apoptosis by regulating the AKT signalling pathway. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Weng, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, W.; Hsu, J.L.; Sun, J.; Atyah, M.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Y. High RPS3A expression correlates with low tumour immune cell infiltration and unfavorable prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Xu, W.; Cai, Y.; Mu, C.; Zhao, X.; Tang, T.; Liang, C.; Yang, T.; Zheng, J. High-fat diet promotes prostate cancer metastasis via RPS27. Cancer Metab. 2024, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Jiang, X.; Yang, C.; Tan, B.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M. High expression of RPL27A predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molavi, G.; Samadi, N.; Hashemzadeh, S.; Halimi, M.; Hosseingholi, E.Z. Moonlight human ribosomal protein L13a downregulation is associated with p53 and HER2/neu expression in breast cancer. J. Appl. Biomed. 2020, 18, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.J.; Gong, G.; Liang, E.; Lv, Y.; Lin, S.; Xu, J. Pan-cancer analysis of 60S Ribosomal Protein L7-Like 1 (RPL7L1) and validation in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 40, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Gou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jin, H.; Cui, L.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y. Downregulation of RPL6 by siRNA inhibits proliferation and cell cycle progression of human gastric cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Shi, Y.; Gou, Y.; Li, J.; Han, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, J.; Ning, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y. Human ribosomal protein S13 promotes gastric cancer growth through down-regulating p27Kip1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, B.; Gonzalez, D.D.; Liu, Z.-B.; Li, X.; Wong, H.; Granados, S.; Ezzedine, N.E.; Sieglaff, D.H.; Ensor, J.E.; Miller, K.D. Role of RPL39 in metaplastic breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao-De, L.; Jing, X. Ribosomal proteins and colorectal cancer. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhai, H.; Wang, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, C.; Lan, M.; Du, J.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K. Ribosomal proteins S13 and L23 promote multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by suppressing drug-induced apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 296, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, V.; Gimeno-Valiente, F.; Tarazona, N.; Ciarpaglini, C.M.; Roda, D.; Fleitas, T.; Tolosa, P.; Cejalvo, J.M.; Huerta, M.; Roselló, S. NRF2 through RPS6 activation is related to anti-HER2 drug resistance in HER2-amplified gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, V.; Gimeno-Valiente, F.; Tarazona, N.; Kanonnikoff, T.F.; Tolosa, P.; Moscardò, M.B.; Garcia-Mico, B.; Huerta, M.; Roselló, S.; Roda, D. NRF2 activation via PI3K/AKT/mTOR/RPS6 causes resistance to anti-HER2 agents among HER2 amplified gastric cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Gao, H. Expression and bioinformatics analysis of RPL38 protein and mRNA in gastric cancer. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-P.; Zhao, C.-X.; Li, Q.-J.; Cai, Y.; Liu, F.-X.; Hu, H.; Xu, X.; Han, Y.-L.; Wu, M.; Zhan, Q.-M. Alteration of RPL14 in squamous cell carcinomas and preneoplastic lesions of the esophagus. Gene 2006, 366, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Singer, R.H. Cellular variability of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, Y.; Naito, Y.; Miura, N.; Mori, T.; Watabe, Y.; Yoshimoto, S.; Shibahara, T.; Takano, M.; Honda, K. RIOK2 contributes to cell growth and protein synthesis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 30, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.J.; Wang, Z.; Goering, L.M.; Johnson, A.W. Utp14 interaction with the small subunit processome. RNA 2018, 24, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Mao, C.Y.; Zhang, J.G.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, X.H.; Bao, T.; Guo, W. Overexpression of U three protein 14a (UTP14a) is associated with poor prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X.; Guan, G. Hypermethylation and downregulation of UTP6 are associated with stemness properties, chemoradiotherapy resistance, and prognosis in rectal cancer: A co-expression network analysis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 607782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, K.; Fu, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, W.; Chen, J. DEAD-box helicase 56 functions as an oncogene promote cell proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer via the FOXO1/p21 Cip1/c-Myc signalling pathway. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 13970–13985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Luo, B.; Qin, Y.; Li, S.; Peng, Z. RNA-seq and integrated network analysis reveals the hub genes and key pathway of paclitaxel inhibition on Adriamycin resistant diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 7607–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Shi, T.; Song, Q.; Zhao, H.; Ma, D. NSA2, a novel nucleolus protein regulates cell proliferation and cell cycle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, Y.; Louvet, E.; Oda, T.; Kumeta, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Horigome, T.; Takeyasu, K. Nucleolar scaffold protein, WDR 46, determines the granular compartmental localization of nucleolin and DDX 21. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 780–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternoga, H.; Früh, A.; Kunze, R.; Bradatsch, B.; Baßler, J.; Hurt, E. Mutational analysis of the Nsa2 N-terminus reveals its essential role in ribosomal 60S subunit assembly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaremba, T.; Thomas, H.; Cole, M.; Plummer, E.R.; Curtin, N.J. Doxorubicin-induced suppression of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) activity and expression and its implication for PARP inhibitors in clinical trials. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; Vazquez, E.S.; Moiola, C.P.; Zalazar, F.; Cotignola, J.; Gueron, G.; Gardner, K.; De Siervi, A. BRCA1 loss induces GADD153-mediated doxorubicin resistance in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Yao, W.; Li, S.; Ren, Z. RAD51 is a potential marker for prognosis and regulates cell proliferation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busatto, F.F.; Viero, V.P.; Schaefer, B.T.; Saffi, J. Cell growth analysis and nucleotide excision repair modulation in breast cancer cells submitted to a protocol using doxorubicin and paclitaxel. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 118990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, F.; Foronda, M.; Martinez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Conditional TRF1 knockout in the hematopoietic compartment leads to bone marrow failure and recapitulates clinical features of dyskeratosis congenita. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 120, 2990–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.P.; Garrobo, I.; Foronda, M.; Palacios, J.A.; Marión, R.M.; Flores, I.; Ortega, S.; Blasco, M.A. TRF1 is a stem cell marker and is essential for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugli, N.; Sotiriou, S.K.; Halazonetis, T.D. The role of SMARCAL1 in replication fork stability and telomere maintenance. DNA Repair 2017, 56, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Reddy, D.; Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Workman, J.L. Elevated levels of the methyltransferase SETD2 causes transcription and alternative splicing changes resulting in oncogenic phenotypes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 945668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mar, B.G.; Chu, S.H.; Kahn, J.D.; Krivtsov, A.V.; Koche, R.; Castellano, C.A.; Kotlier, J.L.; Zon, R.L.; McConkey, M.E.; Chabon, J. SETD2 alterations impair DNA damage recognition and lead to resistance to chemotherapy in leukemia. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2017, 130, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Ni, W.; Tai, G. Expression of MUC1 in different tumours and its clinical significance. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 17, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Jeong, I.H.; Jang, B. Elevated expression of Axin2 in intestinal metaplasia and gastric cancers. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2023, 57, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Tang, B. Inhibition of MGMT-mediated autophagy suppression decreases cisplatin chemosensitivity in gastric cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-I.; Pecha, R.L.; Keihanian, T.; Mercado, M.; Pena-Munoz, S.V.; Lang, K.; Van Buren, G.; Dhingra, S.; Othman, M.O. MUC1 expressions and its prognostic values in US gastric cancer patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, M.; Che, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, C.; Fei, P. Fanconi anemia signalling and cancer. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, M.; Tripathi, S.K.; Biswal, B.K. SOX9: An emerging driving factor from cancer progression to drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2021, 1875, 188517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooch, J.L.; Christy, B.; Yee, D. STAT6 mediates interleukin-4 growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells. Neoplasia 2002, 4, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Shi, D.; Xu, W.; Fu, X.; Lv, Q.; Xia, J.; Shi, F. E3 ubiquitin ligase SYVN1 is a key positive regulator for GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Ye, L.; Liu, Z. GINS2 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells through PTP4A1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Qin, T.; Yu, J.; Giordano, T.J.; Sartor, M.A.; Koenig, R.J. Novel role of ASH1L histone methyltransferase in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 8834–8845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, V.; Barbarino, M.; Angrisani, A.; Correale, P.; Pastina, P.; Cappabianca, S.; Reginelli, A.; Mutti, L.; Miracco, C.; Giannicola, R. CDK4, CDK6/cyclin-D1 complex inhibition and radiotherapy for cancer control: A role for autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassl, A.; Geng, Y.; Sicinski, P. CDK4 and CDK6 kinases: From basic science to cancer therapy. Science 2022, 375, eabc1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimploy, K.; Díaz, G.D.; Li, Q.; Carter, O.; Dashwood, W.M.; Mathews, C.K.; Williams, D.E.; Bailey, G.S.; Dashwood, R.H. E2F4 and ribonucleotide reductase mediate S-phase arrest in colon cancer cells treated with chlorophyllin. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2086–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, K. Cell cycle regulation: P53-p21-RB signalling. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim, D.L.; Millis, S.Z.; Ross, J.S.; Woo, M.S.A.; Ali, S.M.; Kurzrock, R. Cyclin pathway genomic alterations across 190,247 solid tumors: Leveraging large-scale data to inform therapeutic directions. Oncologist 2021, 26, e78–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, L.; Cui, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, Q.; Chen, X.S.; Campbell, J.L.; Lou, H. Cell-cycle-regulated interaction between Mcm10 and double hexameric Mcm2-7 is required for helicase splitting and activation during S phase. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkas, L.H.; Herbert, B.S.; Abdel-Aziz, W.; Dobrolecki, L.E.; Liu, Y.; Agarwal, B.; Hoelz, D.; Badve, S.; Schnaper, L.; Arnold, R.J. A cancer-associated PCNA expressed in breast cancer has implications as a potential biomarker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19472–19477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartek, J.; Lukas, J. Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouery, R.D.; Lukasik, K.; Hsu, C.; Bonacci, T.; Bolhuis, D.L.; Wang, X.; Mills, C.A.; Toomer, E.D.; Canterbury, O.G.; Robertson, K.C. Proteomic analysis reveals a PLK1-dependent G2/M degradation program and a role for AKAP2 in coordinating the mitotic cytoskeleton. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, H.; Kim, M.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Ashida, H.; Ogawa, M.; Fujita, Y.; Muller, D.; Kirikae, T.; Jackson, P.K.; Kotani, S. A bacterial effector targets Mad2L2, an APC inhibitor, to modulate host cell cycling. Cell 2007, 130, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malureanu, L.A.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Hamada, M.; Wasilewski, L.; Davenport, J.; van Deursen, J.M. BubR1 N terminus acts as a soluble inhibitor of cyclin B degradation by APC/CCdc20 in interphase. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, T.S.; Jung, W.H.; Chung, H.C.; Park, B.W.; Sheen, S.S.; Han, J.H. Expression of anaphase-promoting complex7 in fibroadenomas and phyllodes tumors of breast. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-H.; Liao, L.-J.; Yu, C.-H.; Chiang, C.-P.; Jhan, J.-R.; Chang, L.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lou, P.-J.; Lin, J.-J. Overexpression of the pituitary tumour transforming gene induces p53-dependent senescence through activating DNA damage response pathway in normal human fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22630–22638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H.E.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Hasan, A.; Caceci, T.; Pozzoli, G.; Morrione, A.; Giordano, A.; Cenciarelli, C. p53 signalling in cancer progression and therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-X.; Diao, T.-Y.; Yang, X.-L.; Li, K.; Yang, J.-L.; Chen, X.-Q. Implications of the NDC80 complex on the tumour immune microenvironment and cell growth in pan-cancer. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lian, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, M. ESPL1 is a novel prognostic biomarker associated with the malignant features of glioma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 666106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Zhang, X.; Ruan, Y.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.-J.; Yan, W.-H. HLA-F expression is a prognostic factor in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Dai, L.; Yuan, J.; Pang, M.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Shi, Y.; Wu, F.; Nie, R.; Chen, Q. miR-107 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells in vivo and in vitro by targeting TRIAP1. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 855355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.S.; Sennhenn, P.; Yuan, D.S.; Liu, H.; Taddei, D.; Qian, Y.; Luo, W. TMBIM6/BI-1 is an intracellular environmental regulator that induces paraptosis in cancer via ROS and Calcium-activated ERAD II pathways. Oncogene 2025, 44, 494–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L. Bleomycin alters intratumoral immune response of EBV-associated gastric cancer by ENTPD8 and PCOLCE2. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Ann, D.K.; Chen, J.L.-Y.; Kuo, C.-Y. Obesity promotes radioresistance through SERPINE1-mediated aggressiveness and DNA repair of triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de La Vega, M.; Kelvin, A.A.; Dunican, D.J.; McFarlane, C.; Burrows, J.F.; Jaworski, J.; Stevenson, N.J.; Dib, K.; Rappoport, J.Z.; Scott, C.J. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP17 is essential for GTPase subcellular localization and cell motility. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Kong, L.; Hou, Z.; Ji, H. CD44 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in gastric cancer. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, H.; Inageda, K.; Takahashi, K.; Hoshino, S.-i.; Ikeda, K.; Katada, T. Cell surface antigen CD38 identified as ecto-enzyme of NAD glycohydrolase has hyaluronate-binding activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Bi, Q.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W. Fibrogenesis-driven tumour progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Prognostic, therapeutic implications and the dual role of neuropilin-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2025, 25, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbalakshmi, A.R.; Sahoo, S.; McMullen, I.; Saxena, A.N.; Venugopal, S.K.; Somarelli, J.A.; Jolly, M.K. KLF4 induces mesenchymal–epithelial transition (MET) by suppressing multiple EMT-inducing transcription factors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Korona-Głowniak, I.; Forma, A.; Maani, A.; Sitarz, E.; Rahnama-Hezavah, M.; Radzikowska, E.; Portincasa, P. Mechanisms of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and tumour microenvironment in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yun, B.; Hoyle, R.G.; Ma, Z.; Zaman, S.U.; Xiong, G.; Yi, C.; Xie, N.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X. CYTOR facilitates formation of FOSL1 phase separation and super enhancers to drive metastasis of tumour budding cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2305002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kciuk, M.; Gielecińska, A.; Mujwar, S.; Kołat, D.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Celik, I.; Kontek, R. Doxorubicin—An agent with multiple mechanisms of anticancer activity. Cells 2023, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, R. Understanding apoptosis and apoptotic pathways targeted cancer therapeutics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Grant, S. BCL2L11/Bim as a dual-agent regulating autophagy and apoptosis in drug resistance. Autophagy 2015, 11, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.-K.; Chung, K.M.; Park, H.; Hong, J.; Gim, J.-E.; Choi, H.; Lee, Y.W.; Choi, J.; Mun, J.Y.; Yu, S.-W. CASP9 (caspase 9) is essential for autophagosome maturation through regulation of mitochondrial homeostasis. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1598–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Sharma, A.; Weiher, H.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G. Biological mechanisms and clinical significance of endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase 1 alpha (ERO1α) in human cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.N.; Seo, T.W.; Lee, Y.T.; Jeong, D.H.; Yoo, S.J. Nuclear endonuclease G controls cell proliferation in ovarian cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2023, 13, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Oyang, L.; Cui, S.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, M.; Tan, S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress—A key guardian in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Srinivasan, P.R.; Tajiknia, V.; Uruchurtu, A.F.S.S.; Seyhan, A.A.; Carneiro, B.A.; De La Cruz, A.; Pinho-Schwermann, M.; George, A.; Zhao, S. Targeting apoptotic pathways for cancer therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e179570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobezinskaya, Y.L.; Liu, Z. The role of TRADD in death receptor signalling. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Bakiri, L.; Yaniv, M. Induction of apoptosis by the transcription factor c-Jun. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting p53 pathways: Mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorard, C.; Madry, C.; Buhard, O.; Toifl, S.; Didusch, S.; Ratovomanana, T.; Letourneur, Q.; Dolznig, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Duval, A. RAF1 contributes to cell proliferation and STAT3 activation in colorectal cancer independently of microsatellite and KRAS status. Oncogene 2023, 42, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, B.J.; Kelly, G.L.; Janic, A.; Herold, M.J.; Strasser, A. How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ 2018, 25, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechiporuk, T.; Kurtz, S.E.; Nikolova, O.; Liu, T.; Jones, C.L.; D’Alessandro, A.; Culp-Hill, R.; d’Almeida, A.; Joshi, S.K.; Rosenberg, M. The TP53 apoptotic network is a primary mediator of resistance to BCL2 inhibition in AML cells. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Le, L.; Fan, Y.; Lv, L.; Zhang, J. Autophagy is induced through the ROS-TP53-DRAM1 pathway in response to mitochondrial protein synthesis inhibition. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Elf, S.E.; Miyata, Y.; Sashida, G.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G.; Di Giandomenico, S.; Lee, J.M.; Deblasio, A.; Menendez, S. p53 regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, J.-P.; Gu, W. p53 aerobics: The major tumour suppressor fuels your workout. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensaad, K.; Tsuruta, A.; Selak, M.A.; Vidal, M.N.C.; Nakano, K.; Bartrons, R.; Gottlieb, E.; Vousden, K.H. TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 2006, 126, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Mo, W.; Yang, Z. Human/eukaryotic ribosomal protein L14 (RPL14/eL14) overexpression represses proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT process in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Villanueva, S.; Gutiérrez, G.; Kressler, D.; de la Cruz, J. Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins and domains in ribosome production and function: Chance or necessity? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanchick, A.; Zhi, H.; Cavanaugh, A.H.; Rothblum, K.; Schneider, D.A.; Rothblum, L.I. DNA binding by the ribosomal DNA transcription factor rrn3 is essential for ribosomal DNA transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9135–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, F.; Bernabò, P.; Tebaldi, T.; Groen, E.J.N.; Perenthaler, E.; Maniscalco, F.; Rossi, A.; Donzel, D.; Clamer, M.; Marchioretto, M. SMN-primed ribosomes modulate the translation of transcripts related to spinal muscular atrophy. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.S.; Williamson, E.A.; Srinivasan, G.; Kong, K.; Lomelino, C.L.; McKenna, R.; Walter, C.; Sung, P.; Narayan, S.; Hromas, R. The splicing component ISY1 regulates APE1 in base excision repair. DNA Repair 2020, 86, 102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xing, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Lv, J.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Yu, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, K. DCAF13 inhibits the p53 signalling pathway by promoting p53 ubiquitination modification in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhou, D.; Yang, J.; Zhang, D. Doxorubicin promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion via DCAF13. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, W.; Tao, T.; Zhang, J.; Kong, D.; Hao, J.; Yu, C.; Liao, G.; Gong, H. UBE2N promotes cell viability and glycolysis by promoting Axin1 ubiquitination in prostate cancer cells. Biol. Direct 2024, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; Cai, Y.; Huang, X.; Dong, X. Overexpression of PKMYT1 associated with poor prognosis and immune infiltration may serve as a target in triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1002186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.-F.; Chen, C.-F.; Shu, C.-W.; Chang, H.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Liou, H.-H.; Ger, L.-P.; Chen, C.-L.; Kang, B.-H. UBE2C is a potential biomarker for tumorigenesis and prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouette, A.; Trofimov, A.; Haberl, D.; Boucher, G.; Lavallée, V.-P.; D’Angelo, G.; Hébert, J.; Sauvageau, G.; Lemieux, S.; Perreault, C. Expression of immunoproteasome genes is regulated by cell-intrinsic and–extrinsic factors in human cancers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Li, S.; Mei, J.; Lin, W.; Zou, J.; Wei, W.; Guo, R. High SGO2 expression predicts poor overall survival: A potential therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes 2021, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maerki, S.; Olma, M.H.; Staubli, T.; Steigemann, P.; Gerlich, D.W.; Quadroni, M.; Sumara, I.; Peter, M. The Cul3–KLHL21 E3 ubiquitin ligase targets Aurora B to midzone microtubules in anaphase and is required for cytokinesis. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-B.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, M.-C.; Zhong, Q.; Zheng, H.-L.; Wang, J.-B.; Huang, Z.-N.; Wang, H.-G.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.-F. KLHL21 suppresses gastric tumourigenesis via maintaining STAT3 signalling equilibrium in stomach homoeostasis. Gut 2024, 73, 1785–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golebiowski, F.; Kasprzak, K.S. Inhibition of core histones acetylation by carcinogenic nickel (II). Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 279, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscalzo, J.; Handy, D.E. Epigenetic modifications: Basic mechanisms and role in cardiovascular disease (2013 Grover Conference series). Pulm. Circ. 2014, 4, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillou, T.; Kirby, T.J.; McCarthy, J.J. Ribosome biogenesis: Emerging evidence for a central role in the regulation of skeletal muscle mass. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-P.; Denicourt, C. The impact of ribosome biogenesis in cancer: From proliferation to metastasis. NAR Cancer 2024, 6, zcae017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, W.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, M.; Jiang, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Meng, M. XRCC 3 is a promising target to improve the radiotherapy effect of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, S.; Lee, L.; Davalos, A.; Schiestl, R.H.; Campisi, J.; Oshima, J. WRN, the protein deficient in Werner syndrome, plays a critical structural role in optimizing DNA repair. Aging Cell 2003, 2, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L. Ribonucleotide reductase M2 (RRM2): Regulation, function and targeting strategy in human cancer. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative stress in cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Gogal, R.M., Jr.; Walsh, J.E. A new rapid and simple non-radioactive assay to monitor and determine the proliferation of lymphocytes: An alternative to [3H] thymidine incorporation assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 170, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsherbiny, M.A.; Bhuyan, D.J.; Low, M.N.; Chang, D.; Li, C.G. Synergistic interactions of cannabidiol with chemotherapeutic drugs in mcf7 cells: Mode of interaction and proteomics analysis of mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, I.H.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Chang, D.; Li, C.G.; Bhuyan, D.J. Antiproliferative effects of Australian native plums against the MCF7 breast adenocarcinoma cells and UPLC-qTOF-IM-MS-driven identification of key metabolites. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Conc. μg/mL | Cell viability (%) HS738.St/Int | Conc. μg/mL | Cell Growth Inhibition (%) of AGS Cels | Cell Viability (%) HS738.St/Int | Conc. μg/mL | Cell Growth Inhibition (%) of AGS Cels | Cell Viability (%) HS738.St/Int |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APB | Dox | APB+Dox | |||||
| 3000 | 76.59 ± 8.56 a | 0.54 | 73.51 ± 5.16 a | 38.37 ± 7.01 a | 3000 + 0.27 | 103.46 ± 2.24 a | 64.12 ± 8.76 a |
| 1500 | 79.67 ± 8.16 a | 0.27 | 34.69 ± 2.96 b | 62.84 ± 11.53 b | 1500 +0.136 | 102.51 ± 9.05 a | 92.42 ± 10.66 b |
| 750 | 80.98 ± 9.19 a | 0.136 | 20.77 ± 7.29 c | 68.52 ± 7.51 b | 750 + 0.068 | 85.89 ± 8.58 b | 100.54 ± 8.51 b |
| 375 | 85.80 ± 13.04 a | 0.068 | 17.29 ± 7.96 c | 71.51 ± 7.81 b | 375 + 0.034 | 50.34 ± 8.49 c | 105.92 ± 11.80 b |
| 187.5 | 103.99 ± 10.54 b | 0.034 | 9.77 ± 6.90 c | 87.28 ± 9.25 c | 187.5 + 0.017 | 28.04 ± 7.40 d | 112.90 ± 11.32 b |
| 93.75 | 117.67 ± 13.09 b | 0.017 | 1.21 ± 3.84 c | 89.33 ± 11.72 c | 93.75 + 0.0085 | 27.29 ± 11.68 d | 114.72 ± 11.16 b |
| IC50 | >3000 | IC50 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | >0.27 | IC50 | 512.80 ± 18.37 | >3000.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Eladwy, R.A.; Fares, M.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Chang, D.; Li, C.-G.; Bhuyan, D.J. Postbiotics Combination Synergises the Antiproliferative Effects of Doxorubicin in Gastric Cancer Cells: A Cellular and Molecular Deep Dive. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010362
Eladwy RA, Fares M, Alsherbiny MA, Chang D, Li C-G, Bhuyan DJ. Postbiotics Combination Synergises the Antiproliferative Effects of Doxorubicin in Gastric Cancer Cells: A Cellular and Molecular Deep Dive. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010362
Chicago/Turabian StyleEladwy, Radwa A., Mohamed Fares, Muhammad A. Alsherbiny, Dennis Chang, Chun-Guang Li, and Deep Jyoti Bhuyan. 2026. "Postbiotics Combination Synergises the Antiproliferative Effects of Doxorubicin in Gastric Cancer Cells: A Cellular and Molecular Deep Dive" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010362
APA StyleEladwy, R. A., Fares, M., Alsherbiny, M. A., Chang, D., Li, C.-G., & Bhuyan, D. J. (2026). Postbiotics Combination Synergises the Antiproliferative Effects of Doxorubicin in Gastric Cancer Cells: A Cellular and Molecular Deep Dive. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010362









