The Slo1 Y450F Substitution Modifies Basal Function and Cholesterol Response of Middle Cerebral Artery Smooth Muscle BK Channels in a Sexually Dimorphic Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
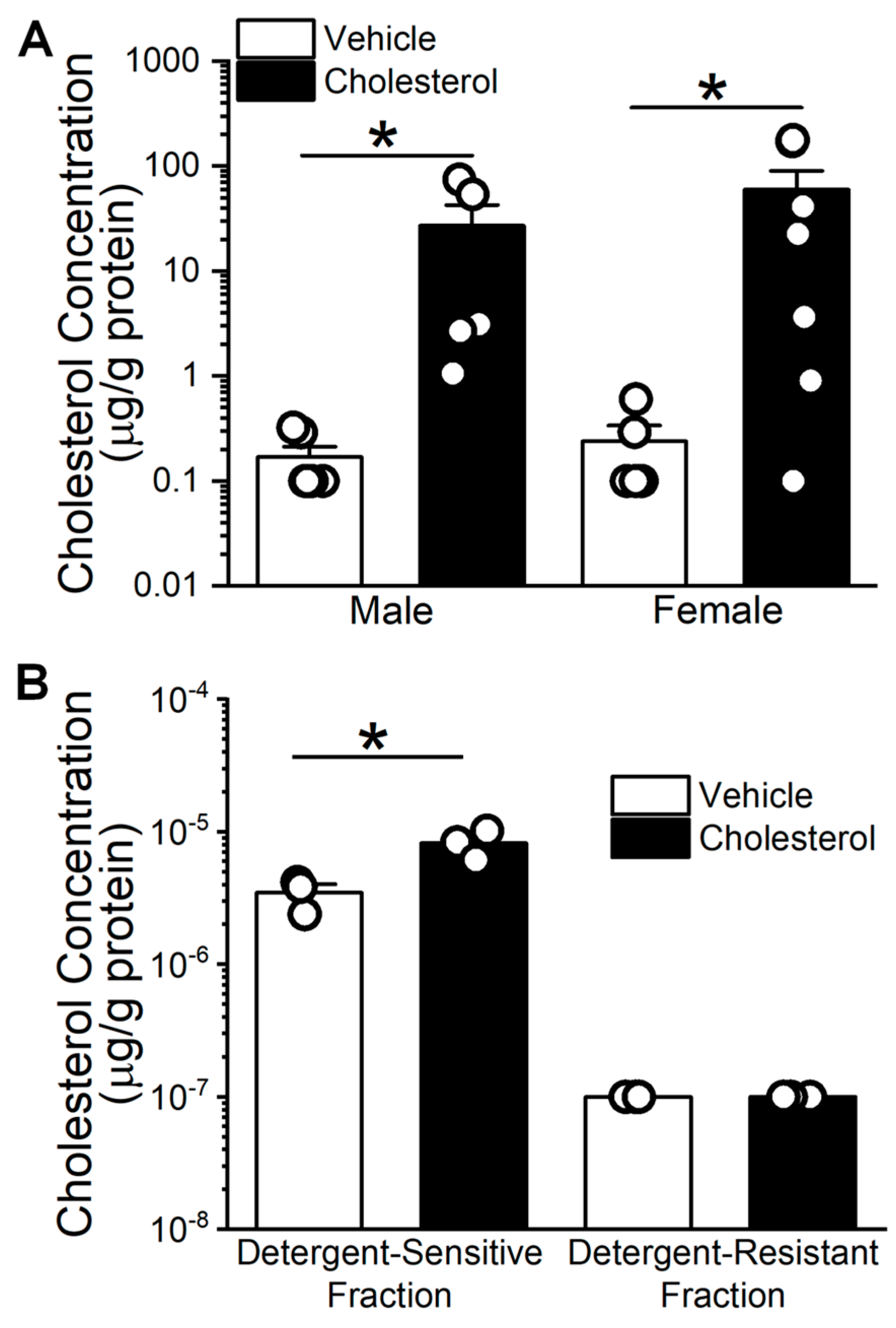
2.1. Cholesterol Enrichment of Middle Cerebral Arteries (MCA) Using Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin (MβCD) as a Vehicle
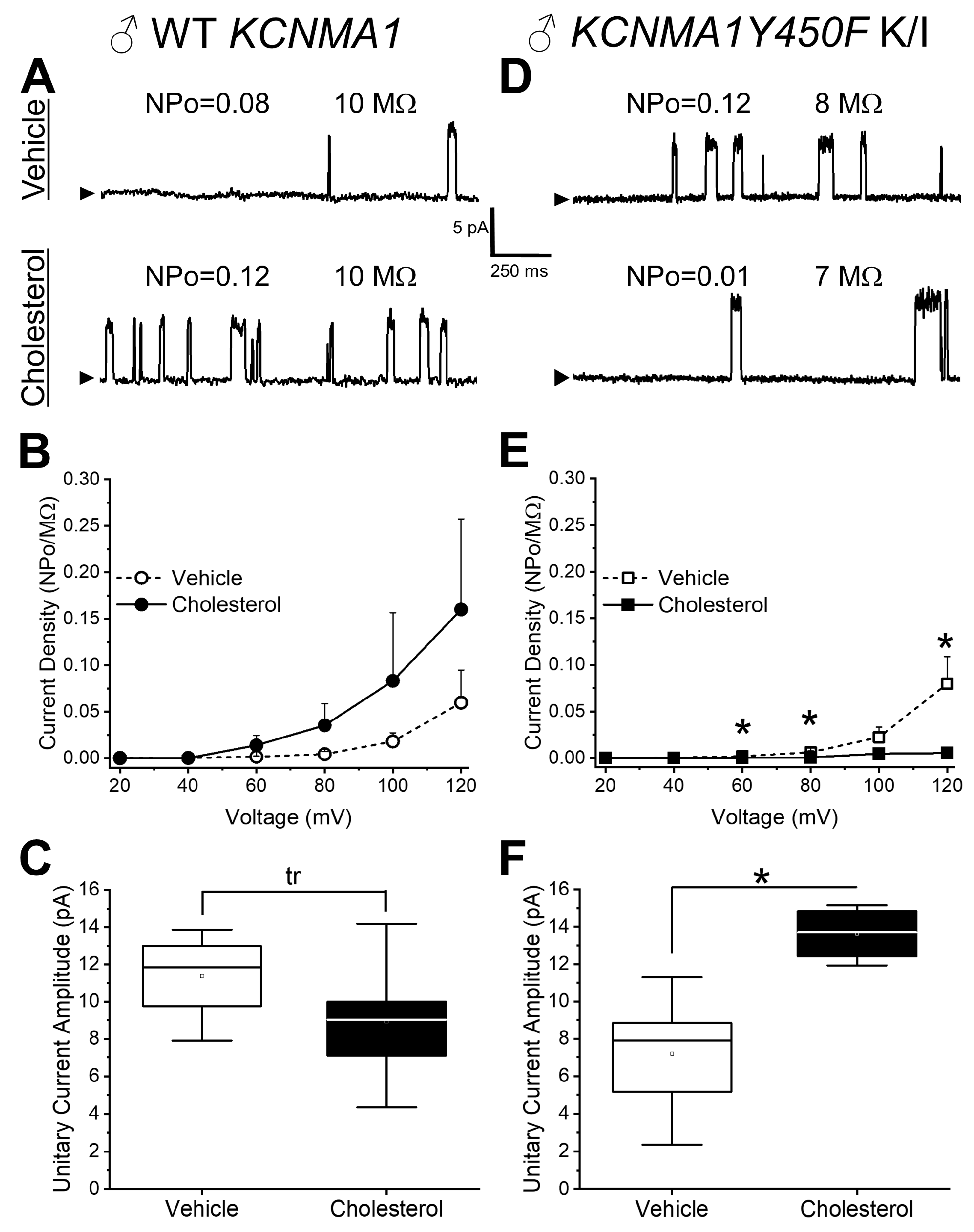
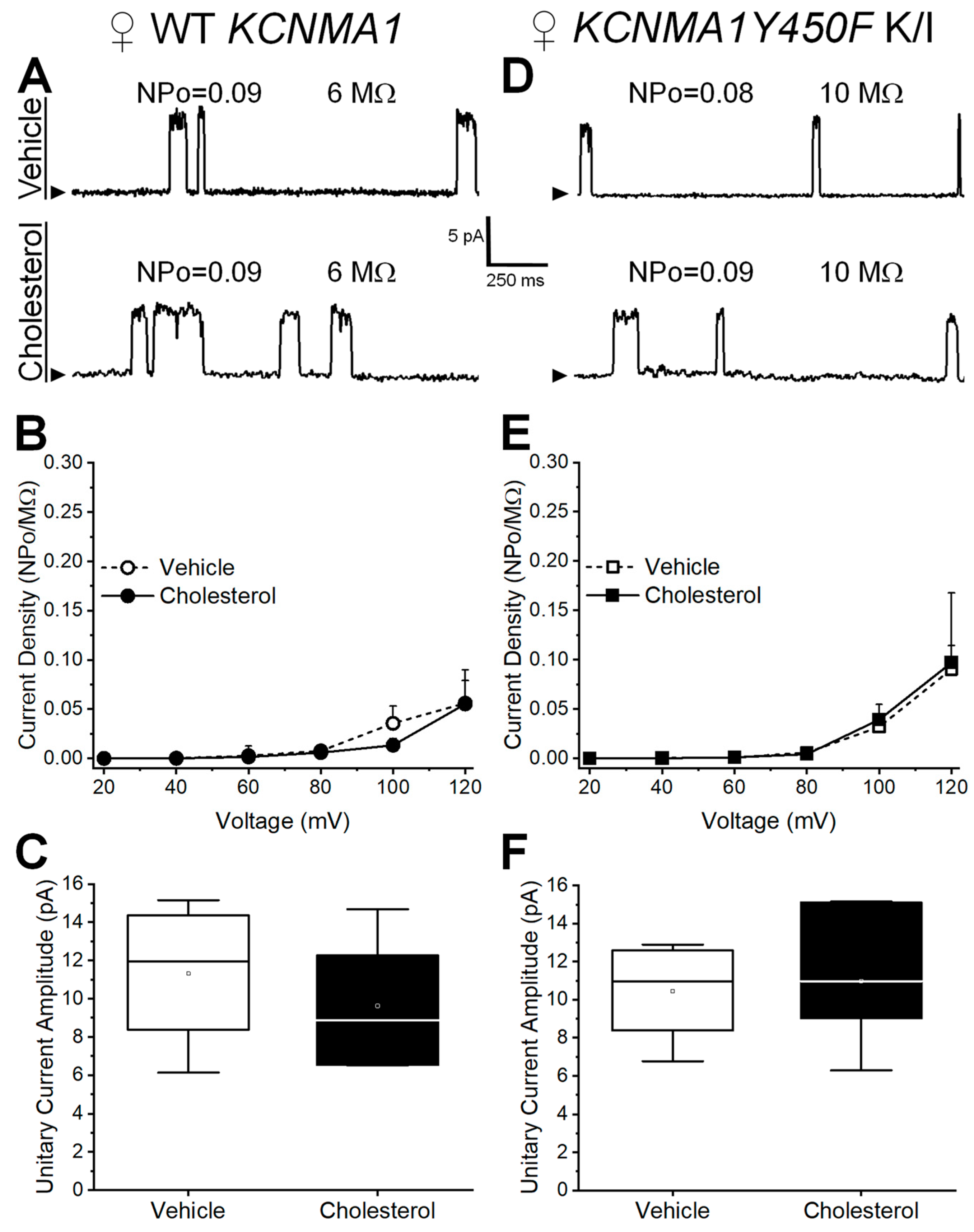
2.2. Effect of Cholesterol Enrichment on Function of Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) Smooth Muscle (SM) Native BK Channels and Role of the slo1Y450 Substitution
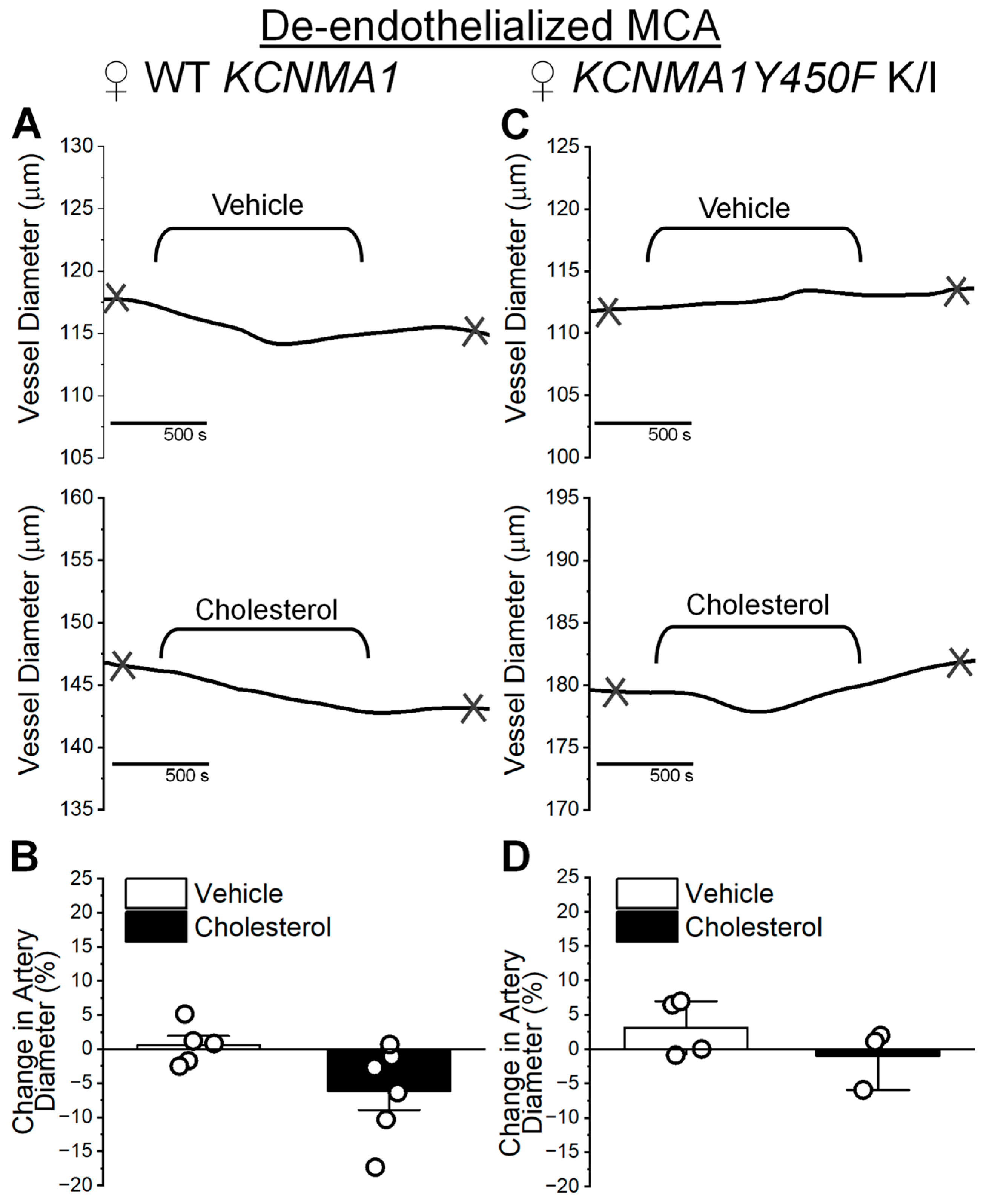
2.3. Cholesterol Enrichment Effect on Middle Cerebral Artery Diameter and Influence of the KCNMA1Y450F Substitution
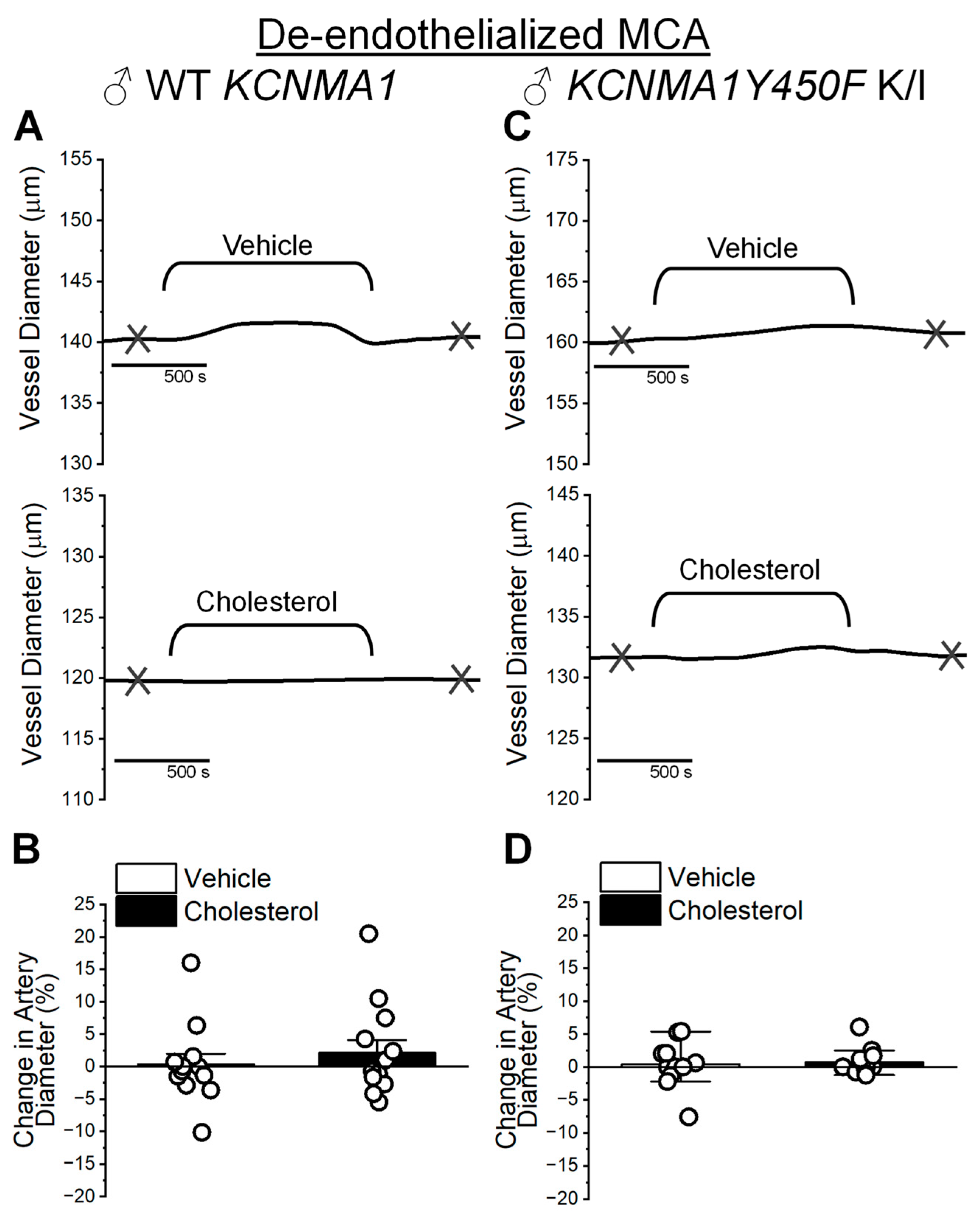
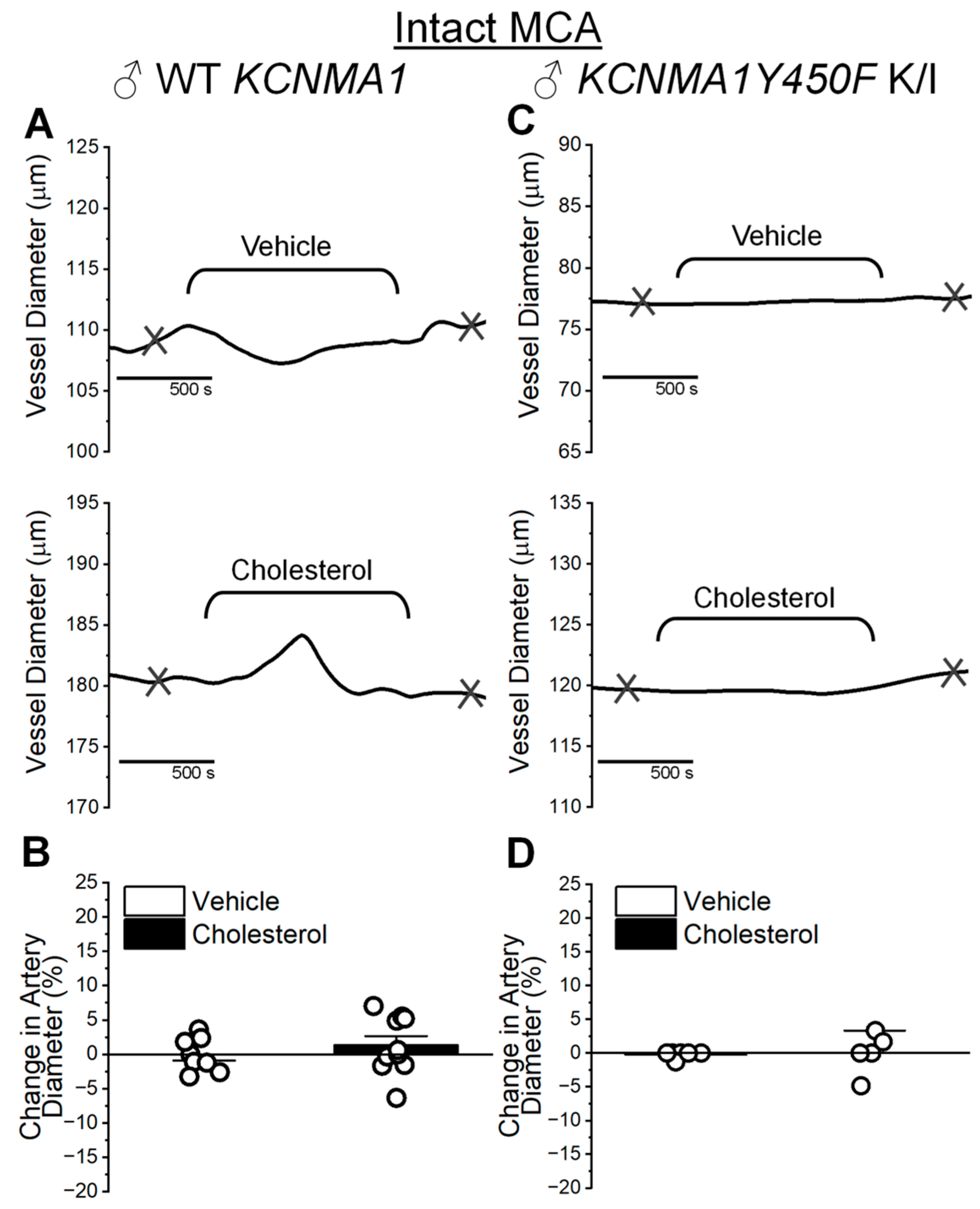
2.4. Cholesterol Enrichment Effect on Cerebral Artery Segments with Intact Endothelium and Role of the KCNMA1Y450F Mutation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Cholesterol Quantification
4.3. Myocyte Isolation and Voltage-Clamp Electrophysiological Recordings
4.4. Cerebral Artery Diameter Measurement Ex Vivo
4.5. Chemicals
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BK | Voltage- and calcium-gated potassium channel of large conductance (“Big K+”) |
| SM | Smooth muscle |
| WT | Wild type |
| K/I | Knock-in |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
| Po | Channel-open probability |
| MβCD | Methyl-β-cyclodextrin |
| RCK | Regulator for conductance of potassium |
References
- Purves, D.; Williams, S.M. Neuroscience, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C.Y.; Tarumi, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Turner, M.; Riley, J.; Tinajero, C.D.; Yuan, L.J.; Zhang, R. Distribution of cardiac output to the brain across the adult lifespan. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2017, 37, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.M. Morphology of cerebral arteries. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 66, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, W.M. On the local reactions of the arterial wall to changes of internal pressure. J. Physiol. 1902, 28, 220–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.T.; Quayle, J.M. Physiological roles and properties of potassium channels in arterial smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, C799–C822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, R.; Peréz, G.J.; Bonev, A.D.; Eckman, D.M.; Kosek, J.C.; Wiler, S.W.; Patterson, A.J.; Nelson, M.T.; Aldrich, R.W. Vasoregulation by the beta1 subunit of the calcium-activated potassium channel. Nature 2000, 407, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, G.C.; Nathan, D.J.; Saundry, C.M.; Perez, G.; Bonev, A.D.; Penar, P.L.; Tranmer, B.I.; Nelson, M.T. Ca2+ sparks and their function in human cerebral arteries. Stroke 2002, 33, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.S.; Moldenhauer, H.J.; Park, S.M.; Keros, S.; Meredith, A.L. KCNMA1-linked channelopathy. J. Gen. Physiol. 2019, 151, 1173–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, R.; Castillo, K.; Carrasquel-Ursulaez, W.; Sepulveda, R.V.; Gonzalez-Nilo, F.; Gonzalez, C.; Alvarez, O. Molecular Determinants of BK Channel Functional Diversity and Functioning. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 39–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, H.G.; Garcia-Calvo, M.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Garcia, M.L. Subunit composition of the high conductance calcium-activated potassium channel from smooth muscle, a representative of the mSlo and slowpoke family of potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 3921–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquel-Ursulaez, W.; Alvarez, O.; Bezanilla, F.; Latorre, R. Determination of the Stoichiometry between α- and γ1 Subunits of the BK Channel Using LRET. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2493–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, Y.; Dolde, J.; Steck, T.L. The rate of transmembrane movement of cholesterol in the human erythrocyte. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 5321–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, V.; Sharpe, L.J.; Alexopoulos, S.J.; Kunze, S.V.; Chua, N.K.; Li, D.; Brown, A.J. Cholesterol homeostasis: How do cells sense sterol excess? Chem. Phys. Lipids 2016, 199, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, Y.; Ye, J.; Rigney, M.; Steck, T.L. Dynamics of lysosomal cholesterol in Niemann-Pick type C and normal human fibroblasts. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, Y.; Steck, T.L. Active cholesterol 20 years on. Traffic 2020, 21, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D. Protein-lipid interactions. Ciba Found. Symp. 1972, 7, 261–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverley, K.M.; Levitan, I. Cholesterol regulation of mechanosensitive ion channels. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1352259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.X. Cholesterol-Dependent Gating Effects on Ion Channels. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1115, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, I.; Fang, Y.; Rosenhouse-Dantsker, A.; Romanenko, V. Cholesterol and ion channels. Subcell. Biochem. 2010, 51, 509–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, I.; Singh, D.K.; Rosenhouse-Dantsker, A. Cholesterol binding to ion channels. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.H.; Fitzgerald, A.C.; Ponnapula, S.S.; Dopico, A.M.; Bukiya, A.N. Differential distribution of cholesterol pools across arteries under high-cholesterol diet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2022, 1867, 159235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, J.J.; Treistman, S.N.; Dopico, A.M. Cholesterol antagonizes ethanol potentiation of human brain BKCa channels reconstituted into phospholipid bilayers. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; McMillan, J.; Bukiya, A.N.; Burton, B.; Parrill, A.L.; Dopico, A.M. Multiple cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motifs in cytosolic C tail of Slo1 subunit determine cholesterol sensitivity of Ca2+- and voltage-gated K+ (BK) channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20509–20521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukiya, A.N.; Leo, M.D.; Jaggar, J.H.; Dopico, A.M. Cholesterol activates BK channels by increasing KCNMB1 protein levels in the plasmalemma. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, A.E.; Haynes, M.P.; Phillips, M.C.; Rothblat, G.H. Use of cyclodextrins for manipulating cellular cholesterol content. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 2264–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lingle, C.J. Paxilline inhibits BK channels by an almost exclusively closed-channel block mechanism. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 144, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Xi, Q.; Ahmed, A.; Jaggar, J.H.; Dopico, A.M. Essential role for smooth muscle BK channels in alcohol-induced cerebrovascular constriction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18217–18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Vasan, R.S. Cohort Profile: The Framingham Heart Study (FHS): Overview of milestones in cardiovascular epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, J.; Faraci, F.M.; Lentz, S.R.; Heistad, D.D. Cerebral vascular dysfunction during hypercholesterolemia. Stroke 2007, 38, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, B.B.; Segal, A.Z. The role of cholesterol and statins in stroke. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2009, 11, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarin, V.; Morovic, S. Ultrasound subclinical markers in assessing vascular changes in cognitive decline and dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42 (Suppl. S3), S259–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postiglione, A.; Nappi, A.; Brunetti, A.; Soricelli, A.; Rubba, P.; Gnasso, A.; Cammisa, M.; Frusciante, V.; Cortese, C.; Salvatore, M.; et al. Relative protection from cerebral atherosclerosis of young patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 1991, 90, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, H.C., Jr. The relationship of dietary cholesterol to serum cholesterol concentration and to atherosclerosis in man. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1979, 32, 2664–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, A.L.; Speer, M.Y.; Scatena, M.; Giachelli, C.M.; Shanahan, C.M. Role of smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification: Implications in atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palasubramaniam, J.; Wang, X.; Peter, K. Myocardial Infarction-From Atherosclerosis to Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e176–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopico, A.M.; Bukiya, A.N.; Jaggar, J.H. Calcium- and voltage-gated BK channels in vascular smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 2018, 470, 1271–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, K.C.; Zhang, M.; Singh, A.K.; Zaytseva, D.; Slayden, A.V.; Bukiya, A.N.; Dopico, A.M. Cholesterol Inhibition of Slo1 Channels Is Calcium-Dependent and Can Be Mediated by Either High-Affinity Calcium-Sensing Site in the Slo1 Cytosolic Tail. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 101, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, M.D.; Bannister, J.P.; Narayanan, D.; Nair, A.; Grubbs, J.E.; Gabrick, K.S.; Boop, F.A.; Jaggar, J.H. Dynamic regulation of β1 subunit trafficking controls vascular contractility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopico, A.M.; Bukiya, A.N.; Singh, A.K. Large conductance, calcium- and voltage-gated potassium (BK) channels: Regulation by cholesterol. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 135, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, G.J.; Bonev, A.D.; Nelson, M.T. Micromolar Ca(2+) from sparks activates Ca(2+)-sensitive K(+) channels in rat cerebral artery smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 281, C1769–C1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meera, P.; Wallner, M.; Jiang, Z.; Toro, L. A calcium switch for the functional coupling between alpha (hslo) and beta subunits (KV,Ca beta) of maxi K channels. FEBS Lett. 1996, 382, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Zehnder, M.; Orio, P.; Norambuena, A.; Wallner, M.; Meera, P.; Toro, L.; Latorre, R.; González, A. Apical sorting of a voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channel alpha -subunit in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells is independent of N-glycosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13114–13119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.S.; Shaw, A.R.; Duszyk, M. Membrane cholesterol content modulates activation of BK channels in colonic epithelia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1667, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukiya, A.N.; Belani, J.D.; Rychnovsky, S.; Dopico, A.M. Specificity of cholesterol and analogs to modulate BK channels points to direct sterol-channel protein interactions. J. Gen. Physiol. 2011, 137, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orio, P.; Latorre, R. Differential effects of beta 1 and beta 2 subunits on BK channel activity. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005, 125, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanson, K.W.; Bannister, J.P.; Leo, M.D.; Jaggar, J.H. LRRC26 is a functional BK channel auxiliary γ subunit in arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; MacKinnon, R. Molecular structures of the human Slo1 K(+) channel in complex with β4. Elife 2019, 8, e51409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellman, G.C.; Bonev, A.D.; Nelson, M.T.; Brayden, J.E. Gender differences in coronary artery diameter involve estrogen, nitric oxide, and Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels. Circ. Res. 1996, 79, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.M.; Ribeiro, R.F., Jr.; Fernandes, A.A.; Fiorim, J.; Travaglia, T.C.; Vassallo, D.V.; Stefanon, I. Na+K+-ATPase activity and K+ channels differently contribute to vascular relaxation in male and female rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.T.; Pareek, T.; Sriramula, S.; Pabbidi, M.R. Aging influences cerebrovascular myogenic reactivity and BK channel function in a sex-specific manner. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1372–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, K.C.; Bukiya, A.N.; Dopico, A.M. BK channel-forming slo1 proteins mediate the brain artery constriction evoked by the neurosteroid pregnenolone. Neuropharmacology 2021, 192, 108603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.S.; Verma, S.; Voronin, D.; Lustigman, S.; Kulke, D.; Robertson, A.P.; Martin, R.J. Emodepside has sex-dependent immobilizing effects on adult Brugia malayi due to a differentially spliced binding pocket in the RCK1 region of the SLO-1 K channel. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, R.; Manso, A.M.; Marín, J. Effect of ouabain in pressurized middle cerebral arteries from normotensive and hypertensive rats. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 21, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukes, A.M.; Vitullo, L.; Zeeman, G.G.; Cipolla, M.J. Pregnancy prevents hypertensive remodeling and decreases myogenic reactivity in posterior cerebral arteries from Dahl salt-sensitive rats: A role in eclampsia? Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H1071–H1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fike, C.D.; Kaplowitz, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dantuma, M.; Madden, J.A. Effect of a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor on pulmonary and cerebral arteries of newborn piglets with chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Neonatology 2012, 101, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, T.; Sohajda, T.; Szente, L.; Nagy, P.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z.; Zakany, F. Cyclodextrins Exert a Ligand-like Current Inhibitory Effect on the K(V)1.3 Ion Channel Independent of Membrane Cholesterol Extraction. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 735357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slayden, A.; North, K.; Bisen, S.; Dopico, A.M.; Bukiya, A.N.; Rosenhouse-Dantsker, A. Enrichment of Mammalian Tissues and Xenopus Oocytes with Cholesterol. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, e60734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, R.; Chettimada, S.; Gupte, S.A. Poly(ethylene glycol)-cholesterol inhibits L-type Ca2+ channel currents and augments voltage-dependent inactivation in A7r5 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, M.; Welsh, D.G. K(IR) channels in the microvasculature: Regulatory properties and the lipid-hemodynamic environment. Curr. Top. Membr. 2020, 85, 227–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehr-Majoros, A.K.; Erostyák, J.; Fenyvesi, É.; Szabó-Meleg, E.; Szőcs, L.; Sétáló, G., Jr.; Helyes, Z.; Szőke, É. Cyclodextrin derivatives decrease Transient Receptor Potential vanilloid 1 and Ankyrin 1 ion channel activation via altering the surrounding membrane microenvironment by cholesterol depletion. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1334130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, L.; Bialecki, R.A.; Smith, E.; Smith, T.W.; Colucci, W.S. Cholesterol increases the L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel current in arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1992, 71, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feletou, M.; Tang, E.H.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Nitric oxide the gatekeeper of endothelial vasomotor control. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4198–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukiya, A.N.; Liu, J.; Dopico, A.M. The BK channel accessory beta1 subunit determines alcohol-induced cerebrovascular constriction. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2779–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schneider, E.H.; Dopico, A.M.; Bukiya, A.N. The Slo1 Y450F Substitution Modifies Basal Function and Cholesterol Response of Middle Cerebral Artery Smooth Muscle BK Channels in a Sexually Dimorphic Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083814
Schneider EH, Dopico AM, Bukiya AN. The Slo1 Y450F Substitution Modifies Basal Function and Cholesterol Response of Middle Cerebral Artery Smooth Muscle BK Channels in a Sexually Dimorphic Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083814
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchneider, Elizabeth H., Alex M. Dopico, and Anna N. Bukiya. 2025. "The Slo1 Y450F Substitution Modifies Basal Function and Cholesterol Response of Middle Cerebral Artery Smooth Muscle BK Channels in a Sexually Dimorphic Manner" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083814
APA StyleSchneider, E. H., Dopico, A. M., & Bukiya, A. N. (2025). The Slo1 Y450F Substitution Modifies Basal Function and Cholesterol Response of Middle Cerebral Artery Smooth Muscle BK Channels in a Sexually Dimorphic Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083814





