Maral Root Extract and Its Main Constituent 20-Hydroxyecdysone Enhance Stress Resilience in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chromatography Analysis
2.1.1. Method Development
2.1.2. Method Validation
- 1.
- Linearity
- 2.
- Accuracy and precision
- 3.
- Limit of detection (LD) and quantification (LQ)
- 4.
- Robustness
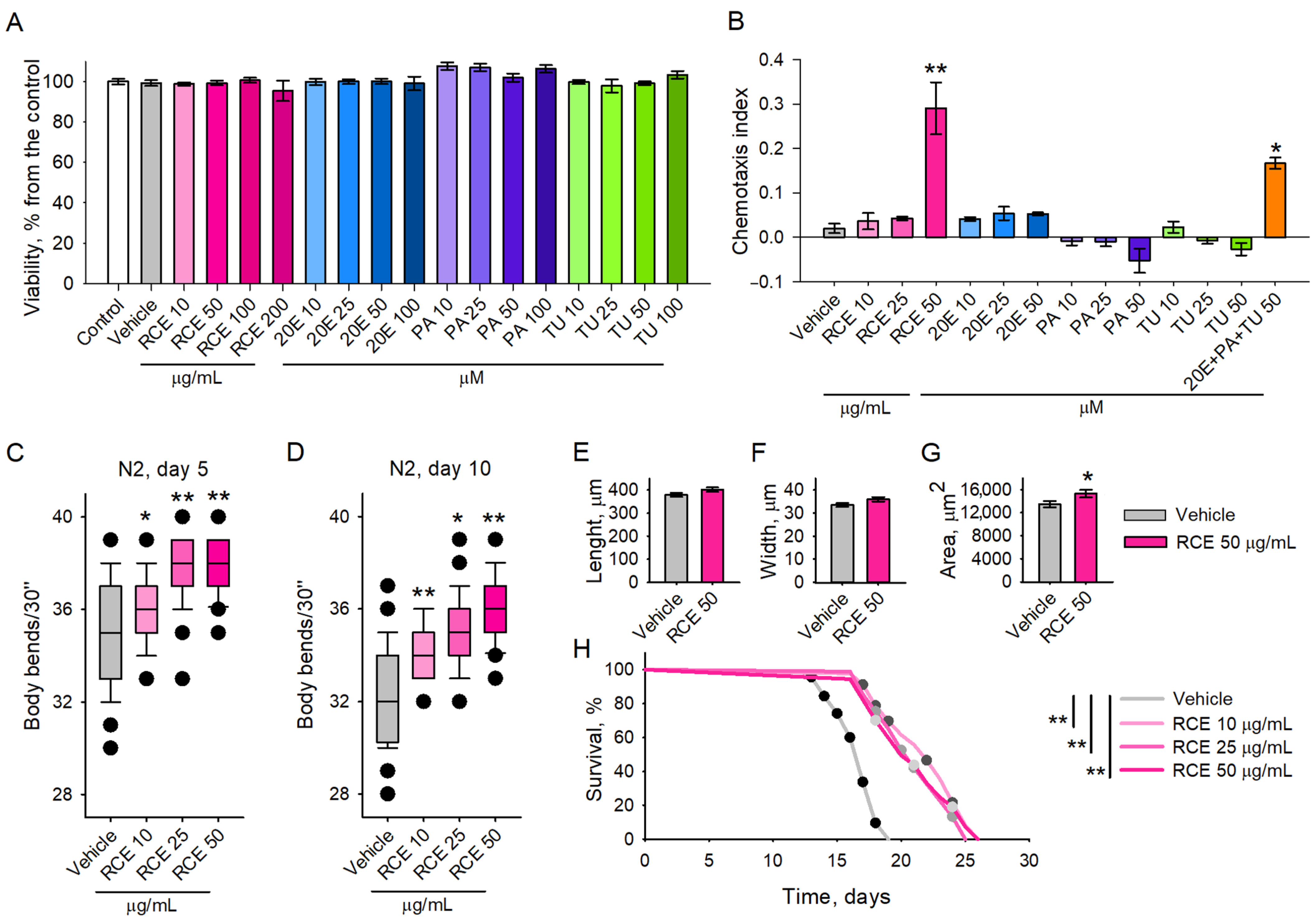
2.2. Maral Root Extract Ameliorates Physiological Aging and Increases Lifespan of C. elegans
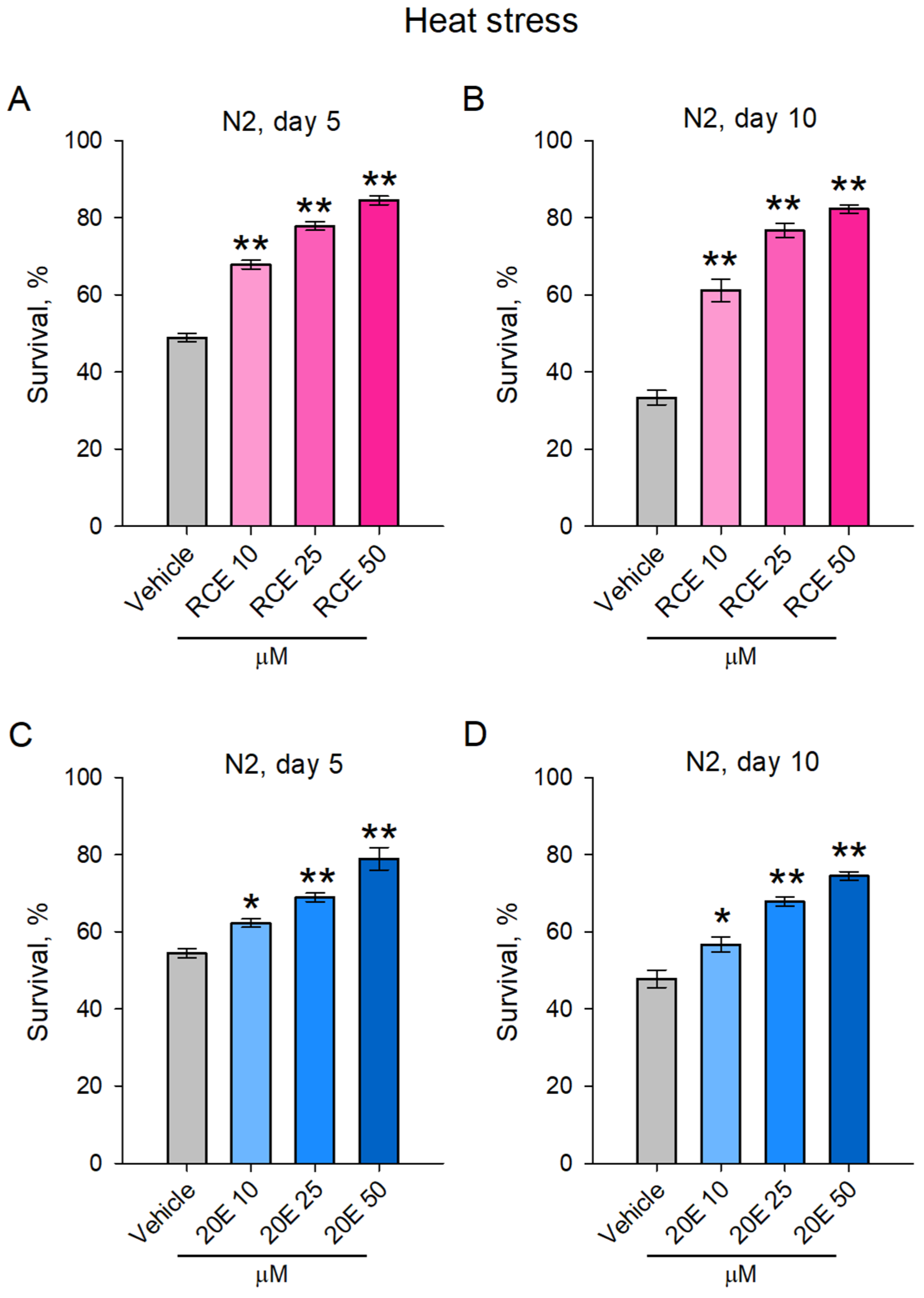
2.3. The RCE and 20E Treatment Improved Heat Stress Resistance in C. elegans
2.4. RCE and 20E Enhance Survival in C. elegans Exposed to Oxidative Stress
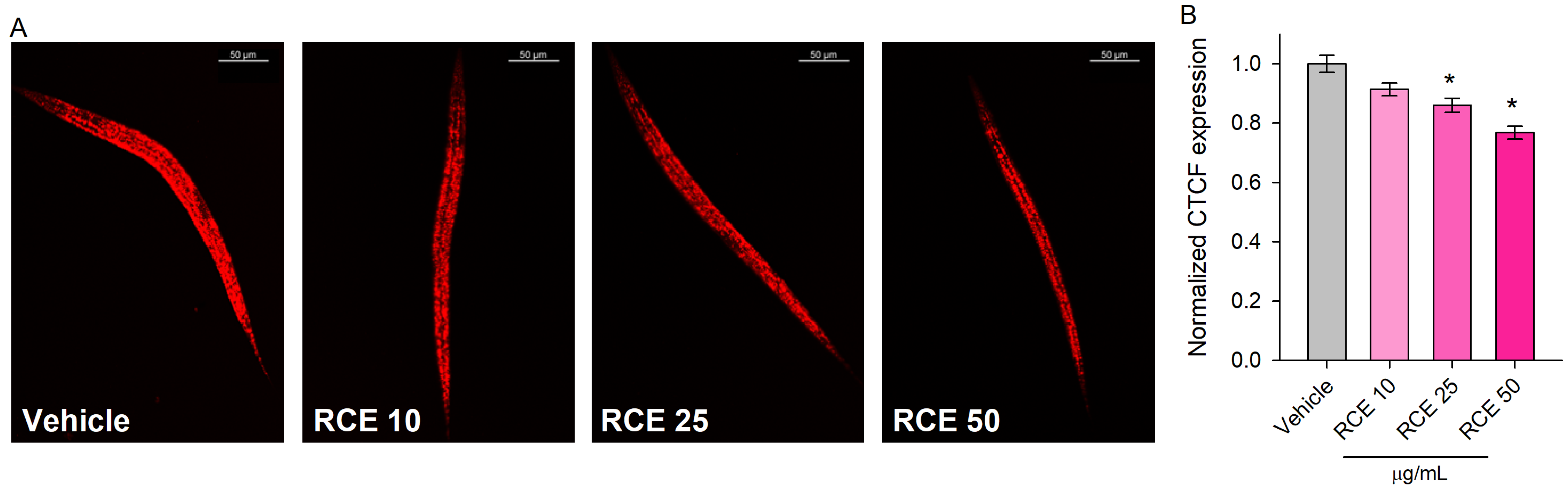
2.5. Rhaponticum Carthamoides Extract Modulates Lipid Metabolism in Glucose-Supplemented C. elegans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Plant Material and Extraction
4.3. HPLC-PDA Analysis
4.3.1. Preparing of Standard and Test Solutions
4.3.2. Instrumentation
4.3.3. Chromatographic Conditions
4.3.4. Validation of HPLC-PDA Method
4.4. Caenorhabditis elegans Maintenance and Treatment
4.5. Locomotion Assay
4.6. Lifespan Measurement
4.7. Chemotaxis Assessment
4.8. Nile Red Staining
4.9. Heat Stress
4.10. Oxidative Stress
4.11. Analysis of Body Morphology
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 20E | 20-Hydroxyecdysone |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HPLC-PDA | High-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection |
| LD | Limit of detection |
| LQ | Limit of quantification |
| NMG | Nematode growth medium |
| PA | Ponasterone A |
| RCE | Rhaponticum carthamoides extract |
| TU | Turkesterone |
References
- Wiegant, F.A.C.; Surinova, S.; Ytsma, E.; Langelaar-Makkinje, M.; Wikman, G.; Post, J.A. Plant Adaptogens Increase Lifespan and Stress Resistance in C. elegans. Biogerontology 2009, 10, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Wikman, G. Effects of Adaptogens on the Central Nervous System and the Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Their Stress—Protective Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.; Seo, E.J.; Efferth, T. Novel Molecular Mechanisms for the Adaptogenic Effects of Herbal Extracts on Isolated Brain Cells Using Systems Biology. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.G.; Efferth, T.; Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Kuchta, K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Banerjee, S.; Heinrich, M.; Wu, W.; Guo, D.; et al. Evolution of the Adaptogenic Concept from Traditional Use to Medical Systems: Pharmacology of Stress- and Aging-Related Diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 630–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, V.; Ivanov, K.; Delattre, C.; Nalbantova, V.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D.; Ivanova, S. Plant Adaptogens—History and Future Perspectives. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, M.N.; Savova, M.S.; Mihaylova, L.V.; Georgiev, M.I. Nurturing Longevity through Natural Compounds: Where Do We Stand, and Where Do We Go? Food Front. 2024, 5, 267–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.A.; Luyten, W.; Gogol, M.; Simm, A.; Saul, N.; Cirulli, F.; Berry, A.; Antal, P.; Köhling, R.; Wouters, B.; et al. Health and Aging: Unifying Concepts, Scores, Biomarkers and Pathways. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, X.; Dou, L.; Yan, M.; Shen, T.; Tang, W.; Li, J. Aging and Aging-Related Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Interventions and Treatments. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. Hallmarks of Aging: An Expanding Universe. Cell 2023, 186, 243–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanoudakis, E.; Tavernarakis, N. Age-Associated Anatomical and Physiological Alterations in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 213, 111827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.G.; Altintas, O.; Kim, E.J.E.; Kwon, S.; Lee, S.J.V. Age-Dependent Changes and Biomarkers of Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.D.; Anderson, R.M. Nutrition, Longevity and Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Interventions. Cell 2022, 185, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoska, L.; Janovska, D. Chemistry and Pharmacology of Rhaponticum carthamoides: A Review. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łotocka, B.; Geszprych, A. Anatomy of the Vegetative Organs and Secretory Structures of Rhaponticum carthamoides (Asteraceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 144, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, V.; Ivanov, K.; Ivanova, S. Comparison between the Biological Active Compounds in Plants with Adaptogenic Properties (Rhaponticum carthamoides, Lepidium meyenii, Eleutherococcus senticosus and Panax ginseng). Plants 2021, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savchenko, R.G.; Veskina, N.A.; Odinokov, V.N.; Benkovskaya, G.V.; Parfenova, L.V. Ecdysteroids: Isolation, Chemical Transformations, and Biological Activity. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 21, 1445–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, V.; Ivanova, S.; Chakarov, D.; Kraev, K.; Ivanov, K. Ecdysterone and Turkesterone—Compounds with Prominent Potential in Sport and Healthy Nutrition. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.R.; de Almeida Takata, L.; Chagas, K.; Justino, A.B.; Saraiva, A.L.; Goulart, L.R.; de Melo Rodrigues Ávila, V.; Otoni, W.C.; Espindola, F.S.; da Silva, C.R. A 20-Hydroxyecdysone-Enriched Fraction from Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng.) Pedersen Roots Alleviates Stress, Anxiety, and Depression in Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, P.; Wuttke, W.; Jarry, H.; Seidlova-Wuttke, D. Beneficial Effects of β-Ecdysone on the Joint, Epiphyseal Cartilage Tissue and Trabecular Bone in Ovariectomized Rats. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Guidance for Industry on Validation of Chromatographic Methods and USP General 200. In Chapter 621 Chromatography; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022; pp. 258–265.
- Todorova, M.N.; Savova, M.S.; Mihaylova, L.V.; Georgiev, M.I. Icariin Improves Stress Resistance and Extends Lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans through Hsf-1 and Daf-2-Driven Hormesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savova, M.S.; Todorova, M.N.; Apostolov, A.G.; Yahubyan, G.T.; Georgiev, M.I. Betulinic Acid Counteracts the Lipid Accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans by Modulation of Nhr-49 Expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dues, D.J.; Andrews, E.K.; Schaar, C.E.; Bergsma, A.L.; Senchuk, M.M.; Van Raamsdonk, J.M. Aging Causes Decreased Resistance to Multiple Stresses and a Failure to Activate Specific Stress Response Pathways. Aging 2016, 8, 777–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumsta, C.; Chang, J.T.; Schmalz, J.; Hansen, M. Hormetic Heat Stress and HSF-1 Induce Autophagy to Improve Survival and Proteostasis in C. elegans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, M.N.; Savova, M.S.; Mihaylova, L.V.; Georgiev, M.I. Punica granatum L. Leaf Extract Enhances Stress Tolerance and Promotes Healthy Longevity through HLH-30/TFEB, DAF16/FOXO, and SKN1/NRF2 Crosstalk in Caenorhabditis elegans. Phytomedicine 2024, 134, 155971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsta, C.; Chang, J.T.; Lee, R.; Tan, E.P.; Yang, Y.; Loureiro, R.; Choy, E.H.; Lim, S.H.Y.; Saez, I.; Springhorn, A.; et al. The Autophagy Receptor P62/SQST-1 Promotes Proteostasis and Longevity in C. elegans by Inducing Autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baev, A.Y.; Charishnikova, O.S.; Khasanov, F.A.; Nebesnaya, K.S.; Makhmudov, A.R.; Rakhmedova, M.T.; Khushbaktova, Z.A.; Syrov, V.N.; Levitskaya, Y.V. Ecdysterone Prevents Negative Effect of Acute Immobilization Stress on Energy Metabolism of Rat Liver Mitochondria. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 219, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth-Mészáros, A.; Garmaa, G.; Hegyi, P.; Bánvölgyi, A.; Fenyves, B.; Fehérvári, P.; Harnos, A.; Gergő, D.; Do To, U.N.; Csupor, D. The Effect of Adaptogenic Plants on Stress: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 108, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abomosallam, M.; Hendam, B.M.; Abdallah, A.A.; Refaat, R.; El-Hak, H.N.G. Neuroprotective Effect of Withania Somnifera Leaves Extract Nanoemulsion against Penconazole-Induced Neurotoxicity in Albino Rats via Modulating TGF-Β1/Smad2 Signaling Pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 1903–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumanille, R.; Vernus, B.; Brioche, T.; Descossy, V.; Van Ba, C.T.; Campredon, S.; Philippe, A.G.; Delobel, P.; Bertrand-Gaday, C.; Chopard, A.; et al. Acute and Chronic Effects of Rhaponticum carthamoides and Rhodiola rosea Extracts Supplementation Coupled to Resistance Exercise on Muscle Protein Synthesis and Mechanical Power in Rats. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skała, E.; Sitarek, P.; Rózalski, M.; Krajewska, U.; Szemraj, J.; Wysokińska, H.; Śliwiński, T. Antioxidant and DNA Repair Stimulating Effect of Extracts from Transformed and Normal Roots of Rhaponticum carthamoides against Induced Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage in CHO Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5753139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naß, J.; Abdelfatah, S.; Efferth, T. Induction of Stress Resistance and Extension of Lifespan in Chaenorhabditis elegans Serotonin-Receptor Knockout Strains by Withanolide A. Phytomedicine 2021, 84, 153482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, V.; Savova, M.S.; Ivanova, S.; Ivanov, K.; Georgiev, M.I. Anti-Adipogenic Activity of Rhaponticum carthamoides and Its Secondary Metabolites. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuvalov, O.; Kirdeeva, Y.; Fefilova, E.; Daks, A.; Fedorova, O.; Parfenyev, S.; Nazarov, A.; Vlasova, Y.; Krasnov, G.S.; Barlev, N.A. 20-Hydroxyecdysone Boosts Energy Production and Biosynthetic Processes in Non-Transformed Mouse Cells. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głazowska, J.; Kamiński, M.M.; Kamiński, M. Chromatographic Separation, Determination and Identification of Ecdysteroids: Focus on Maral Root (Rhaponticum carthamoides, Leuzea carthamoides). J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 4304–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Seo, C.S.; Kim, S.S.; Shin, H.K. Quality Assessment of Ojeok-San, a Traditional Herbal Formula, Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Combined with Chemometric Analysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 607252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Dai, W.; Lv, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhang, W. A Combined HPLC-PDA and HPLC-MS Method for Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of 10 Major Constituents in the Traditional Chinese Medicine Zuo Gui Wan. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa, H.S.; Koetz, M.; Santos, M.C.; Jandrey, E.H.F.; Folmer, V.; Henriques, A.T.; Mendez, A.S.L. Extraction Optimization and UHPLC Method Development for Determination of the 20-Hydroxyecdysone in Sida tuberculata Leaves. Steroids 2018, 132, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosović, E.; Lino, K.; Kuchař, M. HPLC-MS Methodology for R. Carthamoides Extract Quality Evaluation: A Simultaneous Determination of Eight Bioactive Compounds. Diversity 2022, 14, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálinkás, Z.; Békési, D.; Utczás, M. Quantitation of Ecdysterone and Targeted Analysis of WADA-Prohibited Anabolic Androgen Steroids, Hormones, and Metabolic Modulators in Ecdysterone-Containing Dietary Supplements. Separations 2023, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, J.H.; Ham, H.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Baek, S.Y. Development of a Method for Simultaneous Screening of Four Natural-Derived Steroids and Their Analogues Used as Dietary Supplements via Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2022, 39, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, G.; Joseph, J.F.; Wuest, B.; Mazzarino, M.; de la Torre, X.; Diel, P.; Botrè, F.; Parr, M.K. Detection and Quantitation of Ecdysterone in Human Serum by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Steroids 2020, 157, 108603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, V.; Ivanov, K.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D.; Ivanova, S. Development and Validation of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Identification and Quantification of Phytoecdysteroids Ecdysterone and Turkesterone in Dietary Supplements. Processes 2023, 11, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfender, J.L. HPLC in Natural Product Analysis: The Detection Issue. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushkin, M.; Khrapova, M.; Kovshik, G.; Chasovskikh, M.; Menshchikova, E.; Trufakin, V.; Shurlygina, A.; Vereschagin, E. Effects of Rhaponticum carthamoides versus Glycyrrhiza glabra and Punica granatum Extracts on Metabolic Syndrome Signs in Rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koop, T.; Dienel, A.; Heldmann, M.; Münte, T.F. Effects of a Rhodiola rosea Extract on Mental Resource Allocation and Attention: An Event-Related Potential Dual Task Study. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 3287–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.P.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, M.B.; Zhou, X.L.; Lu, L.; Li, Z.X.; Zheng, G.Q. Rhodiola rosea L. Improves Learning and Memory Function: Preclinical Evidence and Possible Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 367723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, H.S.; Han, K.; Sim, W.; Suh, H.J.; Ahn, Y. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal) Root Extract Containing Withanolide a Alleviates Depression-like Behavior in Mice by Enhancing the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Pathway under Unexpected Chronic Mild Stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 340, 119224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, M.N.; Shyamala, B.V. Ashwagandha- Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal as a Multipotent Neuroprotective Remedy for Genetically Induced Motor Dysfunction and Cellular Toxicity in Human Neurodegenerative Disease Models of Drosophila. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xian, Y.; Jin, Z.; Yao, F.; Liu, Y.Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.; Yang, J.; Ren, L.; et al. Rhaponticum carthamoides Improved Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress through the SIRT6/Nrf2 Pathway to Ameliorate Myocardial Injury. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, H.; Lin, D.; Guo, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Guan, S. Ginsenoside Prolongs the Lifespan of C. elegans via Lipid Metabolism and Activating the Stress Response Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Cui, X.H.; Wang, H.B. Polygonum Multiflorum Thunb Extract Extended the Lifespan and Healthspan of Caenorhabditis elegans via DAF-16/SIR-2.1/SKN-1. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8774–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Souza, E.A.; Thompson, M.A.; Taylor, R.C. Olfactory Chemosensation Extends Lifespan through TGF-β Signaling and UPR Activation. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Song, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yan, X.; Shen, Y. The Decrease of Intraflagellar Transport Impairs Sensory Perception and Metabolism in Ageing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyaanga, J.; Goss, C.; Zhang, G.; Ahmed, H.N.; Andersen, E.J.; Miller, I.R.; Rozenich, J.K.; Swarthout, I.L.; Vaughn, J.A.; Mangan, N.M.; et al. Changes in Body Shape Implicate Cuticle Stretch in C. elegans Growth Control. Cells Dev. 2022, 170, 203780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Fu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, H. Structural Damage in the C. elegans Epidermis Causes Release of STA-2 and Induction of an Innate Immune Response. Immunity 2015, 42, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuscher, A.C.; Statzer, C.; Goyala, A.; Domenig, S.A.; Schoen, I.; Hess, M.; Hofer, A.M.; Fossati, A.; Vogel, V.; Goksel, O.; et al. Longevity Interventions Modulate Mechanotransduction and Extracellular Matrix Homeostasis in C. elegans. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhai, L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Ginsenoside Extract from Ginseng Extends Lifespan and Health Span in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6793–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bahramimehr, F.; Shahhamzehei, N.; Fu, H.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Efferth, T.; Hong, C. Anti-Aging Effects of Medicinal Plants and Their Rapid Screening Using the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Deng, N.; Zheng, B.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. Rhodiola Extract Promotes Longevity and Stress Resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans via DAF-16 and SKN-1. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4471–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkrishna, A.; Kumari, P.; Singh, P.; Pathak, N.; Verma, S.; Dev, R.; Varshney, A. Withanolides-Enriched Leaf Extract of Withania somnifera Exert Anti-Obesity Effects by Inducing Brown Adipocyte-like Phenotype via Tuning MAP-Kinase Signaling Axis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, S.G.; Todorova, M.N.; Savova, M.S.; Georgiev, M.I.; Mihaylova, L.V. Maackiain Mimics Caloric Restriction through Aak-2-Mediated Lipid Reduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH Q2(R2) Validation of Analytical Procedures-Scientific Guideline|European Medicines Agency (EMA). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q2r2-validation-analytical-procedures-scientific-guideline (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Senchuk, M.M.; Dues, D.J.; Raamsdonk, J.M. Van Measuring Oxidative Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans: Paraquat and Juglone Sensitivity Assays. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Hao, G.; Cho, J.; Park, Y. Curcumin Reduced Fat Accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Yue, Y.; Shen, P.; Yang, J.J.; Park, Y. Cranberry Product Decreases Fat Accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
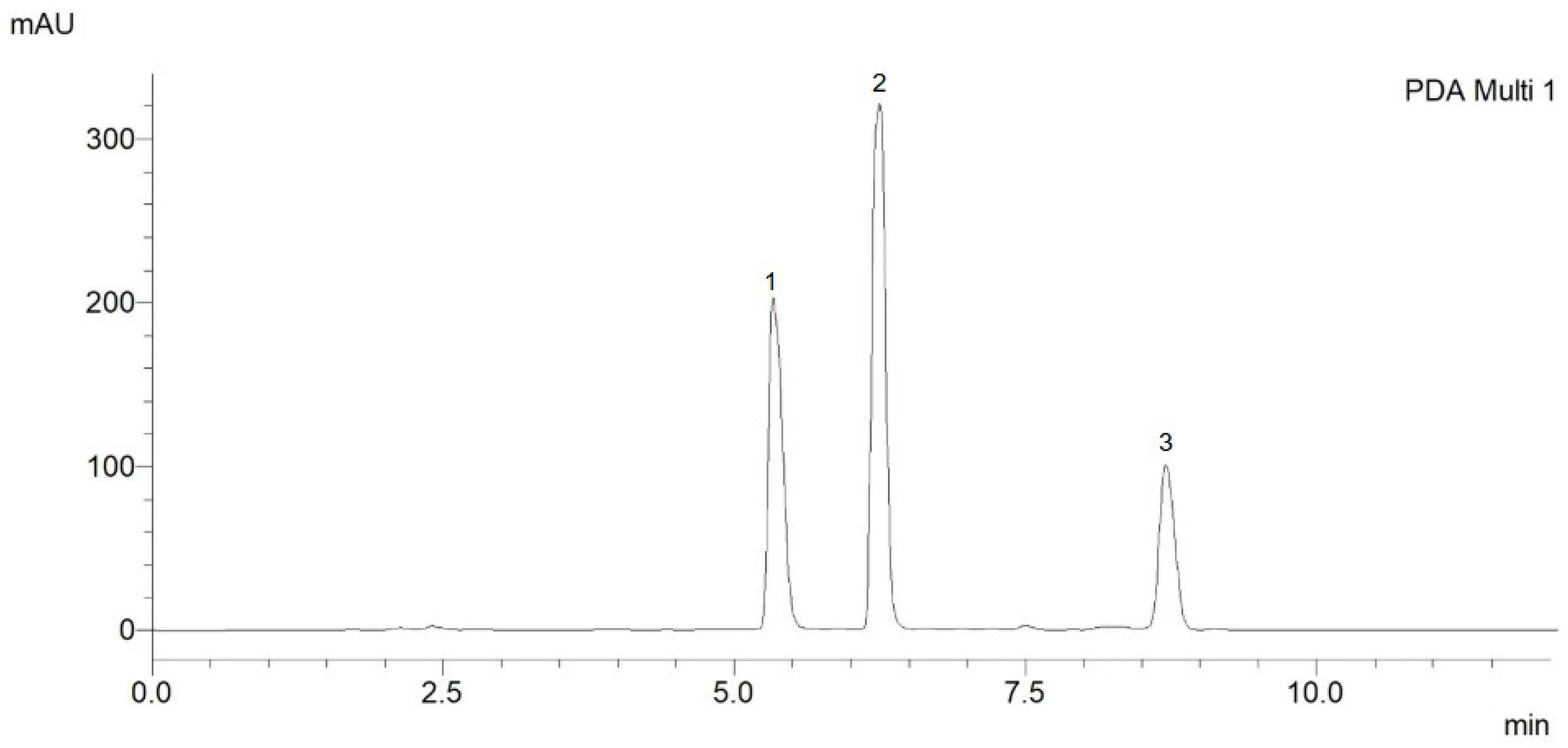
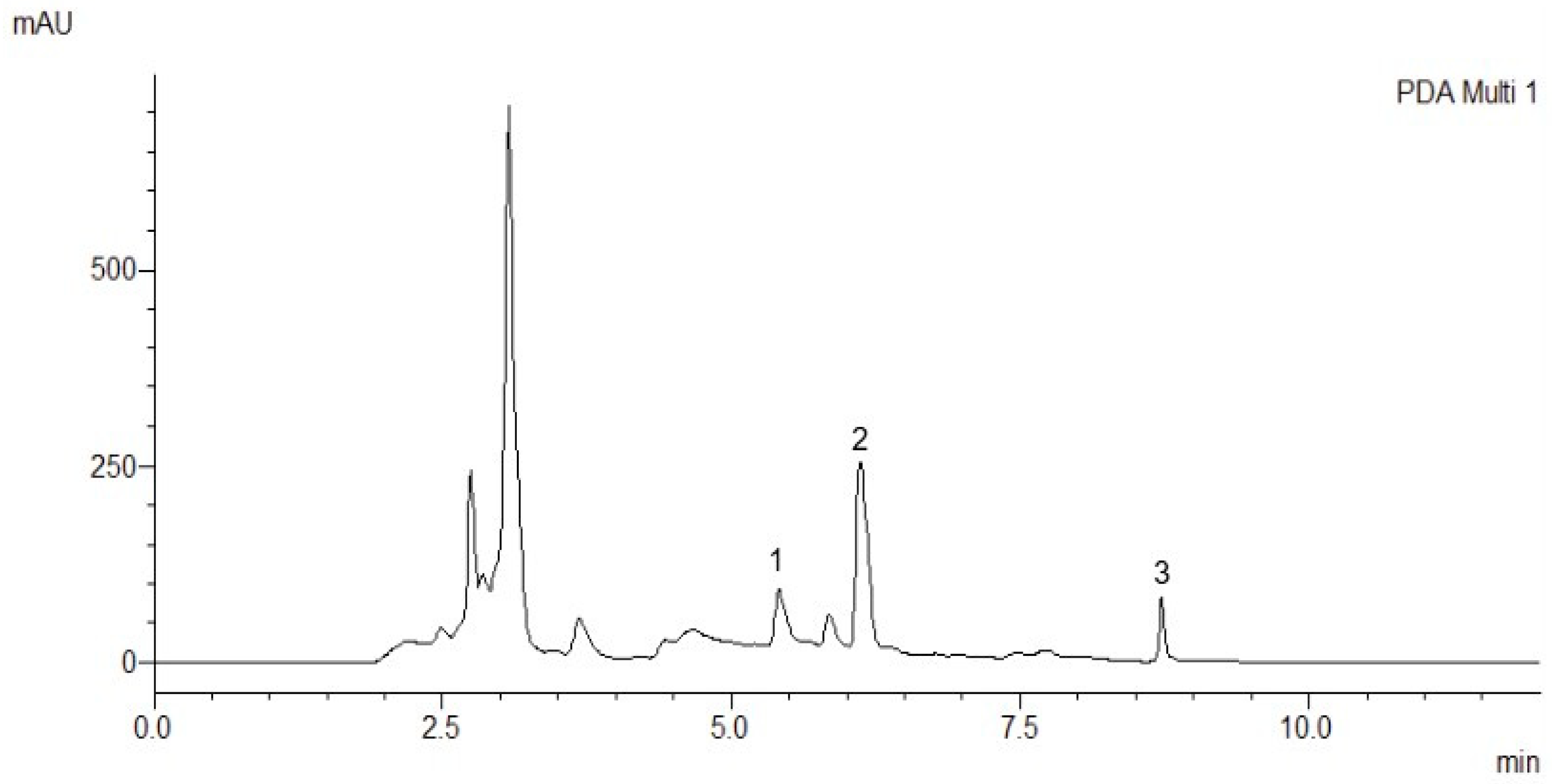

| Parameter | Turkesterone | 20-Hydroxyecdysone | Ponasterone A |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear regression line | y = 46,690x + 173,760 | y = 76,488x + 154,533 | y = 26,176x + 97,062 |
| R2 | 0.9998 | 0.9999 | 0.9998 |
| LD | 1.51 µg/mL | 1.22 µg/mL | 1.57 µg/mL |
| LQ | 4.58 µg/mL | 3.7µg/mL | 4.74 µg/mL |
| Concentration (μg/mL) | Mean (μg/mL ± SD) | Recovery% | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turkesterone | |||
| 40 | 40.06 ± 0.09 | 100.16 | 0.53 |
| 25 | 25.22 ± 0.08 | 100.86 | 0.75 |
| 10 | 9.94 ± 0.01 | 99.77 | 0.24 |
| 20-Hydroxyecdysone | |||
| 40 | 40.22 ± 0.11 | 100.54 | 0.60 |
| 25 | 25.04 ± 0.04 | 100.18 | 0.36 |
| 10 | 9.97 ± 0.02 | 99.77 | 0.18 |
| Ponasterone A | |||
| 40 | 40.31 ± 0.07 | 100.77 | 0.39 |
| 25 | 25.10 ± 0.04 | 100.40 | 0.37 |
| 10 | 9.96 ± 0.01 | 99.55 | 0.30 |
| Concentration (μg/mL) | Intra-Day Precision | Inter-Day Precision | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (μg/mL ± SD) | SEM | CV% | Mean (μg/mL ± SD) | SEM | CV% | |
| Turkesterone | ||||||
| 40 | 40.22 ± 0.51 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 40.30 ± 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.32 |
| 25 | 25.08 ± 0.30 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 25.08 ± 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.66 |
| 10 | 9.94 ± 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 10.01 ± 0.13 | 0.01 | 1.34 |
| 20-Hydroxyecdysone | ||||||
| 40 | 40.22 ± 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 40.06 ± 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.27 |
| 25 | 25.06 ± 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.62 | 25.17 ± 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.77 |
| 10 | 9.98 ± 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.54 | 10.00 ± 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.72 |
| Ponasterone A | ||||||
| 40 | 40.53 ± 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.73 | 40.61 ± 0.43 | 0.17 | 1.06 |
| 25 | 24.99 ± 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.37 | 25.08 ± 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.66 |
| 10 | 9.96 ± 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 9.94 ± 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Todorova, V.; Todorova, M.N.; Savova, M.S.; Ivanov, K.; Georgiev, M.I.; Ivanova, S. Maral Root Extract and Its Main Constituent 20-Hydroxyecdysone Enhance Stress Resilience in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083739
Todorova V, Todorova MN, Savova MS, Ivanov K, Georgiev MI, Ivanova S. Maral Root Extract and Its Main Constituent 20-Hydroxyecdysone Enhance Stress Resilience in Caenorhabditis elegans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083739
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodorova, Velislava, Monika N. Todorova, Martina S. Savova, Kalin Ivanov, Milen I. Georgiev, and Stanislava Ivanova. 2025. "Maral Root Extract and Its Main Constituent 20-Hydroxyecdysone Enhance Stress Resilience in Caenorhabditis elegans" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083739
APA StyleTodorova, V., Todorova, M. N., Savova, M. S., Ivanov, K., Georgiev, M. I., & Ivanova, S. (2025). Maral Root Extract and Its Main Constituent 20-Hydroxyecdysone Enhance Stress Resilience in Caenorhabditis elegans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083739









