An HD-ZIP I Transcription Factor DZHDZ32 Upregulates Diosgenin Biosynthesis in Dioscorea zingiberensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
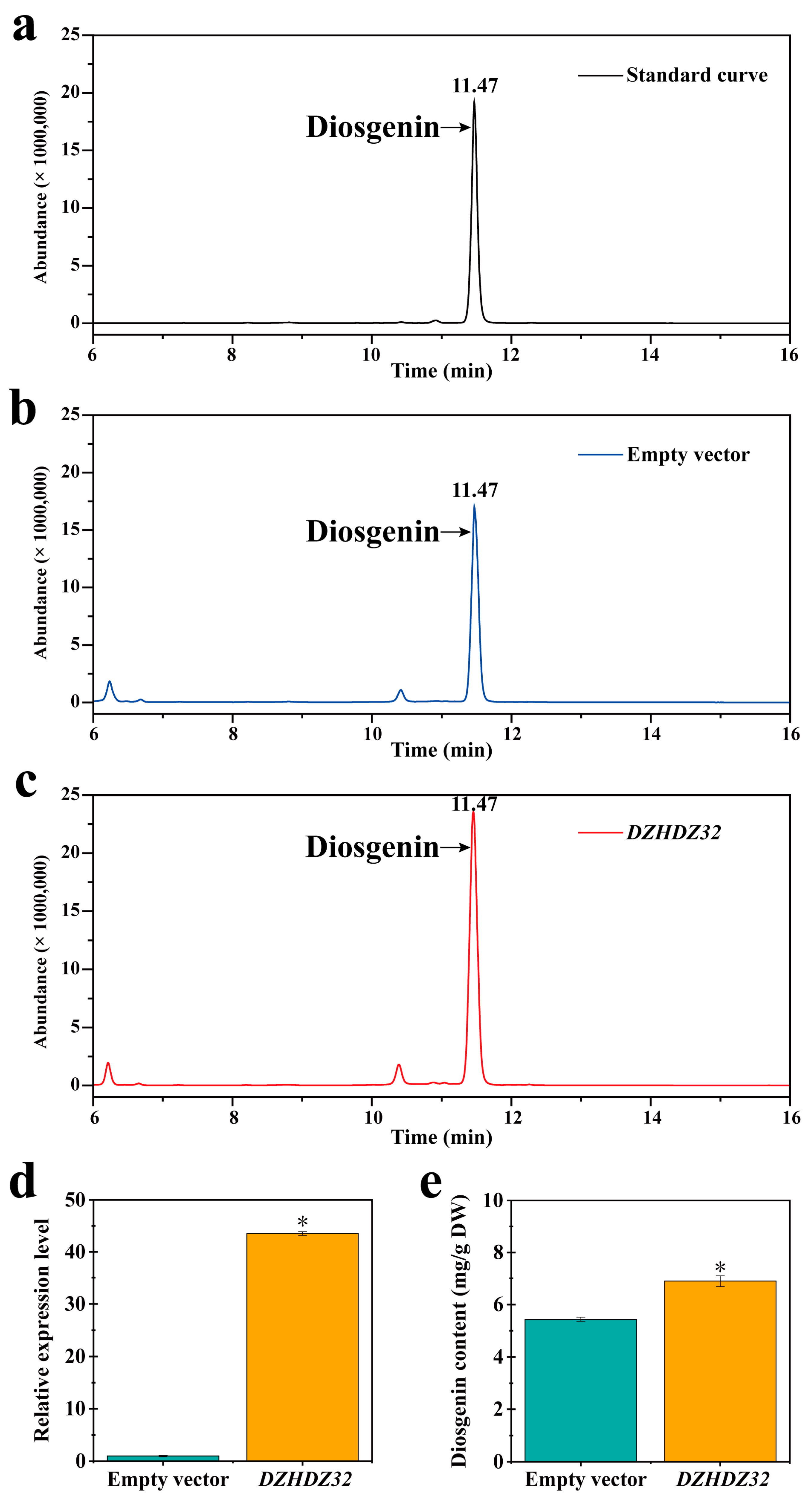
2.1. DZHDZ32 Promotes Diosgenin Accumulation in D. zingiberensis
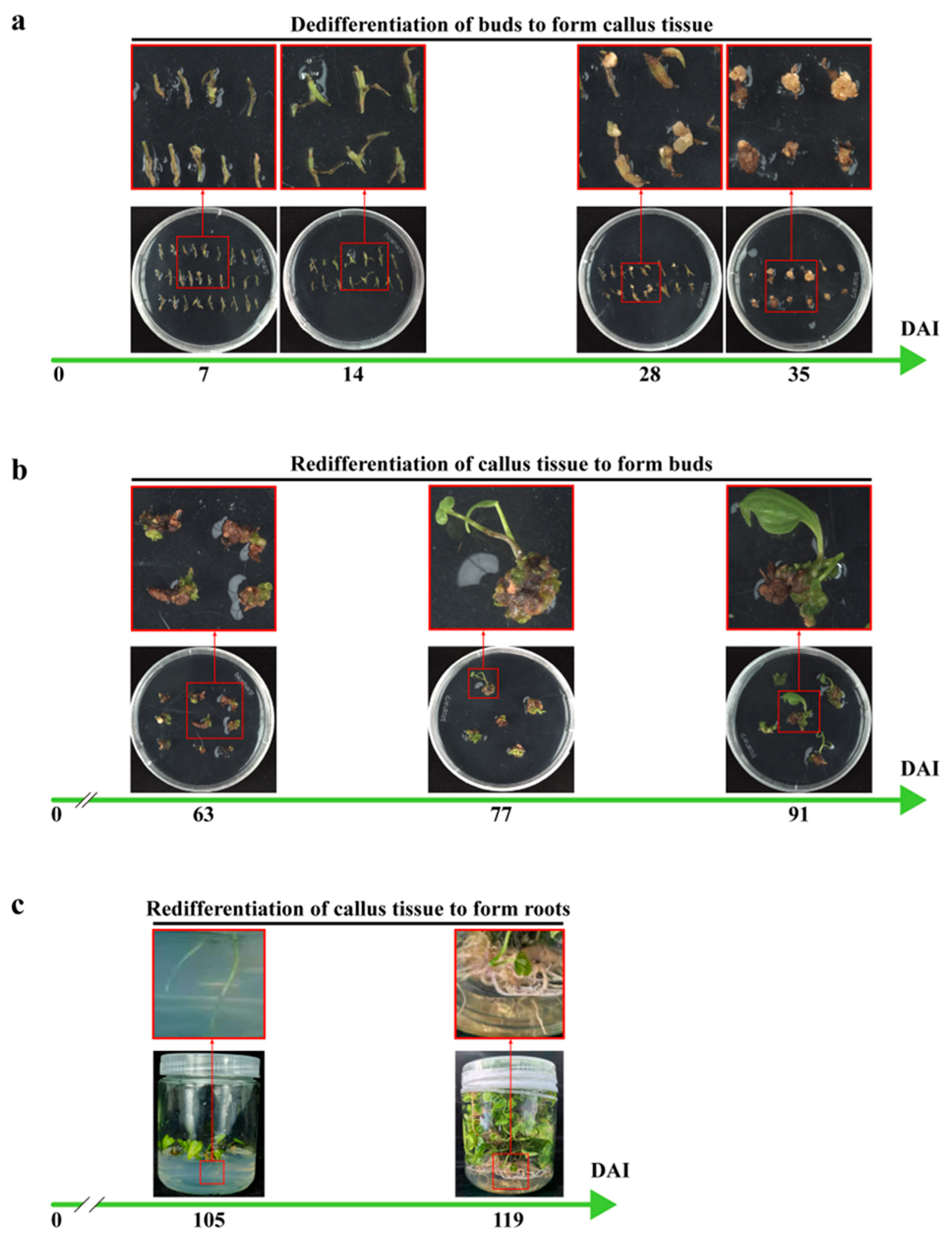
2.2. The Optimization of Genetic Transformation Methods for D. zingiberensis
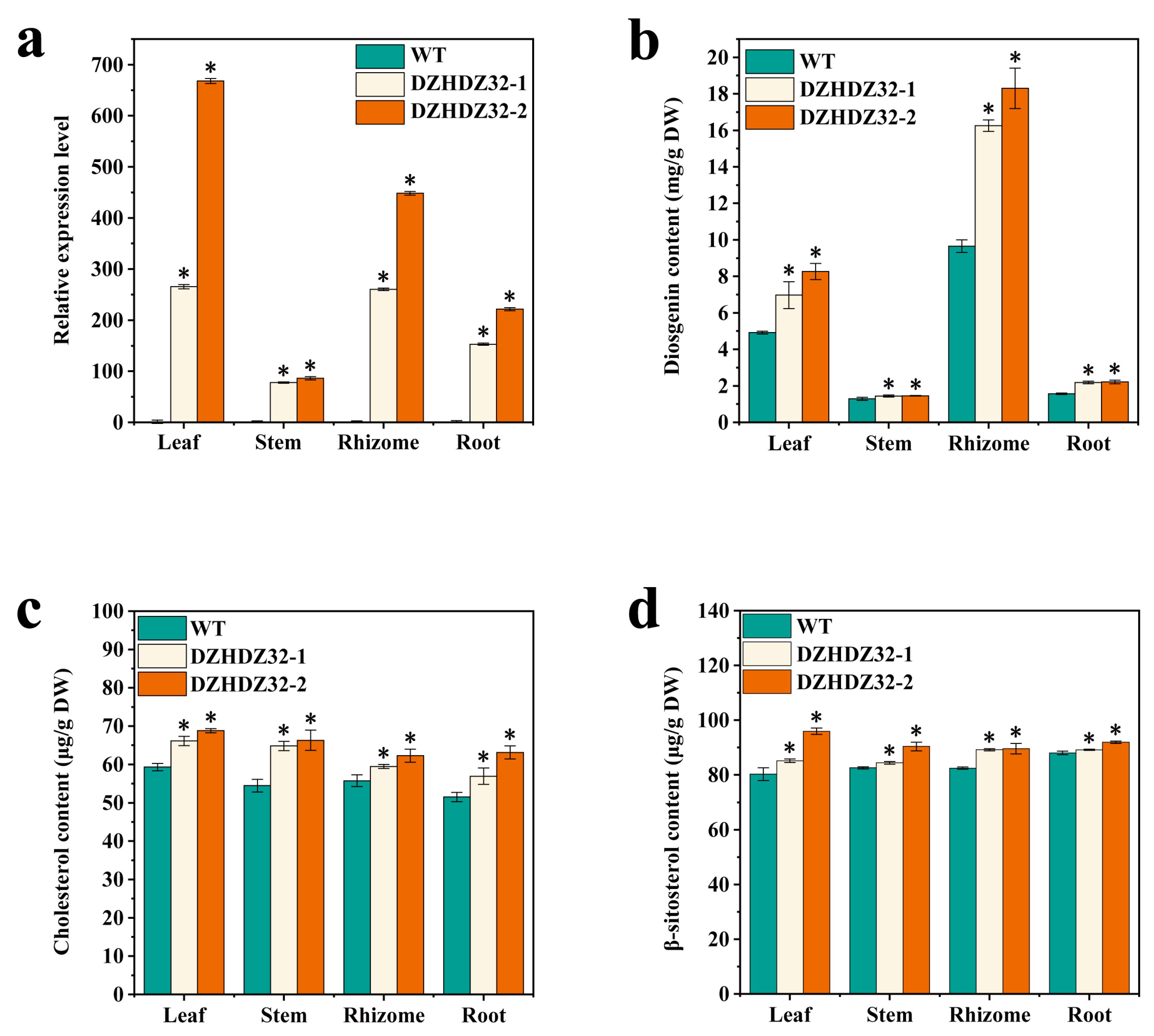
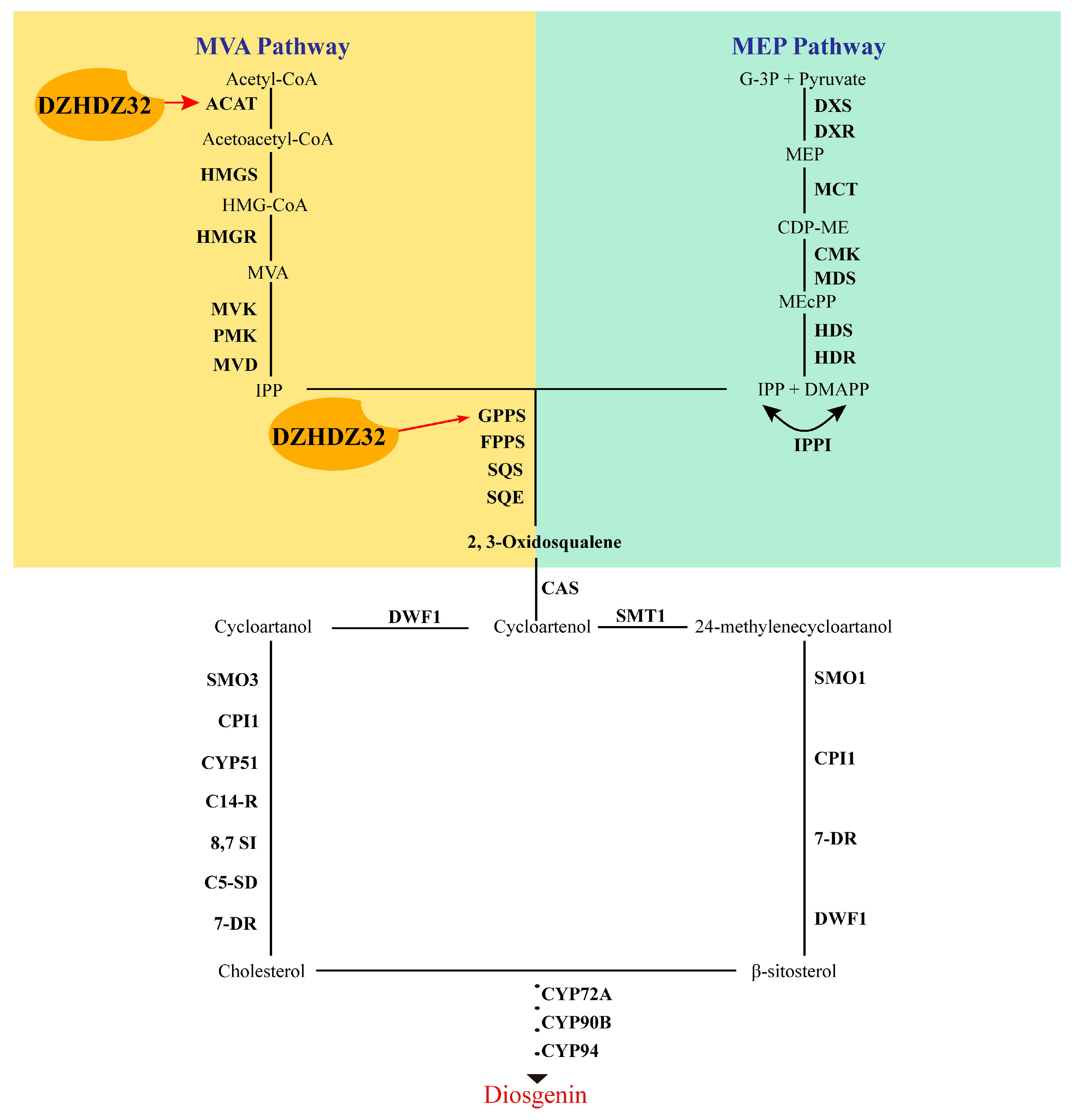
2.3. DZHDZ32 Promotes the Accumulation of Intermediate Metabolites in Diosgenin Synthesis
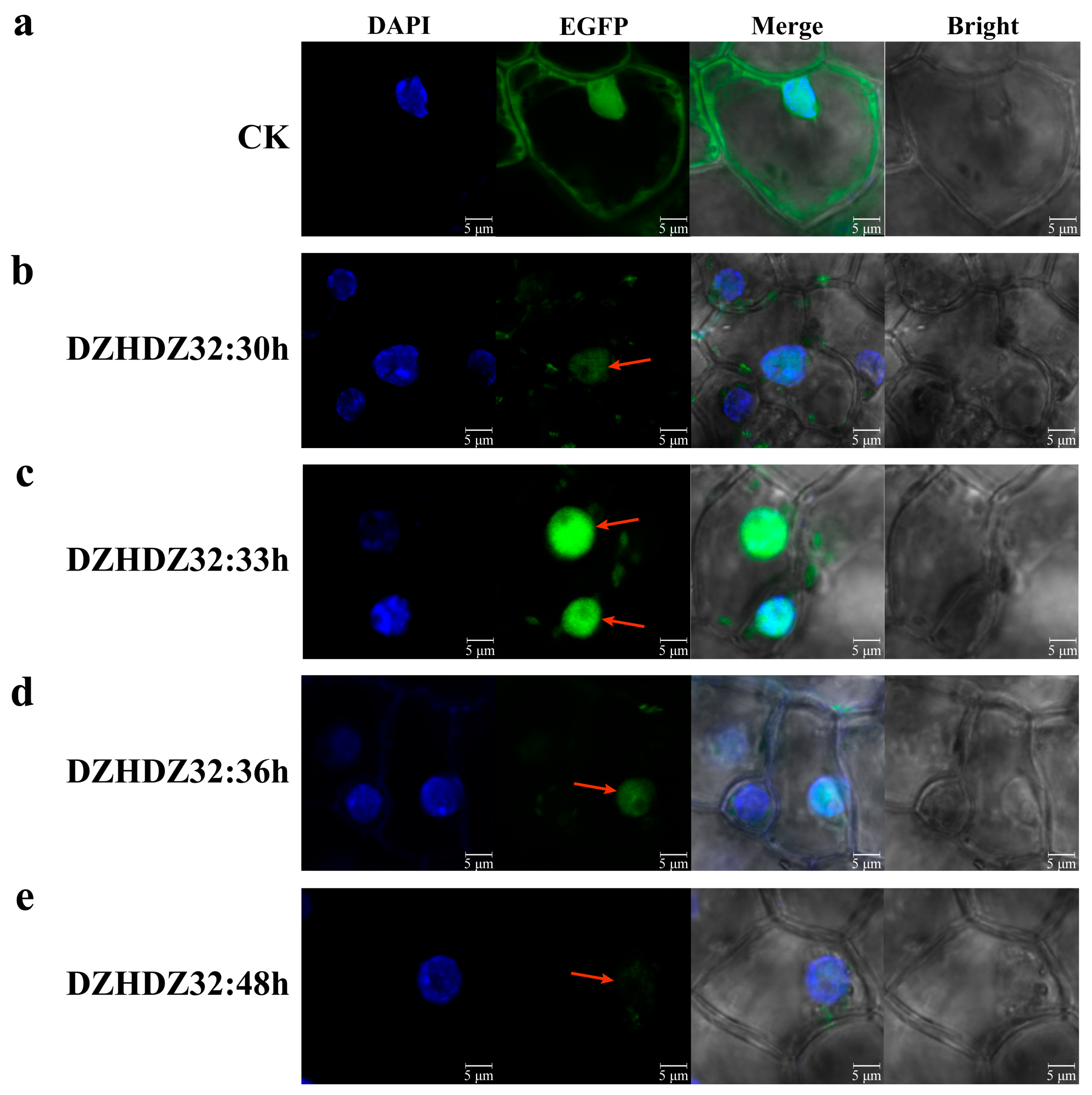
2.4. Subcellular Localization of DZHDZ32
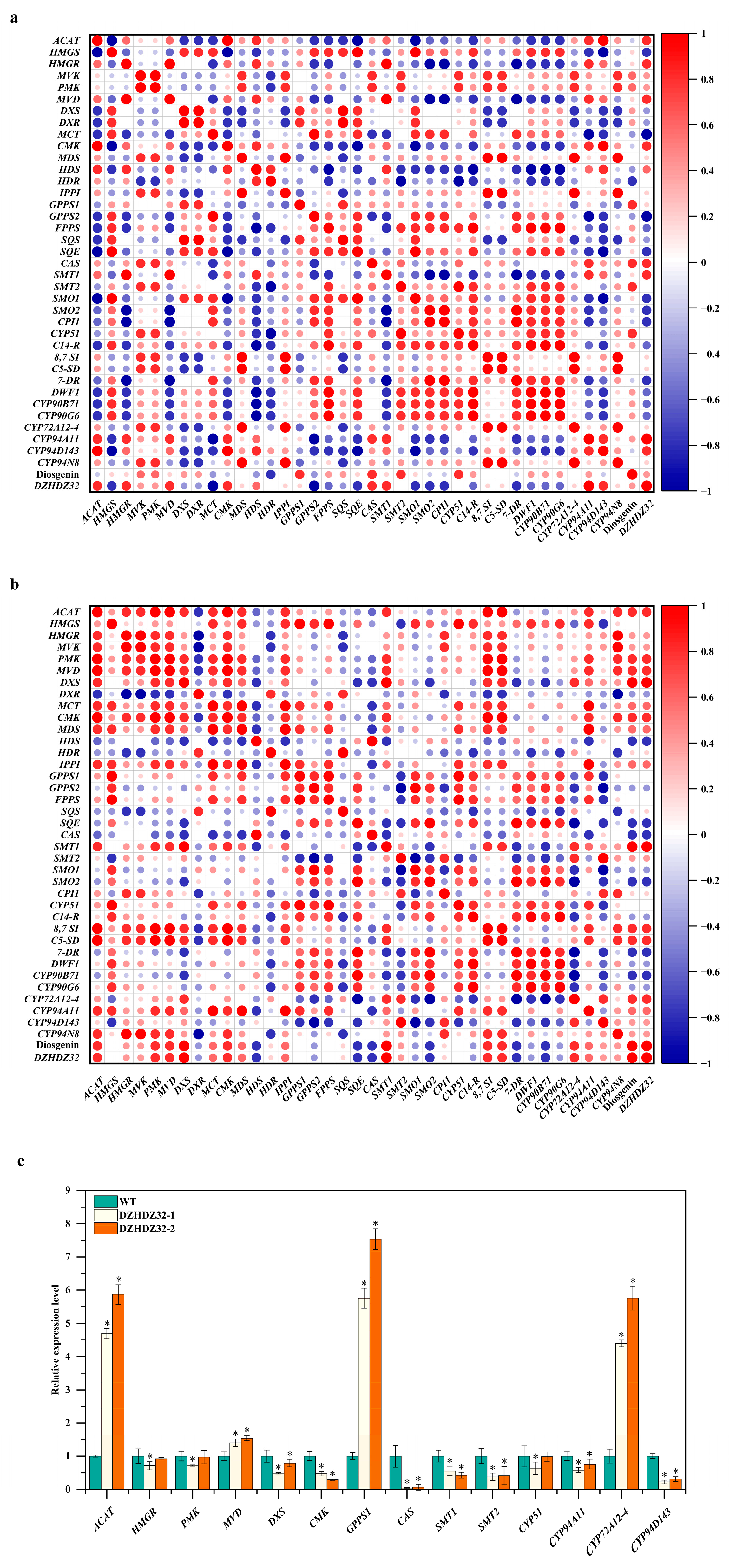
2.5. Correlation Analysis Expression of DZHDZ32 with Genes Involved in the Diosgenin Biosynthetic Pathway
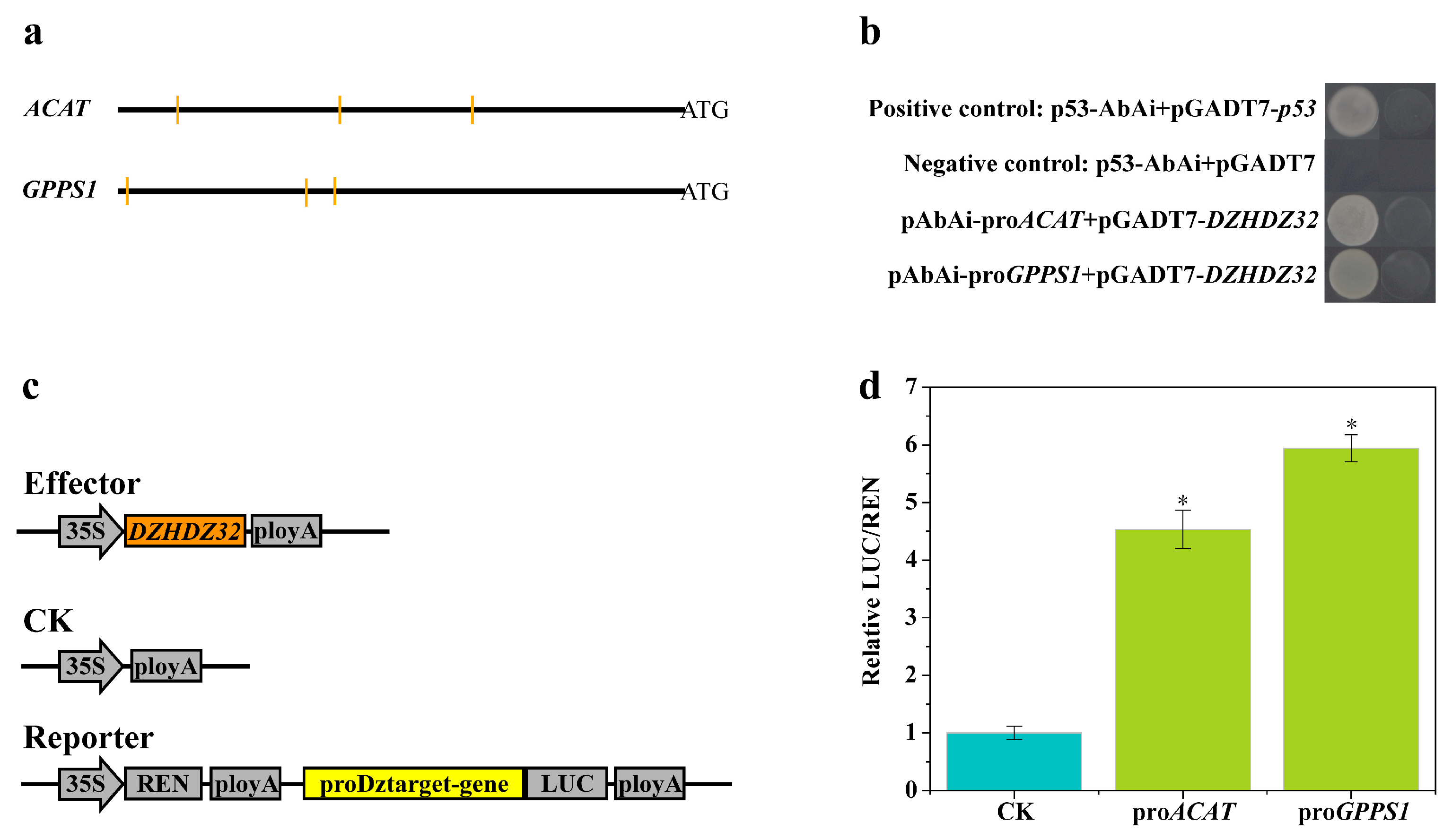
2.6. Promoter Analysis of Genes in the Diosgenin Biosynthetic Pathway Correlated with DZHDZ32
2.7. DZHDZ32 Regulates Genes in the Diosgenin Biosynthetic Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material Selection and Utilization
4.2. Transgenic Overexpression of DZHDZ32 in D. zingiberensis
4.3. Determination and Analysis of Diosgenin and Its Intermediates Cholesterol and β-Sitosterol
4.4. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of HD-ZIP Gene Family Members in D. zingiberensis
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) for Diosgenin Biosynthesis Pathway Genes
4.6. Subcellular Localization
4.7. Correlation Analysis
4.8. Yeast One-Hybrid (Y1H) Assay
4.9. Dual-Luciferase (Dual-LUC) Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MVA | Mevalonate pathway |
| MEP | Methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway |
| HMGS | Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase |
| HMG-CoA | Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA |
| MVK | Mevalonate kinase |
| DXR | 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase |
| CDP-ME | Cytidine 4-diphosphate 2-C-methyl-D erythritol |
| MCT | 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase |
| MDS | 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase |
| MEcPP | Methylerythritol cyclodiphosphate |
| HDS | 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate synthase |
| HDR | 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase |
| DMAPP | Dimethylallyl diphosphate |
| IPP | Isopentenyl diphosphate |
| IPPI | Isopentenyl-diphosphate Delta-isomeras |
| GPPS | Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase |
| FPPS | Farnesyl diphosphate synthase |
| SQS | Squalene synthase |
| SQE | Squalene epoxidase |
| DWF1 | Delta(24)-sterol reductase |
| SMO | C-4 sterol methyloxidase |
| CPI1 | Cyclopropylsterol isomerase |
| CYP51 | CYP51 Sterol C-14 demethylase |
| C14-R | C14-R Sterol C-14 reductase |
| 8,7SI | 8,7SI Sterol 8,7 isomerase |
| C5-SD | C5-SD Delta(7)-sterol-C5(6)-desaturase |
| 7-DR | 7-DR 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase |
| CYP90B | CYP90B Cytochrome P450 90B |
References
- Li, Y.; Tan, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Dai, X.; Yang, H.; Song, W.; et al. The genome of Dioscorea zingiberensis sheds light on the biosynthesis, origin and evolution of the medicinally important diosgenin saponins. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Li, S.; Tong, Z.; Yuan, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Geographical variations in fatty acid and steroid saponin biosynthesis in Dioscorea zingiberensis rhizomes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mosongo, I.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. Identification and characterization of a trillin rhamnosyltransferase from Dioscorea zingiberensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 713036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Geng, L.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, J. Genome-wide methylation, transcriptome and characteristic metabolites reveal the balance between diosgenin and brassinosteroids in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hou, L.; Li, S.; Li, J. The functional characterization of DzCYP72A12-4 related to diosgenin biosynthesis and drought adaptability in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification of CYP72A gene family and expression patterns related to jasmonic acid treatment and steroidal saponin accumulation in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Li, J. Advances in the biosynthesis and molecular evolution of steroidal saponins in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Gu, Y.; Tian, W.; Tian, W.; Wang, J.; Wen, J.; Li, J. Integrated evolutionary pattern analyses reveal multiple origins of steroidal saponins in plants. Plant J. 2023, 116, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Gu, Y.; Li, J. Effect of exogenous jasmonic acid on physiology and steroidal saponin accumulation in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, M.; Tadesse, N.; Dang, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Guo, Z.; Ito, Y. Dioscorea zingiberensis C. H. Wright: An overview on its traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, clinical applications, quality control, and toxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhong, C.; Xie, J. Comparative transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal key regulatory gene for methyl jasmonate-induced steroidal saponins synthesis in Dioscorea composita. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Tao, S.; Hou, G.; Zhao, F.; Tan, S.; Meng, Q. Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive compounds and potential for the treatment of inflammatory and metabolic diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 2878. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, G.; Mohankumar, A.; Kalaiselvi, D.; Nivitha, S.; Murugesh, E.; Shanmughavel, P.; Sundararaj, P. Diosgenin a phytosterol substitute for cholesterol, prolongs the lifespan and mitigates glucose toxicity via DAF-16/FOXO and GST-4 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marker, R.; Tsukamoto, T.; Turner, D. Sterols. C. Diosgenin1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Dinatale, I.; Rivera-Woll, L.; Davison, S. Postmenopausal hormone therapy: From monkey glands to transdermal patches. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, N.; and Negi, A.S. Plant based steroidal and triterpenoid sapogenins: Chemistry on diosgenin and biological aspects. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 279, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Chikara, S.; Sharma, M.; Chaudhary, A.; Alam Syed, B.; Chaudhary, P.; Mehta, A.; Patel, M.; Ghosh, A.; Iriti, M. Elicitation of diosgenin production in Trigonella foenum-graecum (fenugreek) seedlings by methyl jasmonate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29889–29899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, D.; De, B. Elicitation of diosgenin production in Dioscorea floribunda by ethylene-generating agent. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, A.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, P.S. Abiotic metal stress enhances diosgenin yield in Dioscorea bulbifera L. cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hu, Q.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bao, Z.; Li, Y.; Mo, L.J. Diosgenin biosynthesis pathway and its regulation in Dioscorea cirrhosa L. PeerJ 2024, 12, e16702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.X.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Ye, S.; Luan, Y. Identification of genetic variants controlling diosgenin content in Dioscorea zingiberensis tuber by genome-wide association study. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Song, W.; Fu, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, A.; Li, J. Application of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2018, 135, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syombua, E.D.; Zhang, Z.; Tripathi, J.N.; Ntui, V.O.; Kang, M.; George, O.O.; Edward, N.K.; Wang, K.; Yang, B.; Tripathi, L. A CRISPR/Cas9-based genome-editing system for yam (Dioscorea spp.). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 19, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyaboga, E.; Tripathi, J.N.; Manoharan, R.; Tripathi, L. Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of yam (Dioscorea rotundata): An important tool for functional study of genes and crop improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Fu, M.; Zhou, S.; Xie, Q.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Hu, Z. A tomato HD-ZIP I transcription factor, VaHox1, acts as a negative regulator of fruit ripening. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhac236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.W.; Lee, D.K.; Jung, H.; Chung, P.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, Y.D.; Suh, J.W.; Kim, J.K. Overexpression of OsTF1l, a rice HD-ZIP transcription factor, promotes lignin biosynthesis and stomatal closure that improves drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 17, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Ding, Y.; Hu, S.; Ding, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, C. The role of HD-ZIP class I transcription factors in plant response to abiotic stresses. Physiol. Plant. 2019, 167, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agalou, A.; Purwantomo, S.; Övernäs, E.; Johannesson, H.; Zhu, X.; Estiati, A.; de Kam, R.J.; Engström, P.; Slamet-Loedin, I.H.; Zhu, Z.; et al. A genome-wide survey of HD-ZIP genes in rice and analysis of drought-responsive family members. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 66, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yan, T.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; Hassani, D.; Li, Y.; Qin, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Fu, X.; et al. An HD-ZIP-MYB complex regulates glandular secretory trichome initiation in Artemisia annua. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi-Ito, K.; Iwamoto, K.; Yamagami, A.; Nakanob, T.; Fukudaa, H. HD-ZIP III-dependent local promotion of brassinosteroid synthesis suppresses vascular cell division in Arabidopsis root apical meristem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216632120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, A.; Liu, X.; Zhao, M. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling of the medicinal plant Veratrum mengtzeanum reveal key components of the alkaloid biosynthesis. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1023433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Han, Q.; Kang, X.; Rong, T.; Wu, X.; Lin, H.; Zhang, D. The HAT1 transcription factor regulates photomorphogenesis and skotomorphogenesis via phytohormone levels. Plant Physiol. 2025, 197, kiae542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasolla, M.E.a.C. Structure and function of homodomain-leucine zipper HD-Zip proteins. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Han, G. The roles of HD-ZIP proteins in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1027071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, R.; Raza, A.; Chen, P.; Li, Y.; El-Ballat, E.M.; Rauf, A.; Hano, C.; El-Esawi, M.A. HD-ZIP gene family: Potential roles in improving plant growth and regulating stress-responsive mechanisms in plants. Genes 2021, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Guo, M.; Aslam, M.; Wang, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Cao, S. Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of Eucalyptus grandis HD-Zip gene family in response to salt and temperature stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherban, A.B.; Salina, E.A. Dataset of the HOX1 gene sequences of the wheat polyploids and their diploid relatives. Data Brief 2018, 16, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Li, W.; Feng, T.; Shockey, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Lü, S. Triacylglycerol biosynthesis in shaded seeds of tung tree (Vernicia fordii) is regulated in part by Homeodomain Leucine 21. Plant J. 2021, 108, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Comparative transcriptome analysis identifies genes involved in diosgenin biosynthesis in Trigonella foenum-graecum L. Molecules 2019, 24, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, B.; Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Zou, L.; Chen, G.; Cao, B.; Chen, C.; Lei, J. Overexpression of AtEDT1/HDG11 in chinese kale (Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra) enhances drought and osmotic stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1258. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.; Liu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Dossa, K.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, X.; You, J. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of the HD-ZIP gene family in response to drought and salinity stresses in sesame. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalchuk, N.; Chew, W.; Sornaraj, P.; Borisjuk, N.; Yang, N.; Singh, R.; Bazanova, N.; Shavrukov, Y.; Guendel, A.; Munz, E.; et al. The homeodomain transcription factor TaHDZipI-2 from wheat regulates frost tolerance, flowering time and spike development in transgenic barley. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Zhao, L.; Huo, X. Identification of WRKY gene family in Dioscorea opposita Thunb. reveals that DoWRKY71 enhanced the tolerance to cold and aba stress. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17016. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Dai, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhou, X.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. The origin and evolution of the diosgenin biosynthetic pathway in yam. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, B.; Xu, C.; Xu, M.; Li, F.-S.; Wada, N.; Mitchell, A.J.; Han, X.-L.; Wen, M.-L.; Fujita, M.; Weng, J.-K. Repeated evolution of cytochrome P450-mediated spiroketal steroid biosynthesis in plants. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Yin, H.; Yang, J.; Xiong, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. LcERF19, an AP2/ERF transcription factor from Litsea cubeba, positively regulates geranial and neral biosynthesis. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Haider, I.; Kohlen, W.; Jiang, L.; Bouwmeester, H.; Meijer, A.H.; Schluepmann, H.; Liu, C.-M.; Ouwerkerk, P.B.F. Function of the HD-ZIP I gene OsHOX22 in aba-mediated drought and salt tolerances in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, A.; Wen, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, G. Cotton HD-ZIP I transcription factor GhHB4-like regulates the plant response to salt stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Peng, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Shang, Y.; Chen, S.; Bao, X.; Wang, Q. A HD-ZIP I transcription factor from physic nut, JcHDz21, confers sensitive to salinity in transgenic Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1097265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Jia, X.; Gao, H.; Mao, K.; Ma, F. The HD-ZIP I transcription factor MdHB7-like confers tolerance to salinity in transgenic apple (Malus domestica). Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Chakraborty, J.; Ghosh, P.; Basu, D.; Das, S. Chickpea wrky70 regulates the expression of a Homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-ZIP) I transcription factor CaHDZ12, which confers abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco and chickpea. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1934–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimian-Motlagh, S.; Ribone, P.A.; Thirumalaikumar, V.P.; Allu, A.D.; Chan, R.L.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Balazadeh, S. JUNGBRUNNEN1 confers drought tolerance downstream of the HD-ZIP I transcription factor AtHB13. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-X.; Zhu, W.-C.; Cheng, G.-X.; Yu, Y.-N.; Li, Q.-H.; Haq, S.u.; Said, F.; Gong, Z.-H. A novel gene, CaATHB-12, negatively regulates fruit carotenoid content under cold stress in Capsicum annuum. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 64, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perotti, M.F.; Ribone, P.A.; Chan, R.L. Plant transcription factors from the Homeodomain-leucine zipper family I. Role in development and stress responses. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavella, P.A.; Dezar, C.A.; Bonaventure, G.; Baldwin, I.T.; Chan, R.L. HaHB4, a sunflower HD-ZIP protein, integrates signals from the jasmonic acid and ethylene pathways during wounding and biotic stress responses. Plant J. 2008, 56, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, T.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L. GhHB12, a HD-ZIP I transcription factor, negatively regulates the cotton resistance to Verticillium dahliae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Grandío, E.; Pajoro, A.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Tarancón, C.; Immink, R.G.H.; Cubas, P. Abscisic acid signaling is controlled by a BRANCHED1/ HD-ZIP I cascade in Arabidopsis axillary buds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 114, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pu, G.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, Q. Analysis of the HD-ZIP I transcription factor family in Salvia miltiorrhiza and functional research of SmHD-Zip12 in tanshinone synthesis. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, P.; Kumar, P. Comparison of ultrasound and microwave assisted extraction of diosgenin from Trigonella foenum- graceum seed. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 74, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, T.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Acid hydrolysis of saponin-rich extracts of quinoa, lentil, fenugreek and soybean to yield sapogenin-rich extracts and other bioactive compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3157–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plant Species | Transformation Efficiency | Time (From Agro-Infection to Regeneration of Complete Transgenic Plant) | Target Gene | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. zingiberensis | 46.8% | 4 months | DZHDZ32 | In this study |
| Dioscorea rotundata | 9.4 to 18.2% | 3–4 months | GUSA | [24] |
| D. zingiberensis | Very low | Unknown | DZFPS | [22] |
| Dioscorea alata L. | 2.33% | Unknown | DRPDS | [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. An HD-ZIP I Transcription Factor DZHDZ32 Upregulates Diosgenin Biosynthesis in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094185
Yang H, Li Y, Hu Z, Li J. An HD-ZIP I Transcription Factor DZHDZ32 Upregulates Diosgenin Biosynthesis in Dioscorea zingiberensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094185
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Huan, Yi Li, Zixuan Hu, and Jiaru Li. 2025. "An HD-ZIP I Transcription Factor DZHDZ32 Upregulates Diosgenin Biosynthesis in Dioscorea zingiberensis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094185
APA StyleYang, H., Li, Y., Hu, Z., & Li, J. (2025). An HD-ZIP I Transcription Factor DZHDZ32 Upregulates Diosgenin Biosynthesis in Dioscorea zingiberensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094185






