Transcriptional Repression of CCL2 by KCa3.1 K+ Channel Activation and LRRC8A Anion Channel Inhibition in THP-1-Differentiated M2 Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
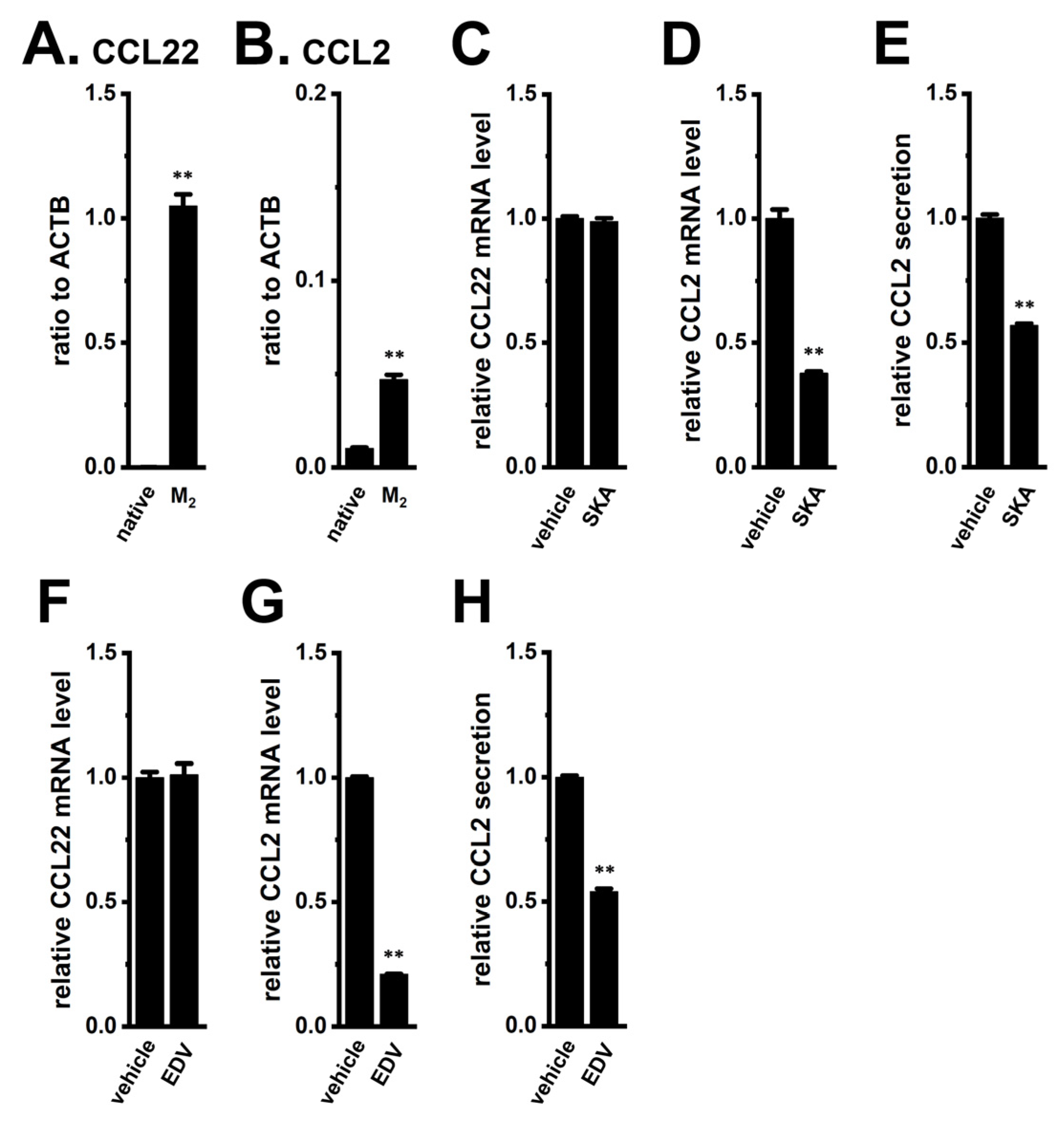
2.1. Decreased Expression and Secretion of CCL2 by KCa3.1 Activation and LRRC8A Inhibition in M2-MACs
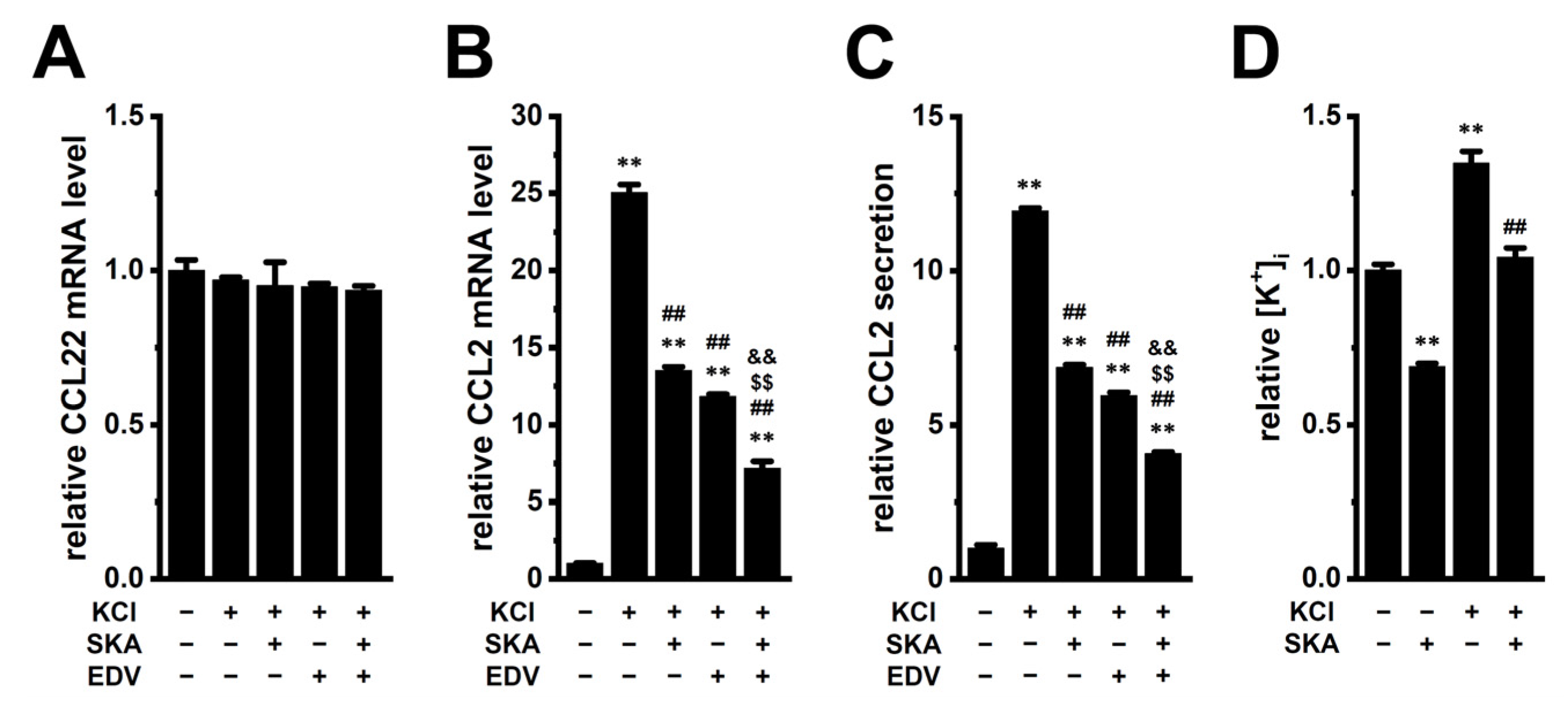
2.2. Increased Expression and Secretion of CCL2 by High [K+]e Exposure in M2-MACs and Suppressive Effects of KCa3.1 Activation and LRRC8A Inhibition
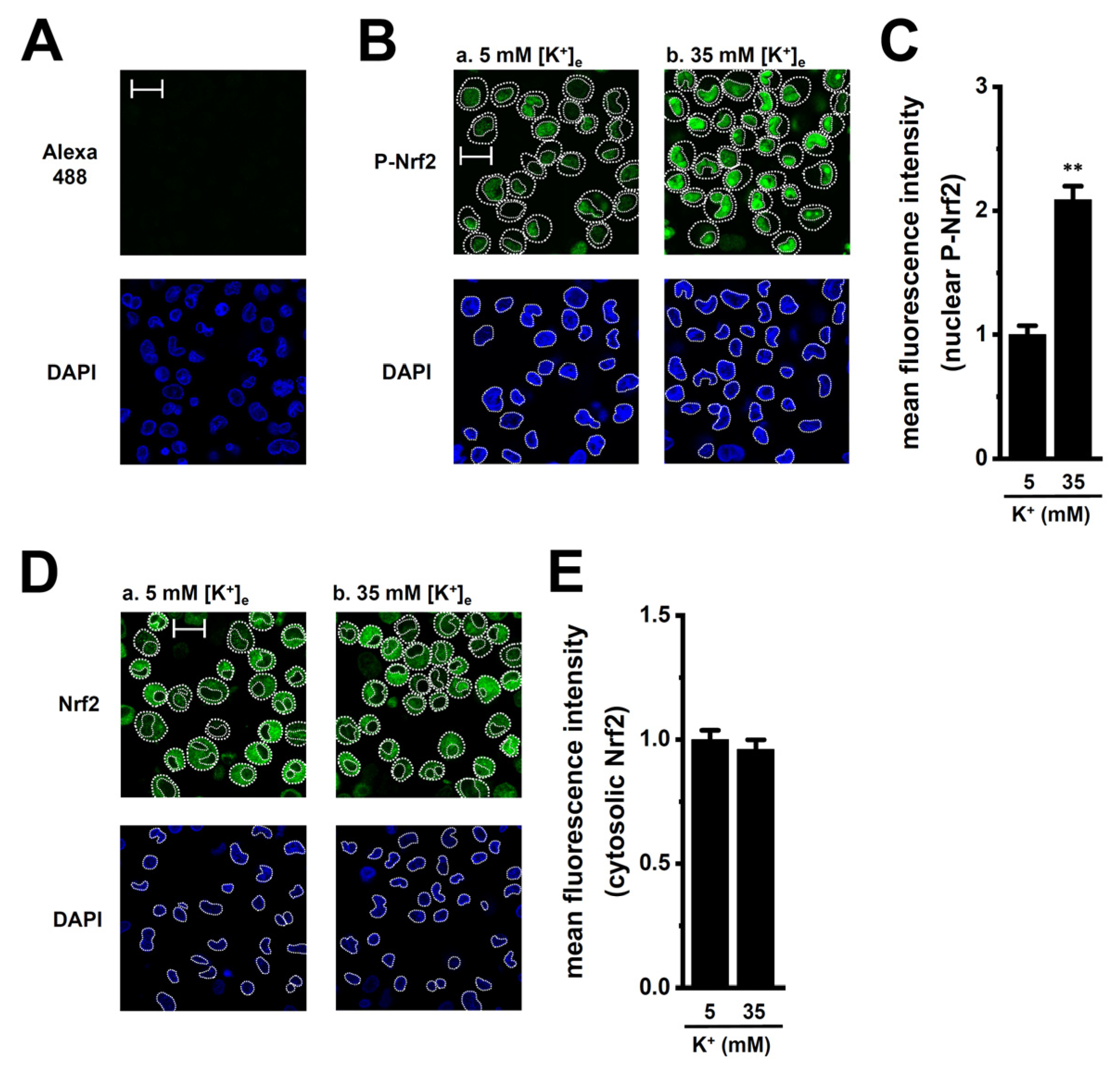
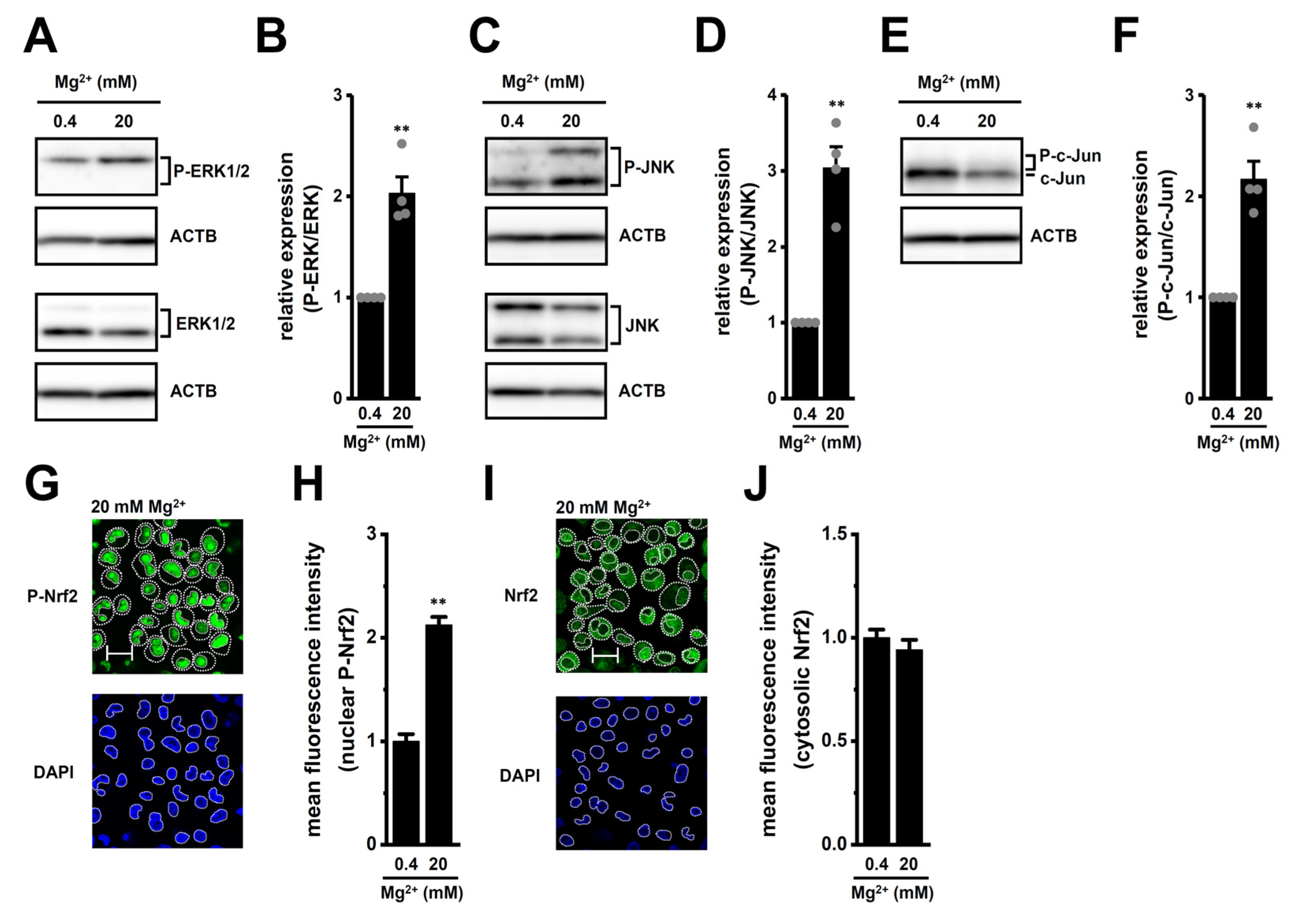
2.3. Transcriptional Regulation via ERK, JNK, and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in M2-MACs
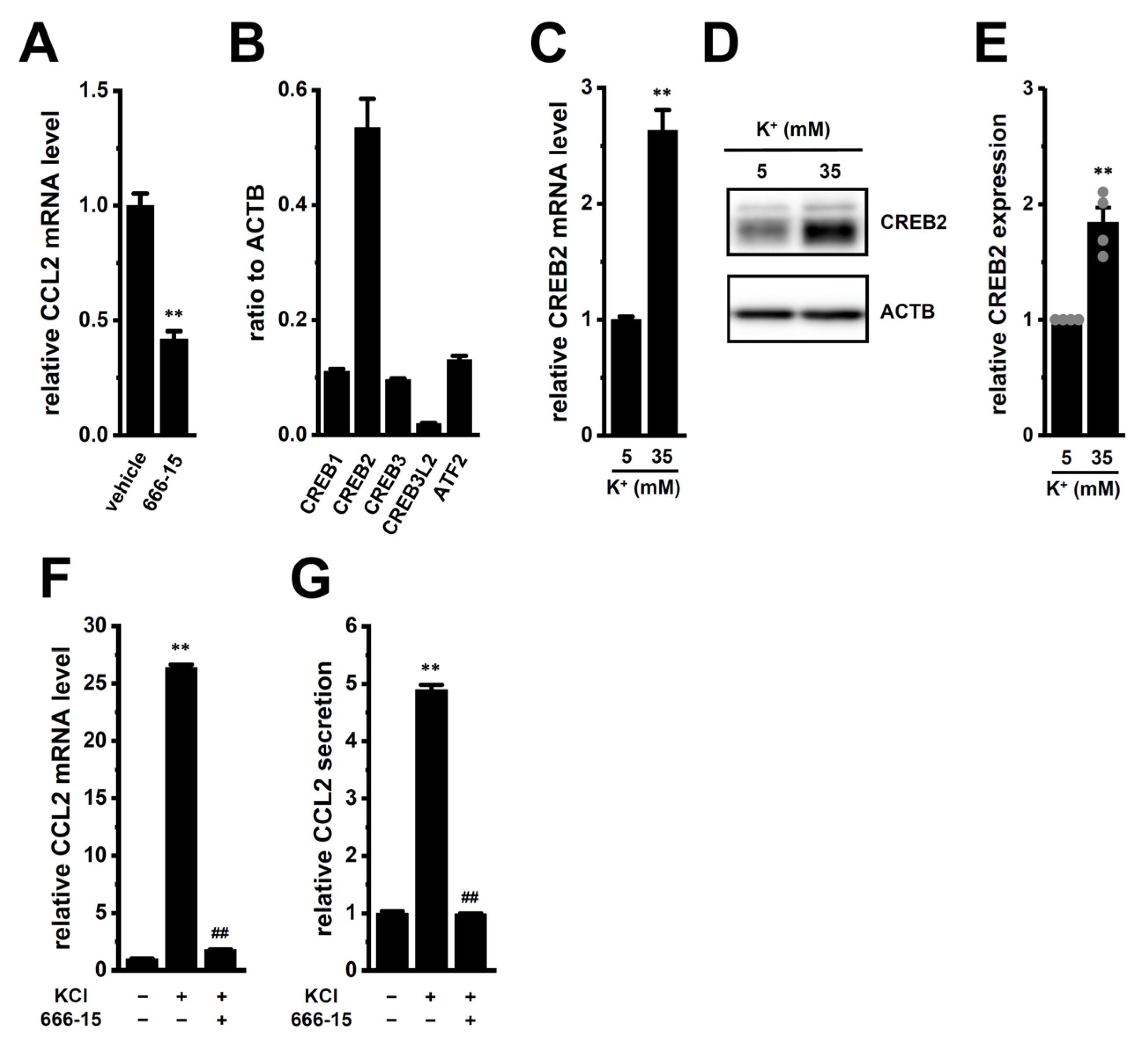
2.4. Possible Involvement of Transcriptional Regulators CEBPB and CREB2 in High [K+]e-Induced Upregulation of CCL2 in M2-MACs
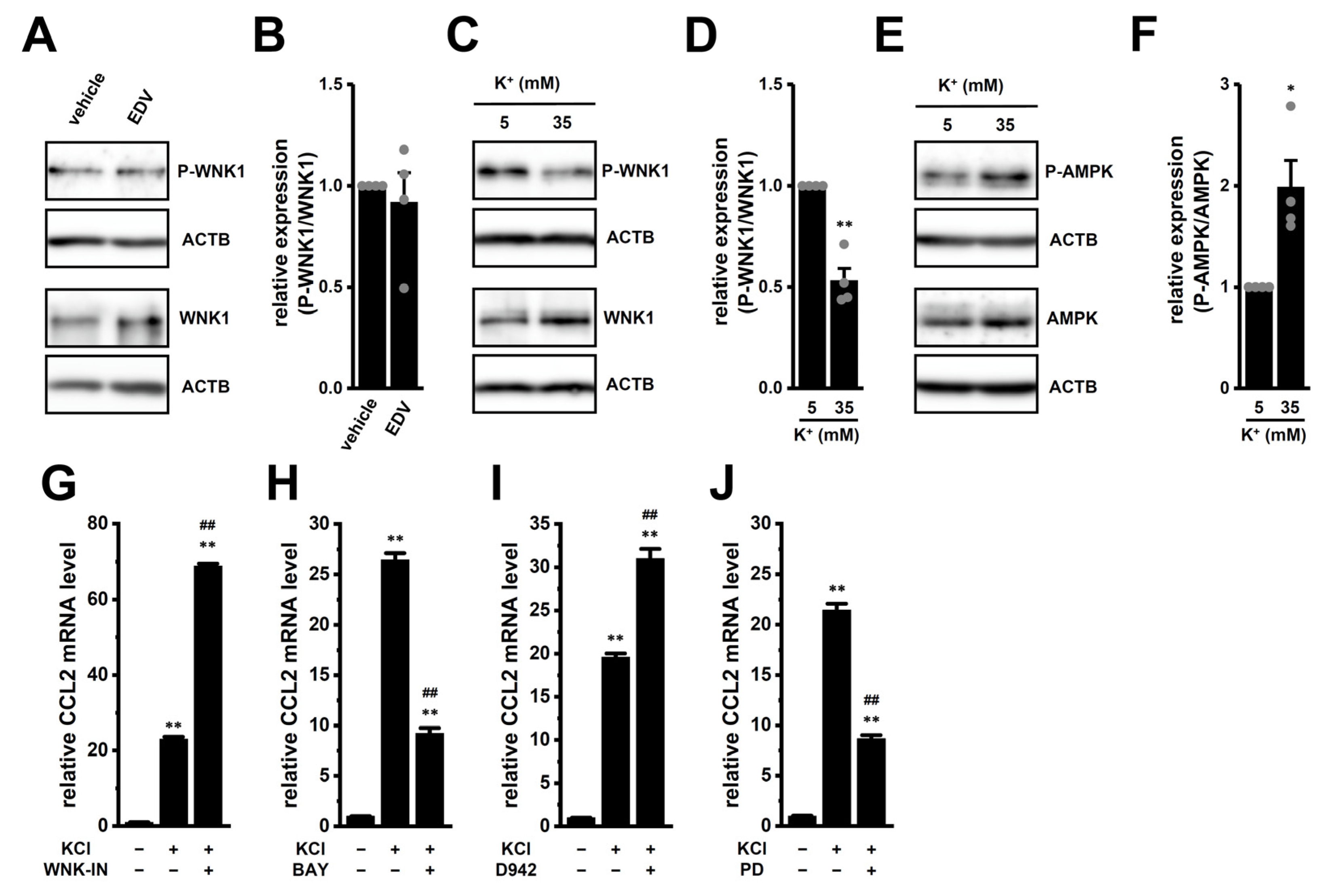
2.5. Possible Involvement of the WNK1–AMPK–p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway in High [K+]e-Induced Upregulation of CCL2 in M2-MACs
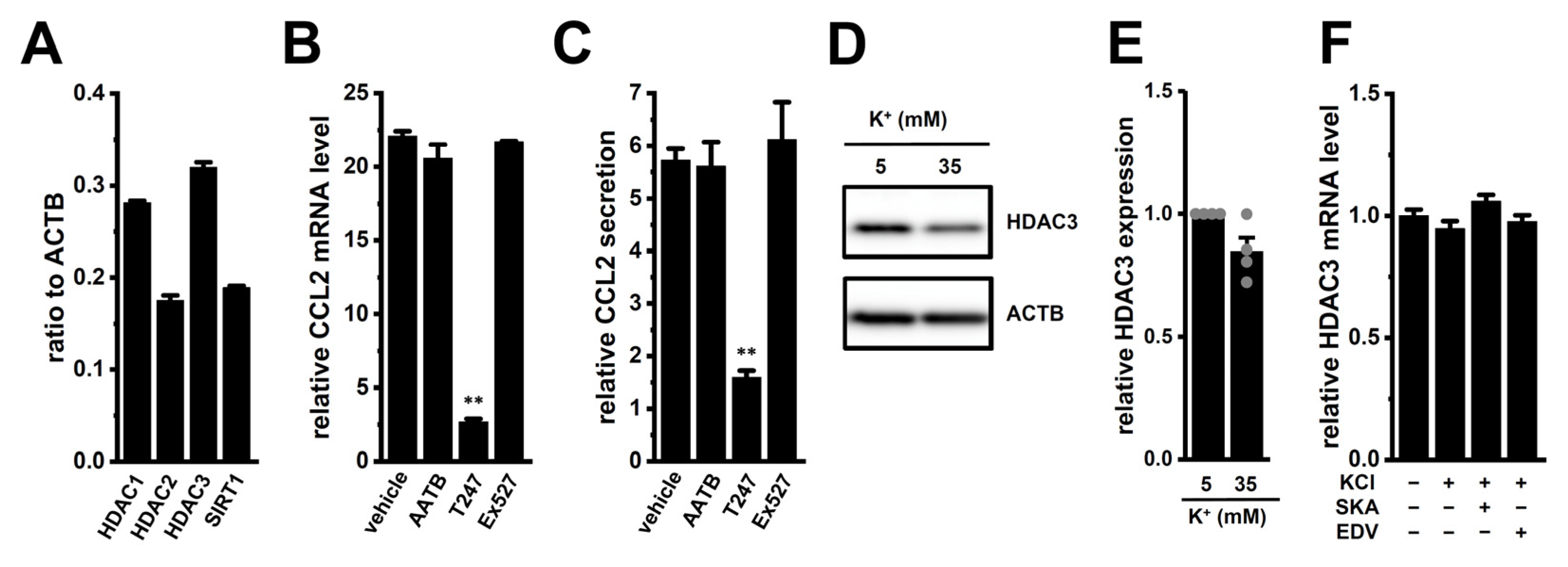
2.6. Possible Involvement of Epigenetic Modification by HDAC3 in High [K+]e-Induced Upregulation of CCL2 in M2-MACs
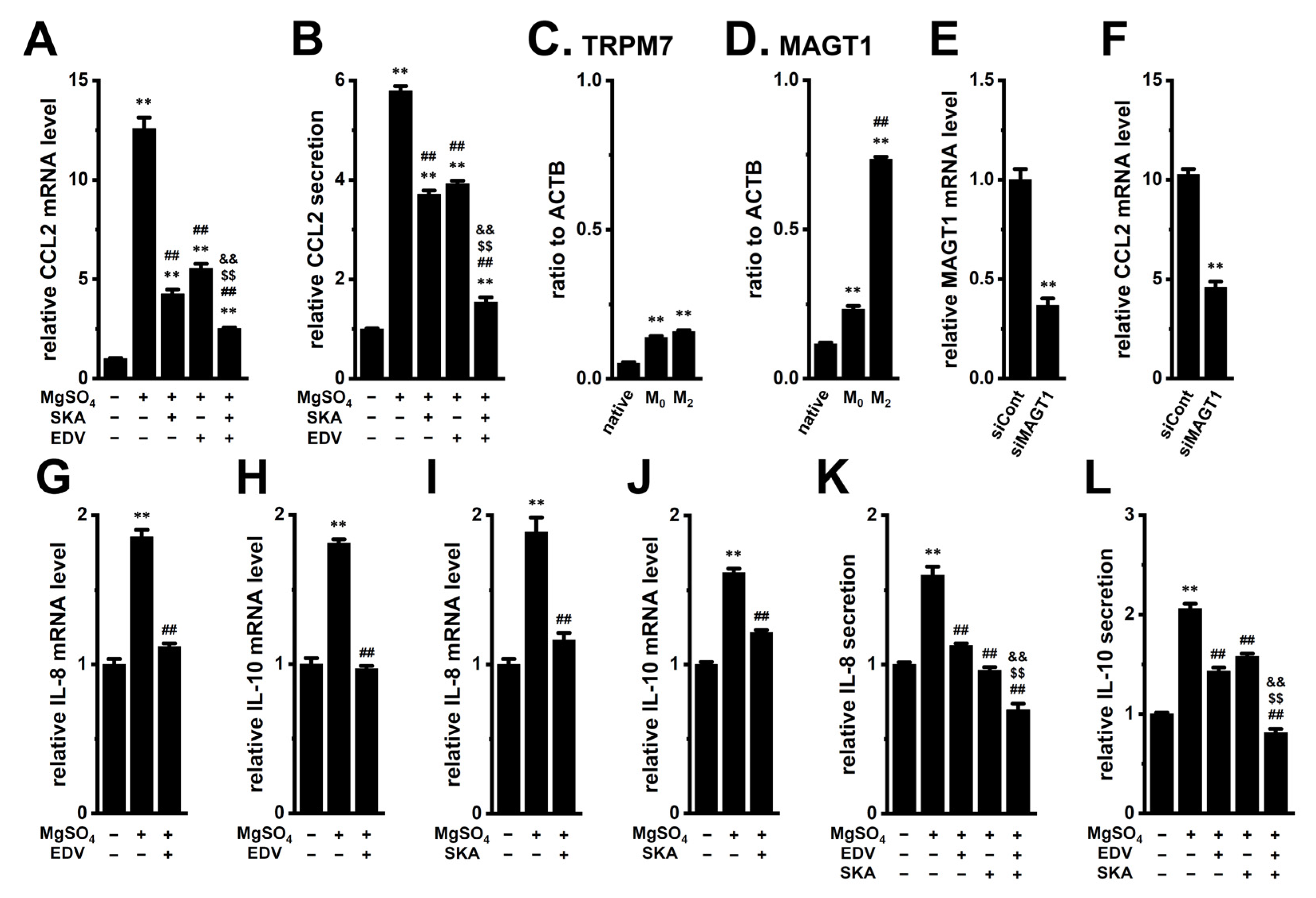
2.7. Increased Expression and Secretion of CCL2 by High [Mg2+]e Exposure in M2-MACs and Suppressive Effects of KCa3.1 Activation and LRRC8A Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Differentiation into M2-MACs
4.3. Real-Time PCR
4.4. Western Blots
4.5. Measurement of Cytokine Production by ELISA
4.6. Measurement of [K+]i by Potassium Turbidimetric Assay
4.7. Confocal Imaging of the Nuclear and Cytosolic Distribution of Nrf2
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basak, U.; Sarkar, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.; Nayak, D.; Kaushik, S.; Das, T.; Sa, G. Tumor-associated macrophages: An effective player of the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1295257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Sioud, M. Tumor-associated macrophage subsets: Shaping polarization and targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Ren, W.; Ya, G.; Wang, B.; He, J.; Ren, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, S. Role of chemokines in the crosstalk between tumor and tumor-associated macrophages. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasser, S.A.; Ozbay Kurt, F.G.; Arkhypov, I.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xia, R.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Role of the CCL2-CCR2 signaling axis in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e13115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.; Heikenwalder, M. CCL2 in the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1302, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadomoto, S.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Roles of CCL2-CCR2 axis in the tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feske, S.; Wulff, H.; Skolnik, E.Y. Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 291–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eil, R.; Vodnala, S.K.; Clever, D.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Sukumar, M.; Pan, J.H.; Palmer, D.C.; Gros, A.; Yamamoto, T.N.; Patel, S.J.; et al. Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cells effector function. Nature 2016, 537, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, S.; Matsui, M.; Kajikuri, J.; Kito, H.; Endo, K. Downregulation of IL-8 and IL-10 by the activation of Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCa3.1 in THP-1-derived M2 macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ping, J.; Tang, J.; He, B.; Chang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, S.; Tang, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Cell volume controlled by LRRC8A-formed volume-regulatory anion channels fine-tunes T cell activation and function. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, S.A.; Stojakovic, P.; Amat, R.; Rubio-Moscardo, F.; Latorre, P.; Seisenbacher, G.; Canadell, D.; Böttcher, R.; Aregger, M.; Moffat, J.; et al. LRRC8A-containing chloride channel is crucial for cell volume recovery and survival under hypertonic conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025013118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirayath, T.W.; Ollivier, M.; Kayatekin, M.; Rubera, I.; Pham, C.N.; Friard, J.; Linck, N.; Hirbec, H.; Combes, C.; Zarka, M.; et al. Activation of osmo-sensitive LRRC8 anion channels in macrophages is important for micro-crystallin joint inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Kajikuri, J.; Kito, H.; Elboray, E.E.; Suzuki, T.; Ohya, S. Downregulation of IL-8 and IL-10 by LRRC8A inhibition through the NOX2-Nrf2-CEBPB transcriptional axis in THP-1-derived M2 macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.T.; El-Ghonaimy, E.A.; El-Shinawi, M.; Hosney, M.; Götte, M.; Woodward, W.A.; Elmamlouk, T.; Mohamed, M.M. IL-8 and MCP-1/CCL2 regulate proteolytic activity in triple negative inflammatory breast cancer a mechanism that might be modulated by Src and Erk1/2. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 401, 115092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Samad, O.A.; Suter, M.R.; Yasuhiko, K.; Xu, Z.Z.; Park, J.Y.; Lind, A.L.; Ma, Q.; Ji, R.R. JNK-induced MCP-1 production in spinal cord astrocytes contributes to central sensitization and neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4096–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, P.; Xi, D.; Zhu, H.; Gao, Y. ATF4 regulates CCL2 expression to promote endometrial cancer growth by controlling macrophage infiltration. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J.H. Phosphorylated nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 promotes the recreation of C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 and the recruitment of M2 macrophages. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.W.Y.; Folz, J.; Kopelman, R.; Wang, X. In vivo photoacoustic potassium imaging of the tumor microenvironment. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 3507–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.T.; Ng, A.S.; Ng, X.R.; Zhuang, Z.; Wong, B.H.S.; Prasannan, P.; Kok, Y.J.; Bi, X.; Shim, H.; Wulff, H.; et al. Extracellular K+ dampens T cell functions: Implications for immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Bioelectricity 2019, 1, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes-Hopfinger, L.; Enache, A.; Xie, J.; Huang, C.L.; Köchl, R.; Tybulewicz, V.L.J.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Alnemri, E.S. Chloride sensing by WNK1 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; He, L.; Du, Y.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.; Yang, M.; Sun, S.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; et al. Macrophage WNK1 senses intracellular hypo-chlorine to regulate vulnerability to sepsis attack during hypochlomia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guragain, D.; Gurung, P.; Chang, J.H.; Katila, N.; Chang, H.W.; Jeong, B.S.; Choi, D.Y.; Kim, J.A. AMPK is essential for IL-10 expression and for maintaining balance between inflammatory and cytoprotective signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzinger, M.; Fischhuber, K.; Pölöske, D.; Mechtler, K.; Heiss, E.H. AMPK leads to phosphorylation of the transcription factor Nrf2, tuning transactivation of selected targeted genes. Redox Biol. 2020, 29, 101393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, E.J.; Rodan, A.R. Intracellular ion control of WNK signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2023, 85, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Heping, H.; Shen, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, A.; Ren, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; et al. AMPK/p38/Nrf2 activation as a protective feedback to restrain oxidative stress and inflammation in microglia stimulated with sodium fluoride. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, K.; Park, D.; Lee, E.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Choe, J.; Jeoung, D. Histone deacetylase 3 mediates allergic skin inflammation by regulating expression of MCP1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 25844–25859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatla, H.R.; Muniraj, N.; Thevkar, P.; Yavvari, S.; Sukhavasi, S.; Makena, M.R. Regulation of chemokines and cytokines by histone deacetylases and an update on histone deacetylase inhibitors in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in man: Implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötscher, J.; i Líndez, A.-A.M.; Kirchhammer, N.; Cribioli, E.; Attianese, G.M.P.G.; Trefny, M.P.; Lenz, M.; Rothschild, S.I.; Strati, P.; Künzli, M.; et al. Magnesium sensing via LFA-1 regulates CD8+ T cells effector function. Cell 2022, 185, 585–602.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, X.; Xu, M.; Yang, F.; Wang, W.; Niu, X. In vitro immunomodulation of magnesium on monocytic cell toward anti-inflammatory macrophages. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; Jang, J.; Lee, J.H. Polarization of THP-1-derived macrophage by magnesium and MAGT1 inhibition in wound healing. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2023, 50, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Wong, K.H.M.; Shen, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Zheng, Y.; et al. TRPM7 kinase-mediated immunomodulation in macrophage plays a central role in magnesium ion-induced bone regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, B.; Garris, C.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kohler, R.H.; Carrothers, J.; Halabi, E.A.; Iwamoto, Y.; Goubet, A.; Xie, Y.; Wirapati, P.; et al. Targeted SPP1 inhibition of tumor-associated myeloid cells effectively decreases tumor sizes. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2410360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; et al. CCL5 derived from tumor-associated macrophages promotes prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis via activating β-catenin/STAT3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, N.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Ren, S. CCL5 might be a prognostic biomarker and associated with immune-therapeutic efficacy in cancers: A pan-cancer analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Luo, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y. Epigenetic regulation of chemokine (CC-motif) ligand 2 in inflammatory diseases. Cell Prolif. 2023, 56, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ozawa, Y.; Lee, H.; Wen, Y.D.; Tan, T.H.; Wadzinski, B.E.; Seto, E. Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) activity is regulated by interaction with protein serine/threonine phosphatase 4. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, M.J.; Lazar, M.A. Integrated regulation of physiology by histone deacetylase 3. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Yan, L.; Sun, K.; Zhou, T.; Zou, Y.; Xiong, W.; Duan, S.Z. Nuclear receptor corepressor 1 deficiency exacerbates asthma by modulating macrophage polarization. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Abellán, A.; Angosto-Bazarra, D.; Alarcón-Vila, C.; Baños, M.C.; Hafner-Bratkovič, I.; Oliva, B.; Pelegrín, P. Sensing low intracellular potassium by NLRP3 results in a stable open structure that promotes inflammasome activation. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, M.E.; Kondolf, H.C.; De Santis, S.; Pizarro, T.T.; Abbott, D.W. Restraint of inflammasome-driven cytokine responses through the mRNA stability protein TTP. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koumangoye, R. The role of Cl- and K+ efflux in NLRP3 inflammasome and innate immune response activation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 322, C645–C652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, S.; Ohta, A.; Sohara, E.; Ohta, E.; Rai, T.; Sasaki, S.; Uchida, S. Regulation of WNK1 kinase by extracellular potassium. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 15, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, M.D.; Williams, M.R.; Ryffel, B. AMP-activated protein kinase regulation of the NLRP3 inflammation during aging. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenkle, N.T.; Serezani, C.H.; Pua, H.H. MicroRNAs in macrophages: Regulators of activation and function. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Tavakkoli Avval, S.; Shoorei, H.; Taheri, M.; Samadian, M. The impact of non-coding RNAs on macrophage polarization. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrito, M.L.; Pucci, F.; Magri, L.; Moi, D.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Ranghetti, A.; Casazza, A.; Mazzone, M.; Lyle, R.; Naldini, L.; et al. MiR-511-3p modulates genetic programs of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Kouwaki, T.; Oshiumi, H. Aging-associated extracellular vesicles contain immune regulatory microRNAs alleviating hyperinflammatory state and immune dysfunction in the elderly. iScience 2020, 23, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Su, R. MiR-192-5p-modified tumor-associated macrophages-derived exosome suppressed endometrial cancer progression through targeting IRAK1/NF-κB signaling. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.A.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Kriegel, A.J.; Geurts, A.M.; Usa, K.; Xue, H.; Wang, D.; Kong, Y.; Liang, M. MiR-192-5p in the kidney protects against the development of hypertension. Hypertension 2019, 73, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; Qin, K.; Lai, Q.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. RUNX1 promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by regulating the crosstalk between tumor cells and tumor associated macrophages. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, J.; Steinauer, N.; Wong, M.; Wu, B.; Dickson, A.; Kalkum, M.; Zhang, J. Histone deacetylase 3 preferentially binds and collaborates with the transcription factor RUNX1 to repress AML1-ETO-dependent transcription in t(8;21) AML. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4212–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Yin, G.; Kong, W.; Zhou, J. Advances in the roles of ATF4 in osteoporosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugarte, G.D.; Diaz, E.; Biscaia, M.; Stehberg, J.; Montecino, M.; van Zundert, B. Transcription of the pain-related TRPV1 gene requires Runx1 and C/EBPβ factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.; Zhang, C.; Pan, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G. Immunomodulatory metal-based biomaterials for cancer immunotherapy. J. Control. Release 2024, 375, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y. Regulation of anti-tumor immunity by metal ion in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1379365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, C.; Insinga, G.; Gimigliano, F.; Morrione, A.; Giordano, A.; Giurisato, E. Insights into CSF-1R expression in the tumor microenvironment. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, Z.; Dou, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, B.; Sun, R.; Zheng, X.; et al. Interleukin-34-orchestrated tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming is required for tumor immune escape driven by p53 inactivation. Immunity 2024, 57, 2344–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, A.; D’Alessandro, G.; Golia, M.T.; Grössinger, E.M.; Di Angelantonio, S.; Ragozzino, D.; Santoro, A.; Esposito, V.; Wulff, H.; Catalano, M.; et al. KCa3.1 inhibition switches the phenotype of glioma-infiltrating microglia/macrophages. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massenzio, F.; Cambiaghi, M.; Marchiotto, F.; Boriero, D.; Limatola, C.; D’Alessandro, G.; Buffelli, M. In vivo morphological alterations of TAMs during KCa3.1 inhibition-by using in vivo two-photon time-lapse technology. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1002487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Su, X.; Dai, X.; Li, S.; Mo, Z. KCNN4 is a potential prognostic marker and critical factor affecting the immune status of the tumor microenvironment in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 2454–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsui, M.; Kajikuri, J.; Kito, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ohya, S. Transcriptional Repression of CCL2 by KCa3.1 K+ Channel Activation and LRRC8A Anion Channel Inhibition in THP-1-Differentiated M2 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157624
Matsui M, Kajikuri J, Kito H, Yamaguchi Y, Ohya S. Transcriptional Repression of CCL2 by KCa3.1 K+ Channel Activation and LRRC8A Anion Channel Inhibition in THP-1-Differentiated M2 Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157624
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsui, Miki, Junko Kajikuri, Hiroaki Kito, Yohei Yamaguchi, and Susumu Ohya. 2025. "Transcriptional Repression of CCL2 by KCa3.1 K+ Channel Activation and LRRC8A Anion Channel Inhibition in THP-1-Differentiated M2 Macrophages" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157624
APA StyleMatsui, M., Kajikuri, J., Kito, H., Yamaguchi, Y., & Ohya, S. (2025). Transcriptional Repression of CCL2 by KCa3.1 K+ Channel Activation and LRRC8A Anion Channel Inhibition in THP-1-Differentiated M2 Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157624






