Expression of Serum and Exosomal microRNA-34a in Subjects with Increased Fat Mass †
Abstract
1. Introduction
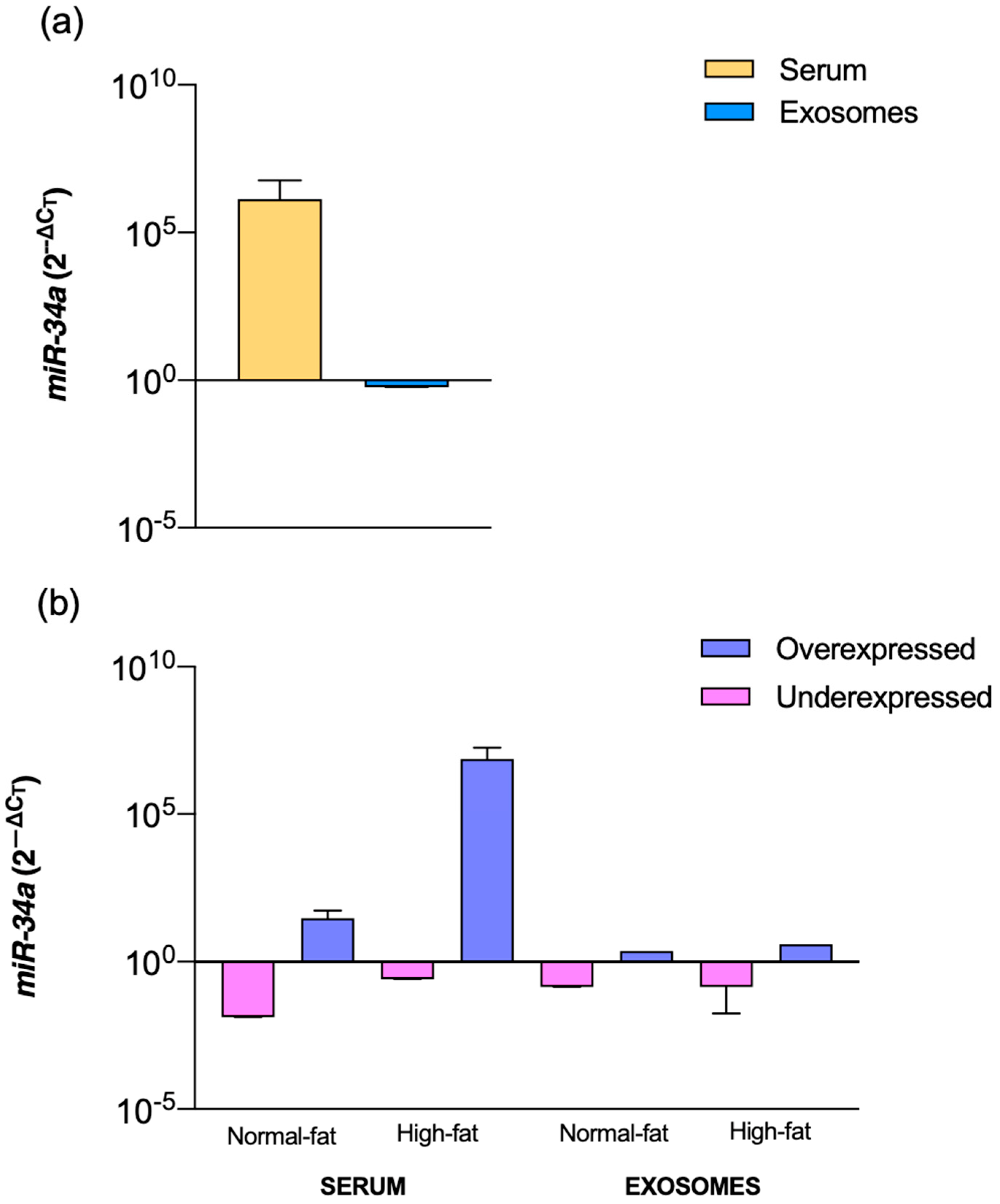
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
4.2. Chemical and Anthropometric Indices
4.3. Exosome Isolation and Characterization
4.4. miRs Extraction from Isolated Exosomes
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujiwara, S.; Morikawa, K.; Endo, T.; Hisamoto, H.; Sueyoshi, K. Size Sorting of Exosomes by Tuning the Thicknesses of the Electric Double Layers on a Micro-Nanofluidic Device. Micromachines 2020, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Zhang, Y. Understanding exosomes: Part 1—Characterization, quantification and isolation techniques. Periodontology 2000 2024, 94, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404, Erratum in J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, H.; Bihl, J.; Borthakur, A. A Simplified Method for the Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles from Probiotic Bacteria and Their Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttiah, B.; Law, J.X. Milk-derived extracellular vesicles and gut health. npj Sci. Food 2025, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathi, V.; Ai, W.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.; Gopal, T.; Kumar, N.; Malhi, H.; Sehrawat, T.; Desouza, C.V. A Pilot Study on the Proteomics Profile of Serum Exosome-Enriched Extracellular Vesicles from Normal versus Individuals with Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Devi, S.; Singh, T.G.; Yadav, N.; Kumar, P.; Chatterjee, A. Exosomes as Crucial Player in Insulin Resistance and Obesity: Potential Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Pharm. Qual. Assur. 2022, 13, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, L.; Al-Jaber, H.; Prince, M.S.; Elrayess, M.A. Role of Inflammatory Cytokines, Growth Factors and Adipokines in Adipogenesis and Insulin Resistance. Inflammation 2021, 45, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.C.; Giordano, C.; Pitrone, M.; Galluzzo, A. Cut-off points of the visceral adiposity index (VAI) identifying a visceral adipose dysfunction associated with cardiometabolic risk in a Caucasian Sicilian population. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-Meraz, F.-I.; Mercado, M.V.-D.; Ortega, F.J.; Ruiz-Quezada, S.-L.; Guzmán-Ornelas, M.-O.; Navarro-Hernández, R.-E. Ageing influences the relationship of circulating miR-33a and miR-33b levels with insulin resistance and adiposity. SAGE J. 2018, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, A.; Lazar, A.L.; Buchman, C.; Tiperciuc, B.; Orasan, O.H.; Cozma, A. MicroRNAs: The Link between the Metabolic Syndrome and Oncogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharanei, S.; Shabir, K.; Brown, J.E.; Weickert, M.O.; Barber, T.M.; Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S. Regulatory microRNAs in Brown, Brite and White Adipose Tissue. Cells 2020, 9, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.D.; Wu, S.N.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, X.J.; Wei, H.Y. Correlation between serum microRNA-122 and insulin resistance in obese children. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2019, 21, 910–914. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, P.; Liu, J.; Xie, X. Exosomal microRNA-122 mediates obesity-related cardiomyopathy through suppressing mitochondrial ADP-ribosylation factor-like 2. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tan, C. miRNAs in Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Multiple Roles in Development of Obesity-Associated Disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.M.; Lin, X.; Xu, F.; Shan, S.K.; Guo, B.; Li, F.X.; Zheng, M.H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.S.; Yuan, L.Q. Exosomes and Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 651996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Imani, S.; Wu, M.Y.; Wu, R.C. MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers 2023, 15, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdoncin, M.; Konrad, A.; Wyner, J.R.; Lohana, S.; Pillai, S.S.; Pereira, D.G.; Lakhani, H.V.; Sodhi, K. A Review of miRNAs as Biomarkers and Effect of Dietary Modulation in Obesity Associated Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 756499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Hui, X.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Ye, D.; Chan, C.Y.C.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Xu, A. Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2024; World Obesity Federation: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesity. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Choe, S.S.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, J.B. Adipose Tissue Remodeling: Its Role in Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders. Front. Endocrinol 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.H.; Ye, T.Q.; Zhang, M.J.; Mu, Y. Exosomes as Vehicles for Noncoding RNA in Modulating Inflammation: A Promising Regulatory Approach for Ischemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 7485–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Gao, J.W.; Yang, L.X.; Yuan, X.X. Roles of Exosomal miRNAs in Asthma: Mechanisms and Applications. J. Asthma Allergy 2024, 17, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagrán-Silva, F.; Loren, P.; Sandoval, C.; Lanas, F.; Salazar, L.A. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: A Narrative Review. Genes 2025, 16, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raucci, A.; Vinci, M.C. miR-34a: A Promising Target for Inflammaging and Age-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Tang, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, X.; Lv, J. IL-6/STAT3/miR-34a protects against neonatal lung injury patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Herter, E.K.; Qian, M.; Toma, M.A.; Wintler, A.M.; Serezal, I.G.; et al. MicroRNA-34 Family Enhances Wound Inflammation by Targeting LGR4. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 465–476.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Deng, W.; Chen, X.; Fan, S.; Peng, J.; Tang, X.; Wang, D.; Yu, Q. Adipose-Derived Circulating Exosomes Promote Protection of the Pulmonary Endothelial Barrier by Inhibiting EndMT and Oxidative Stress through Down-Regulation of the TGF-β Pathway: A Potential Explanation for the Obesity Paradox in ARDS. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5475832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lischka, J.; Schanzer, A.; Hojreh, A.; Ba-Ssalamah, A.; de Gier, C.; Valent, I.; Item, C.B.; Greber-Platzer, S.; Zeyda, M. Circulating microRNAs 34a, 122, and 192 are linked to obesity-associated inflammation and metabolic disease in pediatric patients. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yin, C.; Lan, X.; Wu, L.; Du, X.; Griffiths, H.R.; Gao, D. Adipokines, Hepatokines and Myokines: Focus on Their Role and Molecular Mechanisms in Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 873699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yin, B.; Guo, S.; Umar, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zahoor, A.; Deng, G. Enhanced Expression of miR-34a Enhances Escherichia coli Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Endometritis by Targeting LGR4 to Activate the NF-kappaB Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1744754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huo, J.; Zhang, D.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Y. Chemerin/ChemR23 axis triggers an inflammatory response in keratinocytes through ROS-sirt1-NF-κB signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6459–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheleschi, S.; Giordano, N.; Volpi, N.; Tenti, S.; Gallo, I.; Di Meglio, M.; Giannotti, S.; Fioravanti, A. A Complex Relationship between Visfatin and Resistin and microRNA: An In Vitro Study on Human Chondrocyte Cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheleschi, S.; Tenti, S.; Mondanelli, N.; Corallo, C.; Barbarino, M.; Giannotti, S.; Gallo, I.; Giordano, A.; Fioravanti, A. MicroRNA-34a and MicroRNA-181a Mediate Visfatin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via NF-kappaB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Cells 2019, 8, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Cao, Y.; Ma, L.; Shen, Y.; Velikanova, A.A.; Li, X.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y. miR-34a regulates lipid metabolism by targeting SIRT1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with iron overload. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 695, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zalzala, M.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y. A metabolic stress-inducible miR-34a-HNF4alpha pathway regulates lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, M.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, L.; Bai, Z.; Wang, B.; Guo, Z.; Hou, A.; Li, H. MicroRNA-34a in coronary heart disease: Correlation with disease risk, blood lipid, stenosis degree, inflammatory cytokines, and cell adhesion molecules. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, H.; Pan, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Xia, S.; Shao, Q. miR-34a and miR-125b are upregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5589–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Wahby, A.A.; Ashmawy, I.; Saleh, R.M.; Soliman, H. Association of Exosomal miR-34a with Markers of Dyslipidemia and Endothelial Dysfunction in Children and Adolescents with T1DM. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2020, 12, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Rodriguez Polanco, S.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Peña Genao, E.; Guzman, E.; Kostara, C.E. The Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) Ratio as a Risk Marker for Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xia, B.; Song, B.; Zhang, H. Association of LDLc to HDLc ratio with carotid plaques in a community-based population with a high stroke risk: A cross-sectional study in China. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 88, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, K.; Gu, Z.; Ding, H.; Li, S.; Qin, J.; Chu, X. MicroRNA-34a Mediates High-Fat-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Targeting ENO3. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.H.; Deng, B.; Winkler, J.; Zirnheld, A.L.; Ehringer, S.; Shetty, V.; Cox, M.; Nguyen, H.; Shen, W.J.; Huang, T.T.; et al. Over-expression of miR-34c leads to early-life visceral fat accumulation and insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovis, P.; Roggli, E.; Laybutt, D.R.; Gattesco, S.; Yang, J.Y.; Widmann, C.; Abderrahmani, A.; Regazzi, R. Alterations in microRNA expression contribute to fatty acid-induced pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2728–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuzbashian, E.; de Campos Zani, S.C.; Zarkash, M.; Asghari, G.; Hedayati, M.; Khalaj, A.; Chan, C.B. Elevated miR-143 and miR-34a gene expression in human visceral adipose tissue are associated with insulin resistance in non-diabetic adults: A cross-sectional study. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2022, 27, 3419–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Sasaki, H.; Ueda, S.; Miyamoto, S.; Terada, S.; Konishi, H.; Kogata, Y.; Ashihara, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Serum exosomal microRNA-34a as a potential biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhshiteh, F.; Rahmani, S.; Ostad, S.N.; Madjd, Z.; Dinarvand, R.; Atyabi, F. Exosomes derived from miR-34a-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit in vitro tumor growth: A new approach for drug delivery. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, P.J.; Vergoni, B.; Ohanna, M.; Angot, B.; Gonzalez, T.; Jager, J.; Tanti, J.F.; Cormont, M. The Stress-Responsive microRNA-34a Alters Insulin Signaling and Actions in Adipocytes through Induction of the Tyrosine Phosphatase PTP1B. Cells 2022, 11, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Singh, A.; Gupta, N.; Raja, K.; Singh, P.; Agarwal, S.; Sharma, A. Non-invasive diagnostic potential of microRNA-203 in liquid biopsy of urothelial carcinoma of bladder. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postole, X.; Cimponeriu, D.; Alexiu Toma, O.A.; Radu, I.; Berca, L.; Eremia, I.; Nica, S.; Nica, R. The Impact of miRNAs in Diabetes Mellitus. Rom. J. Mil. Med. 2025, 128, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Abdallah, G.M.; Ibrahim, I.T.; Ali, N.S.; Hussein, M.A.; Thabet, G.M.; Azzam, O.M.; Mohamed, A.Y.; Farghly, M.I.; Al Hussain, E.; et al. Evaluation of miRNA-146a, miRNA-34a, and pro-inflammatory cytokines as a potential early indicators for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Y. miR-34a increases inflammation and oxidative stress levels in patients with necrotizing enterocolitis by downregulating SIRT1 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erceg, S.; Munjas, J.; Sopić, M.; Tomašević, R.; Mitrović, M.; Kotur-Stevuljević, J.; Mamić, M.; Vujčić, S.; Klisic, A.; Ninić, A. Expression Analysis of Circulating miR-21, miR-34a and miR-122 and Redox Status Markers in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Patients with and Without Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrow, J.S.; Webster, J. Quetelet’s index (W/H2) as a measure of fatness. Int. J. Obes. 1985, 9, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freedman, D.S.; Thornton, J.C.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.N., Jr.; Blanck, H.M.; Gallagher, D. The body adiposity index (hip circumference ÷ height(1.5)) is not a more accurate measure of adiposity than is BMI, waist circumference, or hip circumference. Obesity 2012, 20, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Abdominal volume index. An anthropometry-based index for estimation of obesity is strongly related to impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med. Res. 2003, 34, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, R.; Seidell, J.C.; Ahn, Y.I.; Weiss, K.M. A new index of abdominal adiposity as an indicator of risk for cardiovascular disease. A cross-population study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1993, 17, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, M.C.; Giordano, C.; Galia, M.; Criscimanna, A.; Vitabile, S.; Midiri, M.; Galluzzo, A. Visceral Adiposity Index: A reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noboa-Velástegui, J.; León, J.C.; Castro, J.; Fletes, A.; Madrigal, P.; Álvarez, I.; Navarro, R. Comparison of Methods for Isolating Exosomes from Plasma Subjects with Normal and High Fat Percentages. Life 2025, 15, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ThermoFisher. miRNA from Serum and Plasma Samples Reference Guide; Thermo Fisher Scientific: Waltham, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Avcilar, T. 32nd European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025). Obes. Facts 2025, 18, 1–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups | Normal-Fat Percentage | High-Fat Percentage | pValue |
| n | 74 | 68 | |
| Sex (Men:Women) | 33:41 | 25:43 | |
| Age (years) | 40 ± 9 | 33 ± 11 | |
| Blood Pressure (mmHg) | |||
| Systolic | 109 ± 7 | 117 ± 13 | 0.0015 |
| Diastolic | 67 ± 11 | 75 ± 11 | 0.0003 |
| Lipid Profile (mg/dL) | |||
| HDLc | 35.6 ± 13.9 | 33.3 ± 6.8 | NS |
| LDLc | 93.4 ± 47.9 | 108.2 ± 56.1 | NS |
| sdLDLc | 21.8 ± 6.1 | 29.3 ± 18.9 | NS |
| VLDLc | 22.4 ± 13.8 | 40.6 ± 38.1 | <0.0001 |
| TC | 176 ± 46 | 196 ± 45 | 0.0299 |
| Triglycerides | 107 ± 71 | 207 ± 189 | <0.0001 |
| Cardiovascular risk ratios | |||
| sdLDLc/LDLc | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 0.5 ± 0.7 | NS |
| TC/HDLc | 5.2 ± 1.5 | 6.1 ± 2.9 | 0.0003 |
| LDLc/HDLc | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 3.4 ± 2.3 | NS |
| TG/HDLc | 3.1 ± 1.9 | 6.8 ± 8.4 | <0.0001 |
| Inflammatory Parameters | |||
| C3 (mg/dL) | 75.9 ± 12.2 | 94.6 ± 17.4 | <0.0001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 5.7 ± 3.4 | 10.6 ± 7.0 | <0.0001 |
| Insulin Resistance Status | |||
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 76.7 ± 16.5 | 87.7 ± 40.2 | 0.0331 |
| Fasting insulin (μUI/mL) | 12.4 ± 9.2 | 21.7 ± 11.2 | <0.0001 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.5 ± 2.6 | 4.7 ± 4.1 | <0.0001 |
| HOMA-B | 549 ± 878 | 6812 ± 1106 | NS |
| QUICKI | 0.35 ± 0.05 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | <0.0001 |
| Body Adiposity Status Evaluation | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.7 ± 4.3 | 33.8 ± 5.5 | <0.0001 |
| BAI | 27. 6 ± 4.2 | 34.8 ± 9.5 | <0.0001 |
| AVI (cm2) | 14.0 ± 5.8 | 23.0 ± 8.6 | <0.0001 |
| CI | 15.9 ± 44.7 | 5.3 ± 32.4 | <0.0001 |
| VAI | 1.3 ± 3.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | <0.0001 |
| WC (cm) | 79.1 ± 18.5 | 103.7 ± 21.6 | <0.0001 |
| SA | 126 ± 593 | −401 ± 1524 | NS |
| VA | 394 ± 581 | 1294 ± 1556 | <0.0001 |
| Adipokines (ng/mL) | |||
| AdipoQT | 7055 ± 3683 | 6091 ± 3010 | NS |
| AdipoQ-H | 1672 ± 1487 | 1283 ± 1443 | NS |
| Chemerin | 112 ± 73 | 106 ± 52 | NS |
| CCL2 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | NS |
| Parameters | Serum miR-34a (rho) | Exosome miR-34a (rho) |
|---|---|---|
| Lipid Profile(mg/dL) | ||
| HDLc | 0.53 | 0.19 |
| LDLc | 0.17 | −0.26 |
| sdLDLc | 0.35 | −0.62 * |
| TC | −0.11 | −0.27 |
| Triglycerides | −0.42 | −0.82 |
| Cardiovascular risk ratios | ||
| sdLDLc/LDLc | 0.13 | −0.06 |
| TC/HDLc | 0.42 | −0.08 |
| LDLc/HDLc | −0.07 | −0.49 |
| TG/HDLc | −0.60 | −0.01 |
| Inflammatory Parameters | ||
| C3 (mg/dL) | −0.45 | −0.05 |
| CRP (mg/L) | −0.27 | −0.39 |
| Insulin Resistance Status | ||
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 0.03 | −0.24 |
| Fasting insulin (μUI/mL) | −0.35 | −0.25 |
| HOMA-IR | −0.33 | −0.27 |
| HOMA-B | −0.39 | −0.02 |
| QUICKI | 0.36 | 0.29 |
| Body Adiposity Status Evaluation | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | −0.46 | −0.01 |
| BAI | −0.34 | 0.11 |
| AVI | −0.55 | −0.04 |
| SA | −0.17 | −0.13 |
| VA | −0.13 | 0.04 |
| Adipokines(ng/mL) | ||
| AdipoQT | −0.05 | −0.40 |
| AdipoQ-H | −0.06 | −0.04 |
| CHEM | −0.06 | −0.13 |
| CCL2 | −0.07 | −0.35 |
| Model | p Value | Nagelkerke R2 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.6 |
| M2 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 0.6 |
| M3 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 0.9 |
| M4 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Noboa-Velástegui, J.A.; Valdez-Vega, R.I.; Castro-Albarran, J.; Madrigal-Ruiz, P.; Fletes-Rayas, A.L.; Ruiz-Quezada, S.L.; Ramos-Márquez, M.E.; López-Jiménez, J.d.J.; Álvarez, I.; Navarro-Hernández, R.E. Expression of Serum and Exosomal microRNA-34a in Subjects with Increased Fat Mass. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010270
Noboa-Velástegui JA, Valdez-Vega RI, Castro-Albarran J, Madrigal-Ruiz P, Fletes-Rayas AL, Ruiz-Quezada SL, Ramos-Márquez ME, López-Jiménez JdJ, Álvarez I, Navarro-Hernández RE. Expression of Serum and Exosomal microRNA-34a in Subjects with Increased Fat Mass. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010270
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoboa-Velástegui, Jacqueline Alejandra, Rodolfo Iván Valdez-Vega, Jorge Castro-Albarran, Perla Madrigal-Ruiz, Ana Lilia Fletes-Rayas, Sandra Luz Ruiz-Quezada, Martha Eloisa Ramos-Márquez, José de Jesús López-Jiménez, Iñaki Álvarez, and Rosa Elena Navarro-Hernández. 2026. "Expression of Serum and Exosomal microRNA-34a in Subjects with Increased Fat Mass" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010270
APA StyleNoboa-Velástegui, J. A., Valdez-Vega, R. I., Castro-Albarran, J., Madrigal-Ruiz, P., Fletes-Rayas, A. L., Ruiz-Quezada, S. L., Ramos-Márquez, M. E., López-Jiménez, J. d. J., Álvarez, I., & Navarro-Hernández, R. E. (2026). Expression of Serum and Exosomal microRNA-34a in Subjects with Increased Fat Mass. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010270






