Expression and Clinical Significance of MAPK8, MAPK9, MAP2K4, and MAP2K7 Genes in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
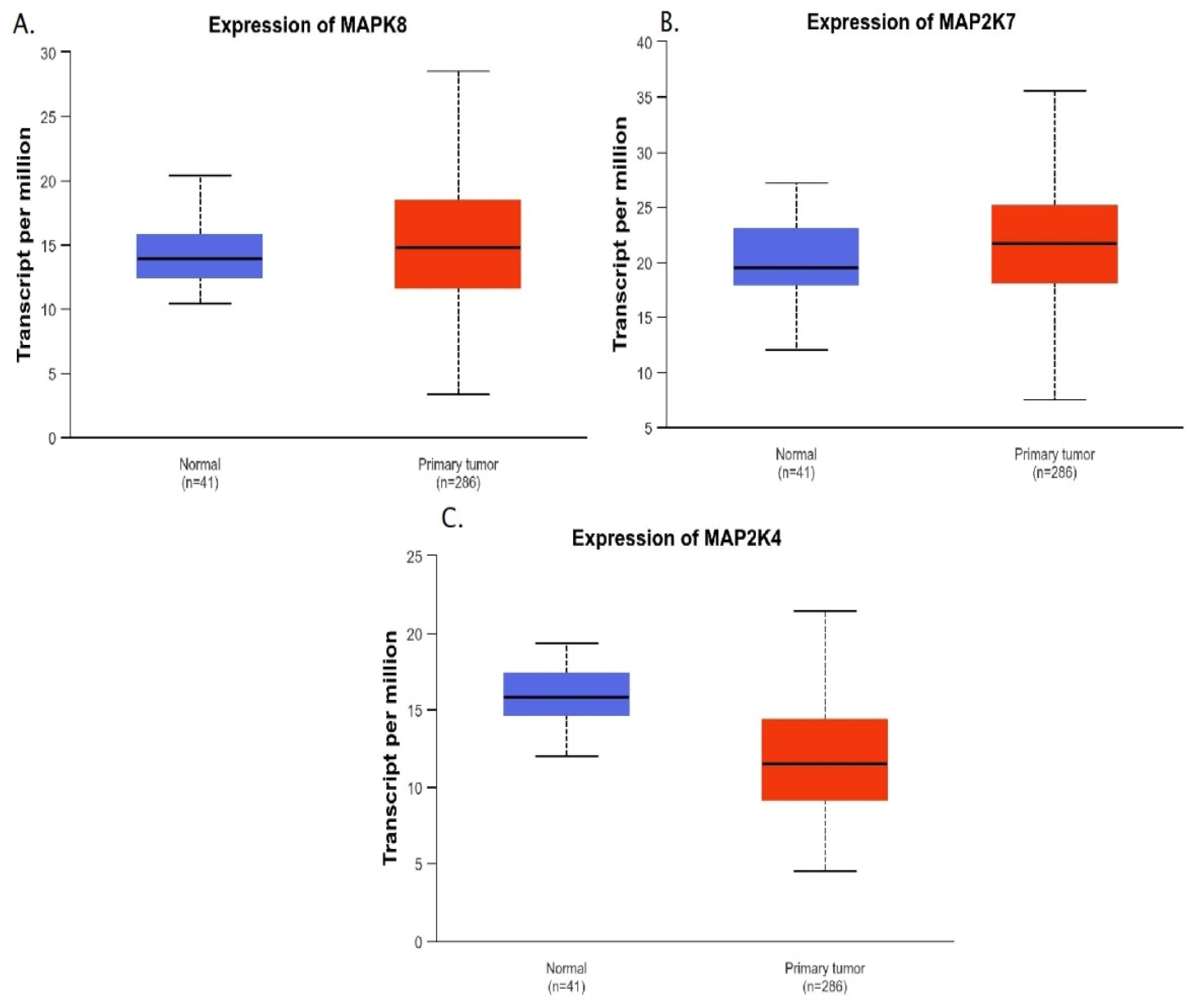
2. Results
Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. RNA Isolation
4.2.2. Reverse Transcription Reaction
4.2.3. Real-Time PCR
4.2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.2.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, P.; Yang, X.; Qiao, L.; Gong, Y. Identification of Six Genes as Diagnostic Markers for Colorectal Cancer Detection by Integrating Multiple Expression Profiles. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 3850674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattray, N.J.W.; Charkoftaki, G.; Rattray, Z.; Hansen, J.E.; Vasiliou, V.; Johnson, C.H. Environmental influences in the etiology of colorectal cancer: The premise of metabolomics. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 3, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanikachalam, K.; Khan, G. Colorectal cancer and nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burotto, M.; Chiou, V.L.; Lee, J.M.; Kohn, E.C. The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: A new perspective. Cancer 2014, 120, 3446–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.F.; Sun, D.F.; Tian, X.Q.; Fang, J.Y. Inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway decreases DNA methylation in colon cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12249–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaj, C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Lamprecht, S.; Hermeking, H.; Jung, A.; Kirchner, T.; Horst, D. Oncogenic Effects of High MAPK Activity in Colorectal Cancer Mark Progenitor Cells and Persist Irrespective of RAS Mutations. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, D.; Keane, M.; Pirianov, G.; Mehmet, H.; Samali, A.; Szegezdi, E. Differential activation of JNK1 isoforms by TRAIL receptors modulate apoptosis of colon cancer cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Richardson, B.C. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacorazza, H.D. Pharmacological inhibition of the MAP2K7 kinase in human disease. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1486756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.N.; Teng, Q.X.; Tian, Q.; Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Wu, K.; Zeng, Q.; Zeng, L.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Z.S.; et al. Signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions in gastric cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.J.; Choong, D.Y.; Ramakrishna, M.; Ryland, G.L.; Campbell, I.G.; Gorringe, K.L. Analysis of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MAP2K4) tumor suppressor gene in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.N.; Huang, J.; Duan, Y.H.; Zhou, J.M.; Huang, P.Z.; Fan, X.J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, J.P.; et al. Downregulation of phosphorylated MKK4 is associated with a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34352–34361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Hao, W.; Gao, W.Q.; Xu, H. hnRNPA2B1 Promotes Colon Cancer Progression via the MAPK Pathway. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 666451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barault, L.; Veyrie, N.; Jooste, V.; Lecorre, D.; Chapusot, C.; Ferraz, J.M.; Lièvre, A.; Cortet, M.; Bouvier, A.M.; Rat, P.; et al. Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI(3)K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a population-based series of colon cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2255–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, S.; Evert, K.; Utpatel, K.; Muggli, A.; Simile, M.M.; Chen, X.; Evert, M.; Calvisi, D.F.; Scheiter, A. Identification of DUSP4/6 overexpression as a potential rheostat to NRAS-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Yu, L.L.; Han, N.; Zhang, B.T. miR-141 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting MAP2K4. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Sato, A.; Aihara, Y.; Ikarashi, Y.; Midorikawa, Y.; Kracht, M.; Nakagama, H.; Okamoto, K. MKK7 mediates miR-493-dependent suppression of liver metastasis of colon cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, G.; Lu, Y.; Zuo, S.; Duan, D.; Luo, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Q.; et al. TIMER3: An enhanced resource for tumor immune analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, W534–W541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinney, J.; Dienstmann, R.; Wang, X.; de Reyniès, A.; Schlicker, A.; Soneson, C.; Marisa, L.; Roepman, P.; Nyamundanda, G.; Angelino, P.; et al. The consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, I.; Kundra, R.; Mastrogiacomo, B.; Tran, T.N.; Sikina, L.; Mazor, T.; Li, X.; Ochoa, A.; Zhao, G.; Lai, B.; et al. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 3861–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, A.; Bruun, J.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Ramirez, L.; Murumägi, A.; Arjama, M.; Danielsen, S.A.; Kryeziu, K.; Elez, E.; et al. Colorectal cancer consensus molecular subtypes translate to distinct oncogenic pathways. Gut 2018, 67, 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, S.K.; Chandrashekar, D.S.; Sahai, S.; Shrestha, S.; Aneja, R.; Singh, R.; Kleer, C.G.; Kumar, S.; Qin, Z.S.; Nakshatri, H.; et al. MammOnc-DB, an integrative breast cancer data analysis platform for target discovery. NPJ Breast Cancer 2025, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posta, M.; Győrffy, B. Pathway-level mutational signatures predict breast cancer outcomes and reveal therapeutic targets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 182, 5734–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrington, G.; Tonge, L.; Branagan, T.; Sudirman, S.; Fang, C.; Luk, L.; Kir, S.; Bolis, M.; Ahmetov, I.I.; Ross, K. The Roles of EDA2R in Ageing and Disease. Aging Cell 2025, 24, e70282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| KRAS Mutant vs. Wild-Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene Expression Level: | MAP2K4 | MAP2K7 | MAPK8 | MAPK9 |
| COAD—colon adenocarcinoma (n = 401) | −0.002 | 0.005 | −0.03 | 0.006 |
| READ—rectum adenocarcinoma (n = 144) | −0.058 | 0.022 | −0.072 | −0.005 |
| PIK3CA Mutant vs. Wild-type | ||||
| COAD (n = 401) | 0.014 | −0.027 | 0.012 | −0.016 |
| READ (n = 144) | 0.059 | −0.038 | −0.033 | 0.021 |
| BRAF Mutant vs. Wild-type | ||||
| COAD (n = 401) | 0.14 higher level in mutant p < 0.05 | 0.021 | 0.112 higher level in mutant p < 0.05 | 0.007 |
| READ (n = 144) | 0.199 | 0.048 | 0.106 | −0.034 |
| TGFB1 Mutant vs. Wild-type | ||||
| COAD (n = 401) | 0.171 higher level in mutants p < 0.05 | 0.017 | 0.064 | 0.055 |
| READ (n = 144) | 0.056 | −0.03 | −0.062 | 0.245 |
| Characteristic | Categories | N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor location | Rectum | 27 (50.9) |
| Sigmoid colon | 12 (22.6) | |
| Ascending colon | 5 (9.4) | |
| Recto-sigmoid junction | 4 (7.6) | |
| Splenic flexure | 2 (3.8) | |
| Hepatic flexure | 2 (3.8) | |
| Transverse flexure | 1 (1.9) | |
| AJCC stage | I | 15 (29.4) |
| II | 16 (31.4) | |
| III | 14 (27.4) | |
| IV | 6 (11.8) | |
| Tumor size (TNM classification) | Tis | 1 (1.9) |
| T2 | 14 (27.5) | |
| T3 | 27 (52.9) | |
| T4 | 9 (17.7) | |
| Lymph nodes metastases (TNM classification) | N0 | 31 (60.8) |
| N1 | 10 (19.6) | |
| N2 | 10 (19.6) | |
| Distant metastases (TNM classification) | M0 | 44 (88.0) |
| M1 | 6 (12.0) | |
| Histological grade | Low grade (G1,G2) | 39 (73.6) |
| High grade (G3,G4) | 14 (26.4) | |
| Angioinvasion | Present | 22 (43.1) |
| Absent | 29 (56.9) | |
| Neuroinvasion | Present | 12 (23.5) |
| Absent | 39 (76.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wosiak, A.; Wodziński, D.; Świechowski, R.; Pietrzak, J.; Mik, M.; Balcerczak, E. Expression and Clinical Significance of MAPK8, MAPK9, MAP2K4, and MAP2K7 Genes in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010100
Wosiak A, Wodziński D, Świechowski R, Pietrzak J, Mik M, Balcerczak E. Expression and Clinical Significance of MAPK8, MAPK9, MAP2K4, and MAP2K7 Genes in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleWosiak, Agnieszka, Damian Wodziński, Rafał Świechowski, Jacek Pietrzak, Michał Mik, and Ewa Balcerczak. 2026. "Expression and Clinical Significance of MAPK8, MAPK9, MAP2K4, and MAP2K7 Genes in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010100
APA StyleWosiak, A., Wodziński, D., Świechowski, R., Pietrzak, J., Mik, M., & Balcerczak, E. (2026). Expression and Clinical Significance of MAPK8, MAPK9, MAP2K4, and MAP2K7 Genes in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010100







