Serum Calprotectin as a Novel Biomarker of Disease Severity and Activity in Systemic Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
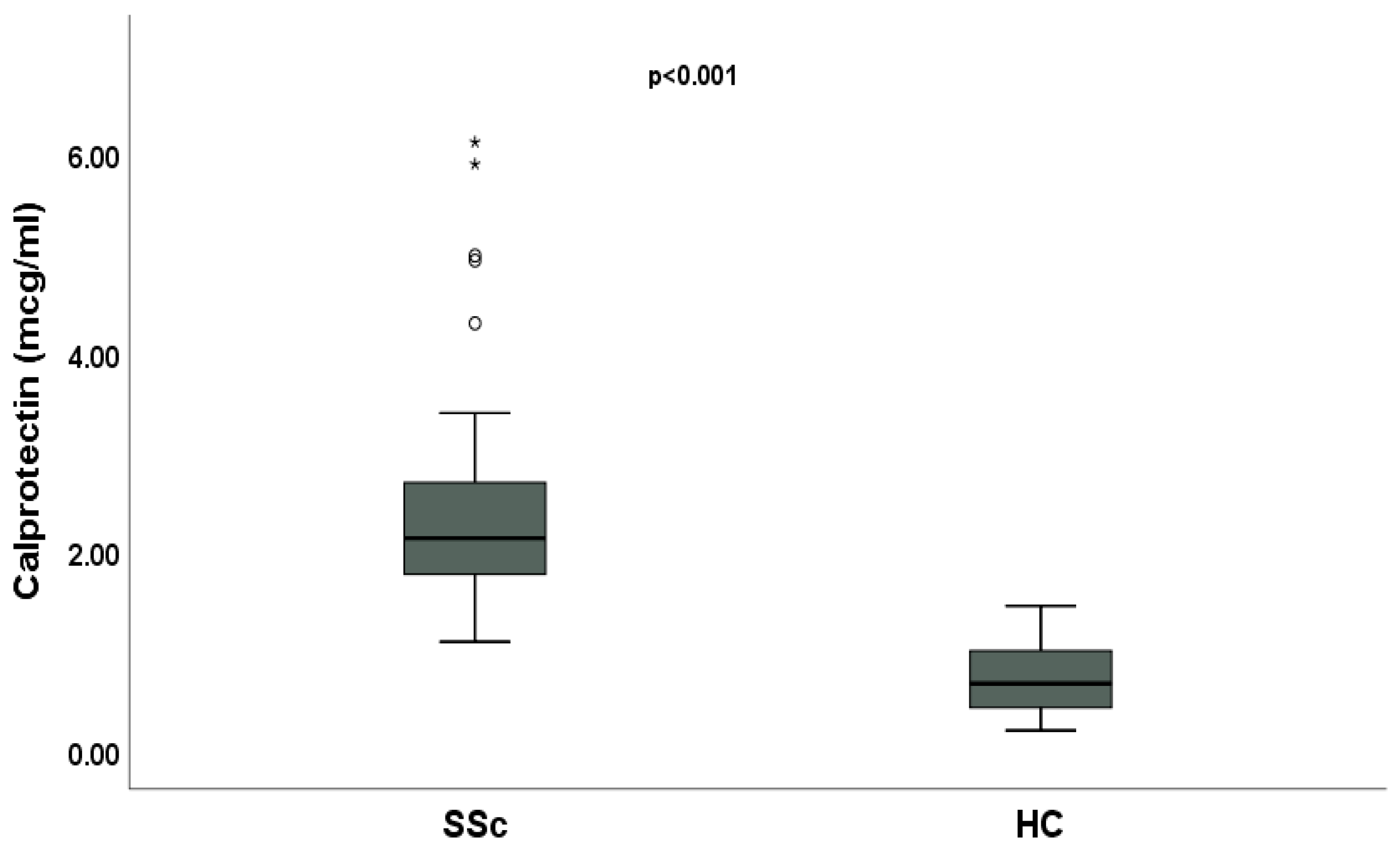
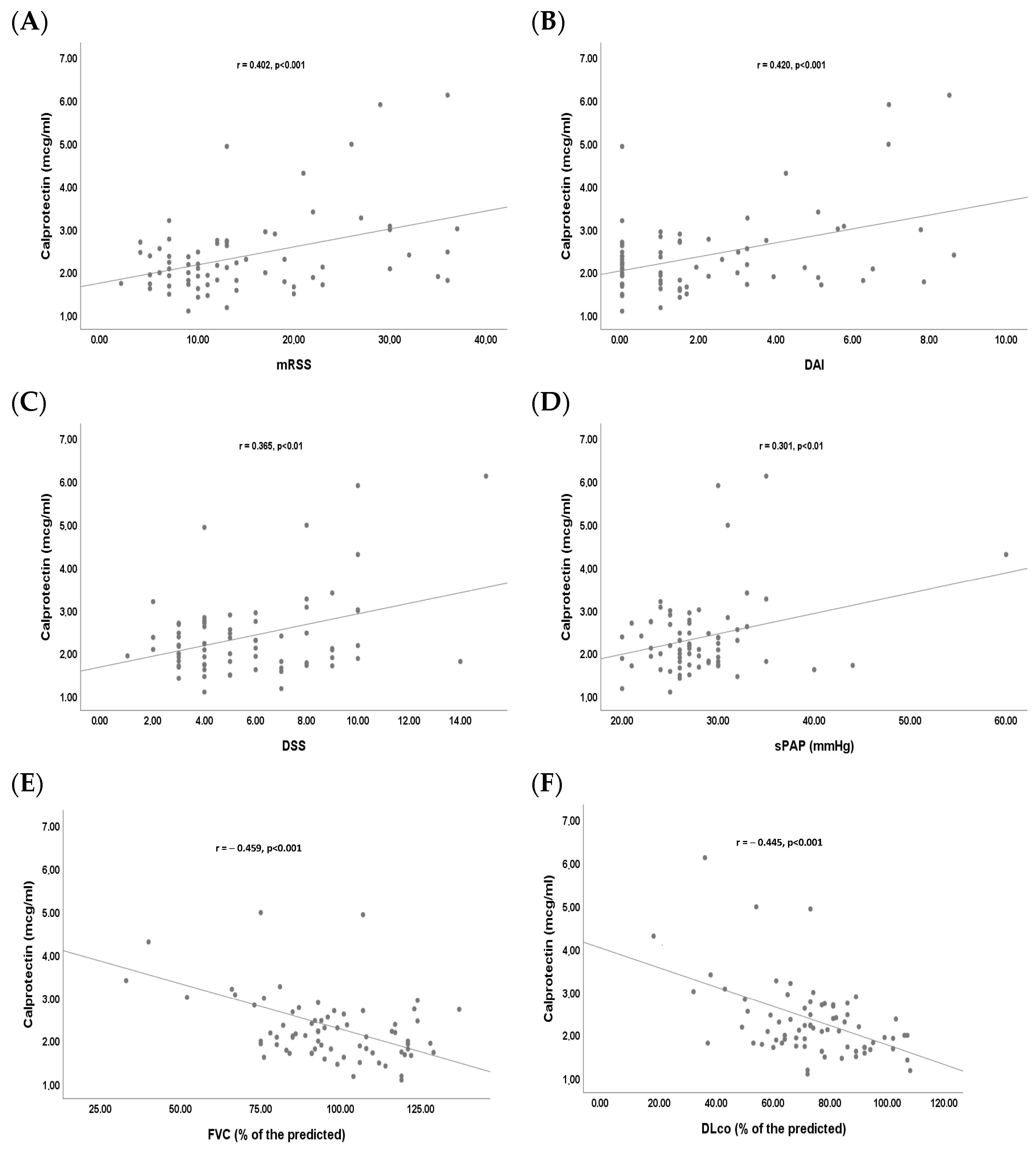
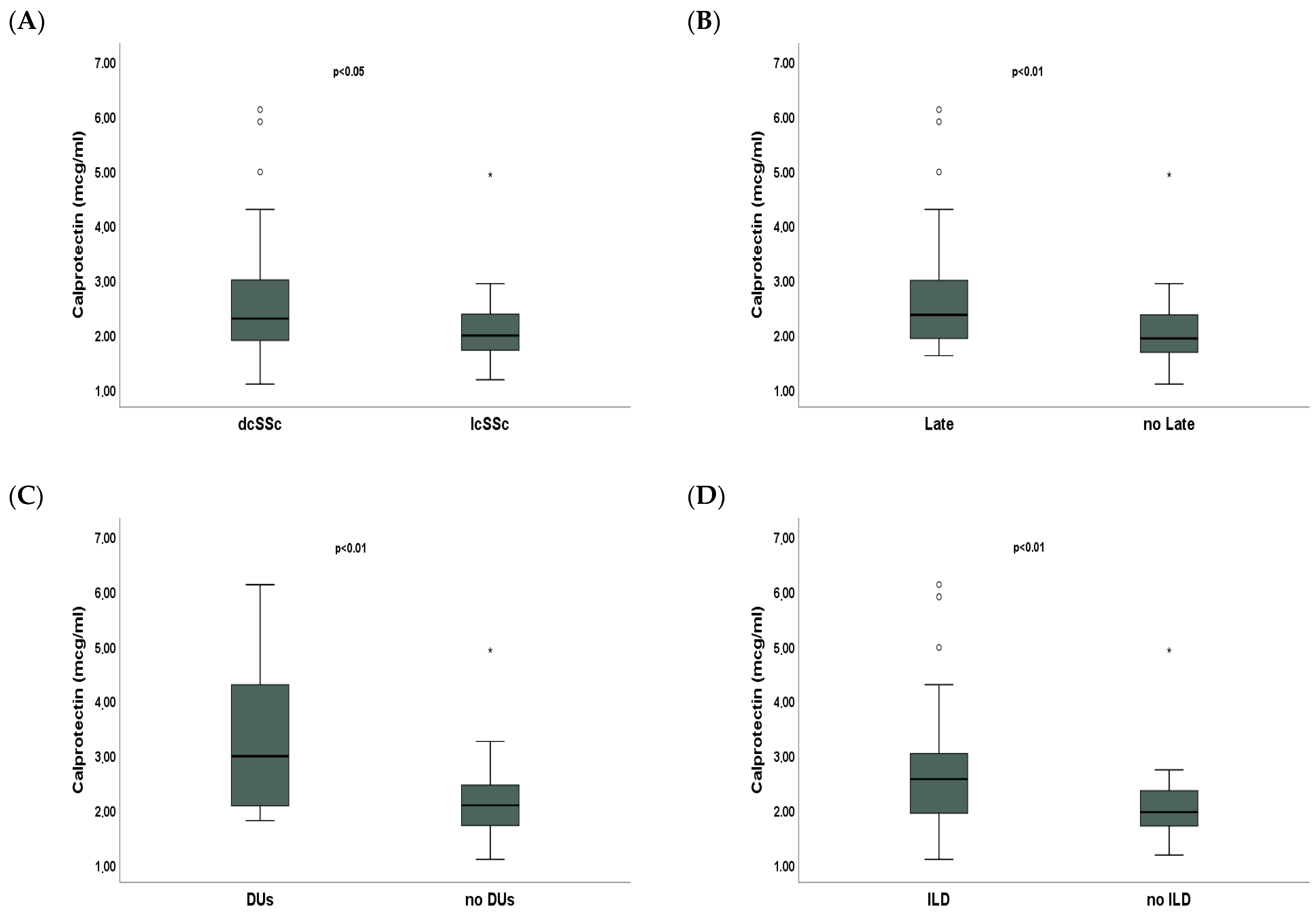
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Clinical Assessment
4.3. Laboratory Assessment
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACR/EULAR | American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Criteria |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DAMP | damage-associated molecular pattern |
| DAI | disease activity index |
| (dc)SSc | diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis |
| DLco | diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide |
| DSS | disease severity scale |
| DUs | digital ulcers |
| EUSTAR | European Scleroderma Trials and Research |
| FVC | forced vital capacity |
| HCs | healthy controls |
| HRCT | high-resolution computed tomography |
| ILD | interstitial lung disease |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| (lc)SSc | limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis |
| mRSS | modified Rodnan skin score |
| NETs | neutrophil extracellular traps |
| NSAIDs | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| NVC | nailfold videocapillaroscopy |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PFTs | pulmonary function tests |
| PMAT | particle-based multi-analyte technology |
| SIBO | small intestinal bacterial overgrowth |
| sPAP | systolic pulmonary artery pressure |
| SSc | systemic sclerosis |
| TGF β | transforming growth factor β |
| TLR4 | toll-like receptor 4 |
References
- Volkmann, E.R.; Andréasson, K.; Smith, V. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2023, 401, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutolo, M.; Matucci, C.M. Nailfold capillaroscopy and classification criteria for systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007, 25, 663–665. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, M.; Hollaender, R.; Rosenberg, D.; Scott, M.; Hunsche, E.; Tyndall, A.; Denaro, V.; Carreira, P.E.; Varju, C.; Gabrielli, B.; et al. An observational cohort study of patients with newly diagnosed digital ulcer disease secondary to systemic sclerosis registered in the EUSTAR database. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S47–S54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amanzi, L.; Braschi, F.; Fiori, G.; Galluccio, F.; Miniati, I.; Guiducci, S.; Conforti, M.-L.; Kaloudi, O.; Nacci, F.; Sacu, O.; et al. Digital ulcers in scleroderma: Staging, characteristics and sub-setting through observation of 1614 digital lesions. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Allanore, Y.; Alves, M.; Brunborg, C.; Airó, P.; Ananieva, L.P.; Czirják, L.; Guiducci, S.; Hachulla, E.; Li, M.; et al. Progressive interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease in the EUSTAR database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloth, C.; Blum, A.C.; Thaiss, W.M.; Preibsch, H.; Ditt, H.; Grimmer, R.; Fritz, J.; Nikolaou, K.; Bösmüller, H.; Horger, M. Differences in Texture Analysis Parameters Between Active Alveolitis and Lung Fibrosis in Chest CT of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuley, R.; Stultz, R.D.; Duvvuri, B.; Wang, T.; Fritzler, M.J.; Hesselstrand, R.; Nelson, J.L.; Lood, C. N-Formyl Methionine Peptide-Mediated Neutrophil Activation in Systemic Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 785275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitorowicz-Buniak, J.; Shiwen, X.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.; Stratton, R. Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S100A9. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bon, L.; Cossu, M.; Loof, A.; Gohar, F.; Wittkowski, H.; Vonk, M.; Roth, J.; Berg, W.v.D.; van Heerde, W.; Broen, J.C.A.; et al. Proteomic analysis of plasma identifies the Toll-like receptor agonists S100A8/A9 as a novel possible marker for systemic sclerosis phenotype. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1585–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselstrand, R.; Wildt, M.; Bozovic, G.; Andersson-Sjöland, A.; Andréasson, K.; Scheja, A.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Bjermer, L.; Wuttge, D.M. Biomarkers from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung disease relate to severity of lung fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machahua, C.; Guler, S.A.; Horn, M.P.; Planas-Cerezales, L.; Montes-Worboys, A.; Geiser, T.K.; Molina-Molina, M.; Funke-Chambour, M. Serum calprotectin as new biomarker for disease severity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A cross-sectional study in two independent cohorts. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2021, 8, e000827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, M.; Van Hoovels, L.; Benucci, M.; De Luca, R.; Coccia, C.; Bernardini, P.; Russo, E.; Amedei, A.; Guiducci, S.; Grossi, V.; et al. Circulating Calprotectin (cCLP) in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnazzo, V.; Redi, S.; Basile, V.; Natali, P.; Gulli, F.; Equitani, F.; Marino, M.; Basile, U. Calprotectin: Two sides of the same coin. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, W.-Y.; Tu, W.-Z.; Chu, H.-Y.; Zhu, X.-X.; Liang, M.-R.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.-C.; Zou, H.-J. Increased expression of S100A8 and S100A9 in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. A correlation with organ involvement and immunological abnormalities. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Leroi, A.-M.; Menard, J.-F.; Levesque, H.; Quillard, M.; Ducrotte, P. Fecal calprotectin in systemic sclerosis and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréasson, K.; Scheja, A.; Saxne, T.; Ohlsson, B.; Hesselstrand, R. Faecal calprotectin: A biomarker of gastrointestinal disease in systemic sclerosis. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 270, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepri, G.; Di Battista, M.; Codullo, V.; Bonomi, F.; Sulis, A.; Guiducci, S.; Della Rossa, A. Systemic sclerosis: One year in review 2024. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2024, 42, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, C.; Romaggioli, L.; Miglionico, M.; Colalillo, A.; Ramaccini, C.; Gigante, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; Rosato, E. Maresin1 is a predictive marker of new digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis patients. Microvasc. Res. 2022, 142, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.C.; Black, C.; Fleischmajer, R.; Jablonska, S.; Krieg, T.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Rowell, N.; Wollheim, F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): Classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini, G.; Iudici, M.; Walker, U.A.; Jaeger, V.K.; Baron, M.; Carreira, P.; Czirják, L.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; Hachulla, E.; et al. The European Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR) task force for the development of revised activity criteria for systemic sclerosis: Derivation and validation of a preliminarily revised EUSTAR activity index. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medsger, T.A.; Silman, A.J.; Steen, V.D.; Black, C.M.; Akesson, A.; Bacon, P.A.; Harris, C.A.; Jablonska, S.; Jayson, M.I.; Jimenez, S.A.; et al. A disease severity scale for systemic sclerosis: Development and testing. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, O.; Highland, K.B.; Gahlemann, M.; Azuma, A.; Fischer, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Raghu, G.; Sauter, W.; Girard, M.; Alves, M.; et al. Nintedanib for Systemic Sclerosis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Radin, M.; Ramirez, C.; Seaman, A.; Bentow, C.; Casas, S.; Cecchi, I.; Rubini, E.; Foddai, S.G.; Baldovino, S.; et al. Evaluation of novel assays for the detection of autoantibodies in antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age, years, median, and IQR | 58 (50;65) |
| Female, n (%) | 63 (85.1) |
| dcSSc, n (%) | 33 (44.6) |
| Disease duration, years, median and IQR | 15 (8;20) |
| mRSS, median and IQR | 12 (9;20) |
| SSc-specific autoantibodies | |
| Anti-topoisomerase I, n (%) | 33 (44.6) |
| Anti-centromere, n (%) | 19 (25.7) |
| Anti-RNA polymerase III, n (%) | 1 (1.3) |
| None, n (%) | 21 (28.4) |
| NVC | |
| Early, n (%) | 17 (23) |
| Active, n (%) | 21 (28.4) |
| Late, n (%) | 36 (48.6) |
| DAI, median and IQR | 1.5 (0;3.26) |
| DSS, median and IQR | 5 (4;8) |
| sPAP, mmHg, median and IQR | 27 (25;30) |
| FVC, % of the predicted, median and IQR | 94.5 (83;112) |
| DLco, % of the predicted, median and IQR | 73 (63;86) |
| ILD, n (%) | 32 (43.2) |
| New DUs, n (%) | 13 (17.6) |
| PAH, n (%) | 3 (4) |
| ILD | ||
| OR (CI 95%) | p | |
| Calprotectin, mcg/mL | 3.687 (1.336;10.170) | <0.05 |
| FVC/DLco | 5.607 (1.317;23.868) | <0.05 |
| Scl70 | 13.744 (3.650;51.752) | <0.001 |
| DUs | ||
| OR (CI 95%) | p | |
| Calprotectin, mcg/mL | 2.531 (1.074;5.961) | <0.05 |
| Late | 1.701 (0.236;12.250) | >0.05 |
| mRSS | 1.121 (1.023;1.229) | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellicano, C.; Villa, A.; Carnazzo, V.; D’Ippolito, G.; Vinante, I.; Laterza, F.; Basile, U.; Rosato, E.; Gigante, A. Serum Calprotectin as a Novel Biomarker of Disease Severity and Activity in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094290
Pellicano C, Villa A, Carnazzo V, D’Ippolito G, Vinante I, Laterza F, Basile U, Rosato E, Gigante A. Serum Calprotectin as a Novel Biomarker of Disease Severity and Activity in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094290
Chicago/Turabian StylePellicano, Chiara, Annalisa Villa, Valeria Carnazzo, Giancarlo D’Ippolito, Ilaria Vinante, Federica Laterza, Umberto Basile, Edoardo Rosato, and Antonietta Gigante. 2025. "Serum Calprotectin as a Novel Biomarker of Disease Severity and Activity in Systemic Sclerosis Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094290
APA StylePellicano, C., Villa, A., Carnazzo, V., D’Ippolito, G., Vinante, I., Laterza, F., Basile, U., Rosato, E., & Gigante, A. (2025). Serum Calprotectin as a Novel Biomarker of Disease Severity and Activity in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094290








